Abstract
In this paper, a study on the feasibility of the treatment of raw cheese whey by anaerobic co-digestion using coffee pulp residues as a co-substrate is presented. It considers raw whey generated in artisanal cheese markers, which is generally not treated, thus causing environmental pollution problems. An experimental design was carried out evaluating the effect of pH and the substrate ratio on methane production at 35 °C (i.e., mesophilic conditions). The interaction of the parameters on the co-substrate degradation and the methane production was analyzed using a response surface analysis. Furthermore, two kinetic models were proposed (first order and modified Gompertz models) to determine the dynamic profiles of methane yield. The results show that co-digestion of the raw whey is favored at pH = 6, reaching a maximum yield of 71.54 mLCH4 gVSrem−1 (31.5% VS removed) for raw cheese whey and coffee pulp ratio of 1 gVSwhey gVSCoffe−1. The proposed kinetic models successfully fit the experimental methane production data, the Gompertz model being the one that showed the best fit. Then, the results show that anaerobic co-digestion can be used to reduce the environmental impact of raw whey. Likewise, the methane obtained can be integrated into the cheese production process, which could contribute to reducing the cost per energy consumption.
1. Introduction
The dairy industry is one of the faster-growing food industries in recent decades, covering a wide range of products (e.g., milk, cheese, yogurt), which generates USD 673.8 billion [1]. Whey is the largest byproduct of this industry, which is generated in the production of cheese. For each kilogram of cheese produced approximately 9–10 L of whey is generated [2]. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), approximately 22.7 million tons of cheese are produced annually, which generates an equivalent to 227 million tons of cheese whey [1]. This industrial by-product contains high organic matter (up to 70,000 mg L−1 of COD), which, if not properly treated, can cause several environmental problems [2]. To value whey, various uses have been proposed, for example as a protein supplement in animal feed (i.e., pre-processed or directly to livestock), sweeteners production, and as feedstock to produce polyethylene-like polymers, as well as for obtaining metabolites of high added value such as galactose, glycerol, xanthan gum, and carotenoids, among others [2,3,4]. However, small-scale artisanal cheesemakers do not always have the technology to implement any of those alternatives for whey valorization. Hence, in the small and medium dairy industries whey is rather considered a waste stream. Although it can be used as a nutritional supplement for livestock, this is not enough to take advantage of all the whey, so it is discharged into bodies of water or crop fields. Due to its high organic load, the continuous discharge of raw whey alters the physicochemical characteristics in the environment, which affects ecosystems, reduces the yield of crops from cultivated fields, and contaminates water. It thus becomes a risk to the health of animals and humans. The anaerobic digestion (AD) of cheese whey in the small and medium dairy industries becomes an adequate strategy for whey treatment [2,3,4,5]. AD is a process in which organic matter is transformed into value-added by-products, such as volatile fatty acids (VFA) and biogas, through four consecutive stages: hydrolysis, acidogenesis, acetogenesis, and methanogenesis [6]. Then, to implement the AD process, it is necessary to establish the operating conditions that maximize the production of value-added products and at the same time ensure the stability of the reactor. In that sense, different studies have demonstrated that the key process variables are pH, temperature, substrate composition, co-substrate proportion, and reactor configuration [5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12]. The reported results show that anaerobic treatment of whey is feasible, however, it is necessary to keep the operation variables regulated in the regions of process stability. In addition, to maintain the yield of the methane produced, a pretreatment of the raw cheese whey can be included, increasing the number of unit operations, which limits its application in the cheese making of small and medium industries. On the other hand, to improve the process stability, a co-substrate can be added, which can balance the nutrients required by the microorganism consortium and reduce inhibition by toxic compounds present in the feedstock [13]. In addition, the proper selection of substrates allows for increasing the methane yield produced. For the treatment of whey, it has been reported that co-digestion can favor methane production. Gelegenis et al. [14] determined that the addition of diluted poultry manure as co-substrate improves methane production as well as the COD removal in mesophilic conditions. They also found that the proportion of whey is essential to maintain the stability of the process, so it is necessary to determine the proportion of the co-substrate. Kavacik et al. [15] reported a study on the co-digestion of cheese whey and dairy manure, evaluating the substrate ratio and hydraulic retention time (HRT) at two operating temperatures (25 and 34 °C). They found that the maximum daily biogas produced was 1.51 m−3 d−1 at 34 °C with HRT = 5 days, obtaining a methane production rate of around 60% in all experiments. Maximum removal efficiencies were obtained at HRT of 10 days, reaching a total solids, volatile solids, and chemical oxygen demand (COD) of 49.5%, 49.4% and 54%, respectively. Recently, Hallaji et al. [16] conducted a study on the anaerobic co-digestion of waste-activated sludge using a mixture of fruit waste and cheese whey as co-substrates. Their results show that the methane production and the quality of the digested sludge were improved in comparison to the anaerobic digestion, obtaining an increase of 31% in the methane produced, as well as an increase in the removal of COD and VS (volatile solids) of 9 and 7%, respectively. In general, co-digestion can offer several benefits over mono-digestion, as it can improve the balance between elements, reduce potential toxicity, and increase organic load [17]. Substrates such as manure, sewage sludge, municipal organic waste, agricultural and industrial residues have been widely investigated to improve biogas production via anaerobic digestion [18]. Coffee pulp residues have not been used as a co-substrate in the anaerobic treatment of cheese whey, as far as the authors of the present manuscript are concerned. Many coffee-producing industries consider coffee pulp as waste, discarding it without proper treatment, which can become a serious environmental pollution problem. Coffee pulp is a by-product obtained during the processing of coffee cherries with a high content of carbohydrates, proteins, and minerals [19]. It is rich in organic material, which makes it an ideal substrate for microbial processes to produce different products [20]. Given that coffee pulp residue is nutrient-rich and biodegradable, its utilization as a co-substrate for energy production could provide an environmentally and economically interesting potential to produce biogas. Nevertheless, even if the coffee pulp could be a good AD co-substrate, it is important to consider that the biodegradability and hence the biogas potential of lignocellulosic rich substrate depends on the content of biodegradable carbohydrates (including cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin fractions) [21].
This paper presents a study on the viability of the anaerobic co-digestion of raw whey and coffee pulp residues to reduce the high organic load of raw whey generated in artisanal cheese factories. To evaluate the potential of the coffee pulp as a co-substrate, an experimental design was carried out at different ratios of raw whey and coffee pulp. The results were analyzed through a response surface analysis and two kinetic models were evaluated for the dynamic prediction of methane produced.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Substrate and Anaerobic Inoculum
For the experimental tests, fresh raw cheese whey and coffee pulp were used as the substrates. The whey cheese is collected from an artisanal community dairy that produces mainly white cheese. The community dairy is located at Coacoatzintla, Veracruz, Mexico. To avoid the chemical composition modification, the cheese whey did not receive pretreatment and was stored at 4 °C until it was used as a co-substrate. Previously, the cheese whey was characterized using standardized analytical techniques to determine the concentration of total carbohydrates (TCH), total solids (TS), volatile fatty acids (VFA), fat, protein, lactose, as well as the chemical oxygen demand (COD). The coffee pulp was collected from a coffee community located in Coatepec, Veracruz. This agro-industrial waste was dried, milled, and screened in a 1 mm mesh. Afterwards, it was stored at 4 °C. The TS and VS were determined before it was used in the experimental tests.
The sludge used as the inoculum was adapted to raw cheese whey with an organic load rate (OLR) = 3.6 gCOD L−1 d−1, in a laboratory-scale anaerobic digester, maintaining conditions of HRT = 30 d, pH = 8.0 and a temperature of 35 °C. Prior to the experimental tests, the initial total volatile solids (TVSi), TCH, TS, VFA, alkalinity, and COD were determined.
2.2. Analytical Methods
A milk-analyzer (Lactoscan) was used to determine the lactose, fat, and protein content. The VFA concentration was determined using esterification (5560C. Distillation Method), the TS, and VS were determined using standard techniques [22]. The COD was determined according to the US-EPA reactor digestion method [23]. The total carbohydrates number was measured using the phenol-sulfuric acid method [24]. Alkalinity was determined by the titration method [20]. Methane production was determined daily by using the volumetric methodology [25], and the biogas was sent to an acid-fixation unit that contains a basic solution of sodium hydroxide (1 N and pH > 12) with a pH indicator to indicate carbon dioxide solution saturation from the biogas [26].
2.3. Experimental Tests
The experiments were performed in 0.25 L batch digesters. The experimental range of pH was from 6 to 8, and substrate ratio of 1 to 4 gVSwhey gVScosubstrate−1, i.e., cheese whey–coffee pulp ratio (gVSwhey gVScoffee−1) at mesophilic conditions (35 °C). In all the experiments, the total volatile solid concentration of substrate (whey and coffee pulp together) was 50 gVS L−1, and the inoculum concentration into the reactor was adjusted at 2 gVS L−1. In order to provide buffering capacity, an Na₃PO₄ solution (1 N) was added to each experimental unit, and the pH was adjusted by using a NaOH solution (3 N). The VFA, TCH, alkalinity, and COD were determined at the beginning and the end of each experimental test. The experiments concluded when biogas stopped being produced. The experimental specific methanogenesis activity (SMA) was determined as [27]:
where M is the product of sludge volume added to the reactor by the VS concentration of the sludge (gTVSi); Rmax is the maximum methane production rate (LCH4 gTVSi d−1).
2.4. Kinetic Models
The kinetic model of methane production allows for analyzing the dynamics of the methane production rate, which helps to establish the operating conditions that favor the degradation of the substrates and improve bioconversion. In this sense, two classic kinetic models were proposed, a first-order kinetic model [28] and a modified Gompertz Equation [29], which are described as follows:
Equations (2) and (3) correspond to the first-order and modified Gompertz models, respectively. VCH4 is the methane production (mLCH4 gTVSi−1); Pmax is the maximum volume accumulated (mLCH4 gTVSi−1); Rmax is the maximum methane production rate (mLCH4 d−1); µ is the rate constant (d−1); e is a constant (e = 2.7183); λ is the lag phase time constant (d); and t is time (d). The coefficient of determination (R2) was obtained to quantify the fit of each proposed mathematical model to the experimental data.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
To be able to perform an inferential statistical analysis, a normality and independence test of the data was performed (Anderson–Darling test and residual plot). A full factorial (22) central composite design (two factors and two levels, 8 cube points, 6 center points in a cube and 8 axial points, and 6 center points axials) was performed. The design was used to evaluate the effect of pH (6–8), substrates ratio (0.37–4.62 gVSwhey gVScoffee−1), and their interaction, considering a 95% confidence (α = 0.05). The effects of the factors (singly or combined) on the process responses were analyzed using the analysis of variance (ANOVA) and regression analysis. The polynomial regression model equation shows the interactions between the factors on the responses as follows:
where Y is the predicted response (methane yield and VS removed) and c0 is the intercept; c1 and c2 are the linear coefficients of the factors; c11 is the interaction coefficient between the factors; c22 and c21 are the quadratic coefficients of the factors; and x1 and x2 represent the pH and substrates ratio, respectively. The results and the second-order polynomial coefficients were analyzed using the analysis of variance (ANOVA) by Statgraphics Centurion V16.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Characterization
The characteristics of the raw cheese whey and inoculum used in the experimental tests are shown in Table 1. The cheese whey showed a pH = 4.8, which indicates that it is acid whey, characteristic in the manufacture of fresh cheeses [30]. Likewise, the whey showed high protein content and, in consequence, also a high COD compared to that reported by Gelegenis et al. [14] and Hublin et al. [31].

Table 1.
Physicochemical parameters of raw cheese whey and inoculum used in experimental tests.
The results described in Table 1 suggest that the white cheese production process is not adequately controlled, which means that the whey contains a high protein content. Therefore, if the whey is discarded without any previous treatment, its contaminating potential increases. On the other hand, the inoculum shows a specific methanogenic activity (SMA) of 0.108 gCOD gTVSi−1 d−1, indicating an acceptable content in the concentration of the methanogenic microbiota, which also suggests an adequate syntrophic relationship among different microorganisms’ consortia involved in AD process. For the coffee pulp, the values of VS and TS were 0.81 g g−1 and 0.72 g g−1, respectively, which corresponds to that reported by Corro et al. [32]. In addition, the coffee pulp had a 77.6% humidity and a COD soluble of 1339.22 mg gDW−1. For the same species of coffee used in this work, the bromatological composition has been reported as protein (10.02 ± 0.14%), ether extract (2.23 ± 0.09), organic matter (89.55 ± 0.21), crude fiber (19.24 ± 0.44), NFE (58.06 ± 0.28), NFD (44.24 ± 1.01), and sugar concentration (10 ± 0.22%) [33,34].
3.2. Methane Yield
As an indicator of the AD process’s stability, the FOS/TAC ratio was determined, where TAC indicates the buffer capacity and FOS indicates the VFA content. If the FOS/TAC ratio is greater than 0.4, the system tends to acidify, thus it is recommended to operate at 0.3 > FOS/TAC > 0.4 [35]. Table 2 shows the FOS/TAC values, where it is observed that for the assay carried out at pH = 6, FOS/TAC > 0.4, while at pH = 7 and 8, most of the trials showed an adequate FOS/TAC < 0.4. Likewise, the higher methane yields, 71.54 mLCH4 gSVrem−1 and 69.22 mLCH4 gSVrem−1, were obtained at pH = 6 (with 1 gVSwhey gVSCoffe−1 substate ratio) and pH = 7 (with 4.62 gVSwhey gVSCoffe−1 substrate ratio), respectively, also showing a high VS removal (30.6 ± 0.27 and 32.8 ± 6.5%). This result means that pH 6 and a low Sw promote the methanation as did pH 7 and a high Sw. This should be related to the increase of the proportion of ionized and non-ionized forms of inhibitors of methanogenesis (e.g., VFA, NH3, H2S) at high Sw/Sc [36]. The highest obtained methane yield (21 LCH4/KgSVfeed experiment 1) was greater than the obtained with whey (12 ± 6 LCH4/KgSVfeed, at pH 6 and 40 °C) according to Flores-Mendoza et al. [37]. Therefore, the results show that it is possible to use the coffee pulp as a co-substrate to produce methane.

Table 2.
Results of the experimental tests of the anaerobic co-digestion of raw cheese whey and coffee pulp residues at 35 °C.
Regarding the FOS/TAC ratio, experiments 1 and 2 (pH = 6) presented values slightly high. The adequate FOS/TAC ratio should maximize biogas production. A lower FOS/TAC ratio could be related to insufficient available substrate for the microorganisms in the system, whereas a higher FOS/TAC ratio denotes the system has an excess of substrate [38]. This could imply that at pH 7, the increment of Sc increases the non-degradable fraction of pulp and reduces the FOS/TAC, which means a decrease of the available substrate; on the other hand, at pH 6 the result suggests that the Sw/Sc did not affect the FOS/TAC (Table 2). This effect may be related to the increment of hydrolysis-acidogenesis at low pH [36]; however, the PCH4, which is similar to that obtained at pH 7, suggests that the acid pH did not favor the activity of methanogenic microorganisms in the co-digestion of whey and coffee pulp. Regarding the TCH, the highest consumption was observed in experiments 2, 10 and 12, which contain a greater amount of whey because the lactose is rapidly degraded, so it becomes the first available substrate for the anaerobic bacteria. For a greater content of coffee pulp, the degradation of carbohydrates is slower because it comes in the form of lignocellulose.
3.3. Kinetic Model
Table 3 shows the experimentally obtained methane yield values through the proposed kinetic models and their corresponding coefficients of determination (R2). Likewise, the maximum CH4 production rate, the growth rate of the microorganisms, the maximum CH4 production, and the lag phase (λ) are reported for each evaluated operating condition.

Table 3.
Kinetic parameters obtained from the experimental tests of the anaerobic co-digestion of raw cheese whey and coffee pulp residues at 35 °C.
The prediction of methane production using the evaluated kinetic models is shown in Figure 1, observing that there is a good correspondence between the experimental data and those obtained with the mathematical models (in all tests the coefficient of determination was greater than 0.91). For pH = 6, the highest methane yield is obtained at 1 gVSwhey gVSCoffe−1 (71.54 mLCH4 gVSrem−1), which suggests that coffee pulp could be used as a potential co-substrate to improve methane production despite the low biodegradability of coffee pulp. pH is an important factor in the co-digestion of coffee pulp since hydrolytic bacteria adapt better in acidic environments (pH = 5.5–6), which favors the breakdown of lignocellulose and increases the available carbohydrates, and consequently, methane production is favored [36]. Under these conditions (pH 6), the increase in the proportion of whey decreases methane yield, which suggests that there may be an inhibition process during the anaerobic co-digestion in accordance whit the obtained µ. In addition, there were differences in the lag phase (λ), meaning that at slightly acid pH, the beginning of the biological reaction does not depend on the Sw/Sc ratio. On the other hand, at pH 7, the increase of Sw/Sc had a negative effect on the lag phase (Table 3).
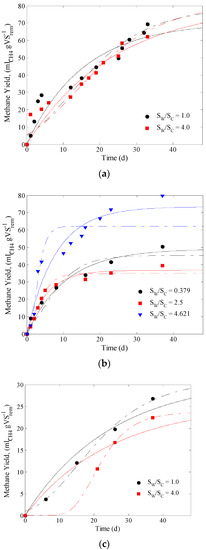
Figure 1.
Methane yield profile obtained in the anaerobic co-digestion of raw cheese whey and coffee pulp residues at different substrates ratio, (a) pH = 6.0, (b) pH = 7.0, and (c) pH = 8.0.
When pH = 7, and as the proportion of whey is reduced, the methane yield and degradation efficiency also decrease, but the microbial methanogenic activity increases, suggesting that a high content of available carbohydrates leads to an increase in the methane yield. Therefore, if a previous hydrolysis of the coffee pulp is carried out for the degradation of the lignocellulose, the methane yield could be increased. Finally, for pH = 8 the best methane yield was 4 gVSwhey gVSCoffe−1, however, at these conditions a low degradation efficiency was obtained, which could be related to the decrease of hydrolytic-acidogenesis activity at alkaline pH [36]. In addition, Corro et al. [32] report that despite the high initial concentration of nutrients in coffee pulp, at pH > 7, the conditions for bacterial growth are not adequate, which limits the biogas production.
3.4. Response Surface Analysis
The response surface analysis shows the effect of the factors on methane yield and substrate degradation in the anaerobic co-digestion of raw cheese whey and coffee pulp residues. The pH variable significantly affected the methane yield (p < 0.05), while the relationship of the substrates, as well as the interaction between them, did not show significance (p > 0.05) in the experimental domain. For VS removal, both the variables as well as their interaction have a p > 0.05, which indicates that within the domain of the experiment their effect was not significant. However, several reports show the importance of substrate composition in the anaerobic digestion [6,7,8,9,10,11,12,36], therefore, the relationship of the substrate and the interaction of the variables were considered during the analysis of the results.
The model response of the influence of the pH and substrate ratio on the methane yields was significant (p = 0.012), obtaining a high value of the coefficient of determination R2 = 0.98, that is, a good agreement between the predicted and the experimental values are obtained. The fitted polynomial for methane yield response is as follows:
The region where the maximum methane yield is reached can be seen in Figure 2a. When the pH becomes alkaline and the proportion of whey is lower, the degradation efficiency (Table 2), methanation activity (Table 3), and yield tend to decrease. For example, at pH = 8 and 1 gVSwhey gVSCoffe−1, 16.24 mLCH4 gVSrem−1 was obtained. That is, the methane yield is favored at a higher proportion of whey and a slightly acidic pH, but it was not the activity of methanogenic archaea (Table 3). These results correspond to those reported by Gelegenis et al. [14], where they found that increasing the amount of whey increased the acidic bacteria in the digester; that is, the greater biogas production was mainly caused by cheese whey biodegradability.
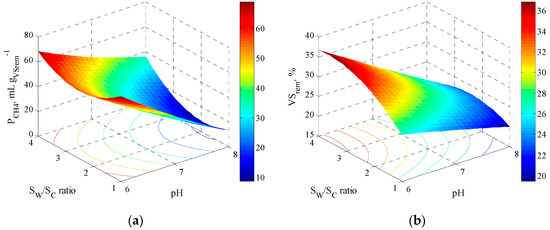
Figure 2.
Response surface plot during anaerobic co-digestion of raw cheese whey and coffee pulp with respect to pH and substrate ratio, (a) methane production, and (b) volatile solids removed.
The model response of the VS removal was not significant (p = 0.34) and a regression coefficient of 68%. The fitted polynomial for the VS removal response is as follows:
Figure 2b shows the response surface of the VS removal, where it is observed that at pH = 6 and 4 gVSwhey gVSCoffe−1, the maximum removal value reached was 31.5%. It can be noted that as the medium becomes more alkaline and the proportion of coffee pulp increases, the removal percentage decreases, which corresponds to that found in methane yield. This behavior could be explained by the fact that alkaline pH does not promote the hydrolysis-acidogenesis of lignocellulosic biomass, which is higher as coffee pulp increases. According to Corro et al. [31], in the co-digestion of cow manure with coffee pulp, the VS conversion rates are low at the start of the process because microorganisms take time to adapt to the compounds present in coffee pulp (e.g., caffeine, phenols, and tannins, among others).
Despite the co-digestion of raw whey and coffee pulp, it does not reach high yields and it is possible to make a significant reduction in the organic load and methane is obtained. The reduction of the organic load contributes to the mitigation of the environmental impact, while the methane can be integrated into the production process which can reduce the energy costs. In other words, through co-digestion, agro-industrial waste can be recovered obtaining economic and environmental benefits.
4. Conclusions
The raw cheese whey generated in the artisanal production of white cheese featured content of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats, suggesting that the artisanal cheese production from a Coacoatzintla community dairy was not properly controlled. The anaerobic co-digestion of crude whey with coffee pulp in one-stage anaerobic digestion showed low yields, however, it is possible to reduce the high organic load and produce methane. The yield of co-digestion depends on the pH and the substrate ratio. The higher production and methane yield are achieved by an equal proportion of whey and coffee pulp, for 1 gVSwhey gVSco-substrate−1, 71.54 mLCH4 VSrem−1 (22.91 mLCH4 VSi−1) are achieved. The results in this work show that the control of the pH is decisive in the stability of the co-digestion process. Methane production is favored at pH = 6, but the methanogenic activity (µ) and degradation efficiency are promoted at a neutral pH. To increase methanization during the co-digestion of cheese whey and coffee pulp, it is necessary to assure adequate conditions for all the microbial groups in the consortia. Therefore, it is advisable to study a two-stage or two-step process. Despite obtaining a low production of methane, this can be integrated into the cheese production process and contribute to reducing energy consumption costs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.H.-G. and E.H.-M.; experimental methodology, S.G.-P., L.A.-D. and J.M.P.-M.; writing—review and editing, H.H.-G., E.H.-M. and J.-R.B.-O.; visualization, J.-R.B.-O.; funding acquisition, E.H.-M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Council for Science and Technology, grant number 247690, and The APC was funded by the University of Southern Denmark through the European Regional Development Fund as part of the Interreg North Sea Region with the project number 38-2-4-17 BIOCAS, circular BIOmass CAScade to 100%, and by the European Regional Development Fund project number BYER-17-0011 Energioptimering og affaldshåndtering.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by “Dynamic characterization of whey anaerobic treatment for biogas production using fractal analysis of time-series” at CONACyT grant 247690.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- FAO. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Statistics Division. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QP/visualize (accessed on 10 January 2021).
- Prazeres, A.R.; Carvalho, F.; Rivas, J. Cheese whey management: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 110, 48–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siso, M.G. The biotechnological utilization of cheese whey: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 1996, 57, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalermthai, B.; Chan, W.Y.; Bastidas-Oyanedel, J.R.; Taher, H.; Olsen, B.D.; Schmidt, J.S. Preparation and characterization of whey protein-based polymers produced from residual dairy streams. Polymers 2019, 11, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigolotti, V.; Moreno, A.; McPhail, S.J. Fuel cells. In Green Energy and Technology; Springer: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, C.; Feng, Y.; Wang, X.; Ren, G. Review on research achievements of biogas from anaerobic digestion. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 45, 540–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeshwari, K.V.; Balakrishnan, M.; Kansal, A.; Lata, K.; Kishore, V.V.N. State-of-the-art of anaerobic digestion technology for industrial wastewater treatment. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2000, 4, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddoud, A.; Hassaïri, I.; Sayadi, S. Anaerobic membrane reactor with phase separation for the treatment of cheese whey. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 2102–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulou, G.; Stamatelatou, K.; Venetsaneas, N.; Kornaros, M.; Lyberatos, G. Biohydrogen and methane production from cheese whey in a two-stage anaerobic process. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 5227–5233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venetsaneas, N.; Antonopoulou, G.; Stamatelatou, K.; Kornaros, M.; Lyberatos, G. Using cheese whey for hydrogen and methane generation in a two-stage continuous process with alternative pH controlling approaches. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 3713–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, C.; Cuetos, M.J.; Martínez, E.J.; Gómez, X. Thermophilic anaerobic digestion of cheese whey: Coupling H2 and CH4 production. Biomass Bioenergy 2015, 81, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalante, H.; Castro, L.; Amaya, M.P.; Jaimes, L.; Jaimes-Estévez, J. Anaerobic digestion of cheese whey: Energetic and nutritional potential for the dairy sector in developing countries. Waste Manag. 2018, 71, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabii, A.; Aldin, S.; Dahman, Y.; Elbeshbishy, E. A review on anaerobic co-digestion with a focus on the microbial populations and the effect of multi-stage digester configuration. Energies 2019, 12, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelegenis, J.; Georgakakis, D.; Angelidaki, I.; Mavris, V. Optimization of biogas production by co-digesting whey with diluted poultry manure. Renew. Energy 2007, 32, 2147–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavacik, B.; Topaloglu, B. Biogas production from co-digestion of a mixture of cheese whey and dairy manure. Biomass Bioenergy 2010, 34, 1321–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallaji, S.M.; Kuroshkarim, M.; Moussavi, S.P. Enhancing methane production using anaerobic co-digestion of waste activated sludge with combined fruit waste and cheese whey. BMC Biotechnol. 2019, 19, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.C.; Gonçalves, P.R.; Nobre, A.; Alves, M.M. Biomethanation potential of macroalgae Ulva spp. and Gracilaria spp. and in co-digestion with waste activated sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 114, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouas, M.; Torrijos, M.; Sousbie, P.; Harmand, J.; Sayadi, S. Modeling the anaerobic co-digestion of solid waste: From batch to semi-continuous simulation. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 274, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadesse, M.; Adamu, M. Design and Development of Biogas Production System from Waste Coffee Pulp and its Waste Water Around Tepi. Int. J. Recent Dev. Eng. Technol. 2017, 6, 18–30. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, A.; Soccol, C.R.; Nigam, P.; Brand, D.; Mohan, R.; Roussos, S. Biotechnological potential of coffee pulp and coffee husk for bioprocesses. Biochem. Eng. J. 2000, 6, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, R.; Takeuchi, H.; Hasegawa, T. Methane production from lignocellulosic agricultural crop wastes: A review in context to second generation of biofuel production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 1462–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association; Water Pollution Control Federation. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- HACH. Chemical Oxygen Demand, Reactor Digestion Method; Method 8000; HACH: Loveland, CO, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, S.R.; Morgan, J.M.; Sawyer, C.L. Measuring anaerobic sludge digestion and growth by a simple alkalimetric titration. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1983, 448–453. [Google Scholar]
- Drosg, B.; Braun, R.; Bochmann, G.; Al Saedi, T. Analysis and characterisation of biogas feedstocks. In The Biogas Handbook; Wellinger, A., Murphy, J., David, B., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 52–84. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, A.; Dubey, S.K. Specific methanogenic activity test for anaerobic treatment of phenolic wastewater. Desalination Water Treat. 2014, 52, 7015–7025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielfa, A.; Cano, R. Theoretical methane production generated by the co-digestion of organic fraction municipal solid waste and biological sludge. Biotechnol. Rep. 2015, 5, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, N.; Zhang, T.; Yin, D.; Yang, G.; Wang, X.; Ren, G.; Feng, Y. Effect of initial pH on anaerobic co-digestion of kitchen waste and cow manure. Waste Manag. 2015, 38, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, R.S.; Shraddha, R.C.; Kumar, A.; Nalawade, T. Whey based beverage: Its functionality, formulations, health benefits and applications. J. Food Process. Technol. 2015, 6, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Hublin, A.; Zokić, T.I.; Zelić, B. Optimization of biogas production from co-digestion of whey and cow manure. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2012, 17, 1284–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corro, G.; Paniagua, L.; Pal, U.; Bañuelos, F.; Rosas, M. Generation of biogas from coffee-pulp and cow-dung co-digestion: Infrared studies of postcombustion emissions. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 74, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoplac, I.; Yalta, J.; Vásquez, H.V.; Maicelo, J.L. Efecto de la Alimentación con Pulpa de Café (Coffea arabica) en los Índices Productivos de Cuyes (Cavia porcellus L) Raza Perú. Rev. Investig. Vet. Del Perú 2017, 28, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, L.; Rodríguez, Z.; Saca, V.; Apolo, V. Bromatological characterization of coffee (Coffea arabica L.) pulp for animal feeding purposes. Cuba, J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 52, 165–172. [Google Scholar]
- Lossie, U.; Pütz, P. Control orientado de plantas de biogás con la ayuda de FOS/TAC. HACH CANGE 2011. Available online: https://de.hach.com/asset-get.download.jsa?id=25593611197 (accessed on 10 January 2021).
- Kwietniewska, E.; Tys, J. Process characteristics, inhibition factors and methane yields of anaerobic digestion process, with particular focus on microalgal biomass fermentation. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 34, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Mendoza, A.P.; Hernández-García, H.; Cocotle-Ronzón, Y.; Hernandez-Martinez, E. Methanogenesis of raw cheese whey: PH and substrate–inoculum ratio evaluation at mesophyll temperature range. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2020, 95, 1946–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, M.; Safi, M.; Lens, P.; Visvanathan, C. Investigating the performance of internet of things based anaerobic digestion of food waste. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 127, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).