Finite Control Set—Model Predictive Control with Non-Spread Spectrum and Reduced Switching Frequency Applied to Multi-Cell Rectifiers †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Topology and Harmonic Cancellation
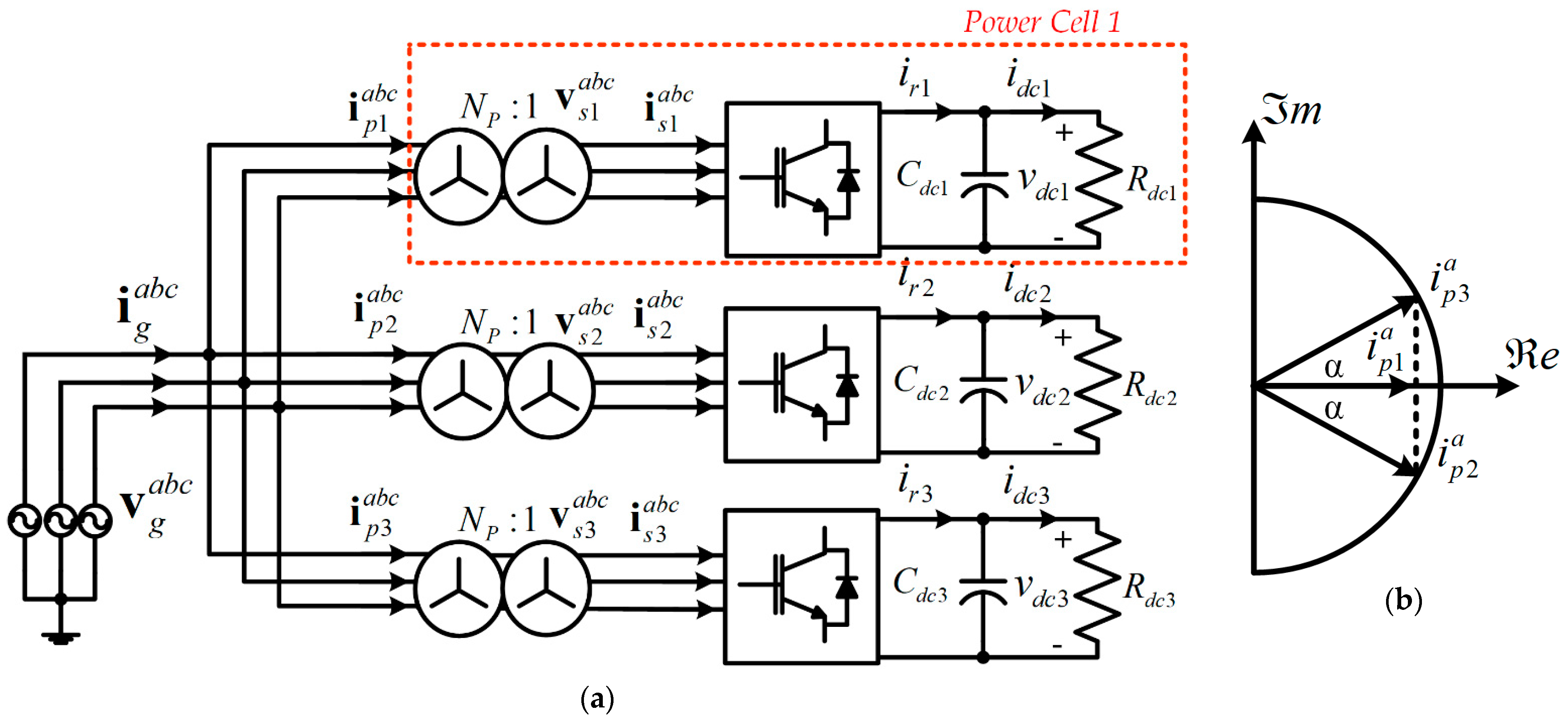

3. AFE Rectifier Model
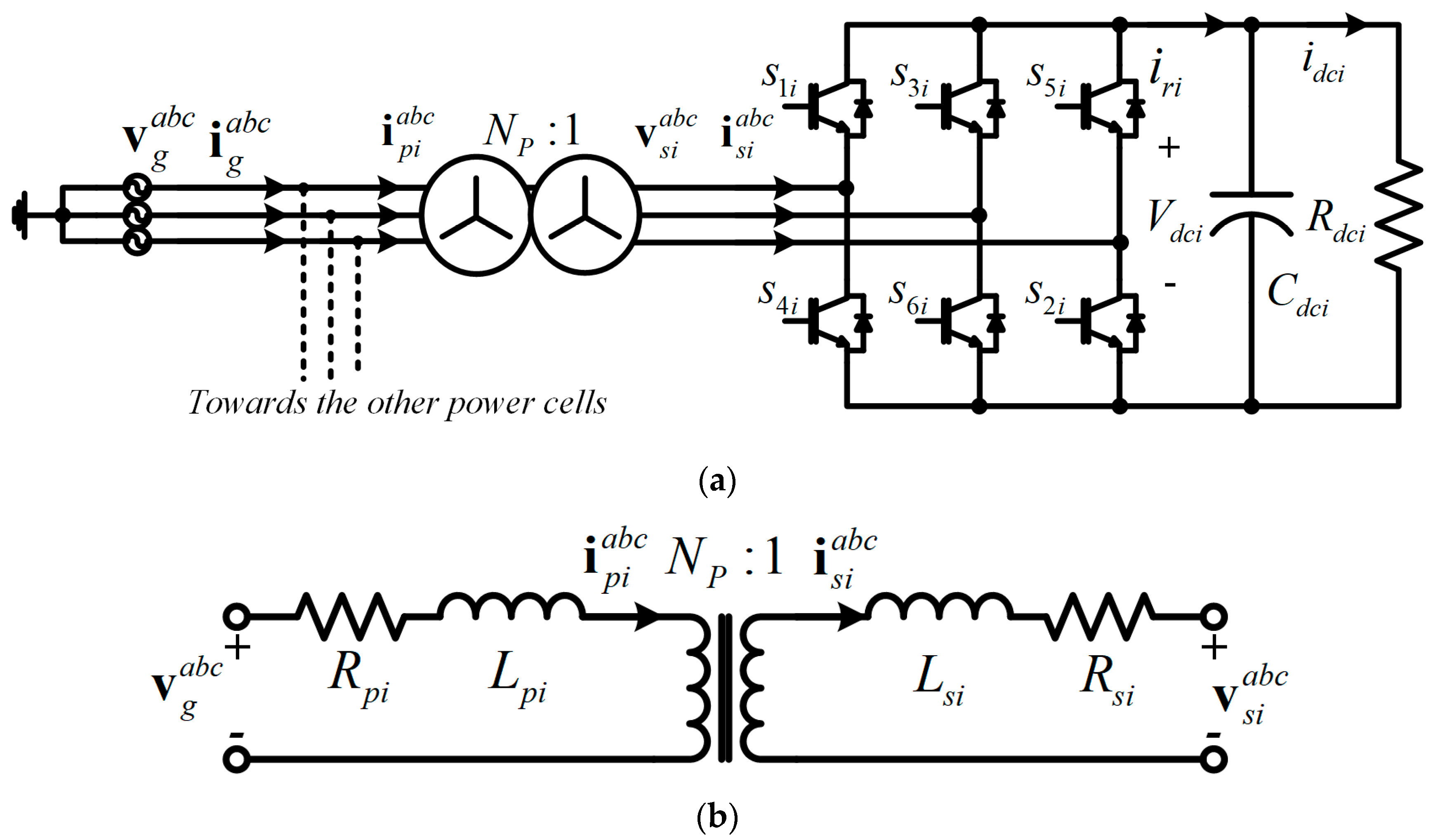
4. Control Scheme
4.1. DC Voltage Link
4.2. Input Current with a Reduced Switching Frequency

5. Semiconductors Losses
5.1. Switching Losses
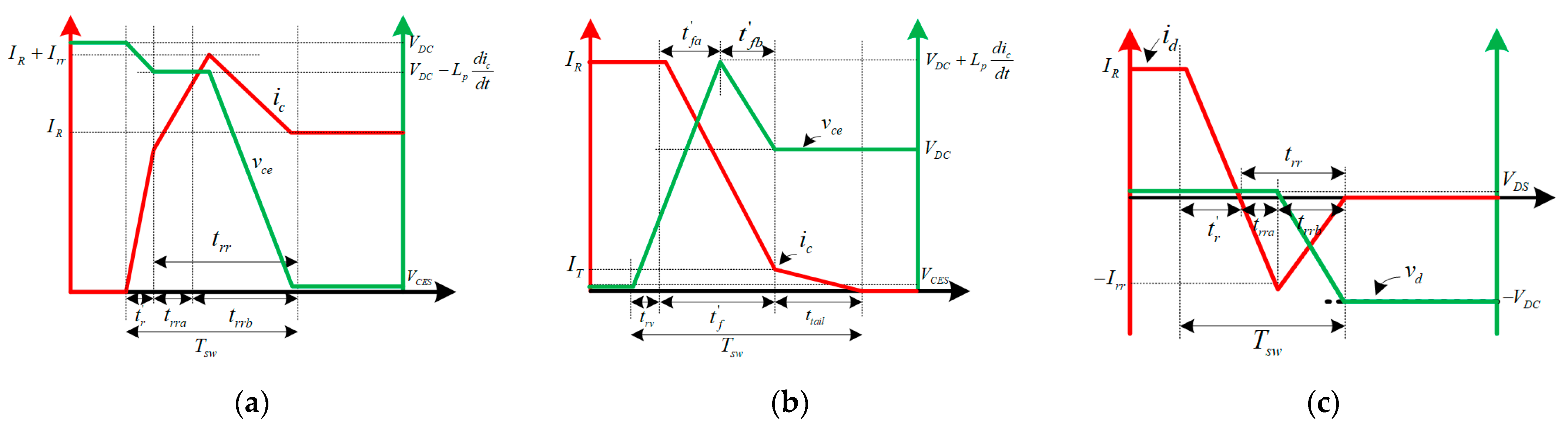
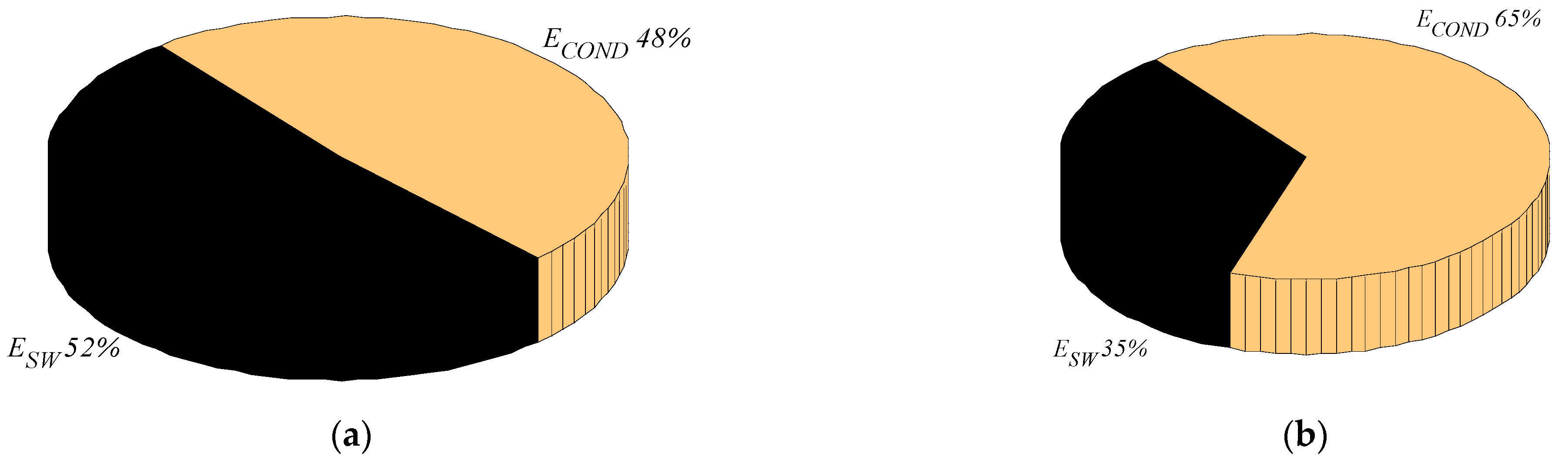
5.2. Conduction Losses
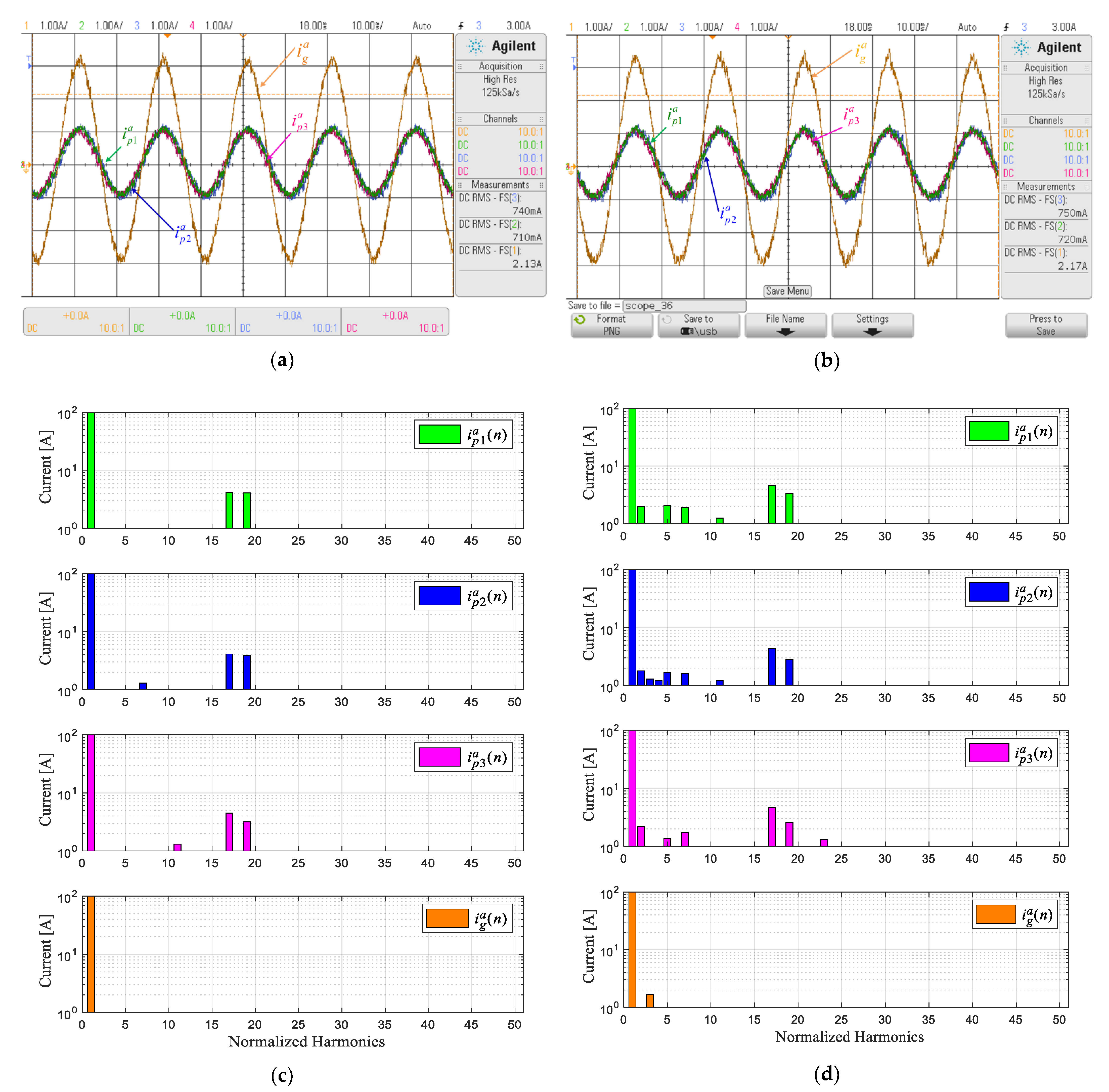
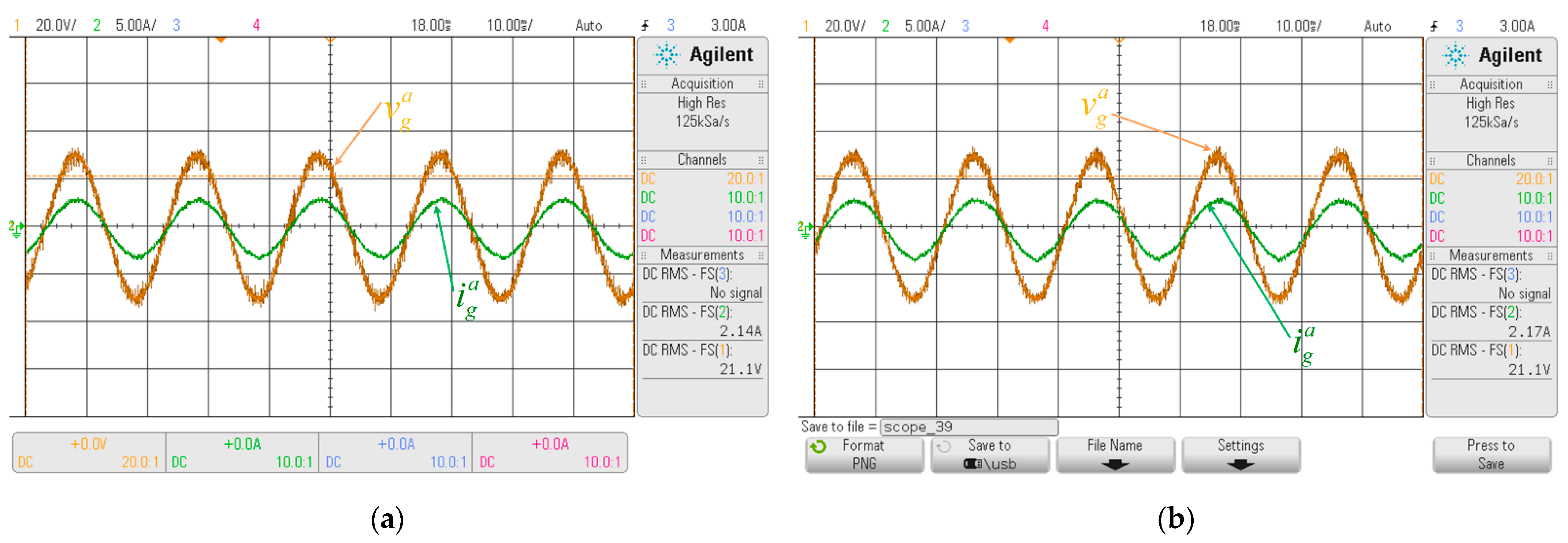
6. Experimental Results

7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kouro, S.; Malinowski, M.; Gopakumar, K.; Pou, J.; Franquelo, L.G.; Wu, B.; Rodriguez, J.; Perez, M.A.; Leon, J.I. Recent Advances and Industrial Applications of Multilevel Converters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 2553–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HAbu-Rub, H.; Holtz, J.; Rodriguez, J.; Baoming, G. Medium-Voltage Multilevel Converters—State of the Art, Challenges, and Requirements in Industrial Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 2581–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabae, A.; Takahashi, I.; Akagi, H. A new Neutral-Point-Clamped PWM Inverter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1981, 1A-17, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, P. A new approach to enhance power quality for medium voltage AC drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1997, 33, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.S.; Peng, F.Z. Multilevel converters-A new breed of power converters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1996, 32, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paice, D.A. Power Electronics Converter Harmonics: Multipulse Methods for Clean Power, 1st ed.; Wiley-IEEE Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocman, S.; Kolar, V.; Vo, T.T. Elimination of harmonics using multi-pulse rectifiers. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Harmonics and Quality of Power (ICHQP), Bergamo, Italy, 9 November 2010; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Gairola, S.; Singh, B.N.; Chandra, A.; Al-Haddad, K. Multipulse AC–DC Converters for Improving Power Quality: A Review. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2008, 23, 260–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, M.; Naderi, M.S.; Blackburn, T.; Phung, B.T. Transformer efficiency and de-rating evaluation with non-sinusoidal loads. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Power System Technology (POWERCON), Auckland, New Zealand, 7 January 2012; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haggerty, N.K.; Malone, T.P.; Crouse, J. Applying high efficiency transformers. IEEE Ind. Appl. Mag. 1998, 4, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolhassani, M. Modular Multipulse Rectifier Transformers in Symmetrical Cascaded H-Bridge Medium Voltage Drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y. PWM rectifier in power cell of cascaded H-bridge multilevel converter. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Seoul, Korea, 8–11 October 2007; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baier, C.R.; Espinoza, J.R.; Muñoz, J.A.; Morán, L.A.; Melín, P.E. A High-Performance Multicell Topology Based on Single-Phase Power Cells for Three-Phase Systems Operating Under Unbalanced AC Mains and Asymmetrical Loads. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 2730–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.; Xie, S. A Multipulse-Structure-Based Bidirectional PWM Converter for High-Power Applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2009, 24, 1233–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.H. High Voltage Regenerative Converter and the Control of Its PWM Rectifier. In Proceedings of the International Conference on E-Product E-Service and E-Entertainment, Henan, China, 7–9 November 2010; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontt, J.A.; Rodriguez, J.R.; Liendo, A.; Newman, P.; Holtz, J.; Martin, J.M.S. Network-Friendly Low-Switching-Frequency Multipulse High-Power Three-Level PWM Rectifier. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, P.; Kazmierkowski, M.P.; Kennel, R.M.; Quevedo, D.E.; Rodriguez, J. Predictive Control in Power Electronics and Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 4312–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouro, S.; Cortes, P.; Vargas, R.; Ammann, U.; Rodriguez, J. Model Predictive Control—A Simple and Powerful Method to Control Power Converters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 1826–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, R.O.; Espinoza, J.R.; Melin, P.; Reyes, M.E.; Espinosa, E.E.; Silva, C.; Maurelia, E. Predictive Controller for a Three-Phase/Single-Phase Voltage Source Converter Cell. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2014, 10, 1878–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, E.; Espinoza, J.R.; Ramirez, R.; Reyes, M.; Melin, P.; Munoz, J.; Baier, C.R. Finite Control Set—Model Predictive Control applied to multi-cell rectifiers. In Proceedings of the 39th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Vienna, Austria, 10–13 November 2013; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 5800–5805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.; Kazmierkowski, M.P.; Espinoza, J.R.; Zanchetta, P.; Abu-Rub, H.; Young, H.; Rojas, C. State of the Art of Finite Control Set Model Predictive Control in Power Electronics. IEEE Trans Ind. Inform. 2013, 9, 1003–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, E.; Espinoza, J.R.; Rohten, J.; Ramirez, R.; Reyes, M.; Munoz, J.; Melin, P. An efficiency comparison between an 18 pulses diode rectifier and a multi-cell AFE rectifier operating with FCS—MPC. In Proceedings of the 40th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Dallas, TX, USA, 29 October–1 November 2014; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1214–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, M.; Kouro, S.; Rodriguez, J.; Wu, B.; Yaramasu, V.; Espinoza, J.R.; Melila, P. Predictive current control in a current source inverter operating with low switching frequency. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Power Engineering, Energy and Electrical Drives, Istanbul, Turkey, 13–17 May 2013; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, J.; Baier, C.; Espinoza, J.; Rivera, M.; Guzmán, J.; Rohten, J. Switching losses analysis of an asymmetric multilevel Shunt Active Power Filter. In Proceedings of the 39th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Vienna, Austria, 10–13 November 2013; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 8534–8539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajapakse, A.D.; Gole, A.M.; Wilson, P.L. Electromagnetic transients simulation models for accurate representation of switching losses and thermal performance in power electronic systems. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2005, 20, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonberger, J.; Feix, G. Modelling turn-off losses in power diodes. In Proceedings of the 11th Workshop on Control and Modeling for Power Electronics, Zurich, Switzerland, 17–20 August 2008; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiechmann, E.P.; Aqueveque, P.; Burgos, R.; Rodriguez, J. On the Efficiency of Voltage Source and Current Source Inverters for High-Power Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 1771–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, P.; Kouro, S.; La Rocca, B.; Vargas, R.; Rodriguez, J.; Leon, J.I.; Vazquez, S.; Franquelo, L.G. Guidelines for weighting factors design in Model Predictive Control of power converters and drives. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology, Churchill, VIC, Australia, 10–13 February 2009; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| State | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 |
| 4 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 5 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| 6 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 7 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Symbol | Variable | Value |
|---|---|---|
| vg | Phase voltage | 31.1 [V] |
| f | Network frequency | 50 [Hz] |
| Rp, Rs | Transformer primary and secondary resistances | 0.5 [Ω] |
| Lp, Ls | Transformer primary and secondary inductances | 6 [mH] |
| NP | Turns ratio | 1 |
| Rdc | DC load resistance | 89 [Ω] |
| Cdc | DC link capacitor | 4.7 [mF] |
| Vdc | DC link voltage | 55 [V] |
| kp | Proportional gain | 0.8 |
| Ti | Integral time | 0.02 |
| Ts | Sampling time | 50 [µs] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Espinosa, E.; Espinoza, J.; Melín, P.; Rohten, J.; Baier, C.; Reyes, M. Finite Control Set—Model Predictive Control with Non-Spread Spectrum and Reduced Switching Frequency Applied to Multi-Cell Rectifiers. Energies 2021, 14, 6045. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14196045
Espinosa E, Espinoza J, Melín P, Rohten J, Baier C, Reyes M. Finite Control Set—Model Predictive Control with Non-Spread Spectrum and Reduced Switching Frequency Applied to Multi-Cell Rectifiers. Energies. 2021; 14(19):6045. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14196045
Chicago/Turabian StyleEspinosa, Eduardo, José Espinoza, Pedro Melín, Jaime Rohten, Carlos Baier, and Marcelo Reyes. 2021. "Finite Control Set—Model Predictive Control with Non-Spread Spectrum and Reduced Switching Frequency Applied to Multi-Cell Rectifiers" Energies 14, no. 19: 6045. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14196045
APA StyleEspinosa, E., Espinoza, J., Melín, P., Rohten, J., Baier, C., & Reyes, M. (2021). Finite Control Set—Model Predictive Control with Non-Spread Spectrum and Reduced Switching Frequency Applied to Multi-Cell Rectifiers. Energies, 14(19), 6045. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14196045











