Sensitivity Analysis of Fuel Injection Characteristics of GDI Injector to Injector Nozzle Diameter
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Basic Mathematical Model
3. Problem Description
4. Validation of Mathematical Model
5. Results and Discussions
5.1. Influences of Injection Pressure on Injection Process
5.2. Sensitivity Analysis of Fuel Injection Characteristics to Nozzle Diameter
5.3. Sensitivity Coefficient of Fuel Mass to the Nozzle Diameter under Different Injection Pressures
5.4. The Effect of the Nozzle Diameter on the Fuel Jet Condition of Near-Nozzle
6. Conclusions and Outlook
- The increase of the injection pressure accelerated the stability of the flow in the injector nozzle, intensified the cavitation in the nozzle, and decreased the liquid fraction volume of the nozzle outlet.
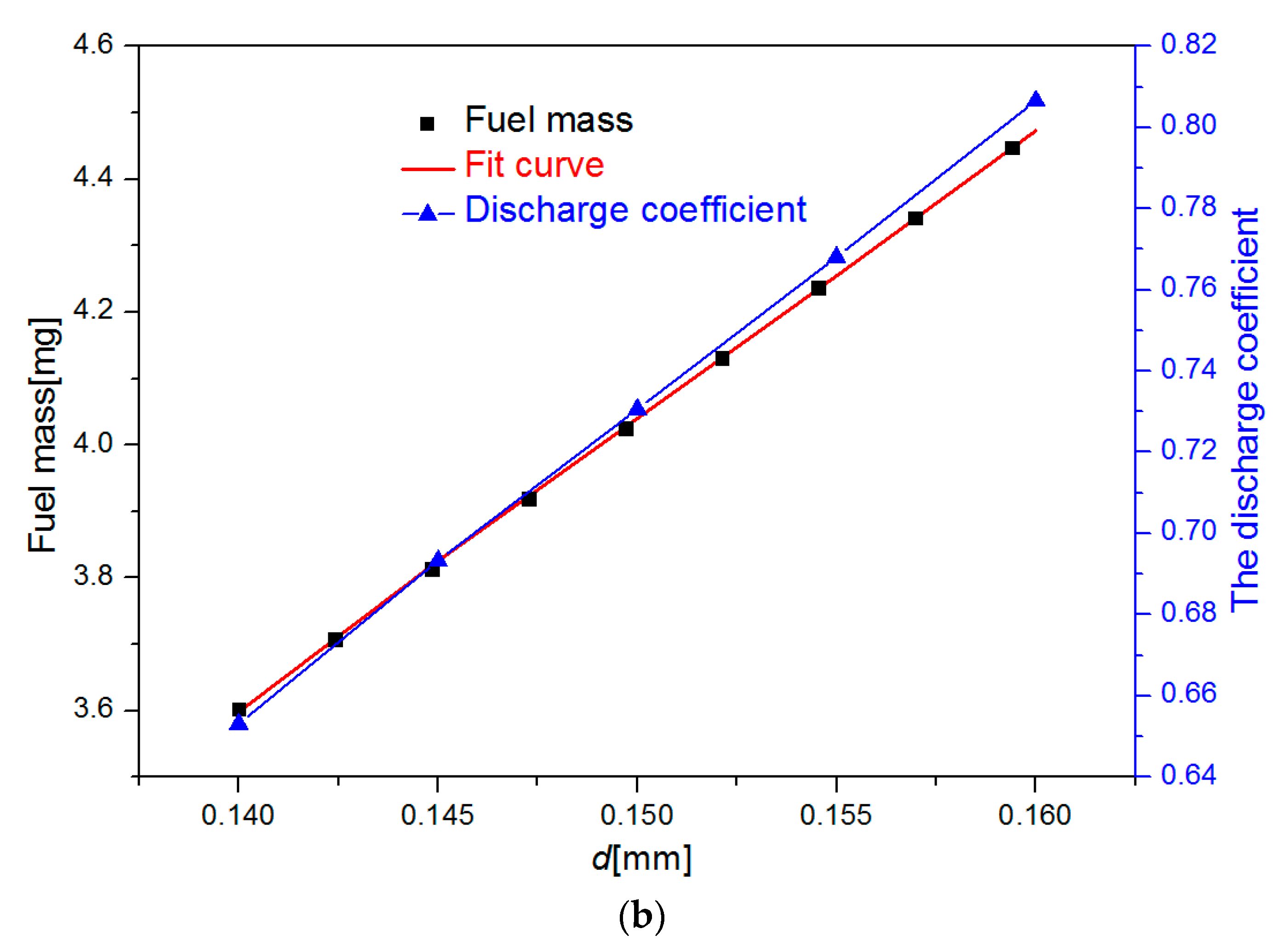
- The increase of the nozzle diameter increased the flow velocity of the nozzle outlet, shortened the transition period, and accelerated the stability of the fuel injection rate. The cycle injection fuel mass increased linearly with the increase of the nozzle diameter.
- The sensitivity of the circulating injection volume to nozzle diameter became strong with the increase of the injection pressure. A fitting function was proposed to calculate the effect of the nozzle diameter and injection pressure on the fuel mass, and it could be used to provide guidance for the choice of machining accuracy of the nozzle diameter.
- Through the analysis of the flow characteristic near-nozzle field, the effect of the fluctuation in the small range of the diameter of the nozzle on the flow near the orifice was small. However, the increase of the injection pressure intensified cavitation in the nozzle and aggravated the deviation of the outlet liquid from the nozzle axis.
Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, B.; Li, Y.Q.; Wang, D.F. Numerical Simulation and Experiment on Spray Characteristics of GDI Engines. Trans. Csice 2012, 1, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, Q.; Xin, S.; Yan, L.; Hui, X. Cavitation Process and Flow Characteristics inside Diesel Injector Nozzle. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knorsch, T.; Mamaikin, D.; Leick, P.; Rogler, P.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Wensing, M. Comparison of Shadowgraph Imaging, Laser-Doppler Anemometry and X-Ray Imaging for the Analysis of Near Nozzle Velocities of GDI Fuel Injectors. Int. Powertrainsfuels Lubr. Meet. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knorsch, T.; Rogler, P.; Miller, M.; Wiese, W. On the evaluation methods for systematic further development of direct-injection nozzles. SAE Int. Powertrainsfuels Lubr. Meet. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Zhong, W.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Fu, Y. An investigation of transient nature of the cavitating flow in injector nozzles. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2013, 54, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.J.; Song, R.Z.; Wang, L.L. The effect of cavitation on the inner-flow and spray characteristic of GDI injector. Veh. Engine 2015, 6, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Xu, M.; Hung, D.L.; Pan, H. Effects of nozzle configuration on internal flow and primary jet breakup of flash boiling fuel sprays. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 110, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yao, C.; Wang, Q.; Han, G.; Dou, Z.; Wei, H.; Wang, B.; Liu, M.; Wu, T. Cylinder-to-Cylinder Variation in a Diesel Engine Fueled with Diesel/Methanol Dual Fuel. J. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2017, 23, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, X.; Jia, C.; Shi, C.; Teng, W. Effects of injection pressure and nozzle diameter and fuel property on spray characteristics of blended diesel fuel. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. (Trans. Csae) 2018, 34, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.Z.; An, Y.Z.; Su, W.H.; Mao, L.W.; Liang, Y.F.; Dai, Y.L. Investigation on the Influence of Injection Pressure and Nozzle Diameter on the Spray of Blended Fuel in Diesel Engine. Trans. Chin. Soc. Intern. Combust. Engines 2013, 31, 200–207. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Moon, S.; Sato, K.; Yokohata, H. A comprehensive study on the factors affecting near-nozzle spray dynamics of multi-hole GDI injectors. Fuel 2016, 190, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.S.; Lu, P.H.; Xie, X.B.; Lai, M.C.; Henein, N.A. Investigation of Diesel Spray Primary Break-up and Development for Different Nozzle Geometries. Simul. Model. 2002, 1, 2528–2548. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, S.; Komada, K.; Sato, K.; Yokohata, H.; Wada, Y.; Yasuda, N. Ultrafast X-ray study of multi-hole GDI injector sprays: Effects of nozzle hole length and number on initial spray formation. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2015, 68, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, K.; Som, S.; Battistoni, M.; Li, Y.; Quan, S.; Senecal, P.K. Numerical simulation of internal and near-nozzle flow of a gasoline direct injection fuel injector. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2015, 656, 012100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, A.; Ranade, V.V. Modelling of Hydrodynamic Cavitation with Orifice: Influence of different orifice designs. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 136, 698–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.W.; Pei, Y.Q.; Peng, Z.J.; Zhang, Y.F.; Qin, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, C.W.; Zhang, X.Y. Characteristics of near-nozzle spray development from a fouled GDI injector. Fuel 2018, 219, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Park, S. Spray atomization characteristics of a GDI injector equipped with a group-hole nozzle. Fuel 2014, 137, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, D.J.; Kastengren, A.L.; Matusik, K.E.; Swantek, A.B.; Powell, C.F.; Payri, R.; Vaquerizo, D.; Itani, L.; Bruneaux, G.; Grover, R.O., Jr.; et al. Internal and near nozzle measurements of Engine Combustion Network “Spray G” gasoline direct injectors. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2017, 88, 608–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.; Song, X.; Lei, Y.; Liu, X.; An, X.; Lai, M. Influence of inlet pressure on cavitation flow in diesel nozzle. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 109, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tang, W.P.; Yan, D.U. Technical Research of Nozzle Spray Hole. Mod. Veh. Pwer 2010, 1, 43–46. [Google Scholar]


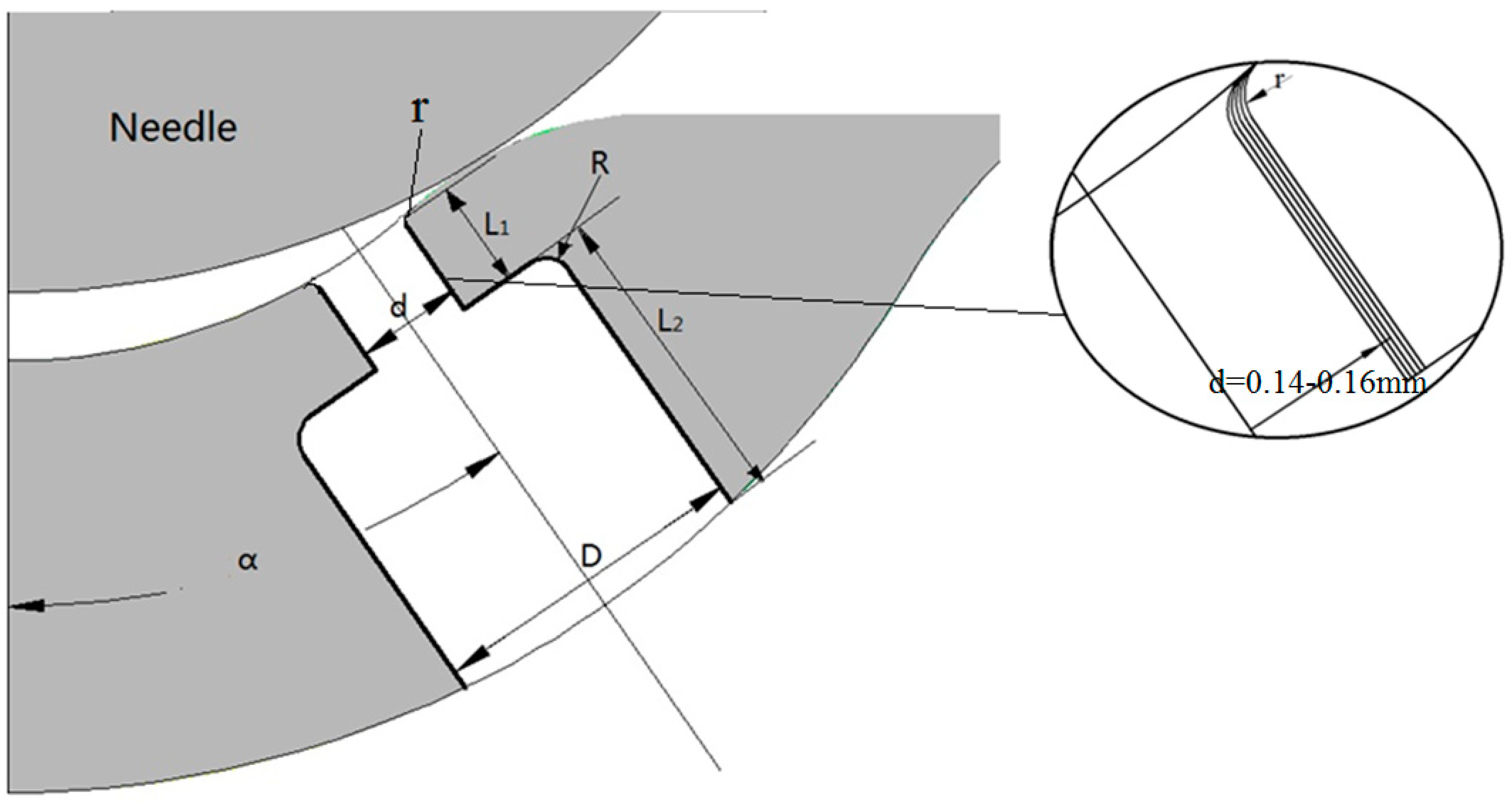










| Parameters | Value | Parameters | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| BND_inlet | 15, 20, 25, 30, 35 MPa | Cavitation model | non-linear cavitaiton model |
| BND_Outlet | 0.5 MPa | d | 0.140, 0.145, 0.150, 0.155, 0.160 mm |
| Fuel type | Gasoline | D | 0.45 mm |
| Fuel density | 725.1 kg/m3 | L1 | 0.15 mm |
| Fuel Viscosity | 0.721 mm2/s | L2 | 0.45 mm |
| Saturated vapor pressure | 44 kPa | R | 0.04 mm |
| Temperature | 293 K | r | 0.02 mm |
| Turbulence model | κ-ε model | α | 35° |
| Cavitation Number/CN | Back Pressure of Baseline Nozzle/MPa | Equivalent Back Pressure/MPa | Inlet Pressure of Baseline Nozzle/MPa | Equivalent Inlet Pressure/MPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.06 | 8 | 0.3 | 140 | 5 |
| 1.08 | 8 | 0.3 | 100 | 4 |
| 1.11 | 8 | 0.3 | 80 | 3 |
| 1.25 | 8 | 0.3 | 40 | 1.5 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Cheng, Y.; Ji, S.; Yang, X.; Wang, L. Sensitivity Analysis of Fuel Injection Characteristics of GDI Injector to Injector Nozzle Diameter. Energies 2019, 12, 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12030434
Li X, Cheng Y, Ji S, Yang X, Wang L. Sensitivity Analysis of Fuel Injection Characteristics of GDI Injector to Injector Nozzle Diameter. Energies. 2019; 12(3):434. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12030434
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xinhai, Yong Cheng, Shaobo Ji, Xue Yang, and Lu Wang. 2019. "Sensitivity Analysis of Fuel Injection Characteristics of GDI Injector to Injector Nozzle Diameter" Energies 12, no. 3: 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12030434
APA StyleLi, X., Cheng, Y., Ji, S., Yang, X., & Wang, L. (2019). Sensitivity Analysis of Fuel Injection Characteristics of GDI Injector to Injector Nozzle Diameter. Energies, 12(3), 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12030434




