Prediction of Contact Angle of Nanofluids by Single-Phase Approaches †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Nanofluids
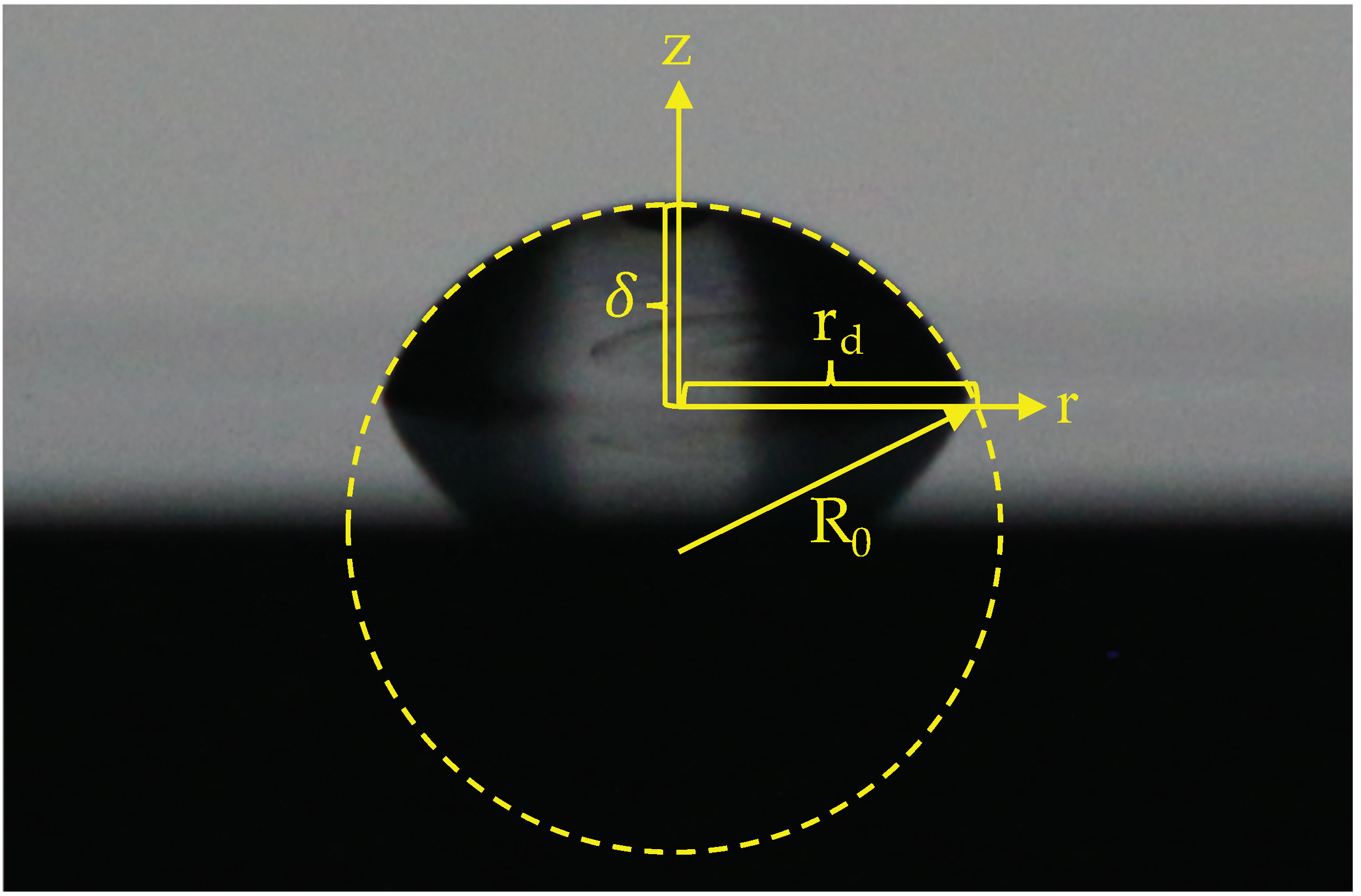
2.2. Experiments on Contact Angle Measurements and Determination of Geometrical Parameters
2.3. Single-Phase Models for Prediction of Contact Angle
2.4. Prediction of Droplet Shape
3. Results and Discussion
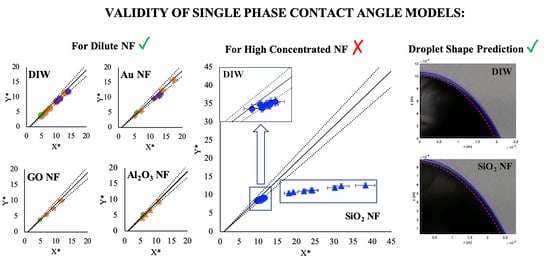
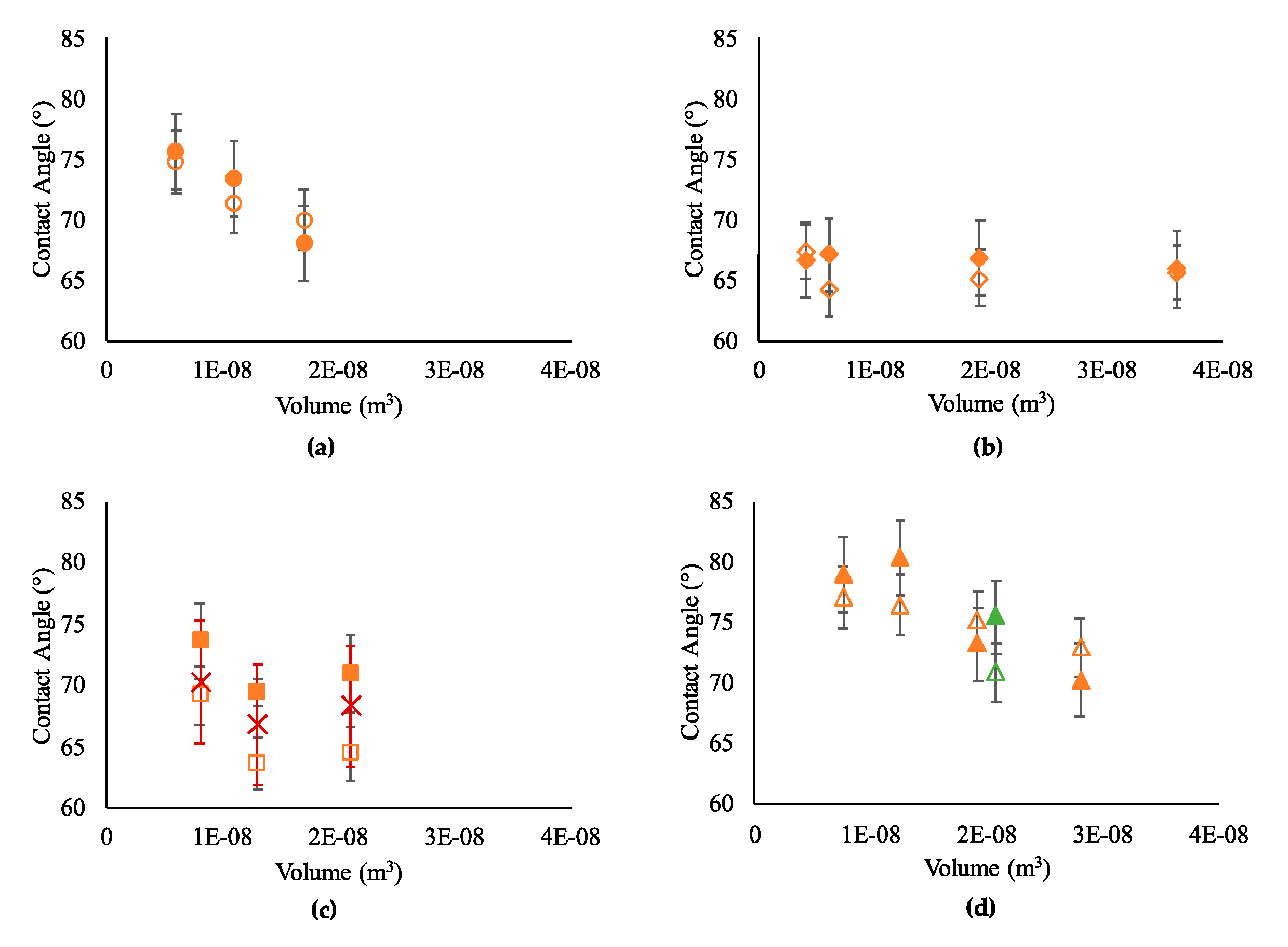
3.1. Contact Angle Prediction with Single-Phase Models
3.2. Droplet Shape Prediction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Bo | Bond Number (–) |
| c | Coefficients |
| g | Gravitational Acceleration (m/s2) |
| G | Geometrical Similarity Simplex (–) |
| k | Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) |
| r | Droplet Wetting Radius (m) |
| R | Radius of Curvature (m) |
| RH | Relative Humidity (%) |
| V | Volume (m3) |
| W | Width of the droplet (m) |
| T | Temperature (°C) |
Abbreviations
| CA | Contact Angle |
| DIW | Distilled Water |
| İKÇÜ | Izmir Katip Çelebi University |
| ILK | ILK-Dresden |
| NF | Nanofluid |
| UJI | Universitat Jaume I Castelló |
| UR1 | Université Rennes 1 |
Subscripts
| 0 | At the apex |
| d | Droplet |
| e | Effective |
| f | Base Fluid |
| lg | Liquid–Gas |
| p | Particle |
| s | Spherical |
| v | Volumetric |
Greek Letters
Surface Tension (mN/m) | |
Location of Apex (m) | |
Density (kg/m3) | |
Contact Angle (°) | |
Mean Absolute Percentage Error (%) | |
Concentration of NF (%) |
References
- Choi, S.U.; Eastman, J.A. Enhancing Thermal Conductivity of Fluids with Nanoparticles; Argonne National Lab.: DuPage County, IL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Cabaleiro, D.; Gracia-Fernández, C.; Legido, J.; Lugo, L. Specific heat of metal oxide nanofluids at high concentrations for heat transfer. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 88, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riazi, H.; Murphy, T.; Webber, G.B.; Atkin, R.; Tehrani, S.S.M.; Taylor, R.A. Specific heat control of nanofluids: A critical review. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2016, 107, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koca, H.D.; Doganay, S.; Turgut, A.; Tavman, I.H.; Saidur, R.; Mahbubul, I.M. Effect of particle size on the viscosity of nanofluids: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 1664–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murshed, S.S.; Estellé, P. A state of the art review on viscosity of nanofluids. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 76, 1134–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniadis, K.D.; Tertsinidou, G.J.; Assael, M.J.; Wakeham, W.A. Necessary conditions for accurate, transient hot-wire measurements of the apparent thermal conductivity of nanofluids are seldom satisfied. Int. J. Thermophys. 2016, 37, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.H.; Mirlohi, A.; Nazari, M.A.; Ghasempour, R. A review of thermal conductivity of various nanofluids. J. Mol. Liquids 2018, 265, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongkratoke, A.; Pramuanjaroenkij, A.; Kakaç, S. Numerical Study of Mixing Thermal Conductivity Models for Nanofluid Heat Transfer Enhancement. J. Eng. Phys. Thermophys. 2018, 91, 104–114. [Google Scholar]
- Murshed, S.S.; Estellé, P. Rheological Characteristics of Nanofluids for Advance Heat Transfer. In Advances in New Heat Transfer Fluids; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 227–266. [Google Scholar]
- Estellé, P.; Cabaleiro, D.; Żyła, G.; Lugo, L.; Murshed, S.S. Current trends in surface tension and wetting behavior of nanofluids. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 94, 931–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radiom, M.; Yang, C.; Chan, W.K. Characterization of Surface Tension and Contact Angle of Nanofluids; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2010; Volume 7522, p. 75221D. [Google Scholar]
- Radiom, M.; Yang, C.; Chan, W.K. Dynamic contact angle of water-based titanium oxide nanofluid. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieśliński, J.T.; Krygier, K.A. Sessile droplet contact angle of water–Al2O3, water–TiO2 and water–Cu nanofluids. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2014, 59, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murshed, S.S.; Tan, S.-H.; Nguyen, N.-T. Temperature dependence of interfacial properties and viscosity of nanofluids for droplet-based microfluidics. J. Phys. Appl. Phys. 2008, 41, 085502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harikrishnan, A.; Dhar, P.; Agnihotri, P.K.; Gedupudi, S.; Das, S.K. Wettability of complex fluids and surfactant capped nanoparticle-induced quasi-universal wetting behavior. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 121, 6081–6095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, Y.H.; Chang, W.J.; Chang, S.H. Wettability of heated surfaces under pool boiling using surfactant solutions and nano-fluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2008, 51, 3025–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajitno, D.; Trisnawan, V.; Syarif, D. Effect of Spreading Time on Contact Angle of Nanofluid on the Surface of Stainless Steel AISI 316 and Zircalloy 4; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2017; Volume 196, p. 012028. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, G.; Duan, Y.-Y.; Wang, X.-D. Experimental study on the dynamic wetting of dilute nanofluids. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 486, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernaiz, M.; Alonso, V.; Estellé, P.; Wu, Z.; Sundén, B.; Doretti, L.; Mancin, S.; Çobanoğlu, N.; Karadeniz, Z.; Garmendia, N.; et al. The contact angle of nanofluids as thermophysical property. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 547, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnam, J.; Das, D.; Vajjha, R.; Satti, J. Measurements of the contact angle of nanofluids and development of a new correlation. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 62, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosu, Y.; González-Fernández, L.; Nithiyanantham, U.; Faik, A. Wettability control for correct thermophysical properties determination of molten salts and their nanofluids. Energies 2019, 12, 3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabaleiro, D.; Hamze, S.; Agresti, F.; Estellé, P.; Barison, S.; Fedele, L.; Bobbo, S. Dynamic Viscosity, Surface Tension and Wetting Behavior Studies of Paraffin–in–Water Nano–Emulsions. Energies 2019, 12, 3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çobanoğlu, N.; Karadeniz, Z.; Estellé, P.; Martínez-Cuenca, R.; Buschmann, M. On the contact angle of nanofluids. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Nanofluids (ICNf2019) & 2nd European Symposium on Nanofluids (ESNf2019), Castelló, Spain, 26–28 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, T.I.; Wang, H.; Wang, F.; Sin, S.L.; Quan, C.G.; Wang, S.J.; Zhou, X. Empirical Formulae in Correlating Droplet Shape and Contact Angle. Aust. J. Chem. 2016, 69, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murshed, S.S. Determination of effective specific heat of nanofluids. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2011, 6, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgut, A.; Sauter, C.; Chirtoc, M.; Henry, J.; Tavman, S.; Tavman, I.; Pelzl, J. AC hot wire measurement of thermophysical properties of nanofluids with 3ω method. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2008, 153, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abràmoff, M.D.; Magalhães, P.J.; Ram, S.J. Image processing with ImageJ. Biophoton. Int. 2004, 11, 36–42. [Google Scholar]
- Stalder, A.F.; Kulik, G.; Sage, D.; Barbieri, L.; Hoffmann, P. A snake-based approach to accurate determination of both contact points and contact angles. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2006, 286, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linstrom, P.J.; Mallard, W.G. The NIST Chemistry WebBook: A chemical data resource on the internet. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2001, 46, 1059–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Villarejo, R.; Aguilar, T.; Hamze, S.; Estellé, P.; Navas, J. Experimental analysis of water-based nanofluids using boron nitride nanotubes with improved thermal properties. J. Mol. Liquids 2019, 277, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafaei, S.; Podowski, M. Analysis of the relationship between liquid droplet size and contact angle. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 113, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuiken, H. A single-parameter method for the determination of surface tension and contact angle. Colloids Surf. 1991, 59, 129–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacy, R. Contact Angle Measurement Technique for Rough Surfaces. Ph.D. Thesis, Michigan Technological University, Houghton, MI, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yonemoto, Y.; Kunugi, T. Wettability model for various-sized droplets on solid surfaces. Phys. Fluids 2014, 26, 082110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

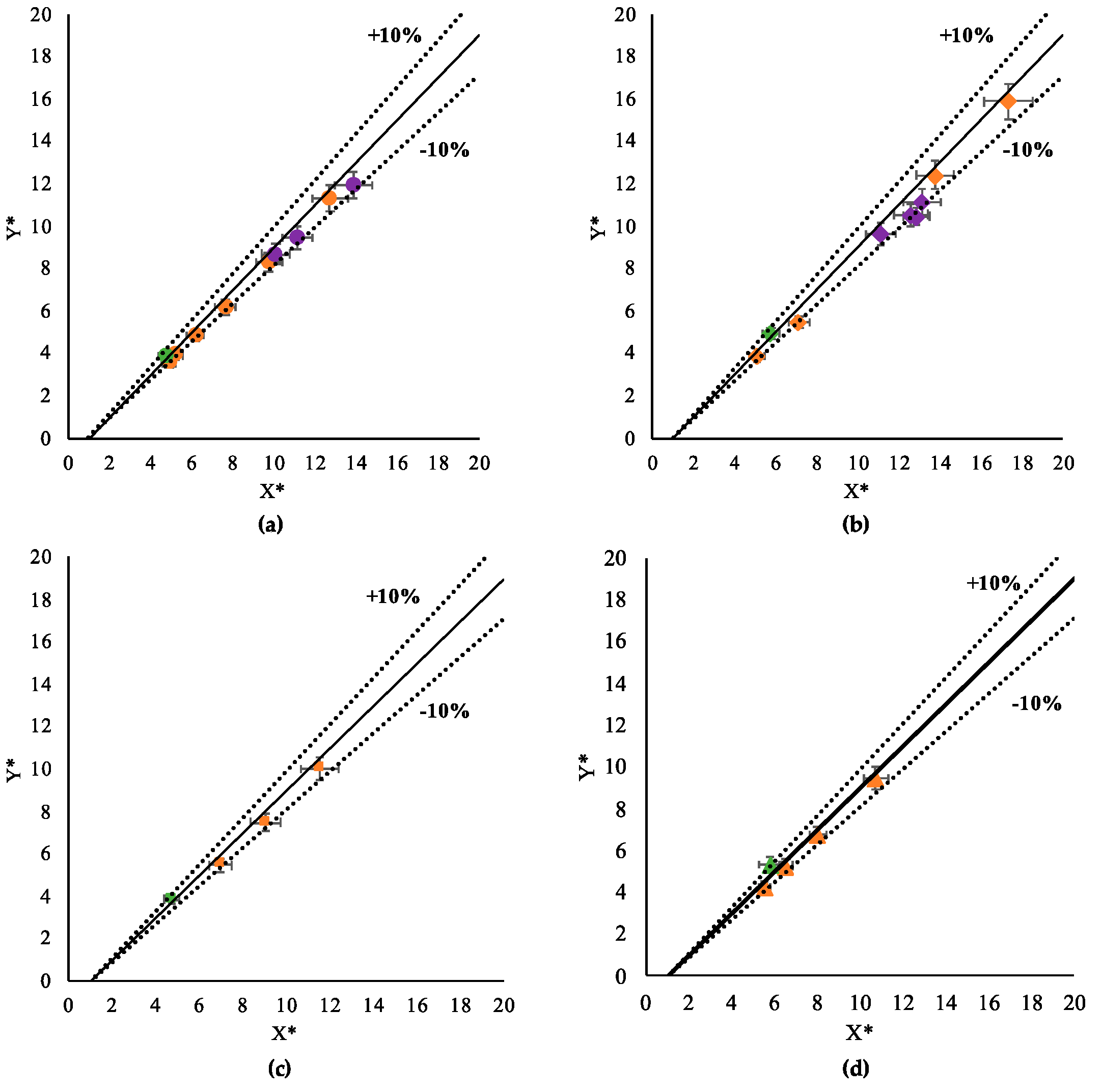



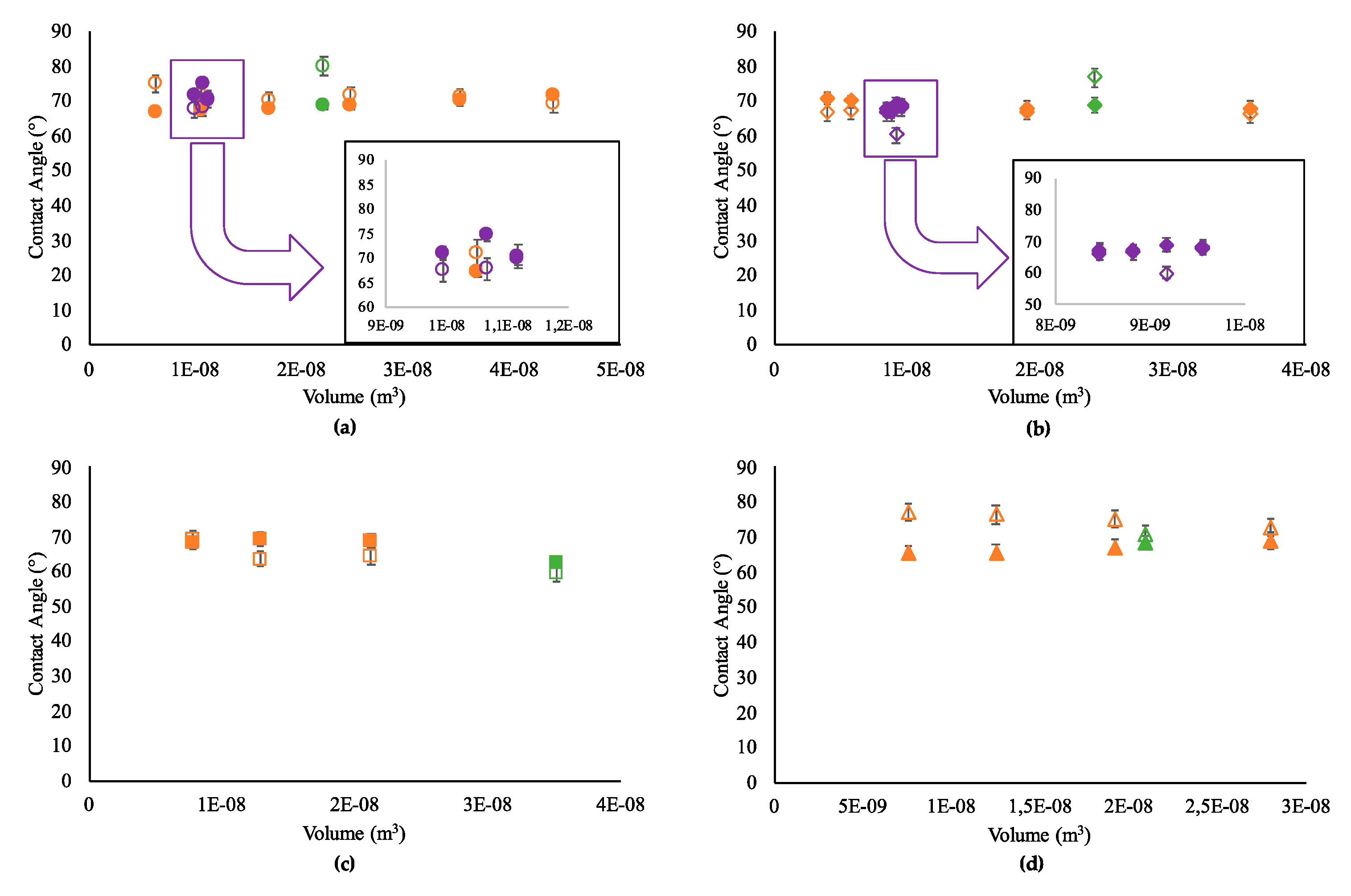
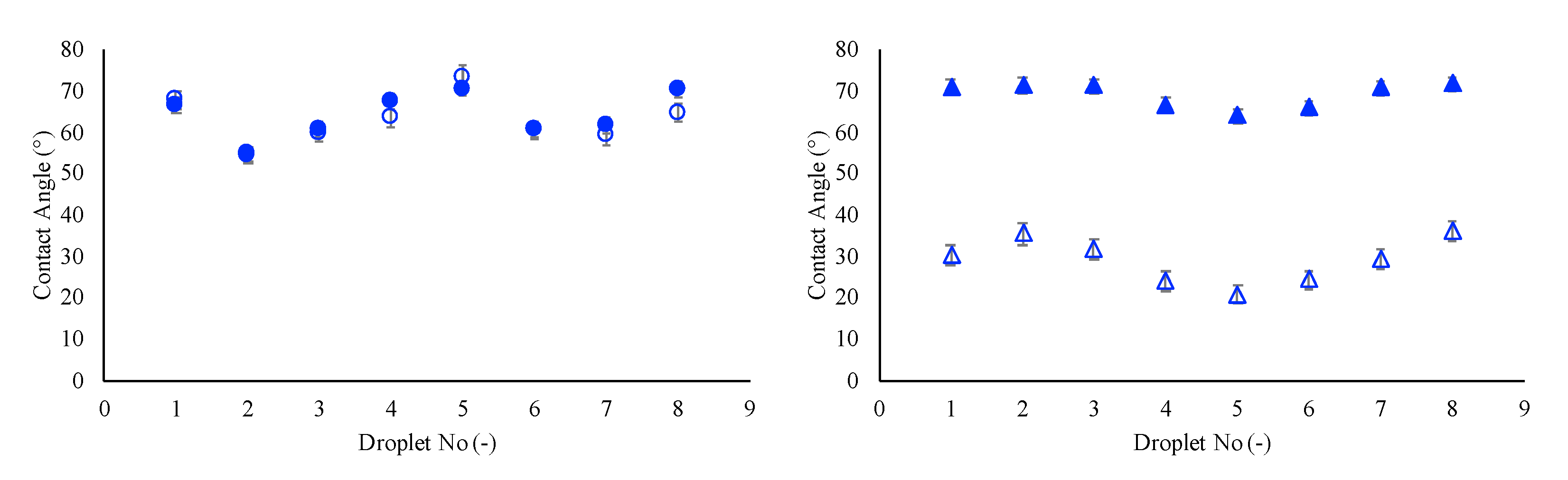
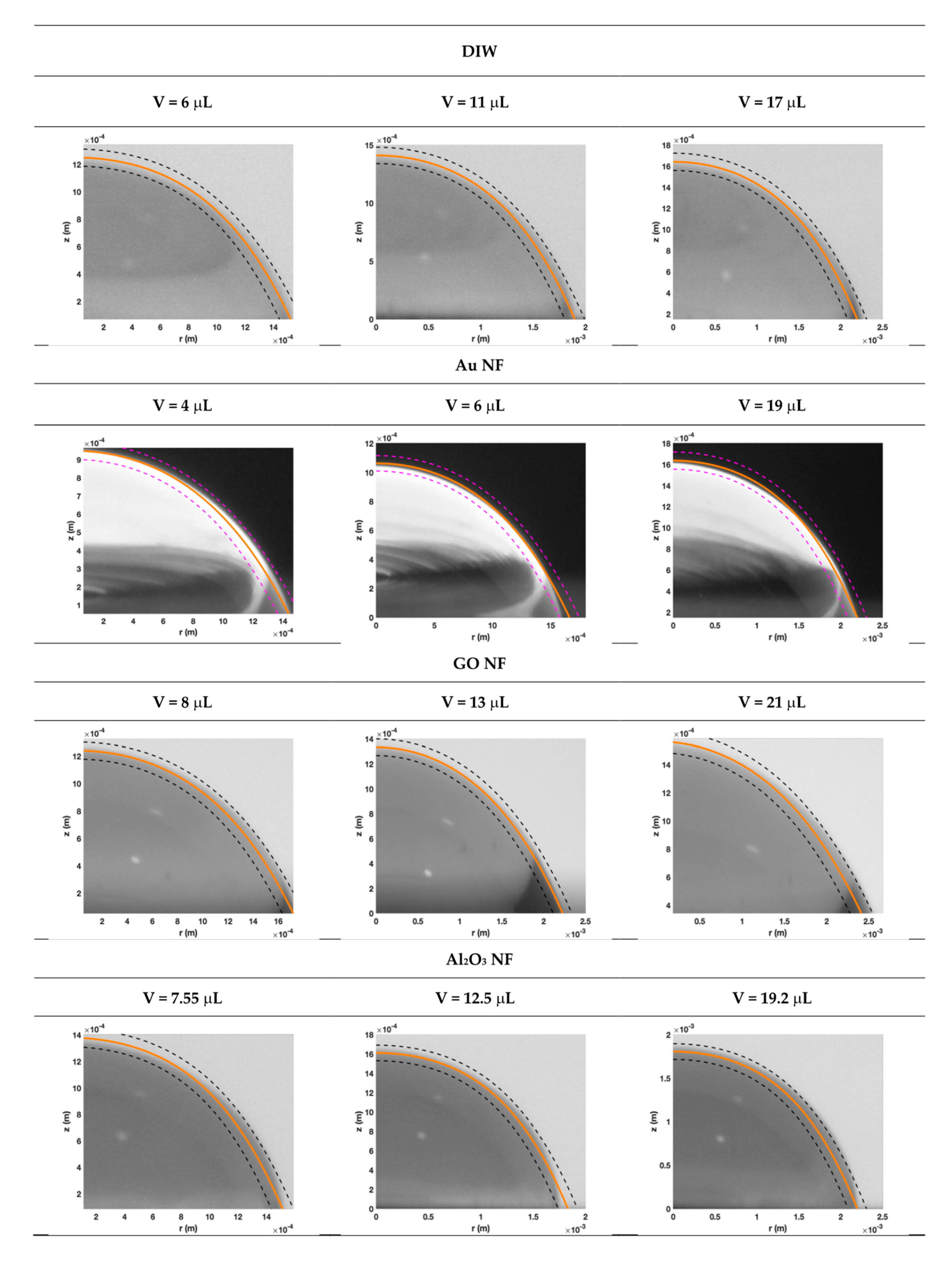
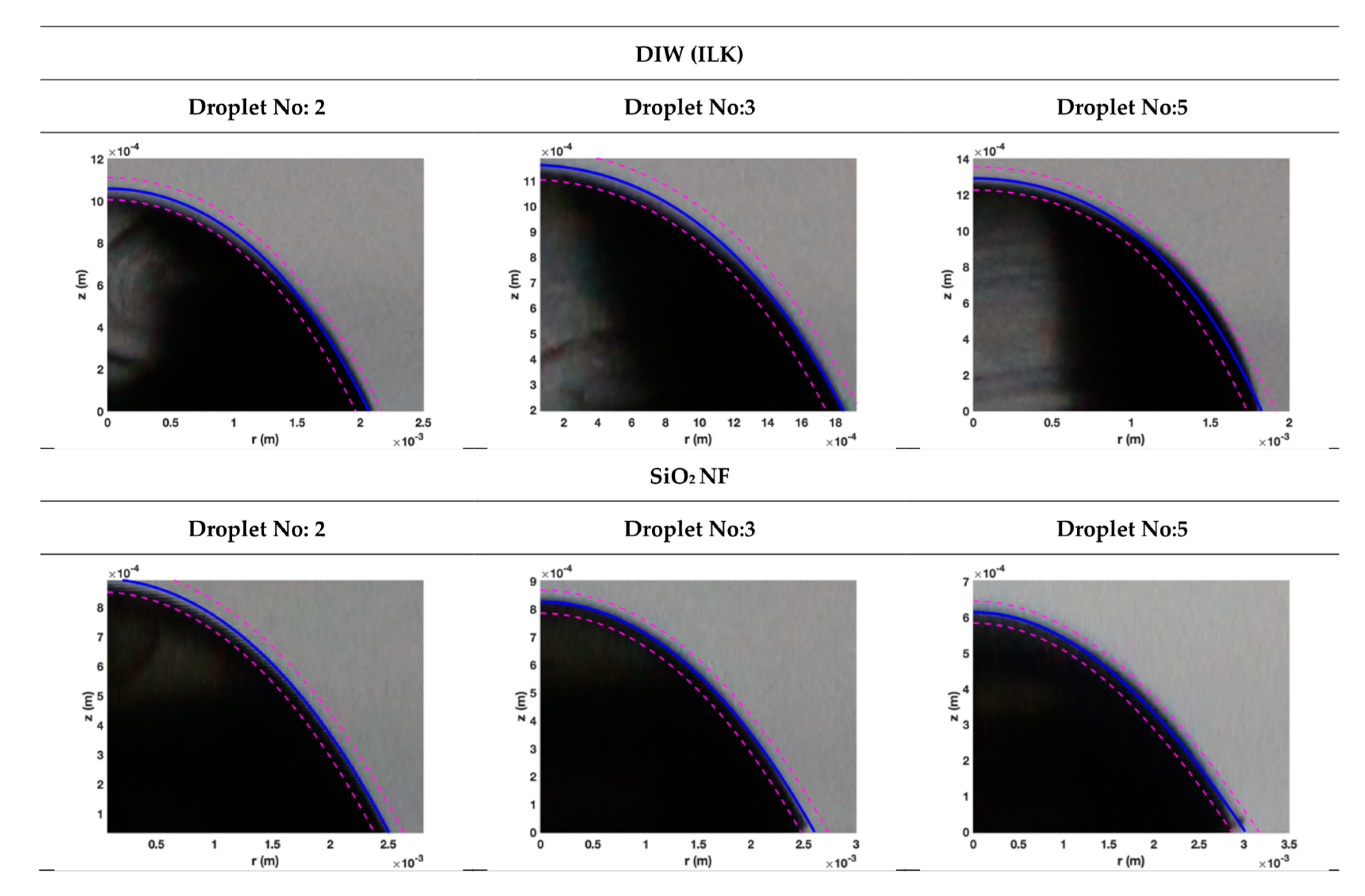
| Nanoparticle | Particle Size | Particle Shape | Density of Nanoparticle (kg/m3) | Density of NF (kg/m3) | Thermal Conductivity Ratio (kNF/kDIW) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gold (Au) | Particle diameter: 8.34 nm | Spherical | 0.001 wt. % (0.000052 vol.%) | 1,9300 | 997.25 | 0.999 |
| Silica (SiO2) | Particle diameter: 117 nm | Spherical | 3.935 wt. % (2 vol.%) | 2000 | 1017.06 | 1.008 |
| Graphene oxide (GO) | Extension of particle: 770 to 900 nm Thickness: 2 nm to 10 nm | Flake | 0.01 wt. % (0.005679 vol.%) | 1500–1900 | 997.25 | 0.9964 |
| Alumina (Al2O3) | Particle Diameter: 123 ± 2 nm | Spherical | 0.4 wt. % (0.1 vol. %) | 3987 | 997.25 | 0.9961 |
| Institutions & Devices | Working Fluids | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIW | Au NF | GO NF | SiO2 NF | Al2O3 NF | |
| İKÇÜ Attention Theta Goniometer (Biolin Scientific, (Sweden/Finland)) | T = 24.2 °C RH = 40% V = 4.6 µL | T = 23.7 °C RH = 40% V = 9.8 µL | T = 23.1 °C RH = 36% V = 4.1 µL | ||
| ILK Lab-made device | T = 22.0 °C RH = 67% V = 10 µL | T = 25.0 °C RH = 64.5 % V = 10 µL | |||
| UJI Lab-made device | T = 24.0 °C RH = 54% V = 5.1–71.1 µL | T = 24.0 °C RH = 54% V = 5.3–68.6 µL | T = 24.0 °C RH = 54% V = 8.4–35.4 µL | T = 24.0 °C RH = 54% V = 5.5–28.8 µL | |
| UR1 DSA-30 Drop Shape Analyzer (KRÜSS GmbH, Germany) | T = 21.0 °C RH = 24% V = 22.3 µL | T = 21.0 °C RH = 24% V = 24.1 µL | T = 21.0 °C RH = 24% V = 34.3 µL | T = 21.0 °C RH = 24% V = 20.9 µL | |
| Working Fluid | T (°C) | RH (%) | (mN/m) | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIW | 21 | 24 | 72.960 | 0.06 |
| GO NF | 21 | 24 | 73.345 | 0.125 |
| Au NF | 21 | 24 | 72.77 | 0.13 |
| Al2O3 NF | 21 | 24 | 72.005 | 0.255 |
| SiO2 NF | 22.8 | 40 | 70.13 | 0.25 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Çobanoğlu, N.; Karadeniz, Z.H.; Estellé, P.; Martínez-Cuenca, R.; Buschmann, M.H. Prediction of Contact Angle of Nanofluids by Single-Phase Approaches. Energies 2019, 12, 4558. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12234558
Çobanoğlu N, Karadeniz ZH, Estellé P, Martínez-Cuenca R, Buschmann MH. Prediction of Contact Angle of Nanofluids by Single-Phase Approaches. Energies. 2019; 12(23):4558. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12234558
Chicago/Turabian StyleÇobanoğlu, Nur, Ziya Haktan Karadeniz, Patrice Estellé, Raul Martínez-Cuenca, and Matthias H. Buschmann. 2019. "Prediction of Contact Angle of Nanofluids by Single-Phase Approaches" Energies 12, no. 23: 4558. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12234558
APA StyleÇobanoğlu, N., Karadeniz, Z. H., Estellé, P., Martínez-Cuenca, R., & Buschmann, M. H. (2019). Prediction of Contact Angle of Nanofluids by Single-Phase Approaches. Energies, 12(23), 4558. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12234558