Energy Use and Labor Productivity in Ethiopia: The Case of the Manufacturing Industry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review on Energy and Productivity Growth
3. Model Specification and Estimation
3.1. Model Specification
3.2. Model Estimation
4. The Data
4.1. Data and Variables
4.2. The Variables’ Development Over Time
5. Empirical Results and Discussion
5.1. Descriptive Statistics
5.2. Regression Results and Analysis
6. Conclusions and Policy Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaldor, N. Causes of the Slow Rate of Economic Growth of the United Kingdom. An Inaugural Lecture; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Cornwall, J. Modern Capitalism. Its Growth and Transformation; St. Martin’s Press: New York, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Guadagno, F. The determinants of Industrialization in Developing Countries, 1960–2005. UNU-MERIT Maastricht Univ. 2016, 31, 26. [Google Scholar]
- UNECA. Dynamic Industrial Policy in Africa: Economic Report on Africa; UNECA: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- UNECA. Industrializing Through Trade. Economic Report on Africa; UNECA: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- UNIDO. Demand for Manufacturing: Driving Inclusive and Sustainable Industrial Development. Industrial Development Report; United Nations Industrial Development Organization UNIDO: Vienna, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Otalu, J.A.; Anderu, K.S. An Assessment of the Determinants of Industrial Sector Growth in Nigeria. J. Res. Bus Man 2015, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Story, D. Time-Series Analysis of Industrial Growth in Latin America: Political and Economic Factors. Soc. Sci. Quart. 1980, 61, 293–307. [Google Scholar]
- UNDP (United Nations Development Program). Transforming Lives Through Renewable Energy Access in Africa UNDP’s Contributions. UNDP Afr. Policy Brief 2018, 1, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.Y.; Chen, S.T.; Chen, C.C. Energy consumption and economic growth—New evidence from meta-analysis. Energy Policy 2012, 44, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddasi, R.; Pour, A.A. Energy Consumption and Total Factor productivity in Iranian Agriculture. Energy Rep. 2016, 2, 218–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebede, E.; Kagochi, J.; Jolly, C.M. Energy consumption and economic development in Sub-Sahara Africa. Energy Econ. 2010, 32, 532–537. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Iriani, M.A. Energy-GDP relationship revisited: An Example from GCC Countries Using Panel Causality. Energy Policy 2005, 34, 3342–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, C.J.; Kaufmann, R.K.; Stern, D.I. Aggregation and the role of energy in the economy. Ecol. Econ. 2000, 32, 301–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaali, F.; Roberts, J.; Taylor, K. The Effect of Energy Consumption and Human Capital on Economic Growth: An Exploration of Oil Exporting and Developed Countries. SERPS (Sheffield Econ. Res. Pap. Ser.) 2015, 2015015. [Google Scholar]
- Fallahi, F.; Sojood, S.; Aslaninia, N.M. Determinants of Labor Productivity in Iran’s Manufacturing Firms: With Emphasis on Labor Education and Training. MPRA 2010, 27447. [Google Scholar]
- Soytas, U.; Sari, R. Energy consumption and GDP: Causality relationship in G-7 countries and emerging markets. Energy Econ. 2003, 25, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinlo, A.E. Energy consumption and economic growth: Evidence from 11 Sub-Sahara African countries. Energy Econ. 2008, 30, 2391–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CSA (Central Statistic Authority). Industry Sector Data Base of Ethiopian Industries; CSA: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- EEA (Ethiopian Economic Association). Data Base on Macroeconomic Variables; EEA: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ejigu, Z.K.; Singh, I.S. Service Sector: The Source of Output and Employment Growth in Ethiopia. Acad. J Econ. 2016, 2, 139–156. [Google Scholar]
- Oqubay, A. Industrial Policy and Late Industrialization in Ethiopia; Working paper Series No. 303; African Development Bank: Abidjan, Cote D’Ivoire, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gebreeyesus, M. Industrial Policy and Development in Ethiopia: Evolution and Present Experimentation; UNU.WIDER Working Paper No 6; UNU.WIDER: Helsinki, Finland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrik, D. Premature deindustrialization. J Econ. Growth 2016, 21, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, D. Development Economics; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Romer, D. Advanced Macroeconomics, 4th ed.; University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Todaro, M.P.; Smith, S.C. Economic Development, 12th ed.; Pearson Education Inc.: New Jersey, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Agénor, P.R.; Montiel, P. Development Macroeconomics, 3rd ed.; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Stern, D.I. The Role of Energy in Economic Growth CCEP; Working Paper 3.10; Crawford School, The Australian National University: Canberra, Australia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Su, B.; Heshmati, A. Development and Sources of Labor Productivity in Chinese Provinces. China Econ. Policy Rev. 2014, 2, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Stern, D.I. Limits to Substitution and Irreversibility in Production and Consumption: A Neoclassical Interpretation of Ecological Economics. Ecol. Econ. 1997, 21, 197–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Energy; OECD Green Growth Studies; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- UNDP (United Nations Development Program). Energy for Sustainable Development a Policy Agenda; UNDP: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Toman, M.A.; Jemelkova, B. Energy and economic development: An assessment of the state of knowledge. Energy J. 2003, 24, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabraal, R.A.; Barnes, D.F.; Agarwal, S.G. Productive Uses of Energy for Rural Development. Ann. Rev. Environ. Res. 2005, 30, 117–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejaz, Z.; Aman, M.U.; Usman, M.K. Determinants of Industrial Growth in South Asia: Evidence from Panel Analysis. In Papers and Proceedings; Unpublished; 2016; pp. 97–110. Available online: https://www.pide.org.pk/psde/pdf/AGM33/papers/M%20Aman%20Ullah.pdf (accessed on 26 May 2020).
- Heshmati, A. Productivity Growth, Efficiency and Outsourcing in Manufacturing and Service Industries. J. Econ. Sur. 2003, 17, 79–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybár, R.; Kudelas, D.; Beer, M. Selected Problems of Classification of Energy Sources: What are Renewable Energy Sources? Acta Montan. Slovaca 2015, 20, 172–180. [Google Scholar]
- Wolde-Rufael, Y. Energy consumption and economic growth: The experience of African countries revisited. Energy Econ. 2009, 31, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schurr, S.H.; Netschert, B.C.; Eliasberg, V.E.; Lerner, J.; Landsberg, H.H. Energy in the American Economy; Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Schurr, S.H. Energy use, technological change, and productive efficiency: An economic-historical interpretation. Ann. Rev. Energy 1984, 9, 409–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgenson, D.W. The role of energy in productivity growth. Energy J. 1984, 5, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudreaux, B.C. The impact of electric power on productivity: A study of US manufacturing 1950–1984. Energy Econ. 1995, 17, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo-Zamorano, L.R. The role of energy in productivity growth: A controversial issue? Energy J. 2005, 26, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walheer, B. Labour productivity growth and energy in Europe: A production-frontier approach. Energy 2018, 152, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevan, R.; Asafu-Adjaye, J. Energy consumption, economic growth and prices: A reassessment using panel VECM for developed and developing countries. Energy Policy 2007, 35, 2481–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velucchi, M.; Viviani, A. Determinants of the Italian Labor Productivity: A Quantile Regression Approach. Statistica 2011, 71, 213–238. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, S.; Shazali, S.S. Determinants of Manufacturing Productivity: Pilot Study on Labor-Intensive Industries. Int. J. Product. Perform. Manag. 2010, 60, 567–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heshmati, A.; Rashidghalam, M. Labour productivity in Kenyan manufacturing and service industries. In Determinants of Economic Growth in Africa; IZA: Bonn, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nagler, P.; Naudé, W. Labor Productivity in Rural African Enterprises: Empirical Evidence from the LSMS-ISA; IZA Discussion Papers 8524; Institute of Labor Economics (IZA): Bonn, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Samuel, B.; Aram, B. The Determinants of Industrialization: Empirical Evidence for Africa. Eur. Sci. J. 2016, 12, 219–239. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Productivity Measurement and Analysis. Proceedings from OECD Workshops; Swiss Federal Statistical Office (FSO): Neuchâtel, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Measuring Productivity—OECD Manual: Measurement of Aggregate and Industry-Level Productivity Growth; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hajkova, D.; Hurnik, J. Cobb-Douglas production function: The case of a converging economy. Czech J. Econ. Financ. 2007, 57, 465–476. [Google Scholar]
- Van Beven, L. Total Factor Productivity: A Practical View. J. Econ. Surv. 2010, 26, 98–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Gatto, M.; Di Liberto, A.; Petraglia, C. Measuring productivity. J. Econ. Surv. 2011, 25, 952–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobb, C.W.; Douglas, P.H. A theory of production. Am. Econ. Rev. 1928, 18, 139–165. [Google Scholar]
- Murthy, K.V. Arguing a case for Cobb-Douglas production function. Rev. Commer. Stud. 2002, 20, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Zellner, A.; Kmenta, J.; Dreze, J. Specification and estimation of Cobb-Douglas production function models. Econom. J. Econom. Soc. 1966, 34, 784–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldridge, L.P.; Price, J. Measuring quarterly labor productivity by industry. Mon. Labor Rev. 2016, 139, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Faustino, H.C.; Leitão, N.C. Intra-industry trade: A static and dynamic panel data analysis. Int. Adv. Econ. Res. 2007, 13, 313–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummels, D.; Levinsohn, J. Monopolistic competition and international trade: Reconsidering the evidence. Q. J. Econ. 1995, 110, 799–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; van Witteloostuijn, A.; Zhou, C. Chinese bilateral intra-industry trade: A panel data study for 50 countries in the 1992–2001 period. Rev. World Econ. 2005, 141, 510–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arellano, M.; Bond, S. Some Tests of Specification for panel data: Monte Carlo Evidence and an Application to Employment Equations. Rev. Econ. Stud. 1991, 58, 277–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arellano, M.; Bover, O. Another look at the Instrumental Variable Estimation of Error-components Model. J. Econ. 1995, 68, 29–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roodman, D. How to do xtbond2: An Introduction to Difference and System GMM in Stata. Stata J. 2009, 9, 86–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrik, D. Unconditional Convergence in Manufacturing. Q. J. Econ. 2013, 128, 165–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
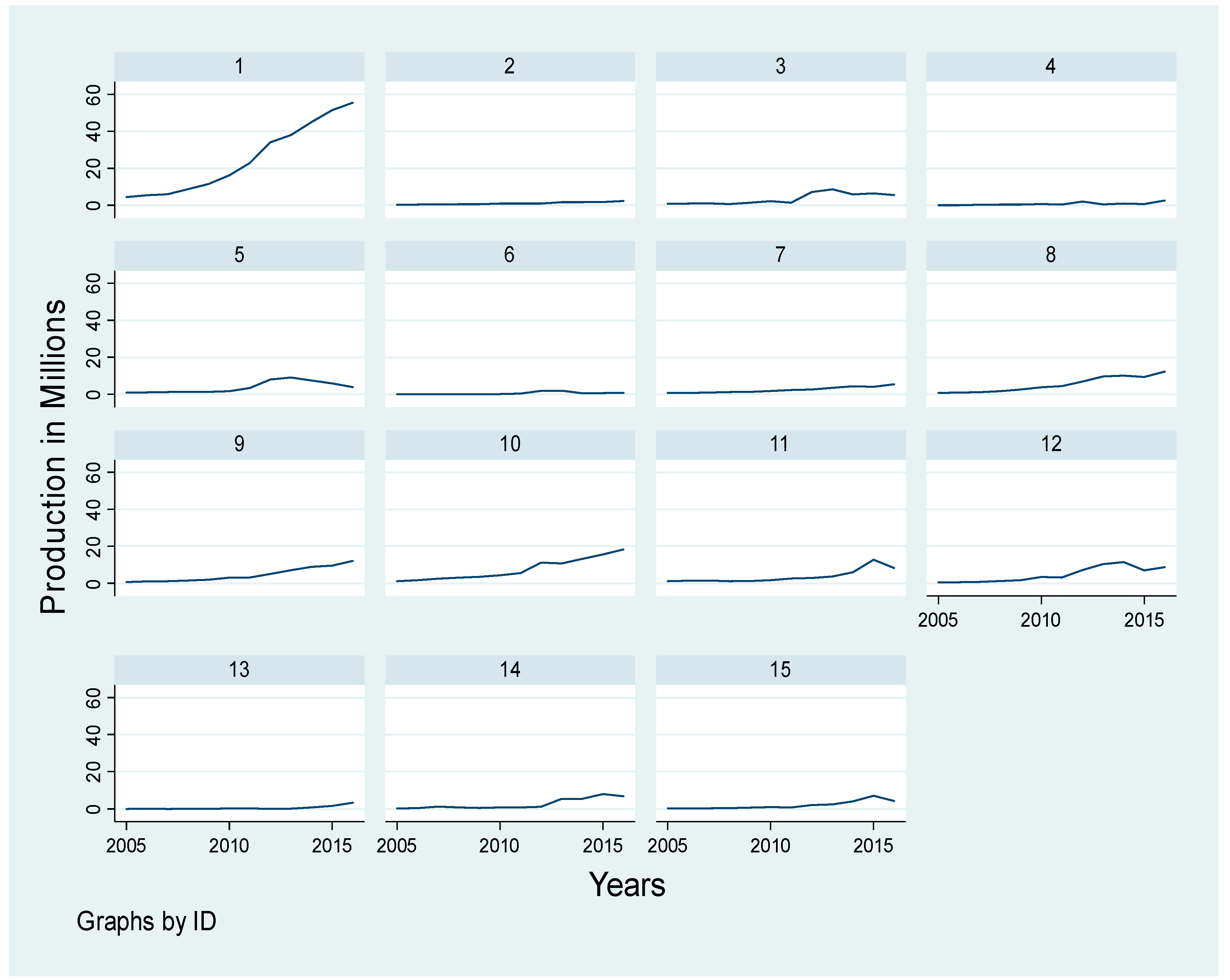

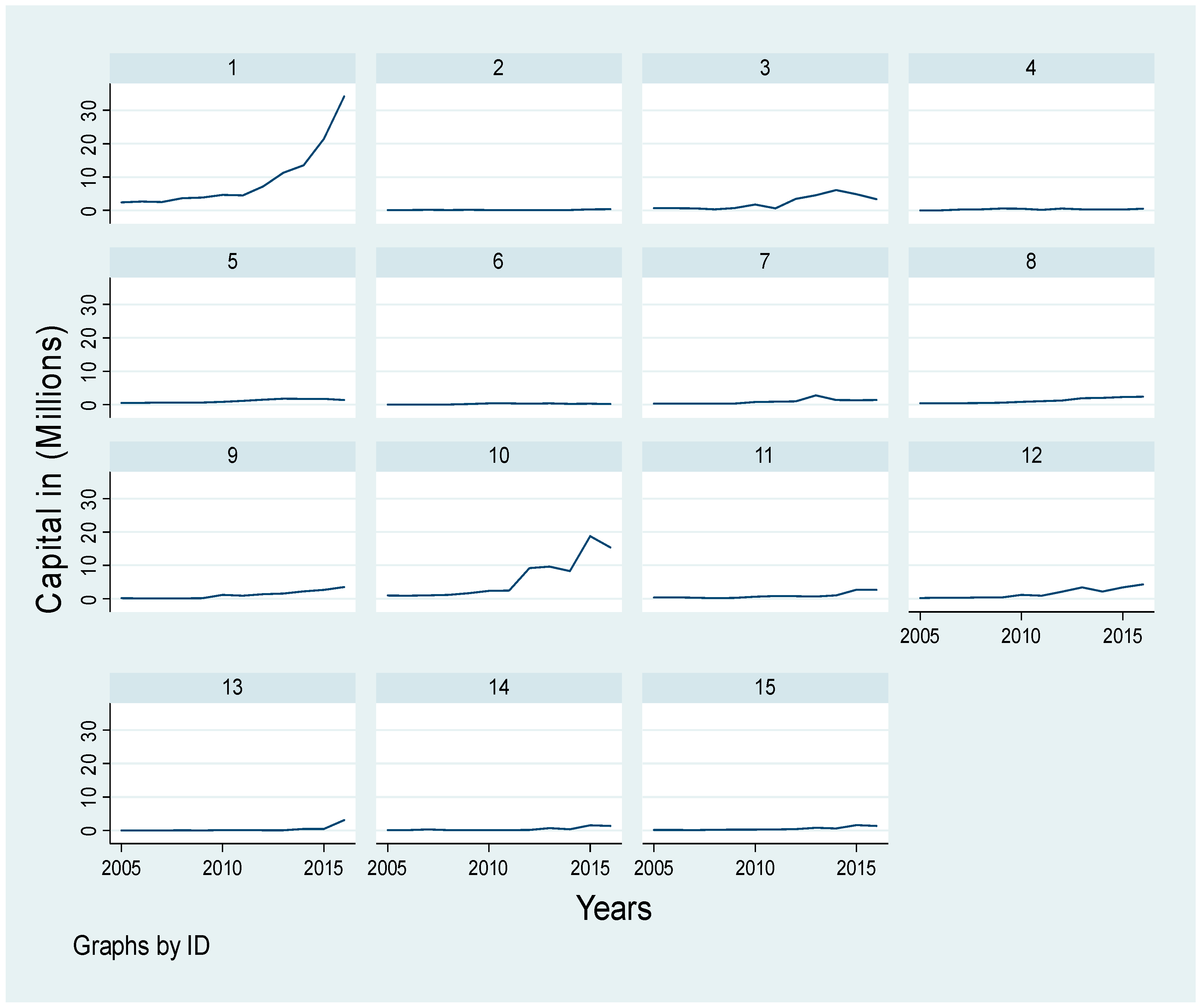
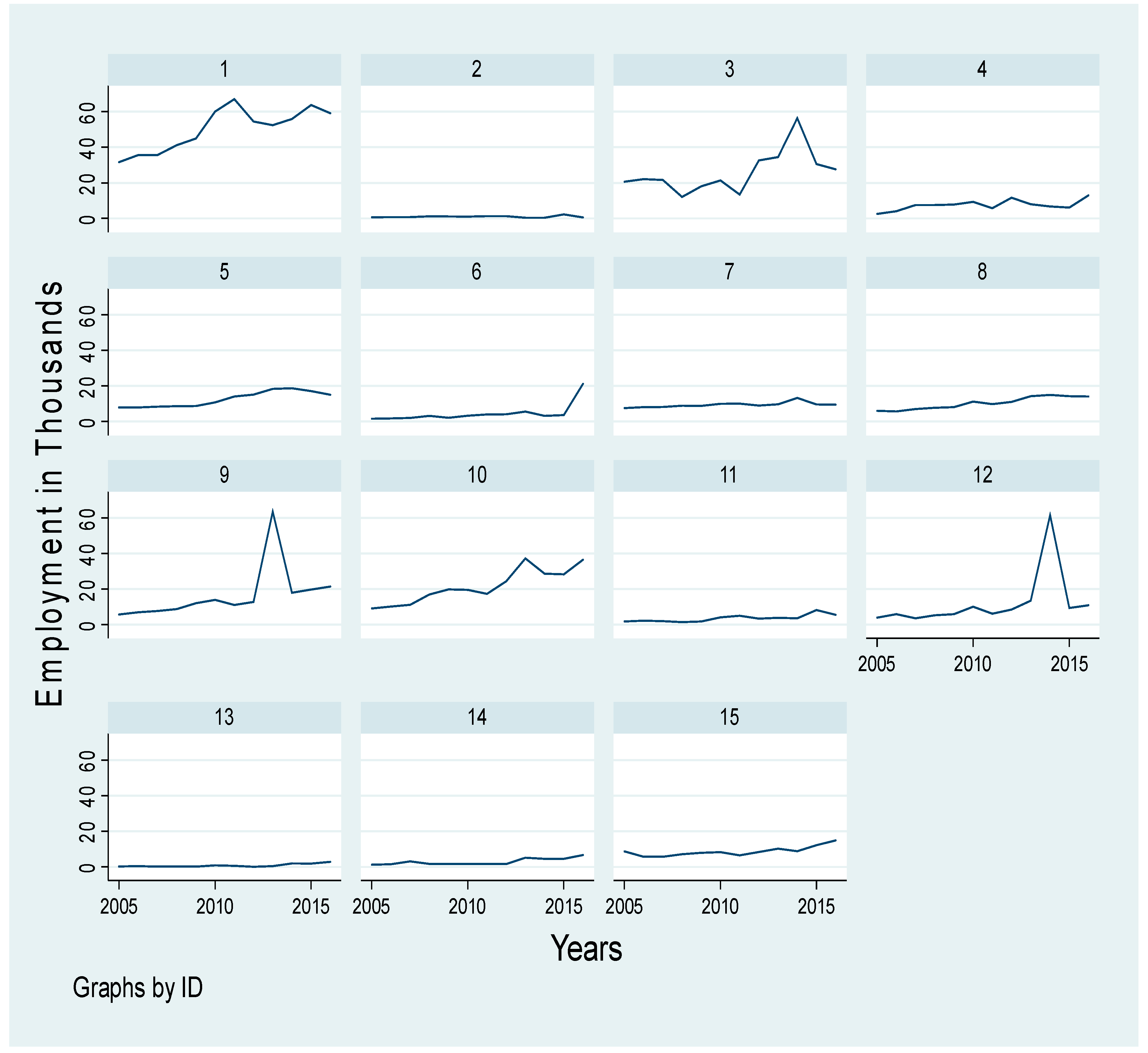


| Industry Code | Industry Group (Sector) |
|---|---|
| 1 | Food Products and Beverages Industry |
| 2 | Tobacco Products Industry |
| 3 | Textiles Industry |
| 4 | Wearing Apparel, Except Fur Apparel Industry |
| 5 | Tanning and Dressing of Leather; Footwear, Luggage, and Handbags Industry |
| 6 | Wood and of Products of Wood and Cork, Except Furniture Industry |
| 7 | Paper, Paper Products, and Printing Industry |
| 8 | Chemicals and Chemical Products Industry |
| 9 | Rubber and Plastic Products Industry |
| 10 | Other Non-Metallic Mineral Products Industry |
| 11 | Basic Iron and Steel Industry |
| 12 | Fabricated Metal Products Except Machinery and Equipment Industry |
| 13 | Machinery and Equipment Industry |
| 14 | Motor Vehicles, Trailers and Semi-Trailer Industry |
| 15 | Furniture; Manufacturing Industry |
| Variables | Variable Definitions | Expected Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Dependent variable: | ||
| Labor Productivity | Ratio of gross value of production to number of employees | - |
| Independent variables: | ||
| Production | Gross value of production by industrial group (in 000 Birr) | - |
| Employment | Number of employees by industrial group | positive |
| Energy | Ratio of value of energy consumed to total industrial expenditure by industry group | positive |
| Capital | Total value of fixed assets by industry group (in 000 Birr) | positive |
| Time trend | Is a proxy for technical change and is included in the model as a control variable | positive |
| Variable | Variations | Mean | Std. Dev. | Minimum | Maximum | Observations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID | Overall | 8 | 4.3349 | 1 | 15 | NT = 180 |
| Between | 4.4721 | 1 | 15 | N = 15 | ||
| Within | 0 | 8 | 8 | T = 12 | ||
| Years | Overall | 2010.5 | 3.4616 | 2005 | 2016 | NT = 180 |
| Between | 0 | 2010.5 | 2010.5 | N = 15 | ||
| Within | 3.4617 | 2007 | 2016 | T = 12 | ||
| Production | Overall | 453,240 | 8,002,421 | 13673 | 5.54 × 107 | NT =180 |
| Between | 5,985,648 | 551,875.1 | 2.50 × 107 | N = 15 | ||
| Within | 5,514,752 | −1.60 × 107 | 3.50 × 107 | T = 12 | ||
| Employment | Overall | 12,512.6 | 14,497.45 | 48 | 67,072 | NT = 180 |
| Between | 12,699.86 | 813 | 50,190.67 | N = 15 | ||
| Within | 7668.181 | −5985.011 | 62,091.91 | T = 12 | ||
| Productivity | Overall | 428.838 | 563.5947 | 19.6428 | 4078.363 | NT = 180 |
| Between | 364.3505 | 85.9931 | 1470.145 | N = 15 | ||
| Within | 439.3695 | −587.8283 | 3037.057 | T = 12 | ||
| Capital | Overall | 175,329 | 3,860,281 | 4686 | 3.42 × 107 | NT = 180 |
| Between | 2,541,552 | 160,494.1 | 9,332,244 | N = 15 | ||
| Within | 2973086 | −5,173,360 | 2.66 × 107 | T = 12 | ||
| Energy | Overall | 0.0730 | 0.11774 | 0.0010 | 0.6210 | NT = 180 |
| Between | 0.11285 | 0.0132 | 0.4650 | N = 15 | ||
| Within | 0.04369 | −0.1539 | 0.2290 | T = 12 | ||
| Cost of Labor | Overall | 275,439 | 488,709.7 | 1329 | 4,023,882 | NT = 180 |
| Between | 351,034.5 | 30,176.83 | 1,466,912 | N = 15 | ||
| Within | 350,976.4 | −867,761 | 2,832,410 | T = 12 |
| Variables | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Robust | Robust | Robust | ||||
| Coef. | Std. Err | Coef. | Std. Err | Coef. | Std. Err | |
| Labor (log) | 0.2730 *** | (0.0755) | −0.7269 *** | (0.0755) | - | - |
| Capital (log) | 0.7029 *** | (0.0544) | 0.7027 *** | (0.0544) | 0.0014 *** | 0.0004 |
| Energy (log) | 0.0895 *** | (0.0146) | 0.0895 *** | (0.0146) | 0.1082 *** | 0.0127 |
| Time trend | 0.0226 *** | (0.0502) | 0.0226 *** | (0.0050) | 0.0374 *** | 0.0088 |
| Constant | 0.7930 *** | (0.1996) | 0.7930 *** | (0.1996) | 1.7272 *** | 0.0541 |
| RTS | 1.0655 | |||||
| AdjR2 | 0.8979 | 0.8285 | 0.6074 | |||
| F-statistics (p-value) | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | |||
| Fixed Effects | Random Effects | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 2 | Model 3 |
| Coef. | Coef. | Coef. | Coef. | |
| Log Labor | −0.5541 *** (0.1287) | - - | −0.5748 *** (0.1311) | - - |
| Log Capital | 0.3545 *** (0.0420) | 0.3807 *** (0.0475) | 0.4205 *** (0.0449) | 0.4513 *** (0.0562) |
| Log Energy | 0.0405 ** (0.0209) | 0.0335 *** (0.0113) | 0.0474 *** (0.0201) | 0.0487 *** (0.0182) |
| Time Trend | 0.0552 *** (0.0075) | 0.0454 *** (0.0045) | 0.0486 *** (0.0065) | 0.0400 *** (0.0046) |
| Constant | 2.0353 *** (0.5567) | 1.3045 *** (0.0822) | 1.7624 *** (0.4978) | 1.1679 *** (0.1056) |
| Test | H0 & H1 | Appropriate Model | Prob of chi2 & chibar2 | Decision |
| Breusch and Pagan LM Test | H0 | Pooled OLS | 0.000 | reject H0 |
| H1 | Random Effects | |||
| Hausman test | H0 | Random Effects | 0.000 | reject H0 |
| H1 | Fixed Effects | |||
| Difference GMM | System GMM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 2 | Model 3 |
| Coef. | Coef. | Coef. | Coef. | |
| Productivity_L1 | 0.1443 (0.1286) | 0.1210 (0.1667) | 0.1342 ** (0.0592) | 0.0990 (0.1004) |
| Log Labor | −0.6557 *** (0.1155) | - - | −0.5997 *** (0.0549) | - - |
| Log Capital | 0.5438 *** (0.0516) | 0.0007 *** (0.0002) | 0.5276 *** (0.0442) | 0.5391 *** (0.0373) |
| Log Energy | 0.0393 *** (0.0188) | 0.0221 (0.0153) | 0.0357 *** (0.0098) | 0.0311 *** (0.0071) |
| Time trend | 0.0263 *** (0.0091) | 0.0451 *** (0.0157) | 0.0255 *** (0.0039) | 0.0251 *** (0.0086) |
| Constant | 1.1946 *** (0.4445) | 1.6935 *** (0.3551) | 1.0919 *** (0.2333) | 0.8973 *** (0.2006) |
| AR (2) | 0.499 | 0.520 | ||
| Test for autocorrelation | 0.1958 | 0.1287 | ||
| Number of instruments | 5 | 4 | ||
| Number of groups | 15 | 15 | ||
| System GMM Dynamic Panel (With Time Dummies) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scale Effect Model (Model 2) | Input Intensity Effect Model (Model 3) | |||
| Coff. | Std. Err | Coff. | Std. Err | |
| Productivity_L1 | 0.1653 * | (0.0877) | 0.1660 * | (0.0874) |
| Log Labor | −0.6872 *** | (0.0607) | - | - |
| Log Capital | 0.6784 *** | (0.0545) | 0.7145 *** | (0.0481) |
| Log Energy | 0.0954 *** | (0.0171) | 0.0947 *** | (0.0108) |
| D.trend(2) | 0.7977 *** | (0.1921) | 0.0709 | (0.0805) |
| D.trend(3) | 0.8422 *** | (0.1929) | 0.1068 ** | (0.0805) |
| D.trend(4) | 0.8978 *** | (0.1933) | 0.1632 | (0.0805) |
| D.trend(5) | 0.8448 *** | (0.1982) | 0.1036 | (0.0807) |
| D.trend(6) | 0.8115 *** | (0.2085) | 0.0744 | (0.0817) |
| D.trend(7) | 0.9268 *** | (0.2058) | 0.1885 ** | (0.0814) |
| D.trend(8) | 0.9867 *** | (0.2121) | 0.2669 *** | (0.0832) |
| D.trend(9) | 1.0325 *** | (0.2178) | 0.2701 *** | (0.0835) |
| D.trend(10) | 1.0505 *** | (0.2191) | 0.2948 *** | (0.0832) |
| D.trend(11) | 0.9460 *** | (0.2271) | 0.1892 ** | (0.0858) |
| D.trend(12) | 0.9808 *** | (0.2277) | 0.2142 ** | (0.0857) |
| AR (2) | 0.853 | 0.779 | ||
| Test for Autocorrelation | 0.1200 | 0.1287 | ||
| Number of Instruments | 14 | 14 | ||
| Number of groups | 15 | 15 | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kebede, S.G.; Heshmati, A. Energy Use and Labor Productivity in Ethiopia: The Case of the Manufacturing Industry. Energies 2020, 13, 2714. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13112714
Kebede SG, Heshmati A. Energy Use and Labor Productivity in Ethiopia: The Case of the Manufacturing Industry. Energies. 2020; 13(11):2714. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13112714
Chicago/Turabian StyleKebede, Selamawit G., and Almas Heshmati. 2020. "Energy Use and Labor Productivity in Ethiopia: The Case of the Manufacturing Industry" Energies 13, no. 11: 2714. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13112714
APA StyleKebede, S. G., & Heshmati, A. (2020). Energy Use and Labor Productivity in Ethiopia: The Case of the Manufacturing Industry. Energies, 13(11), 2714. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13112714





