Artificial Intelligence-Based Weighting Factor Autotuning for Model Predictive Control of Grid-Tied Packed U-Cell Inverter
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Study
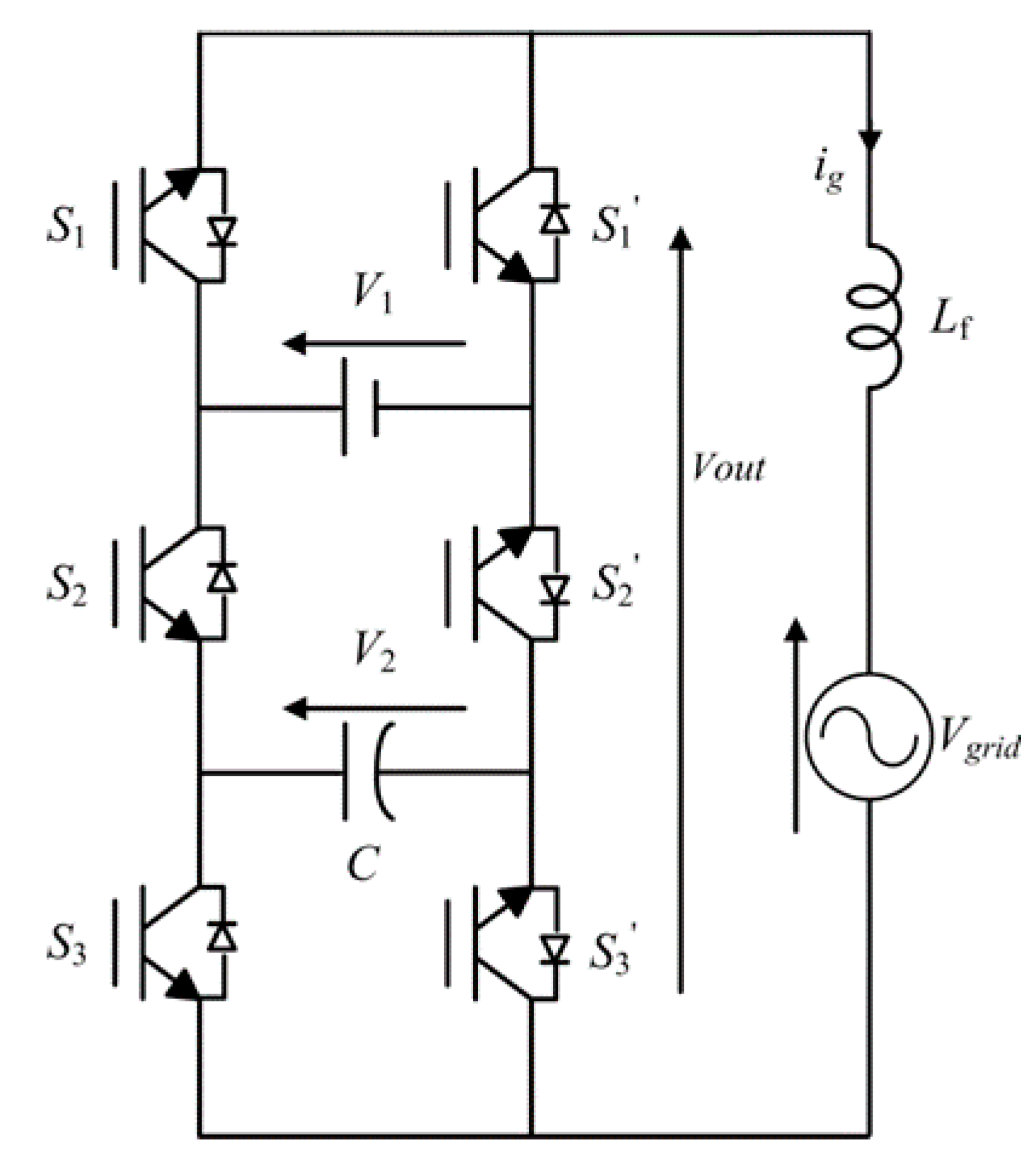
2.1. PUC7 Topology and Modelling
- C: cell capacitors,
- Lf: filtering inductor,
- V1: DC source voltage,
- V2: capacitor voltage,
- Vgrid: grid voltage,
- ig: injected grid current, and
- s1, s2, s3: switching states.
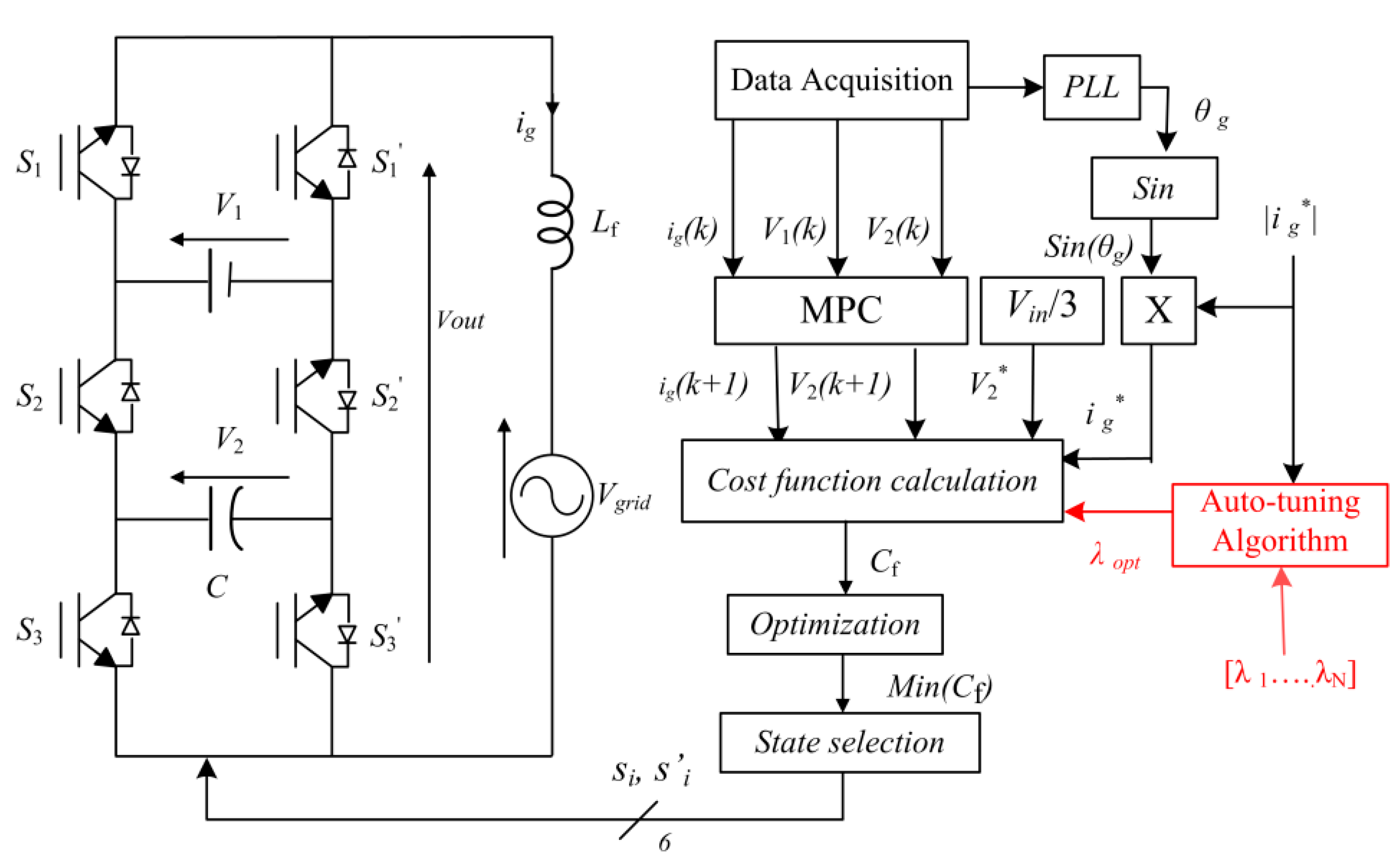
2.2. FCS-MPC for PUC7 Inverter
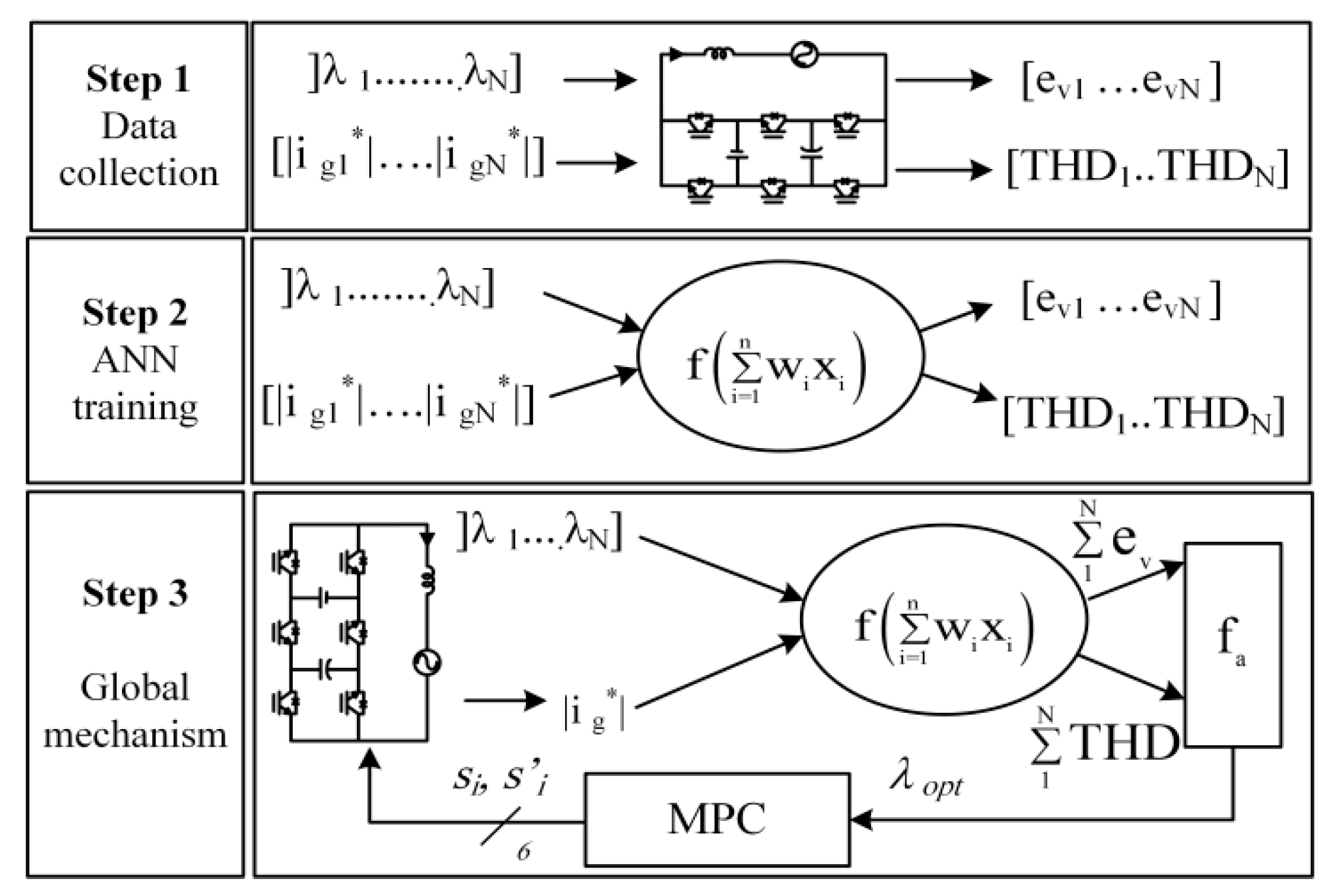
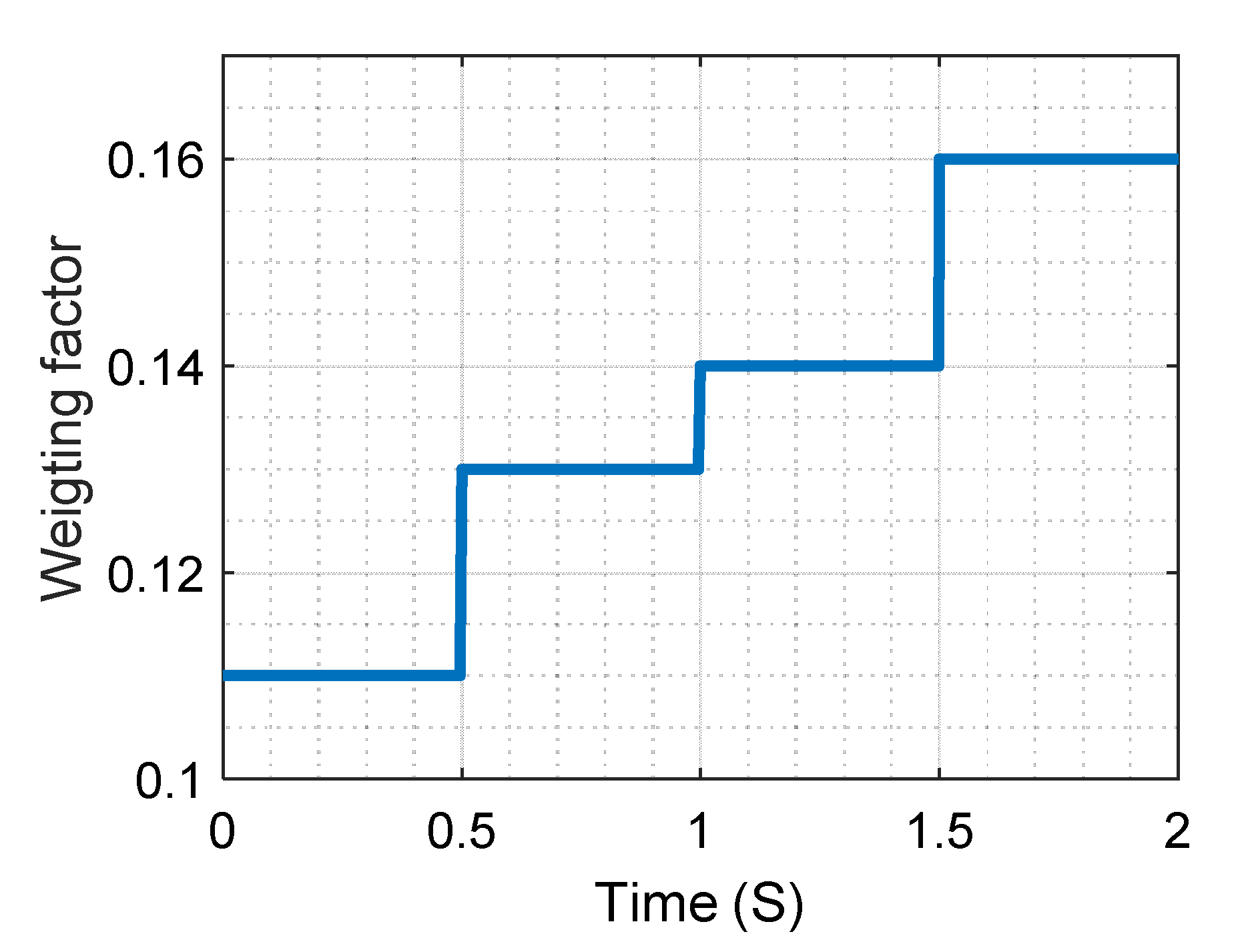
3. Autotuning of the Weighting Factor
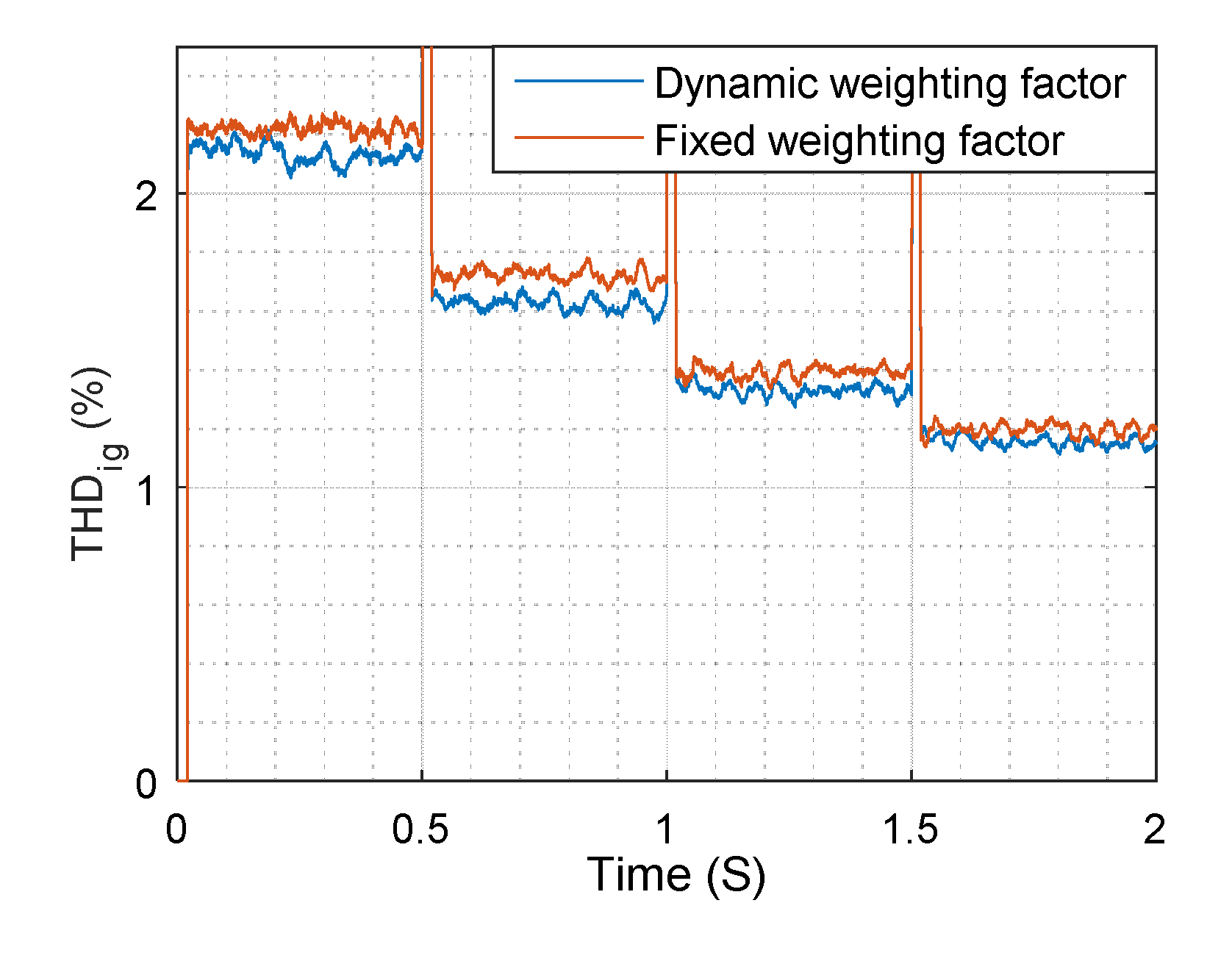
4. Simulation Results
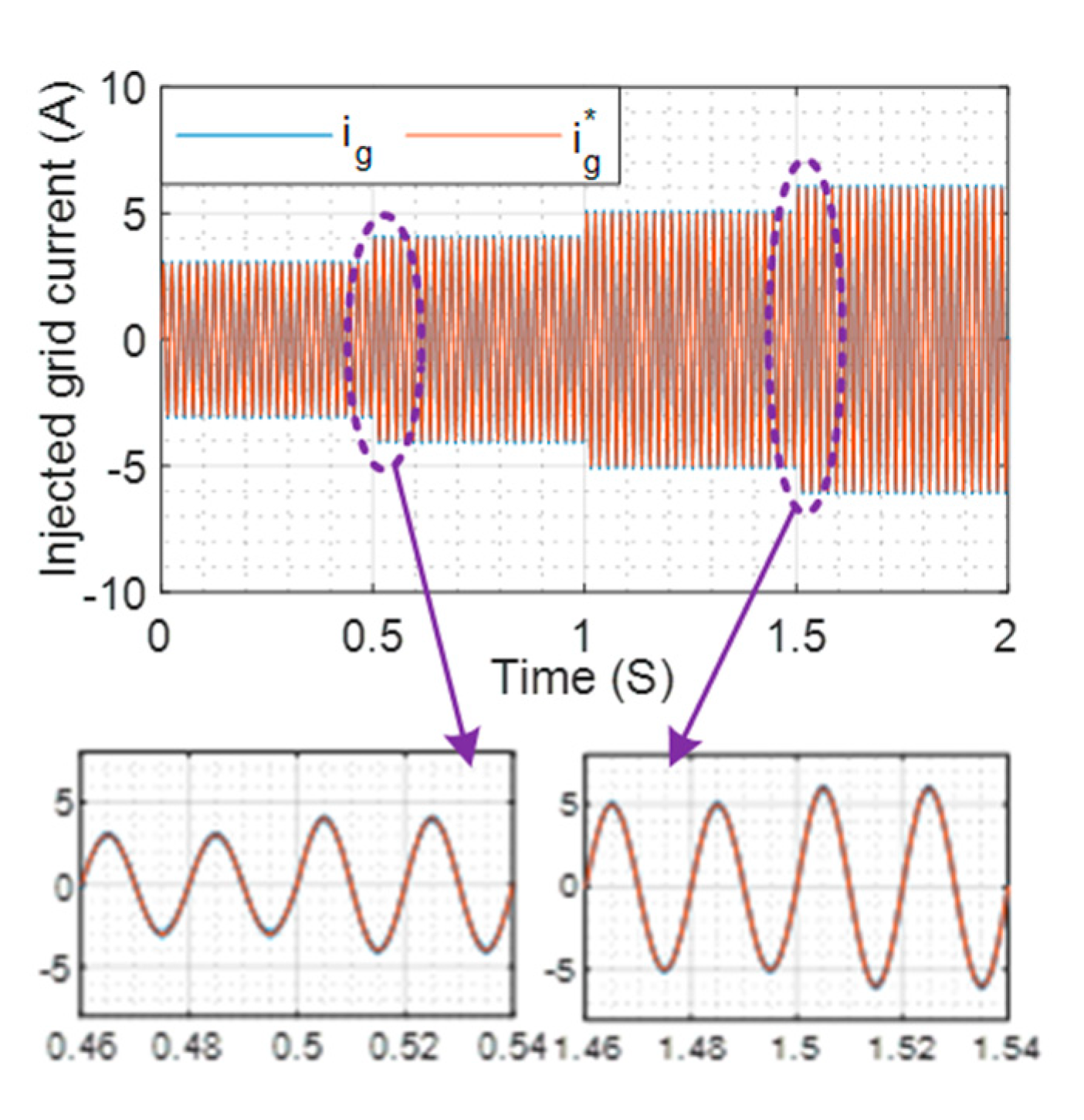
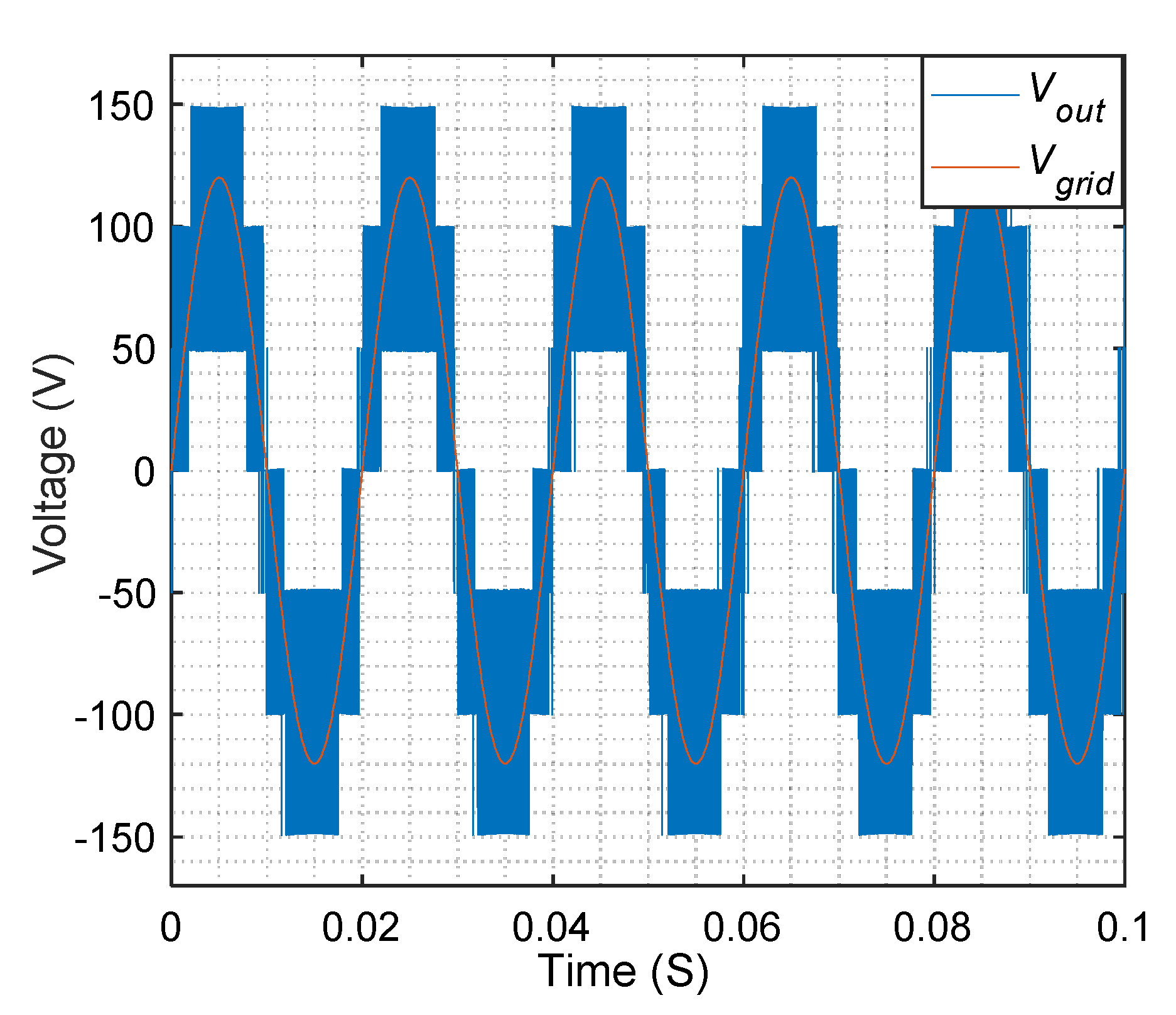
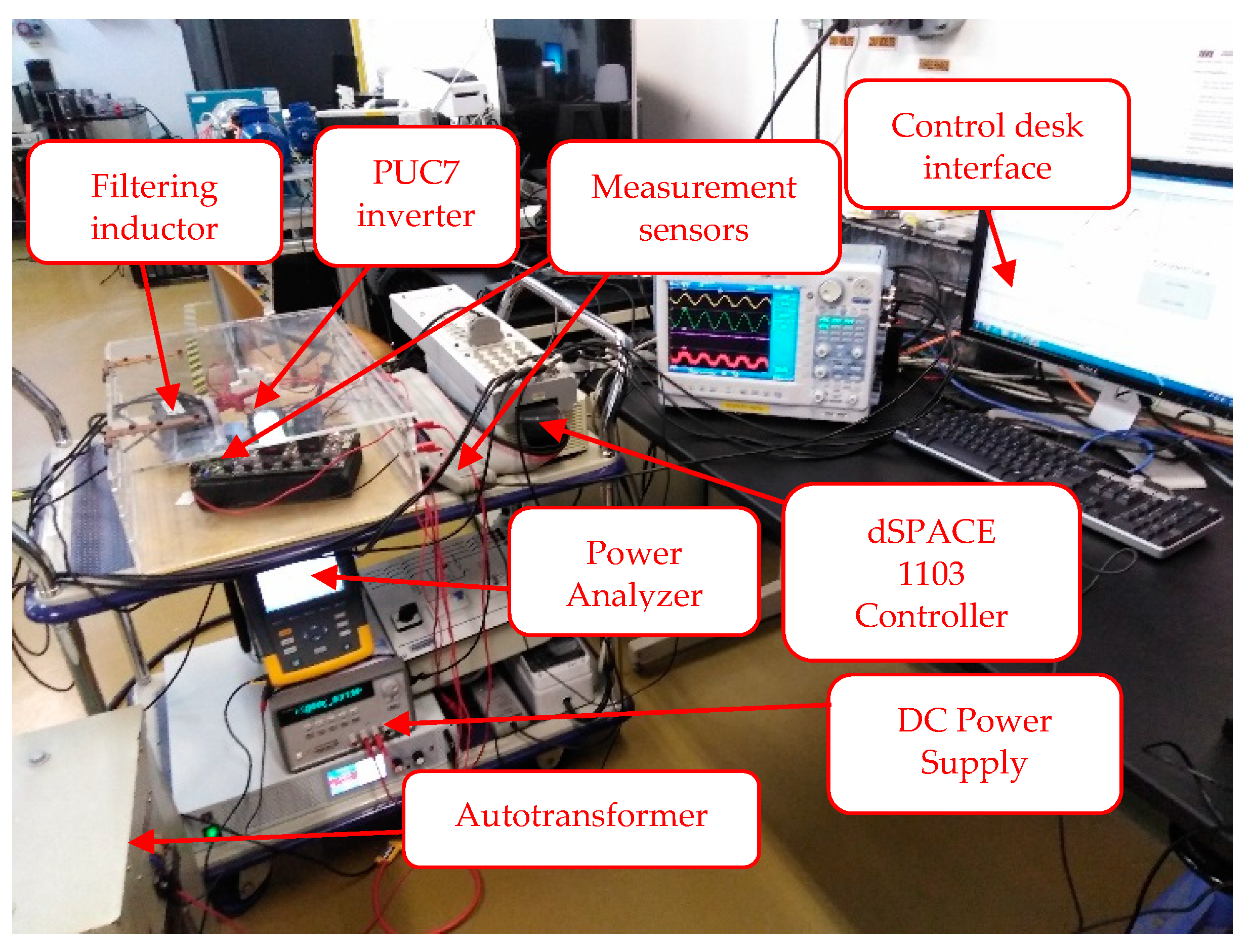
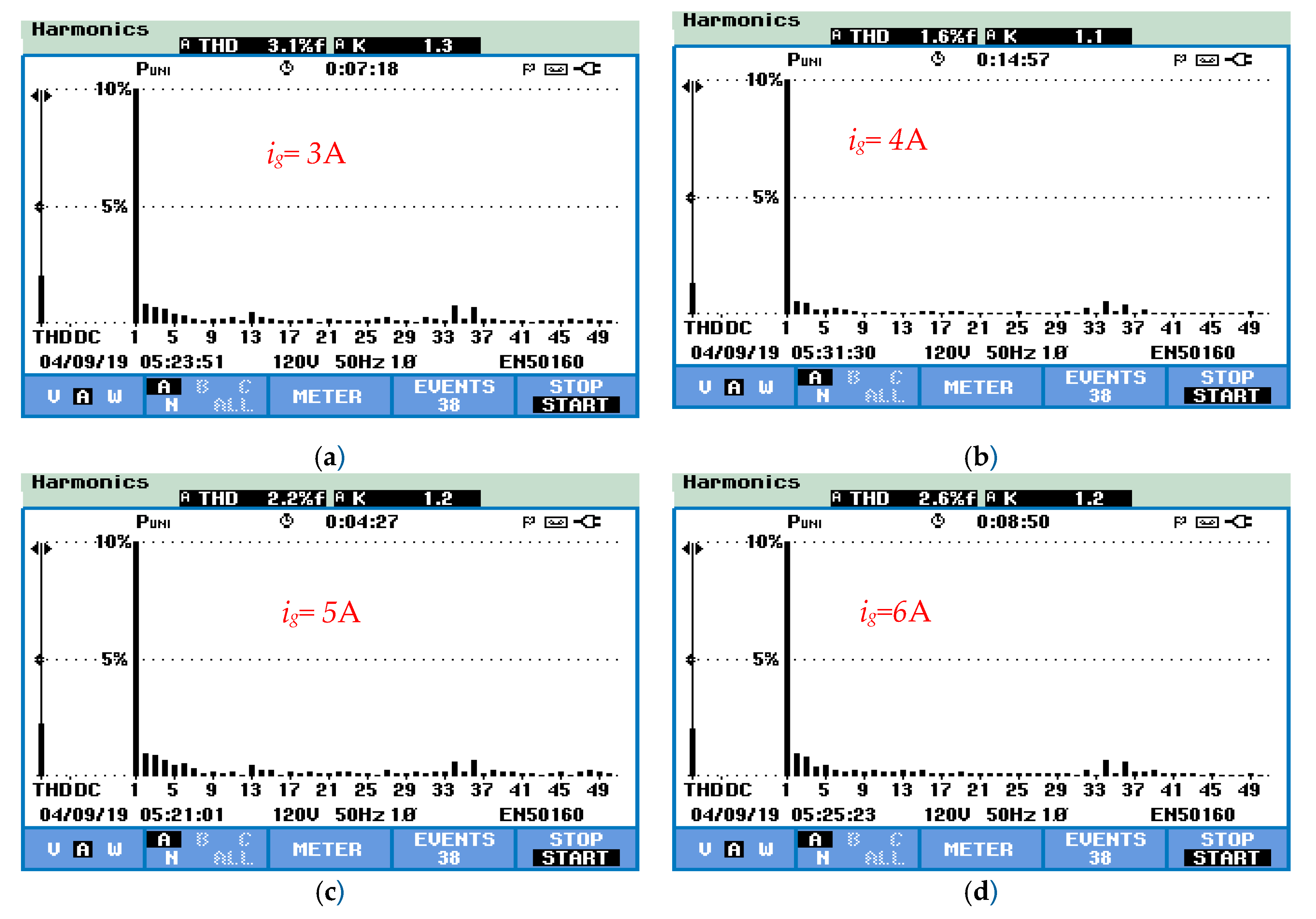
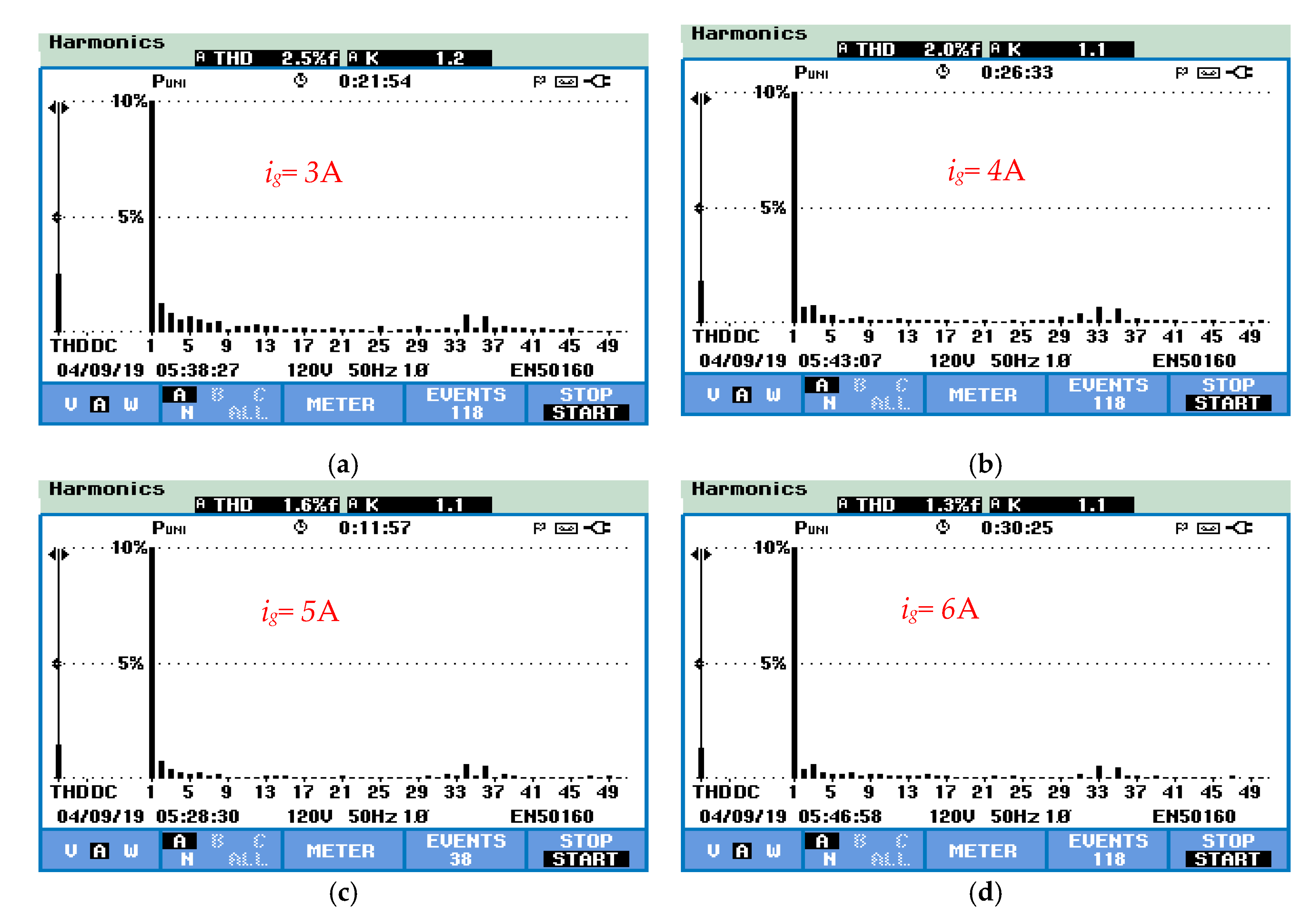
5. Experimental Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodríguez, J.; Lai, J.; Peng, F.Z. Multilevel inverters: A survey of topologies, controls, and applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2002, 49, 724–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Rub, H.; Malinowski, M.; Al-Haddad, K. Power Electronics for Renewable Energy Systems, Transportation and Industrial Applications; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Babaei, E.; Alilu, S.; Laali, S.; Member, S. A new general topology for cascaded multilevel inverters with reduced number of components based on developed h-bridge. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 3932–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Rub, H.; Holtz, J.; Rodriguez, J.; Baoming, G. Medium-voltage multilevel converters state of the art, challenges, and requirements in industrial applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 2581–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Ge, B.; Liang, W.; Abu-rub, H.; Member, S. An energy stored quasi-z-source cascade multilevel inverter-based photovoltaic. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 5458–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavarria, J.; Biel, D.; Guinjoan, F.; Meza, C.; Negroni, J.J. Energy-balance control of PV cascaded multilevel grid-connected inverters under level-shifted and phase-shifted PWMs. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, E.; Laali, S.; Member, S.; Alilu, S. Cascaded multilevel inverter with series connection of novel h-bridge basic units. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 6664–6671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, E.; Laali, S.; Member, S. Optimum structures of proposed new cascaded multilevel inverter with reduced number of components. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 6887–6895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheir, A.; Orabi, M.; Ahmed, M.E.; Iqbal, A.; Youssef, M. A high efficiency single-phase multilevel packed u cell inverter for photovoltaic applications. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 36th International Telecommunications Energy Conference (INTELEC), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 28 September–2 October 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ounejjar, Y.; Al-haddad, K.; Grégoire, L. Packed u cells multilevel converter topology: Theoretical study and experimental validation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 1294–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabelsi, M.; Ghazi, K.A.; Al-Emadi, N.; Ben-Brahim, L. A weighted real-time predictive controller for a grid connected flying capacitors inverter. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2013, 49, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahedi, H.; Trabelsi, M. Single-DC-Source Multilevel Inverters; Springer Nature: Basel, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Krama, A.; Zellouma, L.; Rabhi, B.; Refaat, S.S.; Bouzidi, M. Real-Time Implementation of High Performance Control Scheme for Grid-Tied PV System for Power Quality Enhancement Based on MPPC-SVM Optimized by PSO Algorithm. Energies 2018, 11, 3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.; Kazmierkowski, M.P.; Espinoza, J.R.; Zanchetta, P.; Abu-Rub, H. State of the art of finite control set model predictive control in power electronics. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2013, 9, 1003–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzinski, J.; Abu-rub, H. Speed sensorless induction motor drive with predictive current controller. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurtenechea, S.; Rodríguez, M.A.; Oyarbide, E.; Torrealday, J.R. Predictive control strategy for DC/AC converters based on direct power control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2007, 54, 1261–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrıguez, J.; Abu-Rub, H.; Perez, M.A.; Kouro, S. Application of predictive control. In Power Electronics and Drives; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Trabelsi, M.; Bayhan, S.; Ghazi, K.A.; Haitham, A.-R.; Lazhar, B.-B. Finite-control-set model predictive control for grid-connected packed-u-cells multilevel inverter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 7286–7295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, P.; Kazmierkowski, M.P.; Kennel, R.M.; Quevedo, D.E.; Rodriguez, J. Predictive control in power electronics and drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 4312–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouro, S.; Cortes, P.; Vargas, R.; Ammann, U.; Rodriguez, J. Model predictive control-a simple and powerful method to control power converters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 1826–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelbasset, K.; Refaat, S.S.; Trabelsi, M. Model Predictive Control for a 9-Level Packed U-Cells based Grid-Connected PV System. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference in smart grid and renewable energy, Doha, Qatar, 19–21 November 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, P.; Kouro, S.; La Rocca, B.; Vargas, R.; Rodriguez, J.; Leon, J.I.; Vazquez, S.; Franquelo, L.G. Guidelines for weighting factors design in model predictive control of power converters and drives. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology, Gippsland, VIC, Australia, 10–13 February 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, G. Auto-tuning procedure for model-based predictive controlle. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Cybernetics Evolving to Systems, Humans, Organizations, and Their Complex Interactions, Nashville, TN, USA, 8–11 October 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Shadmand, M.B.; Jain, S.; Balog, R.S. Auto-tuning technique for the cost function weight factors in model predictive control for power electronics interface. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2018, 7, 1408–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davari, S.A.; Khaburi, D.A.; Kennel, R.; Member, S. An improved FCS-MPC algorithm for an induction motor with an imposed optimized weighting factor. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 1540–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmjooy, N.; Khalilpour, M.; Ramezani, M. A new meta-heuristic optimization algorithm inspired by FIFA world cup competitions: Theory and its application in PID designing for AVR system. J. Control. Autom. Electr. Syst. 2016, 27, 419–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, Y. Online tuning of weighting factors based on sugeno fuzzy method in predictive torque control of four-switch three-phase inverter-fed IM. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Symposium on Power Electronics, Electrical Drives, Automation and Motion (SPEEDAM), Anacapri, Italy, 22–24 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kampisios, K.; Zanchetta, P.; Gerada, C.; Trentin, A.; Jasim, O. Induction motor parameters identification using genetic algorithms for varying flux levels. In Proceedings of the 13th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference, Poznan, Poland, 1–3 September 2008; pp. 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragicevic, T.; Novak, M. Weighting factor design in model predictive control of power electronic converters: An artificial neural network approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Urquídez, R.C.; Valencia-Palomo, G.; Rodríguez-Elias, O.M.; Trujillo, L. Systematic selection of tuning parameters for efficient predictive controllers using a multiobjective evolutionary algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 2015, 31, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanchetta, P. Heuristic multi-objective optimization for cost function weights selection in finite states model predictive control. In Proceedings of the PRECEDE 2011-Workshop on Predictive Control. of Electrical Drives and Power Electronics, Munich, Germany, 14–15 October 2011; pp. 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mc, P.; Negenborn, R.R.; De Schutter, B.; Lightbody, G. Weight optimisation for iterative distributed model predictive control applied to power networks. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2013, 26, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, M.; Senent, J.S.; Blasco, X. Generalized predictive control using genetic algorithms (GAGPC). Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2002, 11, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guazzelli, P.R.U.; Pereira, W.C.A.; Oliveira, C.M.R.; Castro, A.G.; Aguiar, M.L. Weighting factors optimization of predictive torque control of induction motor by multi-objective genetic algorithm. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 34, 6628–6638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Haddad, K.; Ounejjar, Y.; Gregoire, L. Multilevel Electric Power Converter. US Patent US9331599B2, 17 November 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kanaesalingam, S.R.K.; Ramachandaramurthy, V.K. Inteligent driven power quality monitoring using pseudomeasurement technique. In Proceedings of the 2009 10th International Conference on Electrical Power Quality and Utilisation, EPQU’09, Lodz, Poland, 15–17 September 2009; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shao, W.; Song, Z. Bayesian regularized Gaussian mixture regression with application to soft sensor modeling for multi-mode industrial processes. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 7th Data Driven Control and Learning Systems Conference (DDCLS), Enshi, China, 25–27 May 2018; pp. 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| State | Vout | S1 | S2 | S3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | −V2 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 3 | V2−V1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 4 | −V1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 5 | V1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 6 | V1−V2 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 7 | V2 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 8 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Inductance of the filter | 5 mH |
| Capacitor C | 100 μF |
| Frequency f | 50 Hz |
| Sampling frequency Fs | 50 KHz |
| DC source voltage V1 | 150 V |
| Grid voltage Vgrid (peak) | 120 V |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohamed-Seghir, M.; Krama, A.; Refaat, S.S.; Trabelsi, M.; Abu-Rub, H. Artificial Intelligence-Based Weighting Factor Autotuning for Model Predictive Control of Grid-Tied Packed U-Cell Inverter. Energies 2020, 13, 3107. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13123107
Mohamed-Seghir M, Krama A, Refaat SS, Trabelsi M, Abu-Rub H. Artificial Intelligence-Based Weighting Factor Autotuning for Model Predictive Control of Grid-Tied Packed U-Cell Inverter. Energies. 2020; 13(12):3107. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13123107
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohamed-Seghir, Mostefa, Abdelbasset Krama, Shady S. Refaat, Mohamed Trabelsi, and Haitham Abu-Rub. 2020. "Artificial Intelligence-Based Weighting Factor Autotuning for Model Predictive Control of Grid-Tied Packed U-Cell Inverter" Energies 13, no. 12: 3107. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13123107
APA StyleMohamed-Seghir, M., Krama, A., Refaat, S. S., Trabelsi, M., & Abu-Rub, H. (2020). Artificial Intelligence-Based Weighting Factor Autotuning for Model Predictive Control of Grid-Tied Packed U-Cell Inverter. Energies, 13(12), 3107. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13123107










