The Influence of the Substrate and External Magnetic Field Orientation on FeNi Film Growth
Abstract
1. Introduction
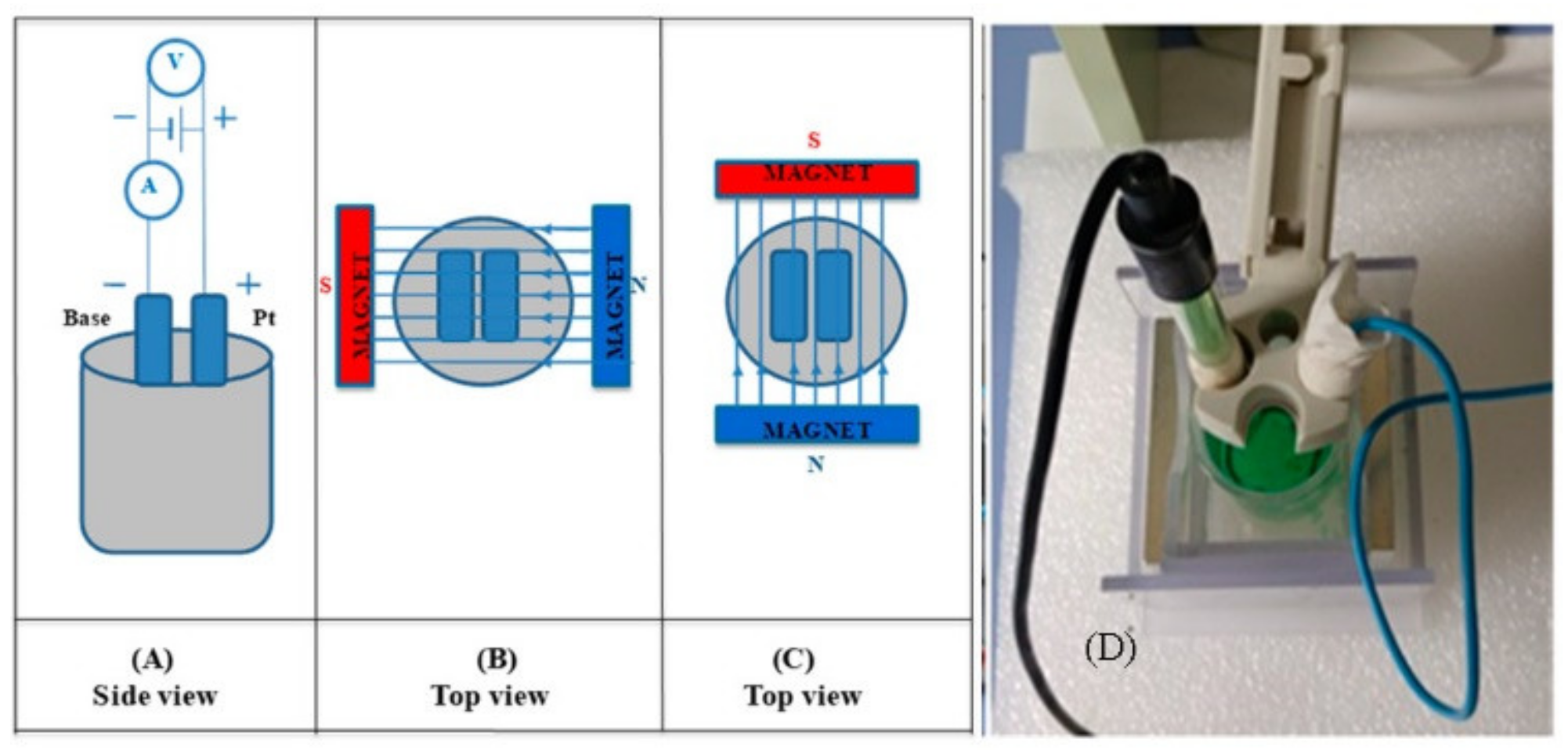
2. Materials and Methods
FeNi Layers Deposition
3. Results and Discussion
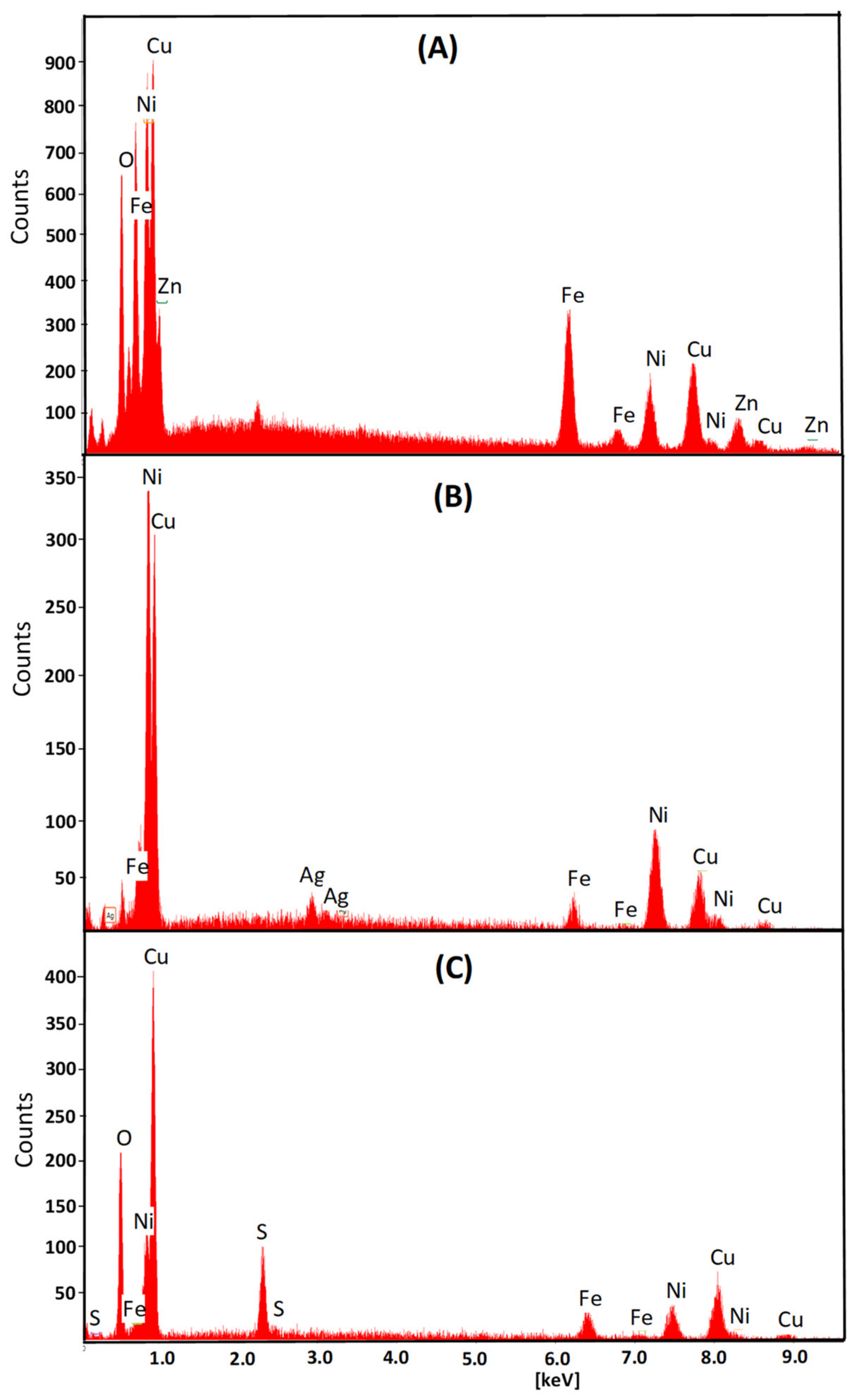
3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
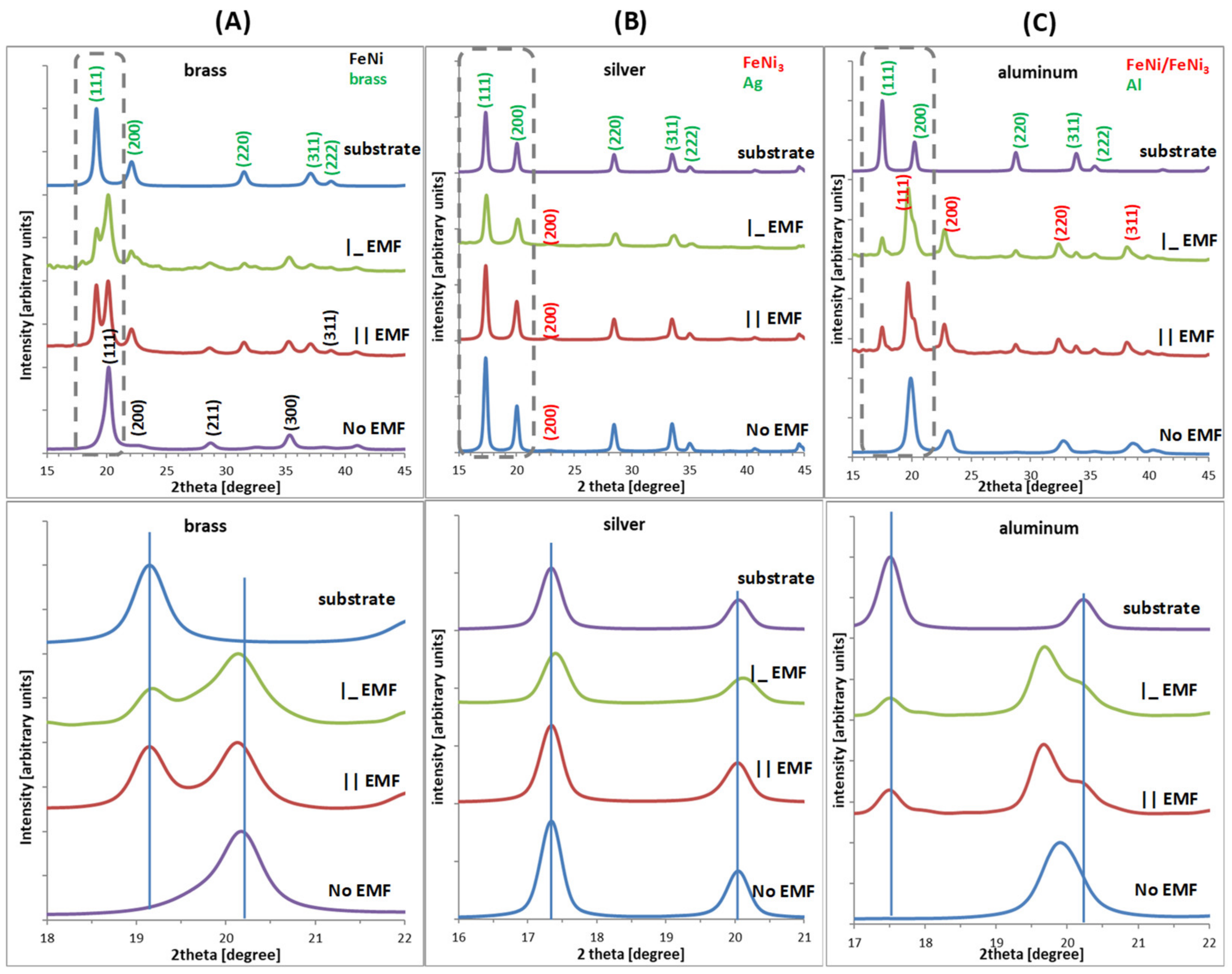
3.2. X-ray Diffraction
3.3. Mössbauer Spectroscopy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tateno, S.; Hirose, K.; Komabayashi, T.; Tateno, H.; Ohishi, Y. The structure of Fe-Ni alloy in Earth’s inner core. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L12305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, P.M. DepositionTechnologies for Films and Coatings. Science, Applications and Technology, 3rd ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Oxford, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Milchev, A.; Heerman, L. Electrochemical nucleation and growth of nano- and microparticles: Some theoretical and experimental aspects. Electrochim. Acta 2003, 48, 2903–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, A. Electrodeposition of Alloys; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrievich, T.R. Normal electrochemical deposition of FeNi films. Adv. Res. 2017, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, K.I.; Djokić, S.S.; Nikolić, N.D.; Jović, V.D. Morphology of Electrochemically and Chemically Deposited Metals; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gurrappa, I.; Binder, L. Electrodeposition o nanostructured coatings and their characterization—A review. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2008, 9, 043001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezende, T.G.L.; Cezar, D.V.; do Lago, D.C.B.; Senna, L.F. A review of Corrosion Resistance Nanocomposite Coatings. In Electrodeposition of Composite Materials; Mohamed, A.M.A., Golden, T.G., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016; pp. 147–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitek, J.; Degmová, J.; Sedlačková, K.; Dekan, J. Mössbauer Spectroscopy of Fe-Ni-Nb-B Alloy in Weak Magnetic Field. J. Mod. Phys. 2012, 3, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kalska-Szostko, B.; Wykowska, U.; Satuła, D. Magnetic nanowires (Fe, Fe-Co, Fe-Ni)—Magnetic moment reorientation in respect of wires composition. Nukleonika 2015, 60, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuru, H.; Kockar, H.; Alper, M. Giant magnetoresistance (GMR) behavior of electrodeposited NiFe/Cu multilayers: Dependence of non-magnetic and magnetic layer thickness. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 444, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, N.; Wang, F.; Watanabe, T. Adhesion of Electrodeposited Copper, Nickel and Silver films on Copper, Nickel and Silver Substrates. Mater. Trans. 2004, 45, 3330–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nweze, C.I.; Ekpunobi, A.J. Electrodeposition of Zinc Selenide Films on Different Substrates and its Characterization. Int. J. Sci. Technol. 2014, 3, 201–203. [Google Scholar]
- Koschichow, D.; Mutschke, G.; Yang, X.; Bund, A.; Fröhlich, J. Numerical Simulation of the Onset of Mass Transfer and Convection in Copper Electrolysis Subjected to a Magnetic Field. Russ. J. Electrochem. 2012, 48, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Białostocka, A.; Idzkowski, A. The Effect of Ground Changes and the Setting of External Magnetic Field on Electroplating FeNi Layers: Progress in Automation, Robotics and Measurement Techniques. In Automation 2019; Szewczyk, R., Zieliński, C., Kaliczyńska, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 684–696. [Google Scholar]
- Thanh, N.T.K.; Maclean, N.; Mahiddine, S. Mechanisms of Nucleation and Growth of Nanoparticles in Solution. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 7610–7630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meena, S.P.; Ashokkumar, R.; Ranjith Kumar, E. Effects o Cr Doping Concentration on Structural, Morphology, Mechanical and Magnetic Properties of Electrodeposited NiCoCr Thin Films. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 2019, 29, 1094–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, M.; Herrault, F.; Park, J.; Allen, M.G. Highly laminated soft magnetic electroplated CoNiFe thick films. IEEE Magn. Lett. 2013, 4, 5000204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalska-Szostko, B.; Giersig, M.; Fumagalli, P. Influence of the shape on the magneto-optic properties of nanosized islands. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 228, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalska-Szostko, B.; Nordström, E.; Häggström, L.; Blomvist, P.; Wäppling, R. Fe/V multilayers studied by CEMS. J. Alloy Compd. 2003, 348, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, E.; Svalov, A.V.; García-Arribas, A.; Feuchtwanger, J.; Barandiaran, J.M.; Kurlyandskaya, G.V. High Performance Magnetoimpedance in FeNi/Ti Nanostructured Multilayers with Opened Magnetic Flux. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 12, 7496–7500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Kavaldzhiev, M.N.; Kosel, J. Flexible magnetoimpedance sensor. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 378, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beach, R.S.; Smith, N.; Platt, C.L.; Jeffers, F.; Berkowitz, A.E. Magneto-impedance effect in NiFe plated wire. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1996, 68, 2753–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melzer, M.; Makarov, D.; Calvimontes, A.; Karnaushenko, D.; Baunack, S.; Kaltofen, R.; Mei, Y.; Schmidt, O.G. Stretchable Magnetoelectronics. Nano. Lett. 2011, 11, 2522–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimes, C.A. Sputter Deposition of Magnetic Thin Films Onto Plastic: The Effect of Undercoat And Spacerlayer Composition On The Magnetic Properties Of Multilayer Permalloy Thin Films. IEEE T. Magn. 1995, 31, 4109–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Białostocka, A.M.; Klekotka, U.; Kalska-Szostko, B. The Effect of a Substrate Material on Composition Gradients of Fe-Ni Films obtained by Electrodeposition. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kądziołka-Gaweł, M.; Babilas, R.; Granek, K. Mössbauer Study of Some Intermetallic Compounds Fe80-xNixB20 (x = 8, 16, 24, 28). Acta Phys. Pol. A 2018, 133, 651–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Białostocka, A.M.; Klekotka, U.; Kalska-Szostko, B. Modulation of Iron-Nickel Layers Composition by an External Magnetic Field. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2018, 206, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Białostocka, A.M.; Klekotka, U.; Żabiński, P.; Kalska-Szostko, B. Microstructure evolution of Fe/Ni layers deposited by electroplating under an applied magnetic field. Magnetohydrodynamics 2017, 53, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ispas, A.; Matsushima, H.; Plieth, W.; Bund, A. Influence of a magnetic field on the electrodeposition of nickel-iron alloys. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 52, 2785–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.-M.; Wei, J.-H.; Fu, J.-R.; Popov, B.N.; Popova, S.N.; White, R.E. Mass Transport Effects on the Electrodeposition of Iron-Nickel Alloys at the Presence of Additives. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1995, 25, 543–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabia, J.; Tajamal, H.; Saliha, S.; Shahid, A.M. Magnetic Field Effects on the Microstructural Variation of Electrodeposited Nickel Film. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2011, 1, 481–487. [Google Scholar]
- Koza, J.A.; Mogi, I.; Tschulik, K.; Uhlemann, M.; Mickel, C.; Gebert, A.; Schultz, L. Electrocrystallisation of metallic films under the influence of an external homogeneous magnetic field—Early stages of the layer growth. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 6533–6541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guittoum, A.; Layadi, A.; Tafat, H.; Bourzami, A.; Souami, N.; Lenoble, O. Structure, Mössbauer and magnetic studies of nanostructured Fe80Ni20 alloy elaborated by mechanical milling. Philos. Mag. 2008, 88, 1085–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokuniaeva, A.O.; Vorokh, A.S. Estimation of particle size using the Debye equation and the Scherrer formula for polyphasic TiO2 powder. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1410, 012057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, K. Materials Data on FeNi (SG:123) by Materials Project. 2016. Available online: https://www.osti.gov/dataexplorer/biblio/dataset/1197364 (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Persson, K. Materials Data on FeNi3 (SG:221) by Materials Project. 2015. Available online: https://www.osti.gov/dataexplorer/biblio/dataset/1190197 (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Rabiei, M.; Palevicius, A.; Monshi, A.; Nasiri, S.; Vilkauskas, A.; Janusas, G. Comparing Methods for Calculating Nano Crystal Size of Natural Hydroxyapatite Using X-ray Diffraction. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzwarth, U.; Gibson, N. The Scherrer equation versus the ‘Debye-Scherrer equation’. Nat. Nanotech. 2011, 6, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ispas, A.; Matsushima, H.; Bund, A.; Bozzini, B. Nucleation and growth of thin nickel layers under the influence of a magnetic field. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2009, 626, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiecinski, P.; Garbacz, H.; Murakami, H.; Kurzydłowski, K. Effect of grain size on reactive diffusion between titanium and aluminium. Phys. Status Solidi 2010, 7, 1395–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wang, X.; Pei, W.; Zhao, D.; Wang, K.; Lia, G.; Wang, Q. Tailoring the shape and size of wet-chemical synthesized FePt nanoparticles by controlling nucleation and growth with high magnetic field. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 15023–15028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trong, D.N.; Long, V.C. Effects of number of atoms, shell thickness, and temperature on the structure of Fe nanoparticles amorphous by molecular dynamics method. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2021, 9976633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, H.D.T.; Coman, G.; Quang, H.N.; Trong, D.N. Influence of heating rate, temperature, pressure on the structure, and phase transition of amorphous Ni material: A molecular dynamics study. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, S.; Ivanov, S.; Dimitrova, A.; Krischok, S.; Bund, A. Understanding the initial stages of Si electrodeposition under diffusion kinetic limitation in ionic liuid-based electrolytes. J. Cryst. Growth 2020, 531, 125346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalsen, S.; Alper, M.; Kockar, H.; Haciismailoglu, M.; Karaagac, O.; Kuru, H. Properites of Electrodeposited CoFeNi/Cu Superlattices: The Effect of CoFeNi and Cu Layers Thicknesses. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2013, 26, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuru, H.; Aytekin, N.Ç.; Köçkar, H.; Haciismailoğlu, M.; Alper, M. Effect of NiFe layer thickness on properties of NiFe/Cu superlattices electrodeposited on titanium substrate. J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 17879–17889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczurek, T.; Rausch, T.; Schlesinger, M.; Snyder, D.D.; Olk, C.H. Induced Crystallographic Orientations in Electrodeposited Ni-Cu Multilayers. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1999, 146, 1777–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokarz, A.; Nitkiewicz, Z.; Wolkenberg, A. The dependence of magnetic properties on crystallographic structure of electrochemically deposited Ni/Cu superlattices. Electron. Technol.-Internet J. 2003, 35, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Kądziołka-Gaweł, M.; Zarek, M.; Popiel, E.; Chrobak, A. The Crystal Structure and Magnetic Properties of Selected fccFeNi and Fe40Ni40B20 Alloys. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2010, 117, 412–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.H.; Kim, J.K.; Yim, T.H.; Park, Y.B. Textures and Grain Growth in Nanocrystalline Fe-Ni Alloys. Mater. Sci. 2005, 475–479, 3483–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Haghshenas, D.F.; Ghorbani, M.; Dolati, A. Electrochemical Behavior of Nanostructured Fe-Pd Alloy During Electrodeposition on Different Substrates. J. Electrochem. Sci. Technol. 2018, 9, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, I.; Mori, H.; Kawakatsu, T.; Takigawa, Y.; Uesugi, T.; Higashi, K. Mechanical Behavior of Electrodeposited Bulk Nanocrystalline Fe-Ni Alloys. Mater. Res. 2015, 18, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalska-Szostko, B.; Klekotka, U.; Satuła, D. Core-shell magnetic nanowires fabrication and characterization. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 396, 1855–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalska-Szostko, B.; Klekotka, U.; Olszewski, W.; Satuła, D. Multilayered and alloyed Fe-Co and Fe-Ninanowires physicochemical studies. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 484, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehlooh, A.F.D.; Mahmood, S.H. Mössbauer Spectroscopy Study of Iron Nickel Alloys. Hyperfine Interact. 2002, 139, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| 450 s | 900 s | 1800 s | 2700 s | 3600 s | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without EMF | 43.3/56.7 | 66.8/33.2 | 48.3/51.7 | 66.0/34.0 | 88.9/11.1 |
| I_ EMF | 53.7/46.3 | 59.2/40.8 | 59.5/40.5 | 60.7/39.3 | 85.8/14.2 |
| II | 27.6/72.4 | 33.3/66.7 | 63.8/36.2 | 63.5/36.5 | 69.0/31.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Białostocka, A.M.; Klekotka, U.; Kalska-Szostko, B. The Influence of the Substrate and External Magnetic Field Orientation on FeNi Film Growth. Energies 2022, 15, 3520. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15103520
Białostocka AM, Klekotka U, Kalska-Szostko B. The Influence of the Substrate and External Magnetic Field Orientation on FeNi Film Growth. Energies. 2022; 15(10):3520. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15103520
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiałostocka, Anna Maria, Urszula Klekotka, and Beata Kalska-Szostko. 2022. "The Influence of the Substrate and External Magnetic Field Orientation on FeNi Film Growth" Energies 15, no. 10: 3520. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15103520
APA StyleBiałostocka, A. M., Klekotka, U., & Kalska-Szostko, B. (2022). The Influence of the Substrate and External Magnetic Field Orientation on FeNi Film Growth. Energies, 15(10), 3520. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15103520






