Hybrid Control of Grid-Feeding and Fuzzy Logic Fault Detection in Solving Voltage Dynamic Problem within the Malaysian Distribution Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Power Quality (PQ) Compensation Devices | Main Function | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Dynamic Voltage Restorer (DVR) |
| |
| Static VAr Compensator (SVC) |
|
|
| Static Synchronous Compensator (STATCOM) |
| |
| Fault Detection Schemes | Drawbacks | |
| Data Driven | ||
| Process Model |
| |
| Conventional Knowledge-Based (fuzzy logic) |
| |
| Potential Solution to Drawbacks of PQ Devices and Fault Detection Schemes | ||
| Technique | Aim | Advantages |
| Hybrid Control of Grid-Feeding Voltage Oriented Control (VOC) and Direct Current (DC) Fuzzy Logic (FL) Fault Detection Scheme | To solve under/overvoltage problem |
|
| To solve sag/swell/voltage fluctuation (fault) | ||
2. Methodology
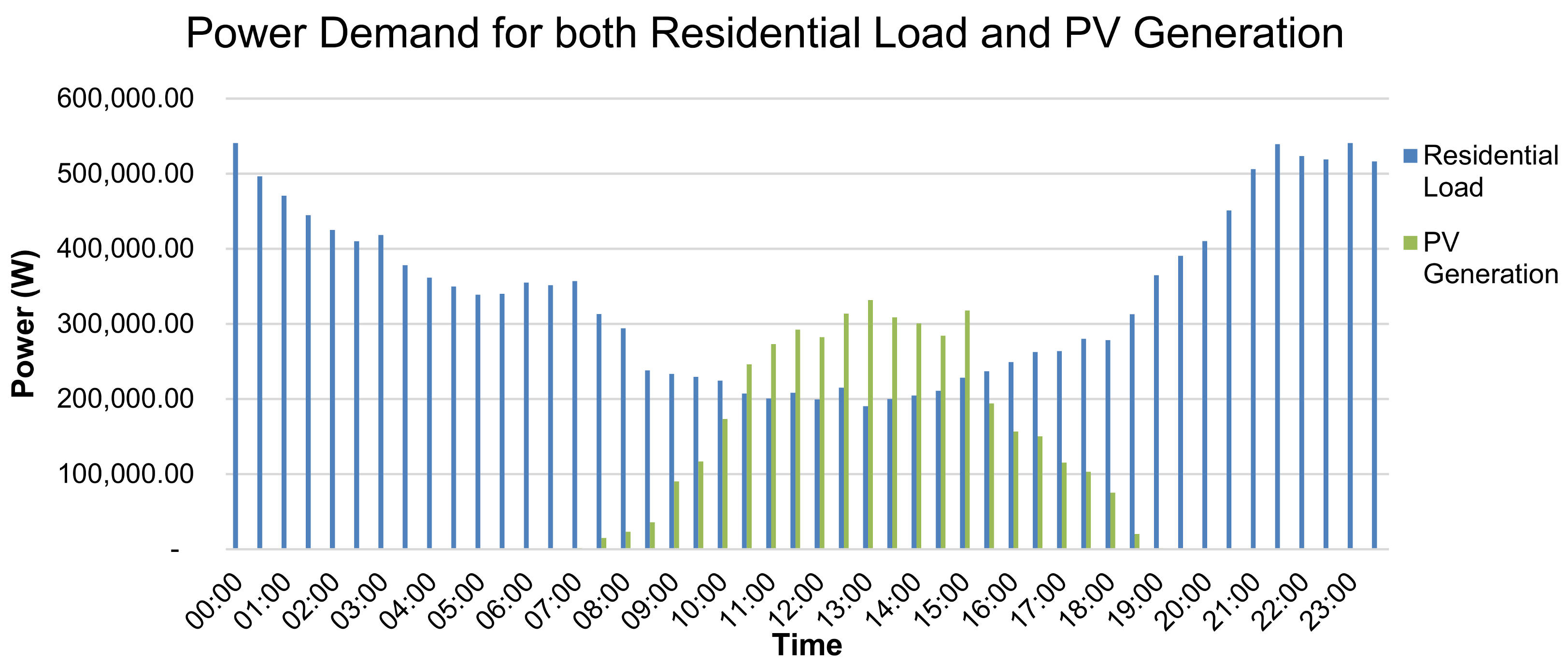
2.1. Development of the Malaysian Representative Network (RN#1)
- Long distance (10 km) of supply to load—Load Type A
- Commercial load—Load Type B
- Small residential load—Load Type C
- Normal residential load—Load Type D
- PV integrated rooftop residential load—Load Type E
| No. | Parameters | Average Value |
|---|---|---|
| RN#1 | ||
| 1 | No of 11 kV feeders per 33/11 kV Tx | 5 |
| 2 | No of 11 kV feeders (unit) for each main intake | - |
| 3 | 11 kV feeder length per feeder (km/feeder) | 2.6 |
| 4 | 11 kV Tx nos per 11 kV feeder (nos) | 5 |
| 5 | LV feeder nos per 11/0.4 KV Tx (nos) | 8 |
| 6 | Average distance between 11/0.4 kV Tx (per feeder in km) | 0.6 |
| 7 | 33/11 kV Tx MD (MW/Tx) | 9.6 |
| 8 | 11 kV Feeder MD per feeder (MW/feeder) | 2.5 |
| 9 | 11/4 kV Tx capacity (MVA) | 1 |
| 10 | 11/0.4 kV Tx MD per 11 kV feeder (kW) | 560 |
| 11 | 11/0.4 kV Tx maximum loading (%) | 65 |
| 12 | 11 kV Feeder MD per km (MW/km) | 1.3 |
| 13 | % ratio of number of LV Overhead (OH) lines over total feeder nos | 52 |
| 14 | % ratio of number of LV Underground (UG) lines over total feeder nos | 48 |
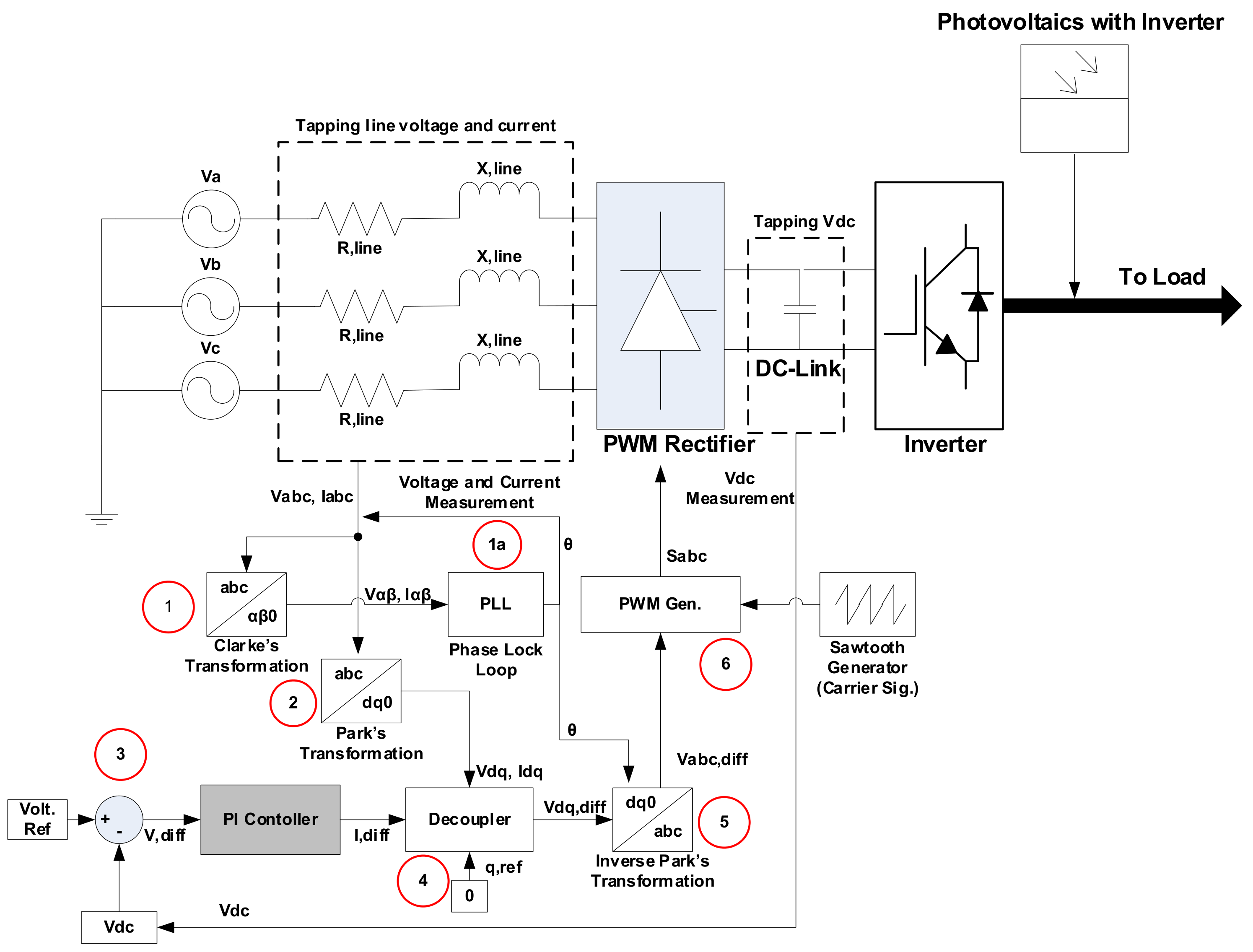
2.2. Grid-Feeding Mode on Weak Bus
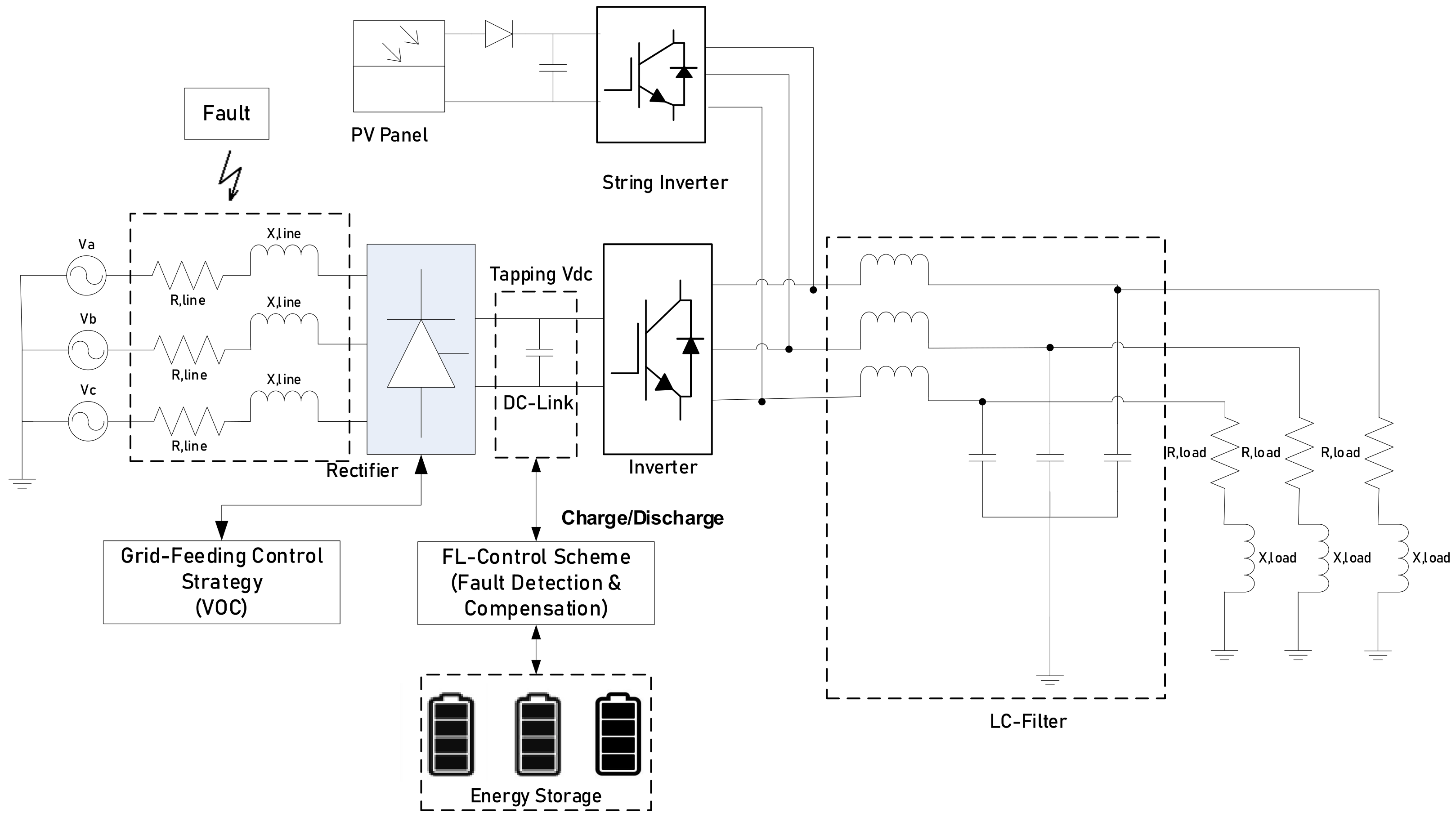
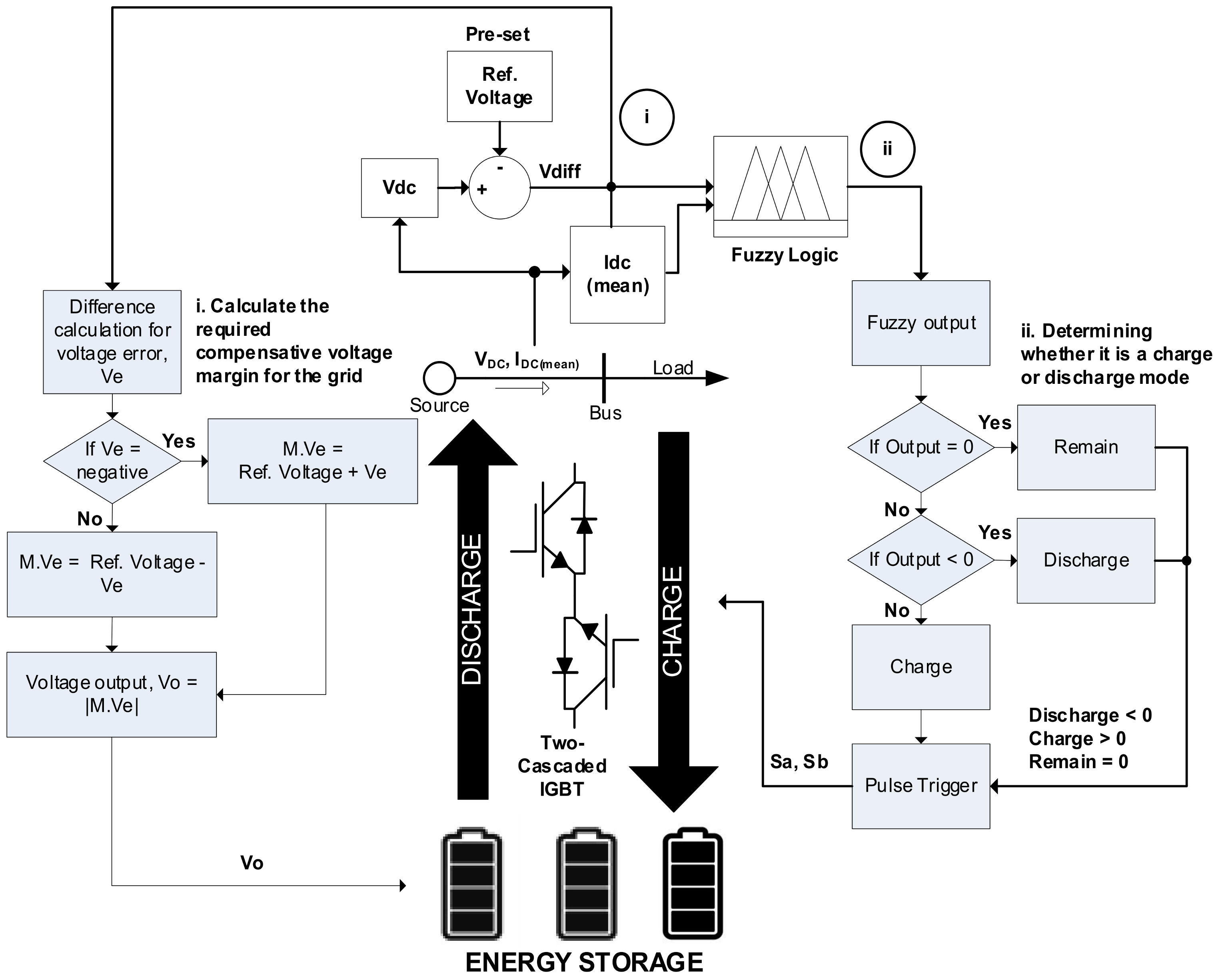
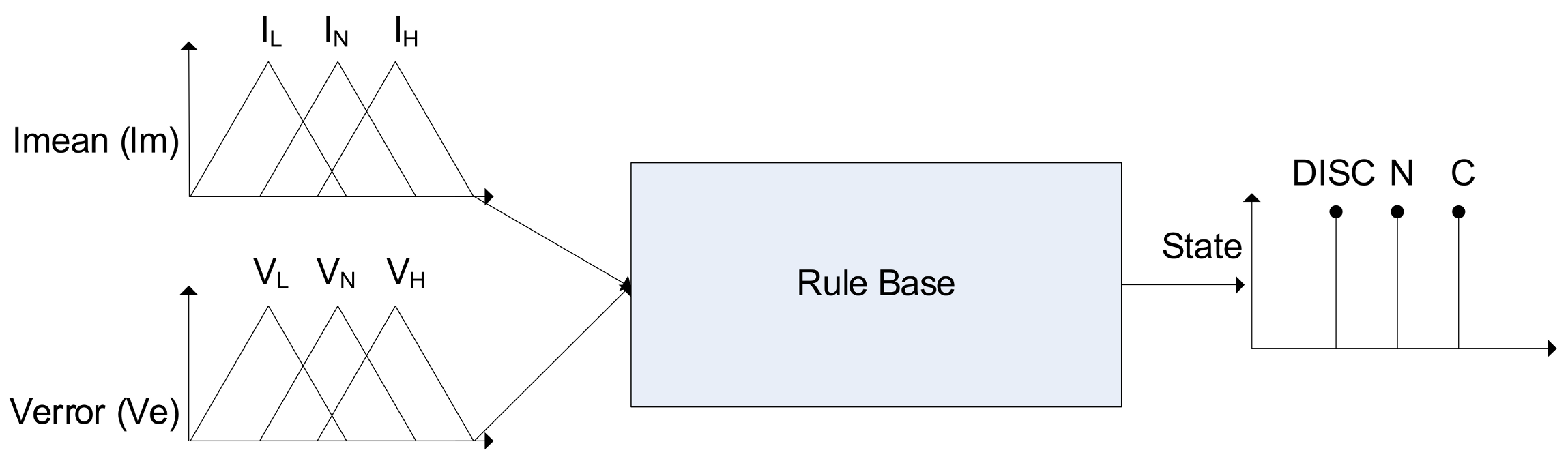
2.3. Grid-Feeding Mode and Energy Storage with Fuzzy Logic Direct Current (DC) Fault Detection Scheme on the Weak Bus
3. Results
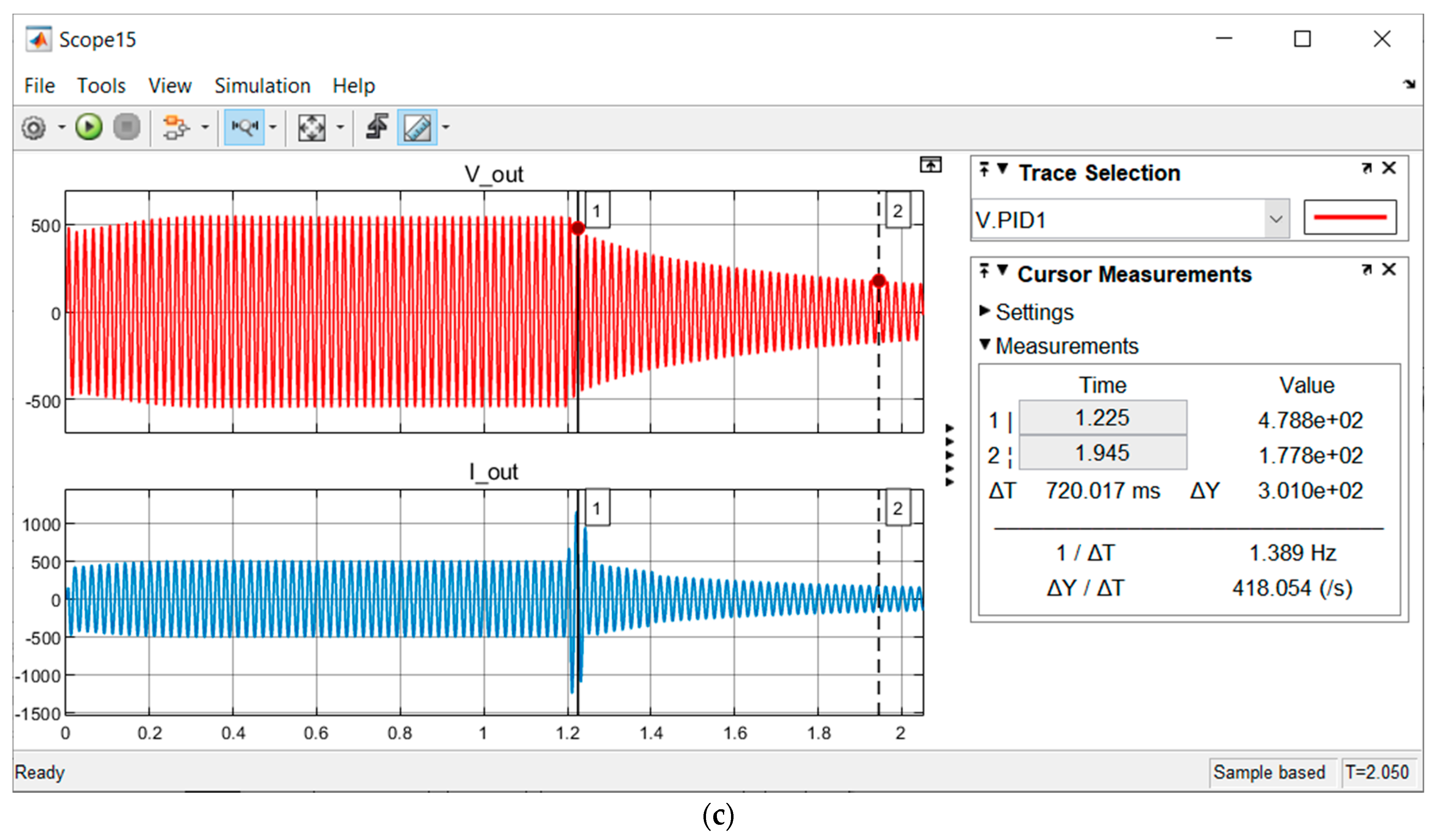
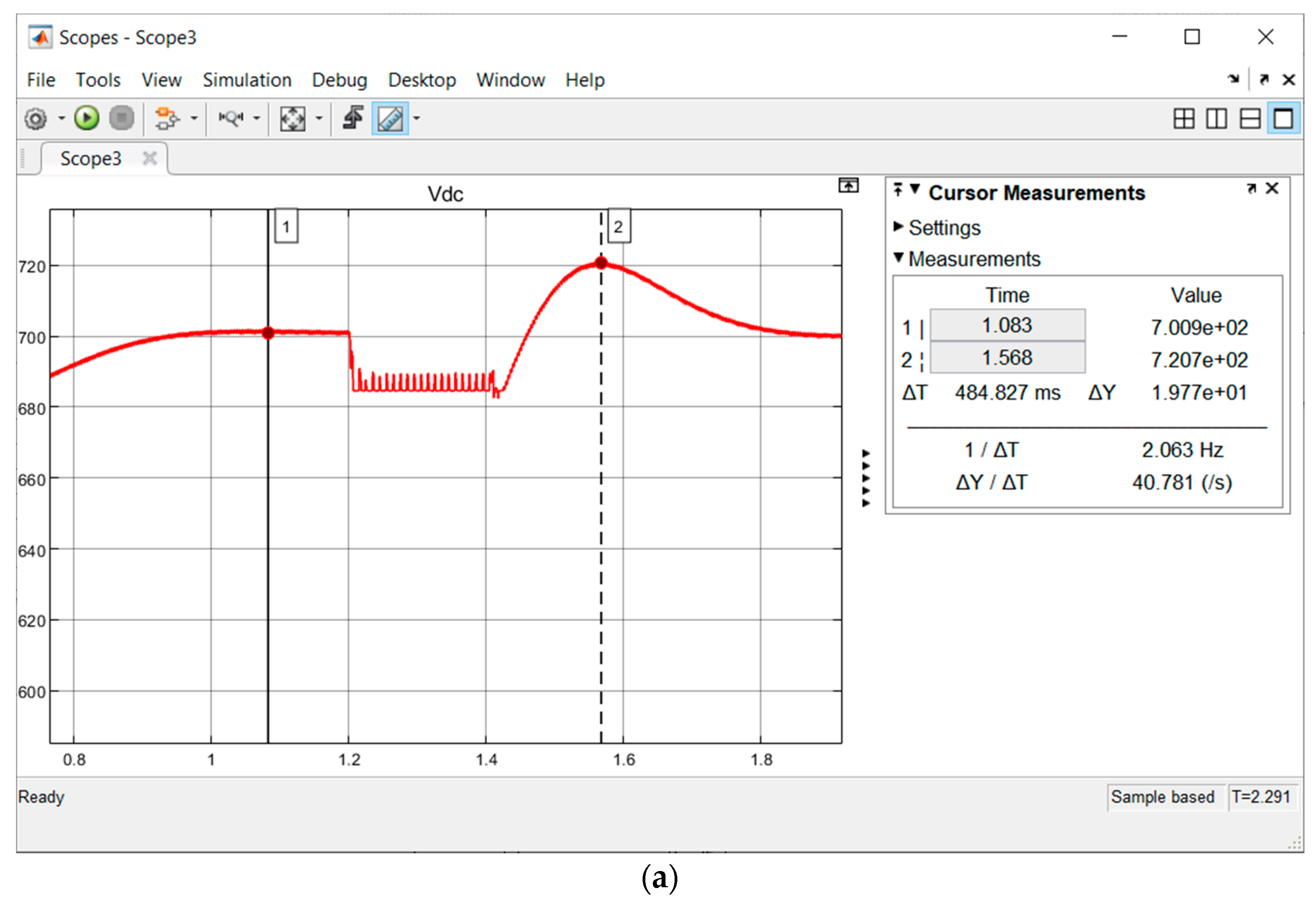
3.1. L-G Fault
3.2. L-L Fault
3.3. L-L-G Fault
3.4. Three-Phase Fault
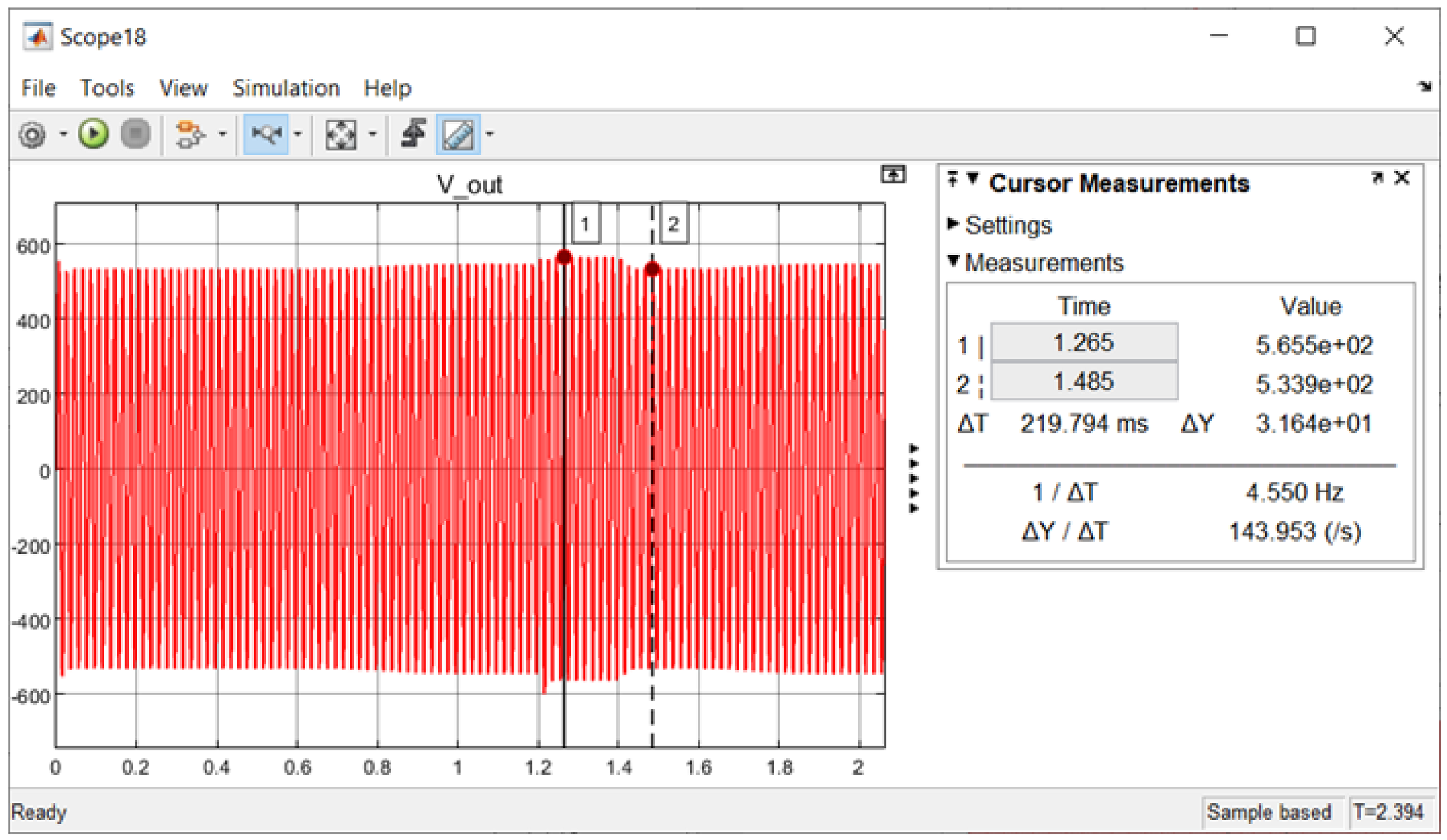
3.5. PV Intermittency (Fluctuation)
4. Discussion
- L-G fault is 6 ms
- L-L, L-L-G and three-phase fault are 20 µs
- PV intermittency is 40 ms.
5. Conclusions
- The developed Grid-Feeding mode with Voltage Oriented Control (VOC) is able to solve the undervoltage problem, whereas the designed Fuzzy Logic (FL) control is capable of solving fault (sag) and PV intermittency issues in the grid-interconnected PV-RES. The novel hybrid control could potentially prolong the lifespan of batteries, which eventually lead to cost reductions in future deployment of energy storage.
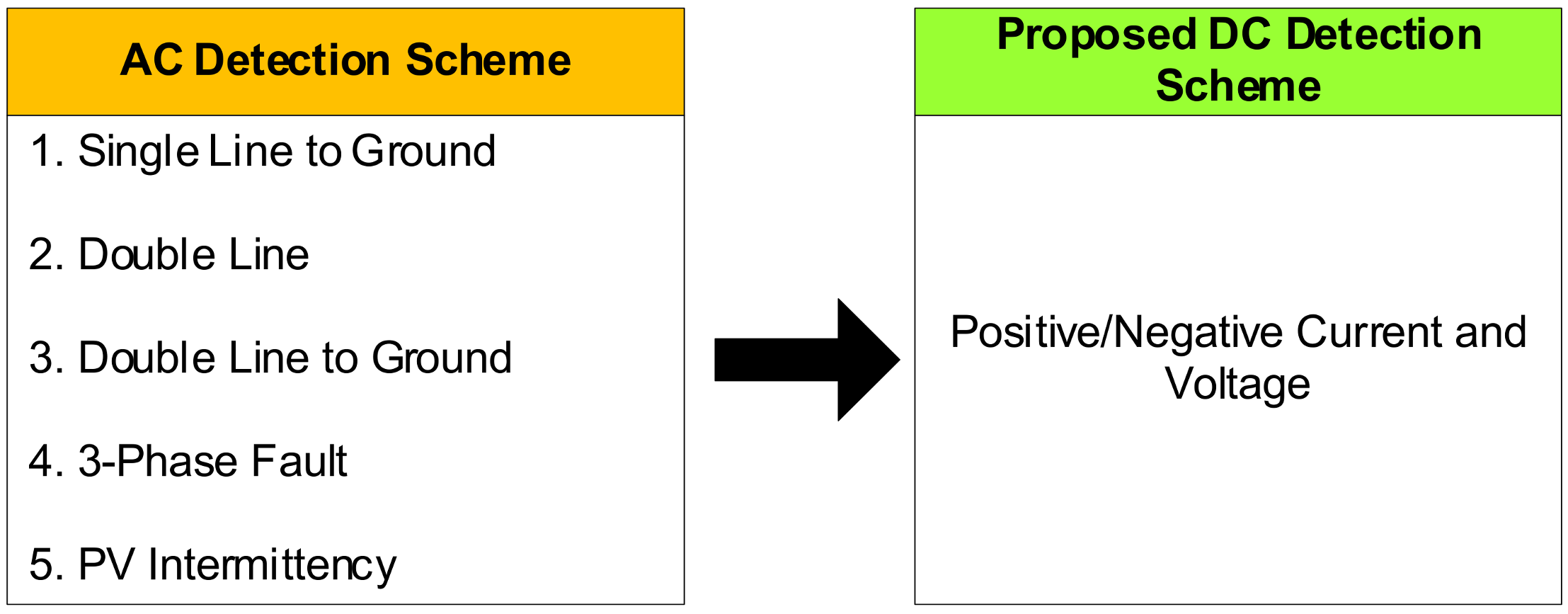
- A DC fault detection scheme using Fuzzy Logic is introduced for this work, which was proven to be more effective than AC schemes for fault detection. The reason is because AC detection in resolving PV intermittency (fluctuation) is still immature. However, the DC scheme could minimize the computational load and complexity of the system, thus inducing a faster Fault Clearance Time (FCT). In addition, the DC scheme with FL control has outperformed several available technologies in terms of the FCT.
- The enhanced DC fault detection scheme has showed a more accurate computation in fault solving by utilizing the mean current (I_mean) instead of DC-Link current (Idc). By computing the average current in the system, the current ripple exhibited in the DC current can be omitted.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gandhi, O.; Kumar, D.S.; Rodríguez-Gallegos, C.D.; Srinivasan, D. Review of power system impacts at high PV penetration Part I: Factors limiting PV penetration. Sol. Energy 2020, 210, 181–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.S.; Gandhi, O.; Rodríguez-Gallegos, C.D.; Srinivasan, D. Review of power system impacts at high PV penetration Part II: Potential solutions and the way forward. Sol. Energy 2020, 210, 202–221. [Google Scholar]
- Chua, K.J. Maximum Penetration Level of Solar Photovoltaic to The Electrical Grid in Peninsular Malaysia. Master’s Thesis, Universiti Tenaga Nasional, Kajang, Malaysia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Aghaie, H. The impact of intermittent renewables on the resource adequacy in electricity markets. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 25th International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE), Santa Clara, CA, USA, 8–10 June 2016; pp. 598–602. [Google Scholar]
- Steurer, M.; Fahl, U.; Voß, A.; Deane, P. Curtailment. In Europe’s Energy Transition—Insights for Policy Making; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Bingham, R.P. Sags and Swells. Available online: https://www.dranetz.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/02/%0Asags-and-swells.pdf (accessed on 6 June 2021).
- Lee, J.Y.; Verayiah, R.; Ong, K.H.; Ramasamy, A.K.; Marsadek, M.B. Distributed Generation: A review on current energy status, grid-interconnected PQ issues, and implementation constraints of DG in Malaysia. Energies 2020, 13, 6479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.A.; Janakiraman, P.; Somasundaram, P. Voltage sag and swell mitigation based on modulated carrier PWM. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2015, 66, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE. 1159-2019, IEEE Recommended Practice for Monitoring Electric Power Quality; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz De Leon, J., II; Lieblick, B.; Wilie, E. How facts on the distribution system are being used to improve power quality. CIRED Open Access Proc. J. 2017, 2017, 691–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jirange, A.P.K.; Snehal, N. A review on power quality compensation devices. Int. J. Sci. Dev. Res. IJSDR 2017, 2, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, Y.; Shentu, X.; Xie, Q.; Ding, Y. Voltage/frequency deviations control via distributed battery energy storage system considering state of charge. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D.T.; Modarres, M.; Hunt, R.M. GOTRES: An expert system for fault detection and analysis. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 1989, 24, 113–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jamil, M.; Sharma, S.K.; Singh, R. Fault detection and classification in electrical power transmission system using artificial neural network. SpringerPlus 2015, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senapati, K.K.; Panda, M.B.; Syed, R.S. A novel algorithm for power quality improvement using dynamic voltage restorer with fuzzy logic. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Signal Processing, Communication, Power and Embedded System (SCOPES), Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). Paralakhemundi, India, 3–5 October 2016; pp. 376–381. [Google Scholar]
- Alcalá, R.; Alcalá-Fdez, J.; Gacto, M.J.; Herrera, F. Improving fuzzy logic controllers obtained by experts: A case study in HVAC systems. Appl. Intell. 2007, 31, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isermann, R. Fault detection with parity equations. In Fault-Diagnosis Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 197–229. [Google Scholar]
- Alcantud, J.C.R. Fuzzy techniques for decision making. Symmetry 2017, 10, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Miljković, D. Fault detection methods: A literature survey. In Proceedings of the 34th International Convention (MIPRO 2011), Opatja, Croatia, 23–27 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Fagarasan, I.; Iliescu, S.S. Parity equations for fault detection and isolation. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Automation, Quality and Testing, Robotics, Cluj-Napoca, Romania, 22–25 May 2008; pp. 99–103. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann, H.-J. Practical Applications of Fuzzy Technologies; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Devaraju, T. Role of custom power devices in Power Quality Enhancement: A Review. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2010, 2, 3628–3634. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Shimray, B.A. Power quality improvement and mitigation of harmonic distortion using DSTATCOM with PI and Fuzzy Logic Controller. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Smart grids, Power and Advanced Control Engineering (ICSPACE), Bangalore, India, 17–19 August 2017; pp. 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Sabberwal, J.S.S.B.; Rajakumar, P.; Saravanakumar, R. Review on power quality issues. Eng. Sci. Technol. An Int. J. 2012, 2, 90–95. [Google Scholar]
- Han, R.; Zhou, Q. Data-driven solutions for power system fault analysis and novelty detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 11th International Conference on Computer Science & Education (ICCSE 2016), Nagoya, Japan, 23–25 August 2016; pp. 86–91. [Google Scholar]
- Alsafasfeh, Q.H. Pattern Recognition for Fault Detection, Classification, and Localization in Electrical Power System. Ph.D. Thesis, Western Michigan University, Kalamazoo, MI, USA, 2010; p. 139. [Google Scholar]
- Bin Ibrahim, K.A.; Au, M.T.; Gan, C.K. Generic characteristic of medium voltage reference network for the Malaysian power distribution system. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Student Conference on Research and Development (SCOReD), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 13–14 December 2015; pp. 204–209. [Google Scholar]
- Tenaga, S. Guidelines for Solar Photovoltaic Installation on Net Energy Metering Scheme. Available online: https://policy.asiapacificenergy.org/node/4392 (accessed on 6 June 2021).
- Perumal, P.; Ramasamy, A.K.; Teng, A.M. Performance analysis of the DigSILENT PV model connected to a modelled Malaysian distribution network. Int. J. Control. Autom. 2016, 9, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Verayiah, R.; Ong, K.H.; Ramasamy, A.; Marsadek, M.B. Voltage Oriented Control and Direct Power Control Strategies in solving under and overvoltage conditions for heavy load application on Malaysian Distribution Representative Network. Electr. Eng. 2021, 103, 1597–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nothing Unusual about the Rain, Other Factors Likely to Contribute to Flood. Available online: https://www.nst.com.my/news/nation/2020/09/623574/nothing-unusual-about-rain-other-factors-likely-contributor-flood?fbclid=IwAR3zKZwpf32b5DVZE3yDCsYf41pTCZz4SOPMZXjo9nr9DHIkYVHXJyXfDPY (accessed on 30 September 2020).
- IEEE. IEEE Recommended Practice for the Analysis of Fluctuating Installations on Power Systems; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hannan, M.A.; Mohamed, A.; Hussain, A. A simulation model of solid-state transfer switch for protection in distribution systems. J. Appl. Sci. 2006, 6, 1993–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Saric, M. Generator dynamic response analysis and improvement following distribution network disturbance. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2017, 7, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Description | Causes | Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Interruption |
|
|
| Voltage Sag |
|
|
| Voltage Swell |
|
|
| Voltage Fluctuation |
|
|
| Load | Terminal | Voltage Max. (p.u.) | Time Point Max | Voltage Min. (p.u) | Time Point Min. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type A | Residential A (1) | 1.035 | 1:00:00 PM | 1.01 | 12:00:00 AM |
| Residential A (2) | 1.033 | 1:00:00 PM | 1 | 12:00:00 AM | |
| Residential A (3) | 1.031 | 1:00:00 PM | 0.99 | 12:00:00 AM | |
| Residential A (4) | 1.03 | 1:00:00 PM | 0.99 | 12:00:00 AM | |
| Residential A (5) | 1.03 | 1:00:00 PM | 0.99 | 12:00:00 AM | |
| Type B | Small Residential (1) | 1.038 | 5:00:00 AM | 1.02 | 12:00:00 AM |
| Small Residential (2) | 1.038 | 5:00:00 AM | 1.02 | 12:00:00 AM | |
| Small Residential (3) | 1.037 | 5:00:00 AM | 1.02 | 12:00:00 AM | |
| Type C | Commercial (1) | 1.037 | 1:00:00 PM | 1.03 | 4:00:00 PM |
| Commercial (2) | 1.036 | 1:00:00 PM | 1.03 | 4:00:00 PM | |
| Commercial (3) | 1.036 | 1:00:00 PM | 1.02 | 4:00:00 PM | |
| Type D | Residential B (1) | 1.037 | 1:00:00 PM | 1.02 | 12:00:00 AM |
| Residential B (2) | 1.037 | 1:00:00 PM | 1.02 | 12:00:00 AM | |
| Residential B (3) | 1.037 | 1:00:00 PM | 1.01 | 12:00:00 AM | |
| Residential B (4) | 1.036 | 1:00:00 PM | 1.01 | 12:00:00 AM | |
| Residential B (5) | 1.036 | 1:00:00 PM | 1.01 | 12:00:00 AM | |
| Type E | Residential C (1) | 1.05 | 1:00:00 PM | 1.02 | 12:00:00 AM |
| Residential C (2) | 1.05 | 1:00:00 PM | 1.02 | 12:00:00 AM | |
| Residential C (3) | 1.05 | 1:00:00 PM | 1.02 | 12:00:00 AM | |
| Residential C (4) | 1.05 | 1:00:00 PM | 1.02 | 12:00:00 AM | |
| Residential C (5) | 1.05 | 1:00:00 PM | 1.01 | 12:00:00 AM |
| Components | Parameter | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Lline | 2 mH | Line impedance |
| Rline | 0.05 Ω | ||
| Vinput | 400 Vrms (three-phase) | Source | |
| LC filter | Lfilter | 1 mH | To remove ripple so that the inverted sinewave output from inverter will be smoother |
| Cfilter | 4.7 mF | ||
| Load at 4:00 pm | Rload | 243 kW | Load |
| Lload | 108 kVAr | ||
| Inverter | fs, inv | 2 kHz | Switching frequency |
| Rectifier | fs,rect | 2 kHz | Switching frequency |
| C,dc-link | 150 μF | DC-Link Rectifier | |
| Solar panel | Wmax | 200 kW | Maximum power |
| Energy Storage | V | 720 V | DC source |
| Case | Weather Condition | PV Generation | Load Condition at 4:00 p.m. | Voltage Dynamic Problem |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rainy | No | Normal (243 kW) | Undervoltage and Fault |
| 2 | Cloudy | Intermittency | Normal (243 kW) | Fluctuation |
| Ve | VL | VN | VH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Im | ||||
| IL | DISC | N | N | |
| IN | N | N | N | |
| IH | N | N | C | |
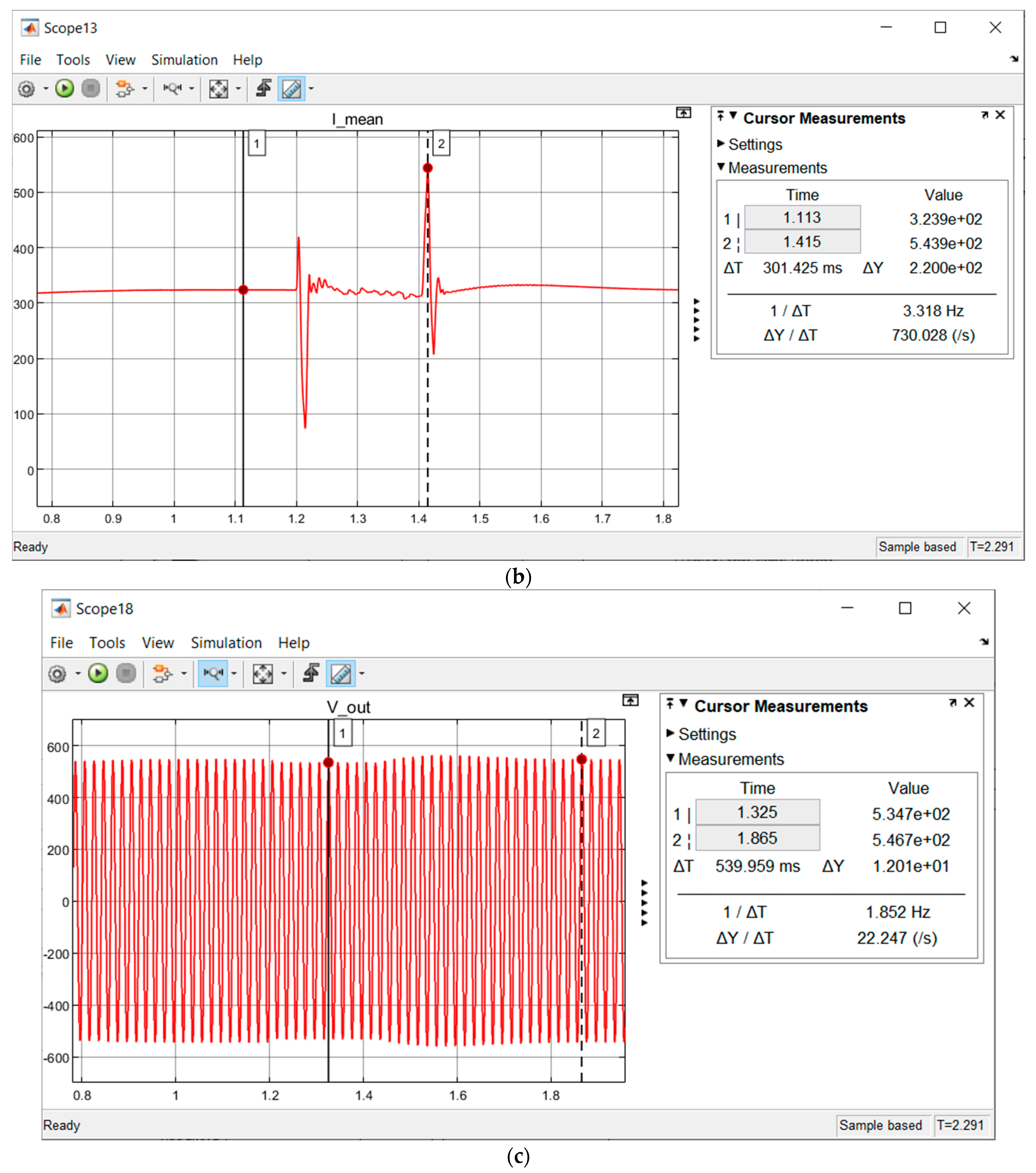
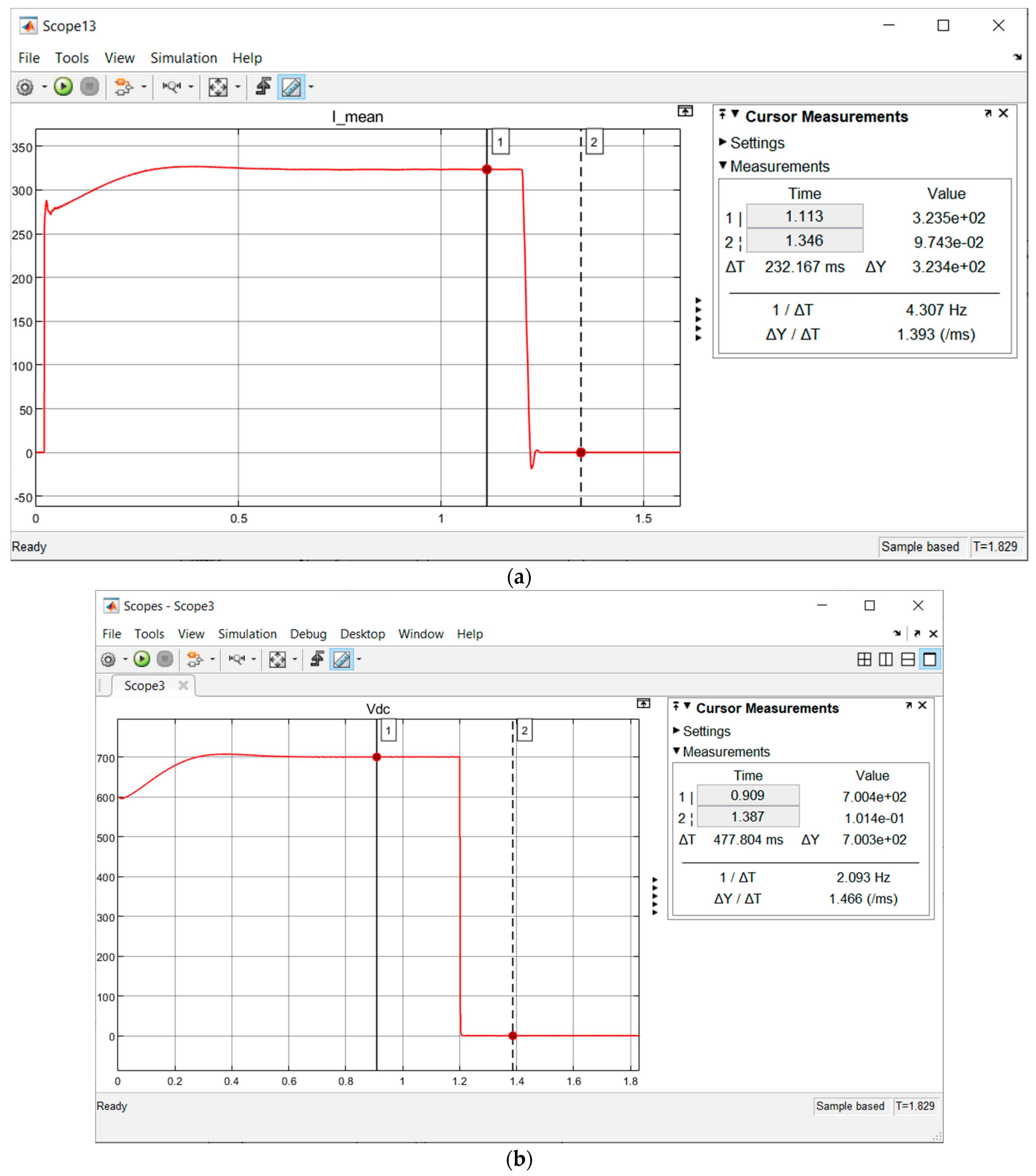
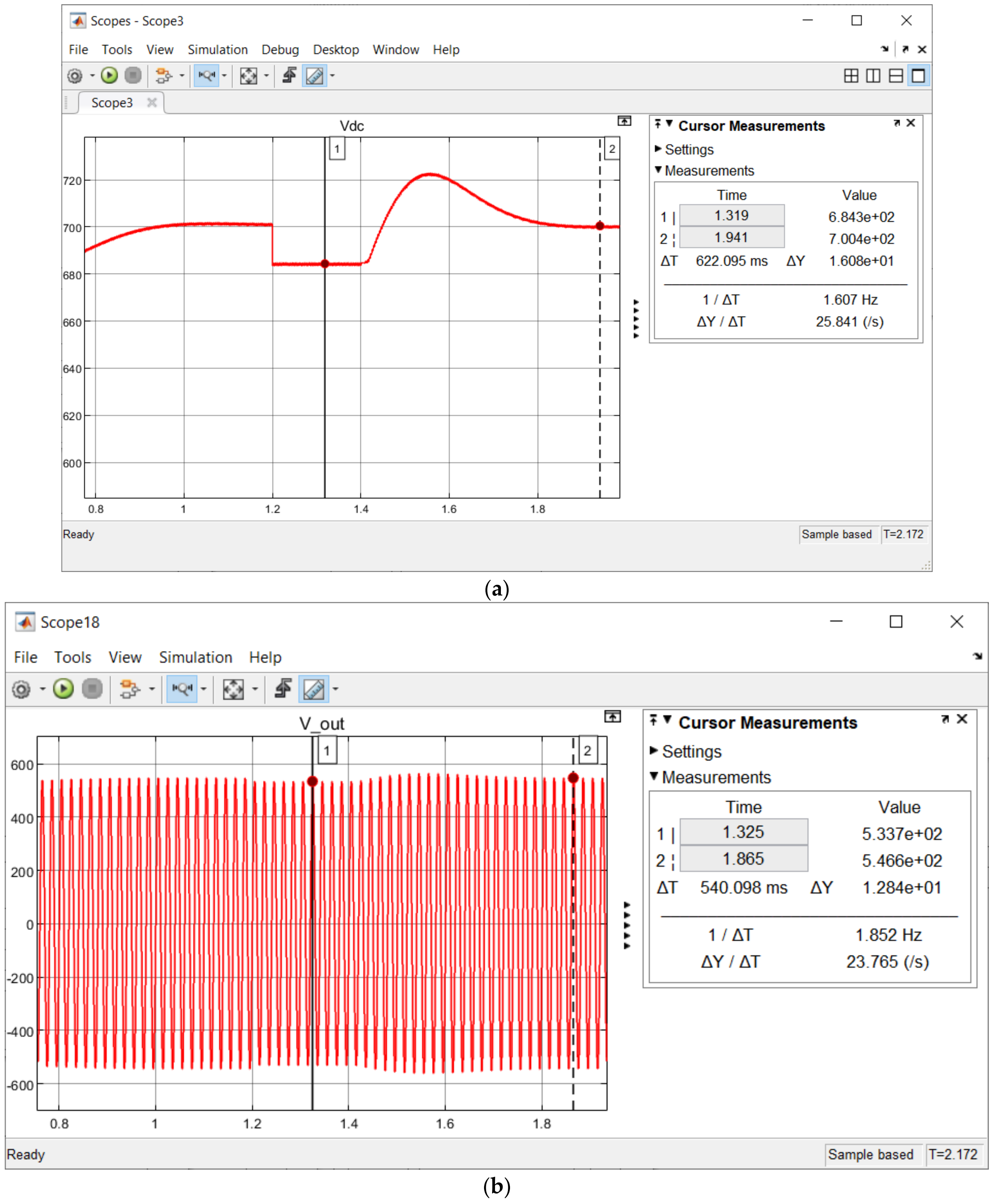
| L-G Fault | Before Fuzzy Integration | |||
| Pre-Fault (VOC Control) | Fault | Post-Fault (VOC Control) | ||
| Vdc (V) | 700 | Steep decrease approaching zero ✘ | Steep decrease approaching zero ✘ | |
| Vout (Vp) | In Range | Out of Range ✘ | Out of Range ✘ | |
| After Fuzzy Integration | ||||
| Vdc (V) | 700 | 685 ✔ | 700 ✔ | |
| Vout (Vp) | In Range | 534.7 ✔ | 546.7 ✔ | |
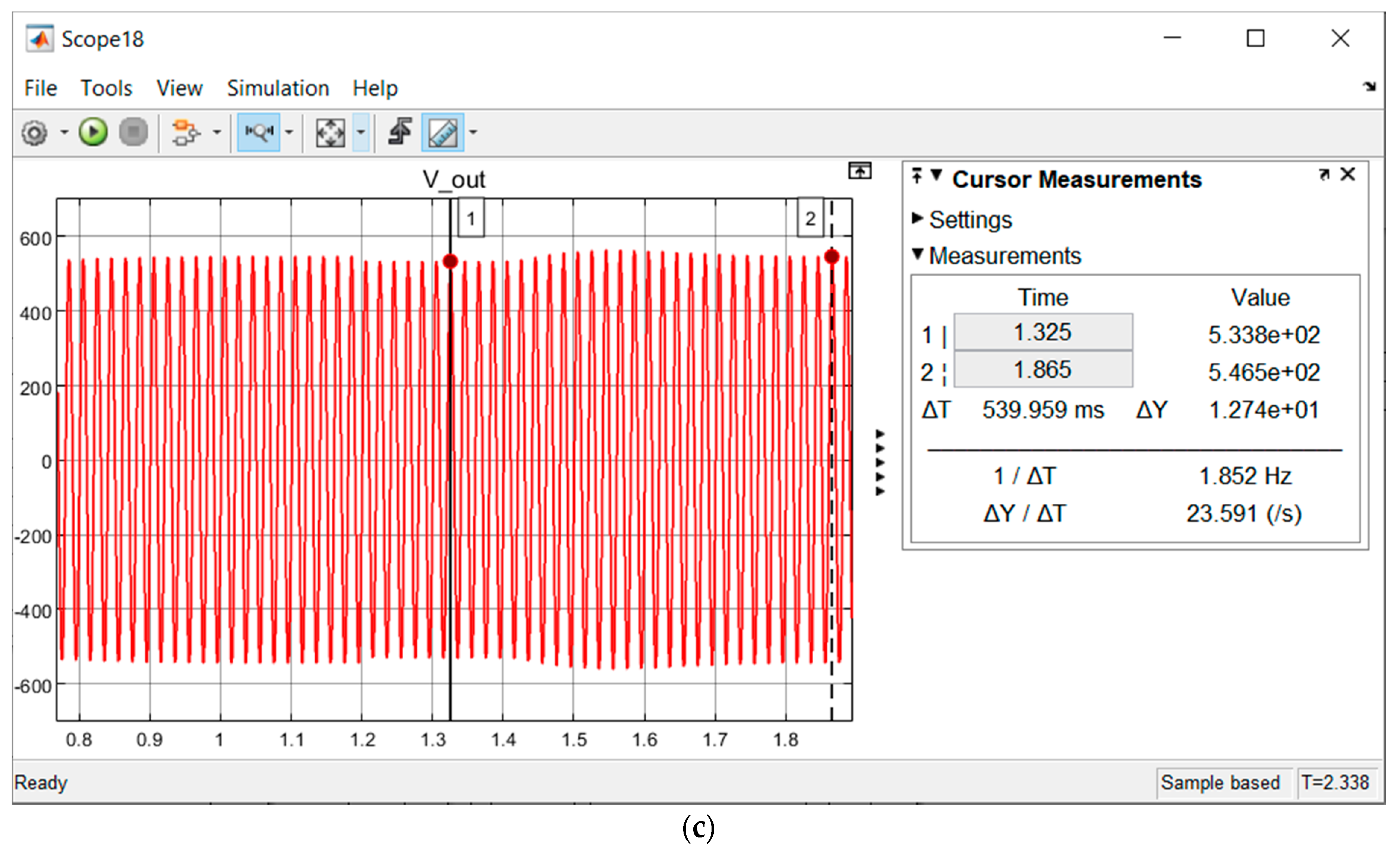
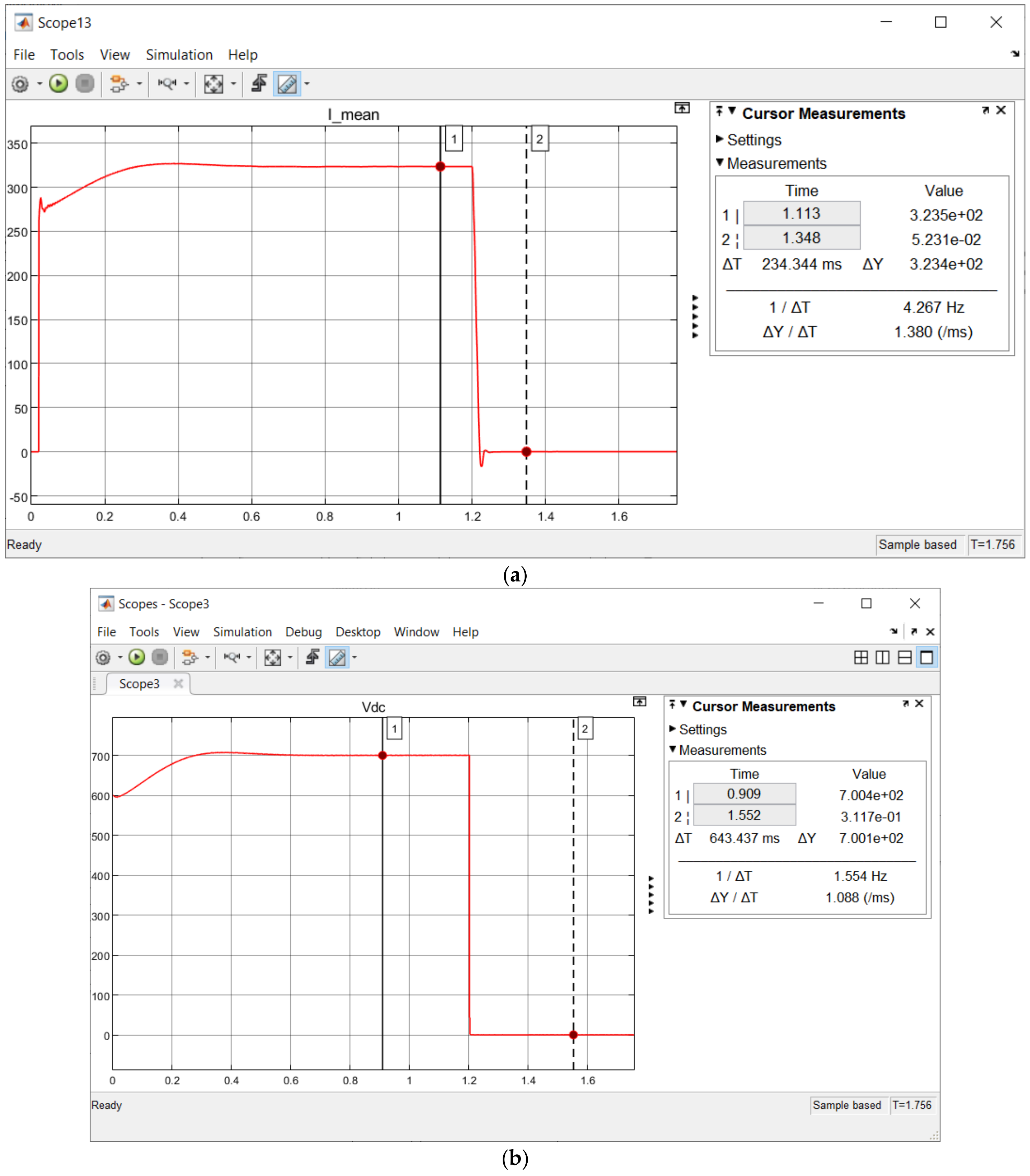
| L-L, L-L-G and Three-Phase Fault | Before Fuzzy Integration | |||
| Pre-Fault (VOC Control) | Fault | Post-Fault (VOC Control) | ||
| Vdc (V) | 700 | 0 ✘ | 0 ✘ | |
| Vout (Vp) | In Range | Out of Range ✘ | Out of Range ✘ | |
| After Fuzzy Integration | ||||
| Vdc (V) | 700 | 684.3–684.7 ✔ | 700 ✔ | |
| Vout (Vp) | In Range | 533.7–533.8 ✔ | 546.5–546.6 ✔ | |
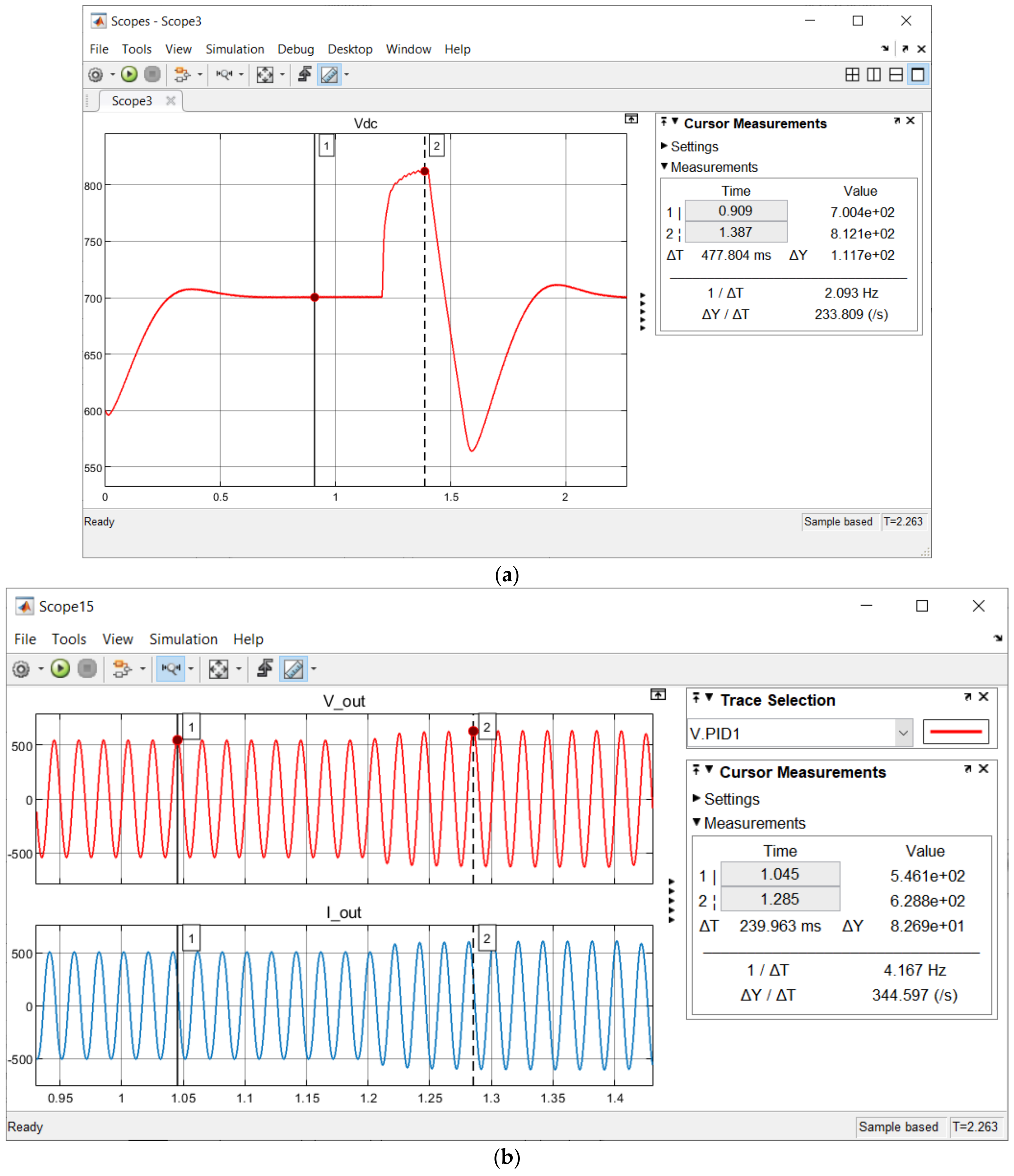
| PV Intermittency | Before Fuzzy Integration | |||
| Pre-Fault (VOC Control) | Fault | Post-Fault (VOC Control) | ||
| Vdc (V) | 700 | Fluctuate reaching max Vdc at 812.1 ✘ | 700 ✔ | |
| Vout (Vp) | In Range | Out of Range ✘ | Out of Range ✘ | |
| After Fuzzy Integration | ||||
| Vdc (V) | 700 | 720 ✔ | 700 ✔ | |
| Vout (Vp) | In Range | 565.5 ✔ | 533.9 ✔ | |
| Type of Fault/Fluctuation | (a) Fault Start | (b) FCT End | (c) Fault End/Post-Fault Start | (d) Post-Fault End | (e) FCT | (f) VOC Buffer Time | Benchmark (FCT) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L-G | 1.2 s | 1.206 s | 1.4 s | 1.8 s | 6 ms | 0.4 s | 0.16 s (STAT-COM) |
| L-L | 1.2 s | 1.20002 s | 1.4 s | 1.8 s | 20 µs | 0.4 s | - |
| L-L-G | 1.2 s | 1.20002 s | 1.4 s | 1.8 s | 20 µs | 0.4 s | - |
| Three-Phase | 1.2 s | 1.20002 s | 1.4 s | 1.8 s | 20 µs | 0.4 s | 12 ms (SSTS) |
| PV Intermittency | 1.2 s | 1.24 s | 1.4 s | 1.7 s | 40 ms | 0.2 s | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hoe, O.K.; Ramasamy, A.K.; Yin, L.J.; Verayiah, R.; Marsadek, M.B.; Abdillah, M. Hybrid Control of Grid-Feeding and Fuzzy Logic Fault Detection in Solving Voltage Dynamic Problem within the Malaysian Distribution Network. Energies 2021, 14, 3545. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14123545
Hoe OK, Ramasamy AK, Yin LJ, Verayiah R, Marsadek MB, Abdillah M. Hybrid Control of Grid-Feeding and Fuzzy Logic Fault Detection in Solving Voltage Dynamic Problem within the Malaysian Distribution Network. Energies. 2021; 14(12):3545. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14123545
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoe, Ong Kam, Agileswari K. Ramasamy, Lee Jun Yin, Renuga Verayiah, Marayati Binti Marsadek, and Muhammad Abdillah. 2021. "Hybrid Control of Grid-Feeding and Fuzzy Logic Fault Detection in Solving Voltage Dynamic Problem within the Malaysian Distribution Network" Energies 14, no. 12: 3545. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14123545
APA StyleHoe, O. K., Ramasamy, A. K., Yin, L. J., Verayiah, R., Marsadek, M. B., & Abdillah, M. (2021). Hybrid Control of Grid-Feeding and Fuzzy Logic Fault Detection in Solving Voltage Dynamic Problem within the Malaysian Distribution Network. Energies, 14(12), 3545. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14123545







