Assessment of Daily Cost of Reactive Power Procurement by Smart Inverters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Reactive Power Control Mechanisms at Smart Inverters
2.1. Constant Voltage Control (Constant V)
2.2. Voltage Q−Droop Control (Q−Droop)
2.3. Voltage Iq−Droop Control (Iq−Droop)
2.4. Constant Reactive Power Control (Constant Q)
2.5. Active Power-Based Control (Watt−Var)
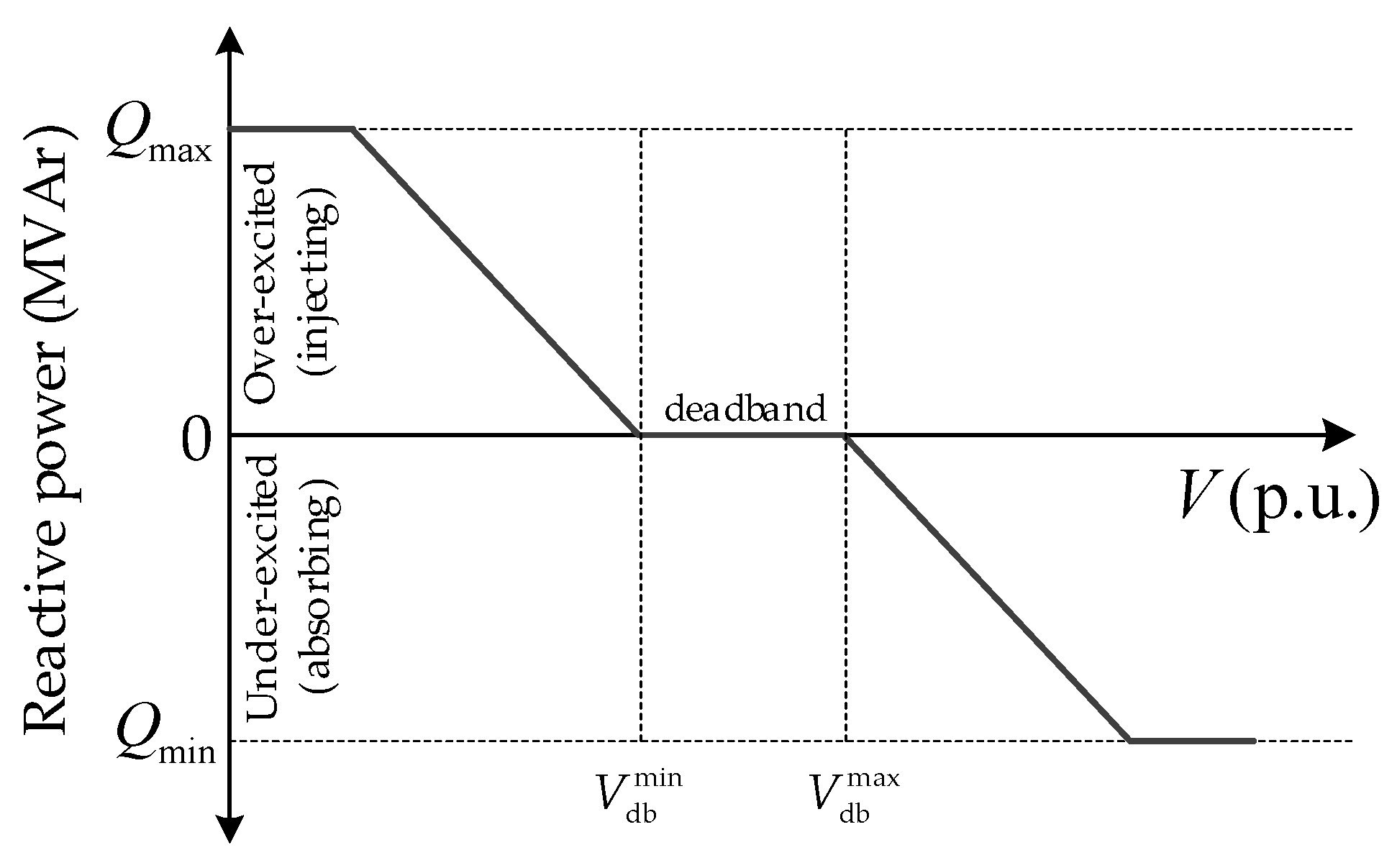
2.6. Voltage-Reactive Power Control (Volt-Var)
2.7. Constant Power Factor Control (Constant ϕ)
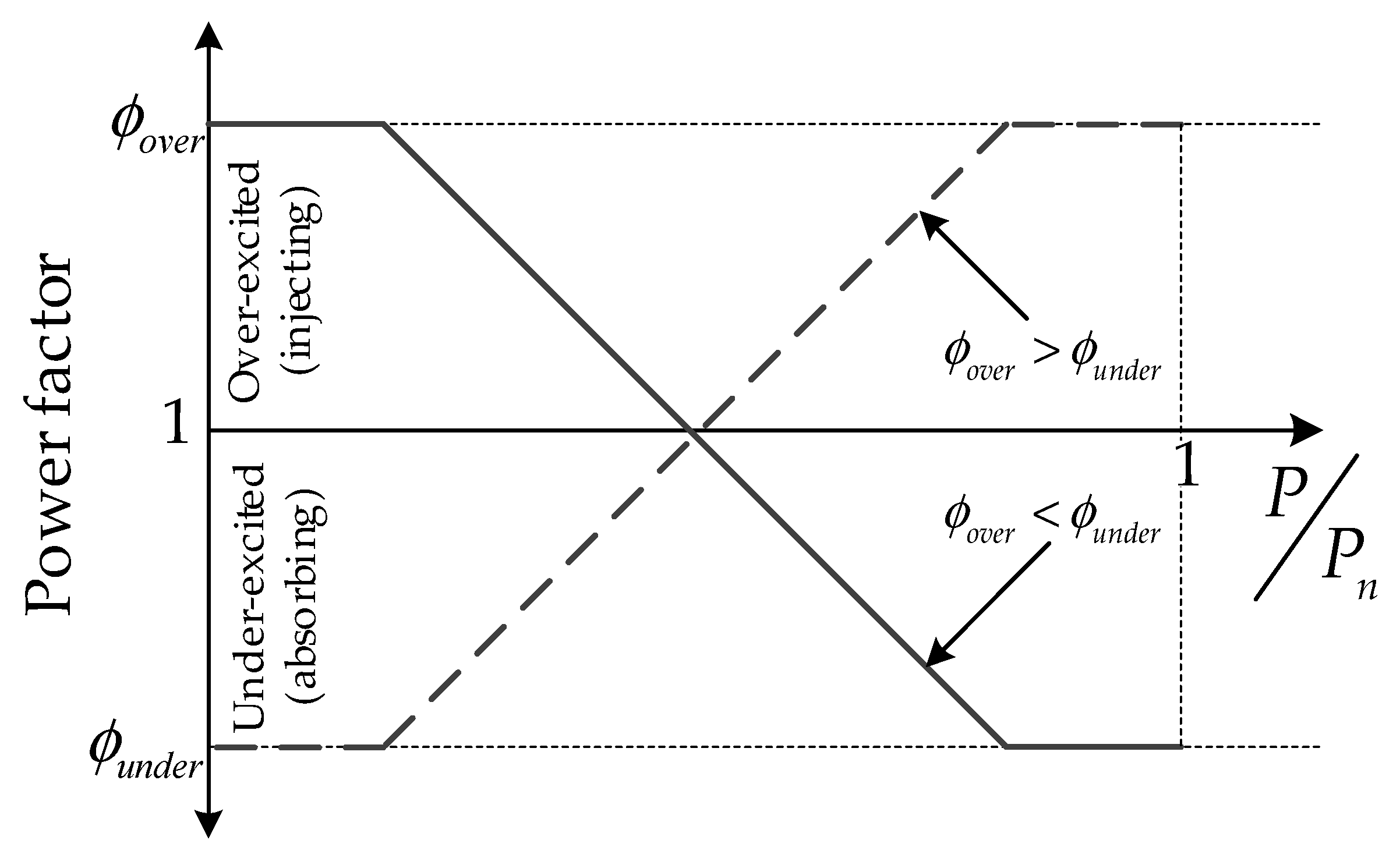
2.8. Power Factor-Active Power-Based Control (ϕ−Watt)
3. Optimum Reactive Power Control at Smart Inverters
4. Cost of Reactive Power Provision by Smart Inverters
5. Results
5.1. Test System
5.2. Study Cases
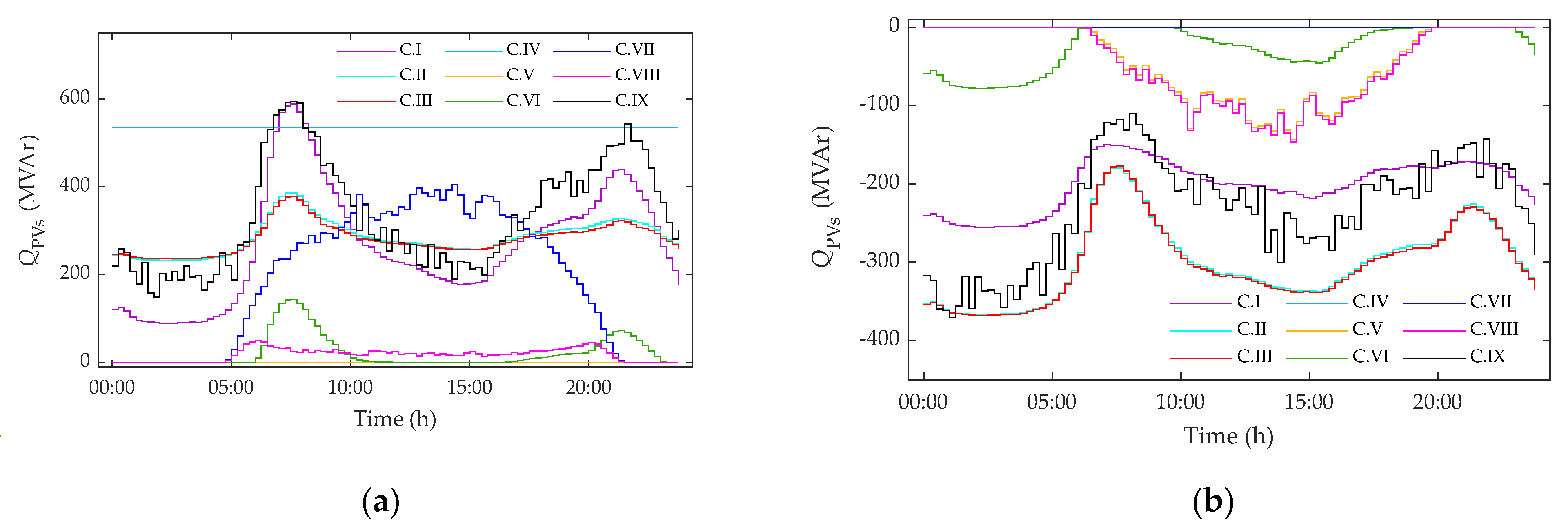
5.3. Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gonzalez-Longatt, F.; Acosta, M.N.; Chamorro, H.R.; Rueda, J.L. Power Converters Dominated Power Systems. In Modelling and Simulation of Power Electronic Converter Controlled Power Systems in Power Factory; Gonzalez-Longatt, F., Rueda, J.L., Eds.; Springer Nature Switzerland AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pettersen, D.; Melfald, E.; Chowdhury, A.; Acosta, M.N.; Gonzalez-Longatt, F.; Topic, D. TSO-DSO Performance Considering Volt-Var Control at Smart-Inverters: Case of Vestfold and Telemark in Norway. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Smart Systems and Technologies (SST), Osijek, Croatia, 14–16 October 2020; pp. 147–152. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Longatt, F.; Acosta, M.N.; Chamorro, H.R.; Topic, D. Short-term Kinetic Energy Forecast using a Structural Time Series Model: Study Case of Nordic Power System. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Smart Systems and Technologies (SST), Osijek, Croatia, 14–16 October 2020; pp. 173–178. [Google Scholar]
- Krechel, F.T.; Sanchez, F.; Gonzalez-Longatt, H.C.; Rueda, J.L. Transmission System Friendly Micro-grids: An option to provide Ancillary Services. In Distributed Energy Resources in Microgrids; Chauhan, R.K., Chauhan, K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ersdal, A.M.; Gonzalez-Longatt, F.; Acosta, M.N.; Rueda, J.L.; Palensky, P. Frequency Support of Fast-Multi-Energy Storage Systems in Low Rotational Inertia Scenarios. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Europe (ISGT-Europe), The Hague, The Netherlands, 26–28 October 2020; pp. 879–883. [Google Scholar]
- Krechel, T.; Sanchez, F.; Gonzalez-Longatt, F.; Chamorro, H.R.; Rueda, J.L. A Transmission System Friendly Micro-grid: Optimising Active Power Losses. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Milan Power Tech, Milan, Italy, 23–27 June 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez, F.; Cayenne, J.; Gonzalez-Longatt, F.; Rueda, J.L. Controller to enable the enhanced frequency response services from a multi-electrical energy storage system. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2019, 13, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Acosta, M.N.; Pettersen, D.; Gonzalez-Longatt, F.; Argos, J.P.; Andrade, M.A. Optimal Frequency Support of Variable-Speed Hydropower Plants at Telemark and Vestfold, Norway: Future Scenarios of Nordic Power System. Energies 2020, 13, 3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkzadeh, R.; Chamorro, H.R.; Rye, R.; Eliassi, M.; Toma, L.; Gonzalez-Longatt, F. Reactive Power Control of Grid Interactive Battery Energy Storage System for WADC. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Europe (ISGT-Europe), Bucharest, Romania, 29 September–2 October 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- IEEE Standard Association IEEE Std. 1547-2018. Standard for Interconnection and Interoperability of Distributed Energy Resources with Associated Electric Power Systems Interfaces; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; ISBN 9781504446396. [Google Scholar]
- Demand Connection Code. Available online: https://www.entsoe.eu/network_codes/dcc/ (accessed on 13 October 2020).
- Acosta, M.N.; Gonzalez-Longatt, F.; Denysiuk, S.; Strelkova, H. Optimal Settings of Fast Active Power Controller: Nordic Case. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 7th International Conference on Energy Smart Systems (ESS), Kyiv, Ukraine, 12–14 May 2020; pp. 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Kaloudas, C.G.; Ochoa, L.F.; Marshall, B.; Majithia, S.; Fletcher, I. Assessing the Future Trends of Reactive Power Demand of Distribution Networks. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2017, 32, 4278–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Acosta, M.; Gonzalez-Longatt, F.; Topić, D.; Andrade, M. Optimal Microgrid–Interactive Reactive Power Management for Day–Ahead Operation. Energies 2021, 14, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X. Power System Support Functions Provided by Smart Inverters—A Review. CPSS Trans. Power Electron. Appl. 2018, 3, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikusato, H.; Ustun, T.S.; Hashimoto, J.; Otani, K. Aggregate Modeling of Distribution System with Multiple Smart Inverters. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Smart Energy Systems and Technologies (SEST), Porto, Portugal, 9–11 September 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Varma, R.K.; Siavashi, E.M. Enhancement of Solar Farm Connectivity with Smart PV Inverter PV-STATCOM. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2019, 10, 1161–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Tang, T.; Yao, J.; Li, M. Active Voltage Control for DFIG-Based Wind Farm Integrated Power System by Coordinating Active and Reactive Powers Under Wind Speed Variations. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2019, 34, 1504–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolenski, R.; Jarnut, M.; Benysek, G.; Kempski, A. Power electronics interfaces for low voltage distribution generation EMC issues. In Proceedings of the 2011 7th International Conference-Workshop Compatibility and Power Electronics (CPE), Tallinn, Estonia, 1–3 June 2011; pp. 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Safari, A.; Salyani, P.; Hajiloo, M. Reactive power pricing in power markets: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Ambient. Energy 2020, 41, 1548–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obligatory Reactive Power Service Default Payment Rates. Available online: https://data.nationalgrideso.com/backend/dataset/7e142b03-8650-4f46-8420-7ce1e84e1e5b/resource/e2e6f74c-ebca-48b3-b2ae-e4652d296dca/download/reactive-default-payment-rate-nov-2020.pdf (accessed on 19 October 2020).
- Elexon. Available online: https://www.bmreports.com/bmrs/?q=balancing/systemsellbuyprices/historic (accessed on 22 September 2020).
- Sanchez, F.; Gonzalez-Longatt, F.; Rodriguez, A.; Rueda, J.L. Dynamic Data-Driven SoC Control of BESS for Provision of Fast Frequency Response Services. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), Atlanta, GA, USA, 4–8 August 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Longatt, F.; Carmona-Delgado, C.; Riquelme, J.; Burgos, M.; Rueda, J.L. Risk-based DC security assessment for future DC-independent system operator. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Energy Economics and Environment (ICEEE), Greater Noida, India, 27–28 March 2015; pp. 1–8.
- Improved Harmony Search (IHS)—Pagmo 2.15.0 Documentation. Available online: https://esa.github.io/pagmo2/docs/cpp/algorithms/ihs.html#_CPPv4N5pagmo3ihsE (accessed on 13 March 2020).


| Case | Control Mechanism | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| C.I | constant V | Vtarget = 1.00 pu. |
| C.II | Q-droop | KQ-droop = 10%, Vtarget,min = 0.98 pu, Vtarget,max = 1.02 pu. |
| C.III | Iq-droop | KIq-droop = 10%, Vtarget,min = 0.98 pu, Vtarget,max = 1.02 pu. |
| C.IV | constant Q | Q = Snsin (θ) @ ϕ = 0.9 |
| C.V | Watt−Var | |
| C.VI | Volt−Var | Vmindb = 0.99 pu, Vmaxdb = 1.01 pu. |
| C.VII | constant ϕ | ϕ = 0.85 |
| C.VIII | ϕ−Watt | ϕover = 0.95, ϕunder = 0.95 |
| C.IX | ORP | ∆V = 0.02 pu., |
| Case | CQ (£/Day) | |
|---|---|---|
| Scenario I | Scenario II | |
| C.I | 14,916.28 | 10,586.55 |
| C.II | 15,958.65 | 10,241.84 |
| C.III | 15,747.87 | 10,066.76 |
| C.IV | 30,001.09 | 18,500.32 |
| C.V | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| C.VI | 1207.83 | 1043.23 |
| C.VII | 10,429.49 | 7148.27 |
| C.VIII | 969.68 | 693.52 |
| C.IX | 18,694.48 | 12,730.06 |
| Case | Eloss (MW/day) | Voltage (pu) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | Maximum | ||
| C.I | 438.50 | 0.997 | 1.024 |
| C.II | 445.04 | 0.980 | 0.997 |
| C.III | 445.28 | 0.980 | 0.997 |
| C.IV | 518.63 | 0.995 | 1.125 |
| C.V | 456.42 | 0.930 | 1.058 |
| C.VI | 450.18 | 0.966 | 1.041 |
| C.VII | 469.52 | 0.959 | 1.098 |
| C.VIII | 456.15 | 0.932 | 1.058 |
| C.IX | 436.43 | 0.987 | 1.020 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Acosta, M.N.; Gonzalez-Longatt, F.; Andrade, M.A.; Torres, J.L.R.; Chamorro, H.R. Assessment of Daily Cost of Reactive Power Procurement by Smart Inverters. Energies 2021, 14, 4834. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14164834
Acosta MN, Gonzalez-Longatt F, Andrade MA, Torres JLR, Chamorro HR. Assessment of Daily Cost of Reactive Power Procurement by Smart Inverters. Energies. 2021; 14(16):4834. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14164834
Chicago/Turabian StyleAcosta, Martha N., Francisco Gonzalez-Longatt, Manuel A. Andrade, José Luis Rueda Torres, and Harold R. Chamorro. 2021. "Assessment of Daily Cost of Reactive Power Procurement by Smart Inverters" Energies 14, no. 16: 4834. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14164834
APA StyleAcosta, M. N., Gonzalez-Longatt, F., Andrade, M. A., Torres, J. L. R., & Chamorro, H. R. (2021). Assessment of Daily Cost of Reactive Power Procurement by Smart Inverters. Energies, 14(16), 4834. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14164834








