Study on the Impact of Clean Power Investment on Regional High-Quality Economic Development in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Definition, Quantification, and Influencing Factors of High-Quality Economic Development
2.2. Research on the Economic and Social Effects of Clean Power Investment
2.3. Clean Power Investment on High-Quality Economic Development
3. Impacting Mechanism
3.1. Clean Power Investment on Innovative Development
3.2. Clean Power Investment on Coordinated Development
3.3. Clean Power Investment on Green Development
3.4. Clean Power Investment on Open Development
3.5. Clean Power Investment on Shared Development
4. Materials and Methods
5. Empirical Findings
5.1. Methodology and Data
5.2. Relevant Test
5.3. Spatial Model Setting
5.4. Empirical Test
5.4.1. Analysis of Spatial Correlation
5.4.2. Spatial Model Econometric Analysis
5.4.3. Decomposition of Spatial Effect
5.5. Robust Test
6. Conclusions and Policy Suggestions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xi Jinping delivers important speech at 75th UN General Assembly general debate. People’s Daily, 23 September 2020. [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Schwarz, P.; Yang, H. Adjusting energy consumption structure to achieve China’s CO2 emissions peak. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 122, 109737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi Jinping Winning to build a well-off society across the board and seizing the great victory of socialism with Chinese characteristics in the new era. People’s Daily, 28 October 2017.
- Ren, B.; Wen, F. Judgment Criteria, Determinants and Realization Ways of China’s High-quality Development in the New Era. Reform 2018, 4, 5–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Z.; Li, F.; Wang, N. The Stage Achievements and Difficulties of High-quality Development of China’s Regional Economy. Reg. Econ. Rev. 2022, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, Q. The temporal and spatial characteristics of China’s high-quality economic development level and its influencing factors. Stat. Decis. 2022, 38, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Hu, S. The realistic dilemma and basic path of high-quality economic development in China: Literature review. Macro Qual. Res. 2018, 6, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, X. The temporal and spatial evolution of high-quality economic development in the Yangtze River Economic Belt and the regional gap. Econ. Geogr. 2020, 40, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wei, L. Spatial econometric analysis of effect of New economic momentum on China’s high-quality development. Res. Int. Bus. Financ. 2022, 61, 101621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Wang, J. High-quality development in China: Measurement system, spatial pattern, and improvement paths. Habitat Int. 2021, 118, 102458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ren, B. Comprehensive evaluation and path selection of high-quality development in China in the new era. Financ. Sci. 2019, 5, 26–40. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, M.; Li, S. Measurement of China’s high-quality economic development level in the new era. Res. Quant. Econ. Technol. Econ. 2018, 35, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, S.; Wan, X.; Yao, Y. Study on the effect of digital economy on high-quality economic development in China. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Liu, C.; Zheng, C.; Li, F. Digital Economy, Technological Innovation and High-Quality Economic Development: Based on Spatial Effect and Mediation Effect. Sustainability 2022, 14, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhou, M.; Xia, Q.; Hao, X.; Wang, J. Has Central Environmental Protection Inspection Promoted High-Quality Economic Development?—A Case Study from China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lu, Y.; Huang, R. Whether foreign direct investment can promote high-quality economic development under environmental regulation: Evidence from the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 21674–21683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wan, J.; Xu, Z.; Lin, T. Impacts of Green Innovation, Institutional Constraints and Their Interactions on High-Quality Economic Development across China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, X.Y.; Zhu, X.J.; Chen, J. Research on the index system of energy investment statistics. Stat. Res. 2013, 30, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Bai, T. Inflfluencing factor, leading superiority and policy effect of renewable energy industry investment of China’s listed companies. Chin. Soft Sci. 2009, 284–289. Available online: https://www.docin.com/p-1592604424.html (accessed on 11 October 2022).
- Zhang, D.Y.; Cao, H.; Zou, P. Exuberance in China’s renewable energy investment: Rationality, capital structure and implications with firm level evidence. Energy Pol. 2015, 95, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, D.; Wang, F. Green credit, renewable energy investment and green economy development: Empirical analysis based on 150 listed companies of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Kong, Q. Renewable energy policy, green investment, and sustainability of energy firms. Renew. Energy 2022, 192, 118–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Jiang, C.; Ma, C.; Su, B. Investment efficiency of the new energy industry in China. Energy Econ. 2018, 70, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, E.; Day, M.; Ivanova, C.; McLeod, A.; Lockshin, J. Intersections of disadvantaged communities and renewable energy potential: Data set and analysis to inform equitable investment prioritization in the United States. Renew. Energy Focus 2022, 41, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahoor, Z.; Khan, I.; Hou, F. clean power investment and financial development as determinants of environment and sustainable economic growth: Evidence from China. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 16006–16016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murshed, M.; Ahmed, Z.; Alam, S.; Mahmood, H.; Rehman, A.; Dagar, V. Reinvigorating the role of clean energy transition for achieving a low-carbon economy: Evidence from Bangladesh. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 67689–67710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.T.; Batool, B.; Sadiq, M.; Zhu, B. How do green energy investment, economic policy uncertainty, and natural resources affect greenhouse gas emissions? A Markov-switching equilibrium approach. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2022, 97, 106887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, X. Investment in renewable energy resources, sustainable financial inclusion and energy efficiency: A case of US economy. Resour. Policy 2022, 77, 102680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yang, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhou, D. Impact of renewable energy investment on carbon emissions in China—An empirical study using a nonparametric additive regression model. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollakota, A.R.; Shu, C.-M. COVID-19 and energy sector: Unique opportunity for switching to clean energy. Gondwana Res. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvořák, P.; Martinát, S.; Van der Horst, D.; Frantál, B.; Turečková, K. Renewable energy investment and job creation; a cross-sectoral assessment for the Czech Republic with reference to EU benchmarks. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 69, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, A.; Zhou, X. Emission reduction effects of the green energy investment projects of China in belt and road initiative countries. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 2020, 6, 1747947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Kuo, T.-H.; Siao-Yun, W.; Vinh, L.T. Role of green finance, volatility and risk in promoting the investments in Renewable Energy Resources in the post-covid-19. Resour. Policy 2022, 76, 102563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, M.; Aghahosseini, A.; Breyer, C. Job creation during the global energy transition towards 100% renewable power system by 2050. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2019, 151, 119682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kul, C.; Zhang, L.; Solangi, Y.A. Assessing the renewable energy investment risk factors for sustainable development in Turkey. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 124164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Luo, J.; Cheng, F.; Yüksel, S.; Dinçer, H. Analysis of risk priorities for renewable energy investment projects using a hybrid IT2 hesitant fuzzy decision-making approach with alpha cuts. Energy 2021, 224, 120184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollin, R.; Heintz, J.; Garrett-Peltier, H. The Economic Benefits of Investing in Clean Energy: How the Economic Stimulus Program and New Legislation Can Boost U.S. Economic Growth and Employment; Published Studies; Political Economy Research Institute, University of Massachusetts at Amherst: Amherst, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Saunila, M.; Ukko, J.; Rantala, T. Sustainability as a driver of green innovation investment and exploitation. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 179, 537–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pueyo, A. What constrains renewable energy investment in Sub-Saharan Africa? A comparison of Kenya and Ghana. World Dev. 2018, 109, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M. Research on the spatial effect of green investment on high-quality economic development in the process of marketization-an empirical analysis based on spatial Durbin model. J. Guizhou Univ. Financ. Econ. 2020, 4, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahani Ashwin, J.; Clarke Amy, J. EU announces European Green Deal 1 billion investment. MRS Bull. 2020, 45, 888. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Tian, F.; Zhou, T. JResearch on the Effect of Green Finance on High-quality Economic Development. Univ. Soc. Sci. Ed. 2022, 1–13. Available online: http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/50.1023.c.20210513.1530.002.html (accessed on 9 October 2022).
- Fang, L.; Jia, P.; Jiang, W. Beijing Economic High-quality Development Report. Sci. Technol. Think Tank 2022, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Lu, G. Analysis of the high-quality development of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei economy and its coupling coordination. J. Tianjin Univ. Commer. 2022, 42, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Guo, H. Evaluation of Beijing’s high-quality economic development based on the new development concept. Urban Issues 2021, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.; Ma, W. Measurement and temporal and spatial characteristics of high-quality development among provinces in China. Reg. Econ. Rev. 2019, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Han, P. Digital Economy and High-Quality Development of Manufacturing Industry. In Business Intelligence and Information Technology; Hassanien, A.E., Xu, Y., Zhao, Z., Mohammed, S., Fan, Z., Eds.; BIIT 2021. Lecture Notes on Data Engineering and Communications Technologies; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ren, L.; Du, Z.; Tong, G. Measurement and spatiotemporal analysis of high-quality development of China’s industry. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Cai, B.; Li, Y. Evaluation Index System and Measurement of High-quality Development in China. Rev. Cercet. Interv. Sociala 2020, 68, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Z.; Deng, H.; Chen, R.; Gan, T. Environmental and economic benefits of central environmental protection inspectors: Evidence from Hebei province. Econ. Rev. 2020, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z. An Empirical Study on the Effect of Green Investment on China’s Economic Growth. Bus. Res. 2011, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Deng, X. An Empirical Analysis of Renewable Energy Investment and Green Economy Development. East China Econ. Manag. 2020, 34, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, P. Study on the Influence of New Energy Investment on Green Industrial Development; China University of Mining and Technology: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X. Research on the Influence of Green Institutional Environment on Renewable Energy Investment; China University of Mining and Technology: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L. Research on Clean Energy Investment Efficiency and Influencing Factors of China’s Electric Power Enterprises; North China Electric Power University: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
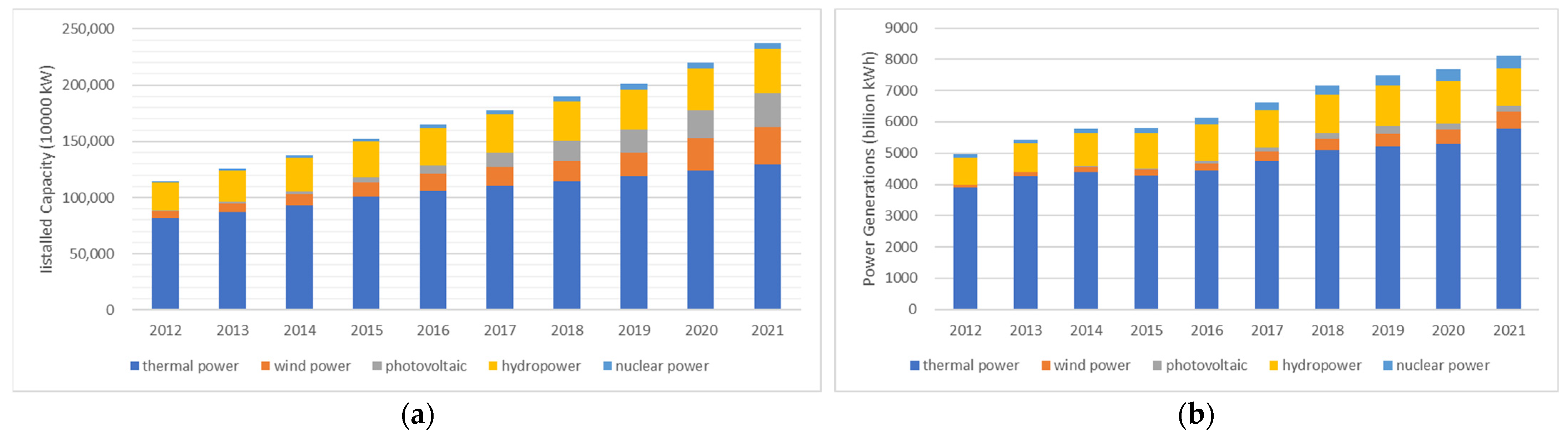
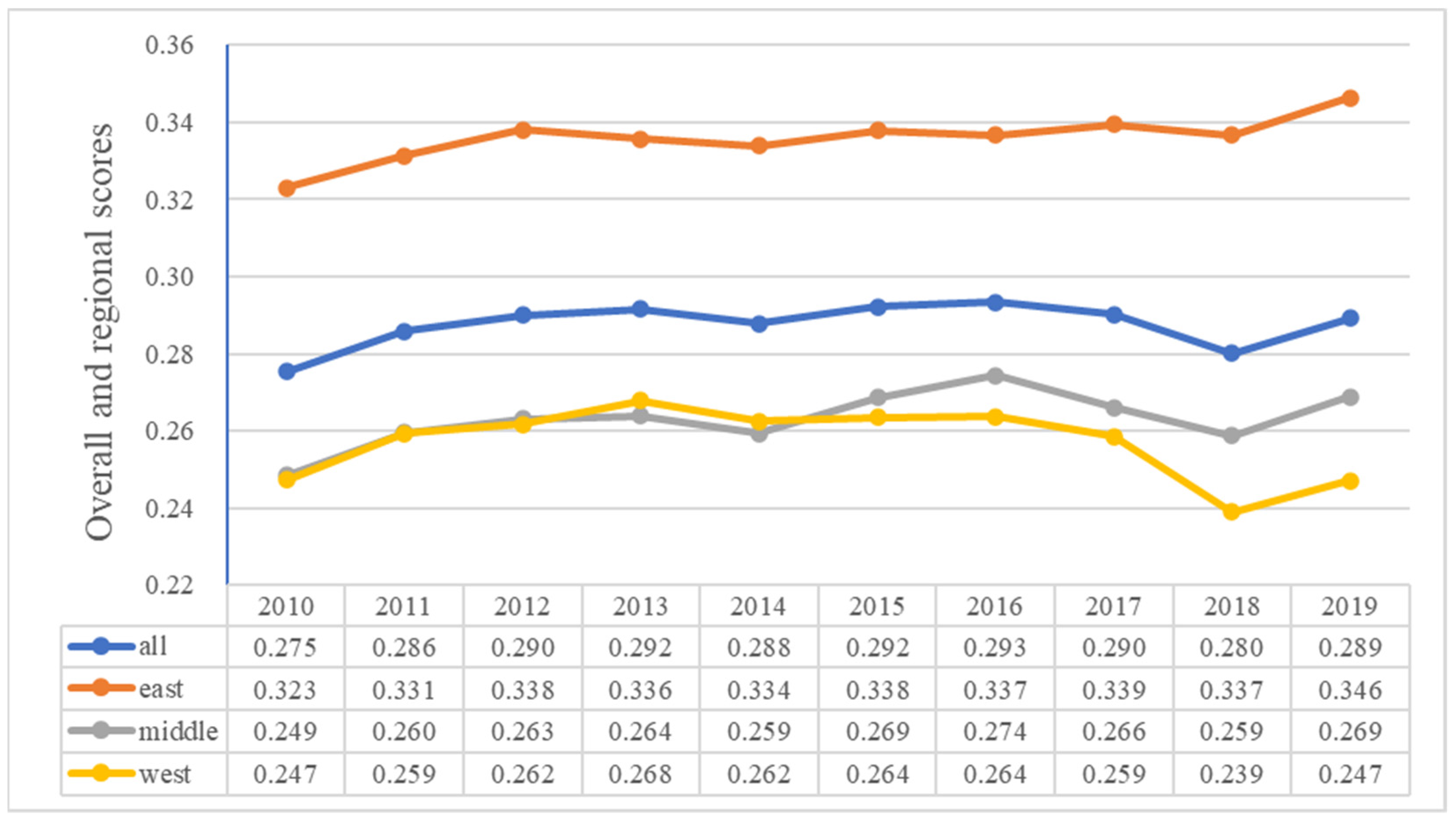
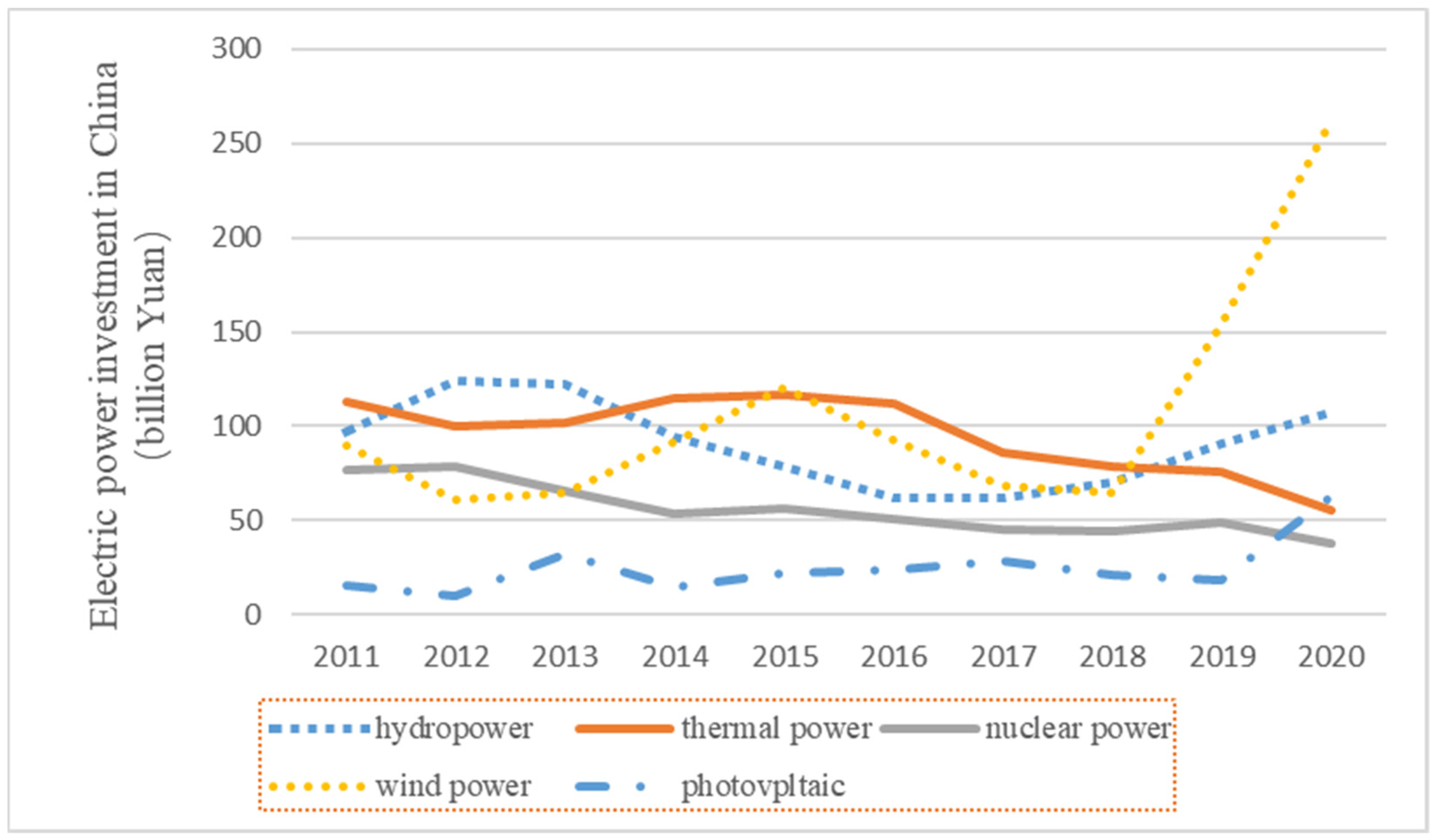
| The First Layer | The Second Layer | Positive or Negative | Weights |
|---|---|---|---|
| Innovative development | R&D investment intensity | + | 0.066 |
| Domestic invention patents granted per 10,000 people | + | 0.194 | |
| R&D personnel full-time equivalents | + | 0.119 | |
| Coordinated development | Urban-rural income gap | − | 0.031 |
| Rationalization of industrial structure | + | 0.059 | |
| Premiumization of industrial structure | + | 0.068 | |
| Green development | Industrial waste gas emissions per capita | − | 0.030 |
| Coal consumption per capita | − | 0.021 | |
| Forest coverage | + | 0.055 | |
| Solid waste generation per capita | − | 0.022 | |
| Total environmental pollution control to GDP ratio | + | 0.047 | |
| Open development | Ratio of total exports and imports of goods to GDP | + | 0.120 |
| FDI to GDP ratio | + | 0.067 | |
| Shared development | Loop length of 35 KV and above transmission lines | + | 0.047 |
| Ratio of social service expenditure to GDP | + | 0.056 |
| Region | 2011 | 2013 | 2015 | 2017 | 2019 | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 0.478 | 0.485 | 0.517 | 0.552 | 0.543 | 0.506 |
| Tianjin | 0.320 | 0.335 | 0.349 | 0.289 | 0.283 | 0.313 |
| Hebei | 0.248 | 0.240 | 0.248 | 0.266 | 0.273 | 0.252 |
| Shanxi | 0.207 | 0.220 | 0.238 | 0.209 | 0.224 | 0.220 |
| Inner Mongolia | 0.236 | 0.242 | 0.247 | 0.251 | 0.241 | 0.240 |
| Liaoning | 0.311 | 0.303 | 0.237 | 0.257 | 0.254 | 0.278 |
| Jilin | 0.251 | 0.245 | 0.240 | 0.243 | 0.248 | 0.244 |
| Heilongjiang | 0.280 | 0.270 | 0.266 | 0.263 | 0.251 | 0.264 |
| Shanghai | 0.379 | 0.369 | 0.378 | 0.377 | 0.381 | 0.376 |
| Jiangsu | 0.334 | 0.346 | 0.352 | 0.357 | 0.372 | 0.349 |
| Zhejiang | 0.328 | 0.339 | 0.360 | 0.362 | 0.386 | 0.352 |
| Anhui | 0.259 | 0.285 | 0.288 | 0.287 | 0.282 | 0.276 |
| Fujian | 0.301 | 0.303 | 0.300 | 0.298 | 0.299 | 0.298 |
| Jiangxi | 0.297 | 0.290 | 0.297 | 0.298 | 0.299 | 0.295 |
| Shandong | 0.269 | 0.284 | 0.291 | 0.300 | 0.301 | 0.285 |
| Henan | 0.240 | 0.249 | 0.256 | 0.262 | 0.268 | 0.251 |
| Hubei | 0.274 | 0.275 | 0.282 | 0.279 | 0.282 | 0.276 |
| Hunan | 0.268 | 0.276 | 0.283 | 0.288 | 0.297 | 0.280 |
| Guangdong | 0.385 | 0.398 | 0.390 | 0.391 | 0.432 | 0.399 |
| Guangxi | 0.273 | 0.287 | 0.292 | 0.289 | 0.291 | 0.283 |
| Hainan | 0.293 | 0.289 | 0.293 | 0.284 | 0.285 | 0.288 |
| Chongqing | 0.282 | 0.289 | 0.253 | 0.253 | 0.259 | 0.264 |
| Sichuan | 0.280 | 0.287 | 0.290 | 0.286 | 0.290 | 0.285 |
| Guizhou | 0.291 | 0.281 | 0.262 | 0.252 | 0.251 | 0.266 |
| Yunnan | 0.272 | 0.273 | 0.277 | 0.259 | 0.244 | 0.265 |
| Shaanxi | 0.245 | 0.307 | 0.282 | 0.280 | 0.296 | 0.281 |
| Gansu | 0.277 | 0.291 | 0.279 | 0.271 | 0.252 | 0.272 |
| Qinghai | 0.242 | 0.214 | 0.218 | 0.228 | 0.199 | 0.217 |
| Ningxia | 0.216 | 0.216 | 0.234 | 0.214 | 0.178 | 0.209 |
| Xinjiang | 0.240 | 0.260 | 0.265 | 0.260 | 0.217 | 0.245 |
| Region | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 26.06 | 29.41 | 30.79 | 39.00 | 50.77 | 51.27 | 51.62 | 45.50 | 50.05 | 48.36 | 42.28 |
| Tianjin | 2.25 | 2.90 | 2.15 | 2.41 | 2.64 | 2.48 | 2.77 | 5.36 | 7.92 | 7.15 | 3.80 |
| Hebei | 11.70 | 10.04 | 4.45 | 4.61 | 7.15 | 9.85 | 11.99 | 14.07 | 12.40 | 15.25 | 10.15 |
| Shanxi | 4.83 | 8.14 | 5.46 | 7.53 | 11.06 | 12.42 | 16.00 | 12.94 | 6.87 | 11.29 | 9.65 |
| Inner Mongolia | 30.56 | 18.34 | 11.07 | 14.68 | 16.87 | 15.53 | 6.51 | 5.84 | 5.30 | 12.27 | 13.70 |
| Liaoning | 18.74 | 16.71 | 14.44 | 10.41 | 4.30 | 6.40 | 5.05 | 7.88 | 9.17 | 10.08 | 10.32 |
| Jilin | 10.34 | 4.29 | 3.03 | 3.61 | 4.59 | 7.94 | 6.70 | 5.56 | 8.11 | 7.43 | 6.16 |
| Heilongjiang | 5.31 | 4.38 | 3.40 | 3.06 | 2.92 | 1.80 | 2.30 | 2.12 | 1.75 | 2.18 | 2.92 |
| Shanghai | 11.04 | 8.87 | 8.43 | 8.65 | 11.43 | 10.52 | 10.72 | 16.51 | 21.24 | 20.56 | 12.80 |
| Jiangsu | 6.26 | 8.62 | 8.03 | 12.25 | 16.88 | 25.59 | 33.06 | 34.12 | 36.57 | 39.87 | 22.13 |
| Zhejiang | 15.46 | 15.52 | 11.55 | 9.11 | 10.45 | 11.23 | 8.55 | 13.84 | 13.42 | 10.70 | 11.98 |
| Anhui | 4.01 | 4.01 | 3.75 | 3.77 | 3.81 | 5.08 | 7.58 | 7.30 | 6.91 | 6.90 | 5.31 |
| Fujian | 16.37 | 17.99 | 19.81 | 16.75 | 11.87 | 12.80 | 13.18 | 14.65 | 15.40 | 19.94 | 15.88 |
| Jiangxi | 0.56 | 0.66 | 1.99 | 2.11 | 2.33 | 2.84 | 3.65 | 3.37 | 4.64 | 7.42 | 2.96 |
| Shandong | 27.65 | 27.87 | 29.26 | 8.47 | 26.12 | 24.11 | 30.05 | 27.69 | 26.87 | 25.44 | 25.35 |
| Henan | 1.19 | 1.42 | 0.63 | 0.40 | 1.90 | 2.23 | 3.06 | 6.29 | 5.42 | 10.69 | 3.32 |
| Hubei | 10.24 | 4.43 | 3.63 | 4.40 | 4.41 | 7.30 | 10.97 | 9.04 | 8.58 | 7.72 | 7.07 |
| Hunan | 5.09 | 6.01 | 6.19 | 5.14 | 4.37 | 3.68 | 4.26 | 5.45 | 4.40 | 6.25 | 5.08 |
| Guangdong | 29.51 | 43.65 | 38.62 | 15.03 | 34.48 | 32.04 | 37.05 | 38.24 | 30.76 | 44.27 | 34.37 |
| Guangxi | 3.84 | 6.50 | 7.83 | 22.39 | 5.84 | 6.58 | 7.77 | 5.68 | 8.40 | 11.15 | 8.60 |
| Hainan | 2.18 | 3.58 | 4.70 | 6.09 | 4.75 | 3.73 | 2.72 | 4.47 | 4.51 | 3.58 | 3.02 |
| Chongqing | 2.72 | 1.88 | 1.06 | 1.97 | 4.56 | 5.27 | 5.44 | 5.16 | 2.86 | 3.57 | 3.45 |
| Sichuan | 38.31 | 50.13 | 61.36 | 57.13 | 45.17 | 38.73 | 35.73 | 40.96 | 47.53 | 43.15 | 45.82 |
| Guizhou | 6.10 | 7.69 | 6.07 | 7.75 | 6.19 | 5.95 | 3.52 | 3.37 | 2.31 | 3.58 | 5.25 |
| Yunnan | 13.64 | 28.27 | 45.37 | 46.28 | 40.83 | 36.99 | 26.74 | 12.02 | 8.91 | 25.43 | 28.45 |
| Shaanxi | 1.74 | 1.58 | 2.54 | 3.64 | 2.66 | 7.51 | 9.93 | 8.93 | 7.82 | 10.82 | 5.72 |
| Gansu | 17.07 | 7.10 | 9.11 | 11.14 | 17.15 | 10.04 | 1.76 | 1.42 | 1.38 | 1.32 | 7.25 |
| Qinghai | 2.70 | 8.65 | 2.98 | 6.13 | 2.15 | 4.68 | 3.19 | 2.55 | 3.90 | 5.53 | 4.25 |
| Ningxia | 3.96 | 12.98 | 3.88 | 5.49 | 7.30 | 11.16 | 4.95 | 3.49 | 1.42 | 5.32 | 5.66 |
| Xinjiang | 10.05 | 13.58 | 15.94 | 31.99 | 15.83 | 31.60 | 21.97 | 9.89 | 14.61 | 24.11 | 18.96 |
| Variable | Observations | Mean | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HQD | 300 | 0.288 | 0.061 | 0.177 | 0.552 |
| CEI | 300 | 127.62 | 127.80 | 3.988 | 613.64 |
| HC | 300 | 9.088 | 0.929 | 6.764 | 12.782 |
| GI | 300 | 24.55 | 10.23 | 10.582 | 62.836 |
| UR | 300 | 57.73 | 12.607 | 33.81 | 89.6 |
| Explaining Variables | Explained Variable HQD | |
|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | t-Value | |
| lnCEI | 0.007 ** | 2.64 |
| HC | 0.014 * | 2.03 |
| GI | 0.001 ** | 2.18 |
| UR | −0.0009 * | −1.71 |
| _cons | 0.156 *** | 2.90 |
| N | 300 | |
| Year | Moran’s Index | Year | Moran’s Index |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 0.374 *** | 2015 | 0.486 *** |
| 2011 | 0.388 *** | 2016 | 0.305 *** |
| 2012 | 0.395 *** | 2017 | 0.232 *** |
| 2013 | 0.420 *** | 2018 | 0.232 *** |
| 2014 | 0.469 *** | 2019 | 0.246 *** |
| Test | Statistics | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| LM lag | 0.100 | 0.752 |
| Robust LM lag | 3.198 * | 0.074 |
| LM error | 2.013 | 0.156 |
| Robust LM error | 5.111 ** | 0.024 |
| LR (H0: SAR nested in SDM) | 21.59 *** | 0.0002 |
| LR (H0: SEM nested in SDM) | 20.77 *** | 0.0004 |
| Wald | 14.91 *** | 0.0049 |
| Hausman | 20.65 ** | 0.014 |
| Statistics | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|
| LR (H0:ind nested in both) | 47.09 *** | 0.0000 |
| LR (H0: time nested in both) | 597.84 *** | 0.0000 |
| Variables | OLS | SDM |
|---|---|---|
| ln CEI | 0.0072 ** (0.0027) | 0.0069 *** (0.0017) |
| HC | 0.0139 * (0.0068) | 0.0100 * (0.0056) |
| GI | 0.0012 ** (0.0005) | 0.0015 *** (0.0005) |
| UR | −0.0009 * (0.0006) | 0.0016 ** (0.0008) |
| W×ln CEI | 0.0190 *** (0.0035) | |
| W×HC | −0.0643 *** (0.0105) | |
| W×GI | −0.0028 *** (0.0008) | |
| W×UR | −0.0041 *** (0.0012) | |
| rho | −0.1698 ** | |
| AIC | −1679.465 | −1736.668 |
| BIC | −1664.649 | −1699.631 |
| Variables | Direct Effects | Indirect Effects | Total Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| ln CEI | 0.006158 *** (3.55) | 0.016171 *** (5.09) | 0.016171 *** (7.14) |
| HC | 0.011907 ** (2.16) | −0.04292 *** (−4.41) | −0.04292 *** (−3.17) |
| GI | 0.001649 *** (3.68) | −0.00282 *** (−3.68) | −0.00282 (−1.56) |
| UR | 0.001779 ** (2.12) | −0.00394 *** (−3.28) | −0.00394 *** (−2.96) |
| Variables | HQD | PGDP | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Effects | Indirect Effects | Total Effects | Direct Effects | Indirect Effects | Total Effects | |
| ln CEI | 0.0061 *** (3.55) | 0.0161 *** (5.09) | 0.0161 *** (7.14) | 0.0911 * (1.48) | 0.3350 *** (2.79) | 0.4261 *** (3.43) |
| HC | 0.0119 ** (2.16) | −0.0429 *** (−4.41) | −0.0429 *** (−3.17) | 0.3072 (1.58) | −0.8616 ** (−2.32) | −0.5544 (−1.42) |
| GI | 0.0016 *** (3.68) | −0.0028 *** (−3.68) | −0.0028 (−1.56) | −0.1976 *** (−12.6) | −0.1017 *** (−3.68) | −0.2993 *** (−10.6) |
| UR | 0.0017 ** (2.12) | −0.0039 *** (−3.28) | −0.0039 *** (−2.96) | −0.1480 *** (−5.08) | −0.2126 *** (−4.86) | −0.3606 *** (−12.3) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhuang, X.; Pan, L. Study on the Impact of Clean Power Investment on Regional High-Quality Economic Development in China. Energies 2022, 15, 8364. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15228364
Zhuang X, Pan L. Study on the Impact of Clean Power Investment on Regional High-Quality Economic Development in China. Energies. 2022; 15(22):8364. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15228364
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhuang, Xianrong, and Lingying Pan. 2022. "Study on the Impact of Clean Power Investment on Regional High-Quality Economic Development in China" Energies 15, no. 22: 8364. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15228364
APA StyleZhuang, X., & Pan, L. (2022). Study on the Impact of Clean Power Investment on Regional High-Quality Economic Development in China. Energies, 15(22), 8364. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15228364










