Constant Output-Voltage Design for Bi-Directional Wireless Power Transfer System with Multiple Stages
Abstract
:1. Introduction
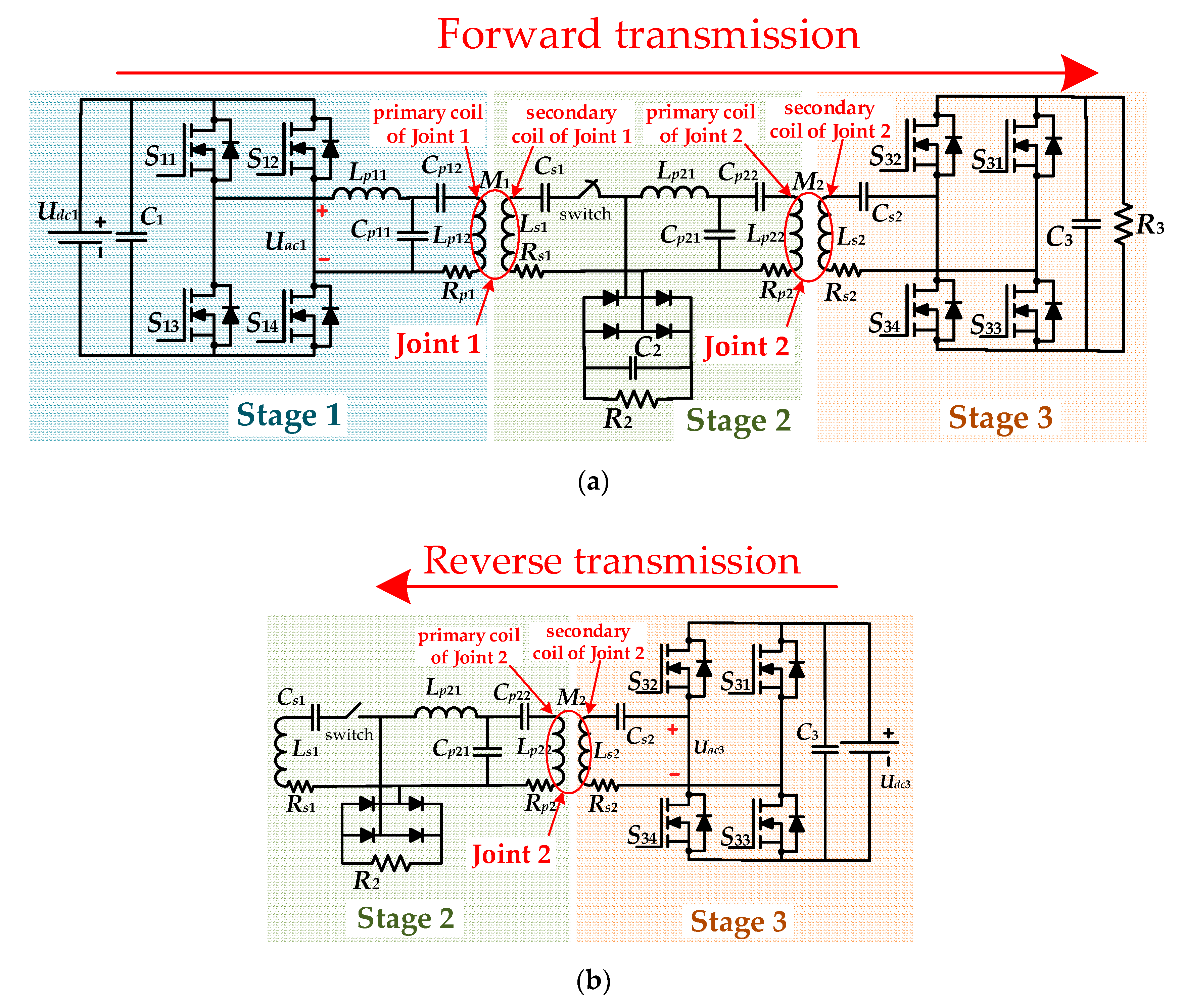
2. Proposed MB-WPT System
3. Two Operation Modes for MB-WPT System
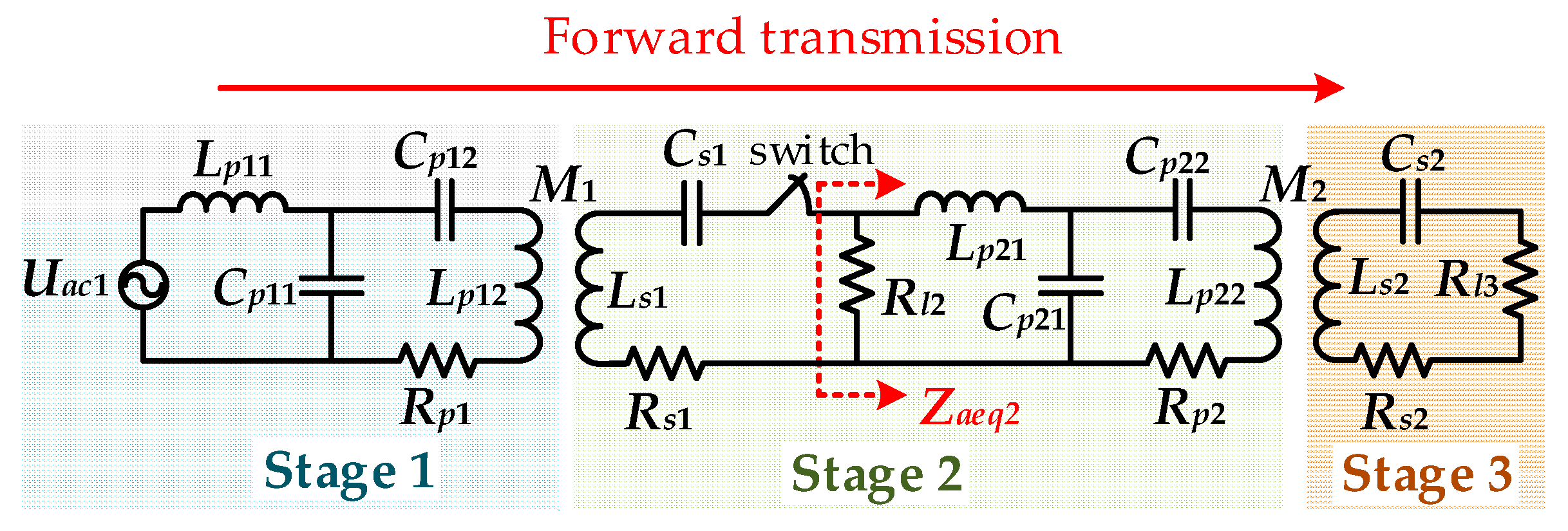
3.1. Mode A
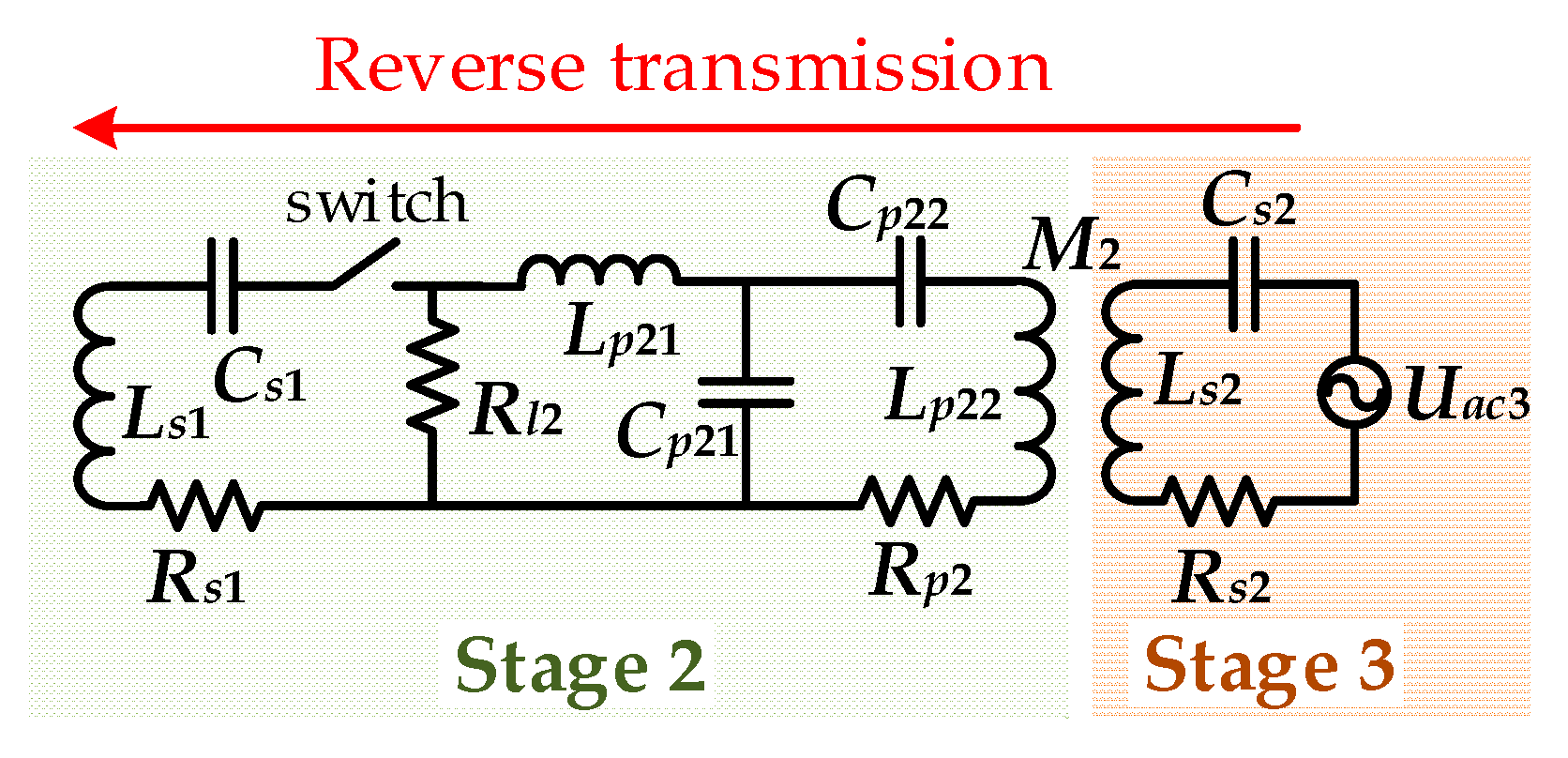
3.2. Mode B
4. Output Characteristic Analysis
4.1. Analysis of the Output Voltage
4.2. Analysis of the Efficiency
4.3. Loss Analysis of Each Stage
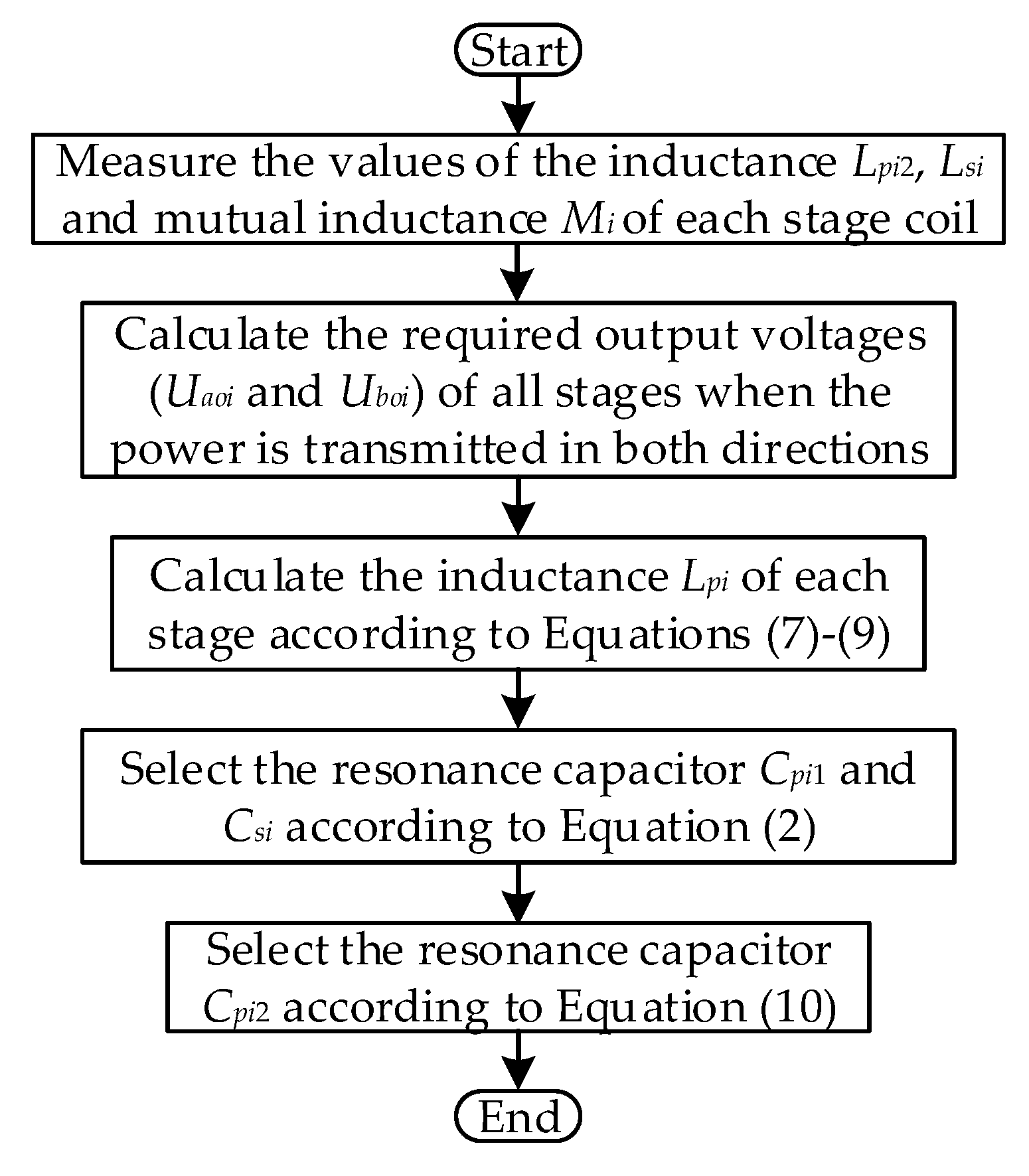
5. Parameter Design Method
6. Experimental Verification
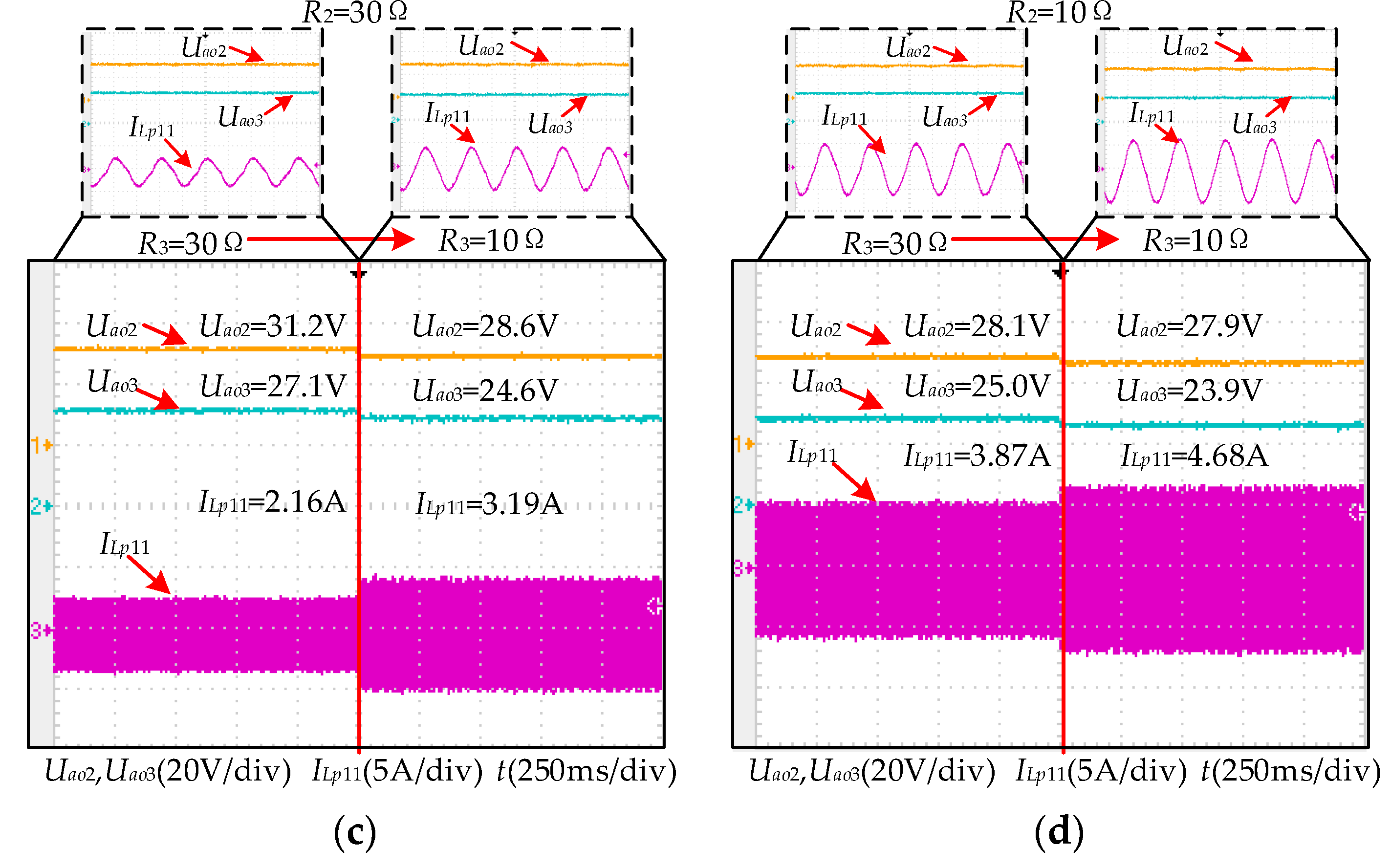
6.1. Mode A
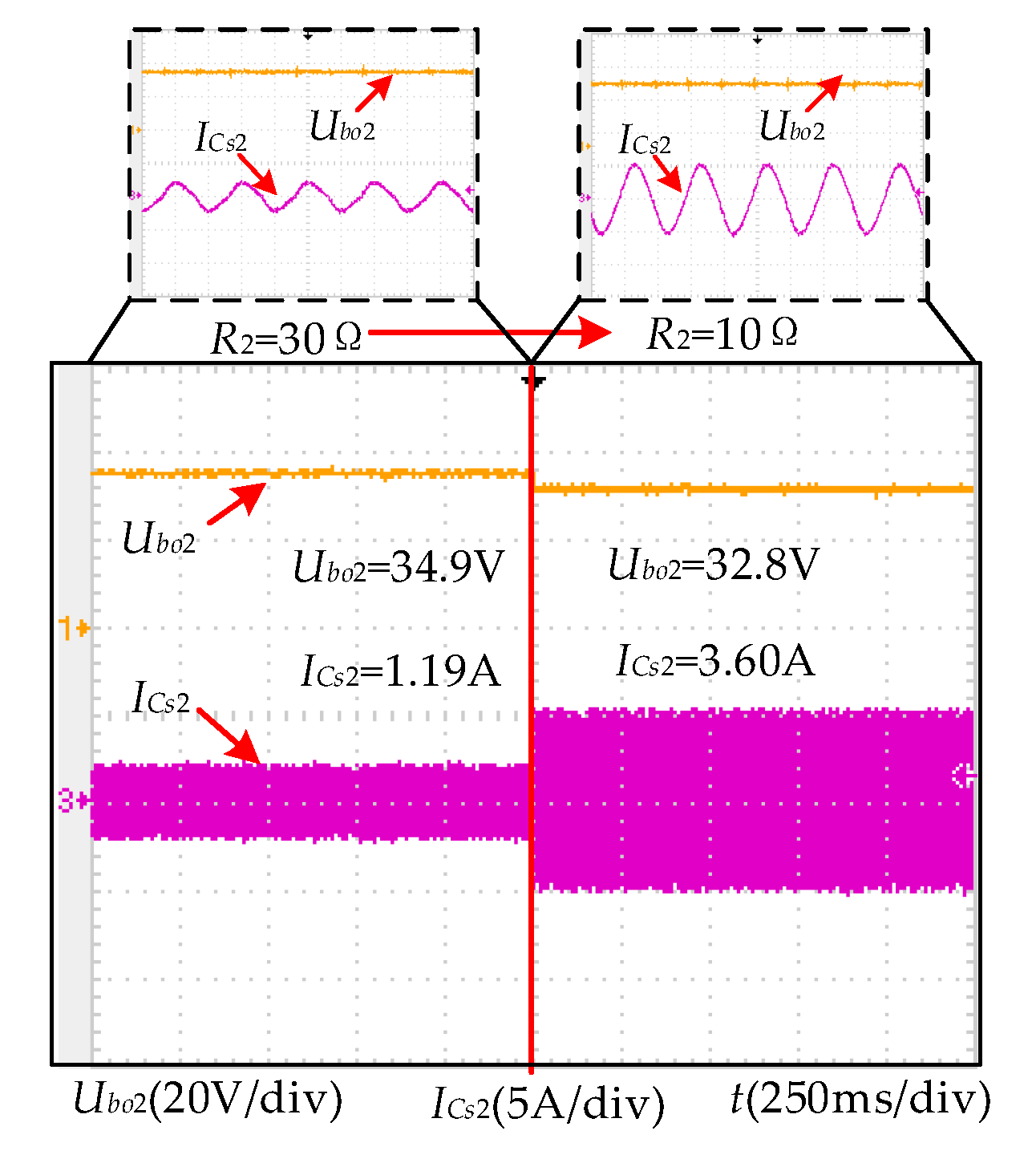
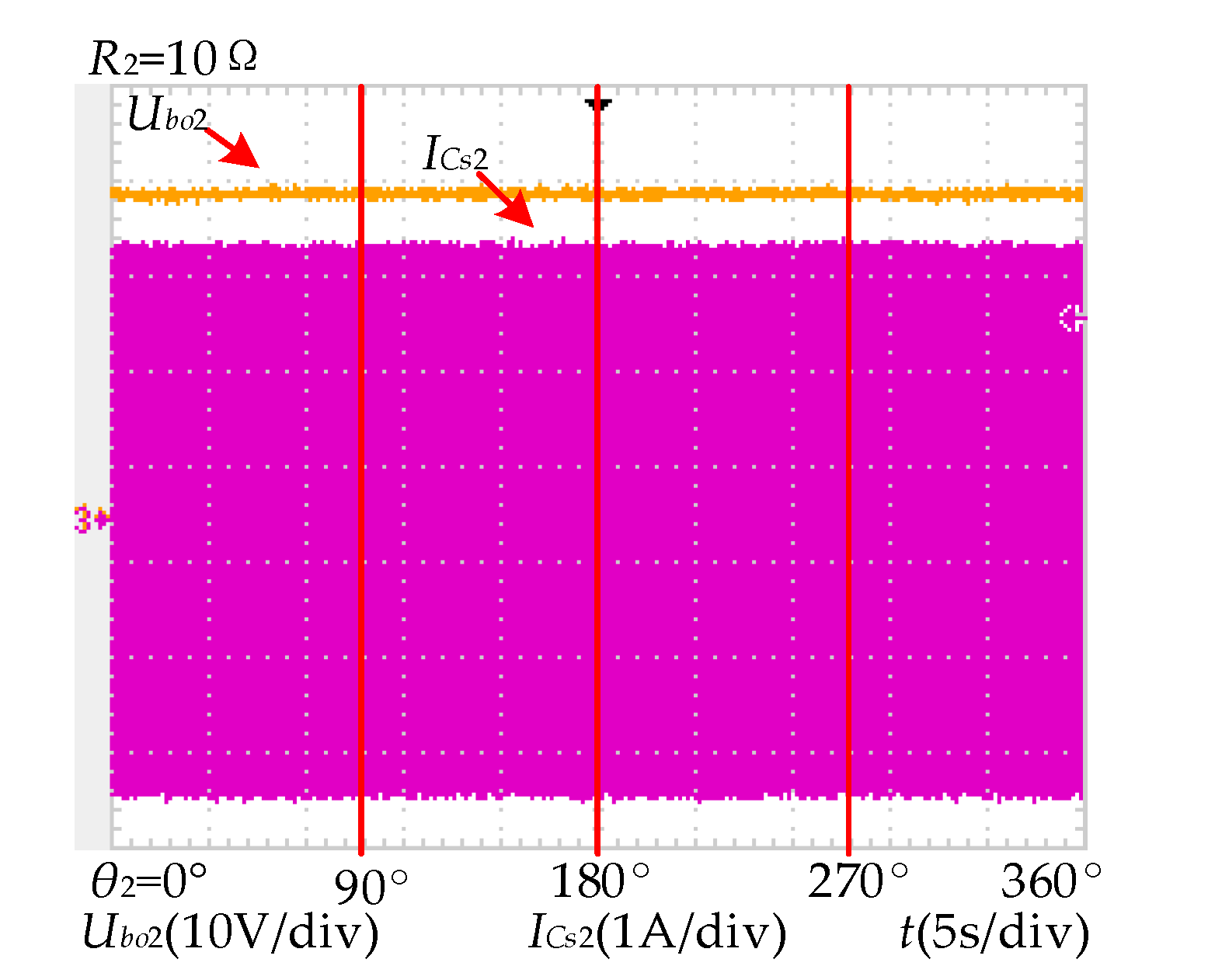
6.2. Mode B
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
| Udci | Input voltage of Stage i |
| Uaci | Output voltage of inverter in Stage i |
| Ri | Load of Stage i |
| Si1, Si2, Si3, Si4 | Driving signal of the inverter in Stage i |
| Ci | Filter capacitor of Stage i |
| Lpi2, Lsi | Primary and secondary coils of Joint i |
| Lpi1, Cpi1, Cpi2, Csi-1 | Compensation inductance and capacitances of Stage i |
| Rpi, Rsi | Resistances of the primary and secondary coils in Joint i |
| f, w | Operation frequency and angle frequency |
| Uaoi, Uboi | Output voltage when the power is transferred in both directions |
| Pout_a, Pout_b | Output power when the power is transferred in both directions |
| Mi | Mutual inductance of Joint i |
| η | The efficiency of the system |
References
- Thrimawithana, D.-J.; Madawala, U.-K. A primary side controller for inductive power transfer systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology, Vina del mar, Chile, 14–17 March 2010; pp. 661–666. [Google Scholar]
- Kissin, M.-L.-G.; Huang, C.-Y.; Covic, G.-A. Detection of the Tuned Point of a Fixed-Frequency LCL Resonant Power Supply. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2009, 24, 1140–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.-H.; Gilchrist, A.; Sealy, K. A review on inductive charging for electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the Electric Machines & Drives Conference, Niagara Falls, ON, Canada, 15–18 May 2011; pp. 143–147. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.-H.; Li, Y.-P.; Sun, Y. Load Detection Model of Voltage-Fed Inductive Power Transfer System. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 5233–5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waffenschmidt, E.; Staring, T. Limitation of inductive power transfer for consumer applications. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications, Barcelona, Spain, 8–10 September 2009; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Mur-Miranda, J.-O.; Fanti, G.; Feng, Y. Wireless power transfer using weakly coupled magnetostatic resonators. In Proceedings of the Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, Atlanta, GA, USA, 12–16 September 2010; pp. 4179–4186. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Hackworth, S.-A.; Fu, W. Relay Effect of Wireless Power Transfer Using Strongly Coupled Magnetic Resonances. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 78–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Wu, S.; Zhou, N. Flexible Design Method for Multi-Repeater Wireless Power Transfer System Based on Coupled Resonator Bandpass Filter Model. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2014, 61, 3288–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, S.-Y.-R.; Zhong, W.; Lee, C.-K. A Critical Review of Recent Progress in Mid-Range Wireless Power Transfer. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 4500–4511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phaebua, K.; Lertwiriyaprapa, T.; Chalermwisutkul, S. Area extension of a wireless battery charging system using multiple power repeater coil antennas. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Green Building and Smart Grid, Prague, Czech Republic, 27–29 June 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, K.-L.; Zhong, W.-X.; Hui, S.-Y.-R. Effects of Magnetic Coupling of Nonadjacent Resonators on Wireless Power Domino-Resonator Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 1905–1916. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, D.; Hong, S. A Study on Magnetic Field Repeater in Wireless Power Transfer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.-X.; Chi, K.-L.; Hui, S.-Y. Wireless Power Domino-Resonator Systems With Noncoaxial Axes and Circular Structures. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 4750–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lower, T.-E.; Fragar, L.; Depcynzksi, J. General Analysis on the Use of Tesla’s Resonators in Domino Forms for Wireless Power Transfer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 261–270. [Google Scholar]
- Mehdi, K.; Maysam, G. A Figure-of-Merit for Designing High-Performance Inductive Power Transmission Links. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 60, 5292–5305. [Google Scholar]
- Mehdi, K.; Uei-Ming, J.; Maysam, G. Design and Optimization of a 3-Coil Inductive Link for Efficient Wireless Power Transmission. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2011, 5, 579–591. [Google Scholar]
- Byunghun, L.; Mehdi, K.; Maysam, G. A Triple-Loop Inductive Power Transmission System for Biomedical Applications. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2016, 10, 138–148. [Google Scholar]
- Kisong, L.; Dong-Ho, C. Diversity Analysis of Multiple Transmitters in Wireless Power Transfer System. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 2946–2952. [Google Scholar]
- Weearsinghe, S.; Thrimawithana, D.-J.; Madawala, U.-K. Modeling Bidirectional Contactless Grid Interfaces With a Soft DC-Link. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 3528–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerasinghe, S.; Madawala, U.-K.; Thrimawithana, D.-J. A Matrix Converter-Based Bidirectional Contactless Grid Interface. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 1755–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namadmalan, A. Bidirectional Current-Fed Resonant Inverter for Contactless Energy Transfer Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madawala, U.-K.; Thrimawithana, D.-J. A Bidirectional Inductive Power Interface for Electric Vehicles in V2G Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 4789–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madawala, U.-K.; Thrimawithana, D.-J. Current sourced bi-directional inductive power transfer system. Power Electron. Iet 2011, 4, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B.-X.; Vilathgamuwa, D.-M.; Foo, G.-H.-B. An Efficiency Optimization Scheme for Bidirectional Inductive Power Transfer Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 6310–6319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madawala, U.-K.; Neath, M.; Thrimawithana, D.-J. A Power–Frequency Controller for Bidirectional Inductive Power Transfer Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.-A.-S.; Berzoy, A.; Mohammed, O. Predictive active power-flow control of two-way wireless power transfer system in V2G services. In Proceedings of the Power Electronics Conference, Auckland, New Zealand, 5–8 December 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Neath, M.-J.; Swain, A.-K.; Madawala, U.-K. An Optimal PID Controller for a Bidirectional Inductive Power Transfer System Using Multiobjective Genetic Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 29, 1523–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, A.-K.; Neath, M.-J.; Madawala, U.-K. A Dynamic Multivariable State-Space Model for Bidirectional Inductive Power Transfer Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 4772–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrimawithana, D.-J.; Madawala, U.-K. A Generalized Steady-State Model for Bidirectional IPT Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 4681–4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.-A.-S.; Berzoy, A.; Mohammed, O.-A. Experimental Validation of Comprehensive Steady-State Analytical Model of Bidirectional WPT System in EVs Applications. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 66, 5584–5594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miskiewicz, R.-M.; Moradewicz, A.-J.; Kazmierkowski, M.-P. Contactless battery charger with bi-directional energy transfer for plug-in vehicles with vehicle-to-grid capability. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, Gdansk, Poland, 27–30 June 2011; pp. 1969–1973. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, C.; Zhou, Z.; Li, W. A Multi-load Wireless Power Transfer System with Series-parallel-series (SPS) Compensation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 7126–7130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
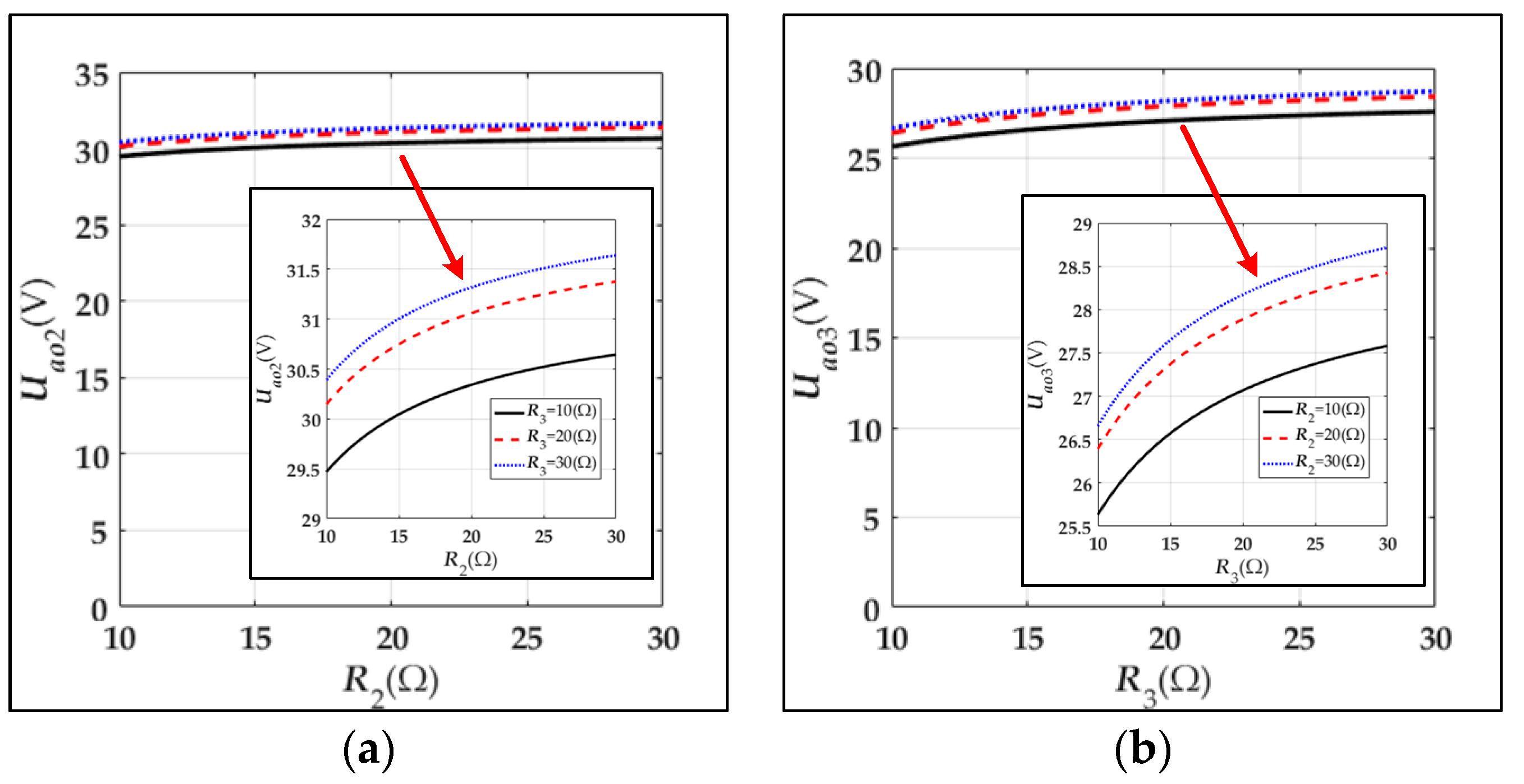
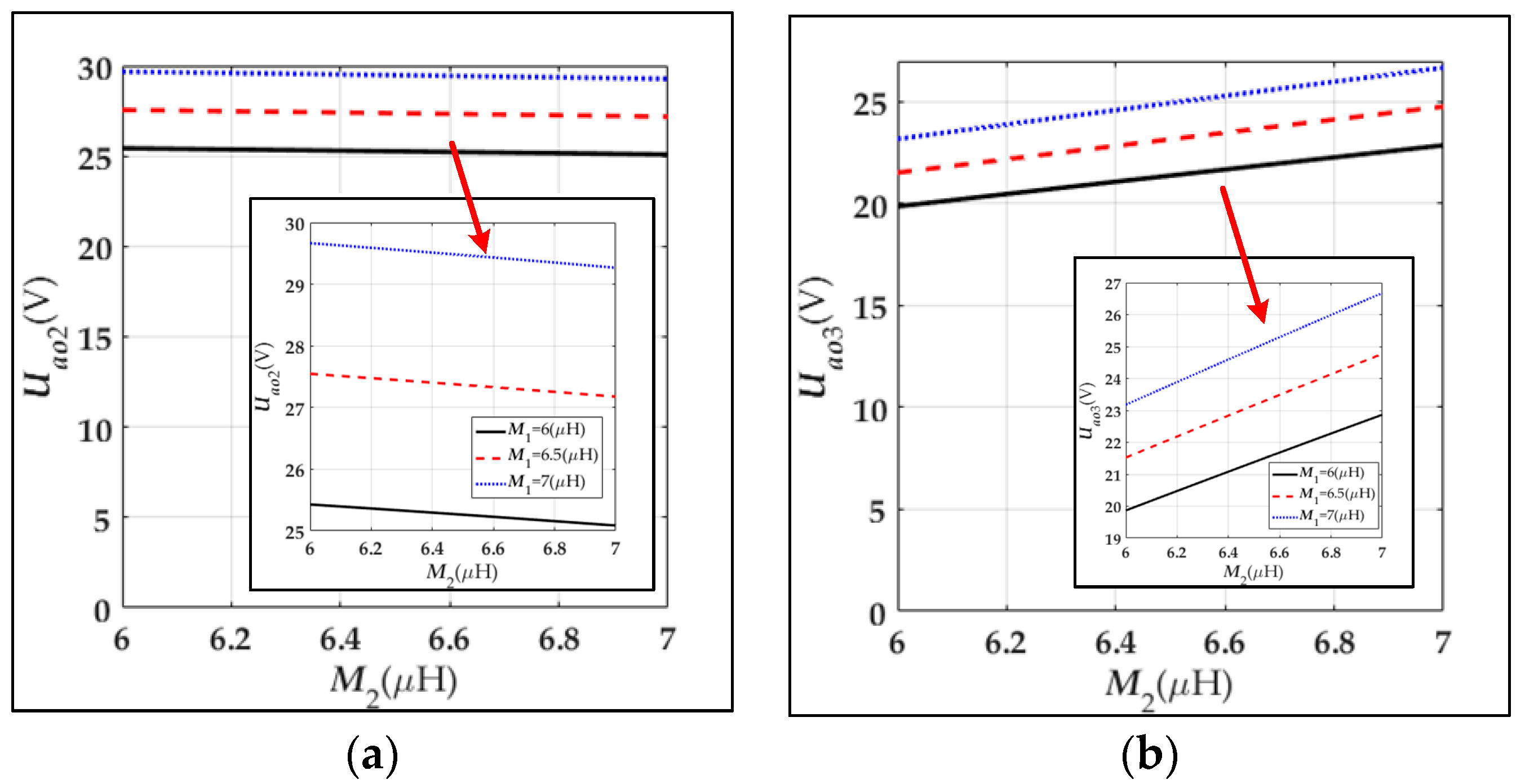


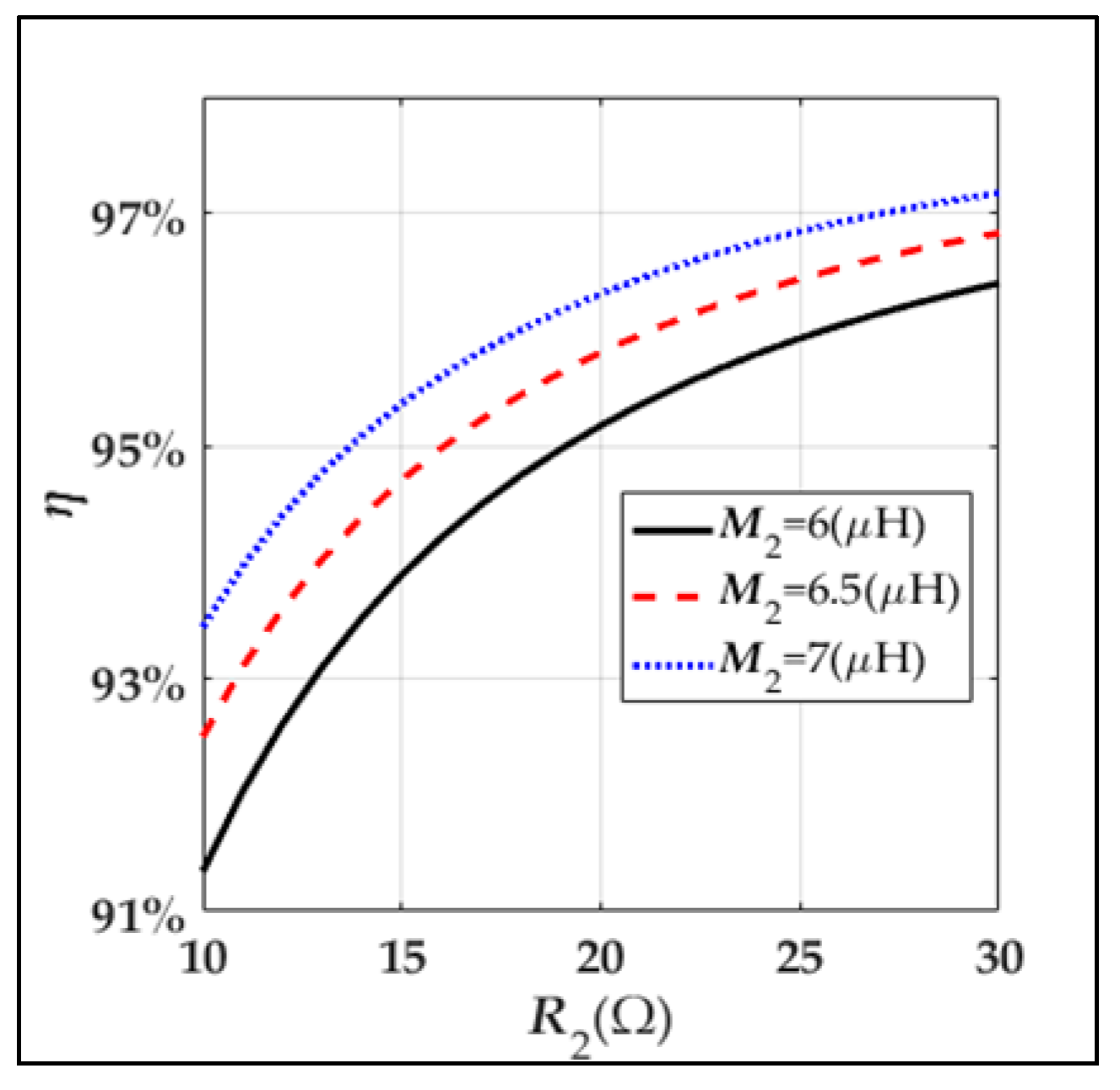
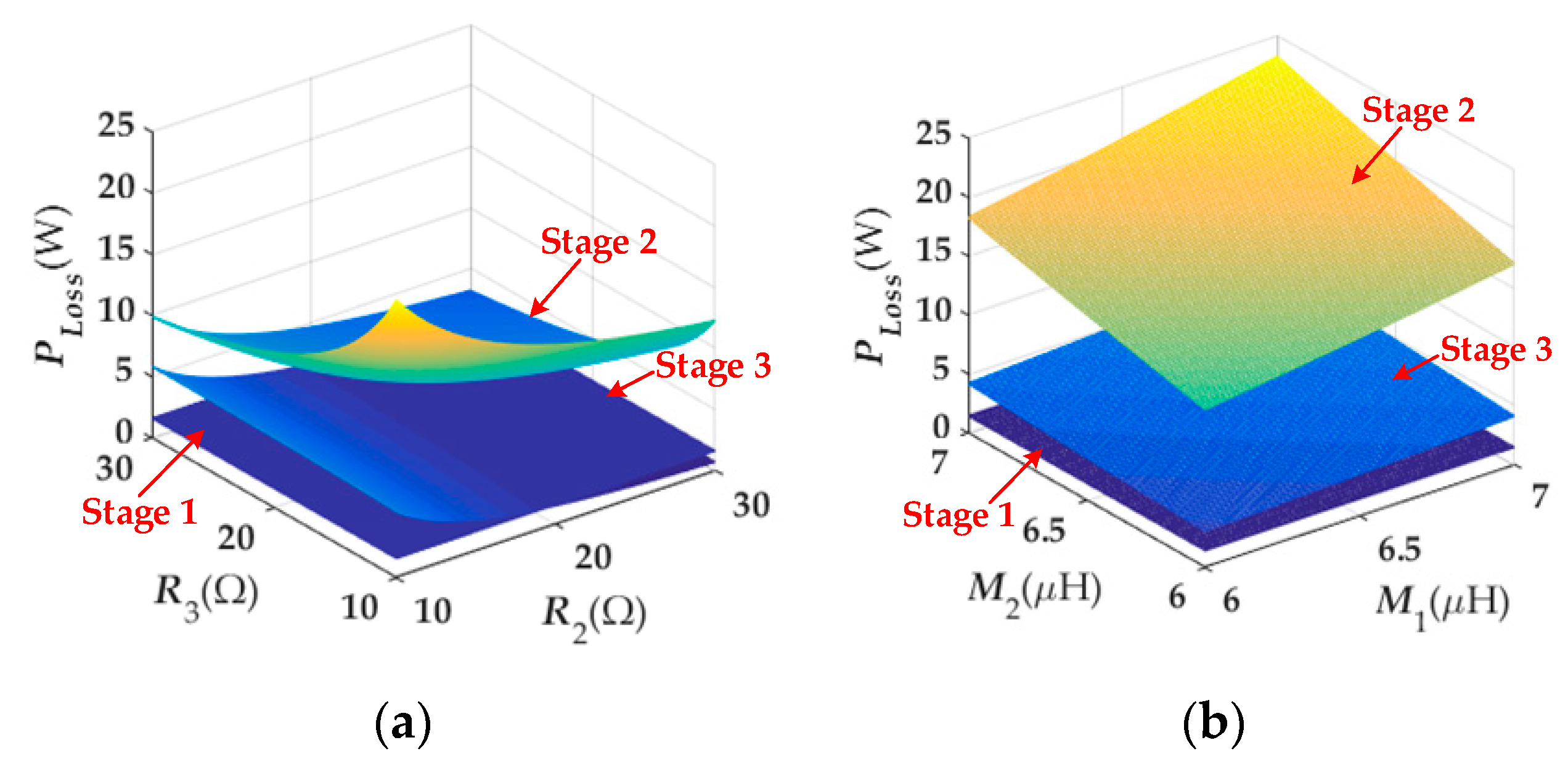
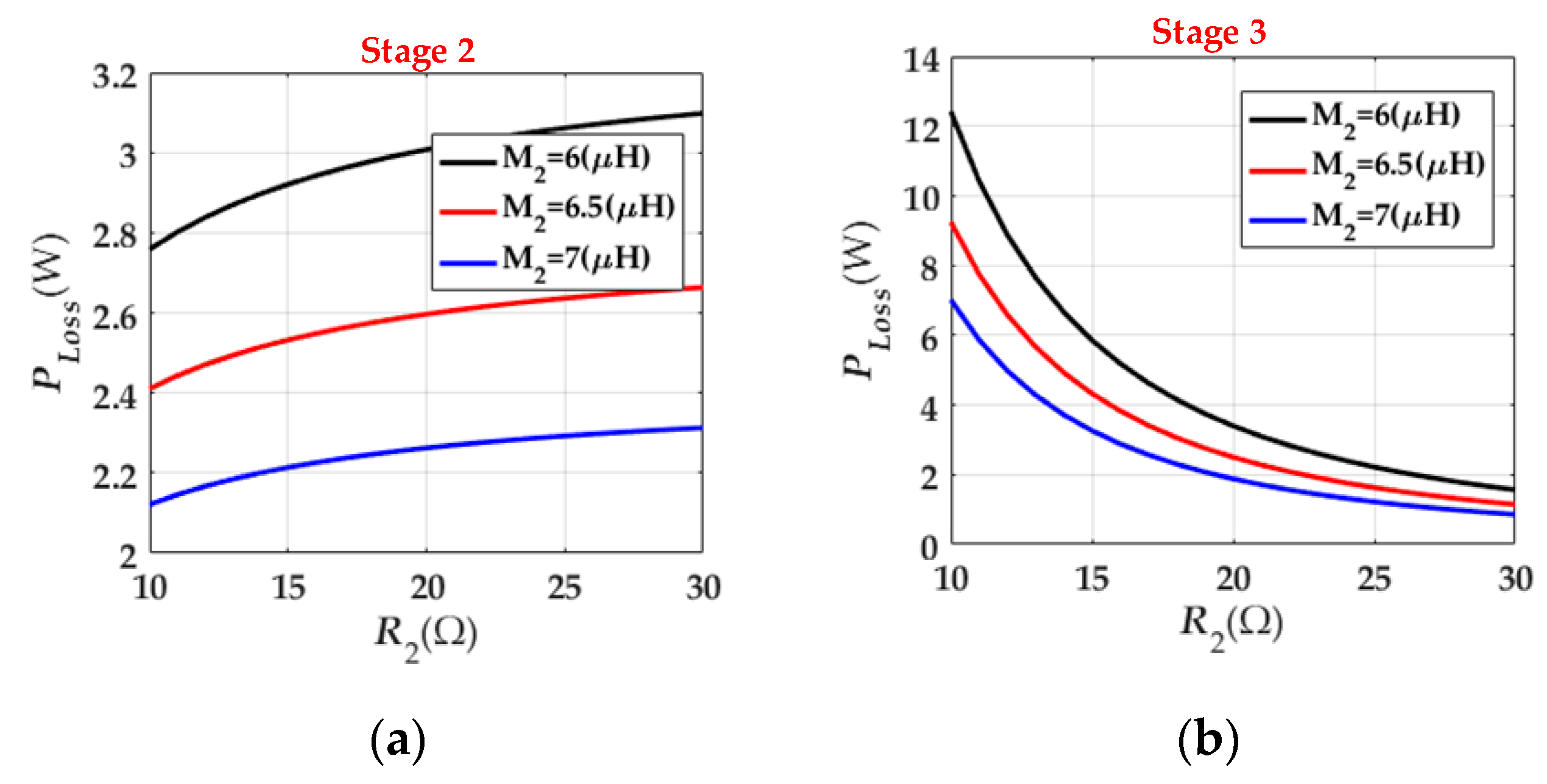



| The output voltage of Rl2 | |
| The output voltage of Rl3 | |
| Output power | |
| Efficiency |
| The output voltage of Rl2 | |
| Output power | |
| Efficiency |
| Parameters | Value | Parameters | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Udc1 | 35 V | Udc3 | 35 V |
| f | 500 kHz | Lp11 | 6.4 μH |
| Cp11 | 15.8 nF | Lp12 | 18.6 μH |
| Cp12 | 8.3 nF | Ls1 | 6.86 μH |
| Cs1 | 14.8 nF | M1 | 6.68 μH |
| Rp12 | 0.54 Ω | Rs1 | 0.13 Ω |
| Lp21 | 7.2 μH | Cp21 | 14 nF |
| Lp22 | 18.1 μH | Cp22 | 9.3 nF |
| Ls2 | 6.88 μH | Cs2 | 14.8 nF |
| M2 | 6.68 μH | Rp22 | 0.52 Ω |
| Rs2 | 0.13 Ω | R2 | 10 Ω/30 Ω |
| R3 | 10 Ω/30 Ω | - | - |
| R2 (Ω) | R3 (Ω) | Output Power (W) | Efficiency (η) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mode a | 30 | 30 | 56.9 | 86.3% |
| 10 | 30 | 99.8 | 83.9% | |
| 30 | 10 | 87.8 | 79.6% | |
| 10 | 10 | 135.0 | 76.9% | |
| Mode b | 30 | - | 40.6 | 85.7% |
| 10 | - | 107.6 | 80.7% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; Dai, X. Constant Output-Voltage Design for Bi-Directional Wireless Power Transfer System with Multiple Stages. Energies 2020, 13, 3739. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13143739
Wu J, Wang Z, Dai X. Constant Output-Voltage Design for Bi-Directional Wireless Power Transfer System with Multiple Stages. Energies. 2020; 13(14):3739. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13143739
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jinde, Zhihui Wang, and Xin Dai. 2020. "Constant Output-Voltage Design for Bi-Directional Wireless Power Transfer System with Multiple Stages" Energies 13, no. 14: 3739. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13143739
APA StyleWu, J., Wang, Z., & Dai, X. (2020). Constant Output-Voltage Design for Bi-Directional Wireless Power Transfer System with Multiple Stages. Energies, 13(14), 3739. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13143739






