Abstract
One of the major environmental problems is the highly toxic agro-industrial waste called olive mill wastewater (OMW), deriving from olive oil production. On the other hand, the continuous development of the biological liquid fuel industry (biodiesel and bioethanol) makes it mandatory the process and exploitation of their main by-products, crude glycerol. This study dealt with the biotechnological conversions of biodiesel-derived crude glycerol with the use of the non-conventional yeast Yarrowia lipolytica in media that had been diluted with OMWs. OMWs, employed as simultaneous liquid medium and substrate, is a new trend recently appearing in Industrial Biotechnology, where value-added metabolites could be produced with simultaneous partial detoxification (i.e. decolorization and phenol removal) of the used residue. In the present study, diluted OMWs (containing 2.0 g/L of total phenolic compounds) blended with 70.0 g/L crude glycerol were employed as substrates. Production of value-added compounds by Y. lipolytica strain ACA-YC 5031 was studied in nitrogen-limited media favoring the production of secondary metabolites (i.e. citric acid, polyols, microbial lipids, polysaccharides). Batch-flask cultures were carried out and the impact of the addition of different NaCl concentrations (1.0%, 3.0%, 5.0% w/w) added upon the biochemical behavior of the strain was studied. Remarkable biomass production was observed in all trials, while in the “blank” experiment (no OMWs and no salt added), the metabolism was shifted toward the synthesis of polyols (Σpolyols = mannitol + arabitol + erythritol > 20 g/L and maximum total citric acid-Cit (sum of citric and isocitric acid) = 10.5 g/L). Addition of OMWs resulted in Citmax = 32.7 g/L, while Σpolyols concentration dropped to <15 g/L. Addition of salt in the OMW-based media slightly reduced the produced biomass, while Cit production drastically increased, reaching a final value of 54.0 g/L (conversion yield of Cit produced per unit of glycerol consumed = 0.82 g/g) in the trial with addition of 5.0% NaCl. Finally, significant color and phenols removal were observed, evaluating the yeast as a decontamination medium for the OMW and a great candidate for the production of value-added compounds.
1. Introduction
Olive-mill wastewaters (OMWs), the major effluent deriving from the olive oil production process, are considered as one of the most challenging agro-industrial wastes to treat, since they are produced in very high quantities. Moreover, their strong odor and dark color and their relatively high organic load have a direct negative impact on the environment if they are released untreated. This important residue of the olive oil industry is one of the most difficult to treat wastes because of its high content in phenolic compounds [,]. The increased concentration of OMWs (without prior treatment) in organic matter and phenolic components results in the reduction of the available concentration of oxygen to the organisms. Lack of oxygen to the organisms upsets the balance of ecosystems and the soil porosity, resulting in contaminated aquifers and polluted environments [,,]. Consequent problems are the production of odors, the excessive growth of algae and bacteria, and the appearance of the eutrophication phenomena in aquatic environments in which OMWs are released untreated. The organic matter in OMW consists of sugars, phenols, tannins, polyphenols, aromatic molecules, ash, and, in some cases, lipids and nitrogen content []. The phenolic compounds are mainly considered responsible for the toxicity of the OMWs constituting, in several cases, the limiting step of their large-scale management [,,,]. It should be noted that, in several cases (i.e. in the case where traditional press extraction process is applied in order to liberate olive oil), OMWs containing very high concentrations of sugars (mostly glucose, in concentrations ≥65 g/L []) are simultaneously liberated. However, a new trend that has appeared in relation to the valorization of these wastewaters refers to their simultaneous utilization as a substrate and water treatment in various fermentation processes. Value-added metabolites could be produced during these fermentation processes with simultaneous partial detoxification (i.e. decolorization and phenol removal) of the residue [,,,,,].
The continuous development of biological liquid fuel industry (principally that of biodiesel and bioethanol production) makes mandatory the process and exploitation of the increased production of its main by-product and principal liquid residue, which is the concentrated glycerol-containing water called crude glycerol (crude glycerin) []. Specifically concerning biodiesel production facilities, the synthesis of 10.0 kg of biodiesel deriving from trans-esterification of various oils, generates c. 1.0 kg of glycerol (purity ≈90.0% w/w) [,]. Global biodiesel production has been growing in recent years. In 2016 more than 30.8 × 106 t. were produced (7.5% more than in 2015), and it is estimated that more than 3.0 × 106 t. of glycerol as an important industrial byproduct were produced only from biodiesel manufacture []. Biodiesel-derived glycerol is a great substrate for microbial growth due to its high concentration in carbon and inorganic constituents. Many studies have reported the ability of eukaryotic microorganisms to convert glycerol into a plethora of value-added compounds, such us microbial lipids (single cell oils; SCOs) [,,,,,,,,,], citric acid [,,,,,,,] polyols [,,,], enzymes, and microbial mass [,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,]. Biodiesel-derived glycerol as a carbon source employed in the Industrial Microbiology has many advantages over other conventional substrates frequently used as microbial substrates (i.e. commercial sugars). One such advantage is the significantly low (or even negative) acquisition cost that this renewable material presents. In spite of the fact that the industrial production of biodiesel is currently being accompanied by the side production of relatively highly purified industrial glycerol feedstock (e.g. purity of ≈85–90% w/w, sometimes >90% w/w), which can be used directly as the starting material for the chemical synthesis of epichlorohydrin, or it can be used in various pharmaceutical applications after further purification processes. The acquisition cost of this relatively highly purified feedstock (i.e. purity ≈85–90% w/w) is significantly low, and at the beginning of 2016, in the Asiatic markets, it was at c. 0.16 US $/kg, with a systematic decreasing trend. Moreover, in several cases, a large fraction of low-quality glycerol deriving from biodiesel production process, the so-called “pitch” glycerol, is a typical waste-stream of the process amenable only for incineration, adding to climate relevant emissions (CO2 as well as N2O) and to the cost of the whole biodiesel production chain. Moreover, utilization of glycerol as microbial substrate is not competitive with substrates that can be used as edible products. It also has inorganic components such as potassium, calcium, sulfur and magnesium that can work favorably for microbial growth [].
Y. lipolytica yeasts are ideal candidates for the remediation and valorization of OMWs as well as of other recalcitrant wastes and residues due to their ability to vigorously grow on a variety of substrates and to tolerate usually hostile growth media []. Moreover, Y. lipolytica yeasts have been reported to be capable of producing SCO having equivalent synthesis and value to that of cocoa-butter [,,,] and a plethora of other value-added compounds during growth on several types of agro-industrial co-products and residues of either fatty or hydrophilic chemical structures [,,,,]. The present study investigated the ability of Y. lipolytica strain ACA-YC 5031, a strain that has been reported capable of producing SCO and citric acid during growth on glucose-based media under nitrogen-limited conditions [], to grow and produce secondary metabolites on mixed nitrogen-limited media consisting of OMWs and biodiesel-derived glycerol. In fact, OMWs were used in order to partially replace tap water from the fermentations performed, whereas the effect of the addition of different sodium chloride (NaCl) concentrations upon the physiological behavior of the strain on osmotic stress over the production of secondary metabolites was assessed. The number of investigations dealing with the cultivation of microorganisms on media that are composed of mixtures of OMWs with other low-cost substrates (i.e. commercial-type glucose, low-cost oils, etc.), in the approach in which OMWs are considered as simultaneous substrate and process water, are relatively restricted in the literature [,,,,]. Moreover, studies in which blends of glycerol and OMWs as substrates were used are indeed very scarce []. On the other hand, the simultaneous effect of the addition of OMWs and NaCl upon the fermentation of glycerol by Y. lipolytica strain, to the best of our knowledge, is studied for the first time in the literature. Therefore, the potential of a new natural Y. lipolytica strain (ACA-YC 5031) to reduce the color and the phenol content and simultaneously to convert the industrial wastes (OMWs blended with glycerol and NaCl) into value-added compounds, useful in Industrial and Food Biotechnology, was investigated, and technological approaches of the bioprocess were critically addressed and discussed.
2. Results
2.1. Batch Fermentations and Production of Value-Added Compounds by Yarrowia lipolytica Growing on OMW/Glycerol Blends Supplemented with NaCl
Experiments were carried out investigating the assimilation of glycerol and its conversion by the yeast Y. lipotytica ACA-YC 5031 to secondary metabolites with and without the addition of OMWs (phenolic compounds into the media = 2.0 ± 0.20 g/L) into the medium. The effect on the microbial reactions and physiology of different concentrations of NaCl (1.0%, 3.0%, and 5.0% w/v) added into the culture medium was also examined. Under all circumstances, there was production of secondary metabolites, such as SCO, citric acid, intracellular polysaccharides (IPS), and polyols (mainly mannitol and erythritol, while small concentrations of arabitol were also detected) during growth on OMW/glycerol blends, where variable quantities of NaCl were added. The secretion of extra-cellular metabolites was enhanced after virtual nitrogen depletion from the growth medium occurring c. 24–30 h after inoculation. Specifically, the initial nitrogen concentration of nitrogen as indicated by the concentration of extra-cellular free amino nitrogen (FAN) was = 85 ± 10 mg/L, whereas the final nitrogen concentration when this compound became the limiting substrate was 25 ± 5 mg/L of FAN into the medium (data not presented). The results of the maximum values of the components obtained during the fermentations carried out are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
values of glycerol consumption, production of biomass, cellular lipids, citric acid, mannitol, erythritol, intra-cellular polysaccharides (IPS) and yield coefficients in culture medium with just glycerol (blank) and glycerol blended with OMWs yielding at initial concentration of 2.0 g/L of phenols using different concentrations of NaCl w/v (0.0%, 1.0%, 3.0%, 5.0%).
The results showed a small reduction of biomass (dry cell weight – DCW; g/L) production and a net reduction of polyols biosynthesis as well as reduced glycerol consumption after the addition of OMWs (viz. phenolic compounds) and NaCl into the culture medium, while concomitantly, citric acid (Cit) production significantly increased. Potentially, the addition of toxic compounds (i.e. OMWs and NaCl) slightly negatively affected biomass production and substrate assimilation, in accordance with several reports in the literature [,,]. Moreover, it was observed that the addition of NaCl combined with the addition of phenolic compounds into the medium favored the yeast to increase the production of lipids in its biomass (YL/X in % w/w). Apparently, the combined effect of the high osmotic pressure and the addition of a “lipogenic” medium, such as the OMWs [,], increased the quantity of lipid accumulated inside the yeast cells. In a restricted number of cases, the addition of several types of natural substances (i.e. phenolic compounds, essential oils, etc.) has been revealed to be capable of increasing the content of cellular fatty acids (FAs) inside Y. lipolytica yeast [,,], similarly to the current investigation. More specifically, the yeast consumed all glycerol without the presence of OMWs and NaCl in the culture medium after 260 h of fermentation, obtaining the highest DCW value between all the experiments (10.8 g/L) with biomass yield (YX/Glol) = 0.14 g/g and endopolysaccharides (IPS) = 0.88 g/L (corresponding to polysaccharides per DCW value (YIPS/X) = 8.1% w/w). However, during this fermentation, maximum production of intracellular lipids, 2.39 g/L, with maximum lipid in DCW value (YL/X) = 23.9% w/w was observed earlier, at 188 h, at the same time producing the maximum value of citric acid 10.5 g/L with YCit/Glol = 0.15 g/g. At the same conditions (no OMWs and no NaCl added), the highest values of mannitol (13.4 g/L at 188 h) and erythritol (8.8 g/L at 164 h) were obtained, and these values corresponded to the highest ones obtained in all trials carried out. The addition of OMWs yielding in initial phenolic compounds concentration of c. 2.0 g/L in the culture medium slightly reduced the produced biomass (Xmax = 8.7 g/L) and the assimilation rate of glycerol. On the other hand, the amount of the maximum produced intracellular lipids and IPS were slightly increased, while citric acid production was significantly higher compared to the trial with no OMWs added (see Table 1). More specifically, maximum production of polyols (8 g/L mannitol with YMan/Glol = 0.16 g/g and 4.9 g/L erythritol with YEry/Glol = 0.10 g/g) was observed at 140 h of fermentation. Maximum production of IPS, 1.52 g/L corresponding to 17.5% of the produced biomass, and 32.7 g/L of citric acid with YCit/Glol = 0.52 g/g were obtained at 188 h. At the same time, YL/X = 28.3% w/w was obtained. Finally, up to 93% glycerol consumption was observed. Similar results were observed when 1.0% NaCl was added, while the highest values of intracellular lipids and IPS were obtained compared to all fermentations. More specifically, 2.52 g/L intracellular lipids were produced at 242 h with an increased percentage of produced lipids per produced biomass (YL/X = 29.9% w/w). The maximum produced IPS was 2.59 g/L at 224 h. At the same time, the maximum production of citric acid, 45.2 g/L, and mannitol, 6.0 g/L, were obtained, with conversion yields of 0.68 and 0.09 g/g, respectively. Maximum produced erythritol was just 2.5 g/L at 144 h with YEry/Glol = 0.05 g/g.
The increased concentration of NaCl to 3.0% in the culture medium resulted in reduced glycerol consumption (up to 76%) and decreased maximum DCW and polyols production. Although the absolute values of produced biomass and intracellular lipids were decreased, the maximum lipid in DCW value YL/X (% w/w) was increased to 31.5% at 280 h. Maximum value of DCW, 5.6 g/L, was observed at 140 h having, however, the highest produced biomass per consumed substrate between the fermentations (YX/Glol = 0.16 g/g). At the same time, maximum production of erythritol was 4.9 g/L with a simultaneous yield 0.14 g/g. Maximum concentration of IPS was decreased to 0.72 g/L at 280 h, corresponding to endopolysaccharides in DCW = 19.8% w/w. Maximum produced citric acid and mannitol were observed at 280 h, with values 42.0 and 3.6 g/L, respectively, suggesting the positive combined effect of NaCl and OMWs addition upon the shift of the cellular metabolism toward citric acid production.
The addition of 5.0% w/v of NaCl favored the growth of the yeast, the assimilation of glycerol, and the production of secondary metabolites more than with the addition of 3.0% w/v NaCl, with the exception of polyols production. At these conditions, the percentage of lipids in produced biomass was further increased, reaching the highest value of 35.1% w/w with a 2.25 g/L maximum of produced intracellular lipid after 308 h of fermentation. At that time, the maximum glycerol consumption was 90% w/w, and the maximum erythritol production was only 3.2 g/L. Maximum DCW concentration was 6.8 g/L, with a yield YX/Glol = 0.10 g/g at 233 h, whereas, at the same time, the highest concentration of citric acid (54.0 g/L with simultaneous yield YCit/Glol = 0.82 g/g) was achieved. Those conditions favored the yeast to produce citric acid in the best conversion yield of citric acid produced per glycerol consumed of all conversions carried out (global conversion yield of citrate produced per unit of glycerol consumed = 0.81 g/g; see Figure 1).
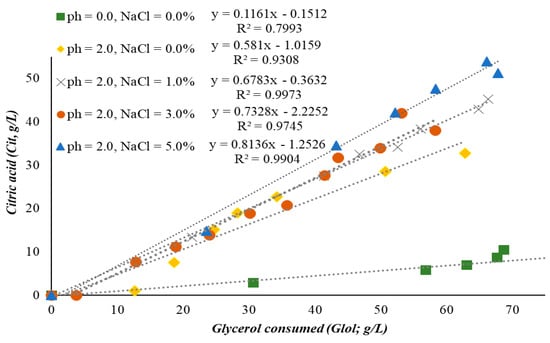
Figure 1.
Citric acid production vs glycerol consumption by Yarrowia lipolytica ACA-YC 5031 in 70.0 g/L glycerol (blank) and glycerol blended with 2.0 g/L phenolic compounds and different concentrations of NaCl (0.0%, 1.0%, 3.0%, and 5.0% w/v).
Figure 1 illustrates the correlation between glycerol consumption and citric acid production, and clearly, the more NaCl is added, the more YCit/Glol increases. The absence of phenolic compounds and NaCl from the culture medium (blank experiment) resulted in much less citric acid production per consumed glycerol (≈0.11 g/g). Citric acid volumetric productivity was 0.05 g/(L·h), with a maximum value 10.5 g/L. While all substrate (glycerol) was consumed with a consumption rate 0.40 g/(L·h), a significant number of polyols was produced (20.0 g/L) at that time, also producing a high amount of biomass (Figure 2). The addition of the phenolic compounds (2.0 ± 0.20 g/L) into the medium resulted in 94% glycerol consumption, with a consumption rate 0.32 g/(L·h) and a bit less biomass (Xmax = 8.7 g/L) compared to the previous fermentation. A clear decrease in polyols production was also observed, while the productivity of citric acid was faster (0.18 g/L·h), and a significantly increased value, up to 32.7 g/L, was observed (Figure 2b). The kinetics of glycerol (Glol) consumption, biomass (X) production, polyols biosynthesis (ΣPolyols), and citric acid (Cit) accumulation into the growth medium for all trials performed is shown in Figure 2a–e. Likewise, the illustration of parameters concerning the trials performed is presented in Table 2.
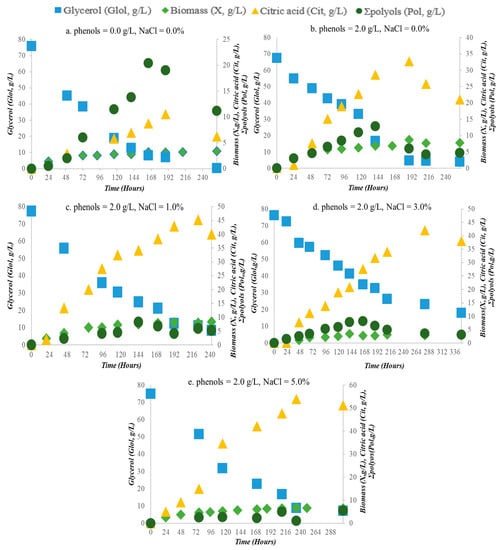
Figure 2.
Kinetics of glycerol consumption (g/L), yeast Yarrowia lipolytica ACA-YC 5031 growth (DCW g/L), citric acid, and polyols production (g/L) in a glycerol-based culture medium containing (a) phenols = 0.0 g/L and NaCl = 0.0%; (b) phenols = 2.0 g/L and NaCl = 0.0%; (c) phenols = 2.0 g/L and NaCl = 1.0%; (d) phenols = 2.0 g/L and NaCl = 3.0% and (e) phenols = 2.0 g/L and NaCl = 5.0% concentration.

Table 2.
Glycerol consumption (%), glycerol consumption rates, citric acid production rates, and specific citric acid production rates during fermentations of glycerol (70.0 g/L) with and without phenolic compounds (2 g/L) and with increased concentrations of NaCl (0.0%, 1.0%, 3.0% and 5.0% w/v).
2.2. Intra-Cellular Lipid Concentration and Fatty Acid Composition
The intra-cellular lipid concentration was in most of the cases steadily increased during all fermentations (Figure 3). However, the combined effect of the addition of OMWs and NaCl into the medium increased lipid in DCW values of Y. lipolytica ACA-YC 5031 (without OMWs and NaCl, YL/Xmax value was 23.9% w/w, while with the addition of OMWs and NaCl at 5%, the respective value was 35.1% w/w—see Table 1). Specifically, the YL/Xmax value increased after the addition of OMW in the culture medium from 23.9% (blank experiment) to 28.3% (OMWs added; no NaCl added). YL/Xmax values continued to increase to 29.9%, 31.5%, and 35.1% with increment of NaCl concentration in the culture medium (1.0%, 3.0%, and 5.0% w/v NaCl, respectively) (see Table 1).
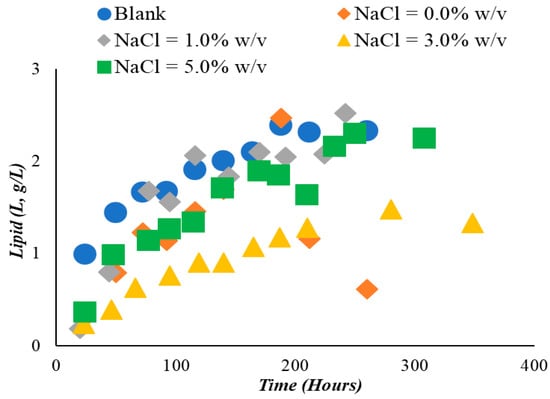
Figure 3.
Single cell oil (SCO) production by Yarrowia lipolytica ACA-YC 5031 in culture medium containing blank glycerol and blended also with phenols and 0.0%, 1.0%, 3.0%, and 5.0% w/v NaCl.
The intracellular fatty acid (FA) composition was analyzed using gas chromatography (GC) and is presented in Table 3. The analyzed fatty acids were palmitic acid, palmitoleic acid, stearic acid, oleic acid, and linoleic acid. The yeast produced a significant amount of C18:1, up to 66.0%, mainly without the presence of phenols and NaCl in the medium. The addition of phenolic compounds, as well as the increased concentration of NaCl, resulted in a slightly decreased concentration of oleic acid, in contrast to the production of palmitic acid, which it slightly increased from 10.0% to 16.0% w/w. Maximum concentration of palmitoleic was observed when phenols and 3.0% w/v NaCl were in the medium (12.0% and 15.0%), while a lower concentration of linoleic acid was observed in their absence (6.0%). The addition of phenols, as well as of 1.0% NaCl, resulted in the same concentration of linoleic acid, 11.0%, which was decreased in time. The same phenomenon was observed for 3.0% and 5.0% w/v NaCl, reaching 9.0% and the highest concentration of 21.0%, respectively. Finally, FA C18:0 was found in low concentrations in all trials performed.

Table 3.
Fatty acid composition (%, w/w) of Yarrowia lipolytica ACA-YC 5031 when grown in a glycerol-based media (70.0 g/L) blended with OMWs (2.0 g/L of phenolic compounds), in which different concentrations of NaCl (0.0%, 1.0%, 3.0%, and 5.0% w/v) were added.
2.3. Color and Phenolic Compounds Removal
Y. lipolytica ACA-YC 50231 efficiently removed color and phenolic compounds from the growth medium during most of the trials performed. There was a remarkable (≈40.0%) color reduction after 50 h of incubation in the presence of OMWs and 1.0% w/v of NaCl, followed by a 30.0% decolorization in 3.0% NaCl and 17.5% in 0.0% NaCl in the medium. The decolorization became slower following that incubation time. During the other time, only 13.0% color was removed between 250 and 300 h of incubation in the presence of a higher concentration (=5.0% w/v) of NaCl in the medium (Figure 4a). On the other hand, significant removal of phenolic compounds (maximum removal ranging between 52.0 – 62.0% w/w irrespective of the quantity of NaCl initially added into the medium) occurred in all trials performed (Figure 4b).
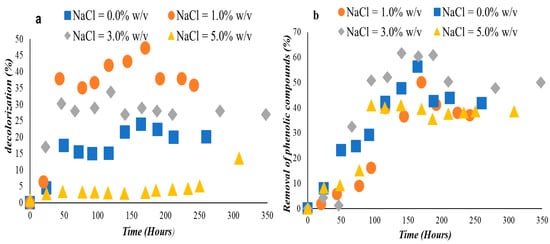
Figure 4.
(a) Decolorization (%) and (b) Removal of phenolic compounds (%) from the culture medium when Yarrowia lipolytica ACA-5031 was grown in 0.0%, 1.0%, 3.0%, and 5.0% NaCl containing 2.0 g/L phenolic compounds.
3. Discussion
Shake-flask batch fermentations were carried out to investigate the physiological behavior of the yeast Y. lipolytica ACA-YC 5031 cultivated on biodiesel-derived glycerol employed as the sole carbon source in nitrogen-limited media enriched with OMWs, into which different NaCl quantities were added. The ability of the yeast to convert crude glycerol into value-added metabolic products was examined, as well as its potential to remove phenolic compounds and color from the medium. The obtained results seemed promising since they demonstrated the ability of the yeast to produce value-added compounds under all circumstances, whereas simultaneously remarkable detoxification (decolorization and removal of phenolic compounds) of the employed wastewaters was realized. The amount of the produced secondary metabolites, however, varied significantly between the trials performed, since the addition of OMWs and NaCl (in various concentrations) had serious impact upon the physiology of the studied strain. The yeast performed a remarkable growth (X = 10.8 g/L, YX/Glol ≈ 0.12–0.15 g/g) in a nitrogen-limited glycerol-based media (Glol0 ≈ 70.0 g/L) comparable to previous studies [,,]. However, in other cases in which trials of Y. lipolytica or other yeasts of Yarrowia clade (i.e. Y. bubula, Y. phangngensis, etc) cultivated in shake-flasks or bioreactor experiments were carried out, significantly higher DCW quantities (i.e. X > 20.0 g/L, in some cases X ≈ 40.0 g/L) were recorded [,,,].
The presence of OMW (added in initial phenolic compounds ≈2.0 g/L, a typical concentration of phenolic compounds found in OMWs liberated from 3.0- and 2.5-phase centrifuge operation modules []) slightly inhibited the cell growth, reducing the DCW to 8.7 g/L as previously reported due to the high toxic effect of the effluent [,,]. The simultaneous addition of increased salt concentrations resulted in further growth reduction, while the produced intra-cellular polysaccharides did not reach very high values. This phenomenon was reasonable and expected, taking into account that conditions of osmotic stress do not induce cell growth, in contrast to citric acid and polyols production.
Sarris et al. [] reported a small biomass reduction of related Y. lipolytica strains after the addition of 2.0 g/L phenolic compounds in a medium containing 35.0 g/L glucose, the principal sugar found in OMWs, and a compound that is metabolized following similar metabolic pathways as those of glycerol. The produced citric acid (=18 g/L) and the conversion yield on glucose consumed (≈0.70 g/g) were not affected and remained almost constant. Similarly, Sarris et al. [] reported a slightly reduced growth of the strain Y. lipolytica ACA-DC 5029 after the addition of OMW in a glycerol-based medium. In that study, the addition of OMW significantly increased citric acid production from 10.5 g/L (YCit/Glol = 0.15 g/g) to 32.7 g/L (YCit/Glol = 0.52 g/g). These results, accompanied with previous studies that reported the successful usage of OMWs in order to dilute concentrated glycerol-based media, suggest that these wastewaters are a suitable medium for citric acid production [,]. In the present investigation, it was also demonstrated that addition of salt, combined with presence of OMW in the culture medium at ideal pH conditions (pH = 5.0–6.0), resulted in biosynthesis of citric acid by Y. lipolytica at remarkably high quantities. The addition of phenols and the increased concentrations of NaCl significantly favored the production of citric acid, which it was steadily increased, reaching a maximum quantity of 54.0 g/L and a YCit/Glol value = 0.82 g/g. On the other hand, Tomaszewska et al. [] observed decreased citric acid production in low pH conditions (pH = 3.0), while the polyols were significantly increased. In contrast, Rzechonek et al. [] reported the ability of a genetically modified Y. lipolytica to produce a high amount of citric acid, up to 75.8 g/L, on media containing crude glycerol at pH = 3.0. Efficient citric acid production by Y. lipolytica strains occurs normally in nitrogen-limited glycerol-based media and pH values between 5.5 and 7.0 [,,]. The results achieved in the current study (Citmax = 54.0 g/L with YCit/Glol = 0.82 g/g) compares favorably with the ones obtained in shake-flask and batch-bioreactor experiments for both the absolute (g/L) and relative (g per g of glycerol consumed) values of produced citric acid. Nevertheless, higher citric acid levels have been reported for conversions carried out in fed-batch bioreactors. A summary of the findings for the conversion of crude glycerol and olive-mill wastewater–based media to citric acid by Y. lipolytica strains in various fermentation configurations, including the current study, is given in Table 4.

Table 4.
Metrics of citric acid production from glycerol- or OMW-based media by Yarrowia lipolytica strains cultivated on various fermentation configurations.
Erythritol and mannitol were the main byproducts of glycerol metabolism. It is worth noting that traces of arabitol were also observed in the culture medium with and without OMW. However, production of arabitol was not observed in salt containing fermentations, indicating that both the salt and the citric acid inhibited its production, whereas mannitol and erythritol were synthesized at low concentrations. More specifically, mannitol and erythritol production reached maximum values 13.4 g/L and 8.8 g/L, respectively, in the glycerol-based medium, while addition of OMW reduced their production. Rymowicz et al. [] and Chatzifragkou et al. [] reported that it is essential for polyol biosynthesis an appropriate high initial glycerol concentration. Although high glycerol concentration favored the production of mannitol, Rywińska et al. [] reported higher erythritol production than mannitol in a crude glycerol substrate. Moreover, it has been found that growth of osmophilic yeasts in glycerol-based medium containing salt at low pH values promoted erythritol production [,,], a fact that was not validated in the current investigation since, as it has been previously reported, the addition of salt in OMW/glycerol blends clearly shifted the cellular metabolism towards citric acid production instead of polyols (see Figure 2a–e).
Although the biochemical events leading to the synthesis of polyols from glycerol in Y. lipolytica strains have not been completely elucidated [,,], it appears that the biosynthesis of polyols depends on the response of the enzyme complexes to the external osmotic environment. More specifically, high osmotic pressure increases the activity of the enzyme erythrose reductase (ΕΡ), while it reduces the activity of the enzyme mannitol-1-phosphate dehydrogenase (M-1-PDH) []. In this study, under all circumstances where salt was added, mannitol production was observed after 24 h incubation until the end of the fermentations, while erythritol production was observed later and for a very short period. Since erythritol molecule with a smaller MW than the mannitol, the osmotic pressure that comes from erythritol is higher than that of mannitol at the same concentrations of both compounds. When the microorganism is exposed to a high osmotic pressure, it produces erythritol to balance the osmotic pressure extra-cellularly and intra-cellularly. The organism accumulates a high amount of erythritol, which compensates for the difference between the extracellular and intracellular water potential []. Other parameters that affect erythritol production are the pH of the culture medium (production of polyols is mainly performed at pH ranging between 2.5 and 3.5), the incubation temperature, the type and the concentration of the carbon source employed, the nitrogen and phosphate source, as well as the presence of some metals []. On the other hand, many studies have reported mannitol to be the only polyol produced by the yeast in order to be protected against the osmotic stress. Without doubt, the cooperative activity between those two polyols can protect the cell from damages by that kind of stress []. In general, the production of polyols from glycerol is not common for Y. lipolytica strains and can be very interesting for Food Technology.
Y. lipolytica is a well-known lipid-producing microorganism employed in the literature for the production of common and non-common fatty acids due to its ability to accumulate over 20.0% and up to 70.0% lipids per dry weight (w/w) [,]. Dobrowolski et al. [] have reported lipid content 25% of DCW in Y. lipolytica A101 on media containing crude glycerol from soap production, similar to this study on the glycerol-based medium. Lipid production by Y. lipolytica ACA YC-5031 increased from 23.9% of DCW on glycerol-based medium to 28.3% after the addition of phenolic compounds into the glycerol-based medium. Similarly, Sarris et al. [,] reported a proportionally increased in SCO production after the addition of OMWs in the culture medium. These results confirm the potential usage of OMW as a “lipogenic” substrate [,]. The addition of salt combined with OMW in the culture medium favored the production of intra-cellular lipids, which increased with increased salt concentration, reaching YL/Xmax = 35.1% w/w when 5.0% w/v NaCl had been added.
Biosynthesis of both citric acid and SCO from carbon sources like glycerol or similarly metabolized compounds in Y. lipolytica are processes that present remarkable similarities in their first steps being triggered by the depletion of an essential nutriment, and in particular nitrogen, from the culture medium [,,,,,,]. Upon nitrogen limitation and in the presence of excess carbon, Y. lipolytica yeast strains produce large amounts of TCA cycle intermediates, including citric acid and iso-citric acid, which are not further catabolized. In essence, nitrogen exhaustion results in a rapid decrease of the intra-cellular AMP (adenosine monophosphate) concentration, as AMP is cleaved to produce NH4+ ions, indispensable for cell growth. This event results in the inactivation of iso-citrate dehydrogenase in the TCA cycle and, consequently, the accumulation of both iso-citric and citric acids into the mitochondria. When the intra-mitochondrial citric acid concentration reaches a critical value, citrate enters the cytoplasm in exchange for malate. Citric acid is then either cleaved by ATP-citrate lyase (ACL), the key enzyme of the lipid accumulation process in oleaginous microorganisms, to yield acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate, or it is secreted to the culture medium [,,]. For the case of lipid-accumulating microorganisms, the resulting acetyl-CoA is carboxylated by acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC1) to form malonyl-CoA, the substrate for the biosynthesis of acyl-CoA esters and, subsequently, triacylglycerols [,,].
Y. lipolytica strains are a most untypical example of the group of oleaginous yeasts []. Lipid content of various strains during growth on glucose under nitrogen limitation (condition favoring lipid storage) is not very high in several cases (e.g. biomass in DCW ≈ 36% w/w). It certainly does not compare favorably for lipid accumulation with species of Rhodotorula/Rhodosporidium, Lipomyces, and other genera [,]. In some cases observed during growth in a shake-flask or batch bioreactor experiments, growth of Y. lipolytica in nitrogen-limited glucose- or glycerol-based media resulted in sequential production of intra-cellular lipid and extra-cellular citric acid. In the first steps of nitrogen limitation, lipid accumulation was triggered (the maximum lipid in DCW was rarely >25%, w/w), and thereafter, lipid content decreased with time, even though significant substrate quantities remained unconsumed in the medium. The period of intra-cellular lipid degradation (turnover) coincided with the secretion of citric acid in non-negligible quantities into the culture medium [,,,,,]. On the other hand, in other studies, as in the current investigation, lipid content as a proportion of the DCW constantly increased over the whole range of the nitrogen-limited batch fermentation, with simultaneous significant citric acid secretion [,]. The above-mentioned complex regulation makes it difficult in many instances to obtain high rates of lipid accumulation in batch culture, since, in such conditions, lipid accumulation and citric acid production occur simultaneously, resulting in only moderate lipid accumulation, as in the current investigation. Potentially, this fact was the reason for which, in the first reports that have appeared, the ability of yeasts of the species Y. lipolytica to produce lipids from glucose, glycerol, or similarly metabolized compounds has been characterized as “dubious” [,,].
In the trials performed by Y. lipolytica ACA-YC 5031, the produced fatty acids (FAs) were palmitic (C16:0), palmitoleic (C16:1), stearic (C18:0), oleic (C18:1), and linoleic (C18:2) acid. Oleic acid being the dominant fatty acid under all circumstances, is in agreement with previous reports [,,,,,,], indicating that SCO produced by Y. lipolytica ACA YC-5031 through the type of the conversion proposed, can constitute perfect precursors for the synthesis of second-generation biodiesel [,]. Fatty acid desaturase activity during cultivation was estimated by calculating the ratios of desaturase product to substrate (C16:1/C16:0; C18:1/C18:0; C18:2/C18:1). High C18:1/C18:0 ratios can be observed, in accordance with previous studies carried out by several wild-type mutant Y. lipolytica strains tested [,,,,], indicating an important Δ9-desaturase activity in the yeast cells, as reported by Rymowicz et al. [] and Sarris et al. []. Sarris et al. [] found that the addition of OMW in the culture medium increased the amount of oleic acid over 60.0% in time, while it reduced that of C18:0. However, in this study, the addition of OMW slightly reduced the amount of oleic acid, while the addition of increased salt concentration resulted in a slightly further reduction of the above-mentioned cellular FA (see Table 3). Nevertheless, cellular C18:0 concentrations were always ≈60.0% w/w, showing that addition of salt to the OMW/glycerol blends affected to the minimum the FA composition of the cellular lipids produced (Table 3).
In all trials performed, and irrespective of the addition of NaCl into the OMW-based media employed, Y. lipolytica ACA-YC 5031 performed a significant removal of phenolic compounds into the medium (between 40.0–62.0% w/w), while a non-negligible decolorization was also observed (Figure 4a,b). At the highest NaCl concentrations employed, a lower decolorization rate was observed, but, in any case and in accordance with the literature [,,,,], the removal of phenolic compounds and the removal of color from the fermented OMW-based media was not proportional, meaning, in fact, that high decolorization did not mean that simultaneously high removal of phenolic compounds occurred, and vice versa. Sarris et al. [] reported 55.9% decolorization and simultaneous 12.9% removal of phenolic compounds when somehow low initial concentrations of phenolic compounds were employed (≈1.80 g/L), while the respective values of removal of phenolic compounds and color were 50.9% w/w and 45.3% when OMW-based media with initial phenolic compounds ≈5.50 g/L were employed for the related strain Y. lipolytica ACA-YC 5033 in OMW and glucose-enriched media. Similarly, the yeast Y. lipolytica ACA-YC 5029, as reported by Sarris et al. [], performed up to 10.0% w/w phenols removal and up to 30.0% color removal during growth on crude glycerol. In general, the ability of some yeasts and fugal strains to remove phenolic compounds depends on the secretion of extracellular oxidases, laccases, and other enzymes, such as lignin peroxidases and manganese-dependent (or independent) peroxidases [,,]. However, the yeasts do not have the appropriate mechanisms to produce those enzymes and to remove the phenolic compounds. Therefore, the phenol and color reduction might be attributed to potential adsorption of phenolic compounds in the yeast cells or even to their partial utilization as carbon source and energy [].
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Microorganism, Media, and Culture Conditions
The yeast Y. lipolytica ACA-YC 5031 isolated from various types of sourdoughs [] was kindly offered by the Laboratory of Dairy Science, Agricultural University of Athens, Greece. The organism was maintained on YPDA slants (10 g/L glucose, 10 g/L yeast extract, 10 g/L peptone, and 20 g/L agar) at 4 °C. The experiments were carried out in 250-mL Erlenmeyer flasks, containing 50 ± 1 mL of growth medium, sterilized at T = 121 °C for 20 min and inoculated with 1 mL of 24-h exponential pre-culture yeast incubated at 3.0 Hz at 28 ± 1 °C. The yeast pre-culture was carried out in yeast extract-glucose-dextrose medium with 10.0 g/L of each. Biodiesel-derived glycerol (initial glycerol concentration—Glol0 = 70 ± 5 g/L) was used as a carbon source in the medium, while peptone and yeast extract, 1.0 g/L each, were used as a nitrogen source. Two types of fermentation were examined a) containing OMWs that were added in order to yield in initial concentration 2.0 ± 0.20 g/L of phenolic compounds and b) without OMW in the culture medium. The origin and the composition of crude glycerol and the chemical composition of OMWs employed in the current investigation were as in Sarris et al. []. Specifically, OMWs were received from a three-phase decanter olive mill located in Chania (Crete, Greece) and were frozen at T = –20 °C. Prior to the experiments, OMWs were de-frozen, and the solids were removed by centrifugation (9000 × g/15 min at T = 21 °C) in a Universal 320R-Hettich centrifuge (Tuttlingen, Germany). OMW phenolic content expressed as gallic acid equivalent was ~3.5 g/L, while no reducing sugars were found into the wastewaters. Moreover, negligible quantities of olive oil (c. 0.2 g/L; determination of oil conducted after triple extraction with hexane) were presented into the OMWs tested. Therefore, in the trials performed, the sole carbon source employed was crude glycerol. The culture medium salt composition was (g/L): KH2PO4,7.0; Na2HPO4×2H2O, 2.5; MgSO4×7H2O, 1.5; MnSO4×H2O, 0.06; ZnSO4×7H2O, 0.02; FeCl3×6H2O, 0.15; CaCl2×2H2O, 0.15 []. As a nitrogen source, peptone and yeast extract were used in a concentration of 1.0 g/L each, imposing nitrogen-limited conditions in all trials. Experiments were carried out evaluating the effect of NaCl at different concentrations (0.0%, 1.0%, 3.0%, and 5.0% w/v) in the culture medium. All fermentations carried out in shake-flask mode, and flasks were placed in an orbital shaker (New Brunswick Sc, USA) at an agitation rate of 3.0 Hz (T = 28 ± 1 °C). Initial pH in the culture media was adjusted to 6.0 while pH value during the trials was measured and when necessary it was adjusted between the range 4.8–5.8 by adding (periodically and aseptically) small quantities NaOH 5M (e.g. 500–600 μl) [,]. The exact volume of NaOH solution needed for the pH correction was evaluated by measuring the volume of NaOH solution required for pH correction in one (at least) flask (collected daily). Then the appropriate volume of NaOH solution was aseptically added in the remaining flasks and the value of pH reached was verified to be in the range of 4.8–5.8.
4.2. Dry Weight Determination
The whole content of the 250 mL flasks was collected, and cells were harvested by centrifugation at 9000 × g/10 min at T = 4 °C using a Universal 320R-Hettich centrifuge (Tuttlingen, Germany). The pellet was then washed with distilled water, and centrifugation was applied one more time under the same conditions. Biomass (X) was dried at T = 90 ± 5 °C for 24 hours to obtain the dry cell weight (DCW) expressed in g/L []. Biomass yield YX/Glol (g/g), was expressed as the grams of cell dry weight (X) produced, per grams of substrate (glycerol; Glol) consumed (g DCW / g glycerol consumed).
4.3. Determination of Total Intra-Cellular Polysaccharides (IPS)
Determination of IPS was carried out using a modified protocol described by Liang et al. [] and the 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid method (DNS) described by Miller []. Specifically, 0.05 g DCW were acidified by adding 10 mL HCl 2M. The solution was then hydrolyzed at T = 100 °C for 30 min, followed by addition of 10 mL NaOH 2M to reach pH = 7.0, and was subsequently filtered through Whatman filter paper twice. Then, 0.5 mL of the sample solution and 0.5 mL DNS reagent were transferred into tubes and left in a water-bath at T = 100 °C for 5 min, followed by 2 min a T = 25 °C. Finally, 5 mL distilled water were added to the samples mixing well, and the absorbance at 540 nm was measured using a Hitachi U-2000 Spectrophotometer (Tokyo, Japan).
4.4. Determination of Glycerol, Polyols, and Citric Acid
The concentration of the remaining glycerol, the produced polyols, and citric acid were determined during the fermentation using Waters 600E High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), (Waters Association, Milford, MA, USA) []. The samples were first filtered using a membrane of 0.2 μm diameter, and 10 μl of the sample were injected. The mobile phase was H2SO4 5 mΜ, while the static phase was the column Amimex HPX-87H (Biorad, Richmond, CA, USA) (30 cm x 7.8 mm). The column flow was 0.5 mL/min, at T = 45 °C. The apparatus type was Waters 600E with RI detector (RI; Waters 410) for the determination of glycerol and polyols and UV detector (Waters 486) for the determination of organic acids. The area of each compound was determined according its retention time, and the concentration of each compound (glycerol, citric acid, mannitol, erythritol) was determined using reference curves and expressed as g/L. Citric and iso-citric acid were not totally separated with the implicated HPLC analysis method, and the reported concentration corresponds to the sum of these acids, expressed as total citric acid (Cit). In order to proceed with a more precise determination of iso-citric acid, in some of the fermentation points, an enzymatic method, based on the measurement of the NADPH2 produced during conversion of the iso-citric to α-ketoglutaric acid, the reaction catalyzed by the iso-citrate dehydrogenase, was employed. In all points where iso-citrate determination occurred, iso-citric acid represented a quantity of 5–7% (w/w) of total citric acid produced, regardless of the culture conditions employed.
Glycerol assimilation rate (in g/L·h) was expressed as substrate removed (g) per L of medium and per hour (= −ΔGlol/Δt) for the respective time in which fermentation was performed.
Total citric acid yield, YCit/Glol (g/g), was calculated based on the grams of produced total citric acid (Cit) per grams of substrate consumed (Glol).
Citric acid volumetric productivity (in g/L·h) was determined as the concentration of citric acid in a given fermentation time divided by this respective time.
The global yield of the produced citric acid per glycerol consumed (YCit/Glol) was determined as the produced citric acid in a plot against the consumed substrate [Cit = f (Glol consumed)] with equation y = ax + b, where “a” represents the citric acid yield YCit/Glol.
Mannitol yield YMan/Glol (g/g), was calculated based on the grams of produced mannitol (Man) per grams of substrate consumed (Glol).
Erythritol yield, YEry/Glol (g/g), was calculated based on the grams of produced erythritol (Ery) per grams of substrate consumed (Glol).
4.5. Quantitative Determination of the Cellular Lipid and Fatty Acid (FA) Composition Analysis
Total cellular lipid was extracted from DCW with a chloroform-methanol mixture (30 mL, 2:1, v/v) after 72 h in the darkness []. After three days, cell debris were removed through filtration (Whatman® filter n° 3) and the solvent mixture was completely evaporated in a rotary evaporator (R-144, Büchi Labortechnik, Flawil, Switzerland) at T = 60–65 °C. Total intra-cellular lipid, L, was determined gravimetrically and was expressed as g/L. Lipid in DCW (%, w/w; YL/X) was calculated based on percentage of the accumulated lipid (L) per produced dry biomass (X).
The extracted intra-cellular lipids were converted to their fatty acid methyl-esters (FAMEs) and analyzed in a gas chromatography (GC) (Fisons 8000 series, Offenbach, Germany) equipped with an FID (Fisons) according to the method described by Zikou et al. []. Methyl-esterification was performed in two phases. One to two boiling stones and 10 mL sodium methoxide (MeO-Na+) were added into the extracted total lipids. The samples were left to boil for 20 min. Methanol hydrochloride (CH3OH-HCl) was then added until the decolorization of the mixture, which reached a milky color. Boiling was then continued for another 20 min before the addition of distilled water to end the reaction. Finally, 6 mL of hexane were added, and the mixture was shaken vigorously. The solvent phase was collected, and a 1 μl sample was injected into GC.
4.6. Phenolic Compounds Determination
Determination of total phenol compounds (pHØ) into the medium was carried out according to the method described by Aggelis et al. []. Sampleof 0.2 mL was mixed with 10.8 mL distilled water, 8 mL Νa2CO3 (75 g/L), and 1 mL Folin-Ciocalteu reagent. Blank samples used as controls were prepared using 0.2 mL of distilled water. The mixture was shaken and remained in darkness for 2 h. The absorbance was measured at 750 nm in a Hitachi U-2000 Spectrophotometer (Tokyo, Japan). The concentration of phenolic compounds was expressed in equivalence of gallic acid according to a reference curve.
4.7. Decolorization
In order to determine the decolorization efficiency (color removal) of the fermentations, a 0.5 mL sample was mixed well with 14.5 mL distilled water, and the absorbance was measured at 395 nm according to Sayadi and Ellouz []. The decolorization percentage was calculated using the equation %A = [(A0− A1)/ A0] × 100, where, A0 is the absorbance at time 0 and A1 is the absorbance at each experimental point during the fermentation.
4.8. Determination of Extra-Cellular Nitrogen Into the Fermentation Medium
Extra-cellular non-assimilated nitrogen was measured in some of the fermentation points of the trials performed according to free amino nitrogen (FAN) determination. FAN concentration into the liquid samples was determined according to Kachrimanidou et al. [].
4.9. Data Analysis
All experiments and analyses were performed in duplicate. Each experimental point of all of the kinetics presented in the tables and figures is the mean value of two independent determinations. Data were plotted using Microsoft Office Excel Version 2007 showing the mean values with the standard error mean. Throughout the text, indices 0 and max represent the initial and the maximum quantity of the elements in each kinetics presented.
5. Conclusions
The addition of increased concentrations of NaCl to OMW/glycerol blends, a novel application, showed an interesting physiological response of the yeast Y. lipolytica. In essence, the combined effect of the addition of OMWs and NaCl into the medium increased lipid in DCW values of Y. lipolytica ACA-YC 5031, while remarkable biomass production was observed in all trials. Although glycerol metabolism, in the experiment with no OMWs and no salt added, was mainly shifted toward the synthesis of polyols, the addition of OMWs resulted in a reduction of Σpolyols concentration and a significant increase in the production of citric acid. The addition of salt in the OMW-based media resulted in a drastic increase in citric acid production. reaching maximum values in the trial with the addition of 5.0% NaCl. These results indicate that the yeast Y. lipolytica is a great candidate for the production of value-added compounds. The results showed that the addition of NaCl positively affected the physiological behavior of the yeast, having a great impact on the production of citric acid and lipids by this microorganism. Additionally, OMWs were found to be a promising substrate for the production of citric acid, mainly combined with salt. Finally, simultaneous with the production of several added-value metabolites, the non-negligible color and phenolic compounds removal from the medium with the aid of Y. lipolytica suggested that the yeast can also be used as an important microbial cell factory amenable for the depollution and detoxification of several phenol-rich recalcitrant wastewaters that are frequently generated during various agro-industrial activities.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.P.; Methodology, M.K., S.P. and D.S; Validation, M.K and S.P.; Formal Analysis, M.T, M.K. and S.P.; Investigation, M.K.; Resources, A.A.K. and S.P.; Writing – Original Draft Preparation, M.T. and S.P.; Writing – Review & Editing, M.T. and S.P.; Supervision, D.S., A.A.K. and S.P.; Project Administration, A.A.K. and S.P; Funding acquisition, S.P.
Funding
This research was funded by the project entitled “Adding value to biodiesel-derived crude glycerol with the use of Chemical and Microbial Technology” (Acronym: Addvalue2glycerol; grant number Τ1ΕΔΚ-03002), which is financially supported by the Ministry of National Education and Religious Affairs, Greece (project action: “Investigate – Create – Innovate 2014-2020, Intervention II”).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mantzavinos, D.; Kalogerakis, N. Treatment of olive mill effluents, Part I. Organic matter degradation by chemical and biological processes-an overview. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crognale, S.; D’Annibale, A.; Federici, F.; Fenice, M.; Quaratino, D.; Petruccioli, M. Olive oil mill wastewater valorization by fungi. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2006, 81, 1547–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarris, D.; Stoforos, N.G.; Mallouchos, A.; Kookos, I.K.; Koutinas, A.A.; Aggelis, G.; Papanikolaou, S. Production of added-value metabolites by Yarrowialipolytica growing in olive mill wastewater-based media under aseptic and non-aseptic conditions. Eng. Life Sci. 2017, 17, 695–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarris, D.; Rapti, A.; Papafotis, N.; Koutinas, A.A.; Papanikolaou, S. Production of Added-Value Chemical Compounds through Bioconversions of Olive-Mill Wastewaters Blended with Crude Glycerol by a Yarrowia lipolytica Strain. Molecules 2019, 24, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdi, M. Toxicity and biodegradability of olive mill wastewaters in batch anaerobic digestion. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 1992, 37, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zervakis, G.; Balis, C. Bioremediation of olive mill wastes water through the production of fungal biomass. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Mushrooms Biology and Mushrooms Products, University Park, PA, USA, 9–12 June 1996; pp. 311–323. [Google Scholar]
- Tsioulpas, A.; Dimou, D.; Iconomou, D.; Aggelis, G. Phenolic removal in olive oil mill wastewater by strains of Pleurotus spp. in respect to their phenol oxidase (laccase) activity. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 84, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggelis, G.; Iconomou, D.; Christou, M.; Bokas, D.; Kotzailias, S.; Christou, G.; Tsagou, V.; Papanikolaou, S. Phenolic removal in a model olive oil mill wastewater using Pleurotus ostreatus in bioreactor cultures and biological evaluation of the process. Water Res. 2003, 37, 3897–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crognale, S.; Federici, F.; Petruccioli, M. β-Glucan production by Botryosphaeria rhodina on undiluted olive-mill waste waters. Biotechnol. Lett. 2003, 25, 2013–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Annibale, A.; Sermani, G.G.; Federici, F.; Petruccioli, M. Olive-mill wastewaters: A promising substrate for microbial lipase production. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1828–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papanikolaou, S.; Galiotou-Panayotou, M.; Fakas, S.; Komaitis, M.; Aggelis, G. Citric acid production by Yarrowia lipolytica cultivated on olive-mill wastewater-based media. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 2419–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarris, D.; Papanikolaou, S. Biotechnological production of ethanol: biochemistry, processes and technologies. Eng. Life Sci. 2016, 16, 307–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivaldi, J.D.; Sarrouh, B.F.; da Silva, S.S. Development of biotechnological processes using glycerol from biodiesel production. In Current Research Topics in Applied Microbiology and Microbial Biotechnology; Mendez-Vilas, A., Ed.; World Scientific Publishing Co. Formatex Research Center: Madrid, Spain, 2009; pp. 429–433. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Z.; Pyle, D.J.; Athalye, S.K. Glycerol waste from biodiesel manufacturing. In Microbial Conversions of Raw Glycerol; Aggelis, G., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro, M.R.; Kugelmeier, C.L.; Pinheiro, R.S.; Batalha, M.O.; da Silva César, A. Glycerol from biodiesel production: Technological paths for sustainability. Ren. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 88, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellou, S.; Moustogianni, A.; Makri, A.; Aggelis, G. Lipids containing polyunsaturated fatty acids synthesized by Zygomycetes grown on glycerol. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 166, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dedyukhina, E.G.; Chistyakova, T.I.; Kamzolova, S.V.; Vinter, M.V.; Vainshtein, M.B. Arachidonic acid synthesis by glycerol-grown Mortierella alpina. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2012, 114, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedyukhina, E.G.; Chistyakova, T.I.; Mironov, A.A.; Kamzolova, S.V.; Morgunov, I.G.; Vainshtein, M.B. Arachidonic acid synthesis from biodiesel-derived waste by Mortierella alpina. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2014, 116, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontanille, P.; Kumar, V.; Christophe, G.; Nouaille, R.; Larroche, C. Bioconversion of volatile fatty acids into lipids by the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 114, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhao, X.; Wang, W.; Du, W.; Liu, D. Microbial conversion of biodiesel byproduct glycerol to triacylglycerols by oleaginous yeast Rhodosporidium toruloides and the individual effect of some impurities on lipid production. Biochem. Eng. J. 2012, 65, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, G.; Luo, Z.; Gu, S.; Wu, Q.; Chang, M.; Wang, X. Fatty acid shifts and metabolic activity changes of Schizochyrium sp. S31 cultured on glycerol. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 142, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Blackburn, J.W.; Liang, Y. Fermentation optimization for the production of lipid by Cryptococcus curvatus: Use of response surface methodology. Biomass Bioenergy 2012, 47, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Jin, G.; Gong, Z.; Shen Bai, F.; Zhao, Z.K. Recycling biodiesel-derived glycerol by the oleaginous yeast Rhodosporidium toruloides Y4 through the two-stage lipid production process. Biochem. Eng. J. 2014, 91, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommareddy, R.R.; Sabra, W.; Maheshwari, G.; Zeng, A.P. Metabolic network analysis and experimental study of lipid production in Rhodosporidium toruloides grown on single and mixed substrates. Microb. Cell Fact. 2015, 14, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchakouteu, S.S.; Kalantzi, O.; Gardeli, C.; Koutinas, A.A.; Aggelis, G.; Papanikolaou, S. Lipid production by yeasts growing on biodiesel-derived crude glycerol: Strain selection and impact of substrate concentration on the fermentation efficiency. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 118, 911–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rymowicz, W.; Rywińska, A.; Źarowska, B.; Juszczyk, P. Citric acid production from raw glycerol by acetate mutants of Yarrowia lipolytica. Chem. Pap. 2006, 60, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rymowicz, W.; Fatykhova, A.R.; Kamzolova, S.V.; Rywinska, A.; Morgunov, I.G. Citric acid production from glycerol-containing waste of biodiesel industry by Yarrowia lipolytica in batch, repeated batch, and cell recycle regimes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 87, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanikolaou, S.; Beopoulos, A.; Koletti, A.; Thevenieau, F.; Koutinas, A.A.; Nikaud, J.M.; Aggelis, G. Importance of the methyl-citrate cycle on glycerol metabolism in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 168, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rywińska, A.; Rymowicz, W. High-yield production of citric acid by Yarrowia lipolytica on glycerol in repeated-batch bioreactors. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 37, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rywińska, A.; Rymowicz, W.; Zarowska, B.; Skrzypiński, A. Comparison of citric acid production from glycerol and glucose by different strains of Yarrowia lipolytica. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 26, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rywińska, A.; Rymowicz, W.; Marcinkiewicz, M. Valorization of raw glycerol for citric acid production by Yarrowia lipolytica yeast. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 13, 9–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamzolova, S.V.; Fatykhova, A.R.; Dedyukhina, E.G.; Anastassiadis, S.G.; Golovchenko, N.P.; Morgunov, I.G. Citric acid production by yeast grown on glycerol-containing waste from biodiesel industry. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2011, 49, 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Tomaszewska, L.; Rywińska, A.; Gładkowski, W. Production of erythritol and mannitol by Yarrowia lipolytica yeast in media containing glycerol. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 39, 1333–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rywińska, A.; Tomaszewska, L.; Rymowicz, W. Erythritol biosynthesis by Yarrowia lipolytica yeast under various culture conditions. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 7, 3511–3516. [Google Scholar]
- Papanikolaou, S.; Rontou, M.; Belka, A.; Athenaki, M.; Gardeli, C.; Mallouchos, A.; Kalantzi, O.; Koutinas, A.A.; Kookos, I.K.; Zeng, A.P.; et al. Conversion of biodiesel-derived glycerol into biotechnological products of industrial significance by yeast and fungal strains. Eng. Life Sci. 2017, 17, 262–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanikolaou, S.; Aggelis, G. Biotechnological valorization of biodiesel derived glycerol waste through production of single cell oil and citric acid by Yarrowia lipolytica. Lipid Technol. 2009, 21, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abghari, A.; Chen, S. Yarrowia lipolytica as an oleaginous cell factory platform for production of fatty acid-based biofuel and bioproducts. Front. Energy Res. 2014, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanikolaou, S.; Chevalot, I.; Komaitis, M.; Marc, I.; Aggelis, G. Single cell oil production by Yarrowia lipolytica growing on an industrial derivative of animal fat in batch cultures. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 58, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rymowicz, W.; Rywinska, A.; Gladowski, W. Simultaneous production of citric acid and erythritol from crude glycerol by Yarrowia lipolytica Wratislavia K1. Chem. Pap. 2008, 62, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rymowicz, W.; Rywinska, A.; Marcinkiewicz, M. High yield production of erythritol from raw glycerol in fed-batch cultures of Yarrowia lipolytica. Biotechnol. Lett. 2009, 31, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rywińska, A.; Juszczyk, P.; Wojtatowicz, M.; Rymowicz, W. Chemostat study of citric acid production from glycerol by Yarrowia lipolytica. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 152, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatzifragkou, A.; Makri, A.; Belka, A.; Bellou, S.; Mavrou, M.; Mastoridou, M.; Mystrioti, P.; Onjaro, G.; Aggelis, G.; Papanikolaou, S. Biotechnological conversions of biodiesel derived waste glycerol by yeast and fungal species. Energy 2011, 36, 1097–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzifragkou, A.; Petrou, I.; Gardeli, C.; Komaitis, M.; Papanikolaou, S. Effect of Origanum vulgare L. essential oil on growth and lipid profile of Yarrowia lipolytica cultivated on glycerol-based media. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2011, 88, 1955–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgunov, I.G.; Kamzolova, S.V.; Lunina, J.N. The citric acid production from raw glycerol by Yarrowia lipolytica yeast and its regulation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 7387–7397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Chen, X.; Xiong, L.; Chen, X.; Ma, L.; Chen, Y. Single cell oil production from low-cost substrates: The possibility and potential of its industrialization. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aly, A.A.; Hasan, Y.N.; Al-Farraj, A.S. Olive mill wastewater treatment using a simple zeolite-based low-cost method. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 145, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papanikolaou, S.; Chevalot, I.; Komaitis, M.; Aggelis, G.; Marc, I. Kinetic profile of the cellular lipid composition in an oleaginous Yarrowia lipolytica apable of producing a cocoa-butter substitute from industrial fats. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2001, 80, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papanikolaou, S.; Muniglia, L.; Chevalot IAggelis, G.; Marc, I. Accumulation of cocoa-butter-like lipid by Yarrowia lipolytica cultivated on agro-industrial residues. Curr. Microbiol. 2003, 46, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, D.; Zhang, H.; Xie, Y.; Tang, N.; Berenjian, A.; Song, Y. Conversion of mutton fat to cocoa butter equivalent by increasing the unsaturated fatty acids at the sn-2 position of triacylglycerol through fermentation by Yarrowia lipolytica. Am. J. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 11, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Li, B.; Xiong, D.; Zhang, H.; Song, Y.; Yang, S. Cocoa-butter equivalent production from Yarrowia lipolytica by optimization of fermentation technology. Am. J. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 12, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Papanikolaou, S.; Aggelis, G. Yarrowia lipolytica: A model microorganism used for the production of tailor-made lipids. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2010, 112, 639–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, J.S.; da Silva, M.A.N.; Siqueira, E.P.; Pasa, V.M.D.; Rosa, C.A.; Valente, P. Microbial lipid produced by Yarrowia lipolytica QU21 using industrial waste: A potential feedstock for biodiesel production. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 161, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanikolaou, S.; Chatzifragkou, A.; Fakas, S.; Galiotou–Panayotou, M.; Komaitis, M.; Nicaud, J.M.; Aggelis, G. Biosynthesis of lipids and organic acids by Yarrowia lipolytica strains cultivated on glucose. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2009, 111, 1221–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juszczyk, P.; Rymowicz, W. Characterization of microbial biomass production from glycerin waste by various yeast strains. In Microbial Conversions of Raw Glycerol; Aggelis, G., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 125–135. [Google Scholar]
- Celińska, E.; Grajek, W. A novel multigene expression construct for modification of glycerol metabolism in Yarrowia lipolytica. Microb. Cell Fact. 2013, 12, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakicka, M.; Kieron, A.; Hapeta, P.; Neuvéglise, C.; Lazar, Z. Sweet and sour potential of yeast from the Yarrowia clade. Biomass Bioenergy 2016, 92, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakicka, M.; Rywinska, A.; Cybulski, K.; Rymowicz, W. Enhanced production of erythritol and mannitol by Yarrowia lipolytica in media containing surfactants. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2016, 47, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dourou, M.; Kancelista, A.; Juszczyk, P.; Sarris, D.; Bellou, S.; Triantaphyllidou, I.E.; Rywinska, A.; Papanikolaou, S.; Aggelis, G. Bioconversion of olive mill wastewater into high-added value products. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 139, 957–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszewska, L.; Rakicka, M.; Rymowicz, W.; Rywińska, A. A comparative study on glycerol metabolism to erythritol and citric acid in Yarrowia lipolytica yeast cells. FEMS Yeast Res. 2014, 14, 966–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzechonek, D.A.; Dobrowolski, A.; Rymowicz, W.; Mirończuk, A.M. Aseptic production of citric and isocitric acid from crude glycerol by genetically modified Yarrowia lipolytica. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 271, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papanikolaou, S.; Fakas, S.; Fick, M.; Chevalot, I.; Galiotou-Panayotou, M.; Komaitis, M.; Marc, I.; Aggelis, G. Biotechnological valorisation of raw glycerol discharged after bio-diesel (fatty acid methyl esters) manufacturing process: Production of 1, 3-propanediol, citric acid and single cell oil. Biomass Bioenergy 2008, 32, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarris, D.; Galiotou-Panayotou, M.; Koutinas, A.A.; Komaitis, M.; Papanikolaou, S. Citric acid, biomass and cellular lipid production by Yarrowia lipolytica strains cultivated on olive mill wastewater-based media. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2011, 86, 1439–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanikolaou, S.; Kampisopoulou, E.; Blanchard, F.; Rondags, E.; Gardeli, C.; Koutinas, A.A.; Aggelis, G. Production of secondary metabolites through glycerol fermentation under carbon-excess conditions by the yeasts Yarrowia lipolytica and Rhodosporidium toruloides. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2017, 119, 1600507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanikolaou, S.; Aggelis, G. Lipids of oleaginous yeasts. Part II: Technology and potential applications. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2011, 113, 1052–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrowolski, A.; Mituła, P.; Rymowicz, W.; Mirończuk, A.M. Efficient conversion of crude glycerol from various industrial wastes into single cell oil by yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 207, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papanikolaou, S.; Aggelis, G. Sources of microbial oils with emphasis to Mortierella (Umbelopsis) isabellina fungus. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 35, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makri, A.; Fakas, S.; Aggelis, G. Metabolic activities of biotechnological interest in Yarrowia lipolytica grown on glycerol in repeated batch cultures. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 2351–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratledge, C. Yeasts, moulds, algae and bacteria as sources of lipids. In Technological Advances in Improved and Alternative Sources of Lipids; Kamel, B.S., Kakuda, Y., Eds.; Blackie Academic and Professional: London, UK, 1994; pp. 235–291. [Google Scholar]
- Paramithiotis, S.; Muller, M.R.A.; Ehrmann, M.A.; Tsakalidou, E.; Seiler, H.; Vogel, R.; Kalantzopoulos, G. Polyphasic identification of wild yeast strains isolated from Greek sourdoughs. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 23, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.N.; Sarkany, N.; Cui, Y.; Blackburn, J.W. Batch stage study of lipid production from crude glycerol derived from yellow grease or animal fats through microagal fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 6745–6750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G. Determination of reducing sugar by DNS method. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachrimanidou, V.; Kopsahelis, N.; Chatzifragkou, A.; Papanikolaou, S.; Yanniotis, S.; Kookos, I.K.; Koutinas, A.A. Utilisation of by-products from sunflower-based biodiesel production processes for the production of fermentation feedstock. Waste Biomass Valor. 2013, 4, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zikou, E.; Chatzifragkou, A.; Koutinas, A.A.; Papanikolaou, S. Evaluating glucose and xylose as cosubstrates for lipid accumulation and γ-linolenic acid biosynthesis of Thamnidium elegans. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 114, 1020–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayadi, S.; Ellouz, R. Decolourization of olive mill waste-waters by the white-rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium: Involvement of the lignin-degrading system. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1992, 37, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).