Synthesis of Superparamagnetic Fe3O4 Nano-Adsorbent Using an Energy-Saving and Pollution-Reducing Strategy for the Removal of Xylenol Orange Dye in Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Fe3O4
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Evaluation of Adsorption Capacity
| Generic Name | Abbreviation | Cas Number | Chemical Structure | λmax (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xylenol orange | XO | 1611-35-4 | 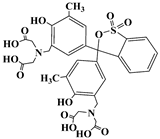 | 435 |
| Basic orange 2 | BO2 | 532-82-1 | 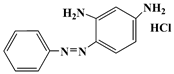 | 452 |
| Acid orange 7 | AO7 | 633-96-5 | 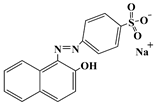 | 484 |
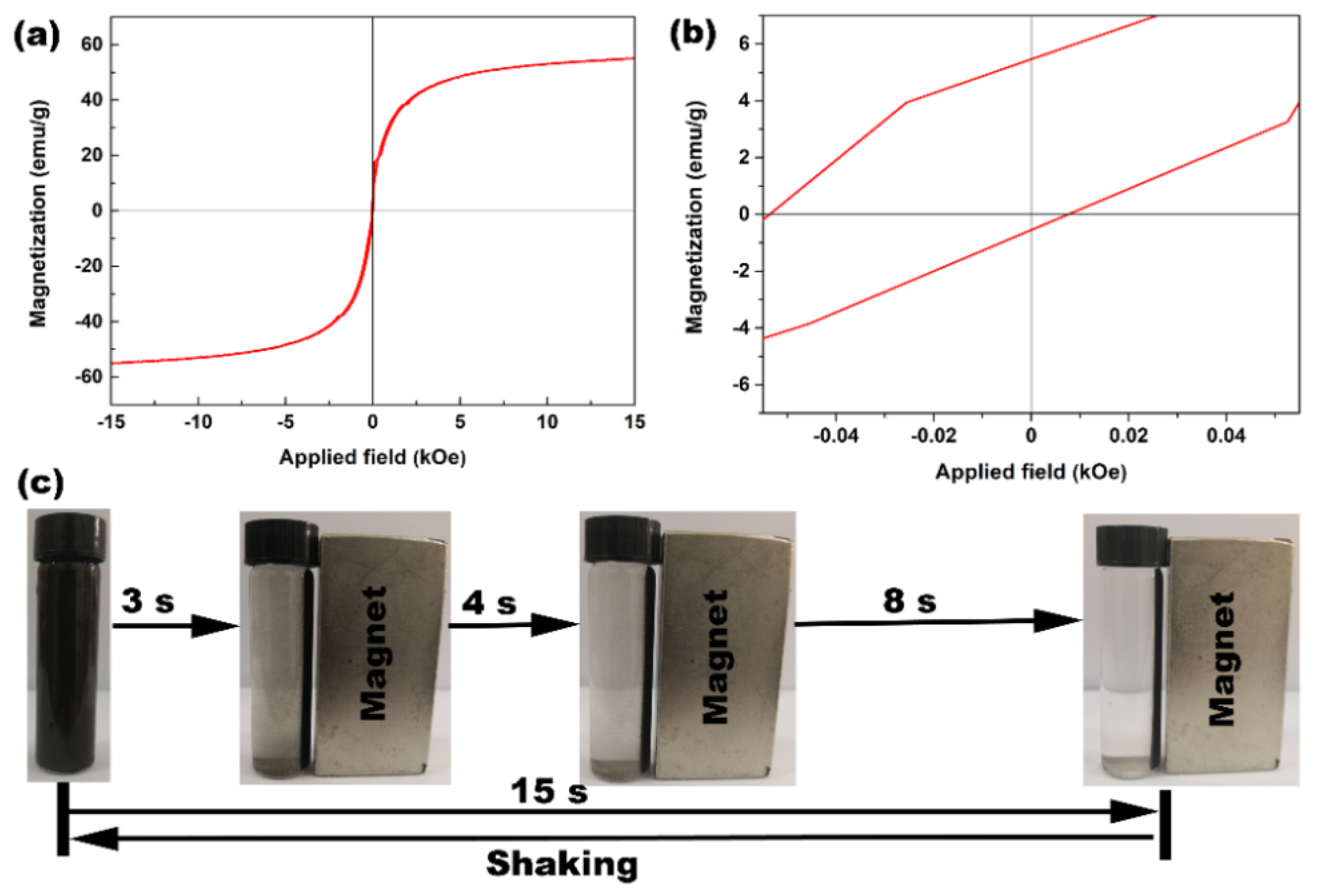
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, Z.; Yang, W.; Huo, K.; Shaw, L. Thermodynamics and Kinetics Tuning of LiBH4 for Hydrogen Storage. Prog. Chem. 2021, 33, 1586–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turky, A.O.; Rashad, M.M.; Hassan, A.M.; Elnaggar, E.M.; Bechelany, M. Optical, electrical and magnetic properties of lanthanum strontium manganite La1−xSrxMnO3 synthesized through the citrate combustion method. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 6878–6886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Chen, Z.; Ma, T.; Lu, C.T.; Ma, W.; Shaw, L. Predicting the hydrogen release ability of LiBH4-based mixtures by ensemble machine learning. Energy Storage Mater. 2020, 27, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turky, A.O.; Rashad, M.M.; Hassan, A.M.; Elnaggar, E.M.; Bechelany, M. Tailoring optical, magnetic and electric behavior of lanthanum strontium manganite La1−xSrxMnO3 (LSM) nanopowders prepared via a co-precipitation method with different Sr2+ ion contents. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 17980–17986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oca, R.M.G.F.-M.; Ramos-Leal, J.A.; Solache-Ríos, M.J.; Martínez-Miranda, V.; Fuentes-Rivas, R.M. Modification of the Relative Abundance of Constituents Dissolved in Drinking Water Caused by Organic Pollution: A Case of the Toluca Valley, Mexico. Water Air Soil Poll. 2019, 230, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Li, H.; Shaw, L. New Insights into the Solid-State Hydrogen Storage of Nanostructured LiBH4-MgH2 System. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 385, 123856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, D.A.; Scholz, M. Comparison of Experimental Ponds for the Treatment of Dye Wastewater under Controlled and Semi-natural Conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 16031–16040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, F.; Wu, P.; Ma, W. LiBH4 for Hydrogen Storage: New Perspectives. Nano Mater. Sci. 2020, 2, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, S.S.; Shah, M.; Muhammad, W.; Ahmad, A.; Ullah, M.A.; Nadeem, M.; Abbasi, B.H. Potentials of Phyto-fabricated Nanoparticles as Ecofriendly Agents for Photocatalytic Degradation of Toxic Dyes and Waste Water Treatment, Risk Assessment and Probable Mechanism. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2021, 98, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Ji, X.; Ma, J.; Tian, G. Preparation and Excellent Adsorption of water Pollution Dyes over Magnetic Fe3O4/C Nanoparticles with Hollow Grape Cluster Morphology. J. Nanopart. Res. 2020, 22, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong, D.T.M.; Chai, W.S.; Show, P.L.; Lin, Y.L.; Chiu, C.Y.; Tsai, S.L.; Chang, Y.K. Removal of Cationic Dye Waste by Nanofiber Membrane Immobilized with Waste Proteins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 3873–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Zheng, H.; Zhao, R.; Xiong, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Ding, W. Sulfonic Acid-modified Polyacrylamide Magnetic Composite with Wide pH Applicability for Efficient Removal of Cationic Dyes. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 319, 114161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Wen, J.; Wang, Q.; Jin, X.; Zhou, X. Preparation and Photocatalytic Properties of Hexagonal and Orthogonal CuS Micro-nanoparticles by an Oil-water Interface Method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 255, 123629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Deng, W.; Feng, X.; Pan, F.; Li, Y. An Integrated Electrocoagulation-Electrocatalysis Water Treatment Process using Stainless Steel Cathodes Coated with Ultrathin TiO2 Nanofilms. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiwaan, H.A.; Mohamed, F.S.; El-Ghamaz, N.A.; Beshry, N.M.; El-Bindary, A.A. Experimental and Electrical Studies of Na-X zeolite for the Adsorption of Different Dyes. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 332, 115877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feizpoor, S.; Habibi-Yangjeh, A.; Chand, H.; Krishnan, V. Integration of Bi5O7I with TiO2: Binary Photocatalysts with Boosted Visible-light Photocatalysis in Removal of Organic Contaminants. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2021, 410, 113190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa-Martínez, J.D.; Balagurusamy, N.; Montañez, J.; Peralta, R.A.; de Fátima Peralta-Muniz-Moreira, R.; Bracht, A.; Peralta, R.M.; Morales-Oyervides, L. Synthetic Dyes Biodegradation by Fungal Ligninolytic Enzymes: Process Optimization, Metabolites Evaluation and Toxicity Assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, X.L.; Shao, C.B. Removal of Xylenol Orange from Solutions by γ-Cyclodextrin-Grafted Carboxymethyl Cellulose. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 204–210, 1180–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Lu, Y.; Li, L.; Shaw, L. High Reversible Capacity Hydrogen Storage Through Nano-LiBH4 + Nano-MgH2 System. Energy Storage Mater. 2019, 20, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Wu, P.; Shaw, L. Solid-state Hydrogen Desorption of 2 MgH2 + LiBH4 Nano-mixture: A Kinetics Mechanism Study. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 806, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayantong, A.R.B.; Shih, Y.-J.; Ong, D.C.; Abarca, R.R.M.; Dong, C.-D.; de Luna, M.D.G. Adsorptive Removal of Dye in Wastewater by Metal Ferrite-enabled Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites. Chemosphere 2021, 274, 129518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.; Zhao, G.; Pan, L.; Chen, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xiao, X.; Xu, W. Efficient Removal of Dye from Wastewater without Selectivity Using Activated Carbon-Juncus Effusus Porous Fibril Composites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 19176–19186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghadhban, M.Y.; Majdi, H.S.; Rashid, K.T.; Alsalhy, Q.F.; Lakshmi, D.S.; Salih, I.K.; Figoli, A. Removal of Dye from a Leather Tanning Factory by Flat-Sheet Blend Ultrafiltration (UF) Membrane. Membranes 2020, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja, Y.S.; Samsudin, M.F.R.; Sufian, S. Development of the Low-Cost and Green Hibiscus cannabinus Bioadsorbent for the Removal of Dye in Wastewater. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2020, 46, 6349–6358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayomie, O.S.; Kandeel, H.; Shoeib, T.; Yang, H.; Youssef, N.; El-Sayed, M.M.H. Novel Approach for Effective Removal of Methylene Blue Dye from Water using Fava Bean Peel Waste. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiralian, N.; Mustapic, M.; Hossain, M.S.A.; Wang, C.; Konarova, M.; Tang, J.; Na, J.; Khan, A.; Rowan, A. Magnetic nanocellulose: A Potential Material for Removal of Dye from Water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 394, 122571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turky, A.O.; Mohamed Rashad, M.; Taha Kandil, A.E.-H.; Bechelany, M. Tuning the optical, electrical and magnetic properties of Ba0.5Sr0.5TixM1-xO3 (BST) nanopowders. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 12553–12560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turky, A.O.; Rashad, M.M.; Bechelany, M. Tailoring optical and dielectric properties of Ba0.5Sr0.5TiO3 powders synthesized using citrate precursor route. Mater. Des. 2016, 90, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Chi, M.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, M.; Wang, C.; Lu, X. A Facile Synthesis of Superparamagnetic Fe3O4 Nanofibers with Superior Peroxidase-like Catalytic Activity for Sensitive Colorimetric Detection of L-cysteine. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 440, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Kou, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, D.; Lu, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.J.; Han, D.; et al. Effects of Amount of Benzyl Ether and Reaction Time on the Shape and Magnetic Properties of Fe3O4 Nanocrystals. Powder Technol. 2017, 319, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Ding, L.; Zhao, X.; Liu, P.; Li, T. Synthesis of Covalently Bonded Reduced Graphene Oxide-Fe3O4 Nanocomposites for Efficient Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 72, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandari, M.J.; Hasanzadeh, I. Size-controlled Synthesis of Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanoparticles via an Alternating Magnetic Field and Ultrasonic-assisted Chemical Co-precipitation. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Adv. 2021, 266, 115050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Xia, Y.; Zai, Y.; Dai, Y.; Liu, X.; Bian, J.; Liu, J.; Li, G. Adsorption and Desorption Behaviors of HPEI and Thermoresponsive HPEI based Gels on Anionic and Cationic Dyes. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 369, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wang, W.; Dong, W. Interpenetrating Polymer Networks in Polyvinyl Alcohol/cellulose Nanocrystals Hydrogels to Develop Absorbent Materials. Carbohyd. Polym. 2018, 200, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, T.; Sun, D.; Li, R. Facile Synthesis of Superparamagnetic Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Just using Ferric Citrate and Water. Integr. Ferroelectr. 2016, 176, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Diao, G. Synthesis of Porous Fe3O4 Nanospheres and Its Application for the Catalytic Degradation of Xylenol Orange. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.H.; Salabas, E.L.; Schüth, F. Magnetic Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Protection, Functionalization, and Application. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1222–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishaq, M.; Saeed, K.; Ahmad, I.; Sultan, S.; Akhtar, S. Coal ash as a low cost adsorbent for the removal of xylenol orange from aqueous solution. Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2014, 33, 53–58. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/293158575 (accessed on 1 March 2014).
- Bai, Q.; Wang, W.; Liang, T.; Bai, H.Y.; Liu, X.Y. Preparation of porous amino-cellulose membrane and their adsorption performance of xylenol orange. J. Cellul. Sci. Technol. 2017, 25, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Yang, C.; Ren, S. Adsorption capacity of expansion graphite for xylenol orange. J. Mater. Sci. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrudo-Guirado, M.I.; Blanco-Flores, A.; Toledo-Jaldin, H.P.; Sanchez-Mendieta, V.; Vilchis-Nestor, A.R. Reuse of sustainable materials for xylenol orange dye and copper (II) ion ammoniacal removal. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 206, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Kong, W.; Xie, W.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, X.; Gao, J. Bi-porous bioinspired chitosan foams with layered structure and their adsorption for xylenol orange. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 197, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

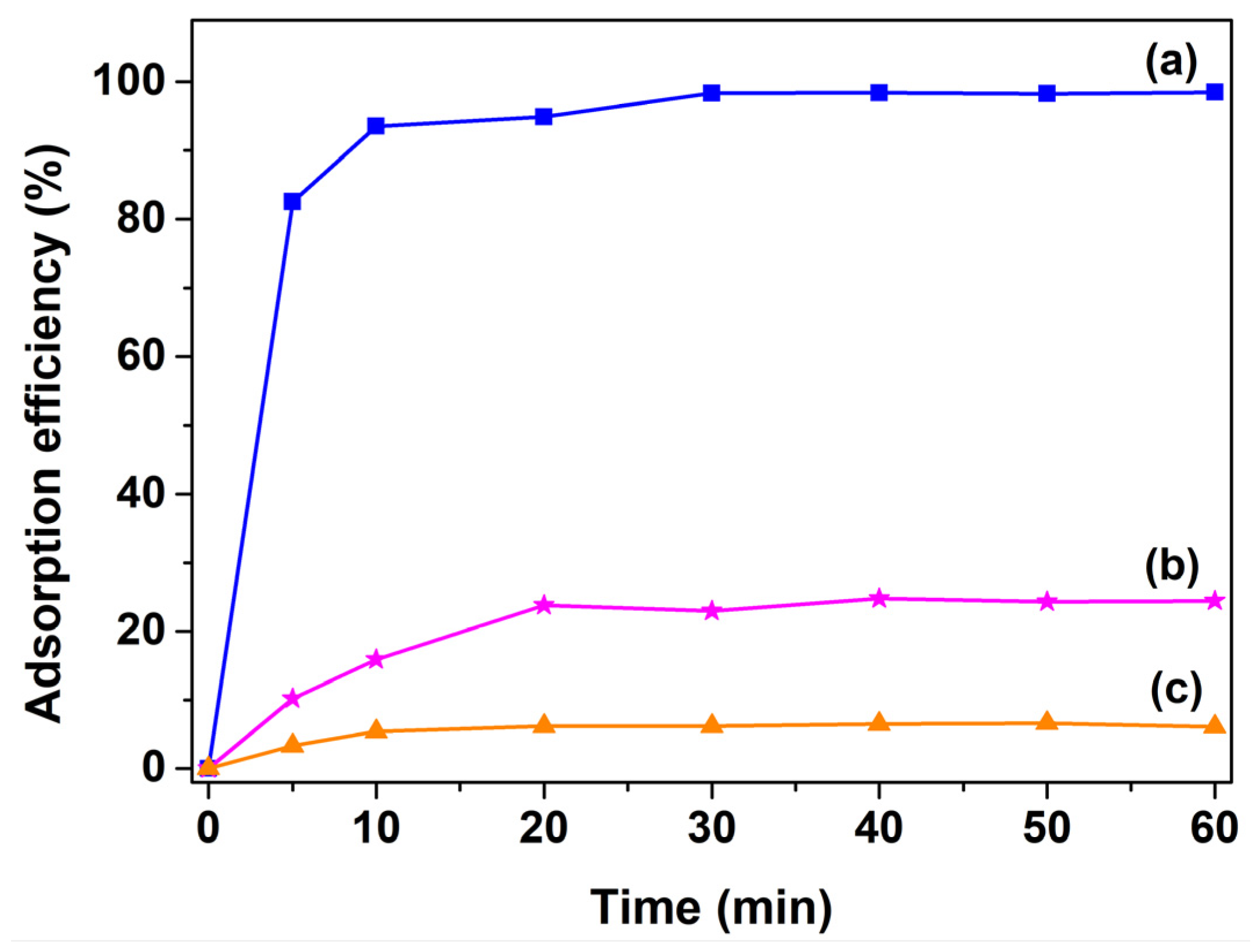
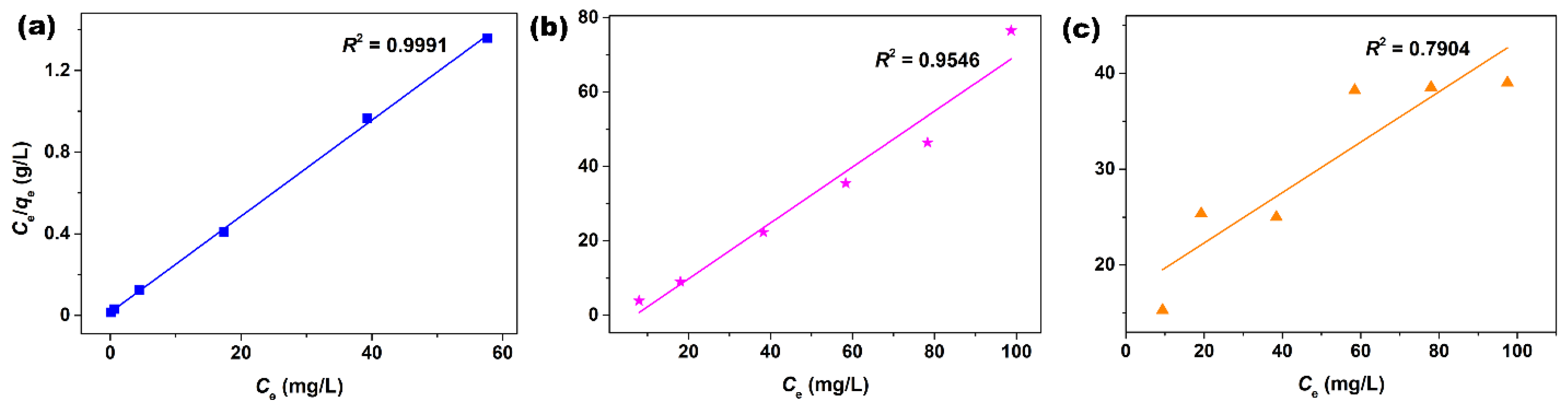

| Langmuir Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| XO Dye | BO2 Dye | AO7 Dye | |
| qm (mg/g) | 42.5 | 1.3 | 3.8 |
| R2 | 0.9991 | 0.9546 | 0.7904 |
| Authors | Adsorbent Name | Synthetic Method | qm (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ishaq [38] | Coal ash | Heated at 750 °C | 0.74 |
| Bai [39] | Porous amino-cellulose membrane | TEMPO oxidation and ethylenediamine grafting | 15 |
| Pang [40] | Expansion graphite | Chemical oxidation intercalation of potassium permanganate and vitriol | 18.15 |
| Garrudo-Guirado [41] | Vitreous tuff mineral (VT) | Milled and sieved to 60 mesh | 45.17 |
| Wang [42] | Bi-porous chitosan monoliths | Unidirectional freeze-drying method under vacuum less than 20 Pa for 48 h | 153.8 |
| Zhu [33] | Hyperbranched polyethyleneimine (HPEI) based gel | Cross-linking reaction between HPEI and N,N′-methylene-bis-acrylamide | 3312.06 |
| Xu in this work | Fe3O4 nanoparticles | One-pot hydrothermal process at 200 °C for 24 h | 42.5 |
| Dye | qe,exp (mg/g) | Pseudo-First-Order Kinetic Model | Pseudo-Second-Order Kinetic Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe1,cal (mg/g) | k1 (1/h) | R2 | qe2,cal (mg/g) | k1 (g/mg·h) | R2 | ||
| XO | 9.847 | 1.7906 | 7.1318 | 0.7328 | 10.0452 | 6.4352 | 0.9998 |
| BO2 | 2.444 | 6.2516 | 0.2983 | 0.6316 | 2.8740 | 2.8272 | 0.9859 |
| AO7 | 0.614 | 8.9600 | 0.0383 | 0.5564 | 0.7223 | 18.9232 | 0.9959 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ding, Z. Synthesis of Superparamagnetic Fe3O4 Nano-Adsorbent Using an Energy-Saving and Pollution-Reducing Strategy for the Removal of Xylenol Orange Dye in Water. Energies 2022, 15, 7378. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15197378
Xu Y, Wang Q, Ding Z. Synthesis of Superparamagnetic Fe3O4 Nano-Adsorbent Using an Energy-Saving and Pollution-Reducing Strategy for the Removal of Xylenol Orange Dye in Water. Energies. 2022; 15(19):7378. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15197378
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Yaohui, Qin Wang, and Zhao Ding. 2022. "Synthesis of Superparamagnetic Fe3O4 Nano-Adsorbent Using an Energy-Saving and Pollution-Reducing Strategy for the Removal of Xylenol Orange Dye in Water" Energies 15, no. 19: 7378. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15197378
APA StyleXu, Y., Wang, Q., & Ding, Z. (2022). Synthesis of Superparamagnetic Fe3O4 Nano-Adsorbent Using an Energy-Saving and Pollution-Reducing Strategy for the Removal of Xylenol Orange Dye in Water. Energies, 15(19), 7378. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15197378







