Drying of Lignite of Various Origins in a Pilot Scale Toroidal Fluidized Bed Dryer using Low Quality Heat
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Drying of Lignite
1.2. Toroidal Bed Reactor
1.3. Aims, Scope and Novelty Aspects of the Performed Work
2. Materials and Methods
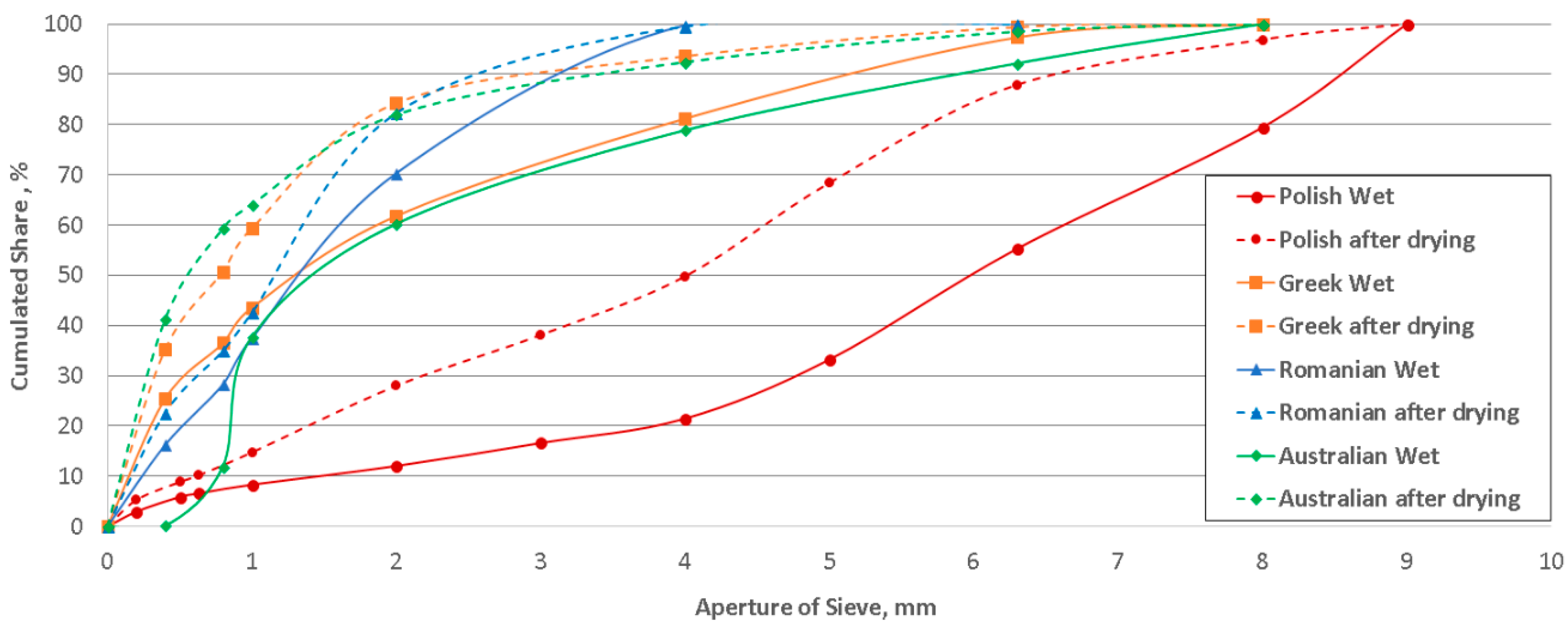
2.1. Characteristics of the Tested Lignites
- (1) Initial stage
- ∘
- Heat up to 105 °C; ramp 10 °C/min
- ∘
- Hold 10 min
- (2 a) To obtain ash content air was used:
- ∘
- Heat up to 815 °C; ramp 50 °C/min
- ∘
- Hold 15 min
- (2 b) To obtain volatile matter content argon was used:
- ∘
- Heat up to 850 °C; ramp 50 °C/min
- ∘
- Hold 15 min
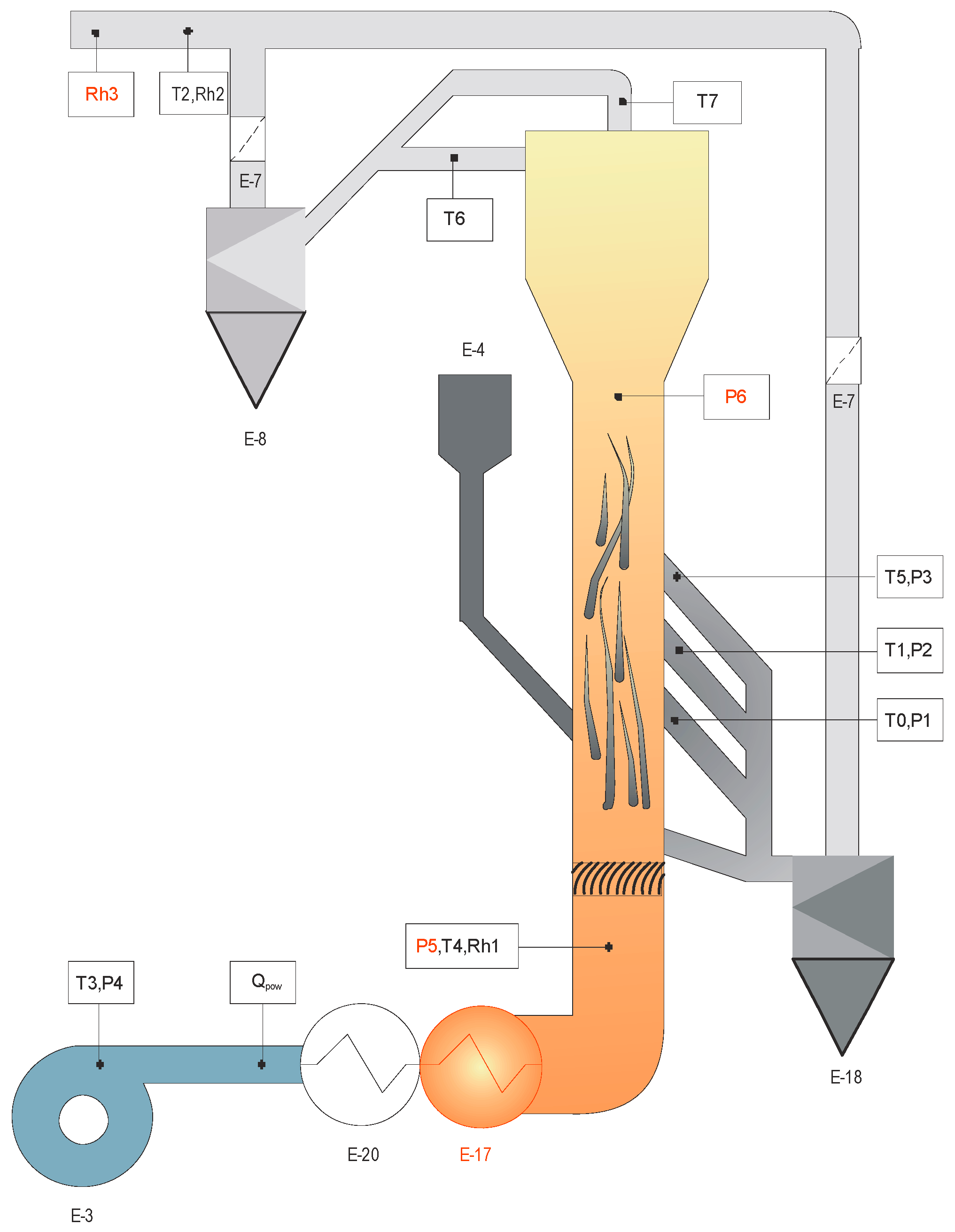
2.2. Test Rig—Toroidal Fluidized Bed Dryer
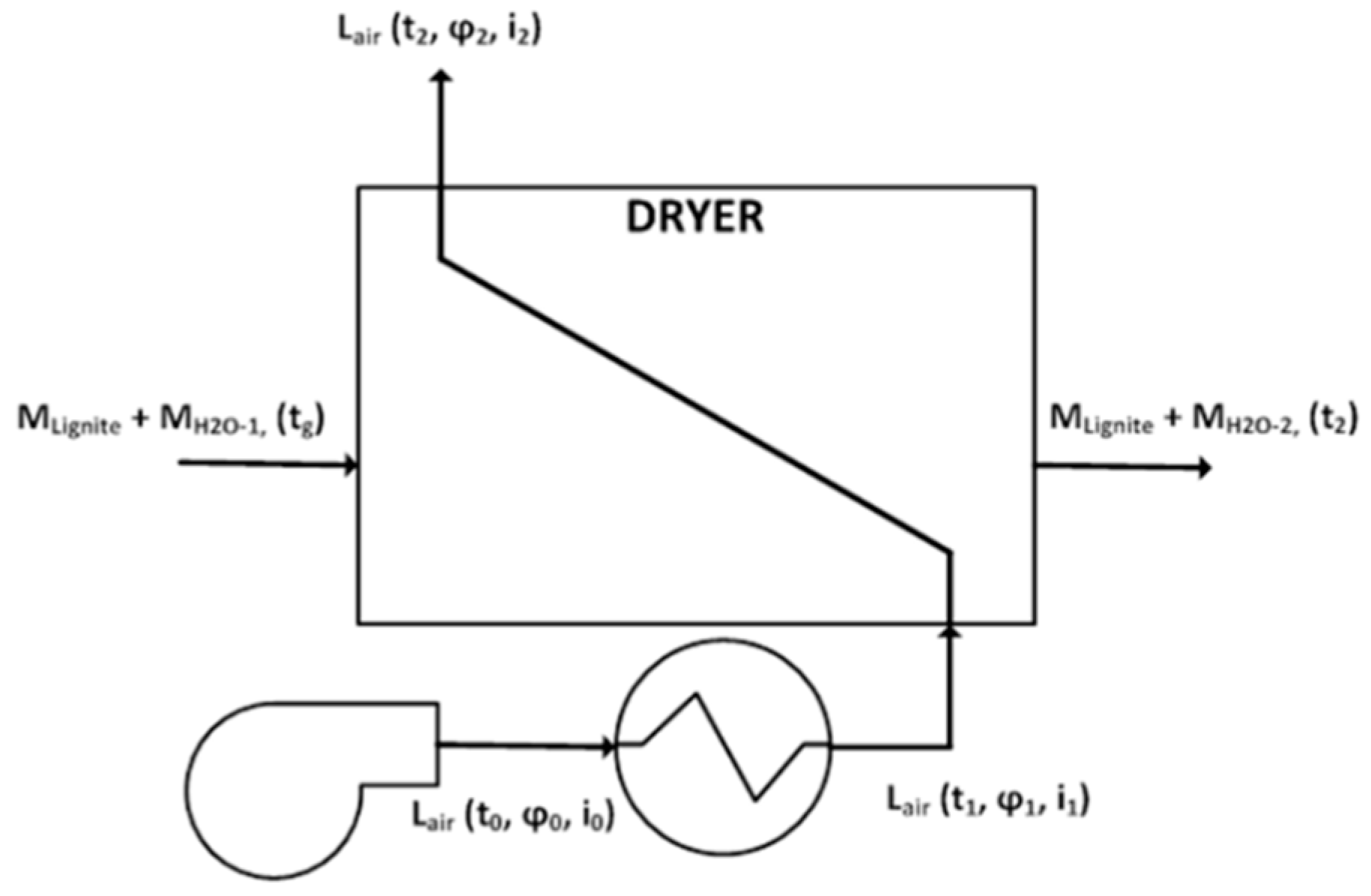
2.3. Zero-Dimensional Calculation Model of Drying—the Heat Balance of the Dryer
- is the enthalpy of the drying air at the exit of the heat exchanger;
- is the enthalpy of wet lignite entering the dryer, which could be separated into the enthalpy of water in the material and the enthalpy of dry matter;
- is the enthalpy of the moist air leaving the dryer;
- is the enthalpy of dried lignite leaving the dryer;
- represents the loss of the enthalpy to the ambient by the casing of the dryer.
- psat—saturated vapour pressure, Pa;
- T—temperature, °C.
- X—absolute moisture content in the air, kg·m−3 (dry air);
- φ—air relative humidity, %;
- p—humid (ambient) air pressure, Pa;
- psat—saturated vapour pressure, Pa.
- ΔX—increase of the absolute moisture of the drying agent (air), kg·m−3;
- Mevap—loss of water in the coal, kg;
- ΔX—increase of the absolute moisture of the drying agent (air), kg·m−3;
- —density of the wet air, kg·m−3;
- —density of the dry air, kg·m−3;
- Vwet—the air flow at the inlet of the dryer, m3·h−1.
2.4. Test Method and Schedule
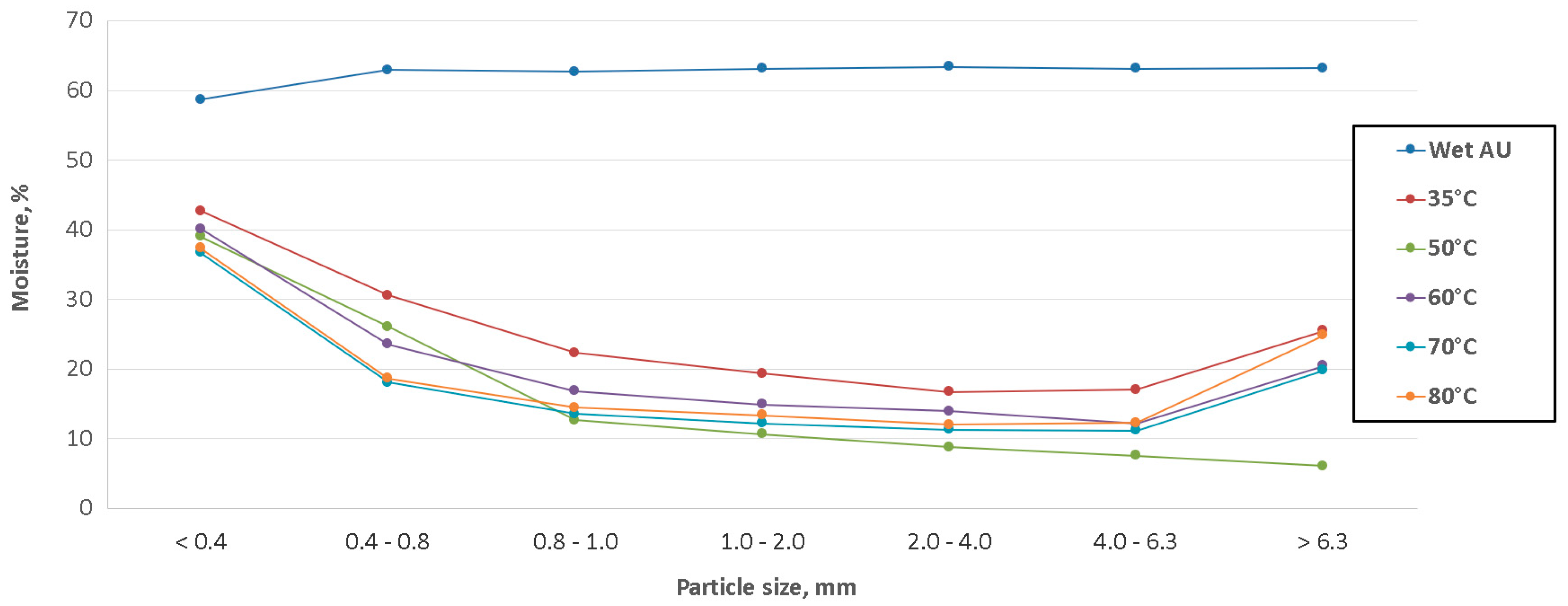
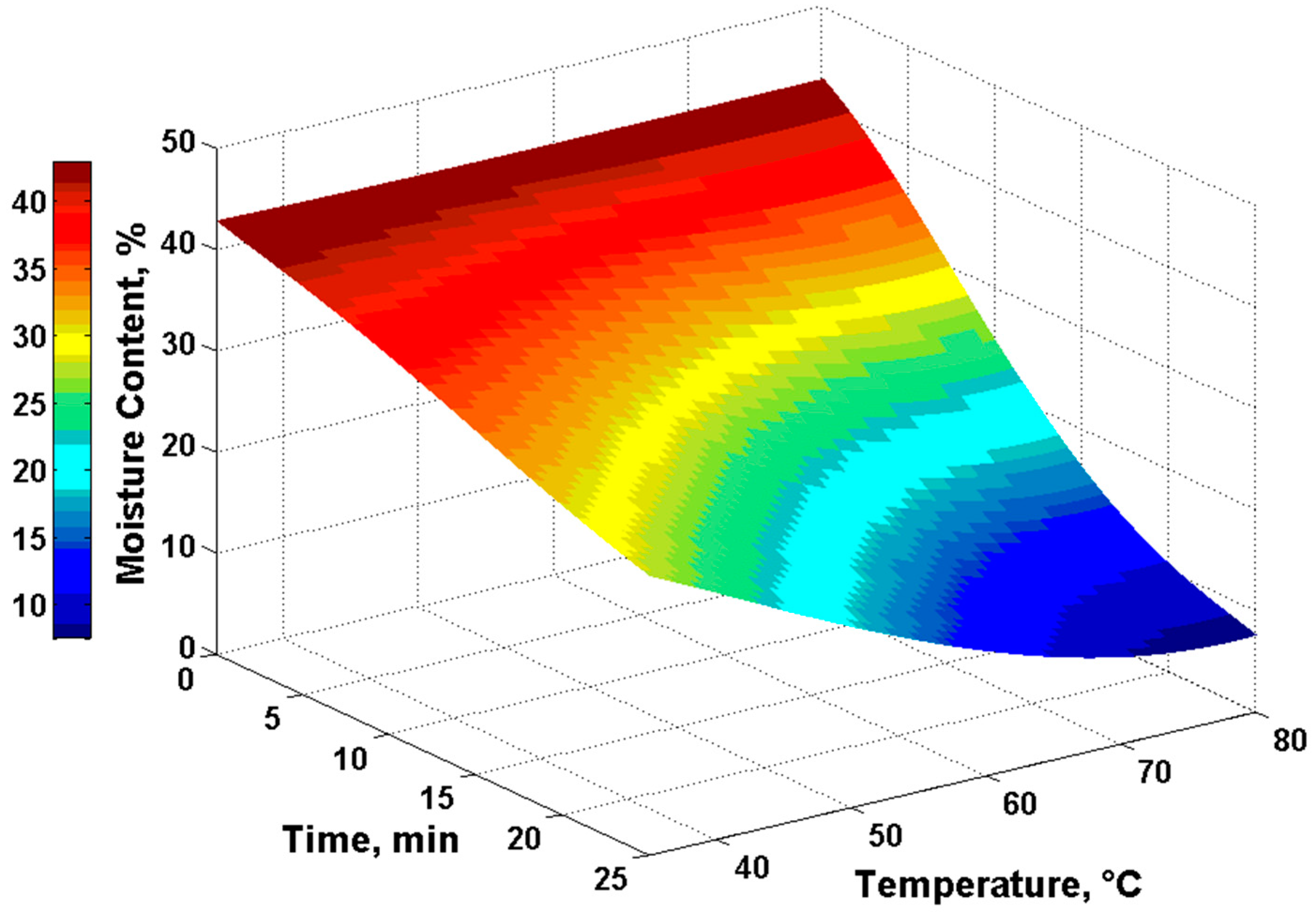
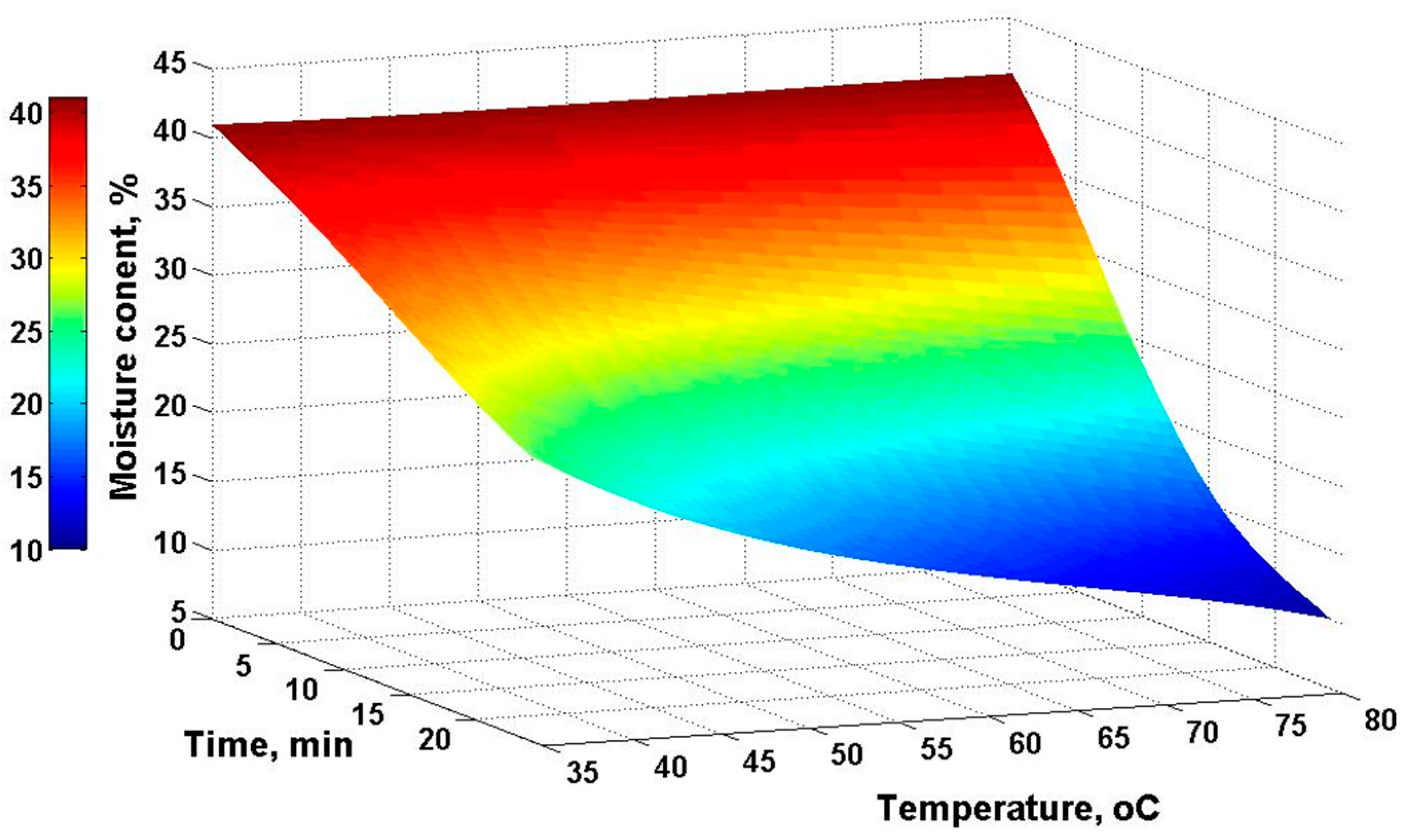
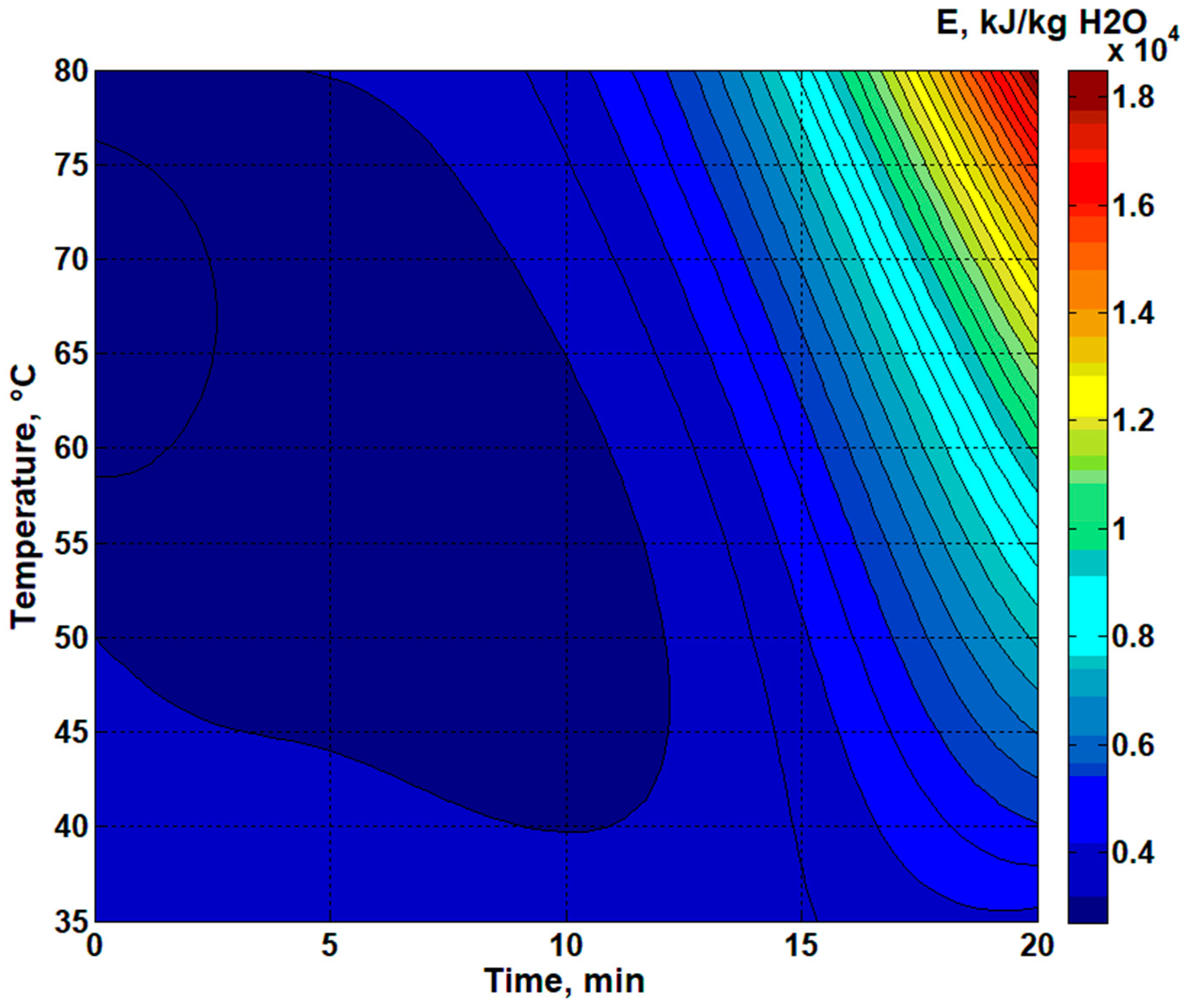
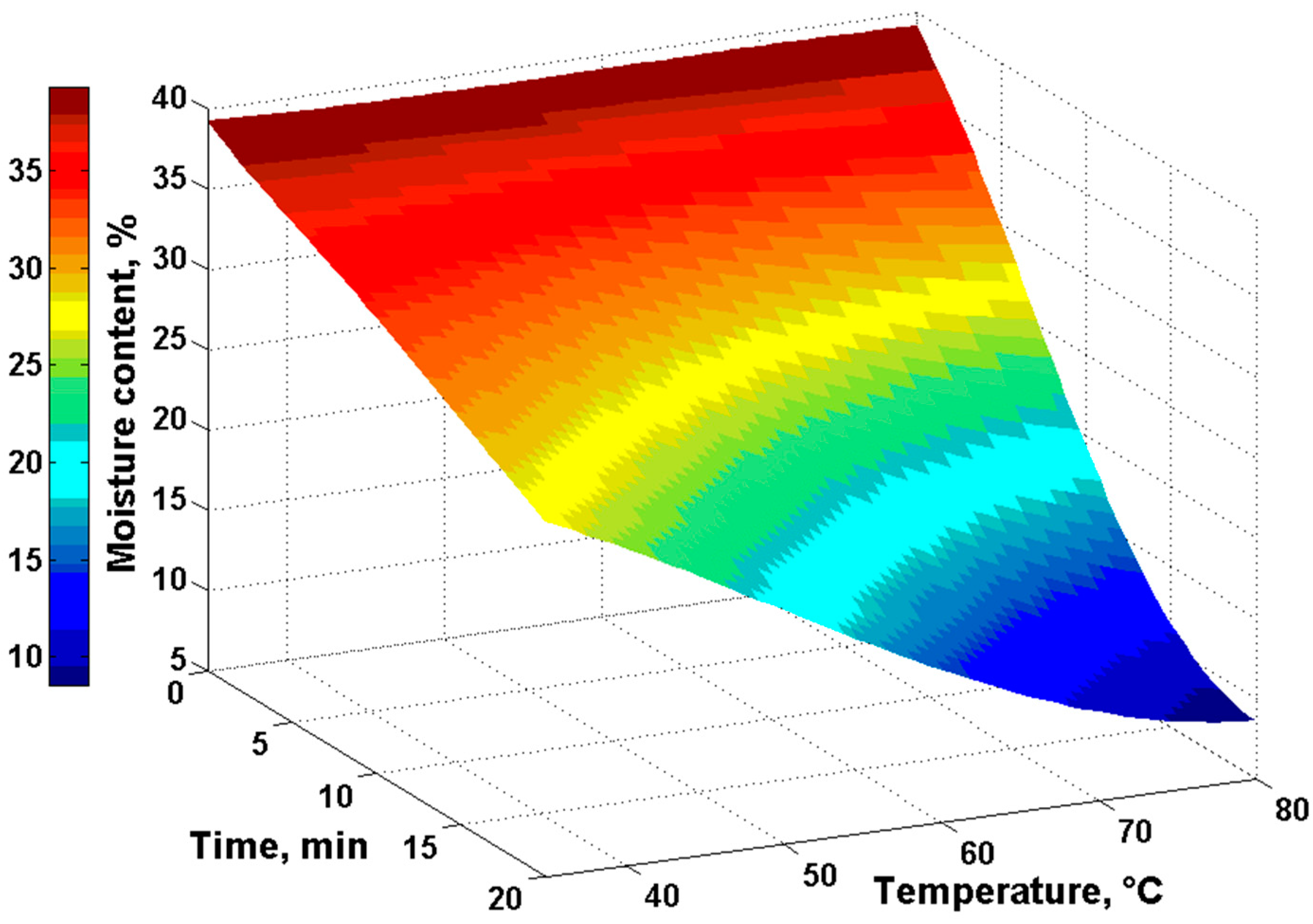
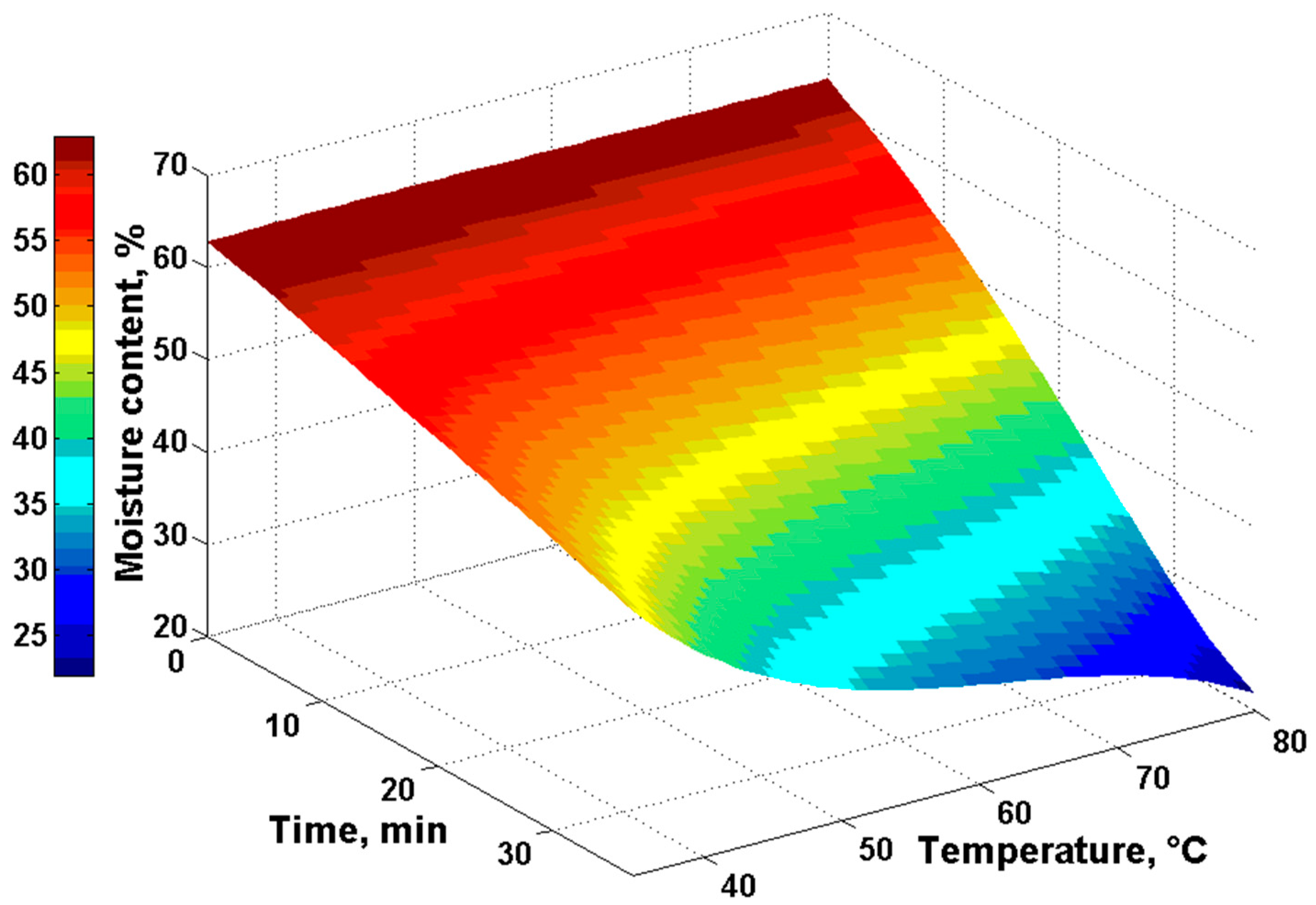
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The International Energy Agency IEA Coal Information. Coal Inf. Overv. 2017.
- EURACOAL. Coal Industry Across Europe, 6th ed.; European Association for Coal and Lignite AISBL: Brussels, Belgium, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pawlak-Kruczek, H. 2—Properties of low rank coals and resulting challenges in their utilization. In Low-Rank Coals for Power Generation, Fuel and Chemical Production; 2017; pp. 23–40. ISBN 9780081008959. [Google Scholar]
- Jóźwiak, W.; Kalewska, B.; Łoziński, M.; Mitura, Z.; Sieciński, J.; Wiśniewska, G. Nawóz organiczno-mineralny i sposób wytwarzania nawozu organiczno-mineralnego. Polish Patent PL 209547, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.H.; Lee, C.H.; Park, Y.C.; Shun, D.; Bae, D.H.; Park, J. Drying Efficiency of Indonesian Lignite in a Batch-Circulating Fluidized Bed Dryer. Dry. Technol. 2014, 32, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, C.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Shang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, G. Experimental study on three-stage microwave-assisted fluidized bed drying of Shengli lump lignite. Dry. Technol. 2016, 34, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Yao, L.; Jing, C.; Zhao, X.; Wang, W.; Ma, C. Drying behavior of lignite under microwave heating. Dry. Technol. 2017, 35, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusat, S.; Erdem, H.H. Drying characteristics of coarse low-rank-coal particles in a fixed-bed dryer. Int. J. Coal Prep. Util. 2017, 37, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Jing, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, L. Effect of Drying Conditions on Moisture Re-Adsorption Performance of Dewatered Lignite. Dry. Technol. 2013, 31, 1430–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Tang, J.; Ma, Z.; Wan, Y. Effect of mechanical thermal expression drying technology on lignite structure. Dry. Technol. 2017, 35, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Liao, J.; Liu, X.; Wei, F.; Chang, L. Removal behaviors of moisture in raw lignite and moisturized coal and their dewatering kinetics analysis. Dry. Technol. 2017, 35, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak-Kruczek, H.; Plutecki, Z.; Michalski, M. Brown Coal Drying in a Fluidized Bed Applying a Low-Temperature Gaseous Medium. Dry. Technol. 2014, 32, 1334–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agraniotis, M.; Stamatis, D.; Grammelis, P.; Kakaras, E. Numerical investigation on the combustion behaviour of pre-dried Greek lignite. Fuel 2009, 88, 2385–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasebi, A.; Zheng, H.; Yu, J. The influences of moisture on particle ignition behavior of Chinese and Indonesian lignite coals in hot air flow. Fuel Process. Technol. 2016, 153, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drosatos, P.; Nikolopoulos, N.; Nikolopoulos, A.; Papapavlou, C.; Grammelis, P.; Kakaras, E. Numerical examination of an operationally flexible lignite-fired boiler including its convective section using as supporting fuel pre-dried lignite. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 166, 237–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, Y.; Sciazko, A.; Zakrzewski, M.; Kimijima, S.; Hashimoto, A.; Kaneko, S.; Szmyd, J.S. An experimental investigation on the drying kinetics of a single coarse particle of Belchatow lignite in an atmospheric superheated steam condition. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 131, 356–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusat, S.; Akkoyunlu, M.T.; Erdem, H.H.; Daʇdaş, A. Drying kinetics of coarse lignite particles in a fixed bed. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 130, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciazko, A.; Komatsu, Y.; Zakrzewski, M.; Akiyama, T.; Hashimoto, A.; Shikazono, N.; Kaneko, S.; Kimijima, S.; Szmyd, J.; Kobayashi, Y. Experimental Attempts to Investigate the Influence of Petrographic Properties on Drying Characteristics of Lignite in Superheated Steam Atmosphere. Energies 2016, 9, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokie, D.; Woo, M.W.; Bhattacharya, S. Attrition of Victorian brown coal during drying in a fluidized bed. Dry. Technol. 2016, 34, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, J.; Lakshmanan, V.I.; Dodson, C.E. Hydrodynamic study of a toroidal fluidized bed reactor. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2000, 39, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, R.; Ramshaw, C.; Reay, D. Process intensification—Overcoming impediments to heat and mass transfer enhancement when solids are present, via the IbD project. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2017, 1, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W. A Review of Techniques for the Process Intensification of Fluidized Bed Reactors. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2009, 17, 688–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Quiroga, A.; Reyniers, P.A.; Kulkarni, S.R.; Torregrosa, M.M.; Perreault, P.; Heynderickx, G.J.; Van Geem, K.M.; Marin, G.B. Design and cold flow testing of a Gas-Solid Vortex Reactor demonstration unit for biomass fast pyrolysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 329, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wilde, J. Gas–solid fluidized beds in vortex chambers. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2014, 85, 256–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekatpure, R.P.; Suryawanshi, V.U.; Heynderickx, G.J.; de Broqueville, A.; Marin, G.B. Experimental investigation of a gas-solid rotating bed reactor with static geometry. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2011, 50, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyogi, K.; Torregrosa, M.M.; Pantzali, M.N.; Heynderickx, G.J.; Marin, G.B. Experimentally validated numerical study of gas-solid vortex unit hydrodynamics. Powder Technol. 2017, 305, 794–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo, W.R.; De Wilde, J. Influence of solids outlets and the gas inlet design on the generation of a gas-solids rotating fluidized bed in a vortex chamber for different types of particles. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017, 173, 74–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reay, D.A. Heat transfer enhancement—A review of techniques and their possible impact on energy efficiency in the U.K. Heat Recover. Syst. CHP 1991, 11, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Mustaffar, A.; Phan, A.N.; Zivkovic, V.; Reay, D.; Law, R.; Boodhoo, K. A review of process intensification applied to solids handling. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2017, 118, 78–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blissett, R.; Sommerville, R.; Rowson, N.; Jones, J.; Laughlin, B. Valorisation of rice husks using a TORBED� combustion process. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 159, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.T.; Dutrizac, J.E. Characterization of the Calcines Produced by the Roasting of Zinc Sulphide Concentrates in a Torbed Reactor. Can. Metall. Q. 2003, 42, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonough, J.R.; Law, R.; Reay, D.A.; Zivkovic, V. Intensified carbon capture using adsorption: Heat transfer challenges and potential solutions. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2018, 8, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batcha, M.F.M.; Salleh, H.; Raghavan, V.R. Studies on Biomass Drying Apparatus Using Swirling Fluidization Technique. In Proceedings of the MUCEET 2009 Malaysian Technical Universities Conference on Engineering and Technology, Kuantan, Pahang, Malaysia, 20–22 June 2009; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolopoulos, N.; Violidakis, I.; Karampinis, E.; Agraniotis, M.; Bergins, C.; Grammelis, P.; Kakaras, E. Report on comparison among current industrial scale lignite drying technologies (A critical review of current technologies). Fuel 2015, 155, 86–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, M.; Zhonghua, W.; Mujumdar, A.S. Low-Rank Coal Drying Technologies—Current Status and New Developments. Dry. Technol. 2009, 27, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, C.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shang, X. Drying of Low-Rank Coals: A Review of Fluidized Bed Technologies. Dry. Technol. 2015, 33, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atsonios, K.; Violidakis, I.; Agraniotis, M.; Grammelis, P.; Nikolopoulos, N.; Kakaras, E. Thermodynamic analysis and comparison of retrofitting pre-drying concepts at existing lignite power plants. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2015, 74, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nenad Sarunac; Mark Ness. Charles Bullinger Improve Plant Efficiency and Reduce CO2 Emissions When Firing High-Moisture Coals. Available online: http://www.powermag.com/improve-plant-efficiency-and-reduce-co2-emissions-when-firing-high-moisture-coals/ (accessed on 15 April 2018).
- Bullinger, C.; Ness, M.; Sarunac, N. Coal Creek Prototype Fluidized Coal Dryer: Performance Improvement, Emissions Reduction and Operating Experience. In Proceedings of the 31st International Technical Conference on Clean Coal & Fuel Systems, Clearwater, FL, USA, 5–9 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sarunac, N.; Bullinger, C.W.; Ness, M. Four Years of Operating Experience with DryFining TM Fuel Enhancement Process at Coal Creek Generating Station. J. Energy Power Eng. 2015, 9, 526–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak-Kruczek, H.; Ostrycharczyk, M.; Plutecki, Z. Potential and Possibilities for Improving Power Unit Efficiency and Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emission. In Proceedings of the XIII International Scientific and Technical Conference, Thermal Power Plant Operation Modernization Rehabilitation, Słok, Bełchatów, Poland, 31 May–2 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Agraniotis, M.; Karellas, S.; Violidakis, I.; Doukelis, A.; Grammelis, P.; Kakaras, E. Investigation of pre-drying lignite in an existing Greek power plant. Therm. Sci. 2012, 16, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkoyunlu, M.T.; Erdem, H.H.; Pusat, S. Determination of economic upper limit of drying processes in coal-fired power plants. Dry. Technol. 2016, 34, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agraniotis, M.; Koumanakos, A.; Doukelis, A.; Karellas, S.; Kakaras, E. Investigation of technical and economic aspects of pre-dried lignite utilisation in a modern lignite power plant towards zero CO2 emissions. Energy 2012, 45, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Xu, G.; Zhao, S.; Zhou, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, D. An improved configuration of lignite pre-drying using a supplementary steam cycle in a lignite fired supercritical power plant. Appl. Energy 2015, 160, 882–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Qi, Z.; Chen, Q.; Wu, Y.; Xu, G.; Yang, Y. Modified high back-pressure heating system integrated with raw coal pre-drying in combined heat and power unit. Energies 2018, 11, 2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widera, M. An overview of lithotype associations of Miocene lignite seams exploited in Poland. Geologos 2016, 22, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Parameter | Symbol | Polish (Sieniawa) | Greek (Agios Dimitrios) | Romanian (Peșteana) | Australian (Yallourn) | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture content 1 | MC | 42.70 | 40.82 | 39.18 | 62.77 | % ar |
| Volatile matter content | VM | 66.70 | 42.30 | 35.00 | 38.60 | % db |
| Ash content | A | 11.00 | 41.21 | 43.46 | 1.90 | % db |
| Higher heating value | HHV | 22.97 | 11.07 | 14.72 | 22.90 | MJ/kg db |
| Lower heating value 2 | LHV | 11.59 | 5.22 | 7.66 | 7.08 | MJ/kg ar |
| Carbon content | C | 51.00 | 27.8 | 31.86 | 61.54 | % db |
| Hydrogen content | H | 4.23 | 2.55 | 3.22 | 3.87 | % db |
| Nitrogen content | N | 0.94 | 0.56 | 0.74 | 0.61 | % db |
| Sulfur content | S | 0.87 | 0.49 | 1.14 | 0.50 | % db |
| Oxygen content 3 | O | 42.96 | 27.39 | 19.58 | 31.58 | % db |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pawlak–Kruczek, H.; Czerep, M.; Niedzwiecki, L.; Karampinis, E.; Violidakis, I.; Avagianos, I.; Grammelis, P. Drying of Lignite of Various Origins in a Pilot Scale Toroidal Fluidized Bed Dryer using Low Quality Heat. Energies 2019, 12, 1191. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12071191
Pawlak–Kruczek H, Czerep M, Niedzwiecki L, Karampinis E, Violidakis I, Avagianos I, Grammelis P. Drying of Lignite of Various Origins in a Pilot Scale Toroidal Fluidized Bed Dryer using Low Quality Heat. Energies. 2019; 12(7):1191. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12071191
Chicago/Turabian StylePawlak–Kruczek, Halina, Michał Czerep, Lukasz Niedzwiecki, Emmanouil Karampinis, Ioannis Violidakis, Ioannis Avagianos, and Panagiotis Grammelis. 2019. "Drying of Lignite of Various Origins in a Pilot Scale Toroidal Fluidized Bed Dryer using Low Quality Heat" Energies 12, no. 7: 1191. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12071191
APA StylePawlak–Kruczek, H., Czerep, M., Niedzwiecki, L., Karampinis, E., Violidakis, I., Avagianos, I., & Grammelis, P. (2019). Drying of Lignite of Various Origins in a Pilot Scale Toroidal Fluidized Bed Dryer using Low Quality Heat. Energies, 12(7), 1191. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12071191







