Theory of the Vom Berg Rheological Model and Its Use in Cloud-Native Application
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The type of flowing fluid;
- Geometry and physical properties of the element in which flow takes place;
- Flow regime.
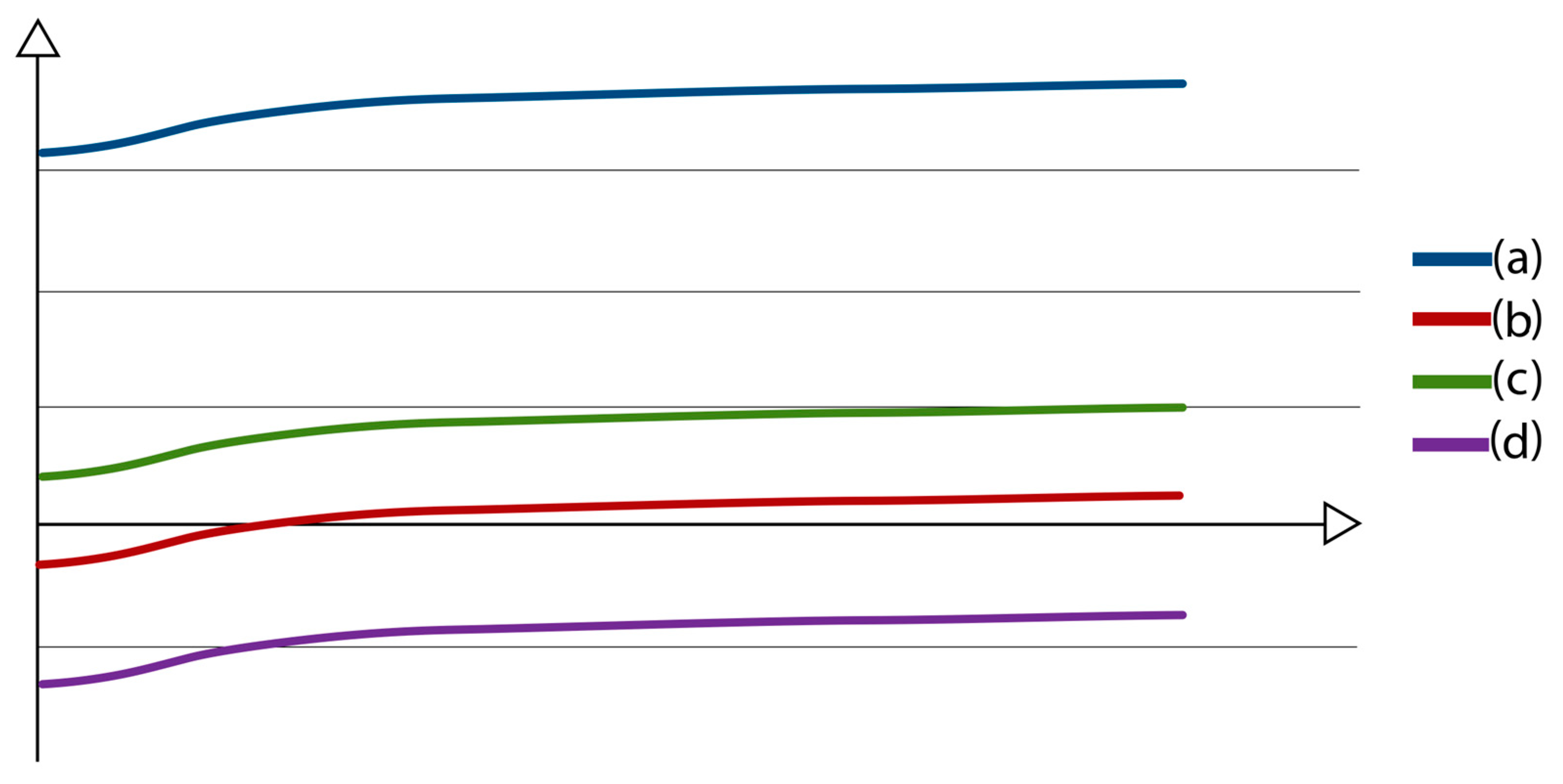
2. Division of Drilling Fluids According to Rheological Properties
- Bingham model:
- Ostwald de Waele model (power law):
- Herschel–Bulkley model (yield power law):
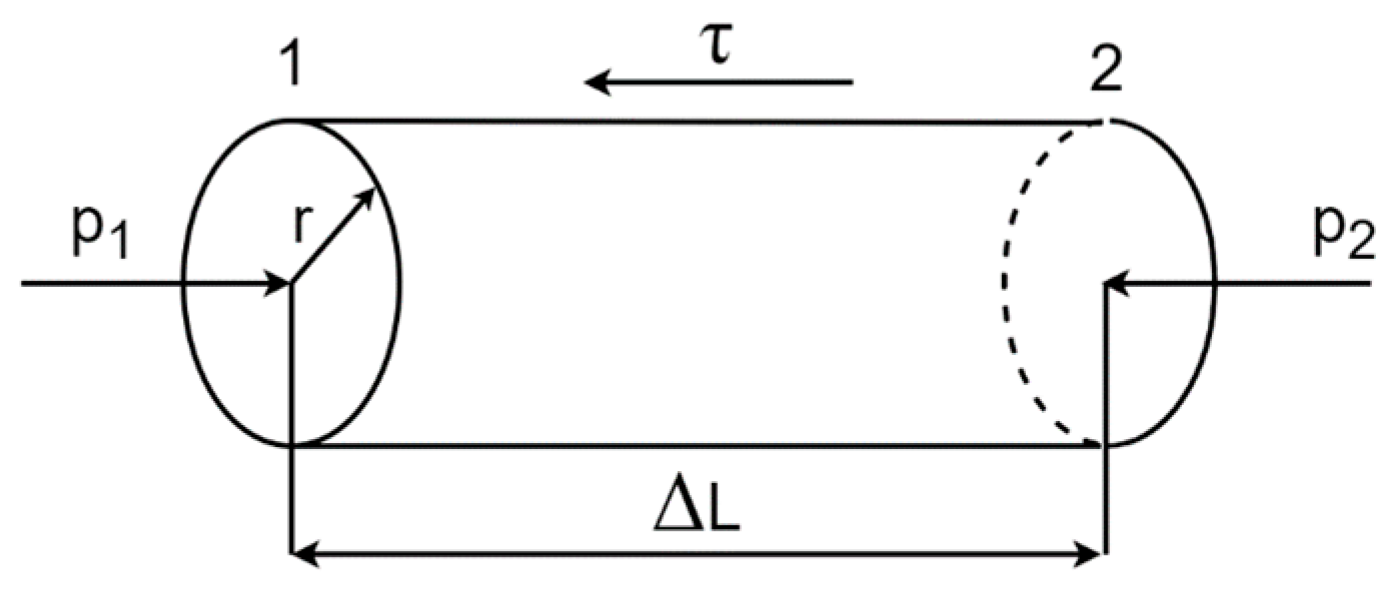
3. Laminar Flow of Reostable Fluids through a Pipe
- Pressure p1 = p acts on cross Section 1 with an area of πr2,
- Pressure p2 acts on cross Section 2 with an area of πr2, that pressure by number equals to pressure p reduced by pressure losses at the length ΔL: p2 = ,
- At the cylinder side with an area of 2πrΔl friction force occurs during flow, which is caused by shear stresses τ coming from the fluid.
4. Determination of Rheological Parameters and Resistances of Drilling Fluid Laminar Flow
- 1.
- Measurement, by means of a viscometer, shear stress dependencies for different drilling fluid shear rate values.
- 2.
- Estimation of the approximated shear rate value (occurring when fluid stream (Q) flows inside a pipe with the radius (R). Formula (20).
- 3.
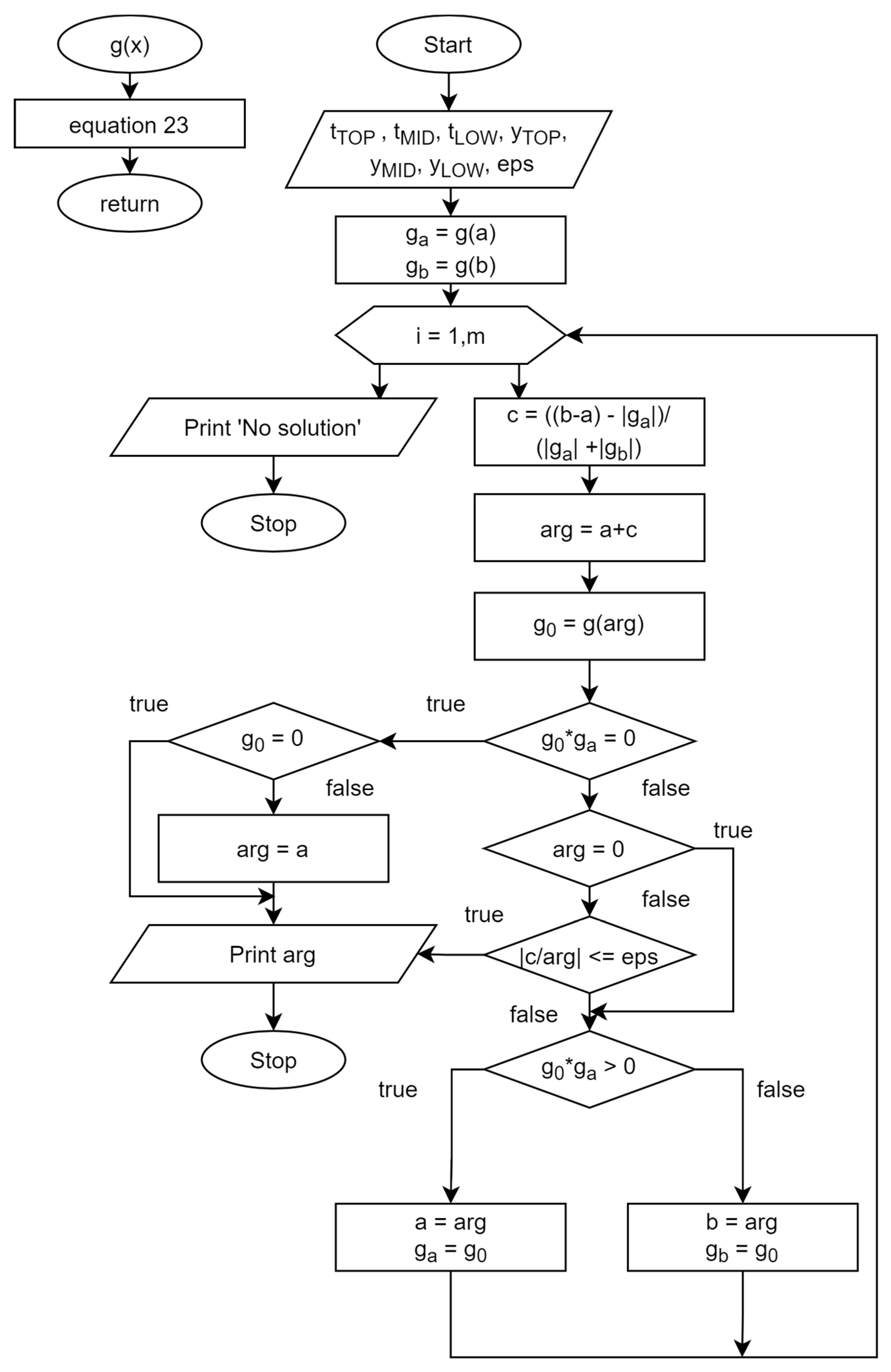
- Determination of the most approximated shear rate value , taking into account shear stress dependencies on shear rate, obtained from a given viscometer; establishment of the value . Determination of the measured values .
- 4.
- Calculation of rheological parameters of the fluid described by the Vom Berg model. Numerical solution of the Equation (22) and use of relationships (27) and (28).
- 5.
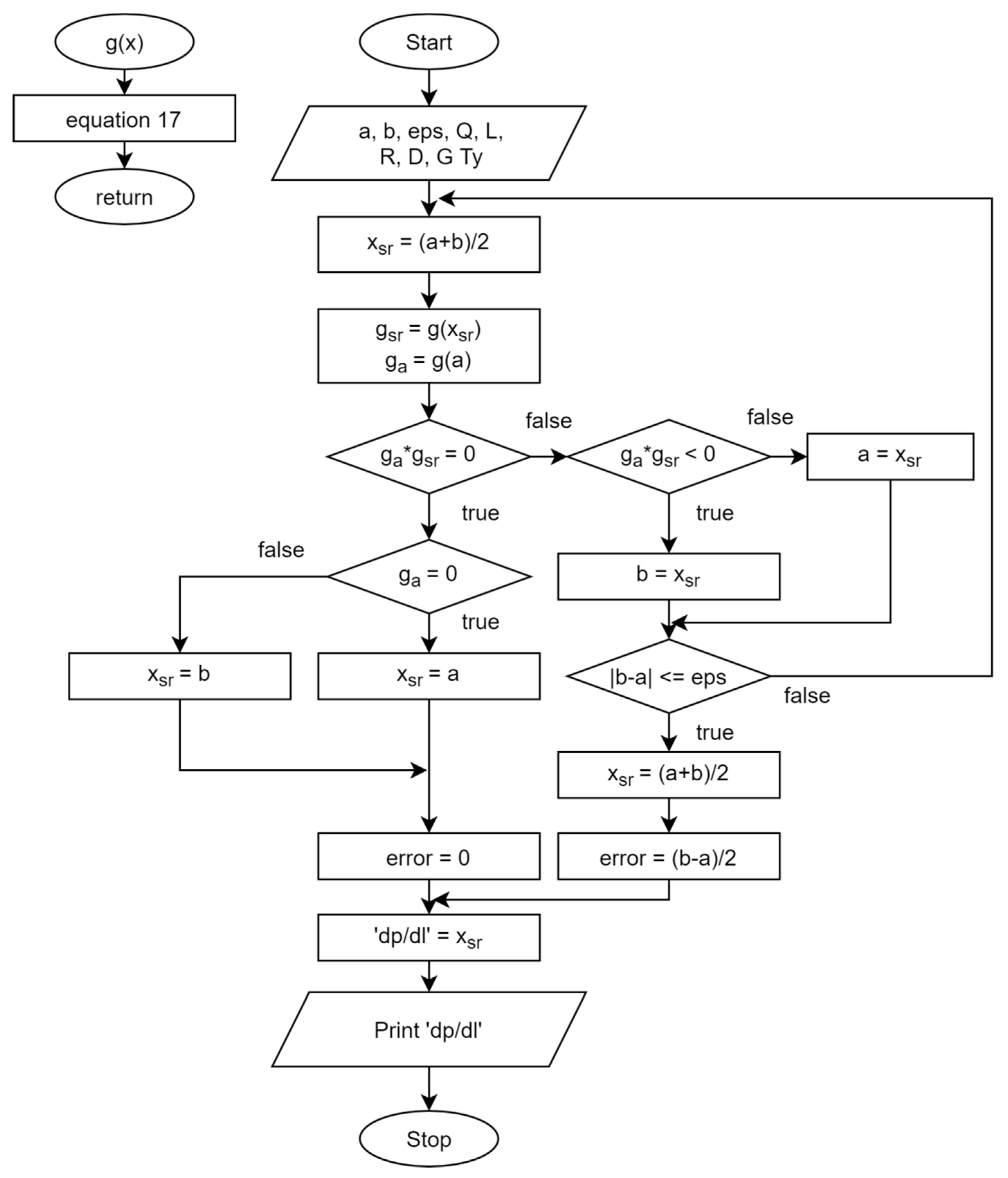
- Calculation of unit flow resistances. Numerical solution of Equation (17).
- 6.
- Calculation of real shear rate , characterising fluid flow, Equation (8).
- 7.
- Evaluation of the accuracy of the assumptions made in Item 3 of the algorithm. Checking of the condition . If this condition is met, calculations of unit flow resistances are considered completed.
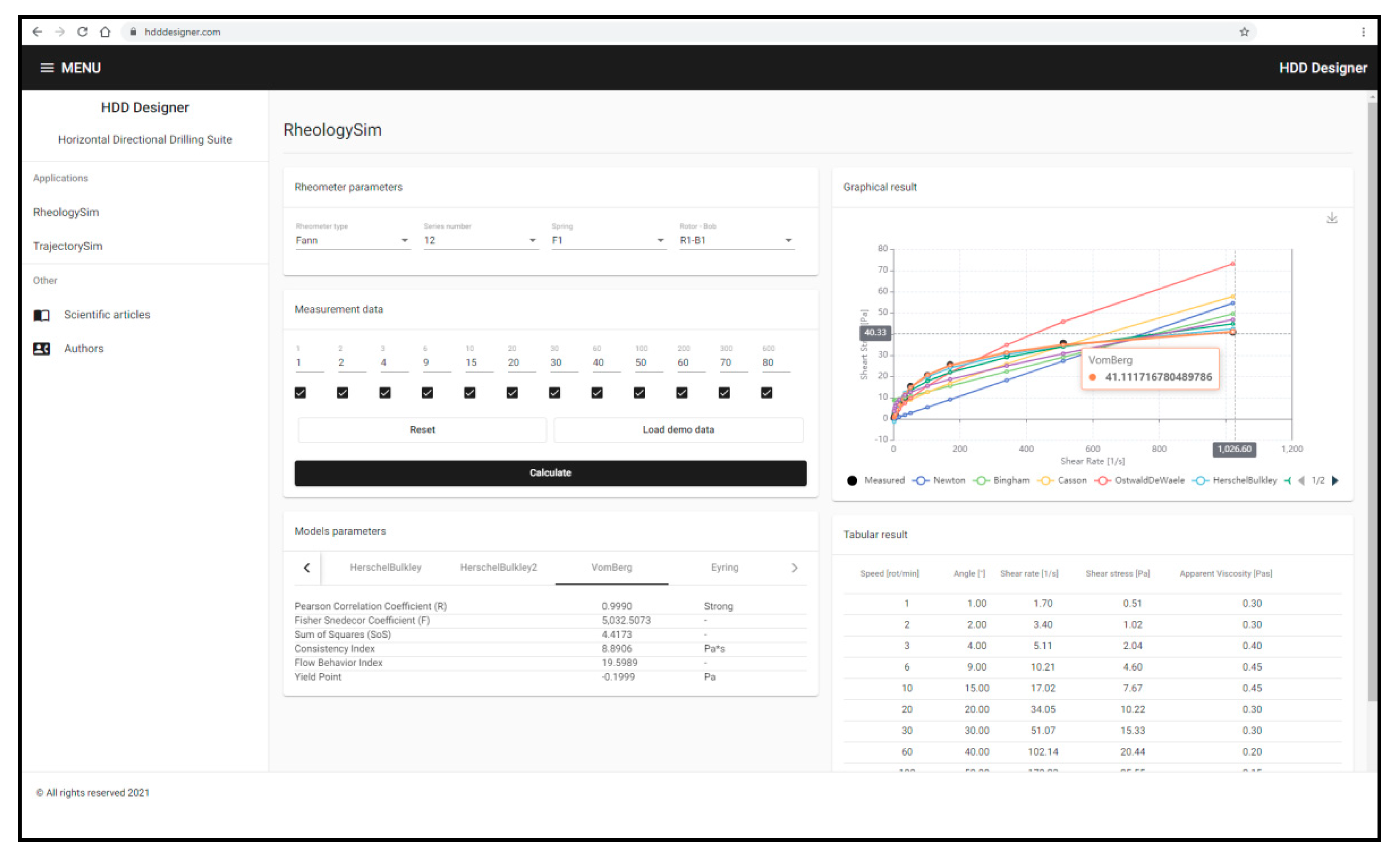
5. Application of Derived Equations in Cloud-Hosted Computer-Aided Design (CAD) Tool
- Rheological parameters calculation.
- Rheological model specific parameters calculation for Newton, Bingham, Casson, Ostwald De Waele, Herschel–Bulkley, Vom Berg and Eyring models.
- Regression parameters calculation.
- Graphical and tabular result presentation.
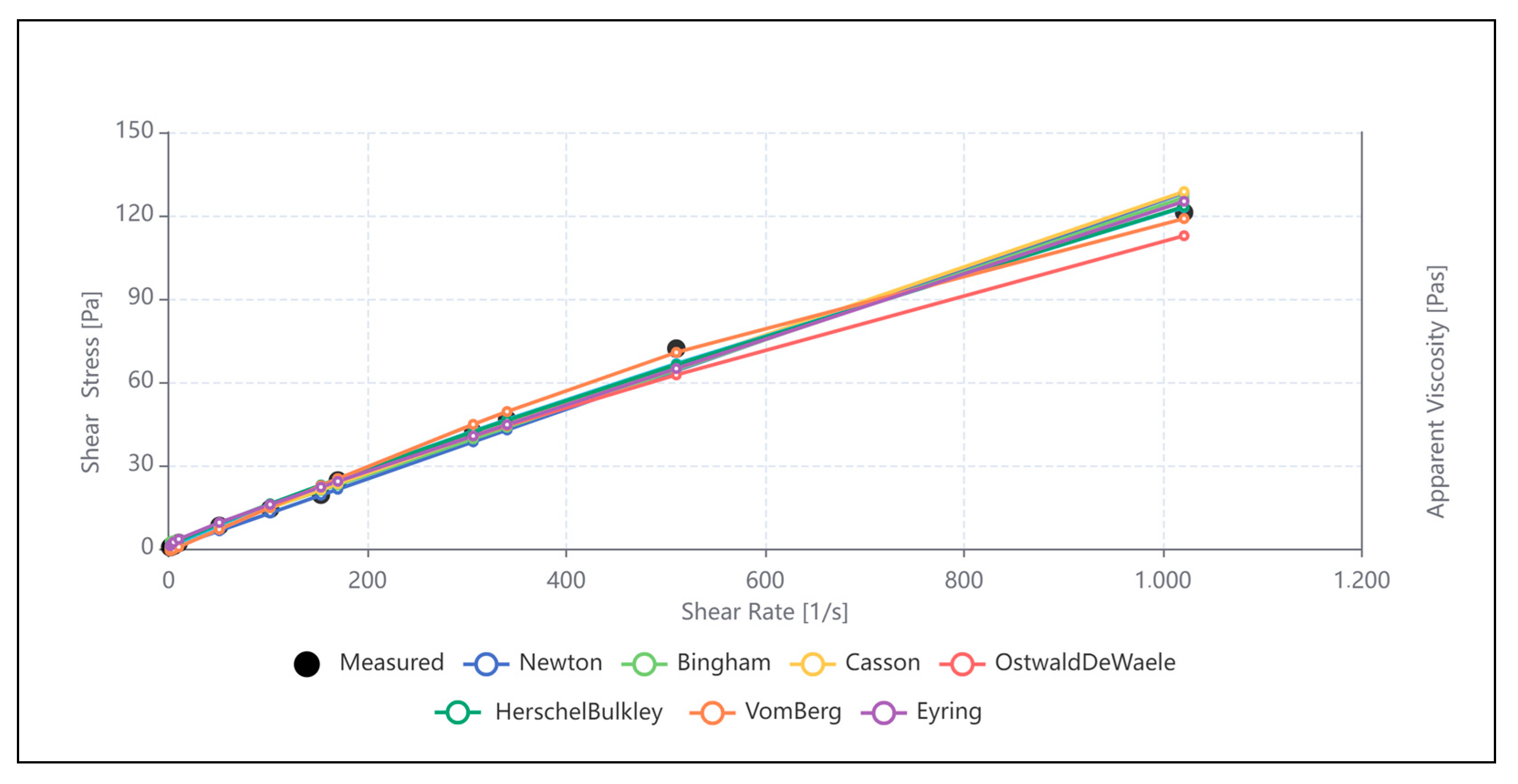
6. A practical Example of the Proposed Methodology Application
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| interval boundaries in the bisection method or the regula falsi method, [-]; | |
| constant; | |
| internal pipe diameter, [m]; | |
| rheological parameter in the Vom Berg model, [Pa]; | |
| plastic viscosity, [Pas]; | |
| rheological parameter in the Vom Berg model, [s−1]; | |
| shear rate gradient, [s−1]; | |
| lower measured value of a shear rate gradient, [s−1]; | |
| middle measured value of a shear rate gradient, [s−1]; | |
| reference shear rate gradient, [s−1]; | |
| upper measured value of a shear rate gradient, [s−1]; | |
| coefficient of drilling fluid consistency, [Pasn]; | |
| exponential index, [-]; | |
| pressure, [Pa]; | |
| flow rate, [m3/s]; | |
| internal radius, [m]; | |
| distance from the pipe axis, [m]; | |
| distance from the axis of a pipe in which fluid flows with constant velocity v0, [m]; | |
| shear stress, [Pa]; | |
| yield point, [Pa]; | |
| lower measured value of shear stress, [Pa]; | |
| middle measured value of shear stress, [Pa]; | |
| upper measured value of shear stress, [Pa]; | |
| flow velocity, [m/s]; | |
| maximum flow velocity, [m/s]; | |
| constant fluid flow velocity at a distance from 0 to r0 from the pipe axis, [m/s]; |
References
- Vom Berg, W. Influence of specific surface and concentration of solids upon the fow behaviour of cement pastes. Mag. Concr. Res. 1979, 31, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiśniowski, R.; Skrzypaszek, K.; Małachowski, T. Selection of a Suitable Rheological Model for Drilling Fluid Using Applied Numerical Methods. Energies 2020, 13, 3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- API RP 13D. Rheology and Hydraulics of Oil-Well Drilling Fluids; Norm of American Petroleum Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- BN-90/1785-01; Płuczka Wiertnicza. Metody Badań w Warunkach Polowych. Wydawnictwa Normalizacjne ”ALFA”: Warszawa, Poland, 1990.
- Wiśniowski, R. Metodyka Określania Modelu Reologicznego Cieczy Wiertniczej; Wiertnictwo, Nafta, Gaz R. 18/1; Wydawnictwo AGH: Kraków, Poland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Wiśniowski, R. Zastosowanie Modelu Herschela-Bulkleya w Hydraulice Płuczek Wiertniczych; Nowoczesne Techniki i Technologie Bezwykopowe, Zeszyt nr 2/2000; HDD Consulting: Kraków, Poland, 2000; pp. 20–28. [Google Scholar]
- Benyounes, K. Rheological behavior of cement-based grout with Algerian bentonite. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, A.G. Comparative Study of Bisection and Newton-Rhapson Methods of Root-Finding Problems. Int. J. Math. Trends Technol. (IJMTT) 2015, V19, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalquist, G.; Biorck, A. Numerical Methods; Dower Publication Inc.: Mineula, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ehiwario, J.C.; Aghamie, S.O. Comparative Study of Bisection, Newton-Raphson and Secant Methods of Root-Finding Problems. IOSR J. Eng. (IOSRJEN) 2014, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Catalogue of Brookfield Company. Brookfield Viscometers/Rheometers; Catalogue of Brookfield Company: Middleboro, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. Haake Series 1; Materials from Thermo Fisher Scientific; Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.: Hanover, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Materials of Rheology Solution Victoria Company. Haake, Material Characterisation & Testing Products; Materials of Rheology Solution Victoria Company: Truganina, Australia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hoechst. Hoechst Polymer Fluids; Information Materials from Hoechst; Hoechst: Höchst, Germany, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Fann Instrument Company. Model 35 Instruction Manual, Manual No. 208878; Fann Instrument Company: Houston, TX, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- OFI Testing Equipment, Inc. Testing Equipment for Drilling Fluids · Cement · Core Analysis · Laboratory Supplies · Reagents, Ofite Catalog. 2017. Available online: https://hiltoninstruments.com/pdfUploads/OFITE%20Catalogue.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2022).
- Klotz, J.A.; Brigham, W.E. To Determine Herschel-Bulkley Coefficients. J. Pet. Technol. 1998, 50, 80–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgoyne, A.T.; Milheim, K.K.; Chenevert, M.E.; Young, F.S. Applied Drilling Engineering. In SPE Textbook; SPE: Houston, TX, USA, 1986; Chapter 4.8. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Li, W. An improved exponential regula falsi method with quadratic convergence of both diameter and point for solving nonlinear equations. Appl. Numer. Math. 2007, 57, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Laboratory Measurement | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rotational speed n, [rot/min] | 0.9 | 1.8 | 3 | 6 | 30 | 60 | 90 | 100 | 180 | 200 | 300 | 600 |
| Torsion | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 16 | 28 | 38 | 48 | 82 | 91 | 141 | 237 |
| Angle Φ, [-] | ||||||||||||
| Calculated Values | ||||||||||||
| Shear rate, [s−1] | 1.53 | 3.07 | 5.11 | 10.22 | 51.10 | 102.20 | 153.31 | 170.34 | 306.61 | 340.68 | 511.02 | 1022.04 |
| Shear stresses τ, [Pa] | 0.51 | 1.02 | 1.02 | 2.04 | 8.18 | 14.31 | 19.42 | 24.53 | 41.90 | 46.50 | 72.05 | 121.11 |
| Model | Newton | Bingham | Casson | Ostwal De Waele | Herschel Bulkley | Eyring | Vom Berg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pearson Correlation Coefficient | 0.9947 | 0.996 | 0.9965 | 0.9939 | 0.998 | 0.997 | 0.9985 |
| Fisher Snedecor Coefficient | 929.58 | 1230.19 | 1425.92 | 805.64 | 2556.01 | 1649.97 | 3379.23 |
| Sum of squares | 156.17 | 118.31 | 102.19 | 179.9 | 57.18 | 88.39 | 43.29 |
| Approximated shear rate, [s−1] | 96 | ||
| Shear rate, [s−1] | |||
| 51.10 | 102.20 | 153.31 | |
| Shear stresses τ, [Pa] | |||
| 8.18 | 14.31 | 19.42 | |
| Rheological parameters of the Vom Berg model | τy | D | G |
| 1.2448 | 18.3547 | 132.16 | |
| Unit flow resistances dp/dl [Pa/m] | 387 | ||
| Real shear rate, [s−1] | 101.6 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wiśniowski, R.; Orłowicz, G. Theory of the Vom Berg Rheological Model and Its Use in Cloud-Native Application. Energies 2022, 15, 4481. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15124481
Wiśniowski R, Orłowicz G. Theory of the Vom Berg Rheological Model and Its Use in Cloud-Native Application. Energies. 2022; 15(12):4481. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15124481
Chicago/Turabian StyleWiśniowski, Rafał, and Grzegorz Orłowicz. 2022. "Theory of the Vom Berg Rheological Model and Its Use in Cloud-Native Application" Energies 15, no. 12: 4481. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15124481
APA StyleWiśniowski, R., & Orłowicz, G. (2022). Theory of the Vom Berg Rheological Model and Its Use in Cloud-Native Application. Energies, 15(12), 4481. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15124481






