Step-Up Series Resonant DC–DC Converter with Bidirectional-Switch-Based Boost Rectifier for Wide Input Voltage Range Photovoltaic Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
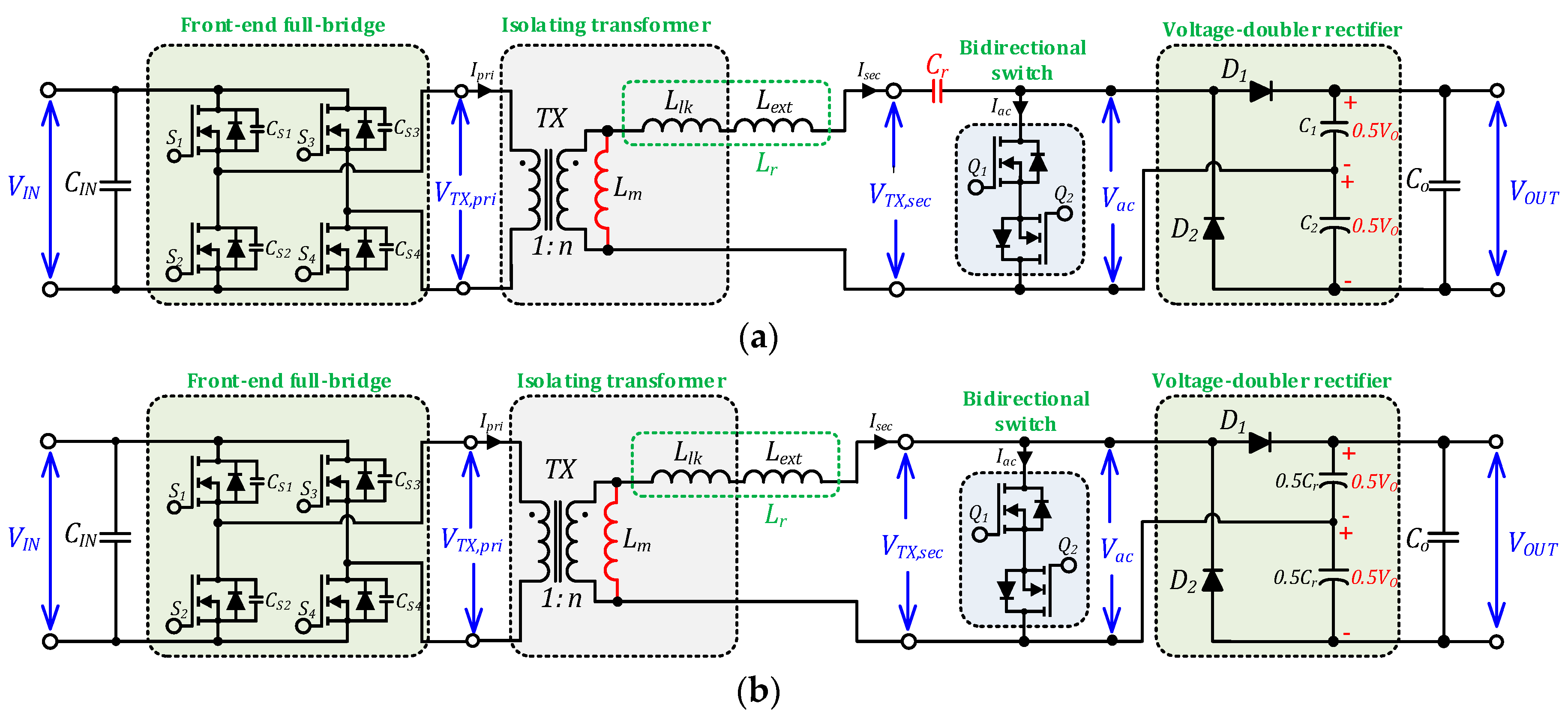
2. Topology Description and Modulation
2.1. Topology Description
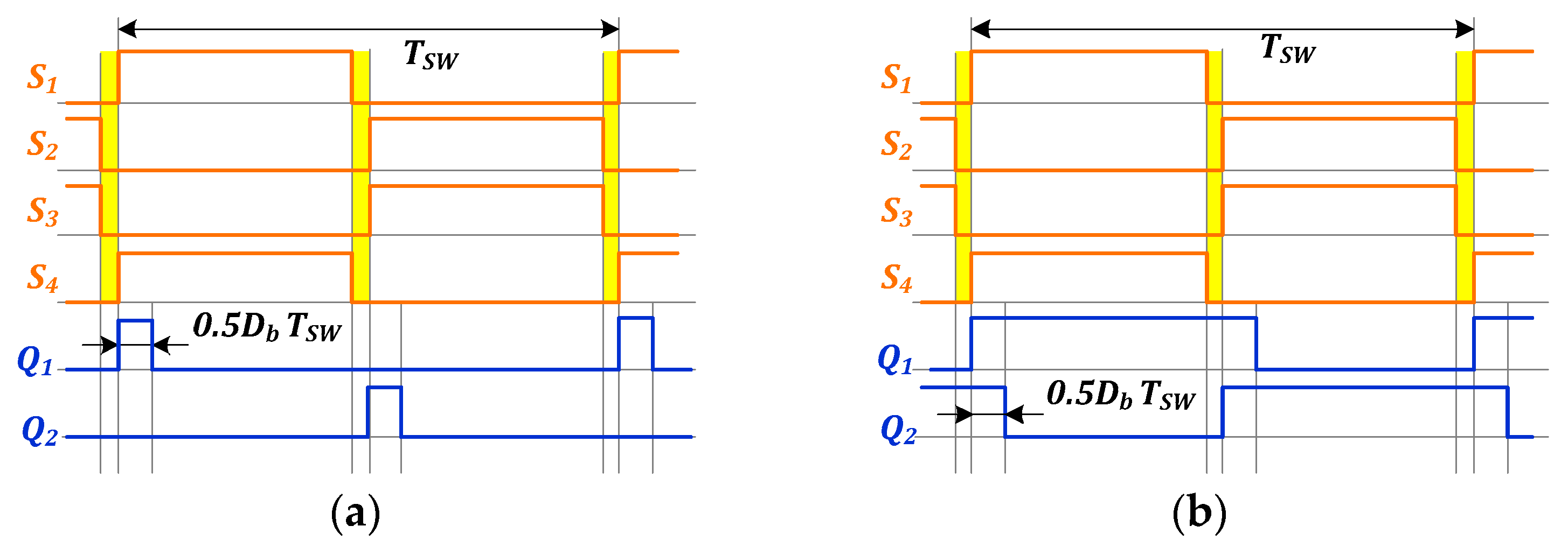
2.2. PWM Schemes for the Boost VDR
3. Steady-State Analysis and Comparison
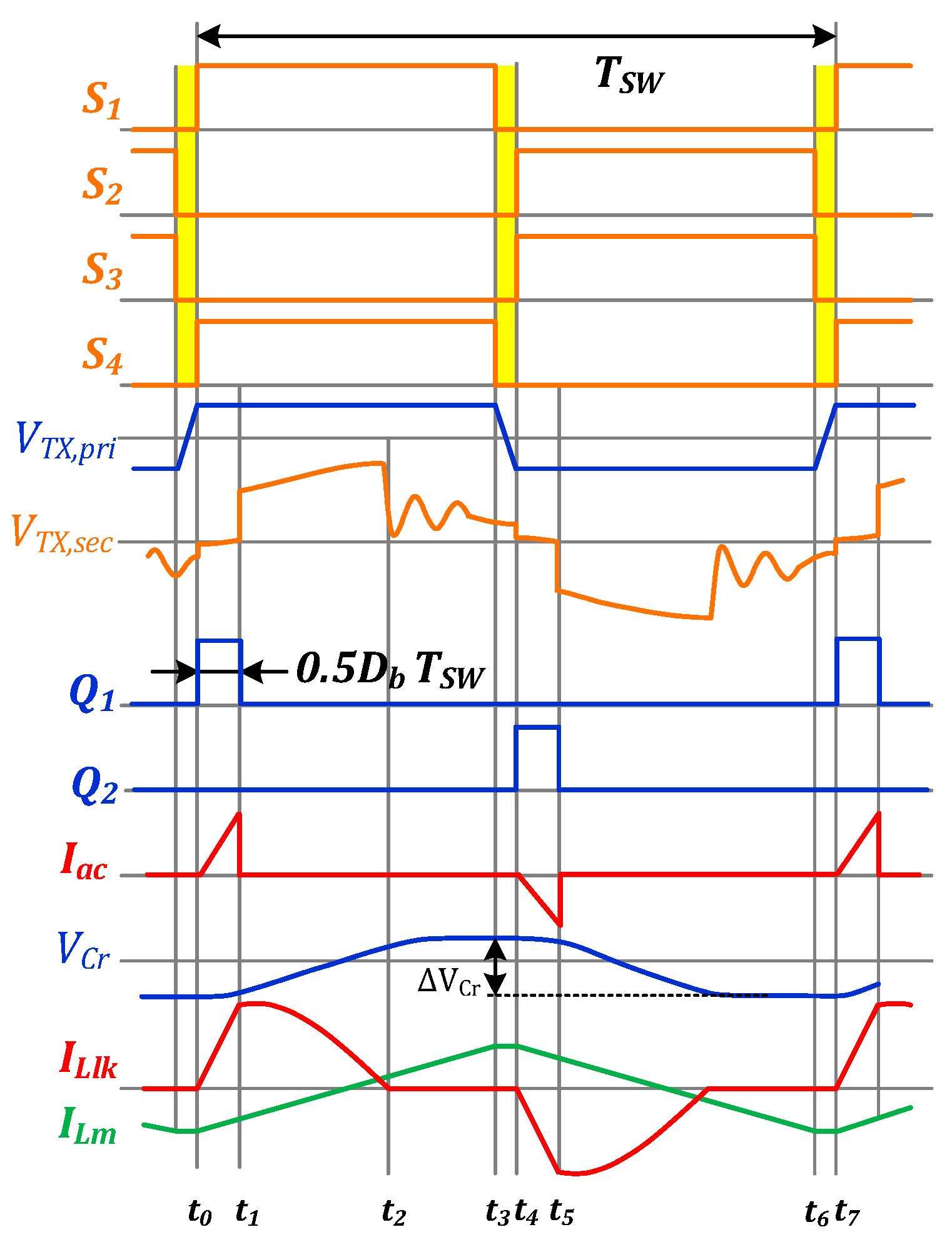
3.1. Description of the Operating Principle
- The output voltage (VOUT) is ripple-free due to the high value of the output capacitance (CO).
- The output capacitances (C1, C2, CO) are much larger than the resonant capacitance (Cr).
- The system is lossless.
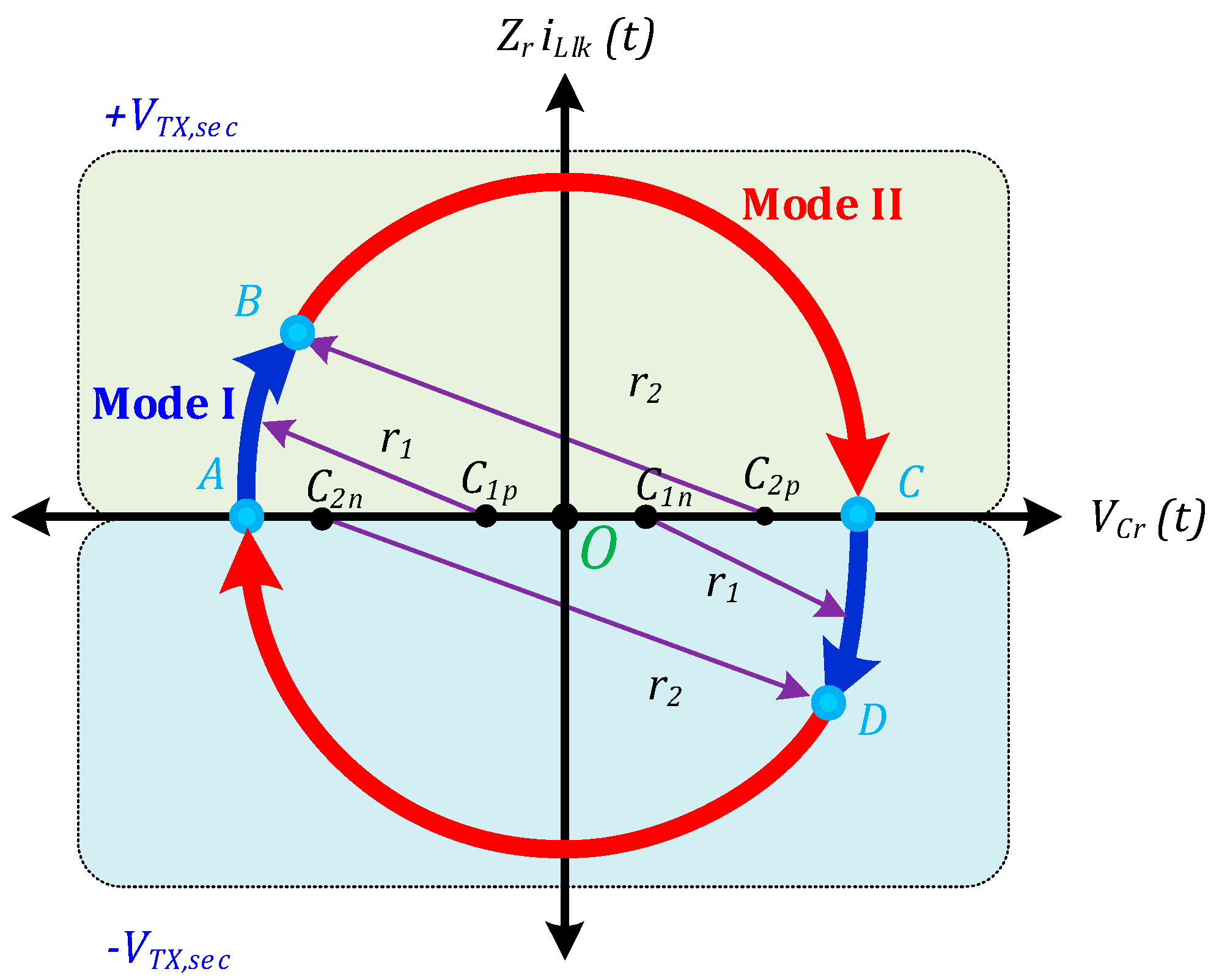
3.2. Modes of Operation
3.3. DC Voltage Gain Derivation
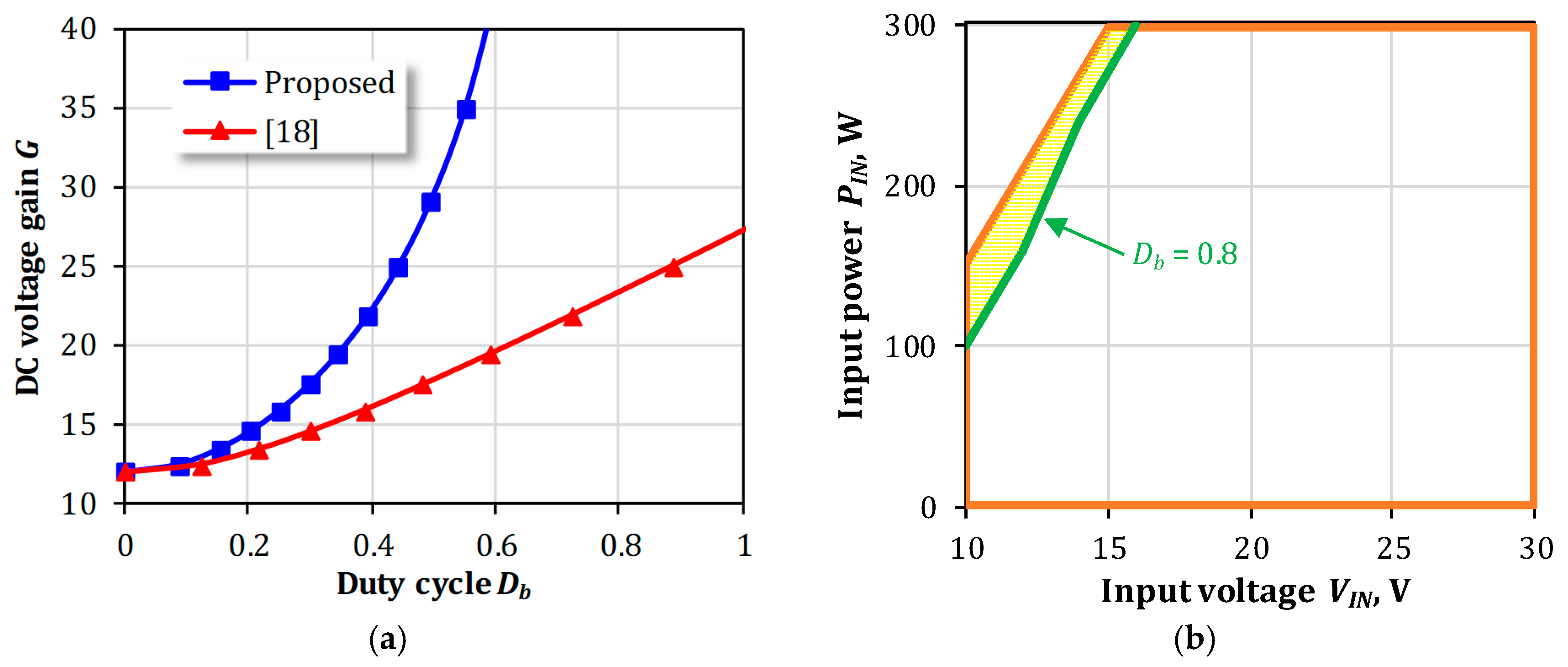
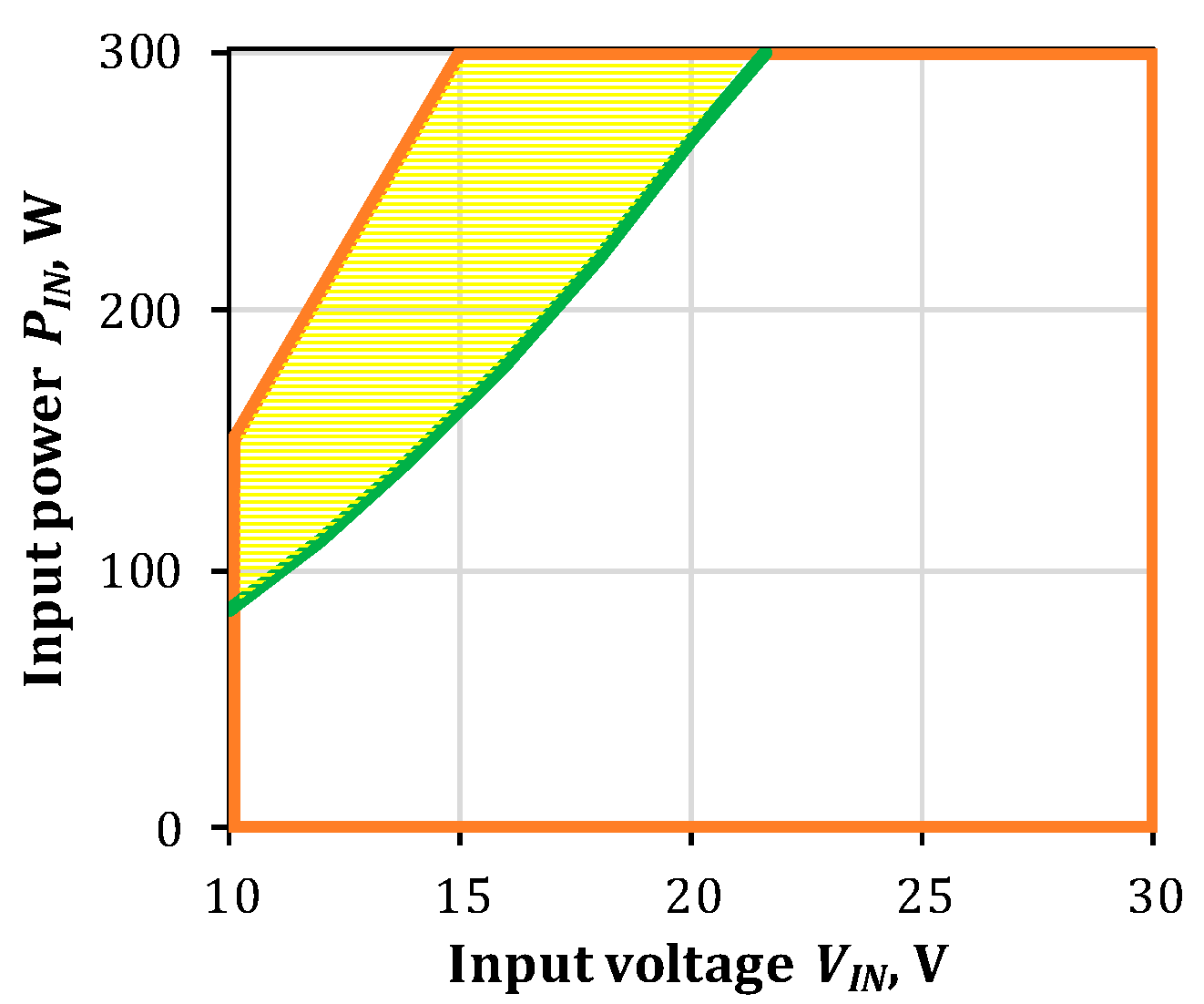
3.4. Comparison of DC Voltage Gain and Input Operating Range
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Description of the Experimental Prototype
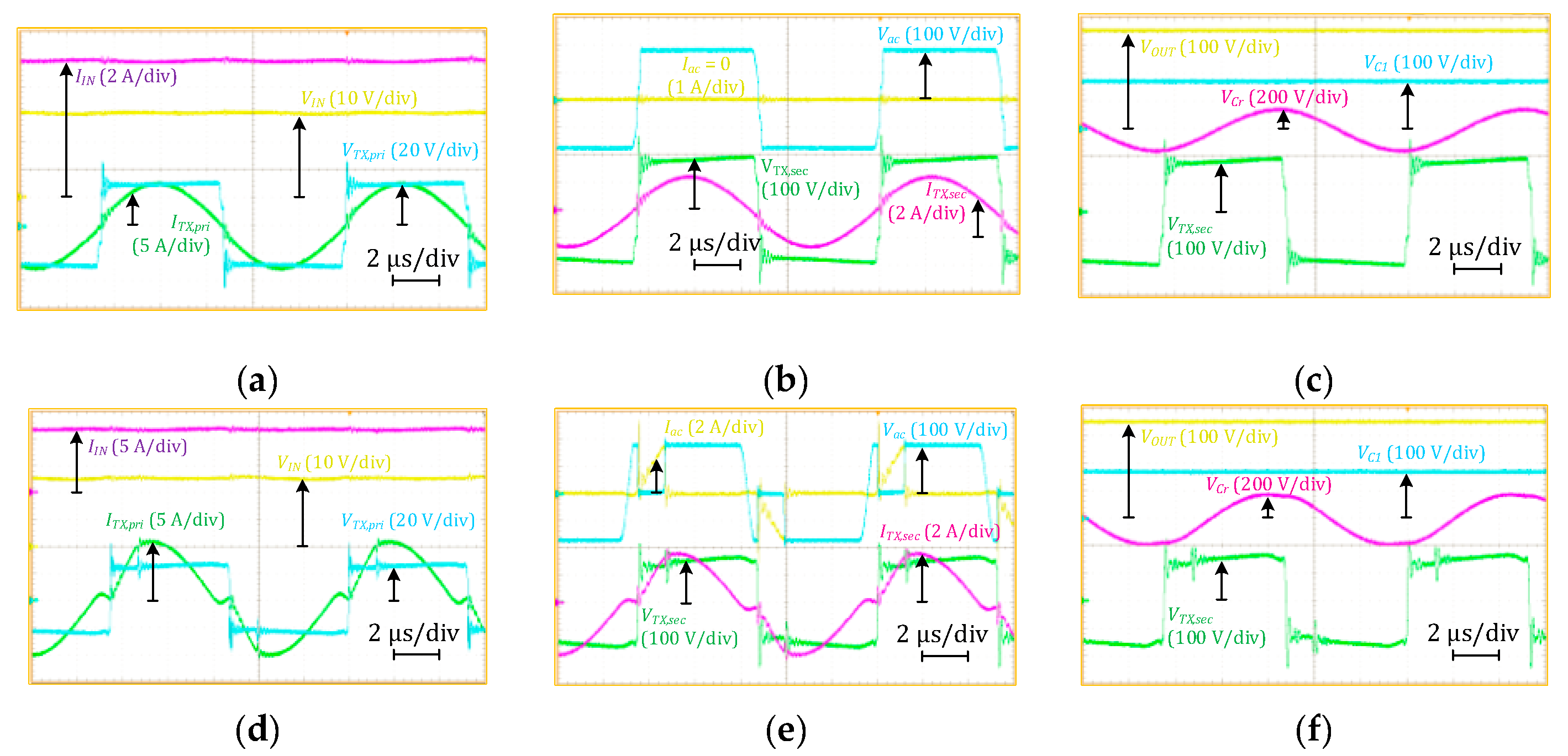
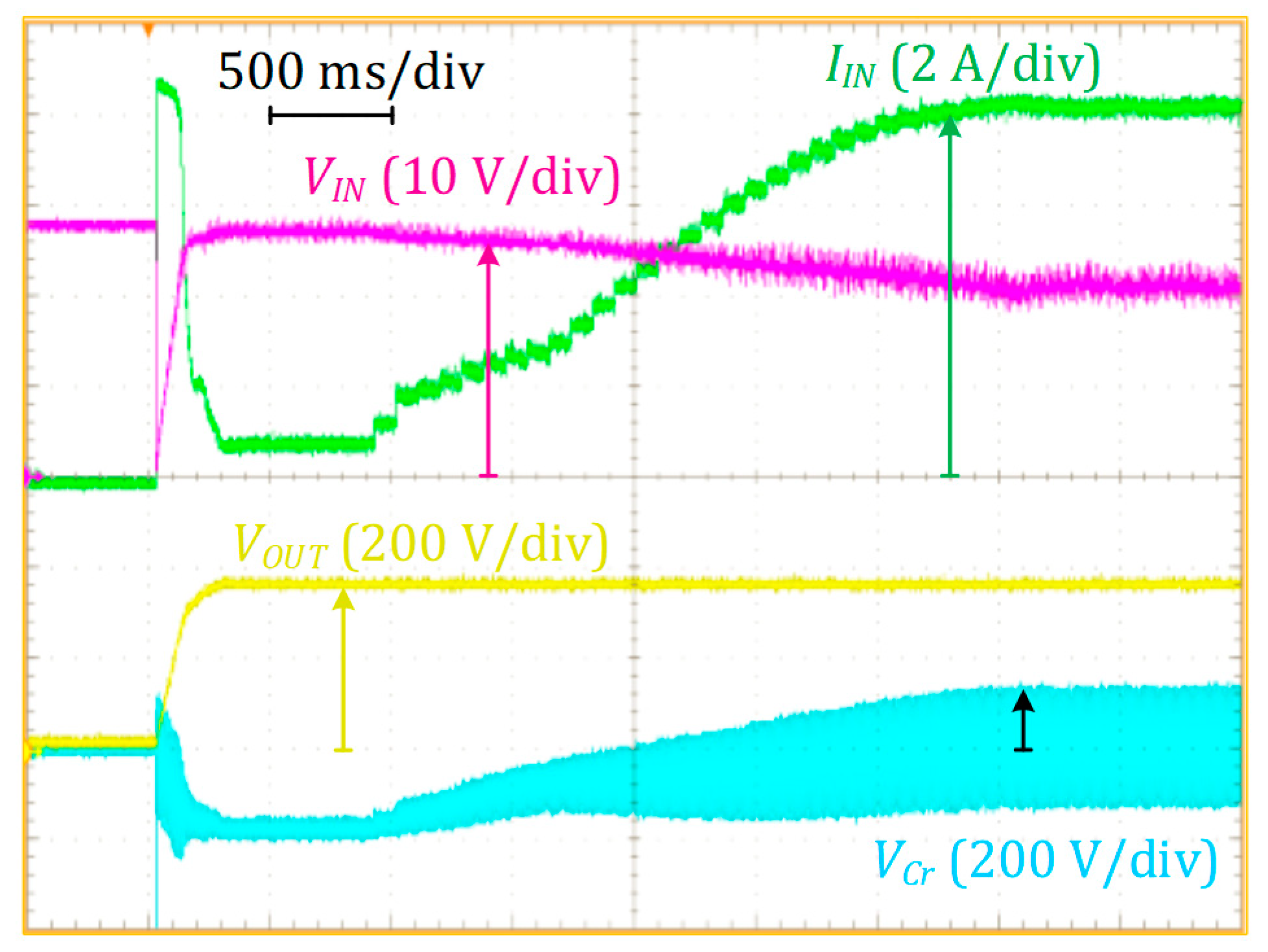
4.2. Steady-State Waveforms
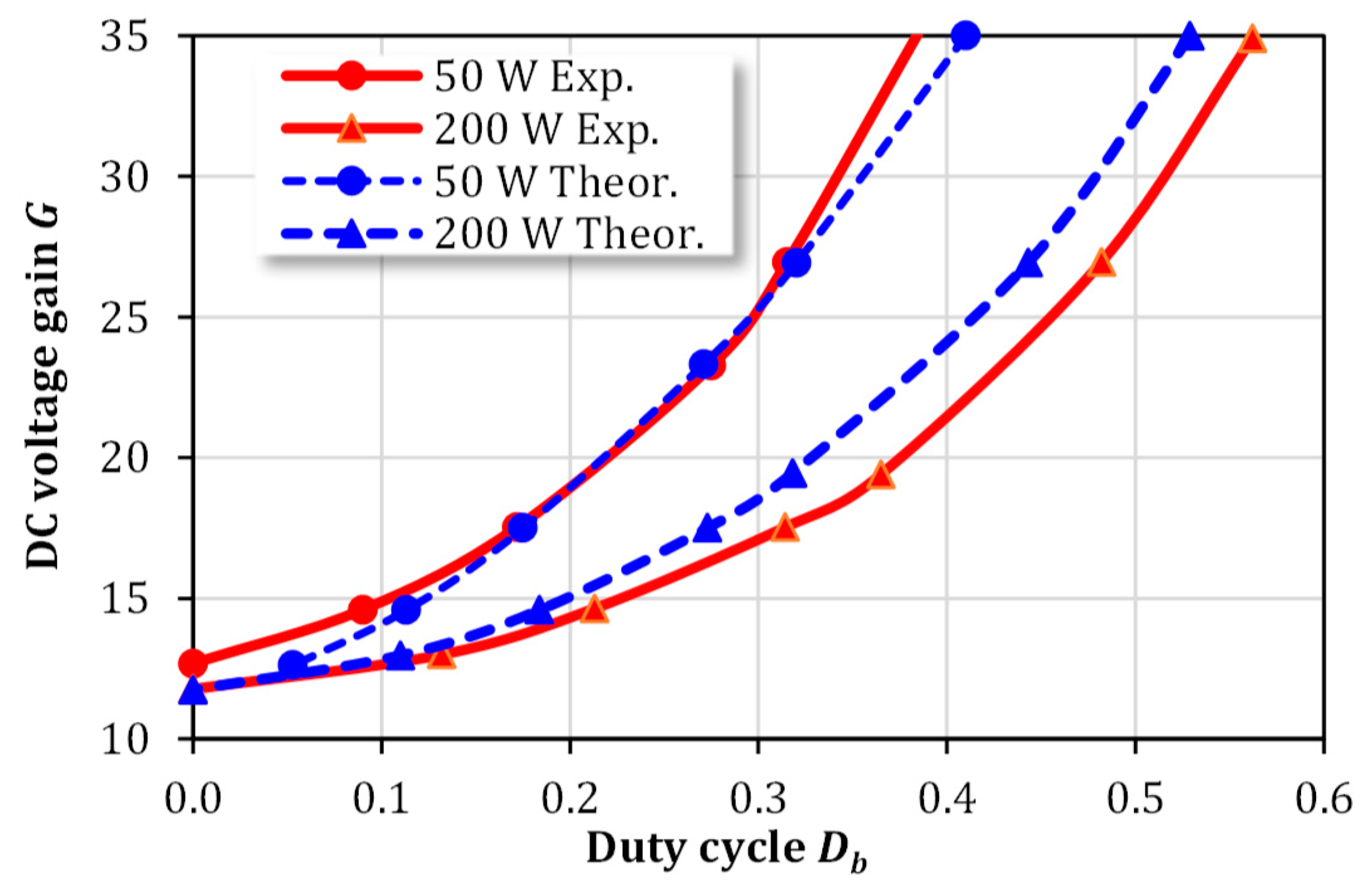
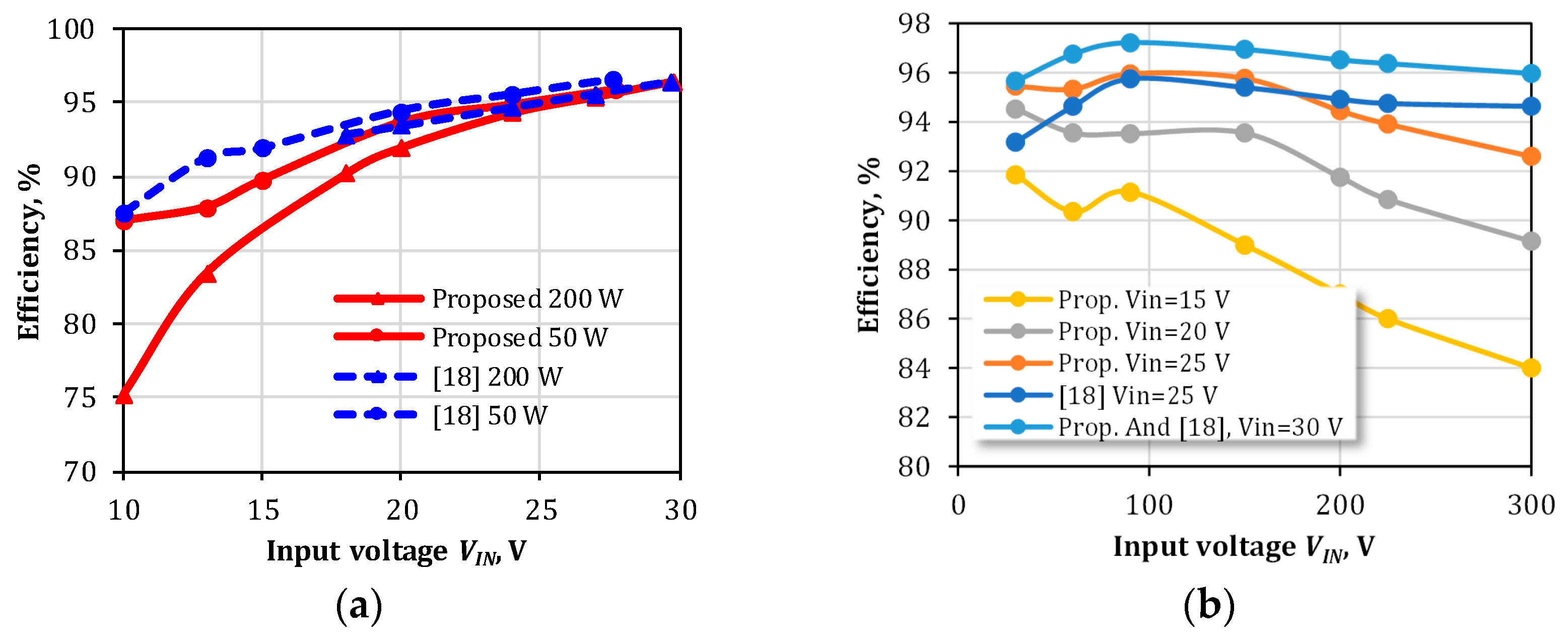
4.3. Performance Verification
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| PV | Photovoltaic |
| SRC | Series resonance converter |
| ZVS | Zero voltage switching |
| LLC | Inductor-inductor-capacitor resonant converter |
| PWM | Pulse width modulation |
| PSM | Phase-shifted modulation |
| VDR | Voltage-doubler rectifier |
| MOSFET | Metal oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor |
| Cr | Resonant capacitance (F) |
| fr | Resonant frequency (Hz) |
| Lr | Resonant inductance (H) |
| Llk | Leakage inductance (H) |
| Lext | External inductance (H) |
| VCr | The average voltage of the resonant capacitor (V) |
| VOUT | Output voltage (V) |
| Lm | The magnetizing inductance of the transformer (H) |
| n | Turns ratio of the transformer |
| Db | Cumulative boosting duty cycle |
| TSW | Switching period (s) |
| POUT | Output power (W) |
| ΔVCr | The peak-to-peak ripple of the resonant capacitor voltage |
| VIN | Input voltage (V) |
| CO | Output capacitance (F) |
| Zr | Resonant impedance (Ω) |
| ZCS | Zero current switching |
| ωr | Angular resonant frequency (rad/s) |
| β | Length of the resonant path (rad) |
| DCM | Discontinuous conduction mode |
| Gn | Normalized DC voltage gain |
| PINm | Maximum input power (W) |
| VINm | Maximum input voltage (V) |
| IINm | Maximum input current (A) |
| PIN | Input power (W) |
| MPPT | Maximum power point tracking |
| SAS | Solar array simulator |
References
- Dennis, K. Environmentally beneficial electrification: Electricity as the end-use option. Electr. J. 2015, 28, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, Z.; Zhang, B.; Halang, W.A. Power electronics converters: Past, present and future. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 2028–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batarseh, I.; Alluhaybi, K. Emerging opportunities in distributed power electronics and battery integration: Setting the stage for an energy storage revolution. IEEE Power Electron. Mag. 2020, 7, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravyts, S.; Van de Sande, W.; Vecchia, M.D.; den Broeck, G.V.; Duraij, M.; Martinez, W.; Daenen, M.; Driesen, J. Practical considerations for designing reliable DC/DC converters, applied to a BIPV case. Energies 2020, 13, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, H.; Peng, F.Z.; Yoo, D. Z-Source resonant DC-DC converter for wide input voltage and load variation. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Power Electronics Conference—ECCE ASIA, Sapporo, Japan, 21–24 June 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaBella, T.; York, B.; Hutchens, C.; Lai, J.-S. Dead time optimization through loss analysis of an active-clamp flyback converter utilizing gan devices. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Raleigh, NC, USA, 15–20 September 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, R.; Han, F.; Yang, L.; Meng, Z. Soft-Switching DC–DC converter with controllable resonant tank featuring high efficiency and wide voltage gain range. IET Power Electron. 2020, 13, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chub, A.; Vinnikov, D.; Lai, J.-S. Input voltage range extension methods in the series-resonant dc-dc converters. In Proceedings of the 15th Brazilian Power Electronics Conference and 5th IEEE Southern Power Electronics Conference (COBEP/SPEC’2019), Santos, Brazil, 1–4 December 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-W.; Park, M.-H.; Han, J.-K.; Lee, M.; Lai, J.-S. PWM resonant converter with asymmetric modulation for ZVS active voltage doubler rectifier and forced half resonance in PV application. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 508–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, C.; Lee, F.C.; Li, Q. High-Efficiency high-power-density LLC converter with an integrated planar matrix transformer for high-output current applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 9072–9082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabih, A.; Ahmed, M.; Li, Q.; Lee, F.C. Transient control and soft start-up for 1 MHz LLC converter with wide input voltage range using simplified optimal trajectory control. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandelac, J.-P.; Ziogas, P.D. A DC to DC PWM series resonant converter operated at resonant frequency. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1988, 35, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.-H.; Kwon, B.-H. Zero-Voltage- and zero-current-switching full-bridge converter with secondary resonance. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlevani, M.; Pan, S.; Jain, P. A hybrid phase-shift modulation technique for DC/DC converters with a wide range of operating conditions. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 7498–7510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, J.; Qin, X.; Mu, T.; Xing, Y. Secondary-Side-Regulated soft-switching full-bridge three-port converter based on bridgeless boost rectifier and bidirectional converter for multiple energy interface. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 31, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.; Montes, O.A.; Junyent-Ferre, A.; Kim, M. High step-up resonant DC/DC converter with balanced capacitor voltage for distributed generation systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 4375–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, C.-W.; Lai, J.-S. A high-efficiency active-boost-rectifier-based converter with a novel double-pulse duty cycle modulation for PV to DC microgrid applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 7462–7473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaBella, T.; Yu, W.; Lai, J.-S.; Senesky, M.; Anderson, D. A Bidirectional-Switch-Based wide-input range high-efficiency isolated resonant converter for photovoltaic applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 3473–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, L.; Born, R.; Lai, J.-S. A high-efficiency hybrid resonant converter with wide-input regulation for photovoltaic applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 3684–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinnikov, D.; Chub, A.; Liivik, E.; Roasto, I. High-Performance quasi-z-source series resonant DC–DC converter for photovoltaic module-level power electronics applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 3634–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chub, A.; Zinchenko, D.; Vinnikov, D.; Blinov, A. Three-Port flyback converter for photovoltaic module integration in bipolar dc microgrids. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Buenos Aires, Argentina, 26–28 February 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameter | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Input voltage range | VIN | 10:30 V |
| Input-side capacitor | CIN | 150 µF |
| Transformer leakage inductance | Llk | 4 µH |
| Transformer magnetizing inductance | Lm | 1.3 mH |
| External inductor | Lext | 92.5 µH |
| Resonance capacitor | Cr | 30 nF, metal film |
| Voltage-doubler capacitors | C1, C2 | 150 µF, electrolytic |
| Output-side capacitors | Co | 150 µF |
| Output voltage | VOUT | 350 V |
| Switching frequency | Fs | 95 kHz |
| Components | Symbol | Part Number |
| Primary-side switches | S1, S2, S3, S4 | FDMS86180 |
| Bidirectional switch | Q1, Q2 | SCT2120AF |
| Output-side diodes | D1, D2 | C3D02060E |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bakeer, A.; Chub, A.; Vinnikov, D. Step-Up Series Resonant DC–DC Converter with Bidirectional-Switch-Based Boost Rectifier for Wide Input Voltage Range Photovoltaic Applications. Energies 2020, 13, 3747. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13143747
Bakeer A, Chub A, Vinnikov D. Step-Up Series Resonant DC–DC Converter with Bidirectional-Switch-Based Boost Rectifier for Wide Input Voltage Range Photovoltaic Applications. Energies. 2020; 13(14):3747. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13143747
Chicago/Turabian StyleBakeer, Abualkasim, Andrii Chub, and Dmitri Vinnikov. 2020. "Step-Up Series Resonant DC–DC Converter with Bidirectional-Switch-Based Boost Rectifier for Wide Input Voltage Range Photovoltaic Applications" Energies 13, no. 14: 3747. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13143747
APA StyleBakeer, A., Chub, A., & Vinnikov, D. (2020). Step-Up Series Resonant DC–DC Converter with Bidirectional-Switch-Based Boost Rectifier for Wide Input Voltage Range Photovoltaic Applications. Energies, 13(14), 3747. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13143747







