Effect of Shale Anisotropy on Hydration and Its Implications for Water Uptake
Abstract
1. Introduction
- How does the imbibition direction (parallel or perpendicular to the bedding planes) influence the shale hydration?
- How do the temperature and pressure affect shale water uptake?
- What are the mechanisms of hydration?
2. Experimental Materials and Procedures
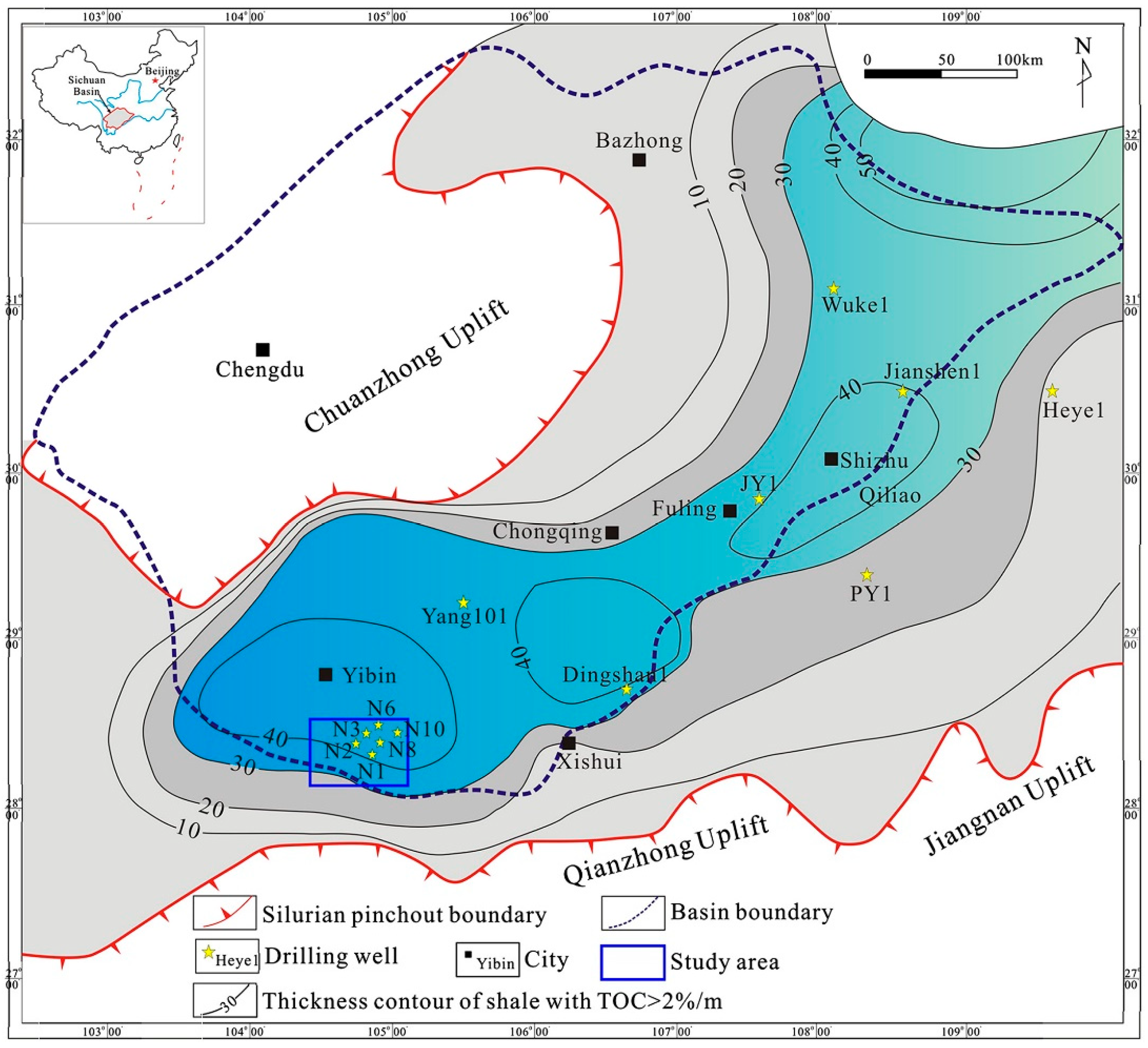
2.1. Mineralogy
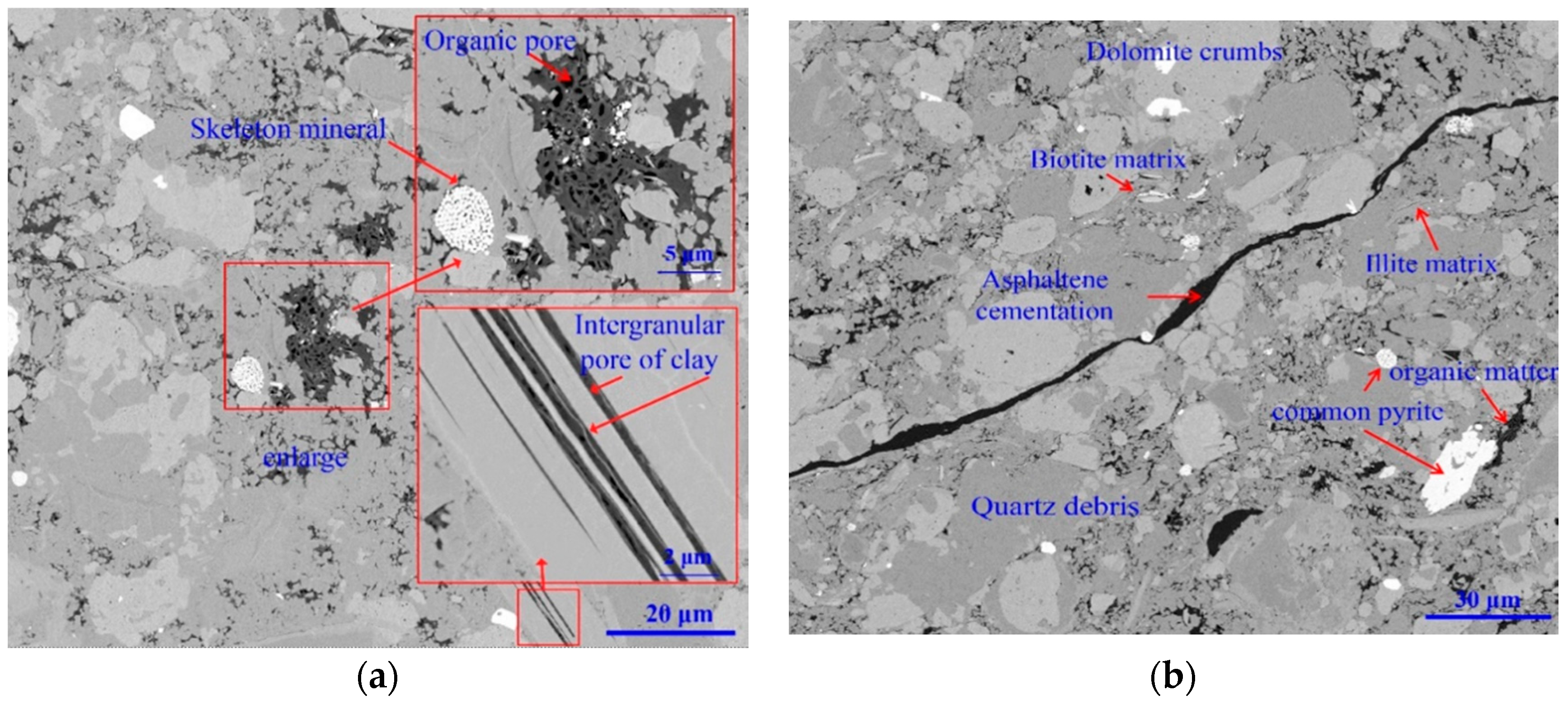
2.2. Sample Preparation and Characterization
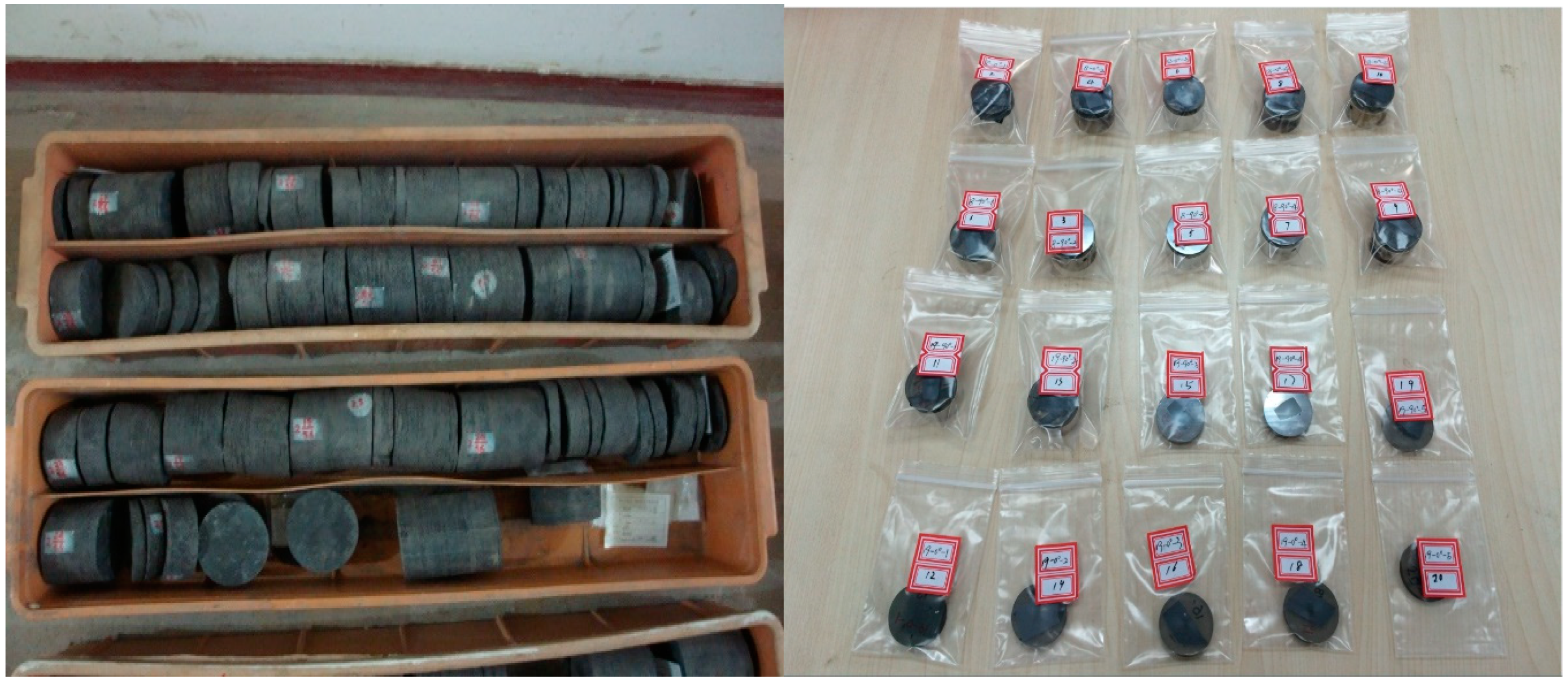
2.3. Sample Slice Preparation
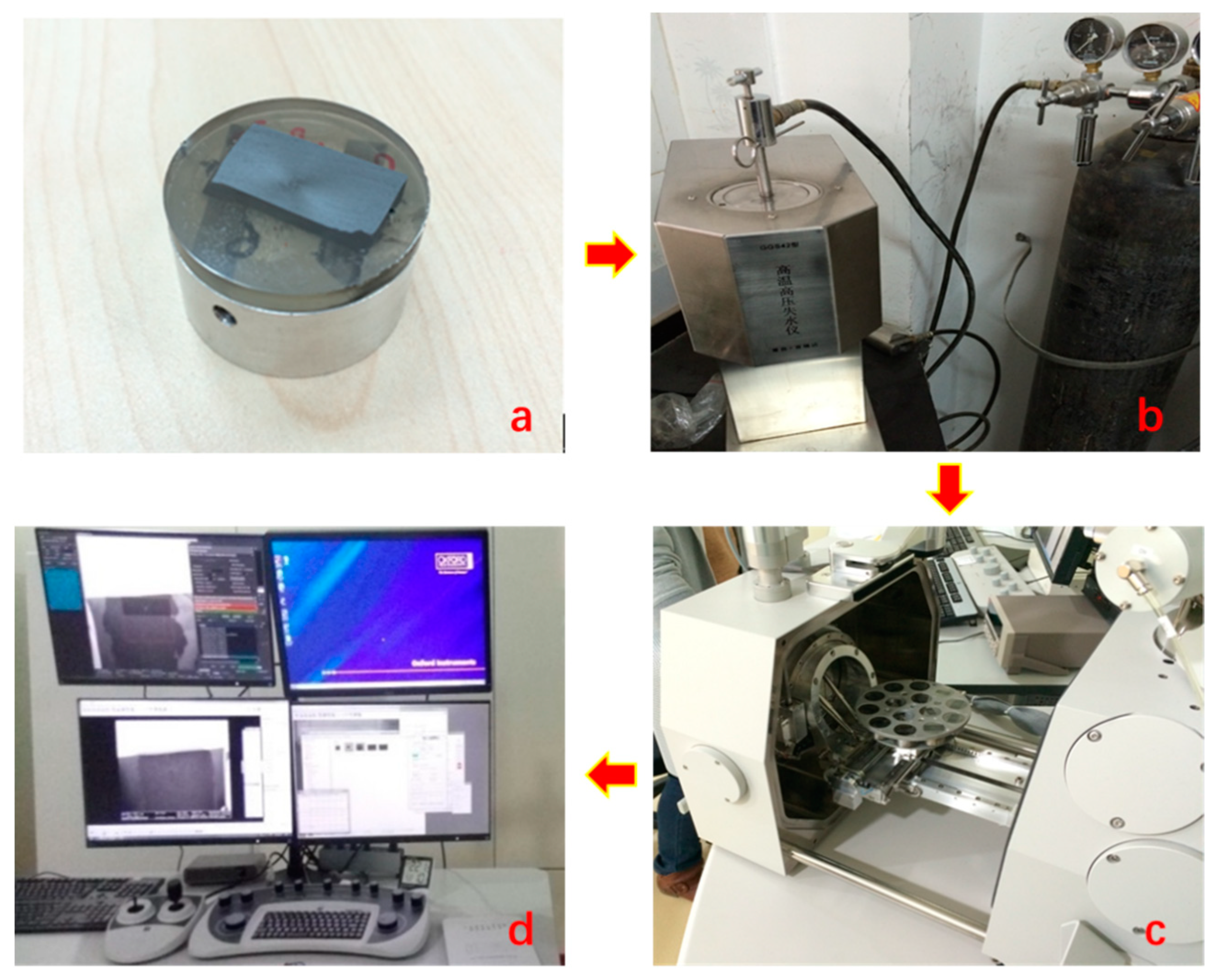
2.4. Experimental Procedures
3. Results and Discussion
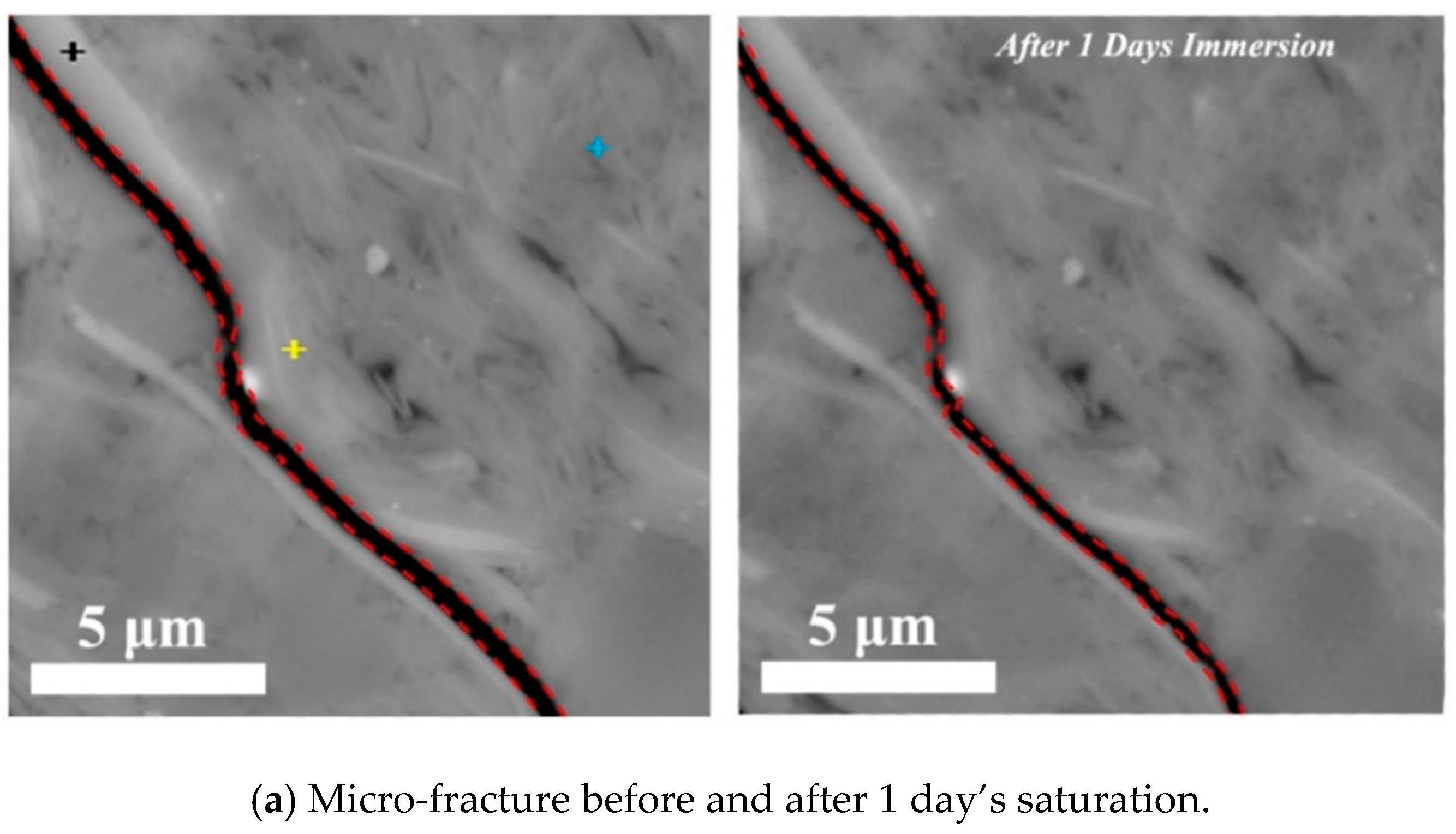
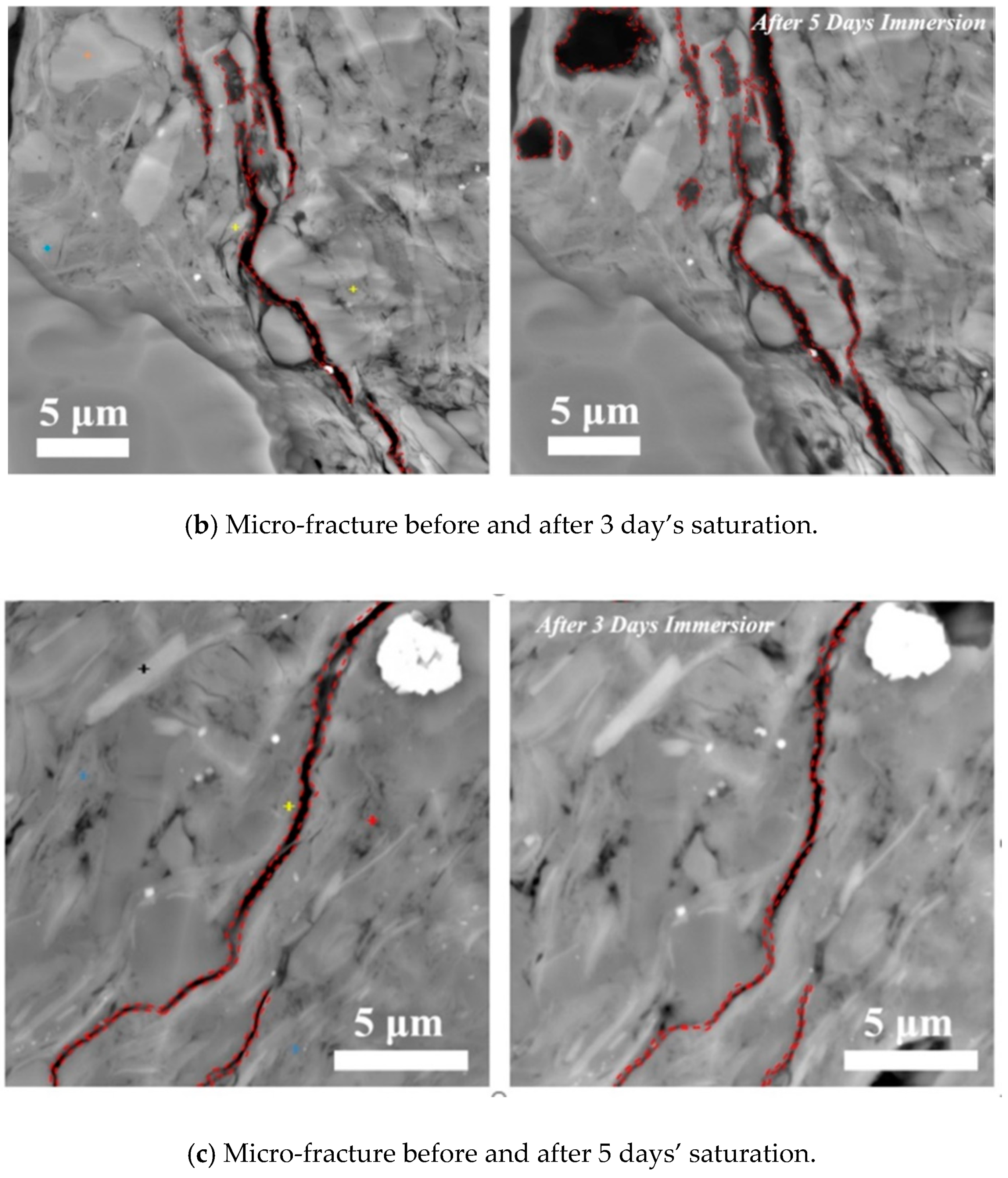
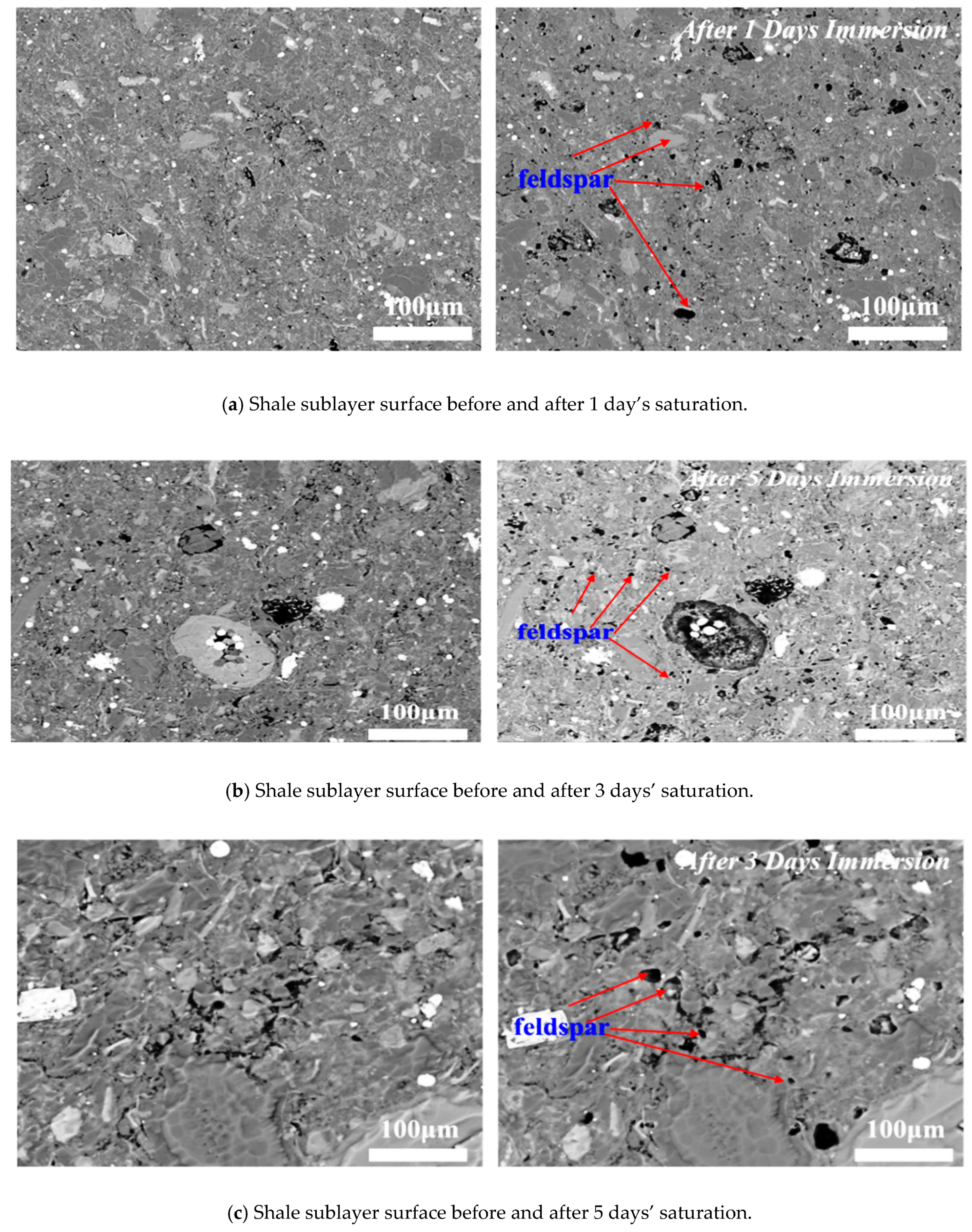
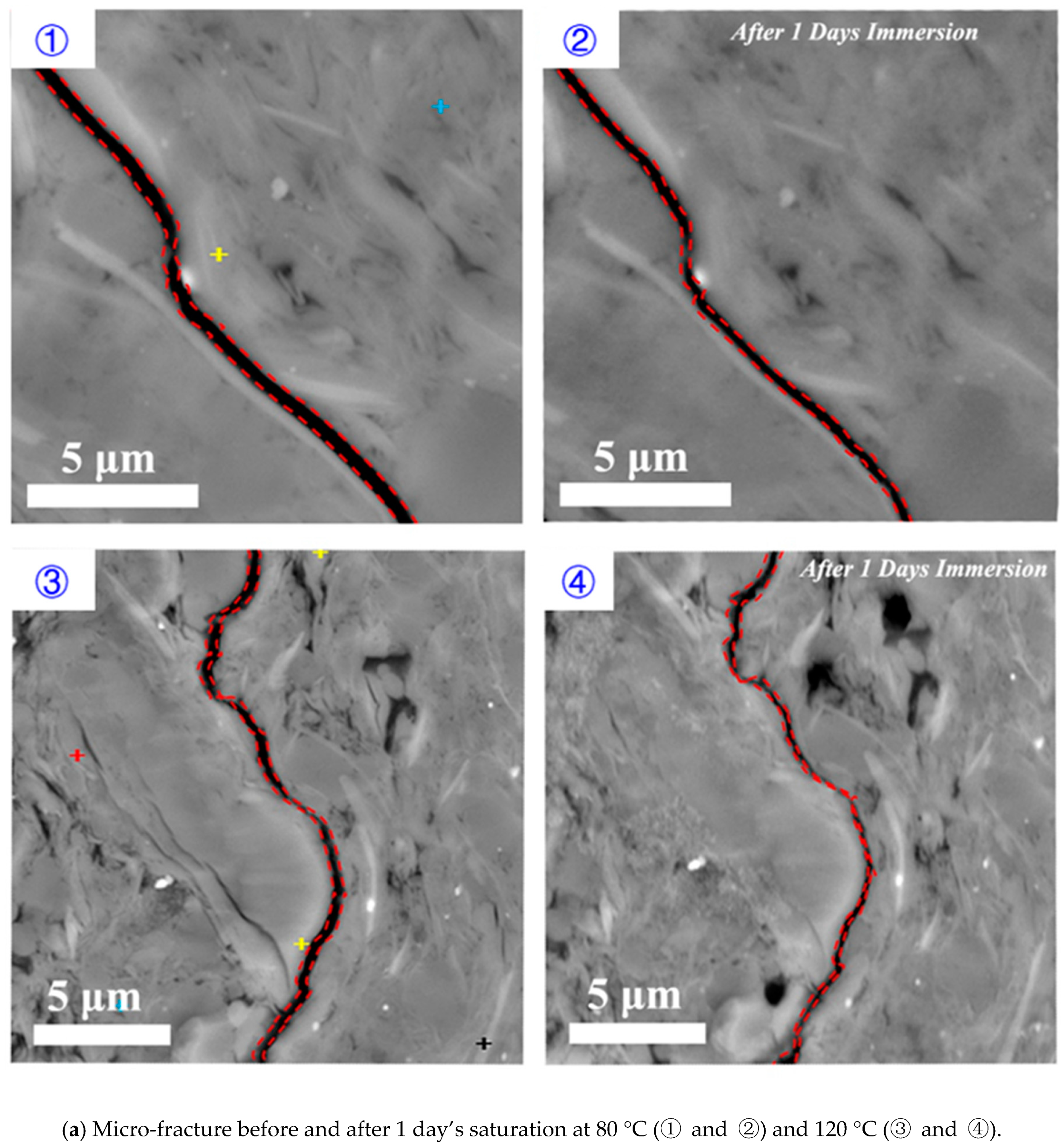
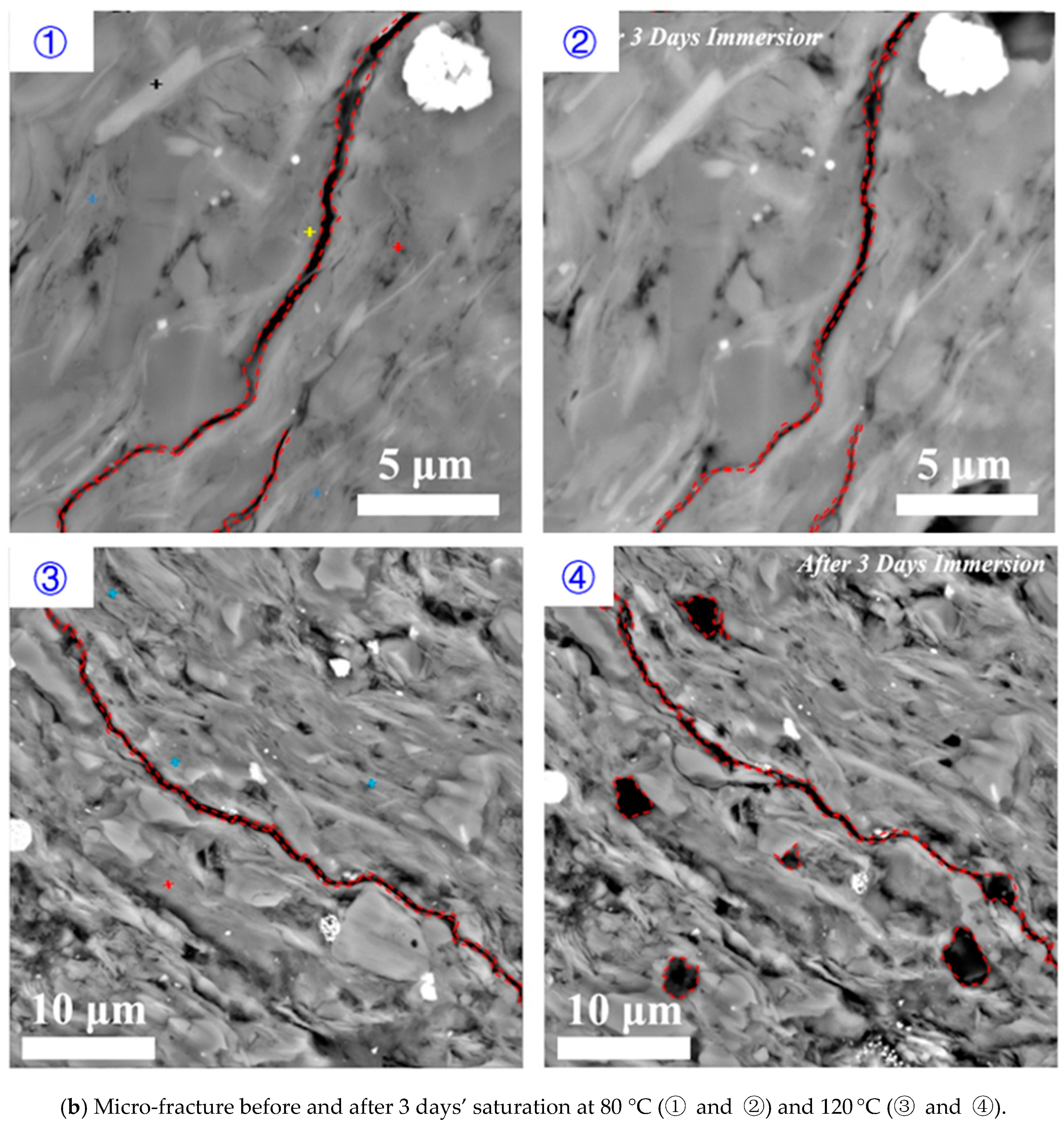
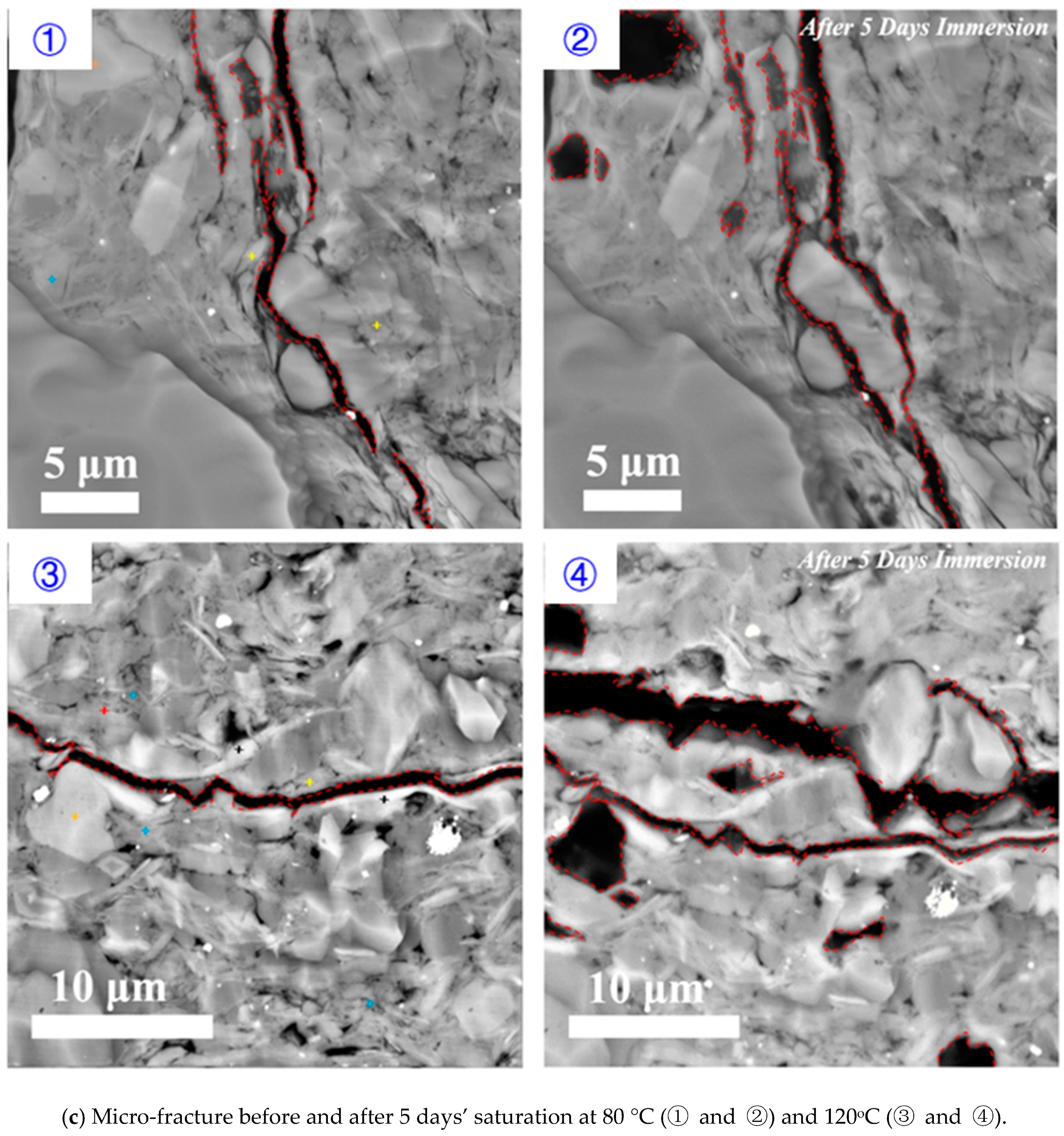
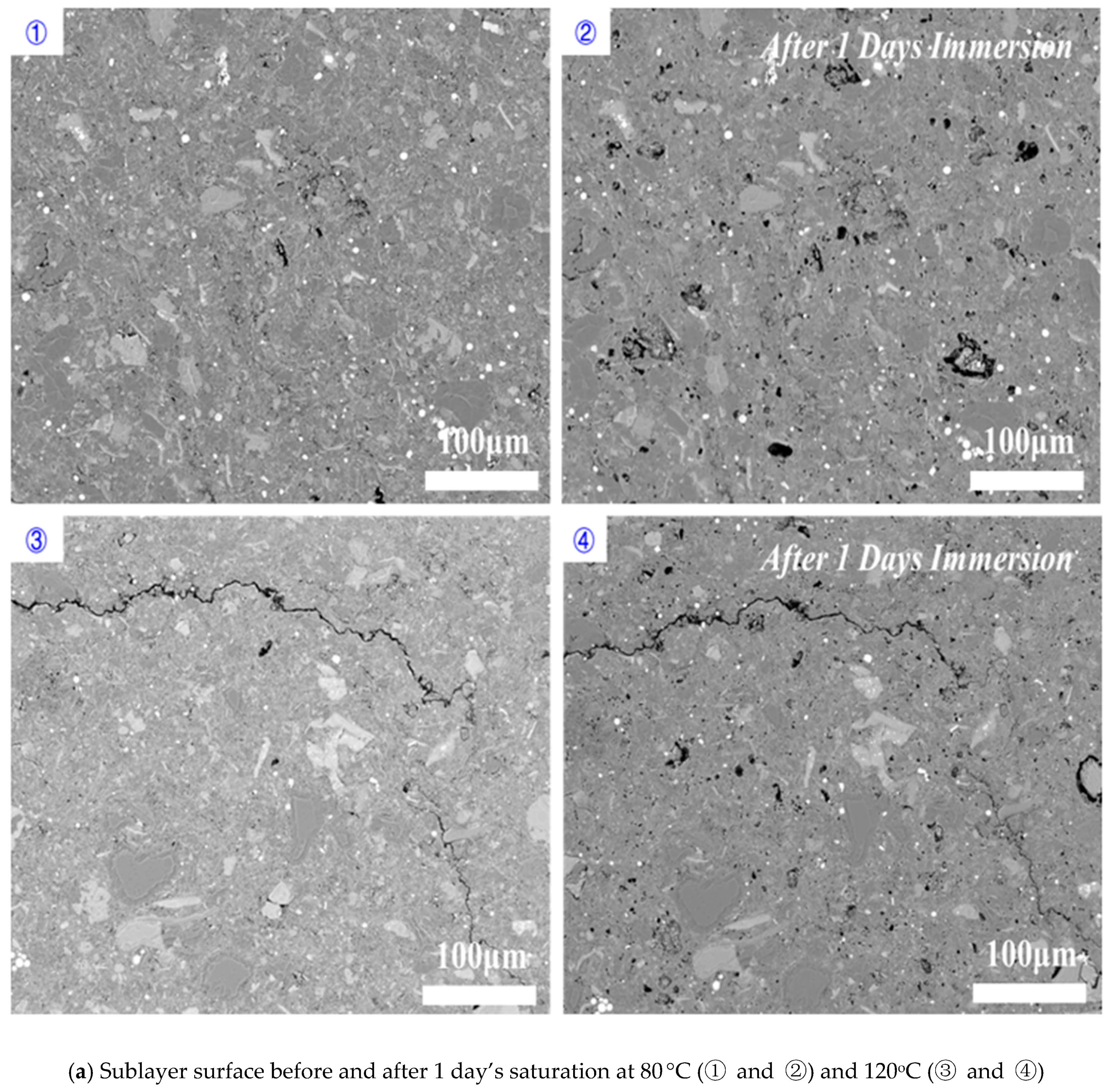
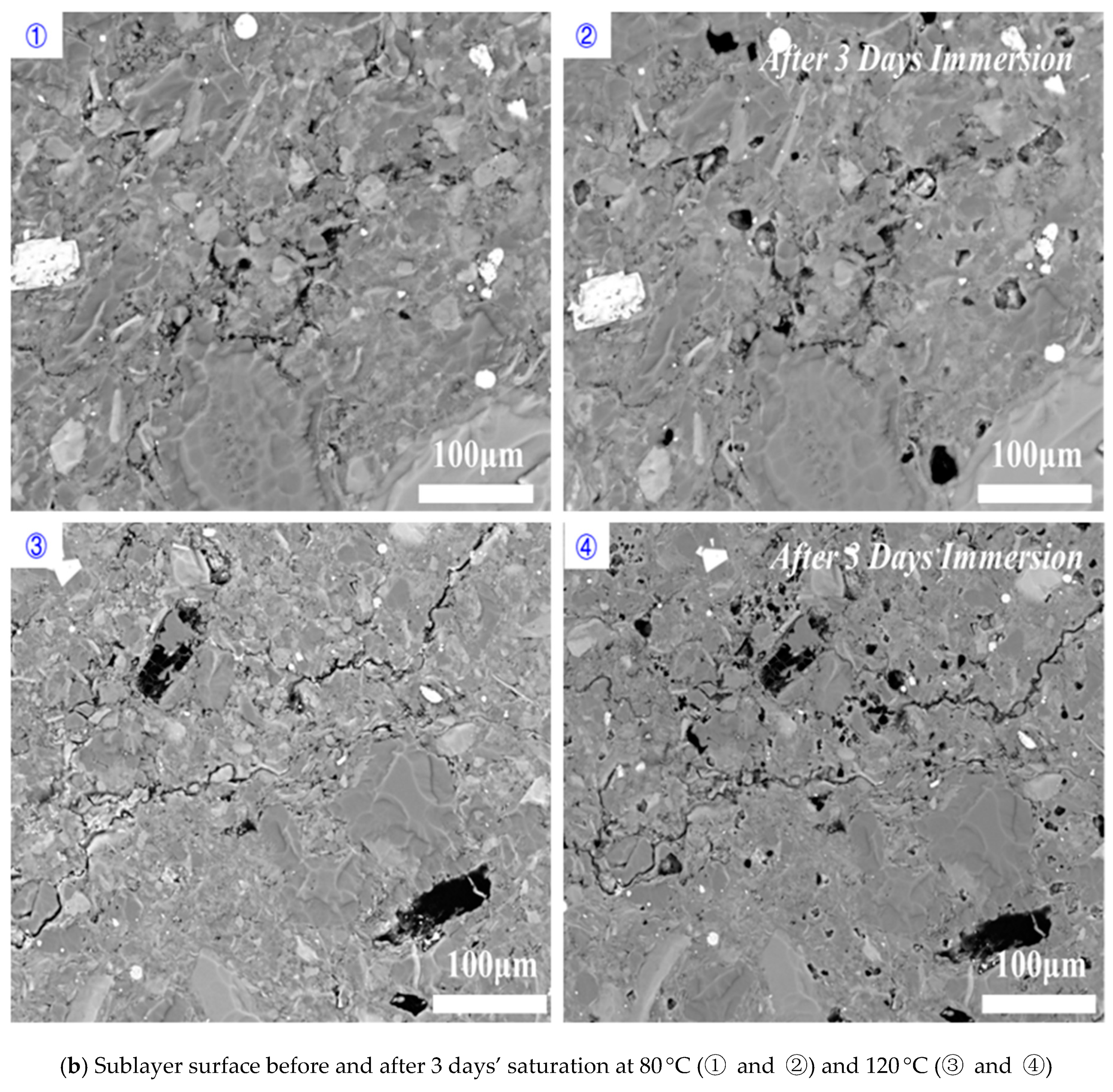
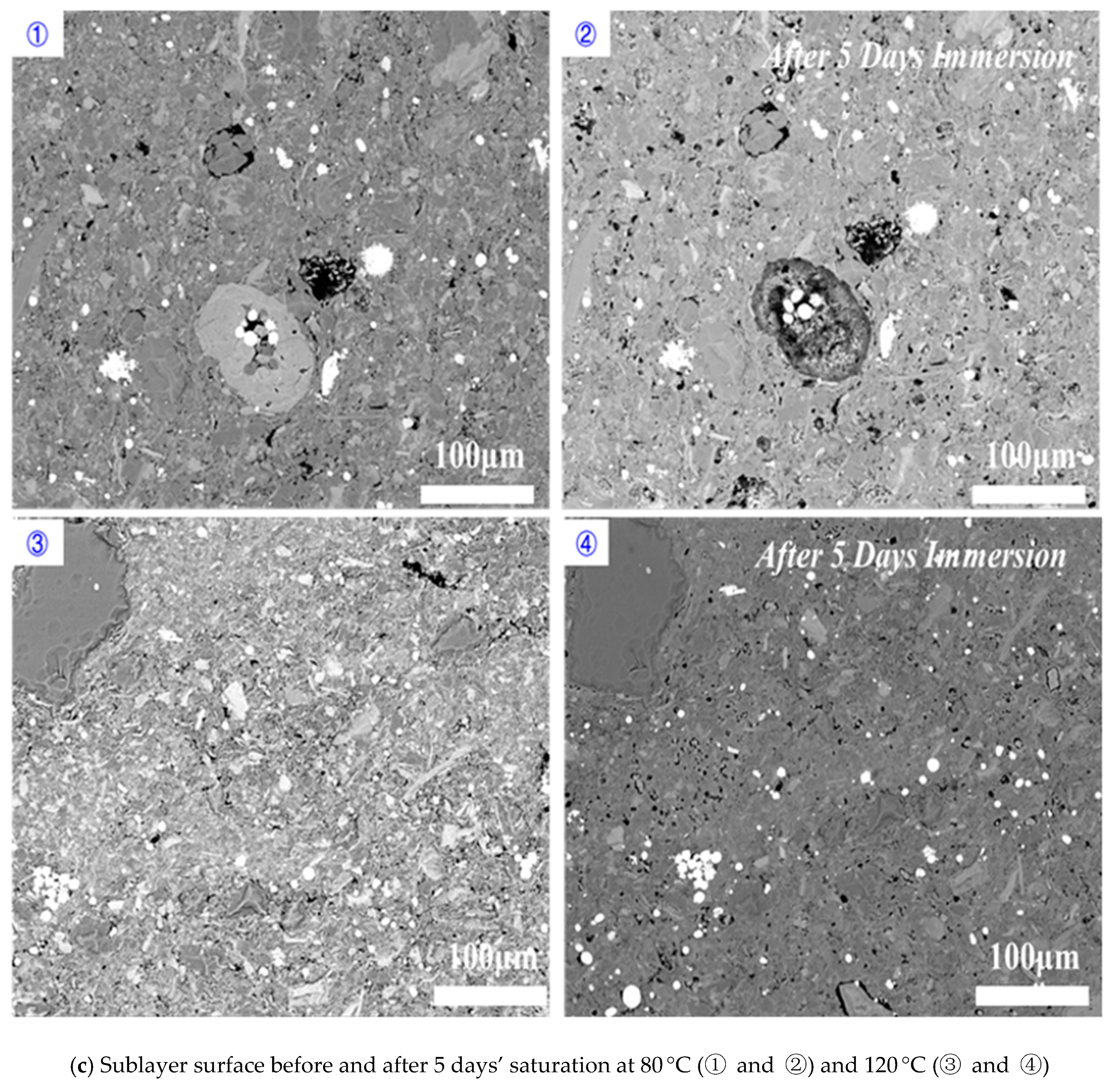
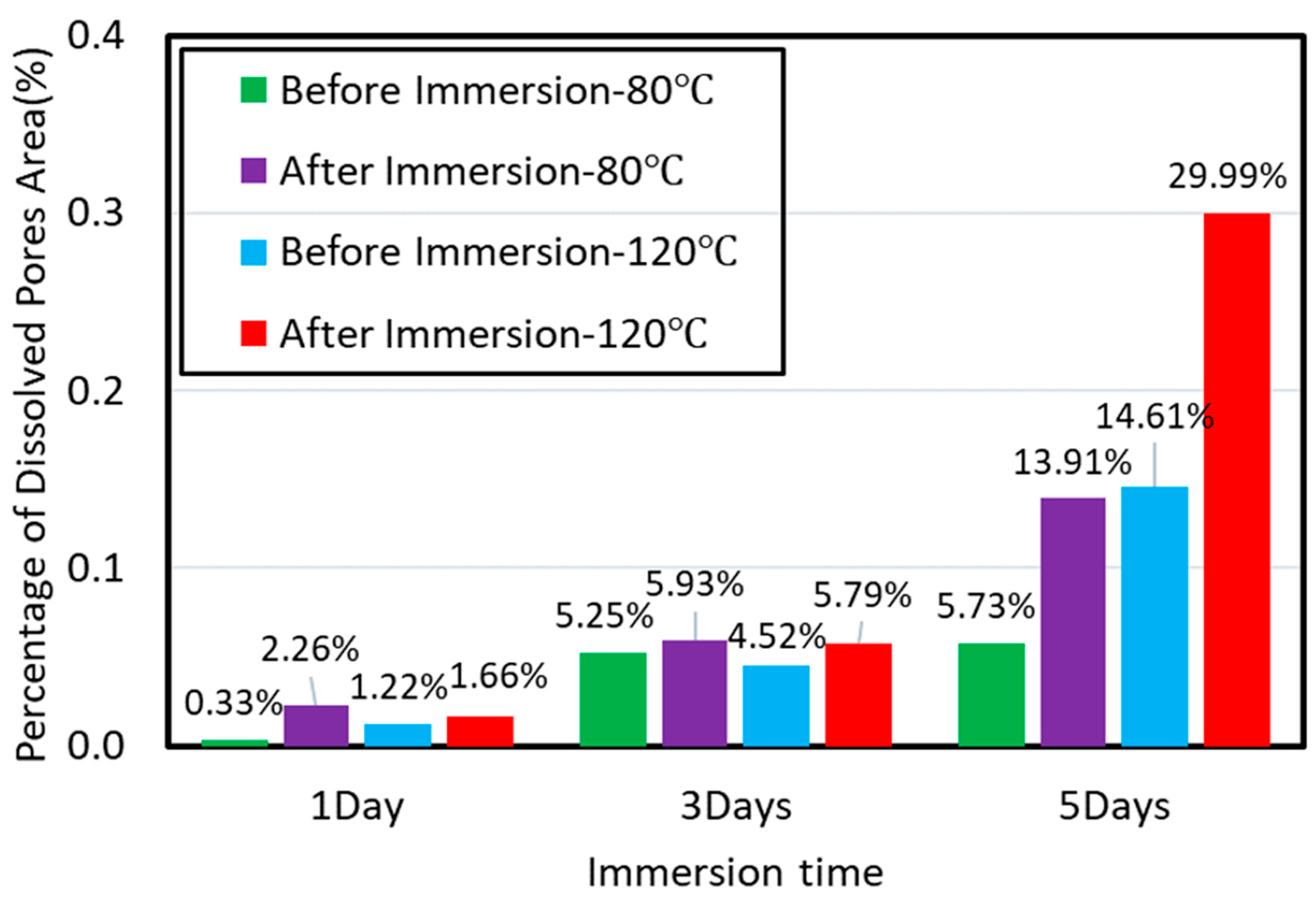
3.1. Effect of Time on Hydration
3.2. Effect of Temperature on Hydration
3.3. Proposed Mechanisms and Implications
- Surfaces in parallel to bedding planes govern the micro-fracture initiation and propagation. Upon the contact of fluid and shale samples, clay minerals such as smectite and illite on the surface of pre-existing micro-fracture would swell initially, which would lead micro-fracture to close and heal. Finally, smectite would collapse, thus generating new micro-fracture with a greater width (Figure 11).
- Imbibition along the direction perpendicular to bedding planes would contribute the increase of porosity at micro-fracture due to feldspar dissolution (Figure 11).
- Hydration process at both parallel and perpendicular to the bedding planes would be accelerated with increasing reservoir temperature.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Melikoglu, M. Shale Gas: Analysis of Its Role in the Global Energy Market. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 37, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EIA, United States Energy Information Administration. Annual Energy Outlook: With Projections to 2040; EIA: Washington, DC, USA, 2013.
- EIA, United States Energy Information Administration. Annual Energy Outlook 2011: With Projections to 2035; EIA: Washington, DC, USA, 2011.
- Fisher, M.K.; Heinze, J.R.; Harris, C.D.; Davidson, B.M.; Wright, C.A.; Dunn, K.P. Optimizing horizontal completion techniques in the Barnett shale using microseismic fracture mapping. In SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Richardson, TX, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Gale, J.F.; Reed, R.M.; Holder, J. Natural fractures in the Barnett Shale and their importance for hydraulic fracture treatments. AAPG Bull. 2007, 91, 603–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zeng, L.; Xie, Q.; Jin, Y.; Hossain, M.M.; Saeedi, A. Analytical modelling of wettability alteration-induced micro-fractures during hydraulic fracturing in tight oil reservoirs. Fuel 2019, 249, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Zhang, Y.; Rezagholilou, A.; Roshan, H.; Sarmadivaleh, M. Brittleness Index: From Conventional to Hydraulic Fracturing Energy Model. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Chen, R.; Sarmadivaleh, M. A practical fracability evaluation for tight sandstone reservoir with natural interface. APPEA J. 2019, 59, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y. Impact of water dynamics in fractures on the performance of hydraulically fractured wells in gas shale reservoirs. In SPE International Symposium and Exhibition on Formation Damage Control; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Richardson, TX, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- King, G.E. Hydraulic fracturing 101: What every representative, environmentalist, regulator, reporter, investor, university researcher, neighbor and engineer should know about estimating frac risk and improving frac performance in unconventional gas and oil wells. In SPE Hydraulic Fracturing Technology Conference; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Richardson, TX, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Nicot, J.P.; Scanlon, B.R.; Reedy, R.C.; Costley, R.A. Source and Fate of Hydraulic Fracturing Water in the Barnett Shale: A Historical Perspective. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 2464–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Reedy, R.C.; Nicot, J.P. Will water scarcity in semiarid regions limit hydraulic fracturing of shale plays? Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 124011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhanov, K.; Habibi, A.; Dehghanpour, H.; Kuru, E. Liquid uptake of gas shales: A workflow to estimate water loss during shut-in periods after fracturing operations. J. Unconv. Oil Gas Resour. 2014, 7, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binazadeh, M.; Xu, M.; Zolfaghari, A.; Dehghanpour, H. Effect of electrostatic interactions on water uptake of gas shales: the interplay of solution ionic strength and electrostatic double layer. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 992–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, E.; Dehghanpour, H. Impact of rock fabric on water imbibition and salt diffusion in gas shales. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2015, 138, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Gordeliy, E.; Prioul, R.; Aidagulov, G.; Bunger, A. Modeling simultaneous initiation and propagation of multiple hydraulic fractures under subcritical conditions. Comput. Geotech. 2018, 104, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshan, H.; Ehsani, S.; Marjo, C.E.; Andersen, M.S.; Acworth, R.I. Mechanisms of water adsorption into partially saturated fractured shales: An experimental study. Fuel 2015, 159, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakcharoenphol, P.; Kurtoglu, B.; Kazemi, H.; Charoenwongsa, S.; Wu, Y.S. The effect of osmotic pressure on improve oil recovery from fractured shale formations. In Spe Unconventional Resources Conference; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Richardson, TX, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bennion, D.B.; Thomas, F.B. Formation damage issues impacting the productivity of low permeability, low initial water saturation gas producing formations. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 2005, 127, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Chen, Y.; Lu, Y.; Lau, H.C.; Hossain, M.M.; Saeedi, A.; Xie, Q. Interpreting Water Uptake by Shale with Ion Exchange, Surface Complexation, and Disjoining Pressure. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 8250–8258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Chen, Y.; Hossain, M.M.; Saeedi, A.; Xie, Q. Wettability alteration induced water uptake in shale oil reservoirs: A geochemical interpretation for oil-brine-OM interaction during hydraulic fracturing. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2019, 213, 103277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sone, H.; Zoback, M.D. Mechanical properties of shale-gas reservoir rocks—Part 1: Static and dynamic elastic properties and anisotropy. Geophysics 2013, 78, D381–D392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Sheng, J.J. Effect of water imbibition on fracture generation in Mancos shale under isotropic and anisotropic stress conditions. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2017, 144, 04017113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhanov, K.K. An Experimental Study of Spontaneous Imbibition in Horn River Shales. Master’s Thesis, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Makhanov, K.; Dehghanpour, H.; Kuru, E. An experimental study of spontaneous imbibition in Horn River shales. In SPE Canadian Unconventional Resources Conference; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Richardson, TX, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Dehghanpour, H.; Lan, Q.; Saeed, Y.; Fei, H.; Qi, Z. Spontaneous imbibition of brine and oil in gas shales: Effect of water adsorption and resulting microfractures. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 3039–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roychaudhuri, B.; Tsotsis, T.; Jessen, K. An experimental and numerical investigation of spontaneous imbibition in gas shales. Paper SPE 147652. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Denver, CO, USA, 30 October–2 November 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Hu, D.; Li, Y.; Liu, R.; Wang, Q. Geological features and reservoiring mode of shale gas reservoirs in Longmaxi Formation of the Jiaoshiba Area. Acta Geol. Sin. 2014, 88, 1811–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Li, J.; Guo, T.; Luo, C. Heterogeneity of the Lower Silurian Longmaxi marine shale in the southeast Sichuan Basin of China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015, 65, 232–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, L.; Qi, L.; Luo, M.; Chen, X.; Tao, Y.; Wang, Z. Characterization of the Lower Silurian Longmaxi marine shale in Changning area in the south Sichuan Basin, China. Geol. J. 2018, 53, 1656–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Ge, H.; Meng, M.; Jiang, Z.; Yang, X. Effect of water imbibition on shale permeability and its influence on gas production. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 4973–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akrad, O.M.; Miskimins, J.L.; Prasad, M. The effects of fracturing fluids on shale rock mechanical properties and proppant embedment. In SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Richardson, TX, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Sonnenberg, S.A. An SEM Study of Porosity in the Organic-Rich Lower Bakken Member and Pronghorn Member, Bakken Formation, Williston Basin. In Proceedings of the Unconventional Resources Technology Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 24–26 July 2017; pp. 3213–3225. [Google Scholar]
- Sondergeld, C.H.; Ambrose, R.J.; Rai, C.S.; Moncrieff, J. Micro-structural studies of gas shales. In SPE Unconventional Gas Conference; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Richardson, TX, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, O.; Kronenberg, A.K.; Gangi, A.F.; Johnson, B.; Herbert, B.E. Permeability of illite-bearing shale: 1. Anisotropy and effects of clay content and loading. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhong, N.; Cheng, L.; Pan, Z.; Dai, N.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L. Pore structure of the graptolite-derived OM in the Longmaxi Shale, southeastern Upper Yangtze Region, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2016, 72, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Yang, Z.; Dai, J.; Dong, D.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.; Deng, S.; Huang, J.; Liu, K.; Yang, C.; et al. The characteristics and significance of conventional and unconventional Sinian–Silurian gas systems in the Sichuan Basin, central China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015, 64, 386–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Petroleum Institute. Recommended Practice for Field Testing of Water-Based Drilling Fluids, 4th ed.; API: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, N.; Karpyn, Z.T.; Liu, S.; Yoon, H. Permeability evolution of shale during spontaneous imbibition. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2017, 38, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Abass, H.; Li, X.; Teklu, T. Experimental investigation of the effect of imbibition on shale permeability during hydraulic fracturing. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 29, 413–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paukert Vankeuren, A.N.; Hakala, J.A.; Jarvis, K.; Moore, J.E. Mineral reactions in shale gas reservoirs: Barite scale formation from reusing produced water as hydraulic fracturing fluid. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 9391–9402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahromostaqim, M.; Sahimi, M. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Hydration and Swelling of Mixed-Layer Clays. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 14631–14639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenevert, M.E. Shale alteration by water adsorption. J. Petroleum Technol. 1970, 22, 1–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.P.; Reed, R.M. Pore networks and fluid flow in gas shales. In SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Richardson, TX, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Heydari, E.; Wade, W.J. Massive recrystallization of low-Mg calcite at high temperatures in hydrocarbon source rocks: Implications for organic acids as factors in diagenesis. AAPG Bull. 2002, 86, 1285–1303. [Google Scholar]
- Baruch, E.T.; Kennedy, M.J.; Löhr, S.C.; Dewhurst, D.N. Feldspar dissolution-enhanced porosity in Paleoproterozoic shale reservoir facies from the Barney Creek Formation (McArthur Basin, Australia). AAPG Bull. 2015, 99, 1745–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, L.S.; Milliken, K.L. Feldspar diagenesis in the Frio Formation, Brazoria County, Texas Gulf Coast. Geology 1981, 9, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieterich, M.; Kutchko, B.; Goodman, A. Characterization of Marcellus Shale and Huntersville Chert before and after exposure to hydraulic fracturing fluid via feature relocation using field-emission scanning electron microscopy. Fuel 2016, 182, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanizadeh, A.; Clarkson, C.R.; Deglint, H.; Vahedian, A.; Aquino, S.; Wood, J.M. Unpropped/propped fracture permeability and proppant embedment evaluation: A rigorous core-analysis/imaging methodology. In Unconventional Resources Technology Conference, San Antonio, TX, USA, 1–3 August 2016; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Tulsa, OK, USA; American Association of Petroleum: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Knauss, K.G.; Wolery, T.J. Dependence of albite dissolution kinetics on pH and time at 25 °C and 70 °C. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1986, 50, 2481–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, B.; Daval, D.; Guyot, F.; Knauss, K.G.; Pollet-Villard, M.; Imfeld, G. pH-dependent control of feldspar dissolution rate by altered surface layers. Chem. Geol. 2016, 442, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, C.; Kutuzov, I.; Ganor, J. The combined effect of temperature and pH on albite dissolution rate under far-from-equilibrium conditions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2016, 186, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Chen, M.; Jin, Y.; Lu, Y. Wellbore stability model for shale gas reservoir considering the coupling of multi-weakness planes and porous flow. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2014, 21, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.H.; Chen, M.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, G.Q. A mechanical model of borehole stability for weak plane formation under porous flow. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2012, 30, 1629–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.H.; Chen, M.; Jin, Y.; Ge, W.F.; An, S.; Zhou, Z. Influence of porous flow on wellbore stability for an inclined well with weak plane formation. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2013, 31, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Chenevert, M.E.; Sharma, M.M.; Friedheim, J.E. Decreasing water invasion into Atoka shale using nonmodified silica nanoparticles. SPE Drill. Complet. 2012, 27, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.M.; Zhang, R.; Chenevert, M.E.; Ji, L.; Guo, Q.; Friedheim, J. A new family of nanoparticle based drilling fluids. In SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Richardson, TX, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- O’Brien, D.E.; Chenevert, M.E. Stabilization of Sensitive Shales Using Inhibited, Potassium-Based Drilling Fluids; Dell Medical School: Austin, TX, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Wang, J.; He, H.; Wang, H. Mechanism on imbibition of fracturing fluid in nanopore. Nanosci. Nanotech. Lett. 2018, 10, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, R.O.; Wattenbarger, R.A. Multi-stage hydraulically fractured horizontal shale gas well rate transient analysis. In North Africa Technical Conference and Exhibition; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Richardson, TX, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]





| Sampling Depth | TOC * | Mineral Composition (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (m) | (%) | Quartz | Feldspar | Calcite | Dolomite | Pyrite | Clay |
| 2321 | 1.78 | 31 | 11.4 | 12.9 | 5.1 | 1.2 | 38.4 |
| 2324 | 2.85 | 31.7 | 5.5 | 8.3 | 5.9 | 3.6 | 45 |
| Sampling Depth | Relative Content of Clay Minerals (%) | Mixed-Layer Ratio (%S) ** | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (m) | I/S * | It | K | C | I/S |
| 2321 | 53 | 28 | 9 | 10 | 12 |
| 2324 | 44 | 34 | 10 | 12 | 12 |
| Immersion Time (Day) | Test Temperature (°C) * | |
|---|---|---|
| 120 | 80 | |
| 1 | YS-01, YS-02 | YS-07, YS-08 |
| 2 | YS-11, YS-12 | YS-15, YS-16 |
| 3 | YS-03, YS-04 | YS-09, YS-10 |
| 4 | YS-13, YS-14 | YS-17, YS-18 |
| 5 | YS-05, YS-06 | YS-19, YS-20 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, Y.; Zeng, L.; Jin, Y.; Chen, G.; Ren, J.; Lau, H.C.; Xie, Q. Effect of Shale Anisotropy on Hydration and Its Implications for Water Uptake. Energies 2019, 12, 4225. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12224225
Lu Y, Zeng L, Jin Y, Chen G, Ren J, Lau HC, Xie Q. Effect of Shale Anisotropy on Hydration and Its Implications for Water Uptake. Energies. 2019; 12(22):4225. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12224225
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Yunhu, Lingping Zeng, Yan Jin, Guanglei Chen, Junfan Ren, Hon Chung Lau, and Quan Xie. 2019. "Effect of Shale Anisotropy on Hydration and Its Implications for Water Uptake" Energies 12, no. 22: 4225. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12224225
APA StyleLu, Y., Zeng, L., Jin, Y., Chen, G., Ren, J., Lau, H. C., & Xie, Q. (2019). Effect of Shale Anisotropy on Hydration and Its Implications for Water Uptake. Energies, 12(22), 4225. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12224225






