Analytical and Experimental Study of Thermoelectric Generator (TEG) System for Automotive Exhaust Waste Heat Recovery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Analytical Design
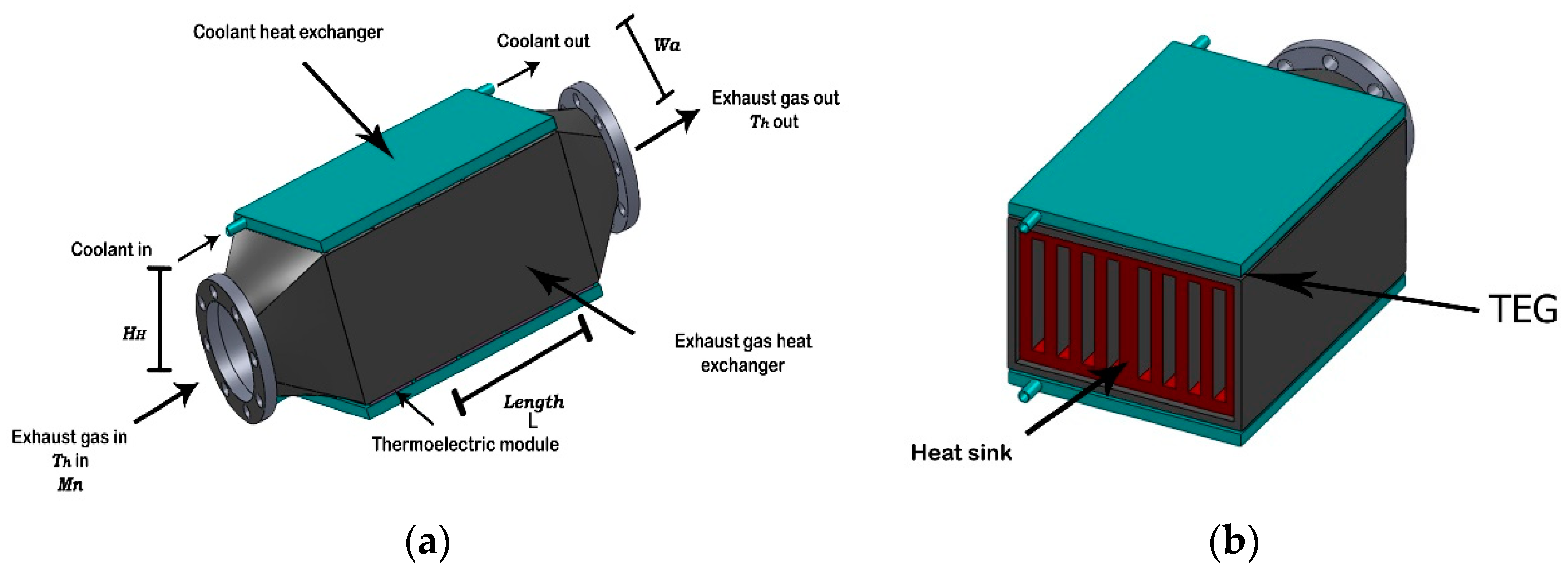
2.1. Automotive Exhaust TEG System
2.2. Thermoelectric Unit Cell Design
- The steady-state heat flow is at a constant rate.
- The TEG module contact resistances are neglected.
- The Thomson effect (which is the temperature-dependent material properties) is neglected.
- The heat transfer that takes place by convection and radiation through the TEG module is neglected.
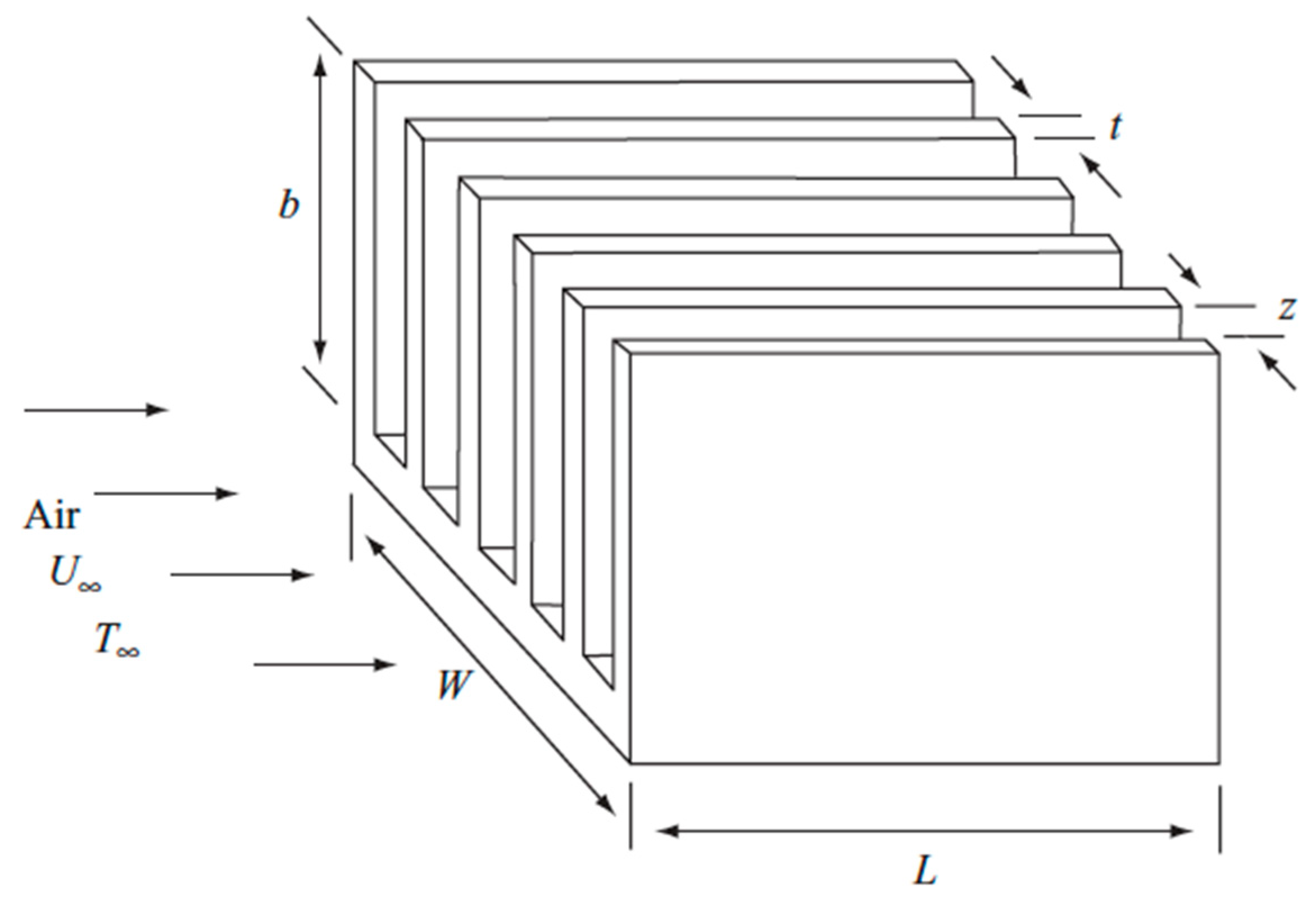
2.3. Heat Sink
2.4. Effective Material Properties
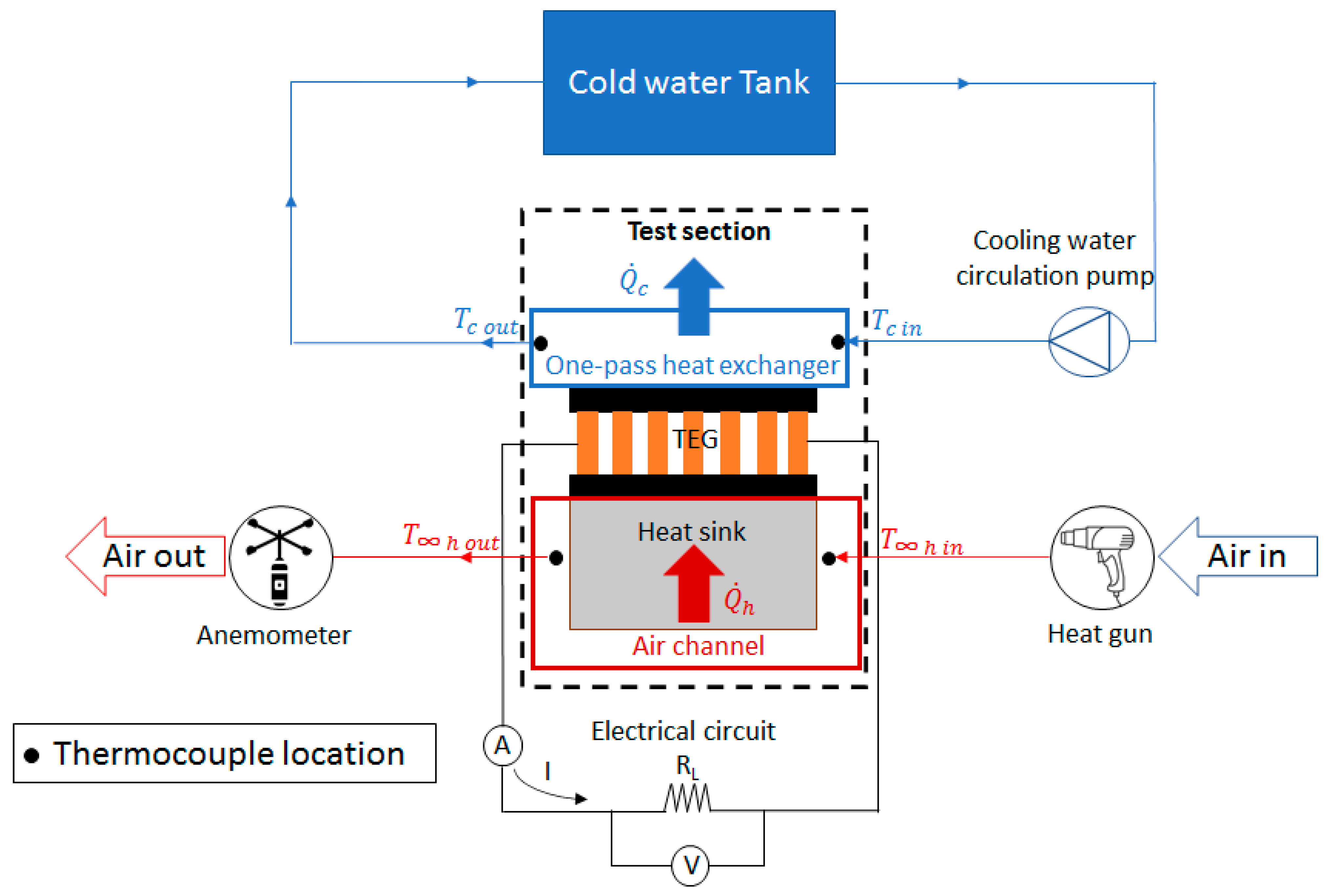
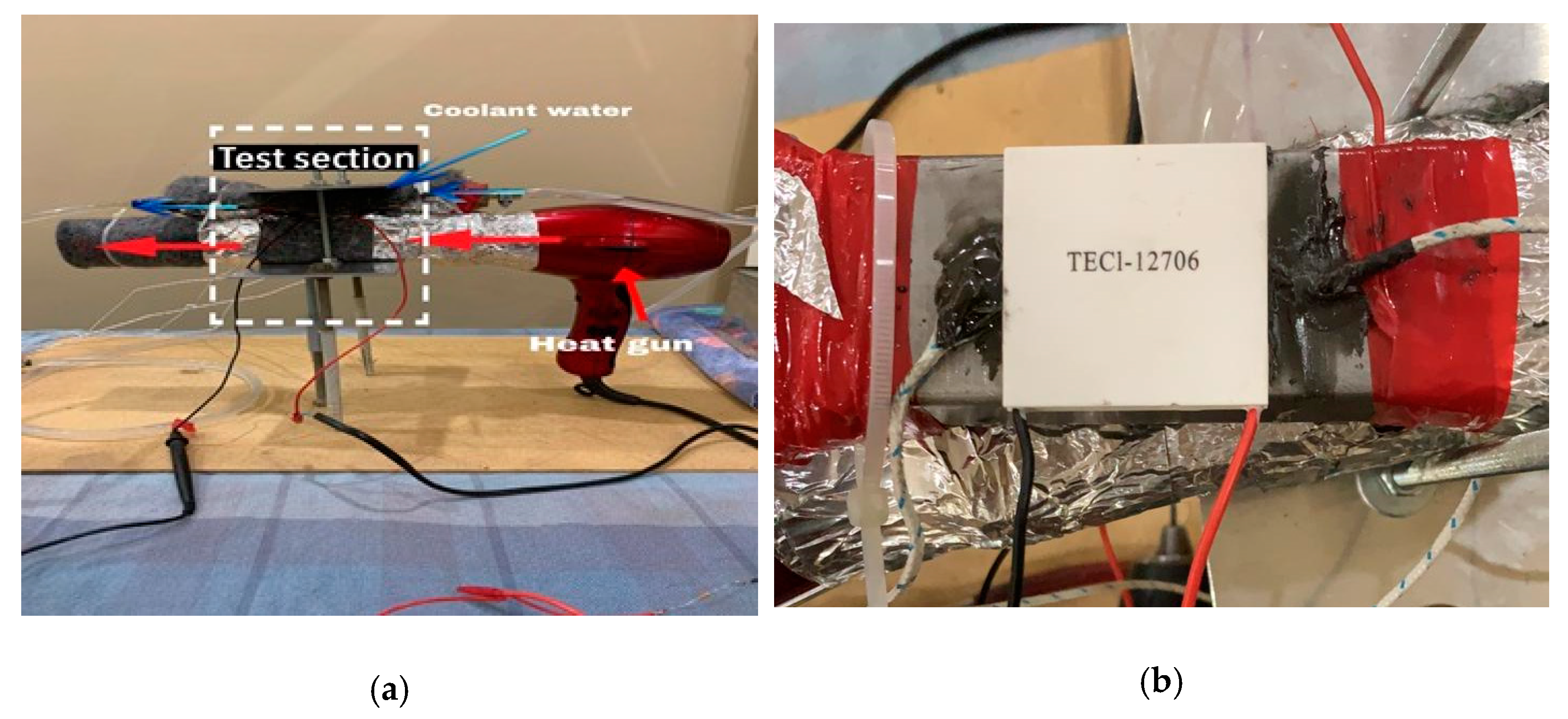
3. Experimental Work
3.1. Experimental Procedure
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Prediction of Effective Material Properties
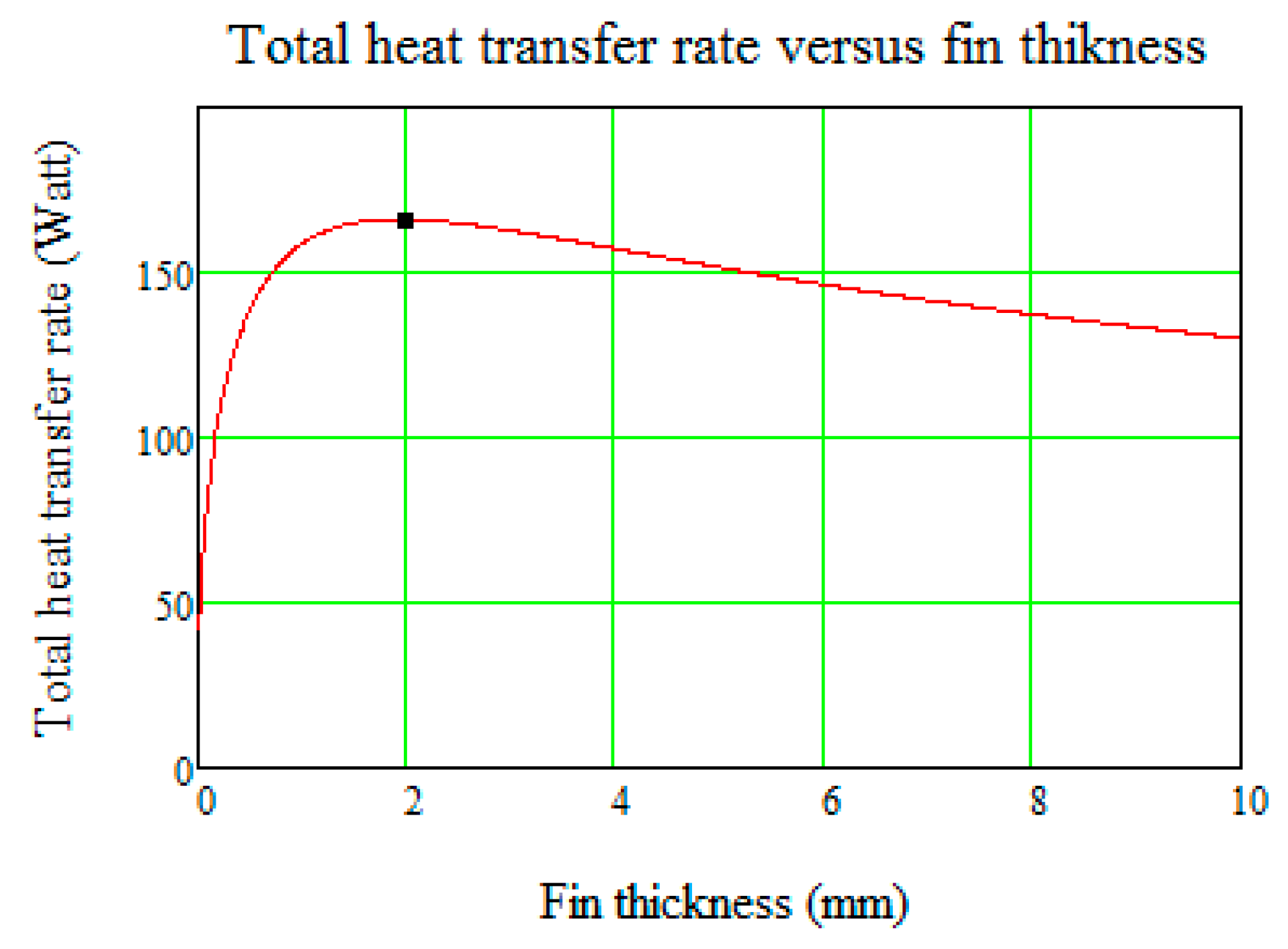
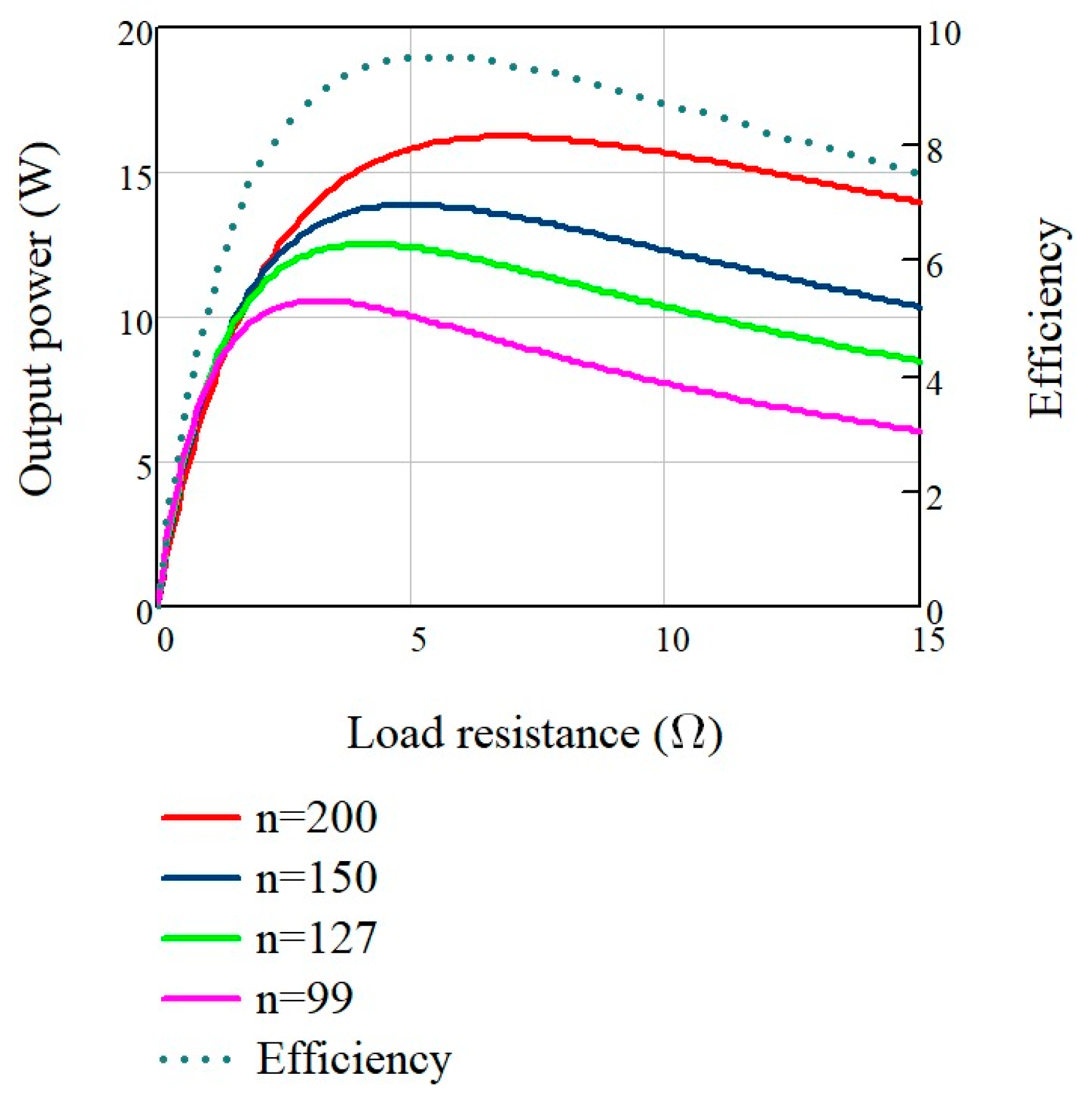
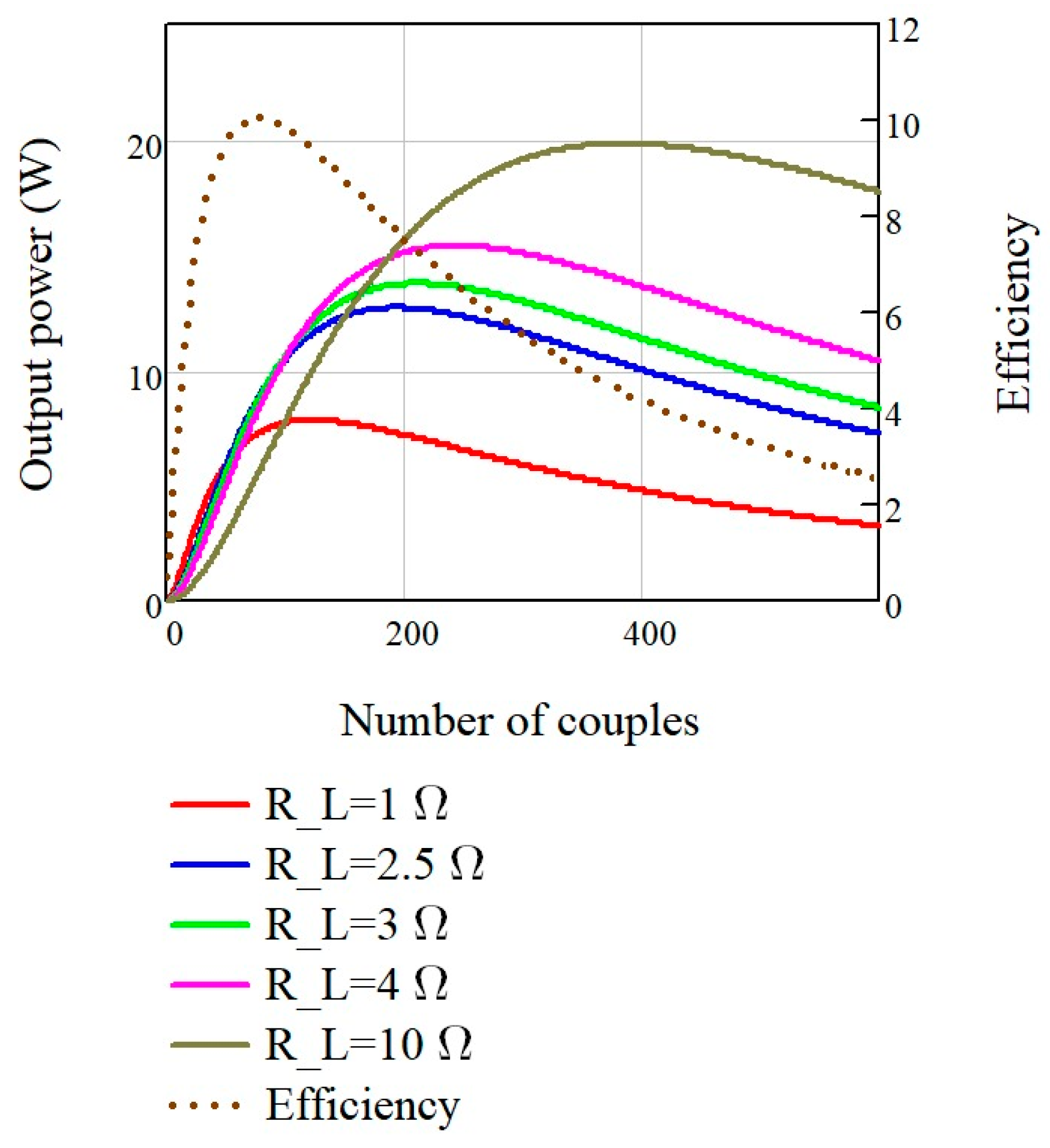
4.2. TEG System Modelling Results
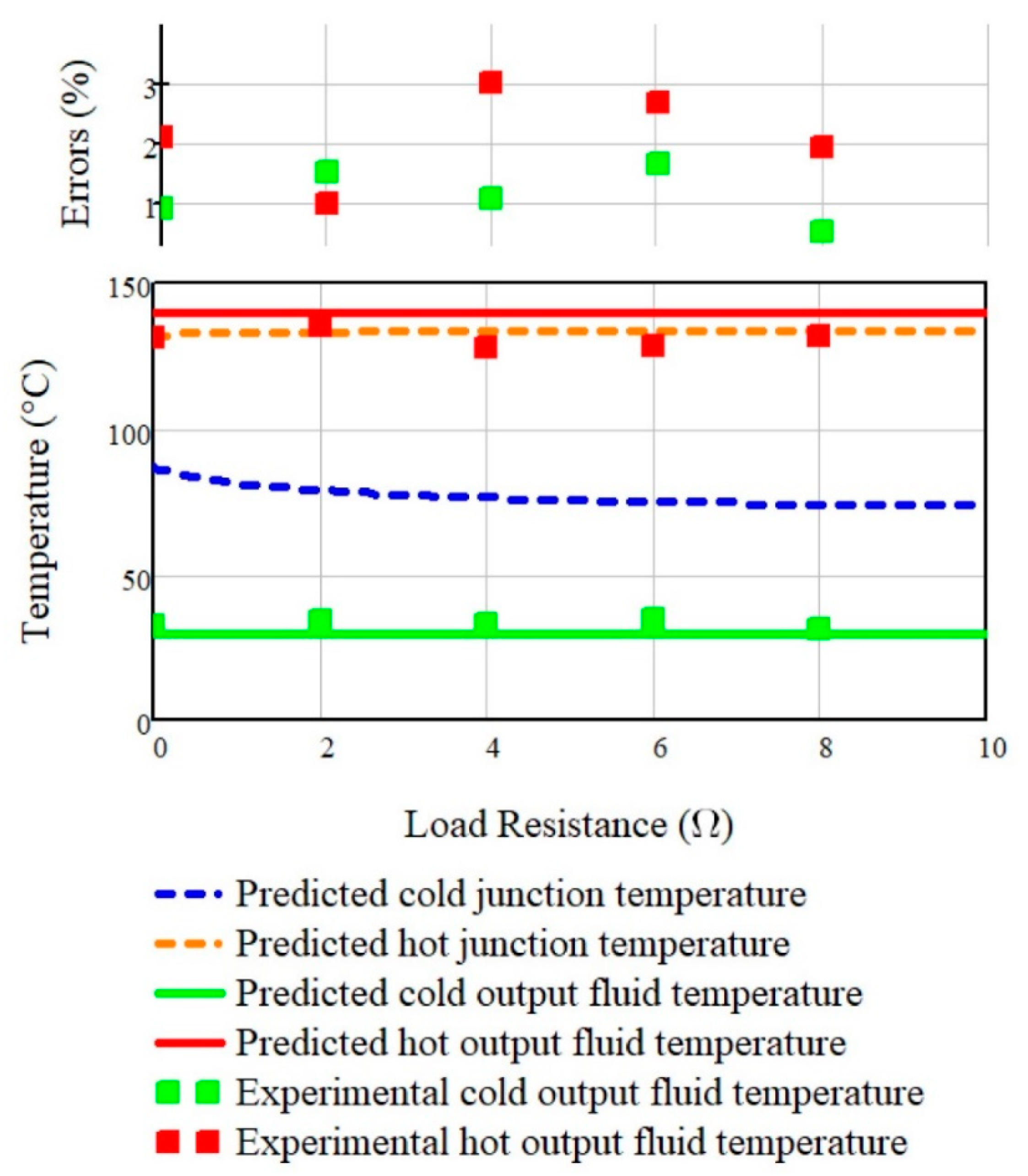
4.3. Experimental Validation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, M.; Subramaniyan, M.; Gurusamy, M. Power generation from waste heat of vehicle exhaust using thermo electric generator: A review. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 402, 12174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagehi, H. Optimal Design of Automotive Exhaust Thermoelectric Generator (AETEG). Master’s Thesis, Westren Michigan University, Kalamazoo, MI, USA, 2016; p. 764. [Google Scholar]
- Fagehi, H.; Attar, A.; Lee, H. Optimal Design of an Automotive Exhaust Thermoelectric Generator. J. Electron. Mater. 2018, 47, 3983–3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkholz, U.; Grob, E.; Stohrer, U.; Voss, K.; Gruden, D.; Wurster, W. Conversion of Waste Exhaust Heat in Automobile using FeSi2 Thermoelements. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Thermoelectric Energy Conversion, Arlington, TX, USA, 16–18 March 1988; pp. 124–128. [Google Scholar]
- Bass, J.C.; Elsner, N.B.; Leavitt, F.A. Performance of the 1 kW thermoelectric generator for diesel engines. AIP Conf. Proc. 1994, 316, 295–298. [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara, K. Development of a high efficient thermoelectric stack for a waste exhaust heat recovery of vehicles. In Proceedings of the Twenty-First International Conference on Thermoelectrics, ICT ’02, Long Beach, CA USA, 25–29 August 2002; pp. 418–423. [Google Scholar]
- Jänsch, D. Thermoelektrik Eine Chance für die Automobilindustrie; Expert verlag GmbH: Tübingen, Germay, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J. Engineering and Materials for Automotive Thermoelectric Applications. In Proceedings of the 2009 Thermoelectrics Applications Workshop, San Diego, CA, USA, 29 September–2 October 2009; Available online: https://www.energy.gov/sites/prod/files/2014/03/f13/yang_0.pdf (accessed on 11 October 2020).
- Salvador, J.R.; Cho, J.Y.; Ye, Z.; Moczygemba, J.E.; Thompson, A.J.; Sharp, J.W.; König, J.; Maloney, R.; Thompson, T.; Sakamoto, J.; et al. Thermal to Electrical Energy Conversion of Skutterudite-Based Thermoelectric Modules. J. Electron. Mater. 2013, 42, 1389–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Chau, K. Thermoelectric automotive waste heat energy recovery using maximum power point tracking. Energy Convers. Manag. 2009, 50, 1506–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Deng, Y.D.; Li, Z.; Su, C.Q. Performance analysis of a waste heat recovery thermoelectric generation system for automotive application. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 90, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cleary, M.; Wang, X.; Kempf, N.; Schoensee, L.; Yang, J.; Joshi, G.; Meda, L. High-temperature and high-power-density nanostructured thermoelectric generator for automotive waste heat recovery. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 105, 946–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.Y.; Negash, A.A.; Cho, G. Waste heat recovery of a diesel engine using a thermoelectric generator equipped with customized thermoelectric modules. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 124, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xie, C.; Quan, S.; Shi, Y.; Tang, Z. Optimization of Thermoelectric Modules’ Number and Distribution Pattern in an Automotive Exhaust Thermoelectric Generator. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 72143–72157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhu, D.; Zheng, Y.; Guo, W. Mesoscale combustor-powered thermoelectric generator with enhanced heat collection. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 205, 112403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaprahasam, D.; Harish, S.; Gopalan, R.; Sundararajan, G. Automotive Waste Heat Recovery by Thermoelectric Generator Technology. In Bringing Thermoelectricity into Reality; Aranguren, P., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.S. Thermoelectrics: Design and Materials; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H. Thermal Design Heat Sinks, Thermoelectrics, Heat Pipes, Compact heat Exchangers, and Solar Cells; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Weera, S.; Lee, H.; Attar, A. Utilizing effective material properties to validate the performance of thermoelectric cooler and generator modules. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 205, 112427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Heister, S.D.; Xu, X.; Salvador, J.R.; Meisner, G.P. Thermoelectric Generators for Automotive Waste Heat Recovery Systems Part I: Numerical Modeling and Baseline Model Analysis. J. Electron. Mater. 2013, 42, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attar, A.; Lee, H.; Snyder, G.J. Optimum load resistance for a thermoelectric generator system. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 226, 113490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Input Parameters (from Manufacturer) | |||
| Effective Material Properties | |||
| The optimum Design of a TEG Cell | |||||
| 127 | 516.47 | 12.5 | |||
| The Optimum Design of the TEG System | |||||
| () | |||||
| 400 | 12,700 | 900 | 516.47 | 139.76 | 1250 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Seebeck coefficient | |
| Electrical resistivity | |
| TE thermal conductivity | |
| Number of thermocouples | |
| The leg length of the TE element | |
| The cross-sectional area of the TE element | |
| The dimensionless figure of merit at 298 K |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Albatati, F.; Attar, A. Analytical and Experimental Study of Thermoelectric Generator (TEG) System for Automotive Exhaust Waste Heat Recovery. Energies 2021, 14, 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14010204
Albatati F, Attar A. Analytical and Experimental Study of Thermoelectric Generator (TEG) System for Automotive Exhaust Waste Heat Recovery. Energies. 2021; 14(1):204. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14010204
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlbatati, Faisal, and Alaa Attar. 2021. "Analytical and Experimental Study of Thermoelectric Generator (TEG) System for Automotive Exhaust Waste Heat Recovery" Energies 14, no. 1: 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14010204
APA StyleAlbatati, F., & Attar, A. (2021). Analytical and Experimental Study of Thermoelectric Generator (TEG) System for Automotive Exhaust Waste Heat Recovery. Energies, 14(1), 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14010204





