Synthesis of TiO2–ZrO2 Mixed Oxides via the Alginate Route: Application in the Ru Catalytic Hydrogenation of Levulinic Acid to Gamma-Valerolactone
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
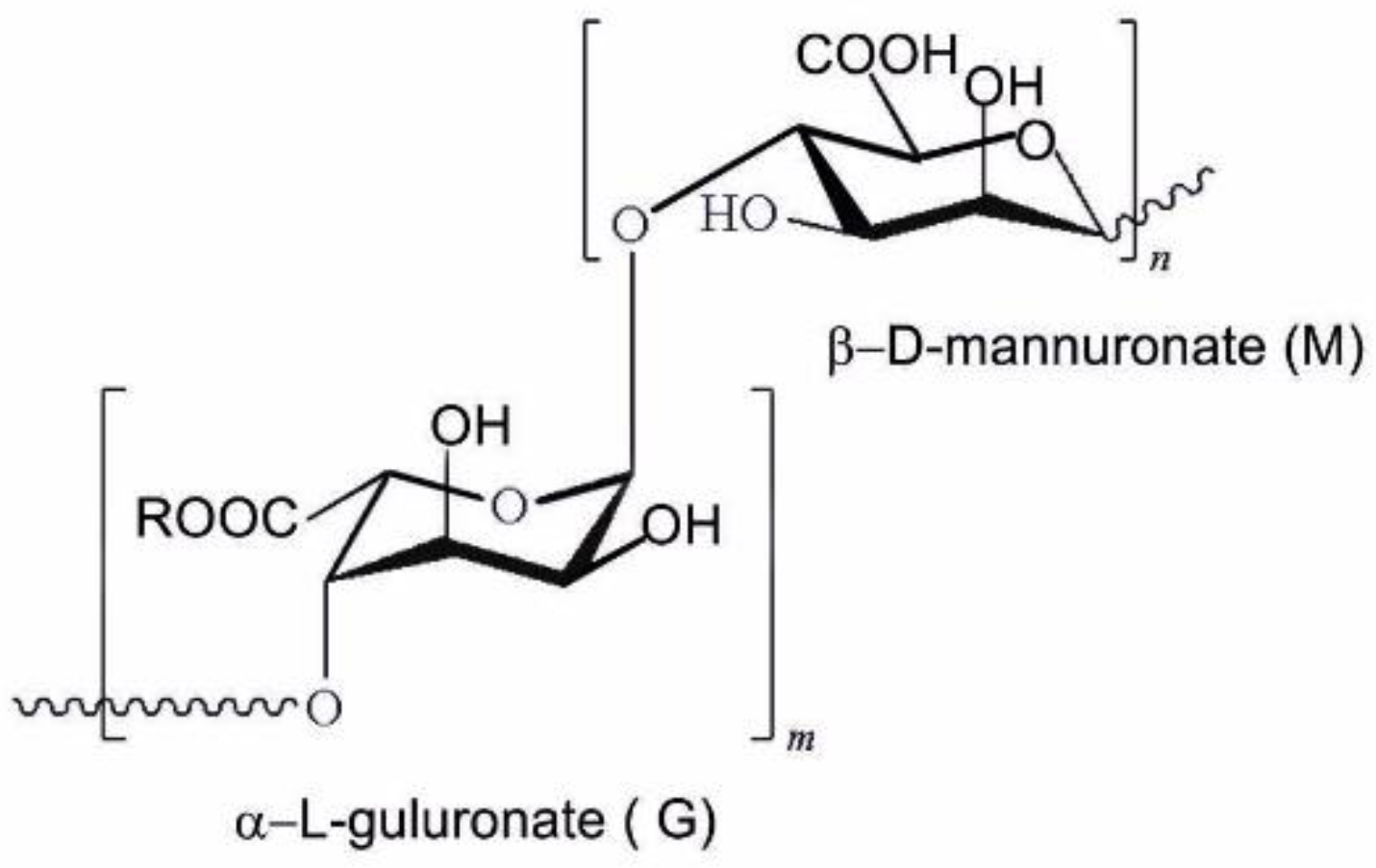
2.1. Preparation of the Oxides from Alginate Hydrogel Solution
- (a)
- For ZR-1, the hydrogel was obtained by gelification in an equimolar mixture of both precursors and kept in this mixture for 18 h;
- (b)
- For ZR-2, the hydrogel was firstly formed in the titanium (IV) solution for 18 h, then washed in deionized water and introduced to the zirconium solution (with a concentration corresponding to half of the titanium atoms) for 18 h; the following procedures were identical to those described above;
- (c)
- For ZR-3, the hydrogel was firstly formed in the zirconium solution for 18 h, then washed in deionized water and introduced to the titanium solution (with a concentration corresponding to half of the zirconium atoms) for 18 h; the following procedures were identical to those described above.
2.2. Catalyst Preparation
2.3. Catalyst Characterization
2.4. Catalytic Tests
Hydrogenation of Levulinic Acid (LA)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Physicochemical Characterization of the Materials
3.1.1. Synthesis and Composition
3.1.2. X-Ray Diffraction Tests
3.1.3. TEM Images and Ru Particle Size Distributions
3.1.4. ToF-SIMS and SEM Study
3.1.5. Reducibility of Catalysts by TPR
3.2. Catalytic Tests
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, X.; Clark, L.A.; Yang, Q.; Anderson, M.A. Enhanced photocatalytic performance of titania-based binary metal oxides: TiO2/SiO2 and TiO2/ZrO2. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996, 30, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quignard, F.; Valentin, R.; Di Renzo, F. Aerogel materials from marine polysaccharides. New J. Chem. 2008, 32, 1300–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horga, R.; Di Renzo, F.; Quignard, F. Ionotropic alginate aerogels as precursors of dispersed oxide phases. Appl. Catal. A 2007, 325, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agulhon, P.; Robitzer, M.; David, L.; Quignard, F. Structural regime identification in ionotropic alginate gels: Influence of the cation nature and alginate structure. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monakhova, Y.; Agulhon, P.; Quignard, F.; Tanchoux, N.; Tichit, D. New mixed lanthanum- and alkaline-earth cation-containing basic catalysts obtained by an alginate route. Catal. Today 2012, 189, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behar, S.; Gonzalez, P.; Agulhon, P.; Quignard, F.; Swierczynski, D. New synthesis of nanosized Cu–Mn spinels as efficient oxidation catalysts. Catal. Today 2012, 189, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agulhon, P.; Constant, S.; Chiche, B.; Lartigue, L.; Larionova, J.; Di Renzo, F.; Quignard, F. Controlled synthesis from alginate gels of cobalt–manganese mixed oxide nanocrystals with peculiar magnetic properties. Catal. Today 2012, 189, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, E.; Travert, A.; Quignard, F.; Tichit, D.; Tanchoux, N.; Petitjean, H. Modulating properties of pure ZrO2 for structure–activity relationships in acid-base catalysis: Contribution of the alginate preparation route. ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 2358–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, C.; Zaffran, J.; Ruppert, A.M.; Matras-Michalska, J.; Jedrzejczyk, M.; Grams, J.; Sautet, P. Role of water in metal catalyst performance for ketone hydrogenation: A joint experimental and theoretical study on levulinic acid conversion into gamma-valerolactone. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 12450–12453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shaal, M.G.; Wright, W.R.H.; Palkovits, R. Exploring the ruthenium catalysed synthesis of γ-valerolactone in alcohols and utilisation of mild solvent-free reaction conditions. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 1260–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Cui, J.; Deng, T.; Cui, X.; Ding, G.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y. Water-promoted hydrogenation of levulinic acid to γ-valerolactone on supported ruthenium catalyst. ChemCatChem 2015, 7, 508–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piskun, A.; Winkelman, J.M.G.; Tang, Z.; Heeres, H.J. Support screening studies on the hydrogenation of levulinic acid to γ-valerolactone in water using Ru catalysts. Catalysts 2016, 6, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruppert, A.M.; Grams, J.; Jedrzejczyk, M.; Matras-Michalska, J.; Keller, N.; Ostojska, K.; Sautet, P. Titania-supported catalysts for levulinic acid hydrogenation: Influence of support and its impact on γ-valerolactone yield. ChemSusChem 2015, 8, 1538–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ftouni, J.; Muñoz-Murillo, A.; Goryachev, A.; Hofmann, J.P.; Hensen, E.J.M.; Lu, L.; Kiely, C.J.; Bruijnincx, P.C.A.; Weckhuysen, B.M. ZrO2 is preferred over TiO2 as support for the Ru-catalyzed hydrogenation of levulinic acid to γ-valerolactone. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 5462–5472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genuino, H.C.; Bruijnincx, P.C.A.; Weckhuysen, B.M. Influence of sulfuric acid on the performance of Ruthenium-based catalysts in the liquid-phase hydrogenation of levulinic acid to γ-valerolactone. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 2891–2896. [Google Scholar]
- Ruppert, A.M.; Grams, J.; Matras-Michalska, J.; Chełmicka, M.; Przybysz, P. ToF-SIMS study of the surface of catalysts used in biomass valorization. Surf. Interface Anal. 2014, 46, 726–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachała, M.; Grams, J.; Kwapiński, W.; Ruppert, A.M. Influence of ZrO2 on catalytic performance of Ru catalyst in hydrolytic hydrogenation of cellulose towards γ-valerolactone. Int. J. Hydrogen Energ. 2016, 41, 8688–8695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, B.; Banfield, J.F.; Waychunas, G.A. Atomic structure of nanometer-sized amorphous TiO2. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 78, 214106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo, I.M.; Granados, M.L.; Garcia Fierro, J.L.; Mariscal, R. Sorbitol hydrogenolysis to glycols by supported ruthenium catalysts. Chin. J. Catal. 2014, 35, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Lin, Y.S. Structural and surface chemical properties of sol–gel derived TiO2–ZrO2 oxides. Appl. Catal. A 2004, 265, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Hernandez, R.; Mendoza-Anaya, D.; Fernandez, M.E.; Gomez-Cortes, A. Synthesis of mixed ZrO2–TiO2 oxides by sol–gel: Microstructural characterization and infrared spectroscopy studies of NOx. J. Mol. Catal. A 2008, 281, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, J.R.; Lee, S.H. Effect of TiO2–ZrO2 composition on catalytic activity of supported NiSO4 for ethylene dimerization. Appl. Catal. A 2007, 321, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Anderson, M.A. Sol–gel route to synthesis of microporous ceramic membranes: Thermal stability of TiO2–ZrO2 mixed oxides. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1993, 76, 2093–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triki, M.; Minh, D.P.; Ksibi, Z.; Ghorbel, A.; Besson, M. Ruthenium catalysts supported on TiO2 prepared by sol–gel way for p-hydroxybenzoic acid wet air oxidation. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2008, 48, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Miyawaki, K.; Yamashita, H. Ru and Ru–Ni nanoparticles on TiO2 support as extremely active catalysts for hydrogen production from ammonia–borane. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 3128–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zeng, J.; Shi, W.; Wang, J.; Zhu, T.; Chen, Y. Catalytic oxidation of benzene over ruthenium–cobalt bimetallic catalysts and study of its mechanism. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debecker, D.P.; Farin, B.; Gaigneaux, E.M.; Sanchez, C.; Sassoye, C. Total oxidation of propane with a nano-RuO2/TiO2 catalyst. Appl. Catal. A 2014, 481, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Qu, L.; Cheng, J.; Li, J.; Hao, Z. Oxidation of nitric oxide to nitrogen dioxide over Ru catalysts. Appl. Catal. B 2009, 88, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.-L.; Hong, Y.-Y.; Lee, C.-C.; Yeh, C.-T.; Wang, C.-B. Novel zirconia-supported catalysts for low-temperature oxidative steam reforming of ethanol. Catal. Today 2007, 129, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjiivanov, K.; Lavalley, J.-C.; Lamotte, J.; Mauge, F.; Saint-Just, J.; Che, M. FTIR study of CO interaction with Ru/TiO2 catalysts. J. Catal. 1998, 176, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez Carballo, J.M.; Finocchio, E.; Garcia, S.; Rojas, S.; Ojeda, M.; Busca, G.; Garcia Fierro, J.L. Support effects on the structure and performance of ruthenium catalysts for the Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2011, 1, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Rodríguez, J.; Rodríguez-Ramos, I.; Guerrero-Ruiz, A.; Gallegos-Suarez, E.; Arcoya, A. Influence of the nature of support on Ru-supported catalysts for selective hydrogenation of citral. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 204–206, 169–178. [Google Scholar]
- Coq, B.; Kumbhar, P.S.; Moreau, C.; Moreau, P.; Figueras, F. Zirconia-supported monometallic Ru and bimetallic Ru-Sn, Ru-Fe catalysts: Role of metal support interaction in the hydrogenation of cinnamaldehyde. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 10180–10188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Catalyst | BET [m2/g] | Total Pore Volume [cm3/g] | Average Pore Radius [nm] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ru/ZR-1 | 100 | 0.62 | 11 |
| Ru/ZR-2 | 127 | 0.64 | 9 |
| Ru/ZR-3 | 125 | 0.58 | 9 |
| Ru/TiO2 | 180 | 0.69 | 7 |
| Ru/ZrO2 | 112 | 0.61 | 10 |
| Catalyst | Ion Intensity (ToF-SIMS) | Elemental Composition (SEM-EDX) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zr+/Ti+ | Cl− | SO4− | Na+ | Zr/Zr+Ti (Atom %) | TiO2/ZrO2+TiO2 (mass %) | |
| Ru/ZR-1 | 0.32 | 0.0064 | 0.0132 | 0.0034 | 58 | 42 |
| Ru/ZR-2 | 0.034 | 0.0070 | 0.0373 | 0.0028 | 11.7 | 82.5 |
| Ru/ZR-3 | 1.10 | 0.0057 | 0.0063 | 0.0024 | 85 | 12 |
| Ru/TiO2 | - | - | - | - | 0 | 100 |
| Ru/ZrO2 | - | - | - | - | 100 | 0 |
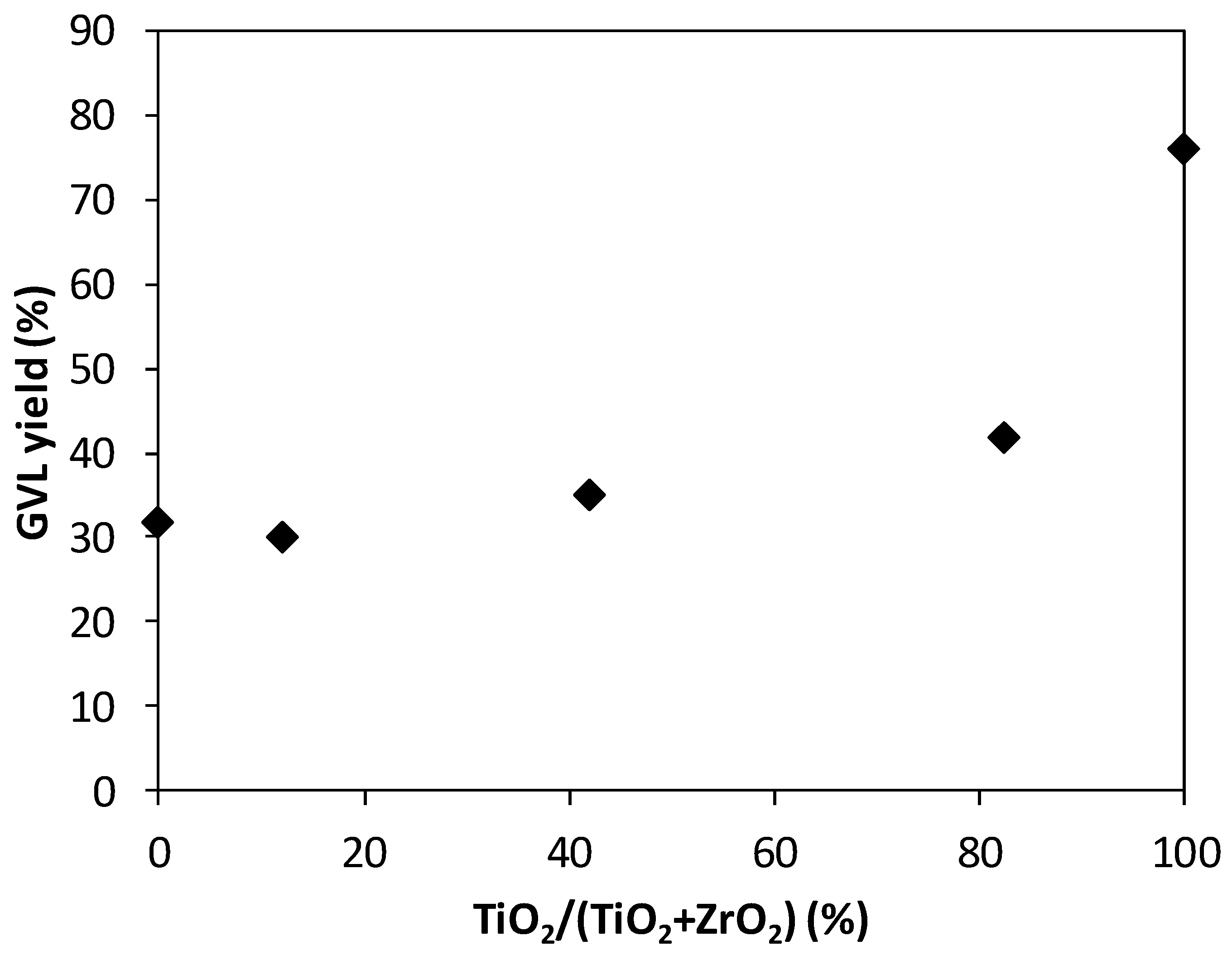
| Catalyst | GVL Yield [%] | LA Conversion [%] |
|---|---|---|
| Ru/ZrO2 | 32 | 32 |
| Ru/ZR-1 | 35 | 35 |
| Ru/ZR-2 | 42 | 42 |
| Ru/ZR-3 | 30 | 33 |
| Ru/TiO2 | 76 | 79 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruppert, A.M.; Agulhon, P.; Grams, J.; Wąchała, M.; Wojciechowska, J.; Świerczyński, D.; Cacciaguerra, T.; Tanchoux, N.; Quignard, F. Synthesis of TiO2–ZrO2 Mixed Oxides via the Alginate Route: Application in the Ru Catalytic Hydrogenation of Levulinic Acid to Gamma-Valerolactone. Energies 2019, 12, 4706. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12244706
Ruppert AM, Agulhon P, Grams J, Wąchała M, Wojciechowska J, Świerczyński D, Cacciaguerra T, Tanchoux N, Quignard F. Synthesis of TiO2–ZrO2 Mixed Oxides via the Alginate Route: Application in the Ru Catalytic Hydrogenation of Levulinic Acid to Gamma-Valerolactone. Energies. 2019; 12(24):4706. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12244706
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuppert, Agnieszka M., Pierre Agulhon, Jacek Grams, Malgorzata Wąchała, Joanna Wojciechowska, Dariusz Świerczyński, Thomas Cacciaguerra, Nathalie Tanchoux, and Francoise Quignard. 2019. "Synthesis of TiO2–ZrO2 Mixed Oxides via the Alginate Route: Application in the Ru Catalytic Hydrogenation of Levulinic Acid to Gamma-Valerolactone" Energies 12, no. 24: 4706. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12244706
APA StyleRuppert, A. M., Agulhon, P., Grams, J., Wąchała, M., Wojciechowska, J., Świerczyński, D., Cacciaguerra, T., Tanchoux, N., & Quignard, F. (2019). Synthesis of TiO2–ZrO2 Mixed Oxides via the Alginate Route: Application in the Ru Catalytic Hydrogenation of Levulinic Acid to Gamma-Valerolactone. Energies, 12(24), 4706. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12244706








