Abstract
Combined economic emission dispatch (CEED) problems are among the most crucial problems in electrical power systems. The purpose of the CEED is to plan the outputs of all production units available in the electrical power system in such a way that the cost of fuel and polluted emissions are minimized while respecting the equality and inequality constraints of the system and efficiently responding to the power load required. The rapid depletion of these sources causes limitation and increases the price of fuel. It is therefore very important that scientific research in the last few decades has been oriented toward the integration of renewable energy systems (RES) such as wind and PV as an alternative source. Furthermore, the CEED problem including RES is the most important problem with regard to electrical power field optimization. In this study, a classification of optimization techniques that are widely used, such as traditional methods, non-conventional methods, and hybrid methods, is summarized. Many optimization methods have been presented and each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages for solving this complex CEED problem, including renewable energy. A review of different optimization techniques for solving this CEED problem is explored in this present paper. This review will encourage researchers in the future to gain knowledge of the best approaches applicable to solve CEED problems for practical electrical systems.
1. Introduction
Electrical energy is the most popular form of energy, because it can be transported easily at high efficiency and at reasonable costs. Therefore, electrical energy is the easiest form of energy to use today. But before consuming it, it will have had to be produced, generally in high-power production units, transported, and then distributed to each consumer. In industrialized countries, this system is now very centralized even if changes in regulations are leading to the beginnings of decentralization of production.
The generation of energy from fossil fuel plays a very important rule in atmosphere pollution phenomenon; because it releases many pollutants, such as sulfur oxides (SOx), nitrogen oxides (NOx) and carbon dioxide (CO2). Systematic use of fossil fuels, such as oil, coal, and natural gas makes it possible to have low production costs but leads to a massive release of polluting gas. Thus, electricity production from fossil fuels is the source of 40% of global CO2 emissions [1]. In addition, the share of the price of fuel in the cost of production is preponderant, which generates, given the sensitive nature of these raw materials, continuous oscillations and long-term instability.
Recently, due to the pressing public demand for a clean environment, this problem has attracted a lot of attention, especially due to similar laws of the Japanese and European governments and the text of amendments to the Clean Air Act of 1990. These environmental constraints have forced utilities to change their design or operational strategies to reduce pollution and air emissions from thermal plants.
Much more accessible and very suitable for decentralized production, renewable energies offer the possibility of producing electricity cleanly and above all with less dependence on resources, provided that their natural and sometimes random fluctuations are accepted. Today, after hydraulics, large wind turbines are becoming competitive in terms of production costs. These turbines contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, but one can wonder, as is the case with large dams, whether large concentrations of wind turbines are not also going to be disturbing sources. Moreover, the large share of aerogen is expected from large offshore farms which will remain centralized systems with their advantages and disadvantages.
Renewable energy sources (RES), after arousing short-lived interest with each oil shock, now seems to be on a real sustainable growth ramp, mainly for environmental reasons but also because fossil fuel reserves are dwindling. In what follows, this paper will only be interested in the production of electricity by wind turbines and photovoltaic panels because it seems that the wind and the sun are the best shared resources and therefore those which lend themselves best to the decentralized production of electricity. Moreover, because large-scale penetration of renewable energy resources undoubtedly constitutes the foundations of a fluctuating production of limited predictability. The possible addition, to this type of system, of production devices from fuel, complicates only very little this difficult problem.
A source of energy is renewable if consuming it does not limit its future use. This is the case for the energy coming from the sun, the wind, the rivers, the earth, and generally the wet or dry biomass, on the scale of the lifespan of humanity. This is not the case for fossil and nuclear fuels. But, in industrialized countries since the 19th century, they were progressively marginalized in favor of other sources of energy that were thought to be more promising. Since then, atmospheric pollution, global warming, nuclear risks, and the limits of resources have raised awareness that economic development that respects the environment in which we live is necessary.
Renewable energies therefore constitute an alternative to fossil energies in several respects. In fact, they are generally less disruptive to the environment, they do not emit greenhouse gases and do not produce waste, they are inexhaustible, they allow decentralized production adapted to both local resources and needs, and they offer significant energy independence. In addition, RES such as wind and solar are a promising option due to environmental concerns, as fossil fuels reserves are being consumed and fuel cost increases rapidly and emissions are getting high.
The balance between electricity production and electricity demand is an important task when considering RES. This is due to the variability and uncertainty of energy production from renewables over time [2,3,4,5,6]. For instance, the generation schedule of a solar panel depends on the solar radiation available at a site. Solar radiation varies from time to time over a day and also with seasons. In addition, concerning wind energy generation, the evaluation of the potential power of a wind site is based on the knowledge of the wind speed, which is actually not stable at any point, in view of the influence of several factors depending on the geographical location. Therefore, stochastic wind speed characteristics and solar radiation must be correctly modeled for exact values of their productions. Many techniques are available for wind speed and solar radiation modelling out of which beta distribution PDF and corresponding CDF have been used by many researchers for its accuracy [7,8,9,10,11].
In recent decades, various optimization techniques have been employed for solving a CEED problem in electrical systems. Generally, these techniques can be classified into three categories as shown in Figure 1, which are conventional or traditional methods, non-conventional methods and hybrid methods.
Figure 1.
Classification of optimization methods.
Over the last two decades, conventional techniques such as the LR method [12,13,14], the GS algorithm [15], the branch-and-bound algorithm (BBA) [16], the Lambda Iteration (LI) method [17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25], the PS algorithm [26], the QP technique [27,28,29], the classical technique based on coordination equations (CTBCE) [30], Linear Programming (LP) [31,32], Non-Linear Programming (NLP) [33], NLCNFP [34], Homogeneous Linear Programming (HLP) [35], Newton–Raphson (NR) [36,37], weighted mini-max (WMM) [38] and interior point method (IPM) [39] have been applied to solve the CEED problem.
However, these classical techniques are not efficient for solving the CEED problem due to their high computational time and they are not able to handle a large number of inequality constraints. To overcome these drawbacks, heuristic algorithms are developed for solving the non-linear, non-convex, and non-differentiable optimization problems.
Due to the limitations of classical methods, there is now an increased emphasis on techniques with artificial intelligence called non-conventional techniques like the ANN technique [40], the MHNN algorithm [41], the adaptive Hopfield neural network method [42], the biogeography-based optimizer (BBO) [43,44,45,46], particle swam optimization (PSO) [47,48,49,50,51], swarm-based MVMOS, which has been presented in [52], ant colony optimization (ACO) [53,54], MBA, which has been introduced in [55], the FPA algorithm presented in [56], the genetic algorithm (GA) [57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64], the niched Pareto genetic algorithm (NPGA) [65], the artificial bee colony (ABC) [66,67,68,69], the bat-inspired algorithm (BA) [70], an improved version of BA, namely QBA [71], the gravitational search algorithm (GSA) [72,73,74], cuckoo search (CS) [75,76,77,78,79], evolutionary programming (EP) [80], fuzzy logic (FL) which has been applied in [81], the technique of MGSO developed in [82], simulated annealing (SA) [83,84], the firefly algorithm (FFA) [85,86,87,88,89], differential evolution (DE) [90,91,92], the bacterial foraging algorithm (BFA) [93,94], the FPA introduced in [95], the non-sorting genetic algorithm (NSGA-II) [96,97,98], ant lion optimization (ALO) [99], tabu search (TS) [100,101], GWO [102,103], IGWO [104], a computational technique of MICA explored in [105], the non-dominated sorting multiobjective opposition based gravitational search algorithm (NSMOOGSA) [106], the charged system search algorithm (CSSA) [107], enhanced CSSA named ECSSA [108], the novel teaching learning based optimization (TLBO) technique [109], the semi-definite programming (SDP) approach [110], the shuffle frog leaping algorithm (SLFA)-based method [111], the θ-MTLBO [112], and the QPSO technique [113] have been successfully applied to solve the CEED problem.
In recent studies, several non-conventional techniques have been also used for solving the CEED problem, including renewable energy [114,115,116,117,118,119,120,121]. For instance, MOALO has been applied for the dynamic CEED problems incorporating solar and wind energy [114]. In [115], an improved version of the ABC method including local search techniques (ABC-LS) has been proposed for solving the non-convex economic power problem considering POZs, VPLE, and transmission losses. The same problem has been also solved in [116] by using another improved version of the ABC algorithm where the grenade explosion mechanism and Cauchy operator have been added to the original ABC to improve its exploitation and exploration abilities. An elitist optimization algorithm using PSO and the non-dominated sorting mechanism (NSPSO-LS) has been developed in [117] for solving the CEED problem including wind energy. A dynamic programming optimization (DPO) algorithm has been applied in [118] for solving the CEED problem with solar and wind energy. The stochastic CEED problem with wind farm farms has been solved in [119] by using an improved biogeography-based optimization (CBBO) method. Guesmi et al. [120] have solved the same problem by incorporating wind energy sources by using CSCA where the wind farm output has been described by Weibull distribution function. The MOPSO algorithm has been introduced in [121] to solve CEED with wind and PV-solar.
Even though these heuristic algorithms generate an optimal solution for the CEED problem, but none of them would guarantee the best optimal solution. Therefore, various research works have focused on the hybridization of these algorithms to improve the performance of the optimization methods and the quality of solutions in large-scale problems [122,123,124,125,126]. Edwin Selva Rex et al. [122] have applied hybrid GA–WOA for solving the CEED problem. Nourianfar and Abdi [123] have solved the CEED problems including CHPEED with fast non-dominated time-varying acceleration coefficient-PSO combined with the exchange market algorithm. The effectiveness of the suggested method has been firstly tested with various benchmark functions, and then it has been applied to various case studies.
Reference [124] has developed a hybrid method based on novel combination of an MGA and an improved version of PSO referred to as MGAIPSO for solving CEED where ramp rate limits and spinning reserve requirement have been added to the system constraints. Mokarram et al. [125] applied a new hybrid JAYA and TLBO algorithm (JAYA–TLBO) to obtain a best solution for highly complicated CEED problems. Beigvand et al. [126] have solved CEED by using a novel optimization technique called hybrid TVAC-GSA-PSO. Ellahi and Abbas [127] have hybridized the PSO and BA algorithms (BA-PSO) for the solution of the power scheduling problem by incorporating thermal power plants and RES. In the problem formulation penalty costs due to overestimation and underestimation of wind power outputs are added to the fuel cost function. Hooshmand et al. [128] applied a combination of the BF method and the NM method called the BF-NM algorithm, for the non-smooth and non-convex CEED problem where spinning reserve constraints and frequency deviation limit have included in the problem modeling. Liang et al. [129] have added power flow constraints to the original CEED problem and then a multiobjective optimization technique, called the hybrid bat algorithm has been used for its solution. Murugan et al. [130] solved nonconvex CEED problem by applying a new technique based on hybridizing the ABC and BA with (CSA), a search strategy known as CSA-BA-ABC. In order to avoid convergence to local optima and enhance the convergence rate of the suggested hybrid algorithm, a chaotic-based search strategy has been used. Sen et al. [131] presented a hybrid ACO-ABC-HS optimization method to solve ED of thermal generators. Similarly, there are many other hybrid techniques like the DHS [132] method, the SDE algorithm [133], DE based on PSO (DEPSO) [134], hybrid PSO, and the gravitational search (HPSO-GSA) algorithm [135], and hybrid (PSO-SQP) [136], which have been used for solving the economic dispatch (ED) problem including VPLE and RRL constraints. Other hybrid methods based on sequential quadratic programming (SQP) techniques and a hybrid CPSO approach named CPSO-SQP have been successfully used for solving the multi-objective economic emission load dispatch problems [137]. Another optimization method combining DE and BBO called DE-BBO has been applied by Bhattacharya et al. [138]. A hybrid of GA, PS, and SQP called GA-PS-SQP has been presented in [139] for solving the same problem.
The main motivations and novelties of this review paper are given as follows:
- The factors or parameters that must be taken into account like the highest performance in terms of solution accuracy, convergence speed, and robustness, with the highest success rate, when solving the CEED problem with the integration of RES in static and dynamic conditions are investigated.
- In order to solve the CEED problem including RES, a summary for different optimization techniques that have been widely used, such as traditional methods, non-conventional, and hybrid methods is considered in this paper.
- This paper also presents the advantages and disadvantages of many optimization techniques which have been used for solving the CEED problem with RES.
- Summary tables containing the techniques applied, the test networks used, the types of RES considered, the constraints respected, and the static or dynamic conditions of each paper which are reviewed.
- A discussion is explored at the end of this paper concerning the strengths and weaknesses of many optimization techniques have been used for solving the CEED problem with RES.
This paper contains six sections. Section 1 highlights the brief introduction. Section 2, describes the mathematical formulation of the CEED problem with all operating constraints. Section 3 explains the deterministic and probabilistic approaches for modeling wind and solar energy integration in electrical power system. Section 4 presents a review of various optimization techniques used for solving CEED problem. Section 5 discusses the reviewed work. Finally, the conclusion is given in Section 6.
2. Problem Formulation
Generally, the CEED problem is formulated as a multiobjective optimization problem. As shown in Figure 2, it aims to simultaneously minimize the total fuel cost and emission of harmful gases subject to several operating constraints.
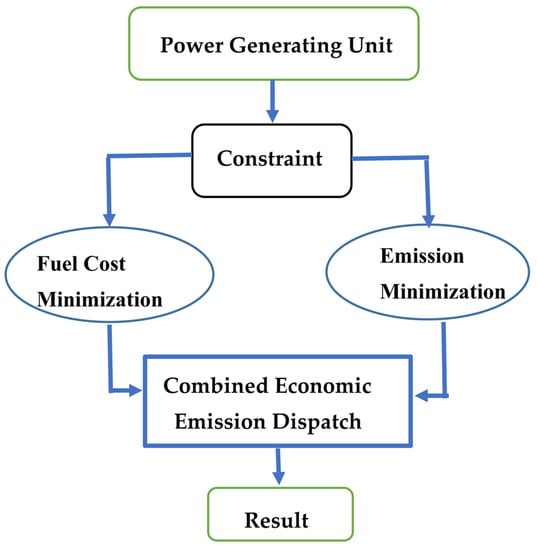
Figure 2.
CEED presentation.
In the CEED problem, cost function, emission function, and problem constraints can be described as follows [140,141,142].
2.1. Cost Function
The mathematical modeling of the cost function in ED can be formulated as follows [143]:
where is the total cost (in $/h), Ng is number of generators, is the active power of the i-th unit (in MW), and is the cost function of the i-th unit (in $/h). m and q are the number of equality constraints and inequality constraints, respectively,
is the j-th equality constraint, and is the j-th inequality constraint. The objective function of the traditional ED problem can be approximated by a quadratic function as follows [144,145,146]:
where , and are cost coefficients of the i-th unit. Practically, the valve-point loading effects (VPLE) should be added to the quadratic function of the production cost. Therefore, the cost function of the i-th unit can be expressed as follows [147]:
where ei and fi are VPLE coefficients of the i-th unit and is the minimum value of active power produced by the i-th unit (in MW).
Figure 3 shows the cost function characteristics for the cases with and without VPLEs. Five VPLEs (A, B, C, D and E) are considered in this figure. It is clear from this figure that when VPLEs are added, the cost function becomes non-convex.
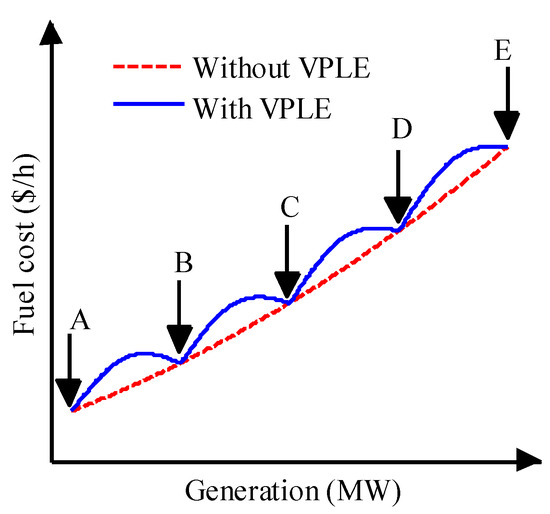
Figure 3.
Cost characteristic with and without VPLE.
Sometimes thermal plants are able to operate on more than one type of fuel. We are talking at this time of economic cost function with multiple fuel units (MFUs). Under these conditions, the cost characteristic is given with piecewise quadratic functions (Figure 4), formulated as follows:
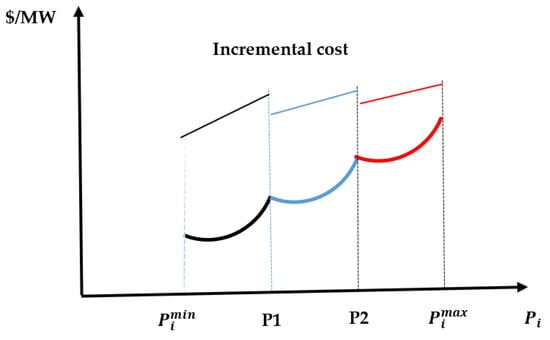
Figure 4.
Piecewise quadratic and incremental cost function.
Figure 4 shows an example of a cost function for three types of fuel, where type 1 is in black color, type 2 is in blue color and type 3 is in red color.
2.2. Emission Function
To obtain emission reduction of harmful gases like NOx, SOx, and CO2, different mathematical formulations have been developed. It can be modeled by a quadratic function [148,149,150], a combination of quadratic polynomials with one exponential term [151,152], or a combination of quadratic equations with multiple exponential terms [153] of production energy:
where , , , , , , and are the emission coefficients.
2.3. Equality and Inequality Constraints
2.3.1. Active Power Balance Constraint
In electrical power systems, the total generation must cover the requirements of the loads and the power losses . Thus, it can be given by the following equation:
The calculation of uses the constant loss formula [154], as follows
where , , and are the loss parameters also called B-coefficients.
2.3.2. Generation Capacity
Respecting generator limits, the active power produced by each generator i should be within its minimum limit and maximum limit :
2.3.3. Generating Unit Ramp Rate Limits (RRLs)
In practice, the production of each unit i during two consecutive time periods, (t − 1) and t, must respect its RRLs given by Equations (11) and (12), when the generation increases or decreases, respectively. Figure 5 shows a description of RRL which helps to update the minimum and maximum productions of units at each time t:
where is the output power of unit i at time t. and are up-ramp and down-ramp limits of the i-th unit, respectively.
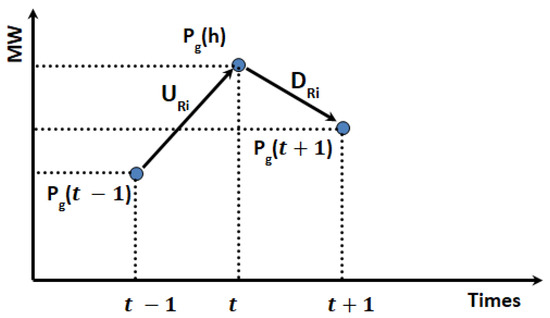
Figure 5.
Ramp rate limits of the generating units.
2.3.4. Prohibited Operating Zones (POZs)
This constraint is described by:
where and are down and up bounds of the k-th POZ. is the number of POZs for the i-th unit [155]. Figure 6 indicates the cost curve for a typical thermal unit including POZ constraints.
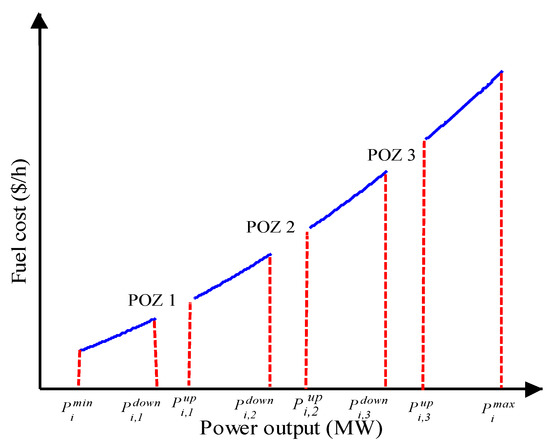
Figure 6.
Cost curve for a thermal plant with POZ constraints (blue color represents the discontinuous fuel cost function and red color represents down and up bounds of the POZs).
2.3.5. Spinning Reserve Requirements (SRRs) Constraints
Spinning reserve requirement constraints can be described by the following equation.
is the system spinning reserve requirement in MW.
2.3.6. Line Flow Constraints
This constraint concerns the thermal limit of line l of the electrical network.
where is the maximum transmitted active power of the transmission line.
2.3.7. Emission Constraint
This constraint concerns the thermal plant limit emission.
where , , and are the gases’ emission, respectively, of SOx, NOx, and CO2. , , and are the maximum limits emission for different gases.
2.4. Dynamic CEED (DEED) Problem
Today’s network loads are described by dynamic characteristics. Therefore, several works have tried to model power dispatch problem in such a way that generation units are scheduled according to power demand variations [26,83,108,112,113,149]. To do this, the static CEED problem has been extended to a new problem called the dynamic economic emission dispatch (DEED) problem. The resolution of such problems can be realized by solving the static CEED problem over a certain period of time, generally one day, subdivided into time intervals of one hour [83,108]. Unlike the static problem, the DEED problem takes into consideration the RRLs of generating units and the system spinning reserve requirement. In the DEED problem, the total cost (TC) and emission (TE) functions to be minimized have been often expressed as follows:
where and are the production cost and emission of unit i at time t, respectively. is the production in MW of unit i at time t.
In various published articles, objective functions TC and TE have been combined in one objective function by using the price penalty factor (PPF) method [120], as follows:
where is the weight factor ω is the PPF calculated as follows:
where and are maximum cost and maximum emission, respectively.
Thus, DEED problem can be formulated as follows:
where is the expected load at time t. is the total loss at time t.
In some research papers, POZ constraints have been included in the problem constraints [83].
3. Economic Dispatch with RES
In recent years, the integration of RES with thermal units in electrical power networks has attracted much attention from researchers. Even though their initial installation cost is higher, the operating costs of solar and wind production units are significantly low [156].
The fundamental characteristic of renewable production is its dependence on climatic conditions, which are wind for wind farms and solar radiation for photovoltaic farms. Therefore, the system operator has limited control over the amount of electricity output from these kinds of RES. Several studies have showed that these primary energies (wind and solar) have a fluctuating behavior. This behavior can be characterized by random variables reflecting the variations over a given period. Several parameters of the electrical system also have a stochastic behavior, such as the availability of conventional generation means, network structures, and load variation.
Thus, the power produced by conventional energy sources can be modeled by a random variable which takes into account the availability of the production units. It is therefore legitimate to think that a probabilistic modeling of the electrical system would be adequate to characterize its operation. Therefore, the analysis of electrical systems by probabilistic methods would be particularly appropriate [157,158].
3.1. Probabilistic Modeling of Wind Energy Integration
The evaluation of the output power of a wind site is based on the knowledge of the wind speed, which is actually not stable at any point, in view of the influence of several factors depending on the geographical location. A PDF probability distribution function is used for the evaluation of its changes over a period.
By using the here-and-now (HN) methodology employed in [159] to give the EED problem model with WES here, the authors proposed the Weibull PDF as an efficient model for wind speed. In [159], the economic dispatch problem with intermittent wind farm has been transformed into a chance constraint problem (CCP) where the power balance constraint has been described by the following chance constraint. In Equation (22), Pa has been called tolerance that power balance constraint cannot be satisfied,
The probability that the wind speed will be v and the corresponding cumulative distribution function (CDF) [159,160] are described by Equations (23) and (24), respectively:
where, k and c are positive parameters called shape factor and scale factor for a given location, respectively. Figure 7 shows the Weibull PDF as a function of wind speed and scale factor for k factors of 1 and 2. It is clear that the shape of the curve is influenced by the value of parameter k.
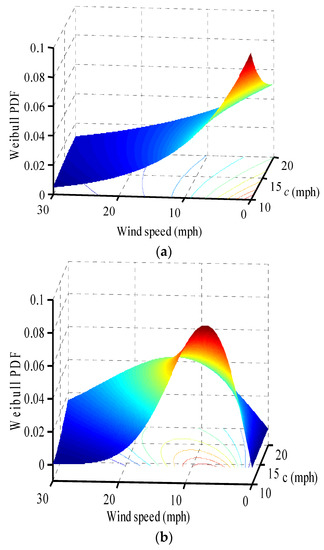
Figure 7.
Three-dimensional Weibull PDF vs. wind speed and scale factor (1 mph = 0.446 m/s). (a) k = 1; (b) k = 2.
Moreover, Figure 8 shows the variation of Weibull PDF as a function of wind speed and shape factor for c factors of 10 and 20. It is noteworthy that if c increases, the curves move toward higher wind speed.
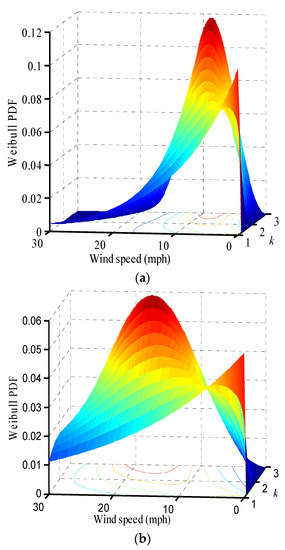
Figure 8.
Three-dimensional Weibull PDF vs. wind speed and shape factor. (a) c = 10; (b) c = 20.
To characterize the relationship between the probability of the random variable wind power and wind speed, the following simplified model cited in [159,160] can be used:
where wr is the rated power of the WPG, Vr, vin and vout are rated, cut-out and cut-in wind speeds, respectively.
Based on probability theories, the combined discrete/continuous characteristic of the WP can be described by its CDF given in the following equation [159].
where
From Equation (26), the chance constraint given by Equation (22) can be converted into the following deterministic constraint:
The tolerance Pa should satisfy the following inequality [159]:
Note that inequality (28) describes the probability that the power balance cannot be satisfied. That inequality has been investigated to avoid overestimation and underestimation of wind power. Therefore, the stochastic CEED problem can be converted into the deterministic optimization problem by adding the constraint given in Equation (28) to the original model of the CEED. Then, any optimization technique can be applied for its solution.
3.2. Probabilistic Modeling of PV Cell Power
The energy produced by a photovoltaic (PV) generator is estimated based on manufacturer data as well as climate data (radiation and temperature). The output power of the PV generator can be calculated as follows [161]:
where
where r is solar radiation, A is total area of the PV module and η is efficiency of PV generation. On the other hand, η varies with the cell temperature T, where ηref is reference efficiency of the PV generator, γ is the temperature coefficient of short-current, and Tref is reference cell temperature. The solar radiation r can be described by a beta distribution [162,163], as follows:
where
where rmax is maximum solar radiation. In this work, PV cell temperature predictions are assumed to be without error. Then the PDF of the PV cell power PPV is described by
where is the maximum generated by the PV generator. Then, the expected values and the CDF of PV generation are expressed in Equations (36) and (37), respectively:
As explained for wind power integration, CDF can be used to find the probability that power balance cannot be met when random PV output is added to the power grid. Therefore, overestimation and underestimation of PV output can be avoided.
4. Reviews for Various Optimization Techniques in Economic Dispatch Problem
In order to test the effectiveness and applicability of the proposed strategies, various test systems under different operating conditions have been used. Table 1 shows a summary of the most test systems used in power scheduling problems.

Table 1.
Definition of test systems studied for the solution related to CEED problem.
4.1. Summary of Conventional Methods Related to CEED
Many conventional techniques which are known as classical methods have been applied for solving the CEED problem. Such approaches include the quadratic programming QP method used by Fan and Zhang [27] and by Reid and Hasdorff [28]. The Newton Raphson (NR) technique has been illustrated in [36] for the economic emission dispatch including line flow constraints. In [26], an improved pattern search-based method has been employed for the dynamic emission dispatch and for the multiobjective DEED problem where one of the main contributions has been the preservation of RRLs during the transition to the next day. LR-based methods have been used in [12,13,33] for the CEED problem where generator limits, line flow, and transmission line losses have been considered. The proposed methods have been tested by using IEEE 14-bus and IEEE 30-bus systems. The LI technique discussed by Aravindhababu and Nayar [23] and by Dike et al. [17] have been developed on 3-, 6-, 13- and 26-unit test systems for proving its efficiency with consideration of generator limits and transmission line losses as constraints. A classical technique based on coordination equations (CTBCE) has been proposed by Nanda et al. [33] for obtaining optimal solution of the CEED problem, taking into account various equality and inequality constraints. This proposed approach has been evaluated on IEEE 14- and 30-bus test systems where a comparison of simulation results with other existing techniques likes QP and LP has been done. IPM has been successfully used for solving the CEED problem in [39]. In this work, VPLE, RRL, POZs, generators limits, line limits, and transmission losses are considered. Another technique called WMM has been employed by [38] to solve the stochastic EELD utilizing 13-, 15-, 38-, and 40-unit test systems. Authors in [35] have employed a homogeneous linear programming (HLP) approach for solving the CEED problem. This proposed algorithm has been examined on the IEEE 24-bus system and a practical 175-bus network. Unfortunately, this approach has two main drawbacks. First, this method is not appropriate to solve non-convex or non-smooth problems. Secondly, it generates only one solution in a single run [164,165,166,167].
Table 2 presents a summary of the conventional methods existing in the literature related to the CEED problem. It presents the techniques of optimization, objective functions and constraints utilized in solving such a problem.

Table 2.
Summary of the conventional method related to CEED.
4.2. Summary of the Nonconventional Methods Related to CEED
ANN has been presented by Yalcinoz et al. [40] for solving the economic dispatch (ED) problem with transmission capacity constraints. In order to demonstrate the robustness and the efficiency of this proposed technique, 3-, 4-, 40-, and 120-unit test systems have to be considered. To solve the ED problem with piecewise quadratic cost function, HMNN and AHNN methods have been applied by Park et al. [41] and Suman et al. [42], respectively. An ABC-based method has been implemented in [169,170] to solve the CEED problem by using generator limits and transmission line losses as constraints. Incremental ABC (IABC) and incremental ABC with local search (IABC-LS) have been employed in [171] with the advantages of better convergence efficiency and the ability to overcome the problem of premature convergence of ABC. Other improved versions of the ABC method which are ABC-based local search (ABC-LS) and ABC combined with Cauchy operator and grenade explosion method (GCABC) for solving the non-convex economic power problem considering POZs, VPLE, and transmission losses, have been presented in [115,116], respectively. These modifications on the classical ABC algorithm have been applied for more improvement of the ABC performance and for providing near optimal solutions. In [57,58], the optimal solution of the CEED problem has been provided by using GA, which is widely used as a meta-heuristic optimization method to obtain optimal solution for optimization problems. This proposed method is carried out on the standard test system including 6 generating units and the IEEE 30-bus system. An NPGA, NSGA, and SPEA have been introduced in [65], [98], and [97], respectively, for improving performance of the original GA and providing near-optimal solutions. An elitist multiobjective evolutionary algorithm referred to as the second version of NSGA (NSGA-II) where the Pareto solutions have been ranked based on the crowding distance mechanism, has been implemented in [90] for the CEED problem. This technique gives the problem solver a better view of the space of possible solutions, and consequently a better final Pareto-optimal front of the multiobjective problem. A stochastic optimization approach similar to GA, referred to as PSO, has been employed by [50], in which the population is initialized by random solutions defined by their positions and velocities. This method has several advantages suitable to heavily constrained non-convex optimization problems. Moreover, a new elitist PSO-based optimization technique with a local search algorithm (NSPSO-LS) has been applied in [117] for solving optimal ED including wind energy. ANS technique has been successfully used for solving the ED problem in [164]. In this work, VPLE, RRL, POZs, generators limits, line limits, and transmission losses are considered. The randomness characteristic of wind power has been described by using the here-and-now (HN) strategy. The proposed strategy has been successfully evaluated on the 10-unit system with consideration of the generators’ limits, VPLE, and transmission losses. The DEED problem, including wind energy, PV solar, thermal and hydro plant, considering RRL and VPLE constraints has been solved by using the multiobjective PSO method in [121]. A short summary of PSO and its variants for solving the CEED problem has been presented in [51]. The authors in [43] have presented a BBO algorithm for minimizing the non-convex cost function, where voltages limits and transmission line flow limits have been added to the problem constraints. To improve overall performance of the classical BBO algorithm, a modified approach called CBBO has been developed in [119], where the Cauchy operator has been incorporated in the BBO to improve the local and global exploration capabilities and to improve its convergence rate. The DE optimization algorithm is a meta-heuristic technique which has the advantage of dealing with non-differentiable, non-linear, and multi-modal optimization problems. The DE technique has been used by Abou El Ela et al. [91] for solving the CEED problem. In this reference, the implementation of DE has been tested on the IEEE 30-bus system. A comparison with other optimization techniques such as LP and NPGA has been carried out to demonstrate the robustness of the proposed method. In order to improve the performance of the conventional DE, two mutation strategies DE/rand/1 and DE/current-to-rand/1 have been developed by Yu et al. [92].
A new meta-heuristic inspired by grey wolves called GWO has been applied by Sharma et al. [102] to obtain an optimal solution to the CEED problem considering power balance, generator limits, and losses. To show the effectiveness of GWO for solving the CEED problem, results have been compared with other existing optimization techniques by using 3 and 6 generating units. In order to improve the overall performance of the original GWO algorithm and obtain competitive and satisfying results, an improved GWO (IGWO) [104] has been developed for solving the CEED problem. A comparison with various methods like GSA, MODE, PDE, SPEA, and NSGA for the 6-unit and the 10-unit systems has been considered in this study. A QPSO approach for solving the CEED problem by using the cubic criterion function, has been presented by Fahad P.M et al. [113]. In this proposed technique, the minimization of SO2, NOx, and CO2 has been considered as three separate objectives. In [99], a novel meta-heuristic motivated by the hunting mechanism of ant lions in nature called ant lion optimization (ALO) has been developed for minimizing total production cost and total emissions. In this work, the multi-objective problem has been transformed into a single objective problem by using price penalty factors. For simulations, 3- and 6-unit systems have been considered, where the results have confirmed that ALO is able to give competitive results in comparison with FFA, PSO, BBO, and GA. To adopt the ALO method for the multi-objective dynamic CEED, a multi-objective ALO (MOALO) has been developed in [114]. The proposed approach has been applied for the 10-unit systems integrating PV and wind energy. TLBO has been introduced by Banerjee et al. [109] to solve the non-convex CEED problem considering VPLE. The proposed methodology has been a newly developed evolutionary approach which has been based on two basic concepts of education which are the teaching phase and the learning phase. In this work, the robustness of this TLBO algorithm has been verified on the 3-, 13-, and 40- test systems with equality and inequality constraints. A comparison with the other existing algorithms has been done to exhibit the superiority, robustness, and effectiveness of the proposed algorithm. The bat algorithm, which is one of the nature-inspired optimization techniques, has been used in references [172] and [173] for obtaining the best optimal solution for ED and CEED problems, respectively. This proposed approach is evaluated on 6 generating units subject to generator limits and transmission losses. A comparison with other techniques has demonstrated that the BA has more efficiency for the CEED problem because it can obtain approximate or best quality solutions compared with other techniques.
A multi-objective EED problem has been solved by Jubril et al. [110] by using an SDP-based method, with consideration of spinning reserve constraints and transmission losses. A comparison elaborated with-without transmission losses has been realized with other existing techniques like NPGA, SPEA, and NSGA-II, utilizing the standard 6 units and 13 units of IEEE systems. Moreover, a conclusion was obtained indicating that the SDP has a good property of convergence and offers a better exploration in the Pareto front for the multi-objective EED problem. Ali et al. [55] have implemented a mine blast algorithm (MBA) for solving ELD and CEED problems, whereby a comparison of simulation results with other approaches has indicated the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm in terms of total cost and computational time. Abdelaziz et al. [56] have suggested the flower pollination algorithm (FPA) for solving ELD and CEED problems. In this work, the obtained results have been compared with other optimization techniques by using six system tests. The robustness of this proposed method has been justified even with a large-scale power system including VPLEs as constraints.
Table 3 presents a summary of the nonconventional methods existing in the published works and associated with the CEED problem. It presents the techniques of optimization, objectives, functions, and constraints utilized for solving the cited problem.

Table 3.
Summary of nonconventional methods related to CEED problem.
4.3. Summary of Hybrid Techniques Associated with the CEED Problem
Hybrid methods make use of two or more algorithms in order to utilize their strengths and mitigate their weakness in solving complex problems, and thus are found to be effective to find global optimal solutions for CEED problems with various constraints. Edwin Selva Rex et al. [122] have presented a hybrid technique combining GA with WOA called GA-WOA to get global optimal results for the CEED problems. The effectiveness of this proposed approach has been examined on four different test systems and a comparison of its performance with other heuristic approaches. Nourianfar and Abdi [123] have exploited the hybrid TVAC-PSO-EMA technique to solve the complex economic emission dispatch problem consisting of CHPEED and DEED multi-objective optimization problems considering different operational constraints. The main contributions and novelties of this work have been the proposing of a new test case, that is more suitable for DEED problems, respecting most practical constraints like RRLs, POZs, SRRs, losses, and MFUs and also the development of a new approach abbreviated as FCM-TOPSIS to select the best compromise solutions and to ensure a best diversity of the Pareto solutions. An improved QPSO algorithm for solving the CEED problem called DE-CQPSO has been employed by Zhao X.et al. [124] wherein the authors have exploited the fast convergence of the DE method and the particle diversity of crossover operators of GA. A comparison of its performances with QPSO by using six- and ten-unit systems to verify the effectiveness and robustness of the DE-CQPSO algorithm has been investigated. Mokarram et al. [125] have explored a new hybrid combination of JAYA and TLBO methods simultaneously to take the advantages of both for solving even non-smooth and non-convex MAED problems. To evaluate the capability and effectiveness of this method, referred to as JAYA–TLBO, in terms of accuracy, robustness, and convergence speed, it has been tested by using three test systems which are 5, 10, and 40 generating units. A novel optimization approach, called hybrid TVAC-GSA-PSO has been developed by Beigvand et al. [126]. It has been applied for solving the CHPED problems including 24, 30, and 48 generating units. The computational results found by this proposed approach in terms of convergence speed and quality solution have been compared with different heuristic techniques like TLBO [174], OTLBO [174], MPSO [175], CPSO [176], TVAC-PSO [176], and GSA [177]. A combined PSO and BA called the BA-PSO approach has been introduced by Ellahi et al. [127] to improve the cost reduction and convergence with lesser computational time. A comparison of the simulation results with different existing approaches has shown a reasonable reduction in cost function, improvement in computation time, and fast convergence when applying this method by using three different combinations of power plants containing RES (wind and PV) and thermal power plants. In [128], a hybrid technique with a combination of BFA and NM methods, namely the BF–NM algorithm, has been developed and used for solving the economic dispatch (ED) problem. VPLE, SRRs, power generation limits, RRL, POZs, frequency deviation limit, minimum frequency constraint, and kinetic energy provision constraint of the generators have been considered. The suggested optimization method has been evaluated on 13 generating units. By investigating the simulation results, it has been found that if the frequency constraints are inserted in the proposed problem, it can be solved by controlling the frequency within the permissible limits. Liang et al. [129] have solved the CEED problem with the multi-objective hybrid bat algorithm MHBA. An elitist non-dominated sorting method and a modified crowding-distance sorting method have been introduced to acquire an evenly distributed Pareto optimal front. In the proposed algorithm, RRL and POZs have been considered, and it has been applied on three test systems, which are the IEEE 30-bus 6-generator system, IEEE 118-bus 19-generator and IEEE 300-bus 57-generator systems with a total load demand of 283.4 MW, 3668 MW, and 23525.85 MW, respectively. A comparison of the performance with other works has been included in this reference. A new method based on hybridizing of BA and ABC with the CSA search strategy (CSA-BA-ABC) for solving the large-scale, highly non-linear, non-convex, non-smooth, non-differential, and non-continuous problems has been introduced by Murugan et al. [130]. Sen et al. [131] have presented a new hybrid method to solve the (ED) problem for a multi-generator system. This algorithm called ACO–ABC–HS combines the framework of ACO, ABC, and HS techniques to obtain the optimal solution of this system. The performance of this approach has been compared with those of conventional ED-solving methods like GS, as well as other evolutionary approaches, namely ABC, ACO, HS, and PSO. VPLE, transmission loss and RRL constraints have been used in the ED analysis to provide more concrete results. This proposed method has been examined on 10 generating units with 300 MW, 500 MW, and 700 MW. A combination of differential evolution (DE) and biogeography-based optimization (BBO) called the DE-BBO algorithm for solving CEED problems of thermal plants of electrical power systems has been applied by Bhattacharya et al. [138]. This DE-BBO method has been applied to improve the convergence speed and solution quality of both algorithms. To demonstrate the advantages of this method, it has been used to solve the multi-objective CEED problem, and it has been applied on a power system test comprising three thermal units with NOX and SOX emissions, six thermal units with NOX emissions, and six thermal units with both VPLE and NOX emissions. Wang and Li [132] have solved the non-convex ED problem with an evolutionary algorithm referred to as the DHS method and combining the mechanisms of both differential evolution and harmony search. This proposed DHS algorithm has been tested on 6, 10, 13, 15, 24, and 40 generating units with various constraints including VPLEs, multi-fuels, RRL, and POZs. For solving the same problem, a hybrid shuffled differential evolution (SDE) method has been developed by Reddy et al. [133]. For validation of this SDE strategy, three test systems which are 13-, 40-, and 140-unit test systems have been investigated and discussed. The B-coefficient matrix has been used for losses calculation. A comparison with other settled nature-inspired solution algorithms has indicated the superior performance of this approach in terms of both solution accuracy and convergence performances. Kundu et al. [178] have implemented a BBO and Butterfly Optimization Algorithm (BOA). The performance of this technique has been tested according to several situations by considering the VPLE and the losses and by integrating the RES. In [179], a hybrid firefly PSO (HFPSO) to obtain reduction on thermal energy consumption and carbon emission in an IEEE 30-bus six-generator system including diverse RES has been introduced. A comparative performance of PSO, FA, and HFPSO methods in solving the problem has been investigated. A hybrid bat-crow search algorithm HBCSA has been implemented by Elbaz et al. [180] in order to resolve the complicated, non-convex, and excessively nonlinear CEED problem consisting of conventional power plants and solar PV power plants (SPVPPs). This proposed HBCSA algorithm has been employed to obtain the minimum of cost and emission functions. The applicability and robustness of the proposed optimization technique and models have been validated on 10 thermal units and a 13 SPVPPs test system. The results of fuel cost, emission, solar cost, and CEED were 44,197 $/h, 1451.1 $/h, 440.000 $/h, and 559,700 $/h, respectively. In [181], Dubey et al. have presented a hybrid FPA (HFPA) for solving wind thermal dynamic multiobjective optimal dispatch problem for simultaneous minimization of cost, emission, and power loss. The wind uncertainty costs have been also included in the optimization model. This method has been examined on two wind-thermal test systems from the literature. An integration of wind power into thermal generation systems and its impact on the dynamic economic dispatch problem (DEDP) has been explored by in [182]. The DEDP formulation including VPLE and MFU options has been solved by utilizing a BBO-based method with integration of SQP, namely the BBO–SQP algorithm, to obtain the better solution. The DEDP formulation also has integrated wind power to validate and assess the economic benefits of incorporating wind power into an electrical power system. A novel hybrid method based on shuffle frog leaping algorithm (SFLA) and simulated annealing (SA) called hybrid SFLA-SA has been introduced in [183] and employed to solve the optimal power flow problem with non-smooth and non-convex generator fuel cost characteristics. This approach has been tested on the IEEE 30-bus system. POZs and VPLE are considered as constraints in this work.
Table 4 presents a summary of the hybrid techniques existing in the published works associated with CEED. It describes the techniques of optimization, objective functions, and constraints utilized for solving the cited problem in the electrical power system.

Table 4.
Summary of the hybrid techniques related to the CEED problem.
4.4. Summary of CEED Problem Considering PV and Wind Energy
Although scientific research and technological development seek to solve CEED, they are finding other best solutions. Within this context, researchers in recent decades have included RES in the dispatch system, instead of focusing mainly on thermal power plants [184]. There are many scientific works related to the CEED problem, including thermal plants and RES. In [24], an ED problem formulation for thermal plant and wind energy has been investigated by implementation of λ-method and lambda iterations (LI). The effectiveness of this proposed algorithm has been validated by numerical simulations on three different cases of the IEEE 118-bus system where POZs, generator limits, and transmission losses have been taken into account. The same technique has been also applied by Muda et al. [25] for thermal and PV generation with regard to the ED problem. Moreover, an optimization of PV production considering transmission losses for ED in [185] and CEED in [186,187] utilizing the PSO technique has been developed to maximize solar availability. In addition, a new elitist PSO-based optimization technique with local search algorithm (NSPSO-LS) has been applied by Marouani et al. [117] for solving optimal economic dispatch including wind energy where the availability of wind power has been described by using the here-and-now (HN) strategy. The proposed approach has been tested successfully on the 10-unit system with consideration of generators’ limits, VPLE, and transmission line losses. Furthermore, in [121], a dynamic CEED problem incorporating wind energy, PV solar, thermal, and hydro plant, considering RRL and VPLE as constraints, has been achieved. The authors of [118] suggested a DPO method for solving a linear ED problem with wind and solar energy considering emission reduction. This work has involved ten thermal units, one PV and two wind units as the test system. Moreover, reference [188] has employed the NSGA-II method for the ED of thermal plants and wind energy. A CMOPEO has been proposed in [48] for solving a CEED problem incorporating renewable energy resources such as PV and wind energy. This proposed algorithm is evaluated with respecting power balance, unit limits, and the security system. It is to be noted that most scientific papers have focused on the emission. Reference [187] has examined CO2 emissions from the electrical power systems and mentioned the use of the necessary energy on the main network to avoid exceeding the local pollution constraint during heavy traffic in the city. Ref. [189] has proposed a strategy for solving the dynamic economic dispatch applied on the hybrid microgrid integrating RESs. In this reference, energy storage system has been used to ensure the system security and maximize the exploitation of the RESs.
A pioneer research work has been introduced Liu and Xu [159] in order to incorporate WP in the economic dispatch problem. The authors have used the here-and-now technique to describe the randomness of WP. Then, the energy balance constraint has been described by a chance constraint. The probability of that constraint has been calculated by using the Weibul distribution function. The studied problem has been solved by using the numerical optimization method implemented in Matlab software. Simulation results have shown that the proposed strategy can avoid problems associated with using the average of WP, like probabilistic infeasibility. Another pioneer formulation of the power dispatch with wind plant has been developed in [157,162], in order to avoid security implications in power grids due to the volatility of wind power.
In reference [163], the authors have developed a probabilistic model for a power grid composed of several WP sources and PV modules and energy-storage systems. The models of the available WP and solar power have been determined by using joint probability distribution. Random characteristics of WP and solar power have been described by Weibull distribution and β-distribution functions, respectively. NSMOOGSA has been used in [165] as an optimization approach for solving CEED problem. This proposed method has been tested on the IEEE 30-bus system. A comparison of results with other techniques reported in the recent literature indicated its robustness and efficiency.
In [3], a PFA-based method has been applied for the static economic dispatch with hybrid energy sources, such as thermal units and WP sources. WP uncertainty has been solved by using the Weibull distribution function. The objective function has been the sum of the fuel cost of thermal generating units and the WP cost. In [190], a meta-heuristic technique CMOPEO has been proposed for the CEED problem by incorporating various RES. The problem model has been studied for three cases of RES, which are the power grid with WPG and PV systems, power grid with WPG, and power grid with the PV system. The studied system has been the IEEE-30 bus and 6 generating unit systems with security constraints, generator limits and transmission losses have been considered as studied cases, in these references. The intermittent characteristic of WPG and PV system has been evaluated by adding overestimation and underestimation costs of these RES to the production cost function. Underestimation occurs when the predicted RES output is less than the actual power generated by that source. In this case, the system operator must pay the surplus of power. The overestimation cost happens when the predicted RES output is higher than the actual output power of the RES. In order to reduce the influence of the WP fluctuations, interactive load characteristics have been studied through the day-ahead dispatch model. The dispatch model has been considered as a multiobjective minimization problem where the objective functions have been total cost and system losses. These two objective functions have been combined in one function and then the quantum particle swarm optimization (QPSO) algorithm has been used for its solution. In [156], the ELD problem with and without WP and solar power integration has been solved by using the backtracking search (BSA)-based method, which combines evolution principles and genetic operators to update solutions. The objective function to be minimized has been the fuel cost used by thermal units along with WP cost. The randomness availability of WP has been described by a probabilistic tolerance. Unfortunately, average values have been used for solar power estimation, which can cause problems linked to probabilistic infeasibility.
Table 5 presents recent papers’ summarization of CEED considering RES such as PV and wind energy. It describes the techniques of optimization, objective functions, and constraints utilized for solving the cited problem in the electrical power system, as well as the test systems used for simulations.

Table 5.
Summary of CEED problem using PV solar and wind power.
5. Discussion
Various methods-based classical optimization techniques like LR, BBA, GS, LI, PS, QP, CTBCE, LP, NLP, NLCNFP, HLP, NR, VMM, IPM, etc. have been applied successfully in the past three or four decades to solve CEED problems. However, there are drawbacks to these traditional techniques. They are greatly dependent on initial solutions, and they have poor convergence characteristics. They have the tendency either to converge to some local optima or diverge completely. They are easy to understand and they are characterized by their adaptation and flexibility for the problem analysis. Unfortunately, they are not able to solve the problem with more than two variables and cannot solve nonlinear and non-convex problems [196,197]. To solve non-convex and non-smooth CEED problems, several analytical techniques have been developed in the literature. The existence of certain constraints and the nonlinearity of the CEED problem make the classical methods based on calculation unable to give satisfactory performances. These methods usually get confined to local optima. Therefore, it is very much necessary to overcome the limitations by developing more reliable and improved methods.
This is why several researches have been oriented toward the use of non-conventional methods. These techniques have been presented with success, recently, in order to solve various CEED problems which are not differentiable, non-smooth, and non-convex in nature. Nevertheless, more authentic, secure, and quicker techniques are required, because these approaches possess too many numerical iterations to be performed. However, a few of these algorithms may perform poorly on various CEED problem sets. In spite of having fantastic global search abilities, some of them possess some restrictions in their local search capability. Most of the aforementioned methods suffer from poor local optima avoidance, slow rate of convergence, and they require huge calculation times. Moreover, there remains fuzziness while selecting the control parameters specific to a particular algorithm. Besides these problems, a few techniques mentioned above face premature convergence. Therefore, more powerful methods are needed for overcoming this CEED problem and also for quickening the search process.
In this context, we can cite some advantages and disadvantages for several optimization techniques like ACO that we can find the targets under any environment and its execution suitability for an implementation under parallel numerical computation and offers the reliability of the method. However, what-if analysis is difficult to understand and requires more convergence time [198]. In [199], the PSO algorithm gives excellent characteristic convergence, computational efficiency, and easy implementation. It is superior in terms of fuel cost as well as computation time but has low local search capability, and the iterative process has low convergence rate. GA is flexible, powerful, needs less computation time, and gives an almost global optimal solution although the response time of a stable optimization cannot be assured and the global optimum is not guaranteed [200]. SA has a simple coding for composite problems and an easy-to-deal-with cost function. Furthermore, it needs hybridization with other methods to get an optimal solution [201,202]. DE is stable and powerful to solve the ED problem, and has the superiority to deal with large-scale systems. However, this technique has a complex size and large computation time [203]. The ABC and HS algorithms are efficiently able to solve the CEED problem and have superiority in the search for optimal results compared to other methods in the literature. The main disadvantages are the complicated structures and the relatively high computation time [204]. GSA [73] is faster in local search ability and possesses faster convergence speed, but it is impossible to maintain population diversity in the swarm. BFA [94] as well as FFA [85] have demonstrated a good performance for solving the single-objective ED problem. TLBO [109] has shown its superiority compared to other meta-heuristic techniques when the VPLE of thermal plants have been considered.
Generally, meta-heuristic techniques like GA, SA, PSO, ALO, and ABC and their various modifications have shown considerable improvement in addressing the ED problem as well as the CEED problem. From the above literature (part review), there can be seen a need to improve the quality of solutions for the CEED problems, in terms of better convergence, lower losses, faster computation times, reduction in fuel costs, and reduction of emissions function. It is worthy of notice that hybrid methods yield superior solutions, either a heuristic and a traditional method or two heuristics, even though both methods yield good solutions individually.
Hybrid algorithms play a prominent role in improving the search capability of algorithms. Hybridization aims to combine the advantages of two or more algorithms, simultaneously trying to minimize any substantial disadvantage [205]. In general, the outcome of hybridization shows some improvements in terms of either computational speed or accuracy [206]. However, the hybrid approach is encouraged by several authors using many hybrid methods existing in open literature like Nourianfar et al. [123], Mokarram et al. [125], Murugan et al. [130], Sen et al. [131], etc. So far, in comparison to other heuristic methods, it shows highly superior features like quality of solution, stable convergence characteristics and good computational efficiency for finding the optimum in hyper search space related to CEED problems. It has the capability of avoiding, to some extent, getting trapped by local optima. Moreover, it converges smoothly towards the optima. On the other hand, the hybridization of two or more algorithms has a fast convergence rate. Indeed, it brings together all the strengths of the algorithms associated. It is computationally more efficient and provides a better solution while incorporating RES in the conventional test systems.
Recently, evolutionary algorithms have attracted much attention in finding optimal solutions. In [207], the NSGA-II is used as the solution methodology. In this way, the group average method is adopted to find the best solution from the Pareto front. Therefore, to solve the non-linear multi-objective CEPDP, NSGA-II is adopted. This algorithm is one of the most significant and powerful heuristic algorithms to solve multi-objective optimization problems. PSO is one of the modern heuristic algorithms. It has been found to be robust in solving CEED problems with RES. It has been proposed in [208] for the static and dynamic CEED problems incorporating solar plants and thermal units. The suggested technique has been a combination of quantum concepts and gravitational search PSO. The quantum concepts have been used to decrease the population size and enhance the convergence rate of the optimization algorithm. The framework has been composed of various solar plants with different characteristics, which has been considered as one of the main contributions of this study. In this reference, the solar data have been taken from a solar simulator.
6. Conclusions
In this work, a review of various optimization techniques for the CEED problem of thermal generation with integration of RES such as PV and wind is presented. The CEED problem containing RES becomes a heavier, more delicate, and more complicated optimization problem for researchers in this axis. In this study, a summary of recent articles on the CEED problem, taking into account RES such as PV and wind energy is considered with a description of the optimization techniques, the objectives, the constraints used, and their advantages and disadvantages. Optimization methods were classified into three types, such as classical methods, non-conventional methods, and hybrid methods. From this detailed study and the discussion explored, it can be clearly proven that hybrid methods and non-conventional methods are safer and more effective to solve the CEED problem. In recent years, the CEED is becoming more complex due to intermittent solar radiation and wind speed. Therefore, new dispatch models and efficient optimization techniques are required to guarantee convergence, robustness, best optimal solutions, and low computational time.
This review will encourage in the future gaining knowledge of the best approaches applicable by researchers for solving CEED problems considering PV and wind energy in a practical electrical power system. An extension of this work in the future is envisaged especially for developing other mathematical models to solve the CEED problem including RES for intelligent networks (smart grids). Moreover, the integration of flexible alternative current transmission systems (FACTS) devices can be considered to improve the transient stability of an electrical network and reduce the effect of the fluctuating behavior when integrating RES in the CEED.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.M., T.G. and B.M.A.; methodology, I.M. and T.G.; software, I.M. and T.G.; validation, T.G., H.H.A. and K.A.; formal analysis, I.M., K.A. and A.S.A.; investigation, S.R. and B.M.A.; writing—original draft preparation, I.M., T.G., H.H.A., B.M.A. and A.S.A.; supervision, H.H.A.; project administration, T.G.; funding acquisition, T.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Deanship of the Scientific Research of the University of Ha’il, Saudi Arabia (project: RG-20 075).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| CEED | Combined economic emission dispatch | BBO | Biogeography-based optimizer |
| RES | Renewable energy systems | PSO | Particle swam optimization |
| LR | Lagrange relaxation | MVMOS | Swarm based Mean-Variance Mapping Optimization |
| GS | Gradient Search | ACO | Ant Colony Optimization |
| BBA | Branch-and-bound algorithm | FPA | Flower pollination algorithm |
| LI | Lambda Iteration | GA | Genetic algorithm |
| PS | Pattern Search | NPGA | Niched Pareto GA |
| QP | Quadratic Programming | ABC | Artificial bee colony |
| CTBCE | Classical technique based on Coordination equations | BA | Bat-Inspired algorithm |
| LP | Linear Programming | GSA | Gravitational search algorithm |
| NLP | Non-Linear Programming | CS | Cuckoo search |
| NLCNFP | New nonlinear convex network flow programming | EP | Evolutionary Programming |
| HLP | Homogeneous Linear Programming | FL | Fuzzy logic |
| NR | Newton-Raphson | SA | Simulated annealing |
| WMM | Weighted mini-max | FFA | Firefly algorithm |
| IPM | Interior point method | DE | Differential evolution |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Networks | BFA | Bacterial foraging algorithm |
| MHNN | Modified Hopfield neural network | FPA | Flower pollination algorithm |
| AHNN | Adaptive Hopfield neural network | NSGA-II | Non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm |
| ALO | Ant Lion optimization | ABC-LS | ABC-LS |
| TS | Tabu Search | GCABC | GCABC |
| GWO | Grey Wolf Optimization | POZs | Prohibited Operating Zones |
| IGWO | Improved Grey Wolf Optimization | VPLE | Valve-point loading effects |
| MICA | Modified Imperialist Competitive Algorithm | NSPSO-LS | Non-dominated sorting PSO with local |
| NSMOOGSA | Non-dominated sorting multi objective opposition based gravitational search algorithm | DPO | Dynamic Programming optimization |
| CSSA | Charged system search algorithm | CBBO | Improved biogeography-based optimization |
| ECSSA | Enhanced CSSA | CSCA | Chaotic sine–cosine algorithm |
| TLBO | Teaching learning based optimization | MOPSO | Multi-objective optimization |
| SDP | Semi-definite programming | GA–WOA | Genetic algorithm–whale optimization algorithm |
| SLFA | Shuffle Frog Leaping Algorithm | CHPEED | Combined Heat and Power Economic Emission Dispatch |
| MSLFA | modified SLFA called | DEED | Dynamic Economic Emission Dispatch |
| θ-MTLBO | θ-multiobjective-teaching–learning-based optimization algorithm | TVAC-PSO | Time-Varying Acceleration Coefficient-Particle Swarm Optimization combined |
| MOALO | Multi-objective ant lion optimizer | QPSO | Quantum PSO |
| TLBO | Teaching-Learning Based Optimization | DHS | Differential harmony search method |
| BF-NM | Bacterial foraging (BF) and the Nelder-Mead (NM) | SDE | Shuffled differential algorithm |
| CPSO | Chaotic particle swarm optimization | ED | Economic dispatch |
| MFUs | Multiple fuel units | RRL | Ramp Rate Limits |
| UR | Up-ramp limits | DR | Down-ramp limits |
| SRRs | Spinning reserve requirements | HN | Here-and-now methodology |
| EED | WES | Wind energy source | |
| Probability distribution function | CDF | Cumulative distribution function | |
| WP | Wind power | WPG | Wind power generator |
| HLP | Homogeneous Linear Programming | PV | Photovoltaic |
| NPGA | Niched Pareto genetic algorithm | SPEA | Strength Pareto evolutionary algorithm |
| MOALO | Multi-objective ant lion optimizer | CPP | Conventional power plant |
| SPVPPs | Solar PV power plants | MBA | Mine blast algorithm |
| CMOPEO | Constrained multi-objective population extremal optimization | ELD | Economic load dispatch |
| DE-CQPSO | Differential evolution-crossover quantum PSO | QBA | Quantum-behaved bat algorithm |
| ANS | Across Neighborhood Search | MGSO | Modified group search optimizer |
| CMOPEO | constrained multi-objective population extremal optimization | ||
| NSMOOGSA | Non-dominated Sorting Multi Objective Opposition based Gravitational Search Algorithm | ||
References
- Boden, T.A.; Marland, G.; Andres, R.J. National CO2 Emissions from Fossil-Fuel Burning, Cement Manufacture, and Gas Flaring: 1751–2014; Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, U.S. Department of Energy: Washington, DC, USA, 2017.
- Ela, E.; Mark, O. Studying the variability and uncertainty impacts of variable generation at multiple timescales Power Systems. IEEE Trans. 2012, 27, 1324–1333. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, F.; Vijay, V.; Gerald, T.H.; Raja, A. Probabilistic power flow analysis with generation dispatch including photovoltaic resources. Power Syst. IEEE Trans. 2013, 28, 1797–1805. [Google Scholar]
- Karthik, N.; Arul, R.; Angalaeswari, S.; Natrayan, L.; Wubishet, D.M. Combined Economic Emission Dispatch of Microgrid with the Incorporation of Renewable Energy Sources Using Improved Mayfly Optimization Algorithm. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 6461690. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, M.R. Wind and Solar Power Systems: Design, Analysis, and Operation; Taylor & Francis Group: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Velamuri, S.; Sreejith, S.; Ponnambalam, P. Static economic dispatch incorporating wind farm using Flower pollination algorithm. Perspect. Sci. 2016, 8, 260–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salameh, Z.M.; Bogdan, S.B.; Atia, R.A. Photovoltaic module-site matching based on the capacity factors. Energy Convers. IEEE Trans. 1995, 10, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Zhou, D.; Zhou, P.; Miao, Z. Environmental/economic power dispatch with wind power. Renew. Energy 2014, 71, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.C. Wind energy dispatch considering environmental and economic factors. Renew. Energy 2010, 35, 2217–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Ilic, M.D. Model predictive economic/environmental dispatch of power systems with intermittent resources. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting, Calgary, AB, Canada, 26–30 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bilil, H.; Aniba, G.; Maaroufi, M. Probabilistic Economic Emission Dispatch Optimization of Multi-Sources Power System. Energy Procedia 2014, 50, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalini, S.P.; Lakshmi, K. Solution to economic emission dispatch problem using Lagrangian relaxation method. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Green Computing Communication and Electrical Engineering (ICGCCEE), Coimbatore, India, 6–8 March 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamurthy, S.; Tzonova, R.I. Comparison of the Lagrange’s and Particule swarm optimization solutions of an economic emission dispatch with transmission constraints. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Power Electronics, Drives and Energy Systems, Bengaluru, India, 16–19 December 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H. Lagrange Multipliers and Their Applications; Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, University of Tennessee: Knoxville, TN, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Dodu, J.C.; Martin, P.; Merlin, A.; Pouget, J. An optimal formulation and solution of short-range operating problems for a power system with flow constraints. IEEE Proc. 1972, 60, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.L.; Wang, S.C. Branch-and-bound scheduling for thermal generating units. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 1993, 8, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dike, D.O.; Adinfono, M.I.; Ogu, G. Economic dispatch of generated power using modified lambda-iteration method. IOSR J. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2013, 3331, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaing, Z.L. Particle swarm optimization to solving the economic dispatch considering the generator constraints. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2003, 18, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad Ramadan, B.M.S.; Logenthiran, T.; Naayagi, R.T.; Charles, S. Accelerated Lambda Iteration Method for Solving Economic Dispatch with Transmission Line Losses Management. In Proceedings of the IEEE Innovative Smart Grid Technologies-Asia (ISGT-Asia), Melbourne, Australia, 28 November–1 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ruey-Hsun, L. A neural-based redispatch approach to dynamic generation allocation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1999, 14, 1388–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, P.K.; Naresh, R.; Sharma, V. Enhanced lambda iteration algorithm for the solution of large scale economic dispatch problem. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Recent Advances and Innovations in Engineering (ICRAIE-2014), 9–11 May 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, J.P.; Wu, Q.H.; Guo, C.X.; Zbou, X.X. Fast Lamda-iteration method for economic dispatch. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2014, 29, 990–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravindhababu, P.; Nayar, K.R. Economic dispatch based on optimal lambda using radial basis function network. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2002, 24, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro, P.; Vergara, H.R.; Shaker, B.N.; Jørgensen, L.C.; da Silva, P. Generalization of the λ-Method for Decentralized Economic Dispatch Considering Reactive Resources. In Proceedings of the 7th IEEE International Conference on Innovative Smart Grid Technologies, Torino, Italy, 26–29 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Muda, H.; Othman, A.; Julai, N. Economic dispatch strategy for solar hybrid system using lambda iteration method. J. Telecommun. Electron. Comput. Eng. 2017, 9, 85–89. [Google Scholar]
- Alsumait, J.S.; Qasem, M.; Sykulski, J.K.; Al-Othman, A.K. An improved pattern search based algorithm to solve the dynamic economic dispatch problem with valve point effect. Energy Convers. Manag. 2010, 51, 2062–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.Y.; Zhang, L. Real-time economic dispatch with line flow and emission constraints using quadratic programming. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1998, 13, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, G.F.; Hasdorff, L. Economic dispatch using quadratic programming. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 1973, 6, 2015–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajanish, K.K.; Tilak, T.; Isarar, A. Combined Economic emission dispatch problem including line losses using quadratic programming. IJEEE 2017, 9, 328–334. [Google Scholar]
- El-Keib, A.A.; Ma, H.; Hart, J.L. Environmentally constrained economic dispatch using the lagrangian relaxation method. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1994, 9, 1723–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashfaq, A.; Khan, A.Z. Optimization of economic load dispatch problem by linear programming modified methodology. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Emerging Trends in Engineering and Technology (ICETET’2014), London, UK, 30–31 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Parikh, J.; Chattopadhyay, D. A multi-area linear programming approach for analysis of economic operation of the Indian power system. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1996, 11, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, J.; Hari, L.; Kothari, M.L. Economic emission load dispatch with line flow constraints using a classical technique. IEEE Proc. Gener. Transm. Distrib. 1994, 141, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; James, A. Multi-area power systems economic dispatch using nonlinear convex network flow programming. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2001, 59, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabr, R.; Coonick, A.H.; Cory, B.J. A homogeneous linear programming algorithm for the security constrained economic dispatch problem. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2000, 15, 930–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.D.; Chen, J.F. A direct Newton-Raphson economic emission dispatch. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2003, 25, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, S. Multiobjective power dispatch with line flow constraints using the fast Newton-Raphson method. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 1997, 12, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, J.; Parti, S.; Kothari, D. Stochastic economic emission load dispatch. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 1993, 26, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishe, H.M.; Kian, A.R.; Dual, M.S. Interior point method for Solving environmental/economic power dispatch. Int. Rev. Electr. Eng. 2011, 6, 1463–1473. [Google Scholar]
- Yalcinoz, T.; Short, M.J. Neural networks approach for solving economic dispatch problem with transmission capacity constraints. IEEE Trans Power Syst. 1998, 13, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Eom, I.K.; Lee, K.Y. Economic load dispatch for piecewise quadratic cost function using Hopfield neural network. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1993, 8, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Sode-Yome, A.; Park, J.H. Adaptive Hopfield neural network for economic load dispatch. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1998, 13, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Chattopadhyay, P. Application of biogeography-based optimization to solve different optimal power flow problems. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2011, 5, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohokare, M.R.; Panigrahi, B.K.; Pattnaik, S.S.; Devi, S.; Mohapatra, A. Neighborhood search-driven accelerated biogeography-based optimization for optimal load dispatch. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybernet Part C Appl. Rev. 2012, 42, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Bao, G.; Ding, K.; Lu, L. Multi-objective optimal dispatch considering wind power and interactive load for power system. Energy Power Eng. 2018, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Chattopadhyay, P.K. Application of Biogeography-based Optimization for Solving Multi-objective economic emission load dispatch problems. Electr. Power Compon. Syst. 2010, 38, 340–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Cao, Y.J. Multiple objective particle swarm optimization technique for economic load dispatch. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. 2005, 6, 420–427. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.B.; Lee, K.S.; Shin, J.R.; Lee, K.S. A particle swarm optimization for economic dispatch with non-smooth cost functions. IEEE Trans Power Syst. 2005, 20, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Kumar, Y. Economic load dispatch with environmental emission using MRPSO. In Proceedings of the 2013 3rd IEEE International Advance Computing Conference (IACC), Ghaziabad, India, 22–23 February 2013; pp. 995–999. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, A.M.; Youssef, M.; Abdelghani, D. Comparative study of the price penalty factors approaches for Bi-objective dispatch problem via PSO. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2020, 10, 3343–3349. [Google Scholar]
- Mahdi, F.P.; Vasant, P.; Kallimani, V.; Watada, J.; Fai, P.Y.S.; Al-Wadud, M.A. A holistic review on optimization strategies for combined economic emission dispatch problem. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 3006–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, K.H.; Vasant, P.; Balbir Singh, M.S.; Vo, D.N. Intelligent Information and Database Systems. In Proceedings of the 7th Asian Conference, ACIIDS 2015, Bali, Indonesia, 23–25 March 2015; Nguyen, T.N., Trawiński, B., Kosala, R., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.H.; Wu, Y.W.; Lu, L.J.; Xiong, X.Y. Generalized ant colony optimization for economic dispatch of power systems. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Power System Technology, Kunming, China, 13–17 October 2002; Volume 1, pp. 225–229. [Google Scholar]
- Dorigo, M.; Brattain, M. Ant colony optimization. Encyclopedia of machine learning. In Ant Colony Optimization: A Component-Wise Overview; Martí, R., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 1, pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelaziz, A.Y.; Ali, E.S.; Abd Elazim, S.M. Combined Economic and Emission Dispatch Solution Using Flower Pollination Algorithm. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2016, 80, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, E.S.; Abd Elazim, S.M. Mine blast algorithm for environmental economic load dispatch with valve loading effect. Neural Comput. Applic. 2018, 30, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, S.; Abo-Sinna, M.A.; Mousa, A.A. A solution to the optimal power flow using genetic algorithm. Appl. Math. Comput. 2004, 155, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koridak, L.A.; Rahli, M. Optimization of the emission and economic dispatch by the genetic algorithm. Prz Elektrotech. 2013, 86, 363–366. [Google Scholar]
- Golpîra, H.; Bevrani, H. A framework for economic load frequency control design using modified multi-objective genetic algorithm. Electr. Power Compon. Syst. 2014, 42, 788–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, S.H.; Lam, H.K.; Leung, H.F.; Lee, Y.S. Improved genetic algorithm for economic load dispatch with valve-point loadings. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Roanoke, VI, USA, 2–6 November 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Deb, K.; Pratap, A.; Agarwal, S.; Meyarivan, T. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2006, 6, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Q.; Xie, J.; Hu, J. Independent tasks scheduling based on genetic algorithm in cloud computing. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Wireless Communications, Networking and Mobile Computing (WiCom’09), Beijing, China, 24–26 September 2009; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Shahbaz, H.; Mohammed, A.; Salman, K.; Asif, H.; Muhammad, A.S. Implementation and Comparison of Particle Swarm Optimization and Genetic Algorithm Techniques in Combined Economic Emission Dispatch of an Independent Power Plant. Energies 2019, 12, 2037. [Google Scholar]
- Uidir, R.O.; Rahali, M.; Abdelhakim Oridak, L. Economic Dispatch using a Genetic Algorithm: Application to Western Algeria’s Electrical Power Network. J. Inf. Sci. Eng. 2005, 21, 659–668. [Google Scholar]
- Abido, M.A. A niched Pareto genetic algorithm for multiobjective environmental/economic dispatch. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2003, 25, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, D.; Ozyon, S.; Yasar, C.; Liao, T.J. Artificial bee colony algorithm with dynamic population size to combine economic and emission dispatch problems. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2014, 54, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akay, B.; Karaboga, D. A modified artificial bee colony algorithm for real-parameter optimization. Inf. Sci. 2010, 192, 120–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaboga, D.; Basturk, B. A powerful and efficient algorithm for numerical function optimization: Artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm. J. Glob. Optim. 2007, 39, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akay, B.; Karaboga, D. Artificial bee colony algorithm for largescale problems and engineering design optimization. J. Intell. Manuf. 2012, 23, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, B.; Chandra, V.; Mohan, J.; Veera Reddy, V.C. Application of bat algorithm for combined economic load emission dispatch. J. Electr. Eng. 2013, 13, 214–219. [Google Scholar]
- Mahdi, F.P.; Vasant, P.; Al-Wadud, M.A.; Kallimani, V.; Watada, J. Quantum-behaved bat algorithm for many-objective combined economic emission dispatch problem using cubic criterion function. Neural Comput. Appl. 2019, 31, 5857–5869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guvenç, U.; Sönmez, Y.; Duman, S. Combined economic and emission dispatch solution using gravitational search. Sci. Iran. 2012, 19, 1754–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duman, S.; Arsoy, A.B.; Yorukeren, N. Solution of Economic Dispatch Problem using Gravitational Search Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Bursa, Turkey, 1–4 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Siddik, N.; Adeli, H. Application of Gravitational Search Algorithm in engineering. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2016, 22, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, K.; Simon, S.P.; Padhy, N.P. Cuckoo search algorithm for emission reliable economic multi-objective dispatch. IETE J. Res. 2014, 60, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, K.; Simon, S.P.; Padhy, N.P. Wind-Thermal Integrated Power System Scheduling Problem Using Cuckoo Search Algorithm. IETE J. Res. 2014, 60, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thao, N.T.P.; Thang, N.T. Improved Firefly Algorithm: A Novel Method for Optimal Operation of Thermal Generating Units. Complexity 2018, 2018, 7267593. [Google Scholar]
- Chiroma, H.; Herawan, T.; Fister, I., Jr.; Fister, I.; Abdulkaree, S.; Shuib, L.; Hamza, M.F.; Saadi, Y.; Abubakar, A. Bio-inspired computation: Recent development on the modifications of the cuckoo search algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 61, 149–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-S.; Deb, S. Cuckoo search: Recent advances and applications. Neur. Comput. 2014, 24, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, N.; Chakrabarti, R.; Chattopadhyay, P. Evolutionary Computation. IEEE Trans. 2003, 7, 83–94. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.H.; Wang, G.S.; Wang, P.Y.; Johns, A. Environmental/economic dispatch using fuzzy logic controlled genetic algorithms. IEE Proc. Generat. Transm. Distrib. 1997, 144, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, K.; Haque, M.T.; Davoodi, E. Solving non-convex economic dispatch problem with valve point effects using modified group search optimizer method. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2012, 84, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, M. A simulated annealing-based goal-attainment method for economic emission load dispatch of fixed head hydrothermal power systems. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2005, 27, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.P.; Fung, C.C. Simulated annealing based economic dispatch algorithm. IEE Proc. C 1993, 6, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theofanis, A.; Aristidis, V. Application of the Firefly Algorithm for Solving the Economic Emissions Load Dispatch Problem. Int. J. Comb. 2011, 2011, 523806. [Google Scholar]
- Amsavalli, A.; Jayaraman, L.; Vigneswaran, D. Solving Combined Economic and Emission Dispatch using Firefly Algorithm. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2017, 2017, 11930–11935. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekaran, K.; Simon, S.P. Firely algorithm for reliable/emission/economic diaptch multiobjective problem. Int. Rev. Electr. Eng. 2012, 7, 3414–3425. [Google Scholar]
- Abedinia, O.; Amjady, N.; Naderi, M.S. Multi-objective Environmental/Economic Dispatch using firefly technique. In Proceedings of the 2012 11th International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering (EEEIC), Venice, Italy, 18–25 May 2012; pp. 461–466. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.-S.; He, X. Firefly algorithm: Recent advances and applications. Int. J. Swarm. Intell. 2013, 1, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rughooputh, H.C.S.; Ah King, R.T.F. Environmental/economic dispatch of thermal units using an elitist multiobjective evolutionary algorithm. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology, Maribor, Slovenia, 10–12 December 2003; Volume 1, pp. 10–12. [Google Scholar]
- Abou El Ela, A.A.; Abido, M.A.; Spea, S.R. Differential evolution algorithm for emission constrained economic power dispatch. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2010, 80, 1286–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Yu, X.; Lu, Y.; Sheng, J. Economic and Emission Dispatch Using Ensemble Multi-Objective Differential Evolution Algorithm. Sustainability 2018, 10, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, N.; Tripathi, A.; Tapaswi, S.; Pandit, M. An improved bacterial foraging algorithm for combined static/dynamic environmental economic dispatch. Appl. Soft Comput. 2012, 12, 3500–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, I.A.; El-Hawary, M.E. Bacterial Forging Algorithm for optimum Economic-Emission Dispatch. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Electrical Power and Energy Conference, Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 3–5 October 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelaziz, A.Y.; Ali, E.S.; Abd Elazim, S.M. Implementation of flower pollination algorithm for solving economic load dispatch and combined economic emission dispatch problems in power systems. Energy 2016, 101, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ah King, R.T.F.; Rughooputh, H.C.S. Elitist Multi-Objective Evolutionary Algorithm for Environmental/Economic Dispatch. Congr. Evol. Comput. 2003, 2, 1108–1114. [Google Scholar]
- Abido, M.A. Environmental/economic power dispatch using multiobjective evolutionary algorithms. IEEE Trans Power Syst. 2003, 18, 1529–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinesh, T.; Varma, D.M.; Vinod, K. Multi-Objective Economic Emission Load Dispatch using Teacher-Learning-Based Optimization Technique. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Advances in Control and Optimization of Dynamical Systems, Kanpur, India, 13–15 March 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chopra, N.; Mehta, S. Multi-objective optimum generation scheduling using Ant Lion Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2015 Annual IEEE India Conference (INDICON), New Delhi, India; 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naama, B.; Bouzeboudja, H.; Allali, A. Solving the economic dispatch problem by using tabu search algorithm. Energy Proc. 2013, 36, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.P.; Fung, C.C. Generation, Transmission and Distribution. IEEE Proc. C 1993, 140, 509–515. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.; Mehta, S.; Chopra, N. Economic Load Dispatch using Grey Wolf Optimization. Int. J. Eng. Res. Appl. 2015, 5, 128–132. [Google Scholar]
- Nitish, C.; Gourav, K.; Shivani, M. Multi-objective Economic Emission Load Dispatch using Grey Wolf Optimization. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Res. Sci. 2016, 3, 26–33. [Google Scholar]
- Prashar, G.M.S. Formulation of Improved Grey Wolf Optimization Methodology for ELD Problem. Int. J. Res. Advent Technol. 2016, 4, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Devibala, B.; Padmanabhan, K.K. Efficient Emission Reduction in Thermal Power Plant using Modified Imperialist Competitive Algorithm in Green Sigma Framework. Int. J. Control Theory Appl. 2017, 10, 291–305. [Google Scholar]
- Ratan Bhowmik, A.; Kumar Chakraborty, A. Solution of optimal power flow using non dominated sorting multiobjective opposition based gravitational search algorithm. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2015, 64, 1237–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özyön, S.; Temurtaş, H.; Kuvat, G. Charged system search algorithm for emission constrained economic power dispatch problem. Energy 2012, 46, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niknam, T.; Azizipanah-Abarghooee, R.; Narimani, M.R. Reserve constrained dynamic optimal power flow subject to valve-point effects, prohibited zones and multi-fuel constraints. Energy 2012, 47, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumit, B.; Deblina, M.; Chandan, K.C. Teaching learning based optimization for economic load dispatch problem considering valve point loading effect. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2015, 73, 456–464. [Google Scholar]
- Jubril, A.M.; Olaniyan, O.A.; Komolafe, O.A.; Ogunbona, P.O. Economic-emission dispatch problem: A semi-definite programming approach. Appl. Energy 2014, 134, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niknam, T.; Narimani, M.R.; Jabbari, M.; Malekpour, A.R. A modified shuffle frog leaping algorithm for multi-objective optimal power flow. Energy 2011, 36, 6420–6432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niknam, T.; Golestaneh, F.; Sadeghi, M.S. θ-Multiobjective Teaching–Learning-Based Optimization for Dynamic Economic Emission Dispatch. IEEE Syst. J. 2012, 6, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, F.P.; Vasant, P.; Al-Wadud, M.A.; Watada, J.; Kallimani, V. A quantum-inspired particle swarm optimization approach for environmental/economic power dispatch problem using cubic criterion function. Int. Trans. Electr. Energ. Syst. 2018, 28, 2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Chefai, D.; Hsan Hadj, A. Dynamic Economic Emission Dispatch Optimization integrated wind and solar energy systems. Int. Trans. J. Eng. Manag. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2020, 11, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, M.; Taoufik, G.; Hsan Hadj, A. ABC algorithm with local search applied to Economic Dispatch Problem. Int. J. Future Gener. Commun. Netw. 2020, 13, 2483–2490. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, M.; Boudjemline, A.; Taoufik, G.; Hsan Hadj, A. A Modified Artificial Bee Colony for the NonSmooth Dynamic Economic/Environmental Dispatch. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. Res. 2018, 8, 3321–3328. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, M.; Chefai, D.; Taoufik, G. Optimal cost of power system incorporating wind energy using Here-And-Now approach. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2020, 15, 1488–1496. [Google Scholar]
- Chefai, D.; Ismail, M.; Hsan Hadj, A. Unit Commitment Problem with Wind and Solar Energy Considering Emission Reduction using Dynamic Programming. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 29, 4152–4162. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, M.; Taoufik, G.; Hsan Hadj, A. An improved Biogeography-Based Optimization for economic/Environmental dispatch. IIOABJ 2019, 10, 24–33. [Google Scholar]
- Taoufik, G.; Anouar, F.; Ismail, M.; Badr, A.; Hsan Hadj, A. Chaotic sine–cosine algorithm for chanceconstrained economic emission dispatch problem including wind energy. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2020, 14, 1808–1821. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, M.; Chefai, D.; Hsan Hadj, A. Optimization Hydro-Thermal-Wind-PV Solar Using MOPSO Algorithm Applied to Economic/ Environmental Dispatch. Biosci. Biotechnol. Res. Commun. 2021, 14, 118–125. [Google Scholar]
- Edwin, C.R.; Selva, R.; Marsaline Beno, M.; Annrose, J. A Solution for Combined Economic and Emission Dispatch Problem using Hybrid Optimization Techniques. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2019, 2019, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Hossein, N.; Hamdi, A. Solving the multi-objective economic emission dispatch problems using Fast Non-Dominated Sorting TVAC-PSO combined with EMA. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 2019, 85, 105770. [Google Scholar]
- Xin-Gang, Z.; Ji, L.; Jin, M.; Ying, Z. An improved quantum particle swarm optimization algorithm for environmental economic dispatch. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 152, 113370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, J.M.; Taher, N.; Jamshid, A.; Miadreza, S.K.; Joao, P.S.; Catal, A. Hybrid Optimization Algorithm to Solve the Nonconvex Multiarea Economic Dispatch Problem. IEEE Syst. J. 2018, 10, 1109. [Google Scholar]
- Soheil, D.B.; Hamdi, A.; Massimo, L.S. Hybrid Gravitational Search Algorithm-Particle Swarm Optimization with Time Varying Acceleration Coefficients for Large Scale CHPED Problem. Energy 2017, 3, 54. [Google Scholar]
- Manzour, E.; Ghulam, A. A Hybrid Metaheuristic Approach for the Solution of Renewables-Incorporated Economic Dispatch Problemsx. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 3008570. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmat-Allah, H.; Moein, P.; Mohammad, J.M. Emission, reserve and economic load dispatch problem with non-smooth and non-convex cost functions using the hybrid bacterial foraging-Nelder–Mead algorithm. Appl. Energy 2012, 89, 1443–1453. [Google Scholar]
- Huijun, L.; Yungang, L.; Fengzhong, L.; Yanjun, S. A multiobjective hybrid bat algorithm for combined economic/emission dispatch. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2018, 101, 103–115. [Google Scholar]
- Murugan, R.; Mohan, M.R.; Christober, C.; Rajan, A.; Deiva, S.P.; Arunachalam, S. Hybridizing Bat Algorithm with Artificial Bee Colony for Combined Heat and Power Economic Dispatch. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 72, 189–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanuj, S.; Hitesh, D.M. A new approach to solve Economic Dispatch problem using a Hybrid ACO–ABC–HS optimization algorithm. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2016, 78, 735–744. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Li, L.P. An effective differential harmony search algorithm for solving non-convex economic load dispatch problems. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2013, 44, 832–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, A.S.; Vaisakh, K. Shuffled differential evolution for large scale economic dispatch. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2013, 96, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayah, S.; Hamouda, A. A hybrid differential evolution algorithm based on PSO for non convex economic dispatch problems. Appl. Soft Comput. 2013, 13, 1608–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Ji, Z.; Shen, Y. A novel hybrid PSO and gravitational search algorithm for solving economic emission load dispatch problems with various practical constraints. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2014, 55, 628–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victoire, T.A.A.; Jeyakumar, A.E. Hybrid PSO-SQP for economic dispatch with valve-point effect. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2004, 71, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiejin, C.; Qiong, L.; Lixiang, L.; Haipeng, P.; Yixian, Y. A hybrid CPSO-SQP method for economic dispatch considering the valve-point effects. Int. J. Energy Convers. Manag. 2012, 53, 175–181. [Google Scholar]
- Aniruddha, B.; Pranab, K.C. Solving economic emission load dispatch problems using hybrid differential evolution. Appl. Soft Comput. 2011, 11, 2526–2537. [Google Scholar]
- Alsumait, J.S.; Sykulski, J.K.; Al-Othman, A.K. A hybrid GAePSeSQP method to solve power system valve-point economic dispatch problems. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 1773–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, A.Y. Flower pollination algorithm to solve combined economic and emission dispatch problems. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2016, 19, 980–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, A.L.; Krishna, O.V. Combined economic and emission dispatch using evolutionary algorithms—A case study. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2008, 3, 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Sangiamvibool, W.; Pothiya, S.; Ngamroo, I. Multiple tabu search algorithm for economic dispatch problem considering valve-point effects. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2011, 4, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, G.; Shi, D. Orthogonal learning competitive swarm optimizer for economic dispatch problems. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 66, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Li, Q.; Li, L.; Peng, H.; Yang, Y. A hybrid FCASO-SQP method for solving the economic dispatch problems with valve point effects. Energy 2012, 38, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.B.; Jeong, Y.M.; Shin, J.R.; Lee, K.Y. An improved particle swarm optimization for nonconvex economic dispatch problems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2010, 25, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbaraj, P.; Rengaraj, R.; Salivahanan, S. Enhancement of Self-adaptive real-coded genetic algorithm using Taguchi method for Economic dispatch problem. Appl. Soft Comput. 2011, 11, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, E.S.; Yang, L.; Papageorgiou, L.G. On the modelling of valve point loadings for power electricity dispatch. Appl. Energy 2012, 91, 301–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talaq, J.H.; Ferial, F.; EI-Hawary, M.E. A summary of environmental/economic dispatch algorithms. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1994, 9, 1508–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, Z.; Guo, C.; Cao, Y. Dynamic economic dispatch in electricity market using particle swarm optimization algorithm. In Proceedings of the 5th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation, Hangzhou, China, 15–19 June 2004; pp. 5050–5054. [Google Scholar]
- Yalcinoz, T.; Altun, H. Environmentally constrained economic dispatch via a genetic algorithm with arithmetic crossover. In Proceedings of the 6th Africon Conference in Africa, Abuja, Nigeria, 23–26 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tarek, B.; Labdani, R.; Slimani, L. Economic power dispatch of power system with pollution control using multi objective particle swarm optimization. Univ. Sharjah J. Pure Appl. Sci. 2007, 4, 57–76. [Google Scholar]
- Abido, M.A. Multiobjective particle swarm optimization for environmental/ economic dispatch problem. In Proceedings of the 8th International Power Engineering Conference (IPEC-2007), Singapore, 3–6 December 2007; pp. 1385–1390. [Google Scholar]
- Gent, M.R.; Lamont, J.W. Minimum emission dispatch. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 1972, 6, 2650–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, Y. Two modified artificial bee colony algorithms inspired by grenade explosion method. Neurocomputing 2015, 151, 1198–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, G.; Quintana, V. On a nonlinear multiple centrality corrections interior-point method for optimal power flow. IEEE Trans Power Syst. 2011, 16, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitin, T.; Hari, M.D.; Manjaree, P. Economic load dispatch of wind-solar-thermal system using backtracking search algorithm. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2016, 8, 16–27. [Google Scholar]
- Miranda, V.; Hang, P.S. Economic dispatch model with fuzzy constraints and attitudes of dispatchers. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2005, 20, 2143–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadaee, M.; Radzi, M. Multi-objective optimization of a stand-alone hybrid renewable energy system by using evolutionary algorithms: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 3364–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, W. Economic load dispatch constrained by wind power availability: A here-and-now approach. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2010, 1, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetzer, J.; Yu, D.C.; Bhattarai, K. An economic dispatch model incorporating wind power. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2008, 23, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.X.; Gooi, H.B.; Wang, M.Q. Sizing of energy storage for microgrids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2012, 3, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, M.; Deshmukh, S. Modeling of hybrid renewable energy systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2008, 12, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaki, S.H.; Chedid, R.B.; Ramadan, R. Probabilistic performance assessment of autonomous solar wind energy conversion systems. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 1999, 14, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, G.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, X.; Shi, D. A Novel Method for Economic Dispatch with Across Neighborhood Search: A Case Study in a Provincial Power Grid, China. Complexity 2018, 2018, 2591341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Singh, C. Balancing risk and cost in fuzzy economic dispatch including wind power penetration based on particle swarm optimization. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2008, 78, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuswamy, R.; Krishnan, M.; Subramanian, K.; Subramanian, B. Environmental and economic power dispatch of thermal generators using modified NSGA-II algorithm. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2015, 25, 1552–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sumait, J.S.; AL-Othman, A.K.; Sykulski, J.K. Application of pattern search method to power system valve-point economic load dispatch. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2007, 29, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, J.; Kothari, O.F.; Linyamurthy, K.S. Economic-Emission load dispatch through goal programming techniques. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 1988, 3, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.N.; Sim, G.Y.; Azmi, A.; Shamsudin, S.H. Combined Economic and Emission Dispatch Solution using Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm with Fuzzy Approach. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2018, 7, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Prasad, D.G.; Mohan, D.H.; Pandit, M.; Panigrahi, B.K. Artificial Bee Colony Optimization for Combined Economic Load and Emission Dispatch. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Sustainable Energy and Intelligent System (SEISCON 2011), Chennai, India, 20–22 July 2011; pp. 340–346. [Google Scholar]
- Serdar, O.; Dog, A. Incremental artificial bee colony with local search to economic dispatch problem with ramp rate limits and prohibited operating zones. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 65, 397–407. [Google Scholar]
- Lili, A.; Wulandhari, A.; Siti, S.; Wisnu, W. Bat Algorithm Implementation on Economic Dispatch Optimization Problem. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 135, 275–282. [Google Scholar]
- Thang, T.; Nguyen, S.; Dang, H. Bat Algorithm for Economic Emission Load Dispatch Problem. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Technol. 2016, 86, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, P.K.; Paul, C.; Sultana, S. Oppositional teaching learning based optimization approach for combined heat and power dispatch. Electr. Power Syst Res. 2014, 57, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, M. Modified particle swarm optimization for non-smooth non-convex combined Heat and power economic dispatch. Electr. Power Compon. Syst. 2015, 43, 2146–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi-Ivatloo, B.; Moradi-Dalvand, M.; Rabiee, A. Combined heat and power economic dispatch problem solution using particle swarm optimization with time varying acceleration coefficients. Electr. Power Syst Res. 2013, 95, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derafshi, B.S.; Abdi, H.; La Scala, M. Combined heat and power economic dispatch problem using gravitational search algorithm. Electr. Power Syst Res. 2016, 133, 160–172. [Google Scholar]
- Subham, K.; Provas, K.R.; Barun, M. Renewable Energy-Based Economic Load Dispatch Using Two-Step Biogeography-Based Optimization and Butterfly Optimization Algorithm. Int. J. Swarm Intell. Res. 2020, 11, 24–61. [Google Scholar]
- Kameswara, K.; Kumar, P.; Nirmala, S.; Latif, A.; Chandra, D.D.; Suhail, H.S.M.; Al-Durra, A.; Ustun, T.S. Day-Ahead DSM-Integrated Hybrid-Power Management Incorporated CEED of Solar Thermal/Wind/Wave/BESS System Using HFPSO. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1169. [Google Scholar]
- Abdurazaq, E.; Muhammet, T.G. Multi-objective Optimization of Combined Economic Emission Dispatch Problem in Solar PV Energy Using a Hybrid Bat-Crow Search Algorithm. Int. J. Renew. Energy 2021, 11, 383–391. [Google Scholar]
- MohanDubey, H.; Manjaree, P.; Panigrahi, B.K. Hybrid flower pollination algorithm with time-varying fuzzy selection mechanism for wind integrated multi-objective dynamic economic dispatch. Renew. Energy 2015, 83, 188–202. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnasamy, U.; Nanjundappan, D. Hybrid weighted probabilistic neural network and biogeography based optimization for dynamic economic dispatch of integrated multiple-fuel and wind power plants. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2016, 77, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niknam, T.; Mohammad, R.N.; A-Abarghooee, R. A new hybrid algorithm for optimal power flow considering prohibited zones and valve point effect. Energy Convers. Manag. 2012, 58, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, P.M.; Verma, H. An improved TLBO based economic dispatch of power generation through distributed energy resources considering environmental constraints. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2019, 18, 100207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, L.; Zhengyu, L.; Zhen, C. Economic dispatch of off-grid photovoltaic generation system with hybrid energy storage. In Proceedings of the 2018 2nd IEEE Conference on Energy Internet and Energy System Integration (EI2), Beijing, China, 20–22 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.; Anand, H. Analysis of scheduling of solar sharing for economic/environmental dispatch using PSO. In Proceedings of the 2015 Annual IEEE India Conference (INDICON), New Delhi, India, 17–20 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wadhawan, A.; Verma, P.; Grover, S.; Anand, H. Economic environmental dispatch with PV generation including transmission losses using PSO. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 7th Power India International Conference (PIICON), Bikaner, India, 25–27 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaoyan, Y.; Chunlin, G.; Xuan, X.; Dequan, H.; Zhou, M. Research on large scale electric vehicles participating in the economic dispatch of wind and thermal power system. In Proceedings of the 2017 China International Electrical and Energy Conference (CIEEC), Beijing, China, 25–27 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wibowo, R.S.; Firmansyah, K.R.; Aryani, N.K.; Soeprijanto, A. Dynamic economic dispatch of hybrid micro grid with energy storage using quadratic programming. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Region 10 Conference (TENCON), Singapore, 22–25 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.-R.; Zeng, G.-Q.; Lu, K.-D. Constrained multi-objective population extremal optimization based economic-emission dispatch incorporating renewable energy resources. Renew. Energy 2019, 143, 277–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, B.; Roy, S.K.; Bhattacharyya, B. Solving multi-objective economic emission dispatch of a renewable integrated micro grid using latest bio-inspired algorithms. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2019, 22, 55–66. [Google Scholar]
- Santillán-Lemus, F.D.; Minor-Popocatl, H.; Aguilar-Mejía, O.; Tapia-Olvera, R. Optimal economic dispatch in micro grids with renewable energy sources. Energies 2019, 12, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elattar, E.E. Modified harmony search algorithm for combined economic emission dispatch of micro grid incorporating renewable sources. Energy 2018, 159, 496–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfi, V.; Livani, H.; Yliniemi, L. A new multi-objective economic-emission dispatch in micro grids. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting, Chicago, IL, USA, 16–20 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Shilaja, C.; Ravi, K. Optimization of emission/economic dispatch using Euclidean affine flower pollination algorithm (eFPA) and binary FPA (BFPA) in solar photo voltaic generation. Renew. Energy 2017, 107, 550–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, A.; Al-Baiyat, S.; Cheng, T. Economic load dispatch multiobjective optimization procedures using linear programming techniques. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1995, 10, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, M.; Kuppusamy, K.; Khan, M.A. Optimal short-term hydrothermal scheduling using decomposition approach and linear programming method. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 1992, 14, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pothiya, S.; Ngamroo, I.; Kongprawechnon, W. Ant colony optimisation for economic dispatch problem with non-smooth cost functions. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2010, 32, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, G.; Gu, J.; Farooq, U.; Raza, A.; Asad, M.U.; El-Hawary, M.E. Solution of an economic dispatch problem through particle swarm optimization: A detailed survey—Part II. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 24426–24445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afandi, A.; Fadlika, I.; Sendari, S.; Miyauchi, H.; Fujita, G.; Tutkun, N. Comparison of ABC and genetic algorithms on economic power dispatch. In Proceedings of the 2018 10th International Conference on Information Technology and Electrical Engineering (ICITEE), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 24–26 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Panigrahi, C.K.; Chattopadhyay, P.K.; Chakrabarti, R.N.; Basu, M. Simulated annealing technique for dynamic economic dispatch. Electr. Power Compon. Syst. 2006, 34, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlünz, E.; Van-Vuuren, J. An investigation into the effectiveness of simulated annealing as a solution approach for the generator maintenance scheduling problem. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2013, 53, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, E.; Azizivahed, A.; Narimani, H.; Fathi, M.; Narimani, M.R. A comprehensive study of practical economic dispatch problems by a new hybrid evolutionary algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 61, 1186–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motaeb, E.A.; Makbul, A.M.R.; Ibrahim, M.M. A New Chaotic Artificial Bee Colony for the Risk-Constrained Economic Emission Dispatch Problem Incorporating Wind Power. Energies 2021, 14, 4014. [Google Scholar]
- Fister, I.; Strnad, D.; Yang, X.S.; Fister, J.I. Adaptation and hybridization in nature inspired algorithms. In Adaptation and Hybridization in Computational Intelligence; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 3–50. [Google Scholar]
- Ting, T.; Yang, X.S.; Cheng, S.; Huang, K. Hybrid metaheuristic algorithms: Past, present, and future. In Recent Advances in Swarm Intelligence and Evolutionary Computation; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 71–83. [Google Scholar]
- Golmohamadi, H.; Reza, K.; Keypour, R.; Pouya, M. Multi-objective co-optimization of power and heat in urban areas considering local air pollution. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2021, 24, 2372–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodha, K.D.; Yadav, V.K.; Mukherjee, V. A novel quantum inspired hybrid metaheuristic for dispatch of power system including solar photovoltaic generation. Energy Sources Part B Econ. Plan. Policy 2021, 16, 558–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).