CFD Study of Diffuse Ceiling Ventilation through Perforated Ceiling Panels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Suspended Ceiling
3. Methods
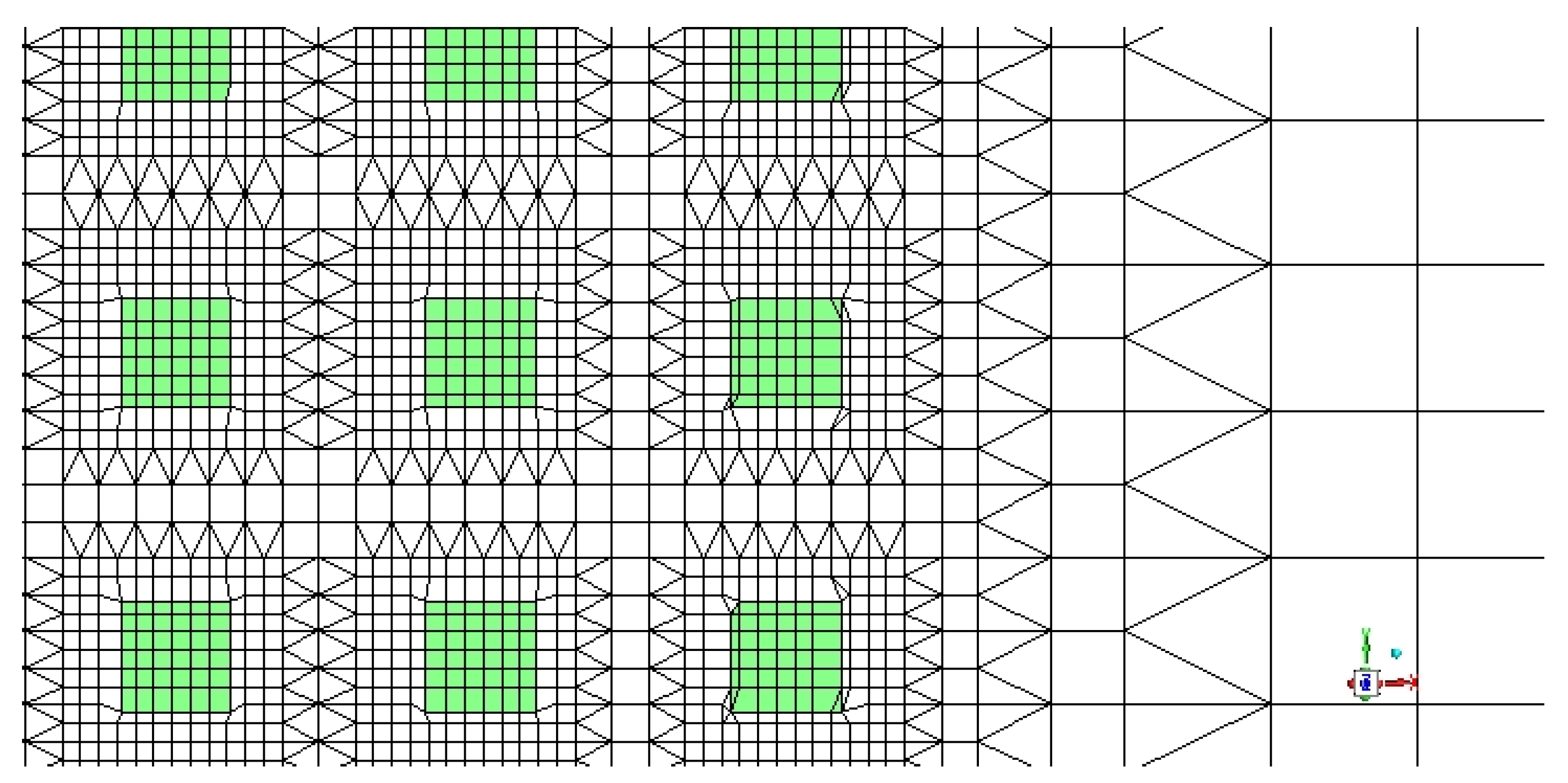
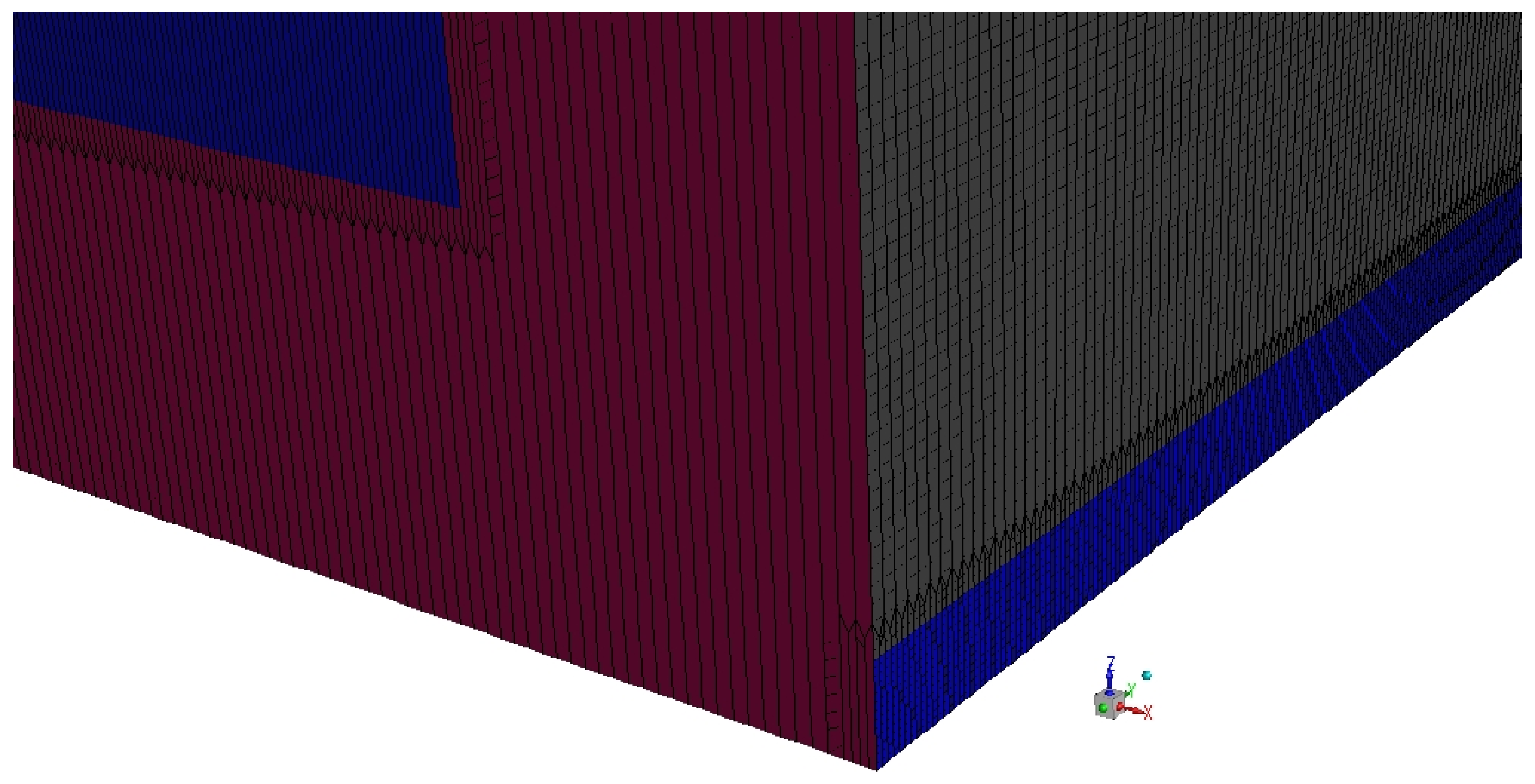
3.1. Computational Domain
3.2. Numerical Model
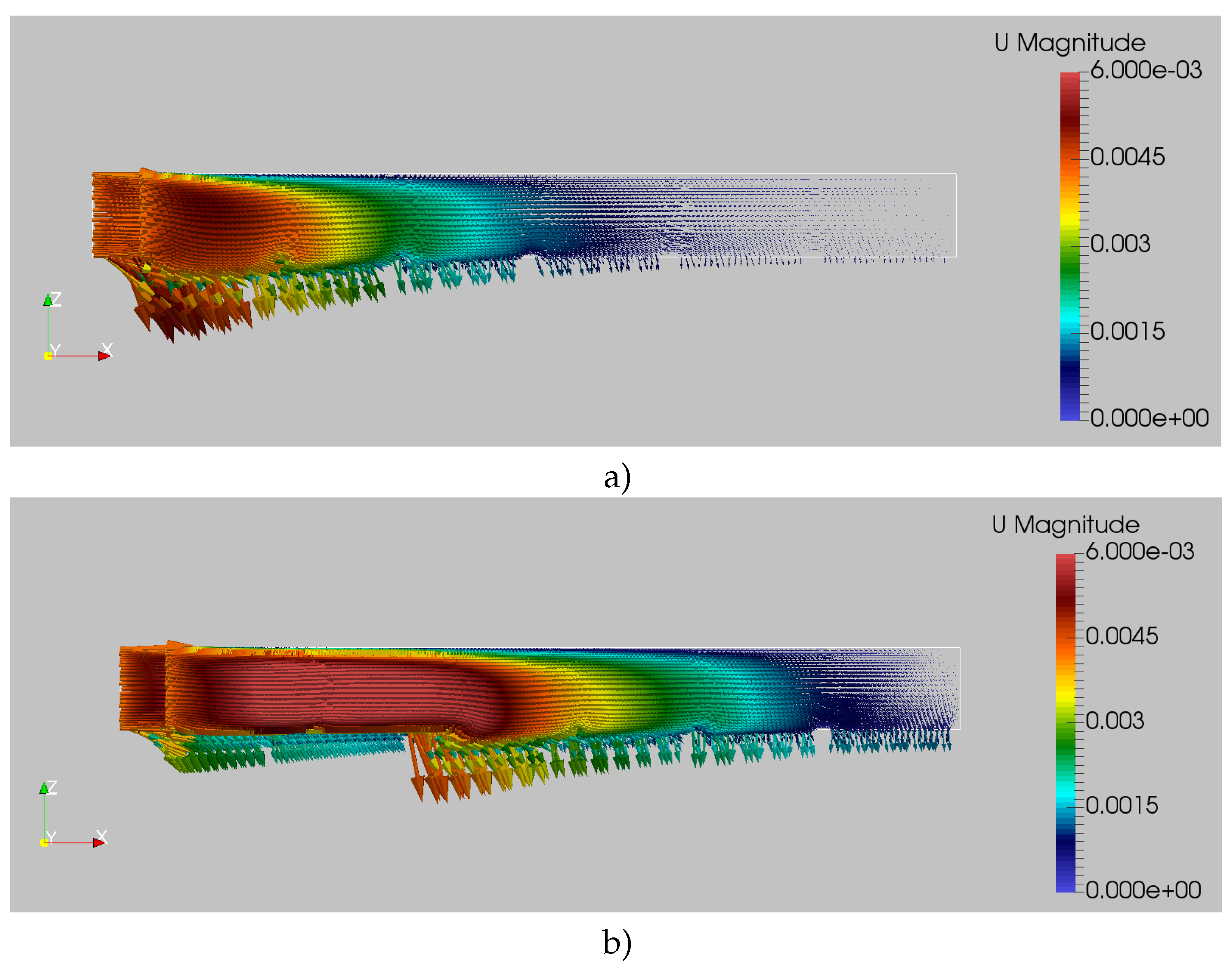
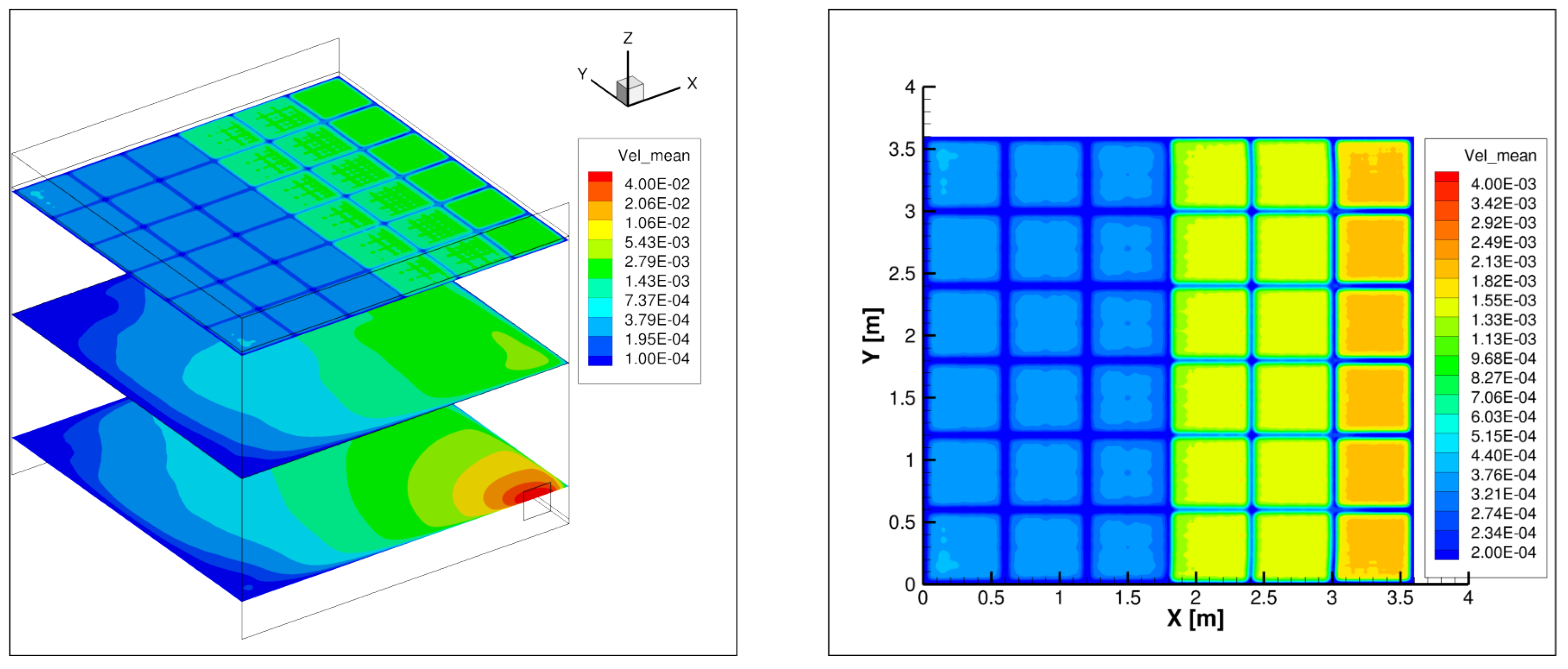
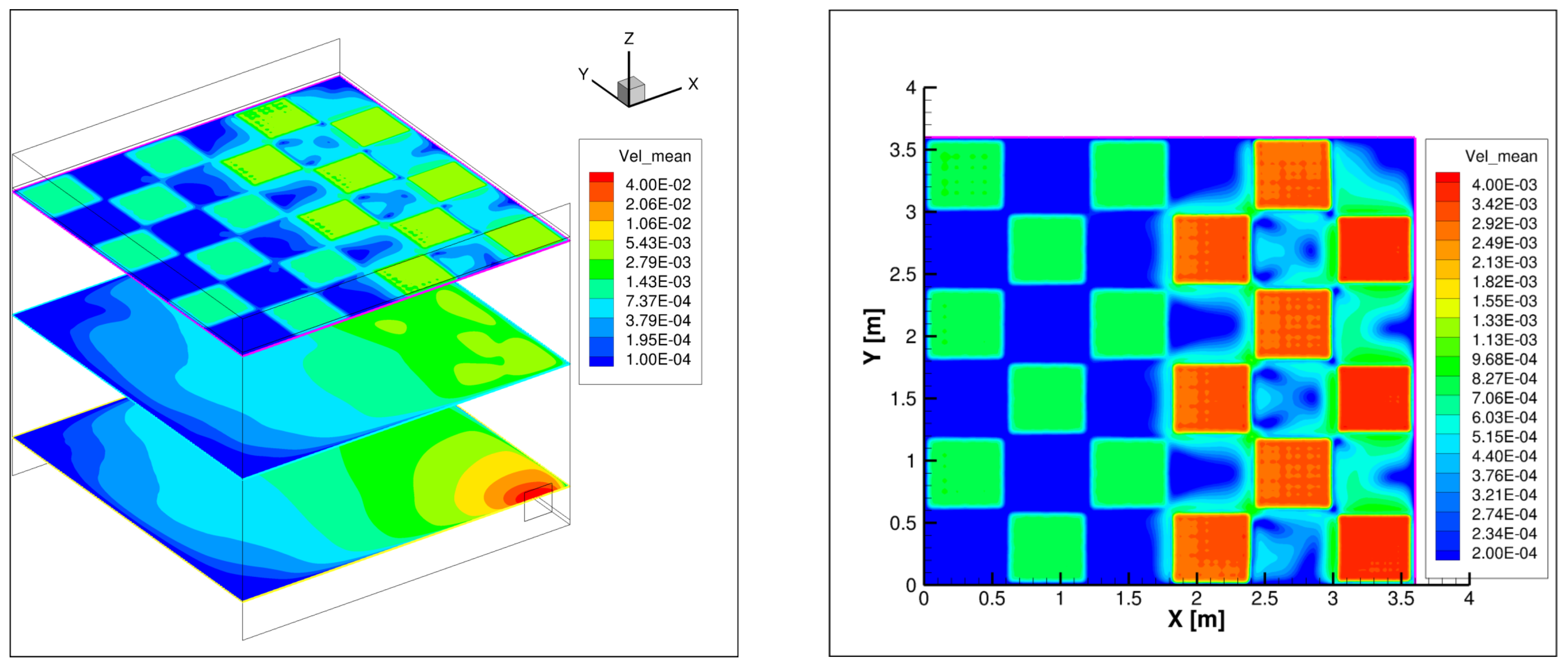
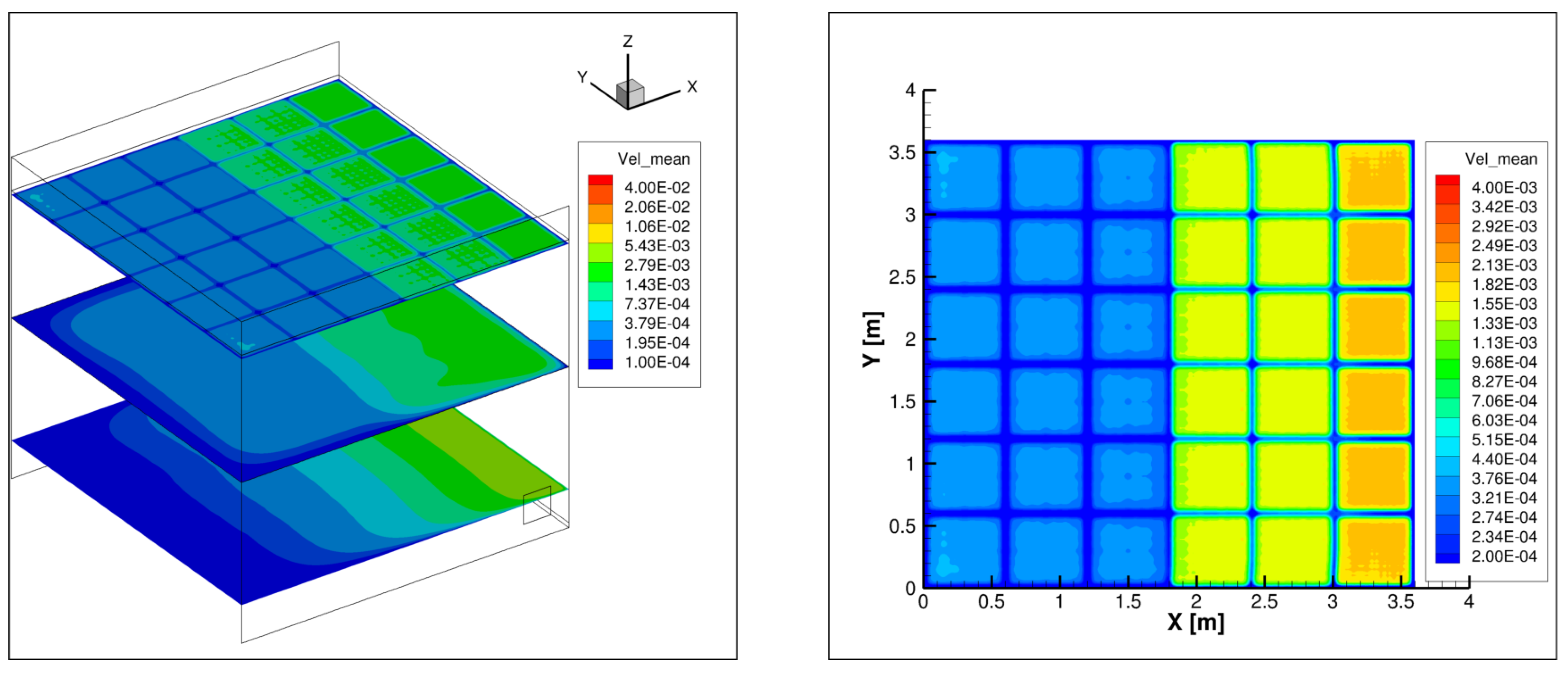
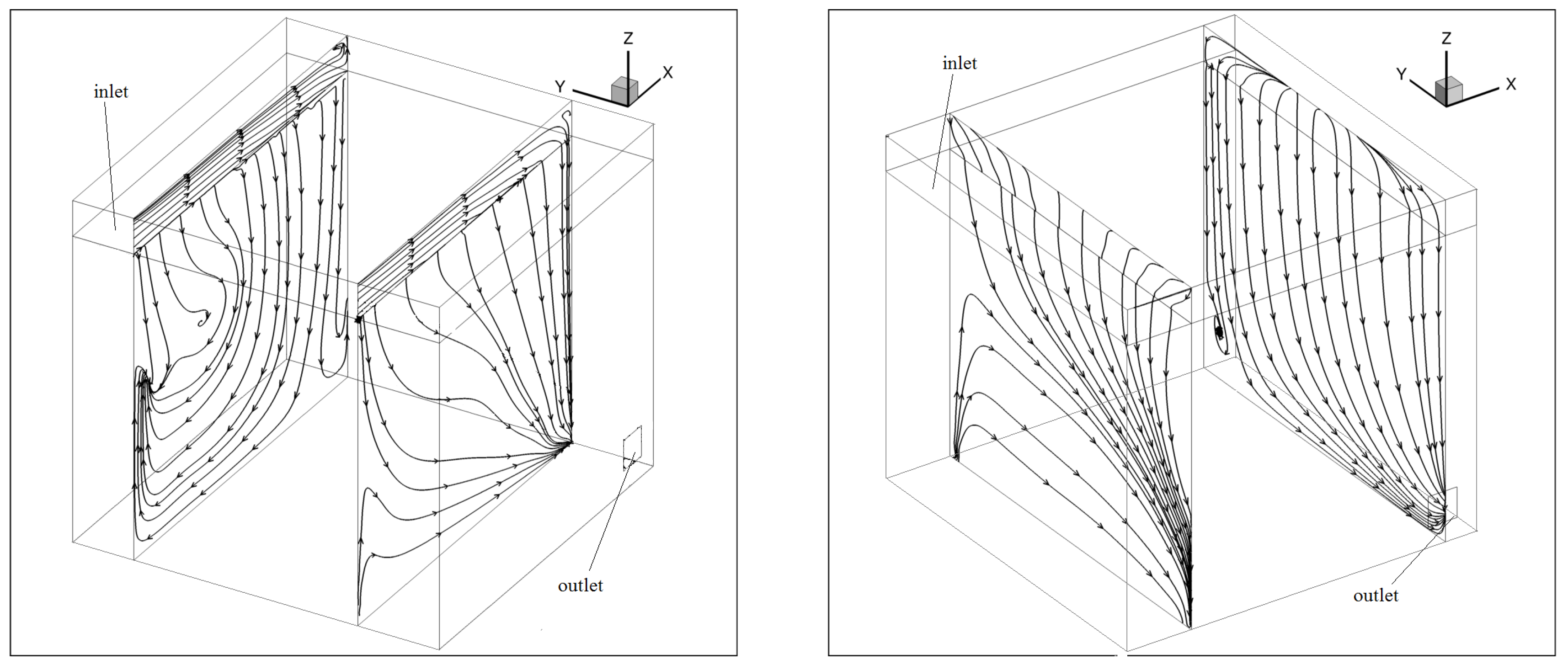
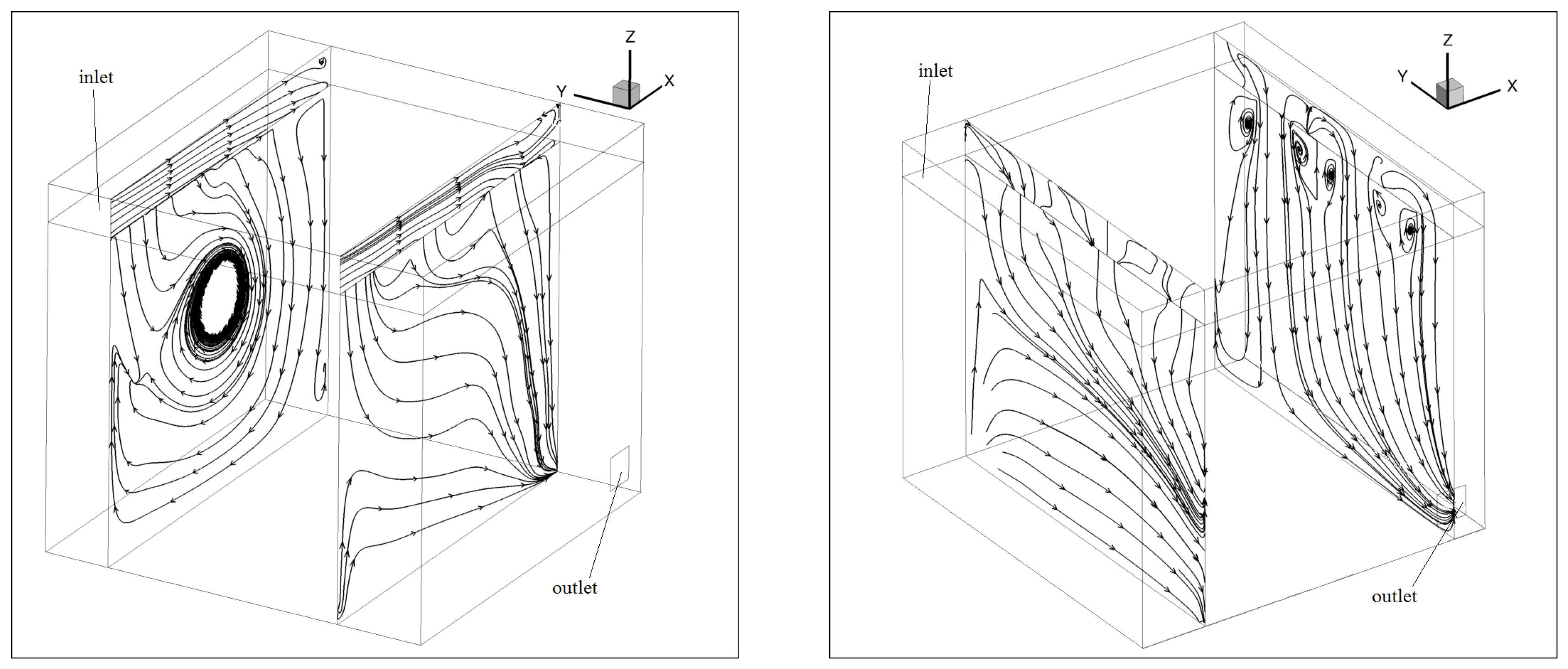
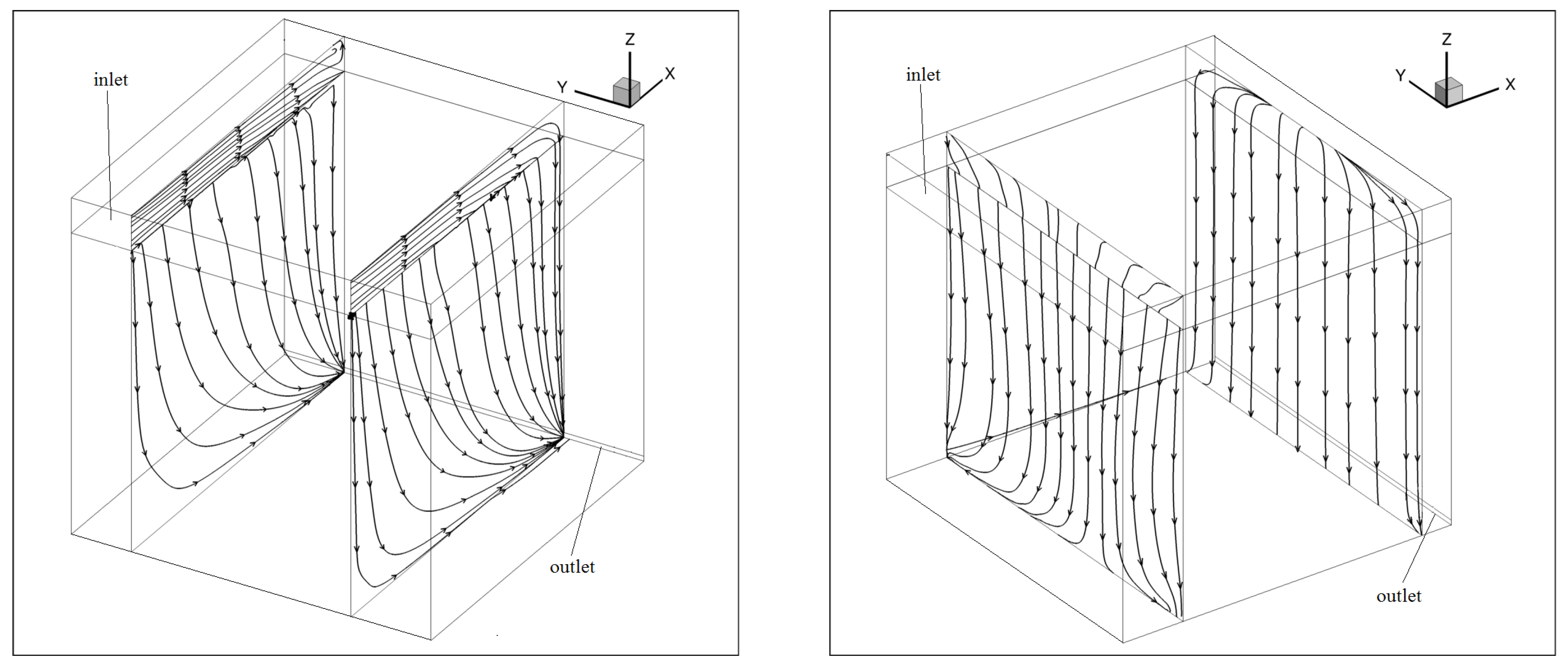
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhan, J.; Liu, W.; Wu, F.; Li, Z.; Wang, C. Life cycle energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions of urban residential buildings in Guangzhou city. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 194, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Gou, Z.; Lau, S.S.Y. Cost-effectiveness of active and passive design strategies for existing building retrofits in tropical climate: Case study of a zero energy building. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 183, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Yoon, N.; Tong, Z.; Chen, Y.; Lv, Y.; Ærenlund, T.; Benner, J. Diffuse ceiling ventilation for buildings: A review of fundamental theories and research methodologies. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 211, 1600–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yu, T.; Heiselberg, P.K.; Pomianowski, M.Z.; Nielsen, P.V. Diffuse Ceiling Ventilation-Design Guide; Department of Civil Engineering, Aalborg University: Aalborg, Denmark, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Van Wagenberg, A.V.; Smolders, M. Contaminant and heat removal effectiveness of three ventilation systems in nursery rooms for pigs. Trans. ASAE 2002, 45, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, P.; van Oeffelen, E.C.; Knoll, B. Diffuse ceiling ventilation, a new concept for healthy and productive classrooms. In Proceedings of the Indoor Air 2008, Copenhagen, Denmark, 17–22 August 2008; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, S.; Christensen, N.; Heinsen, C.; Hansen, A. Investigation of the displacement effect of a diffuse ceiling ventilation system. Energy Build. 2014, 85, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Hviid, C.; Yang, H. Performance analysis of a new design of office diffuse ceiling ventilation system. Energy Build. 2013, 59, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hviid, C.A.; Svendsen, S. Experimental study of perforated suspended ceilings as diffuse ventilation air inlets. Energy Build. 2013, 56, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Heiselberg, P.K.; Pomianowski, M.; Yu, T.; Jensen, R.L. Experimental study of diffuse ceiling ventilation coupled with a thermally activated building construction in an office room. Energy Build. 2015, 105, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikeska, T.; Fan, J. Full scale measurements and CFD simulations of diffuse ceiling inlet for ventilation and cooling of densely occupied rooms. Energy Build. 2015, 107, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Heiselberg, P.; Chen, Q.; Pomianowski, M. Numerical analysis of diffuse ceiling ventilation and its integration with a radiant ceiling system. Build. Simul. 2017, 10, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocente, A.; Grynning, S.; Mathisen, H.M.; Goia, F. Computational fluid dynamics study of a diffuse ceiling ventilation system through perforated sound absorbing ceiling panels. In Proceedings of the Roomvent & Ventilation 2018, Espoo, Finland, 2–5 June 2018; pp. 899–904. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 15251:2007. Indoor Environmental Input Parameters for Design and Assessment of Energy Performance of Buildings Addressing Indoor Air Quality, Thermal Environment, Lighting and Acoustics. 2007. Available online: https://shop.bsigroup.com/ProductDetail/?pid=000000000030133865 (accessed on 17 April 2020).
- Nocente, A.; Goia, F.; Grynning, S. Numerical investigation of a diffuse ventilation ceiling system for buildings with natural and hybrid ventilation. In Proceedings of the 7th International Building Physics Conference, Syracuse, NY, USA, 23–26 September 2018; pp. 859–864. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Heiselberg, P. Diffuse ceiling ventilation. Rehva J. 2019, 56, 78–82. [Google Scholar]
- Fluent, A. 19.2 Theory Guide; ANSYS: Canonsburg, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Vilje. Available online: https://www.hpc.ntnu.no/display/hpc/Vilje (accessed on 17 April 2020).
- ISO 7730:2005. Ergonomics of the Thermal Environment-Analytical Determination and Interpretation of Thermal Comfort Using Calculation of the PMV and PPD Indices and Local Thermal Comfort Criteria; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]

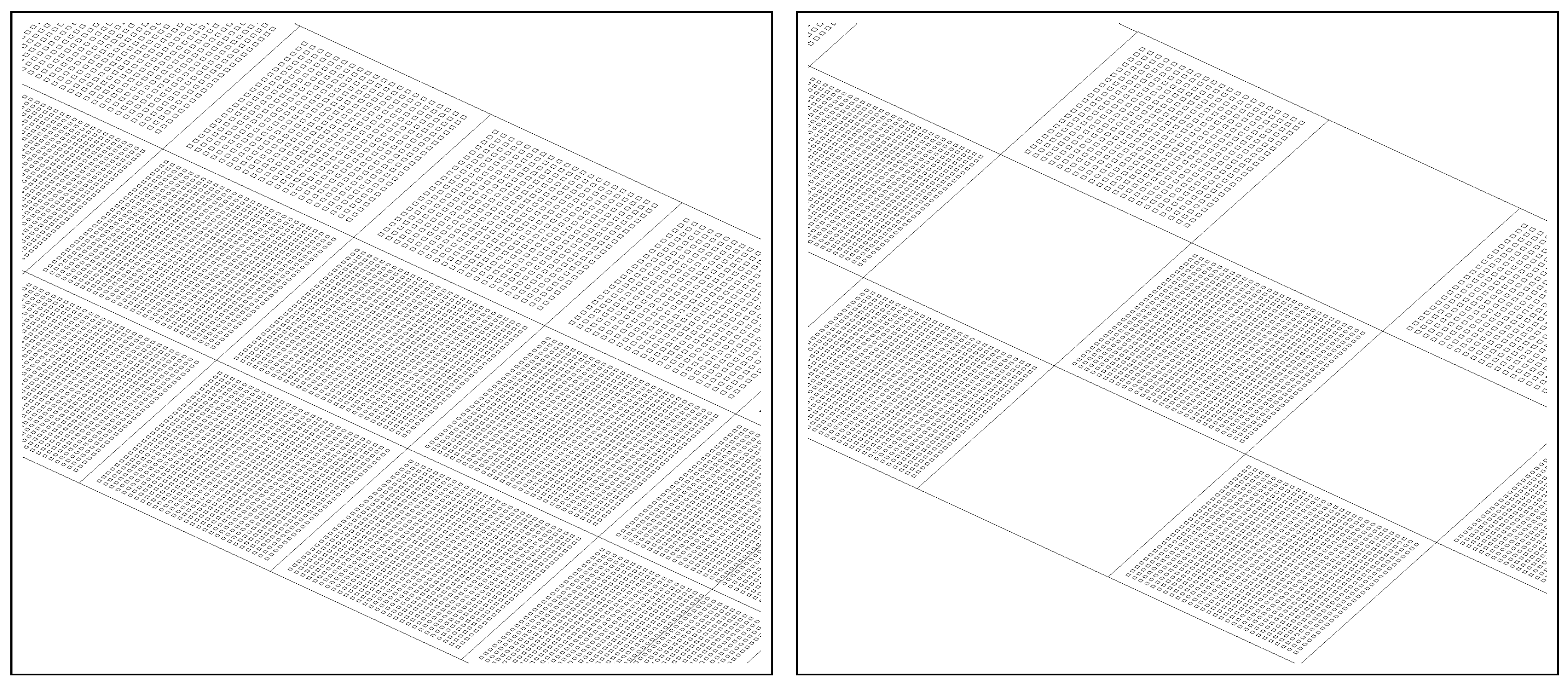
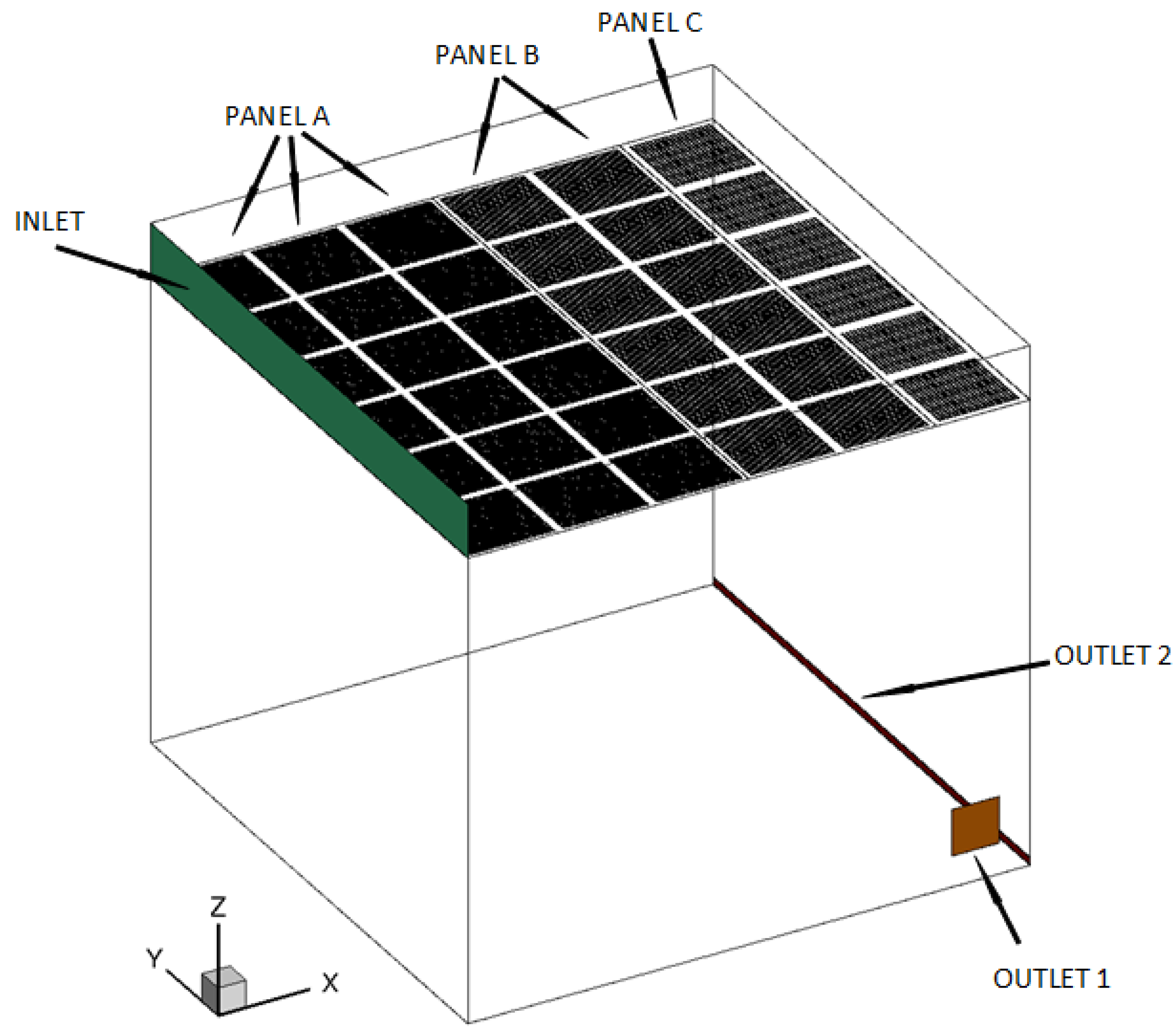


| Panel | Perforation Size (mm) | Perforation Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| A | 3 × 3 | 11 |
| B | 9 × 9 | 18 |
| C | 12 × 12 | 18 |
| Case | Panel A | Panel B | Panel C | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| max (m/s) | min (m/s) | max (m/s) | min (m/s) | max (m/s) | min (m/s) | |
| Case 1 (6 × A) | 0.0046 | 0.0029 | ||||
| Case 2 (6 × B) | 0.005 | <0.001 | ||||
| Case 3 (6 × C) | 0.0052 | <0.001 | ||||
| Case 4 (3 × A + 2 × B + 1 × C) | 0.0032 | 0.0013 | 0.0035 | 0.0018 | 0.002 | 0.0018 |
| Case 5 (2 × A + 2 × B + 2 × C) | 0.0039 | 0.0017 | 0.0044 | 0.0021 | 0.0023 | 0.0017 |
| Configuration Outlet 1 | Configuration Outlet 1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous Distribution | Chessboard Distribution | ||||||
| Panels | A | B | C | Panels | A | B | C |
| Average z velocity (m/s) | 0.0025 | 0.0064 | 0.0077 | Average z velocity (m/s) | 0.0059 | 0.0013 | 0.0014 |
| Mass flow rate (full surface avg) (kg/s) | 0.0023 | 0.006 | 0.0037 | Mass flow rate (full surface avg) (kg/s) | 0.0026 | 0.0059 | 0.0033 |
| Pressure drop (Pa) | 0.01 | Pressure drop (Pa) | 0.01 | ||||
| Max velocity (m/S) | 0.13 (at the outlet) | Max velocity (m/S) | 0.13 (at the outlet) | ||||
| Outlet Configuration 2 | Outlet Configuration 2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous Distribution | Chessboard Distribution | ||||||
| Panels | A | B | C | Panels | A | B | C |
| Average z velocity (m/s) | 0.0025 | 0.0064 | 0.0077 | Average z velocity (m/s) | 0.0059 | 0.0013 | 0.0014 |
| Mass flow rate (full surface avg) (kg/s) | 0.0022 | 0.006 | 0.0036 | Mass flow rate (full surface avg) (kg/s) | 0.0026 | 0.0059 | 0.0033 |
| Pressure drop (Pa) | 0.0034 | Pressure drop (Pa) | 0.0034 | ||||
| Max velocity (m/S) | 0.063 (at the outlet) | Max velocity (m/S) | 0.063 (at the outlet) | ||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nocente, A.; Arslan, T.; Grynning, S.; Goia, F. CFD Study of Diffuse Ceiling Ventilation through Perforated Ceiling Panels. Energies 2020, 13, 1995. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13081995
Nocente A, Arslan T, Grynning S, Goia F. CFD Study of Diffuse Ceiling Ventilation through Perforated Ceiling Panels. Energies. 2020; 13(8):1995. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13081995
Chicago/Turabian StyleNocente, Alessandro, Tufan Arslan, Steinar Grynning, and Francesco Goia. 2020. "CFD Study of Diffuse Ceiling Ventilation through Perforated Ceiling Panels" Energies 13, no. 8: 1995. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13081995
APA StyleNocente, A., Arslan, T., Grynning, S., & Goia, F. (2020). CFD Study of Diffuse Ceiling Ventilation through Perforated Ceiling Panels. Energies, 13(8), 1995. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13081995





