Steam Electrolysis vs. Co-Electrolysis: Mechanistic Studies of Long-Term Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Voltage Development
Degradation Behavior under Different Measurements Conditions
3.2. Overview of Electrochemical Performance Analysis
3.3. Electrochemical Impedance Analysis
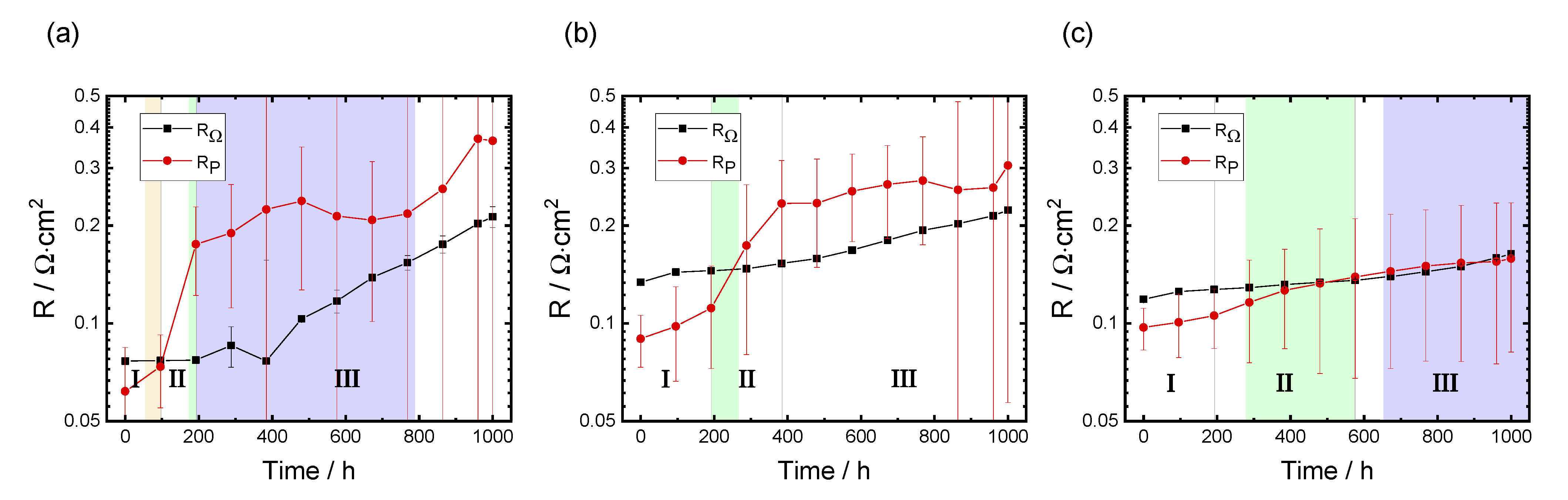
3.3.1. Evolution of RΩ and RP
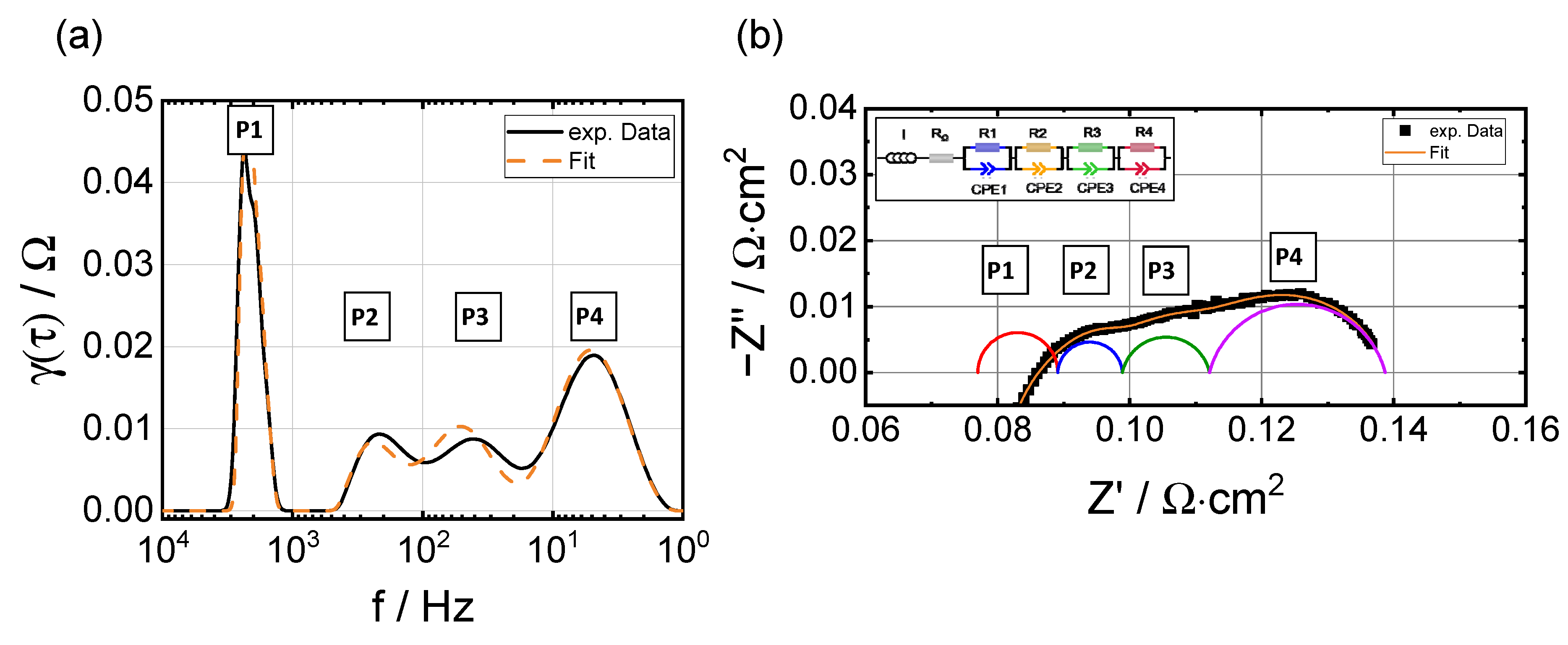
3.3.2. Breakdown of the Polarization Resistance
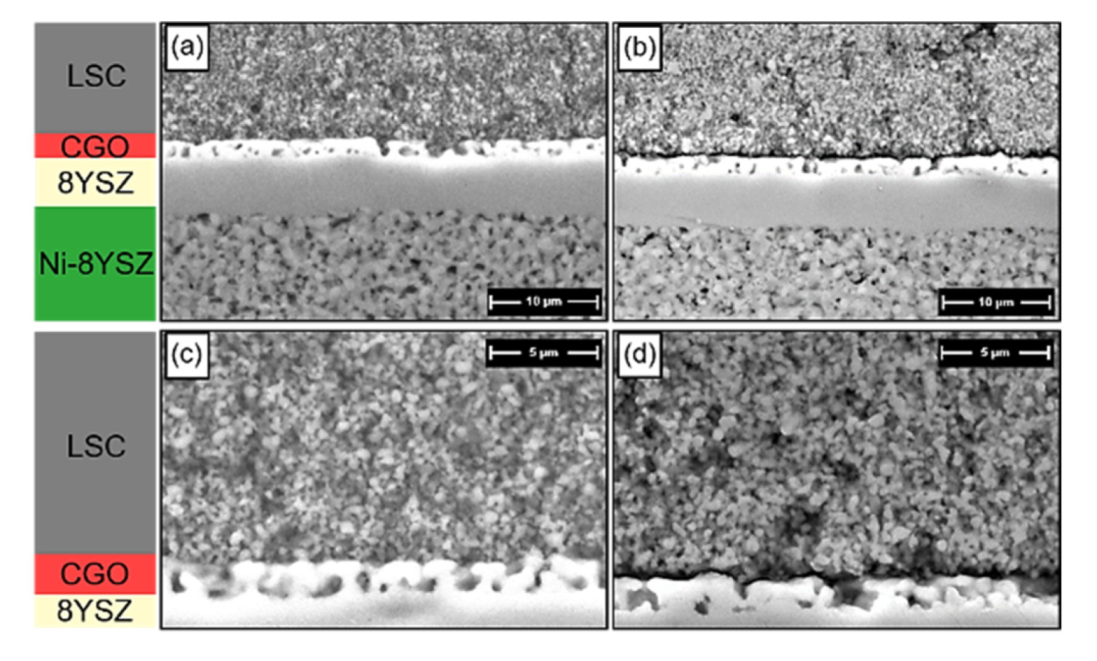
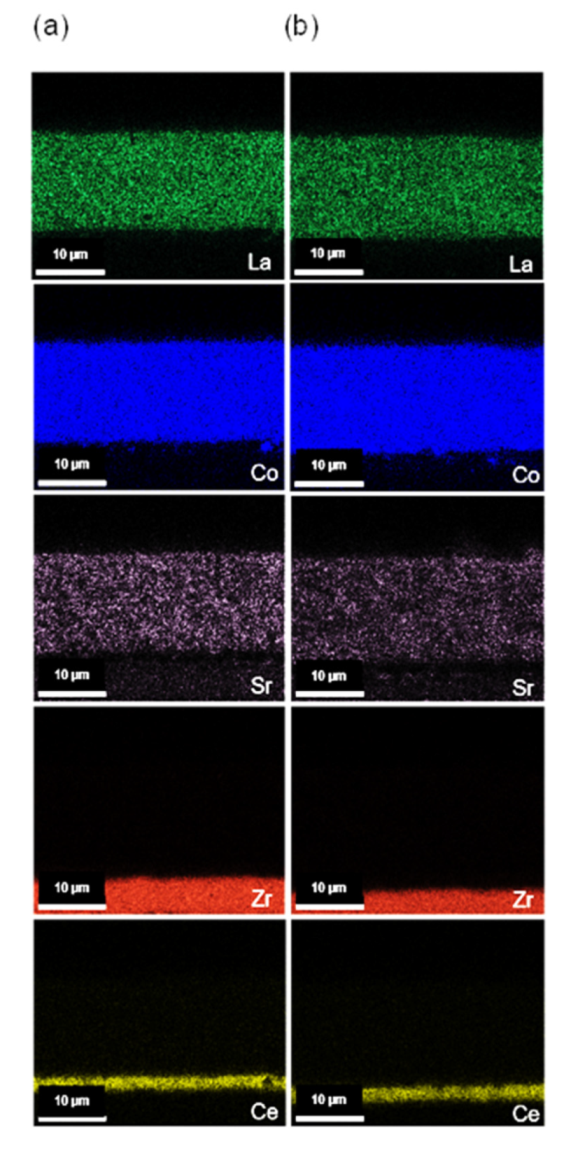
3.4. Microstructural Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dittrich, L.; Nohl, M.; Jaekel, E.E.; Foit, S.; de Haart, L.; Eichel, R.-A. High-Temperature Co-Electrolysis: A Versatile Method to Sustainably Produce Tailored Syngas Compositions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, F971–F975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachsman, E.D.; Lee, K.T. Lowering the temperature of solid oxide fuel cells. Science 2011, 334, 935–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foit, S.R.; Vinke, I.C.; de Haart, L.G.J.; Eichel, R.-A. Power-to-Syngas: An Enabling Technology for the Transition of the Energy System? Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 5402–5411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, B.; Zhang, W.; Chen, J.; Qiao, J.; Zhang, J. A review of high temperature co-electrolysis of H2O and CO2 to produce sustainable fuels using solid oxide electrolysis cells (SOECs): Advanced materials and technology. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 1427–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmo, M.; Fritz, D.L.; Mergel, J.; Stolten, D. A comprehensive review on PEM water electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 4901–4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapountzi, F.M.; Gracia, J.M.; Weststrate, C.J.; Fredriksson, H.O.; Niemantsverdriet, J.W. Electrocatalysts for the generation of hydrogen, oxygen and synthesis gas. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2017, 58, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mogensen, M.B. Thermodynamics of High Temperature H2O and CO2 Electrolysis; Technical University of Denmark: Lyngby, Denmark, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Brisse, A.; Schefold, J.; Zahid, M. High temperature water electrolysis in solid oxide cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2008, 33, 5375–5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiva Kumar, S.; Himabindu, V. Hydrogen production by PEM water electrolysis—A review. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2019, 2, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Blum, L.; Menzler, N.H.; Stolten, D. Solid Oxide Electrolyzer Stack with 20,000 h of Operation. ECS Trans. 2017, 78, 2885–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauch, A.; Ebbesen, S.D.; Jensen, S.H.; Mogensen, M. Highly efficient high temperature electrolysis. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, L.; Packbier, U.; Vinke, I.C.; de Haart, L.G.J. Long-Term Testing of SOFC Stacks at Forschungszentrum Jülich. Fuel Cells 2013, 13, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawdsley, J.R.; David Carter, J.; Jeremy Kropf, A.; Yildiz, B.; Maroni, V.A. Post-test evaluation of oxygen electrodes from solid oxide electrolysis stacks☆. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 4198–4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fergus, J.W. Electrolytes for solid oxide fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2006, 162, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knibbe, R.; Traulsen, M.L.; Hauch, A.; Ebbesen, S.D.; Mogensen, M. Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cells: Degradation at High Current Densities. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2010, 157, B1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momma, A.; Kato, T.; Kaga, Y.; Nagata, S. Polarization Behavior of High Temperature Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cells (SOEC). J. Ceram. Soc. Japan 1997, 105, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brichzin, V. The geometry dependence of the polarization resistance of Sr-doped LaMnO3 microelectrodes on yttria-stabilized zirconia. Solid State Ion. 2002, 152–153, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, S.B. Factors governing oxygen reduction in solid oxide fuel cell cathodes. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4791–4843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The, D.; Grieshammer, S.; Schroeder, M.; Martin, M.; Al Daroukh, M.; Tietz, F.; Schefold, J.; Brisse, A. Microstructural comparison of solid oxide electrolyser cells operated for 6100 h and 9000 h. J. Power Sources 2015, 275, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjalmarsson, P.; Sun, X.; Liu, Y.-L.; Chen, M. Influence of the oxygen electrode and inter-diffusion barrier on the degradation of solid oxide electrolysis cells. J. Power Sources 2013, 223, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Hendriksen, P.V.; Mogensen, M.B.; Chen, M. Degradation in Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cells During Long Term Testing. Fuel Cells 2019, 19, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trini, M.; Hauch, A.; de Angelis, S.; Tong, X.; Hendriksen, P.V.; Chen, M. Comparison of microstructural evolution of fuel electrodes in solid oxide fuel cells and electrolysis cells. J. Power Sources 2020, 450, 227599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, F.; Hubert, M.; Vulliet, J.; Ouweltjes, J.P.; Montinaro, D.; Cloetens, P.; Piccardo, P.; Lefebvre-Joud, F.; Laurencin, J. Degradation of Ni-YSZ Electrodes in Solid Oxide Cells: Impact of Polarization and Initial Microstructure on the Ni Evolution. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, F1229–F1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trini, M.; Jørgensen, P.S.; Hauch, A.; Bentzen, J.J.; Hendriksen, P.V.; Chen, M. 3D Microstructural Characterization of Ni/YSZ Electrodes Exposed to 1 Year of Electrolysis Testing. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, F158–F167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, X.; Liu, Y.; Hendriksen, P.V.; Chen, M. An operation strategy for mitigating the degradation of solid oxide electrolysis cells for syngas production. J. Power Sources 2021, 506, 230136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoerlein, M.P.; Riegraf, M.; Costa, R.; Schiller, G.; Friedrich, K.A. A parameter study of solid oxide electrolysis cell degradation: Microstructural changes of the fuel electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 276, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauch, A.; Brodersen, K.; Chen, M.; Mogensen, M.B. Ni/YSZ electrodes structures optimized for increased electrolysis performance and durability. Solid State Ion. 2016, 293, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blum, L.; de Haart, L.; Malzbender, J.; Menzler, N.H.; Remmel, J.; Steinberger-Wilckens, R. Recent results in Jülich solid oxide fuel cell technology development. J. Power Sources 2013, 241, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, L.; de Haart, L.G.J.; Malzbender, J.; Margaritis, N.; Menzler, N.H. Anode-Supported Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Achieves 70,000 Hours of Continuous Operation. Energy Technol. 2016, 4, 939–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Høgh, J.V.T.; Nielsen, J.U.; Bentzen, J.J.; Ebbesen, S.D.; Hendriksen, P.V. High Temperature Co-Electrolysis of Steam and CO2 in an SOC Stack: Performance and Durability. Fuel Cells 2013, 13, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Jiang, S.P. Review—Materials Degradation of Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, F3070–F3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Frey, C.E.; Menzler, N.H.; Blum, L. Electrochemical Performance and Preliminary Post-Mortem Analysis of a Solid Oxide Cell Stack with 20,000 h of Operation. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, F38–F45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elcogen, A.S. Solid Oxide Cells. Available online: https://elcogen.com/products/solid-oxide-fuel-cells/ (accessed on 23 July 2022).
- Schiemann, K.; Vibhu, V.; Yildiz, S.; Vinke, I.C.; Eichel, R.-A.; de Haart, L. Chrome Poisoning of Non-Manganiferous Cathode Materials in Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFCs). ECS Trans. 2017, 78, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schefold, J.; Brisse, A.; Poepke, H. 23,000 h steam electrolysis with an electrolyte supported solid oxide cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 13415–13426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schefold, J.; Poepke, H.; Brisse, A. Solid Oxide Electrolyser Cell Testing Up to the Above 30,000 h Time Range. ECS Trans. 2020, 97, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.; Sun, X.; Hagen, A. A Comparative Study of Durability of Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cells Tested for Co-Electrolysis under Galvanostatic and Potentiostatic Conditions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, F748–F755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jerôme, A. Modeling and Experimental Validation of High Temperature Steam and Carbon Dioxide Co-Electrolysis. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Grenoble, Saint-Martin-d’Hères, France, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lillmaa, K.; Maide, M.; Kanarbik, R.; Nurk, G.; Lust, E. Electrochemical Characteristics and Gas Composition Generated by La 0.8 Sr 0.2 Cr 0.5 Mn 0.5 O 3–δ Cathode at Electrolysis and Co-Electrolysis Modes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, F3190–F3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Ebbesen, S.D.; Mogensen, M.B. Degradation of solid oxide cells during co-electrolysis of steam and carbon dioxide at high current densities. J. Power Sources 2016, 328, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, S.E.; Dittrich, L.; Nohl, M.; Duyster, T.; Vinke, I.C.; Eichel, R.-A.; de Haart, L. Boundary Investigation of High-Temperature Co-Electrolysis towards Direct CO2 Electrolysis. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 034531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliandro, P.; Nakajo, A.; Diethelm, S.; van Herle, J. Model-assisted identification of solid oxide cell elementary processes by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy measurements. J. Power Sources 2019, 436, 226838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, L. SOFC Modelling and Parameter Identification by Means of Impedance Spectroscopy. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität Karlsruhe, Karlsruhe, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sonn, V.; Leonide, A.; Ivers-Tiffée, E. Combined Deconvolution and CNLS Fitting Approach Applied on the Impedance Response of Technical Ni∕8YSZ Cermet Electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2008, 155, B675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonide, A.; Sonn, V.; Weber, A.; Ivers-Tiffée, E. Evaluation and Modeling of the Cell Resistance in Anode-Supported Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2008, 155, B36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, C.; Ebbesen, S.D.; Mogensen, M. Co-electrolysis of CO2 and H2O in solid oxide cells: Performance and durability. Solid State Ion. 2011, 192, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Jiang, S.P. Failure mechanism of (La, Sr)MnO3 oxygen electrodes of solid oxide electrolysis cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 10541–10549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Ji, H.-I.; Dasari, H.P.; Shin, D.; Song, H.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, B.-K.; Je, H.-J.; Lee, H.-W.; Yoon, K.J. Degradation mechanism of electrolyte and air electrode in solid oxide electrolysis cells operating at high polarization. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 1225–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Choi, G.M. Stability of LSCF electrode with GDC interlayer in YSZ-based solid oxide electrolysis cell. Solid State Ion. 2014, 262, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Kim, K.J.; Choi, G.M. Effect of Ce0.43Zr0.43Gd0.1Y0.04O2−δ contact layer on stability of interface between GDC interlayer and YSZ electrolyte in solid oxide electrolysis cell. J. Power Sources 2015, 284, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vibhu, V.; Vinke, I.C.; Zaravelis, F.; Neophytides, S.G.; Niakolas, D.K.; Eichel, R.-A.; de Haart, L.G.J. Performance and Degradation of Electrolyte-Supported Single Cell Composed of Mo-Au-Ni/GDC Fuel Electrode and LSCF Oxygen Electrode during High Temperature Steam Electrolysis. Energies 2022, 15, 2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjalmarsson, P.; Sun, X.; Liu, Y.-L.; Chen, M. Durability of high performance Ni–yttria stabilized zirconia supported solid oxide electrolysis cells at high current density. J. Power Sources 2014, 262, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauch, A.; Ebbesen, S.D.; Jensen, S.H.; Mogensen, M. Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cells: Microstructure and Degradation of the Ni/Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia Electrode. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2008, 155, B1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lay-Grindler, E.; Laurencin, J.; Villanova, J.; Cloetens, P.; Bleuet, P.; Mansuy, A.; Mougin, J.; Delette, G. Degradation study by 3D reconstruction of a nickel–yttria stabilized zirconia cathode after high temperature steam electrolysis operation. J. Power Sources 2014, 269, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogensen, M.B.; Chen, M.; Frandsen, H.L.; Graves, C.; Hauch, A.; Hendriksen, P.V.; Jacobsen, T.; Jensen, S.H.; Skafte, T.L.; Sun, X. Ni migration in solid oxide cell electrodes: Review and revised hypothesis. Fuel Cells 2021, 21, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
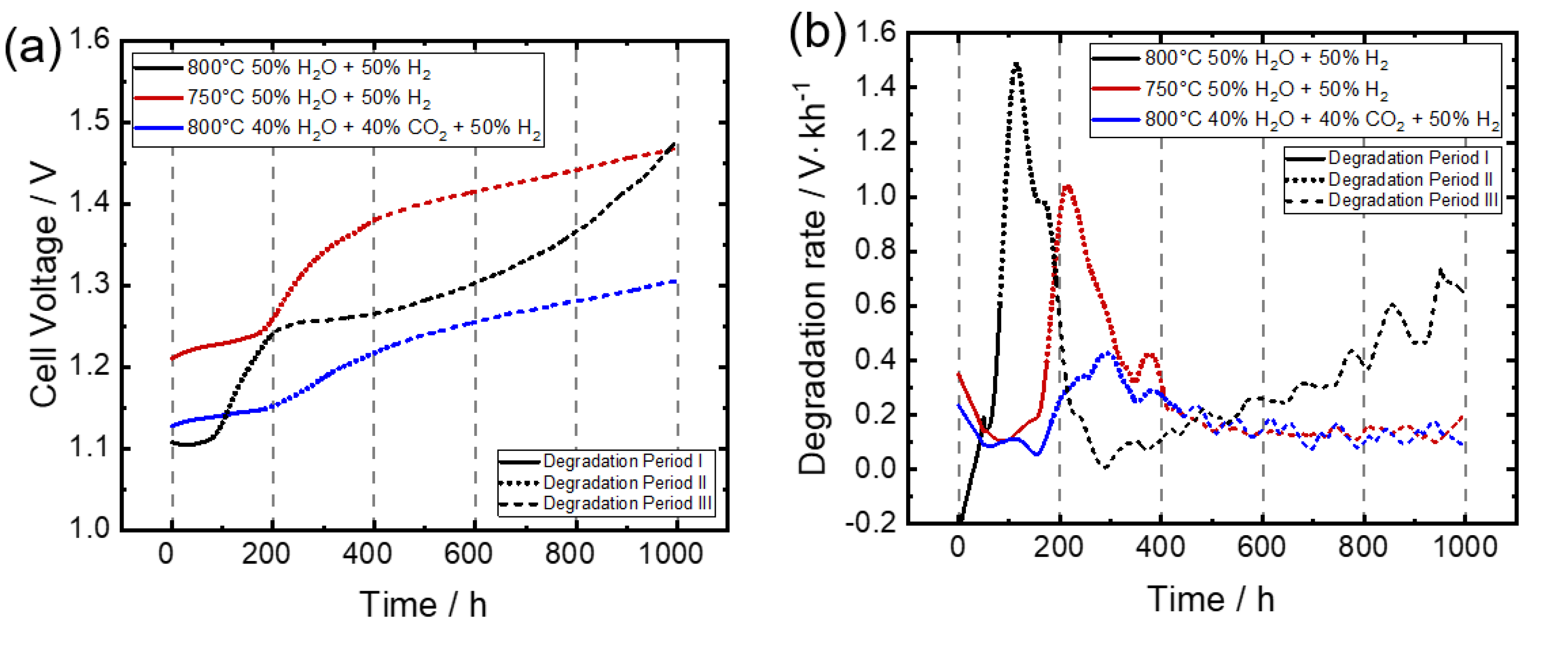
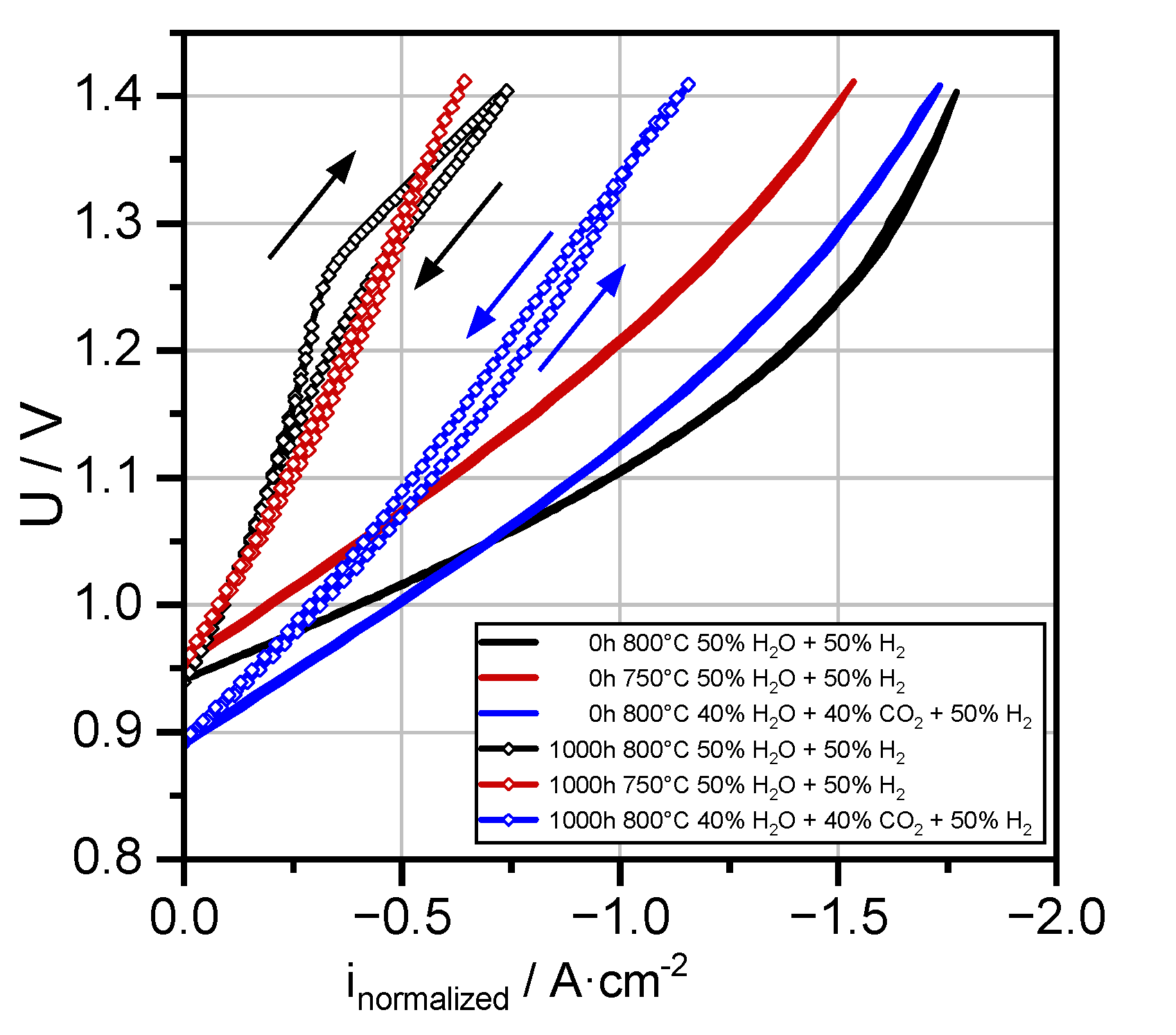
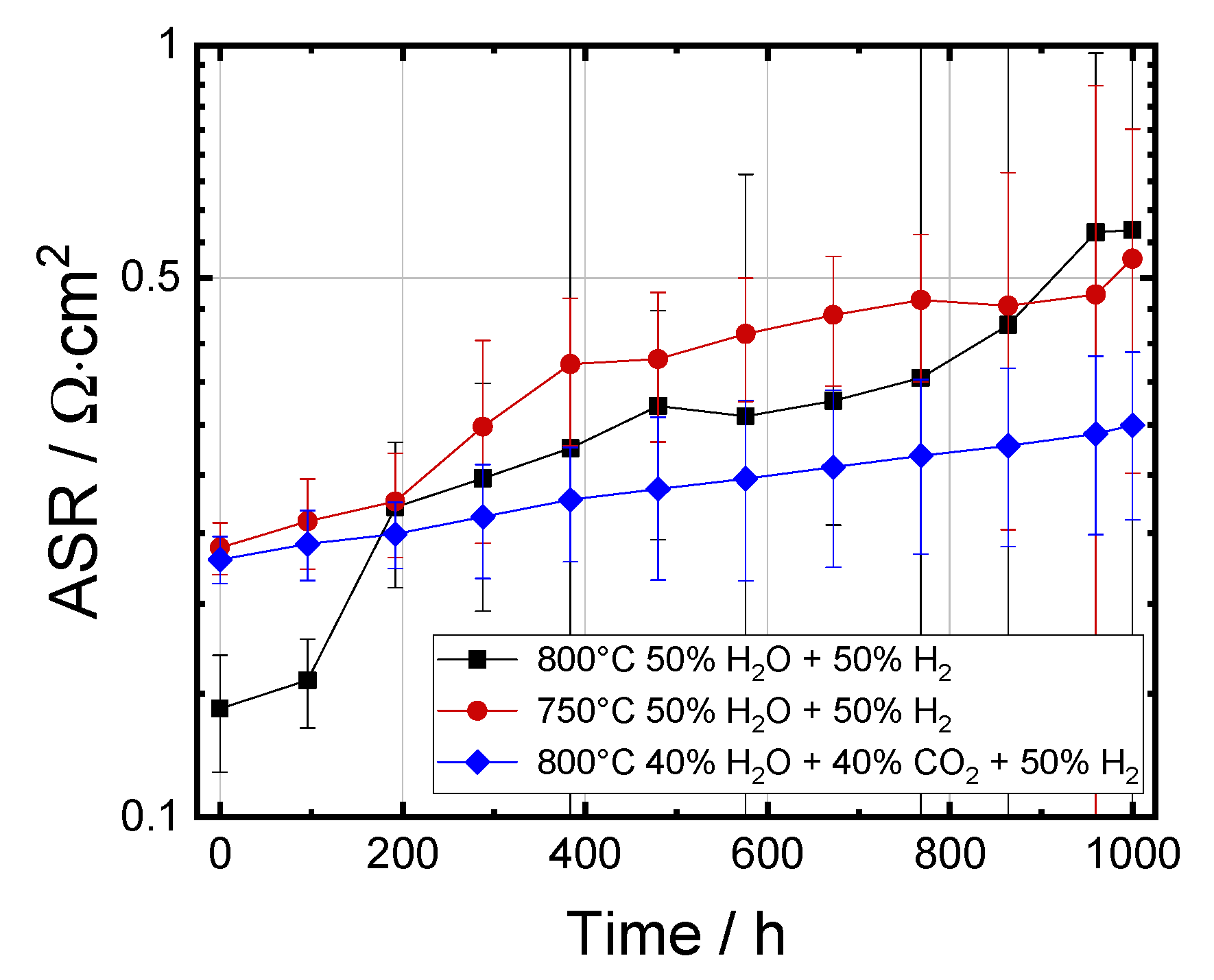
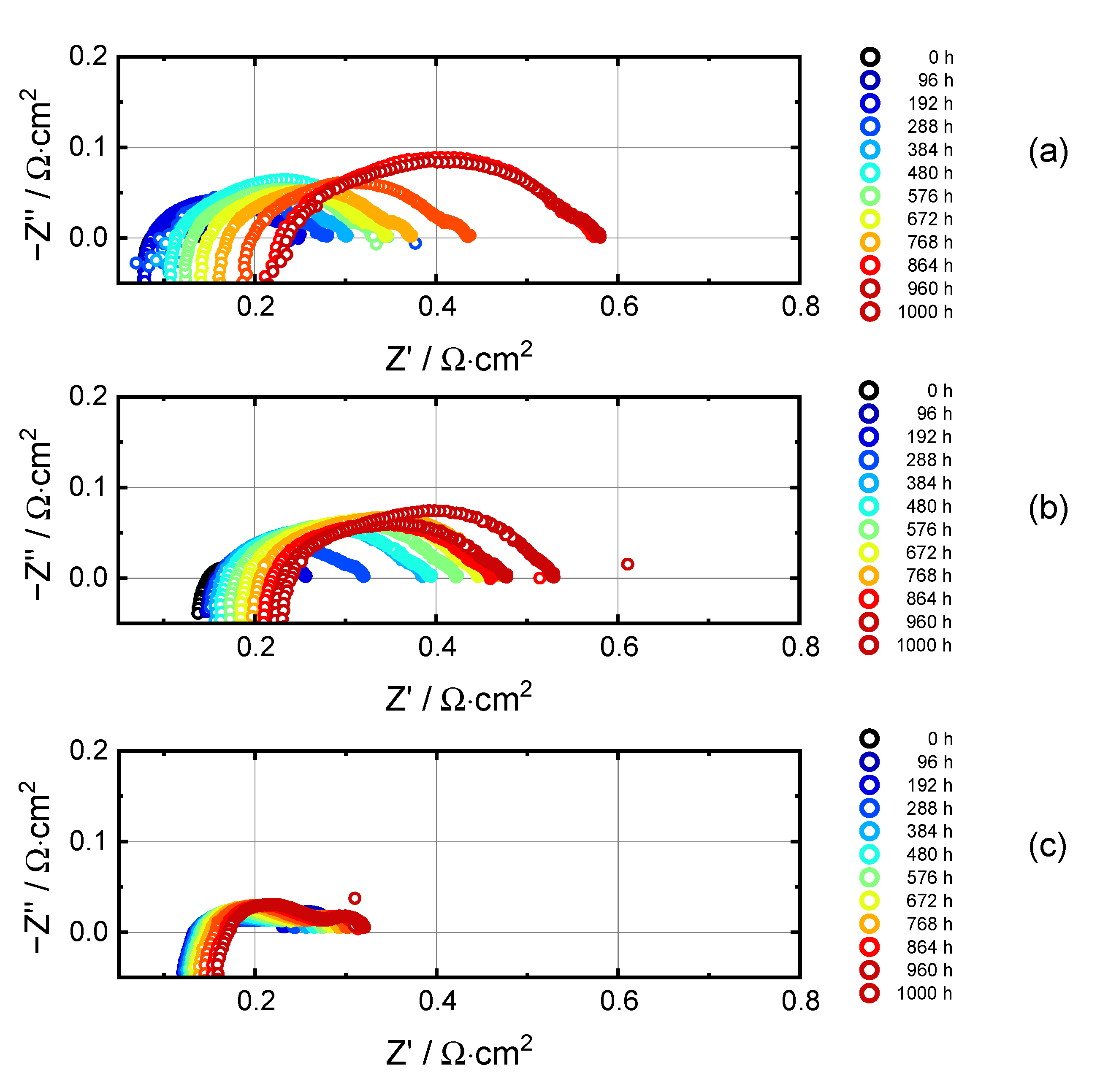

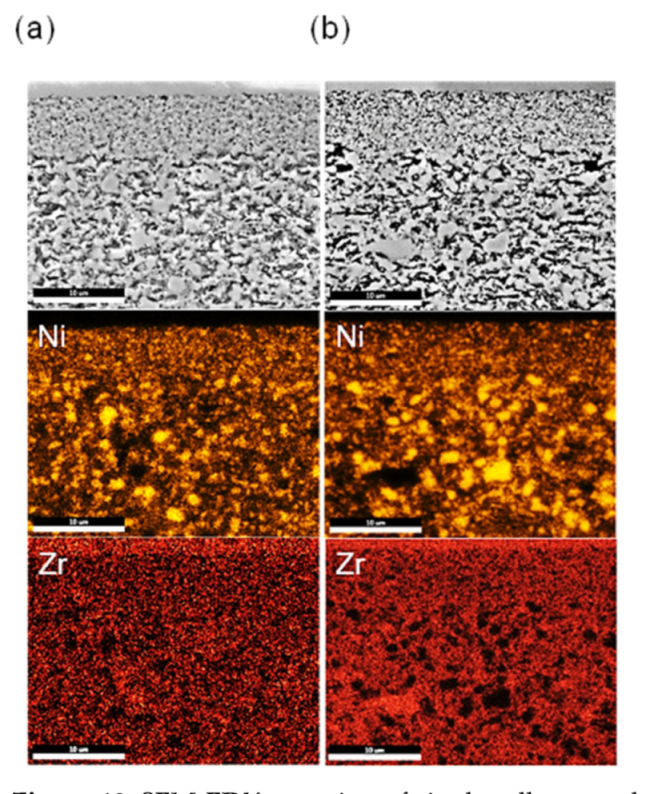
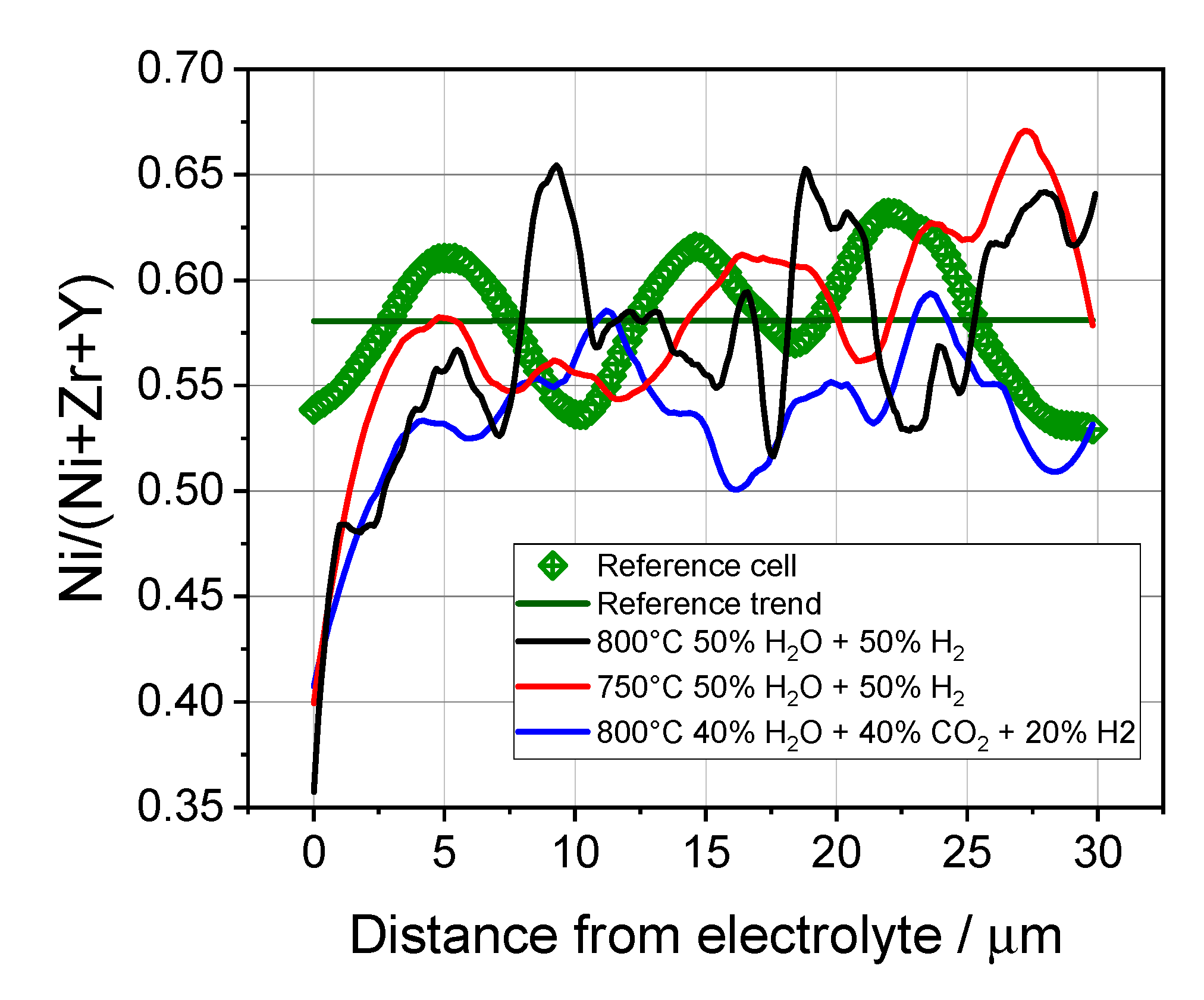
| Gas Inlet/% | T/°C | U0h/V | U1000h/V | ∆U/V | % Degradation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50% H2 + 50% H2O | 800 | 1.106 | 1.476 | 0.370 | 33 |
| 50% H2 + 50% H2O | 750 | 1.209 | 1.468 | 0.259 | 22 |
| 40% H2O + 40% CO2 + 20% H2 | 800 | 1.127 | 1.306 | 0.179 | 16 |
| Gas Inlet/% | T/°C | ∆RΩ/mΩ∙cm2 | ∆RP/mΩ∙cm2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50% H2 + 50% H2O | 800 | 136 | 302 |
| 50% H2 + 50% H2O | 750 | 89 | 216 |
| 40% H2O + 40% CO2 + 20% H2 | 800 | 45 | 61 |
| Process | Steam Electrolysis, 800 °C (Hz) | Co-Electrolysis, 800 °C (Hz) |
|---|---|---|
| RRQ1 | 18,600 | 5105 |
| RRQ2 | 2950 | 1100 |
| RRQ3 | 457 | 85 |
| RRQ4 | 7.9 | 1.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wolf, S.E.; Vibhu, V.; Tröster, E.; Vinke, I.C.; Eichel, R.-A.; de Haart, L.G.J. Steam Electrolysis vs. Co-Electrolysis: Mechanistic Studies of Long-Term Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cells. Energies 2022, 15, 5449. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15155449
Wolf SE, Vibhu V, Tröster E, Vinke IC, Eichel R-A, de Haart LGJ. Steam Electrolysis vs. Co-Electrolysis: Mechanistic Studies of Long-Term Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cells. Energies. 2022; 15(15):5449. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15155449
Chicago/Turabian StyleWolf, Stephanie E., Vaibhav Vibhu, Eric Tröster, Izaak C. Vinke, Rüdiger-A. Eichel, and L. G. J. (Bert) de Haart. 2022. "Steam Electrolysis vs. Co-Electrolysis: Mechanistic Studies of Long-Term Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cells" Energies 15, no. 15: 5449. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15155449
APA StyleWolf, S. E., Vibhu, V., Tröster, E., Vinke, I. C., Eichel, R.-A., & de Haart, L. G. J. (2022). Steam Electrolysis vs. Co-Electrolysis: Mechanistic Studies of Long-Term Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cells. Energies, 15(15), 5449. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15155449









