Application of Shallow-Hole Blasting in Improving the Stability of Gob-Side Retaining Entry in Deep Mines: A Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
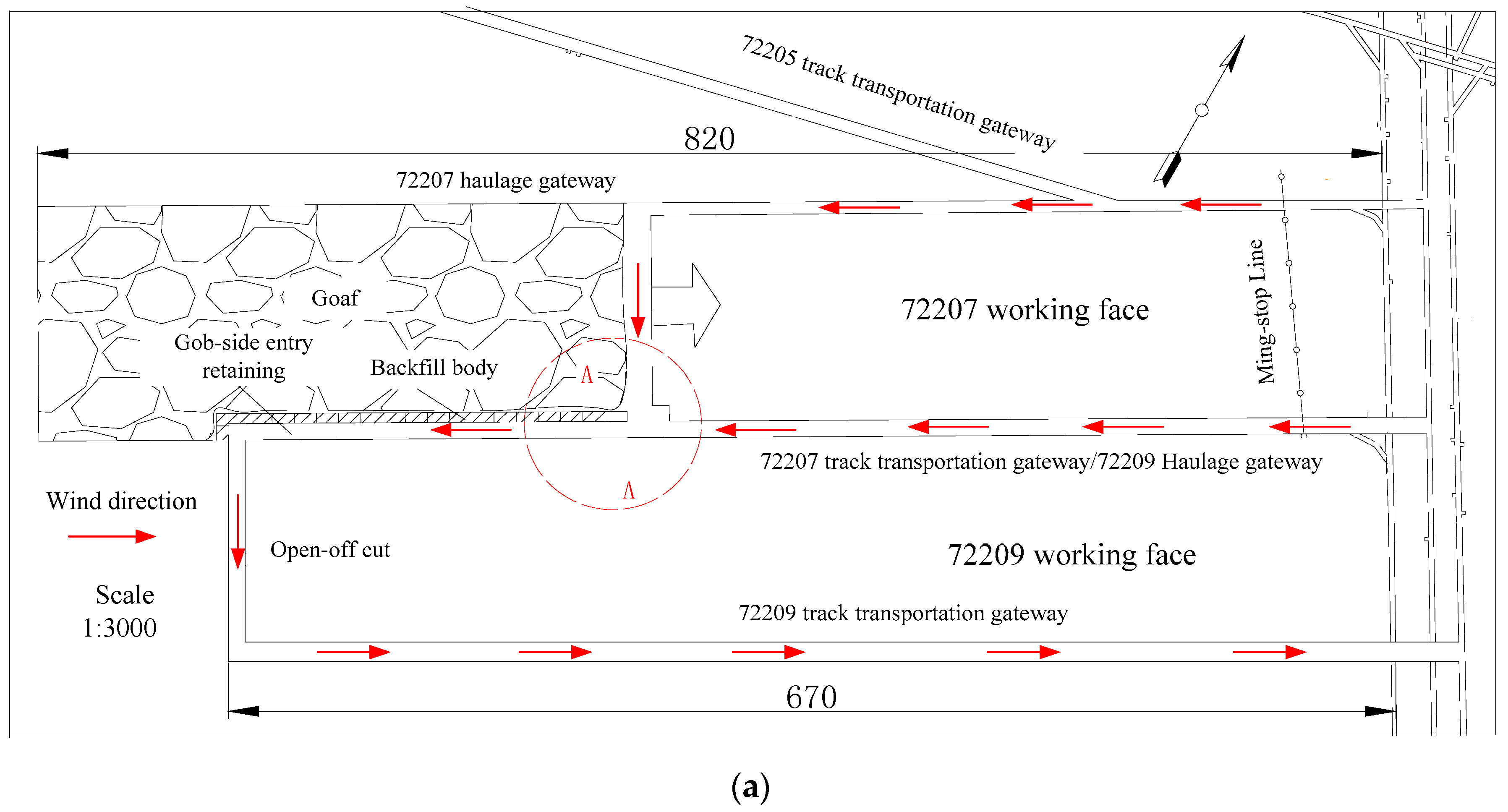
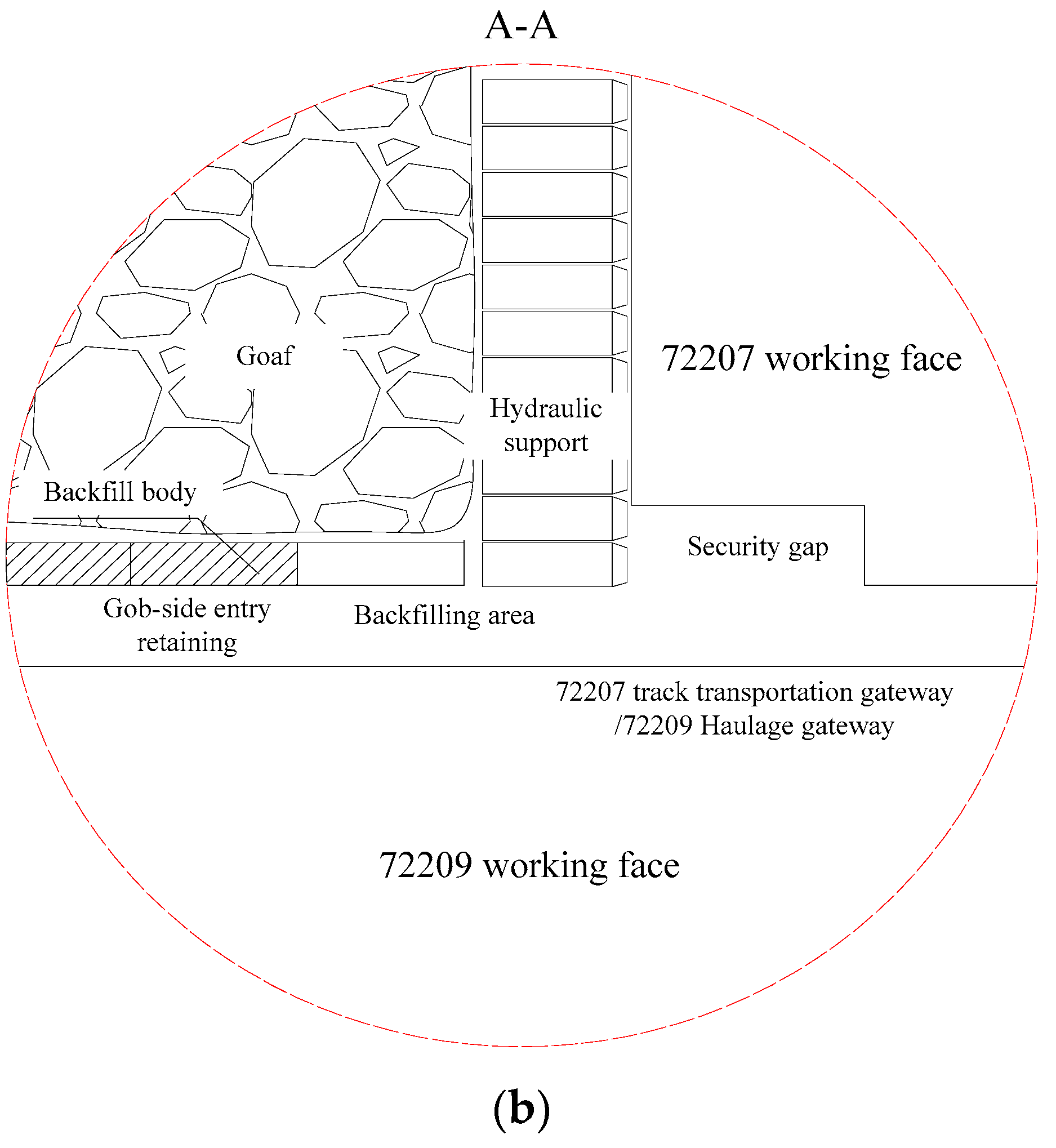
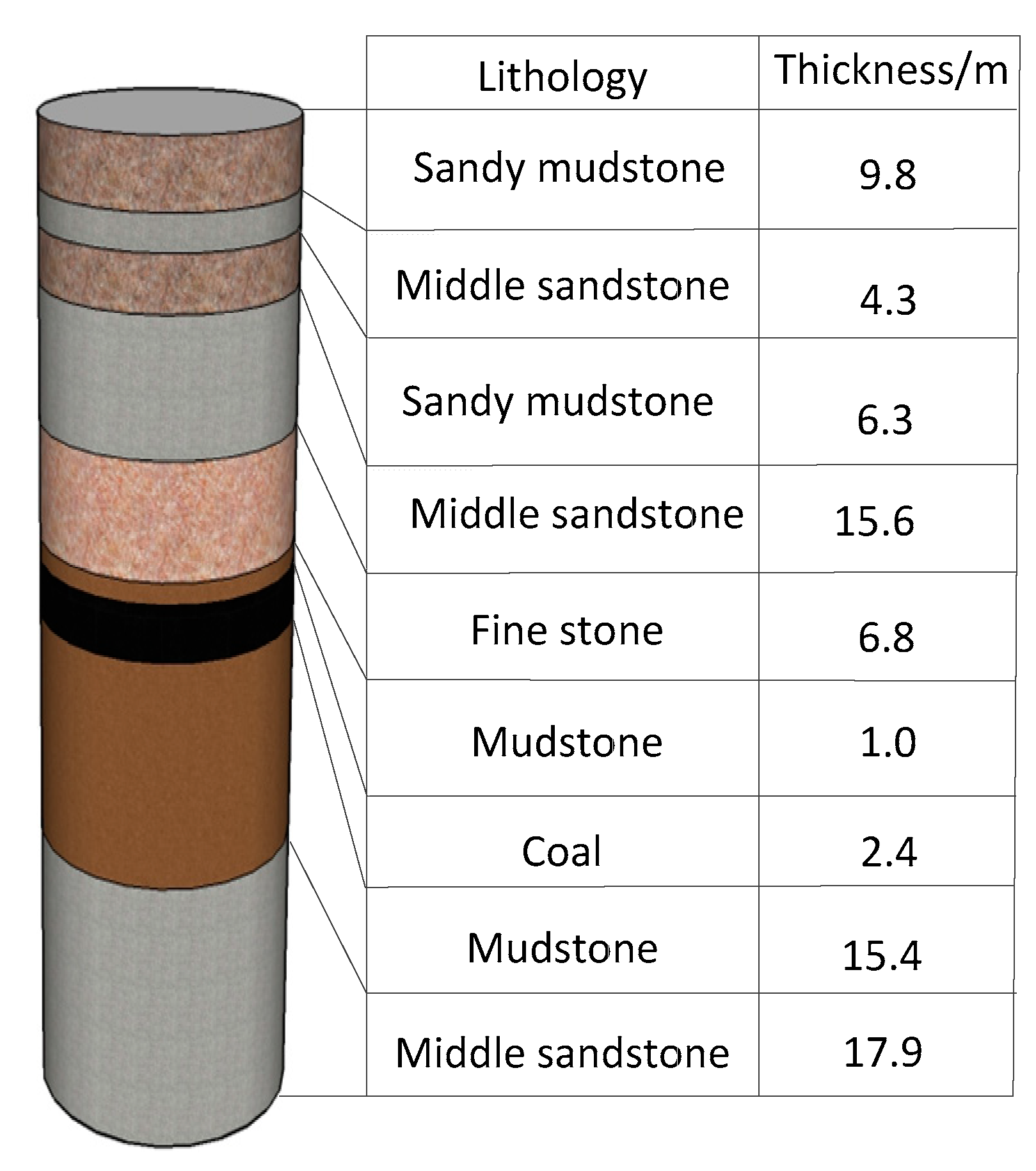
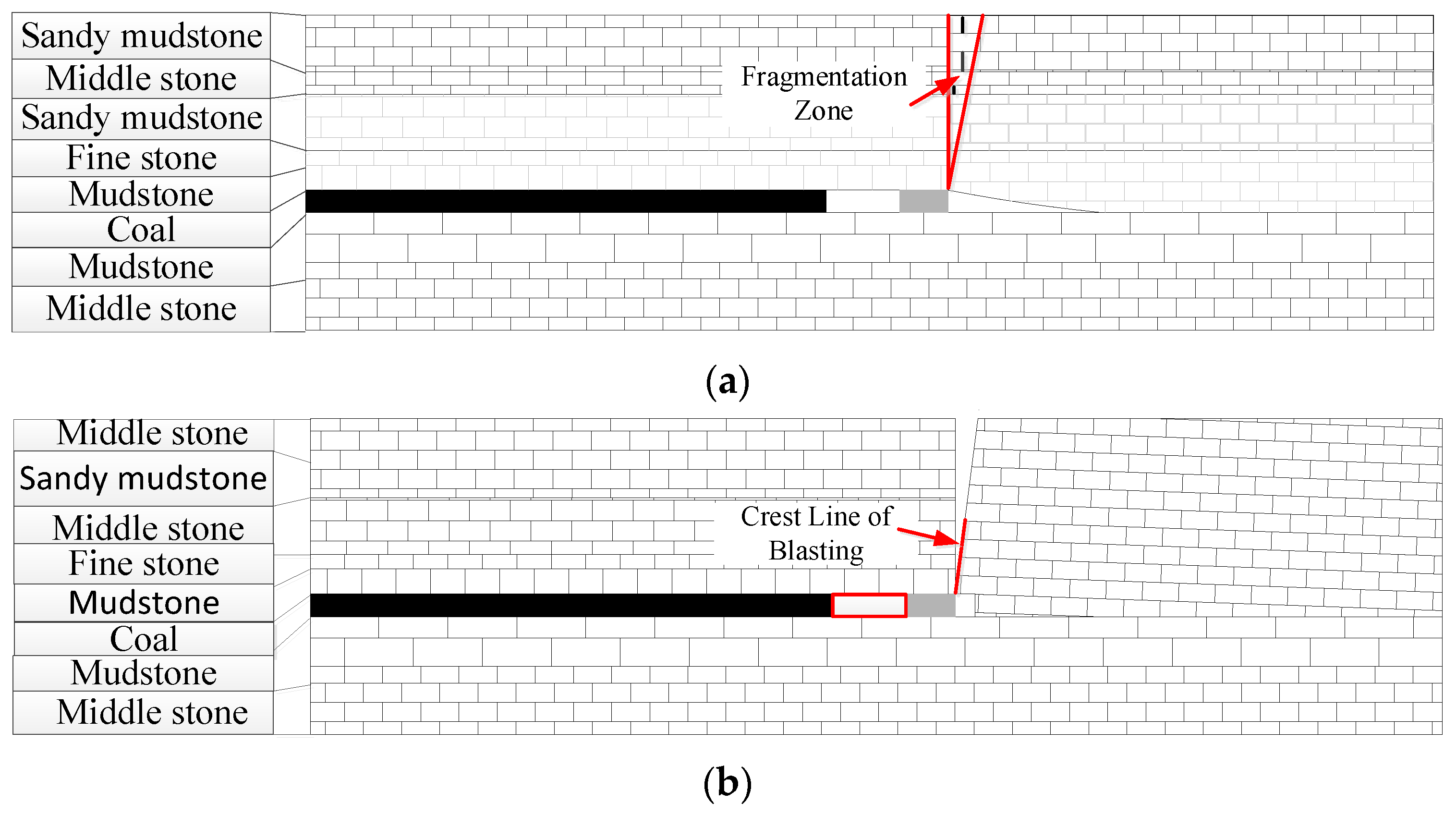
2. Geological Conditions
3. Mechanism of Gob-Side Entry Retaining Weighting of Deep Hard Roof
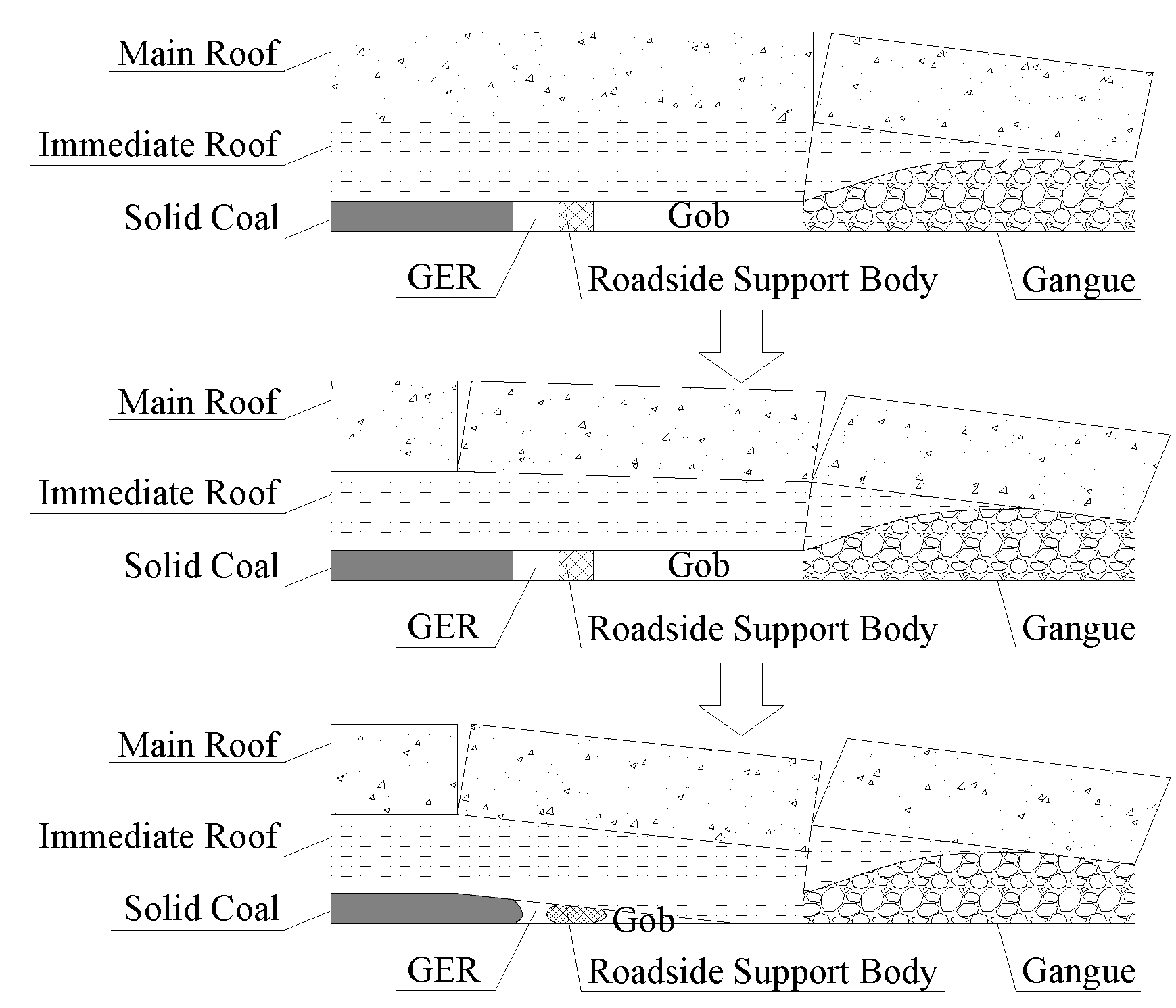
3.1. Mechanism of Gob-Side Entry Retaining Weighting of Hard Roof
3.2. Determination of Critical Parameters for Shallow Blasting
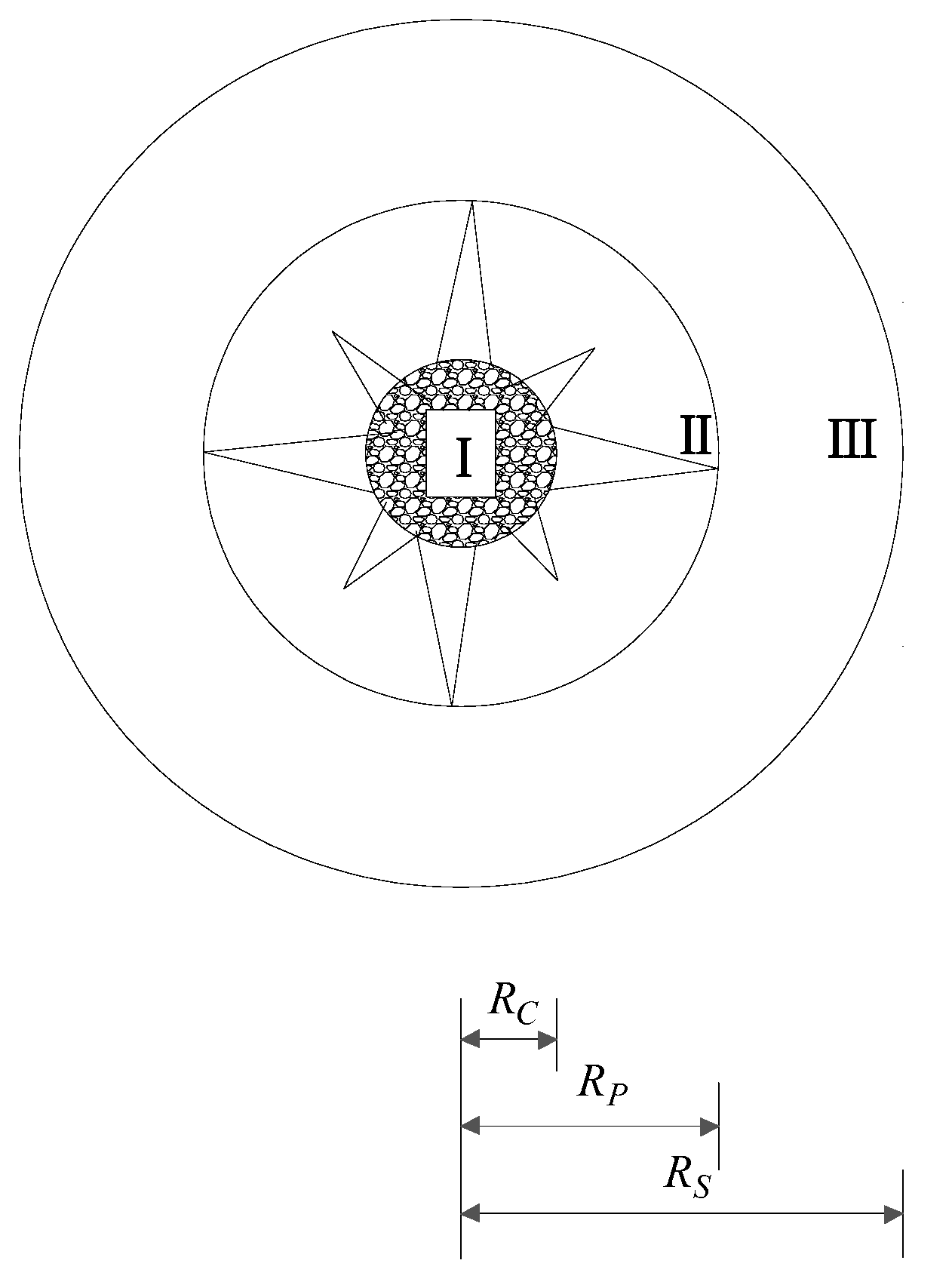
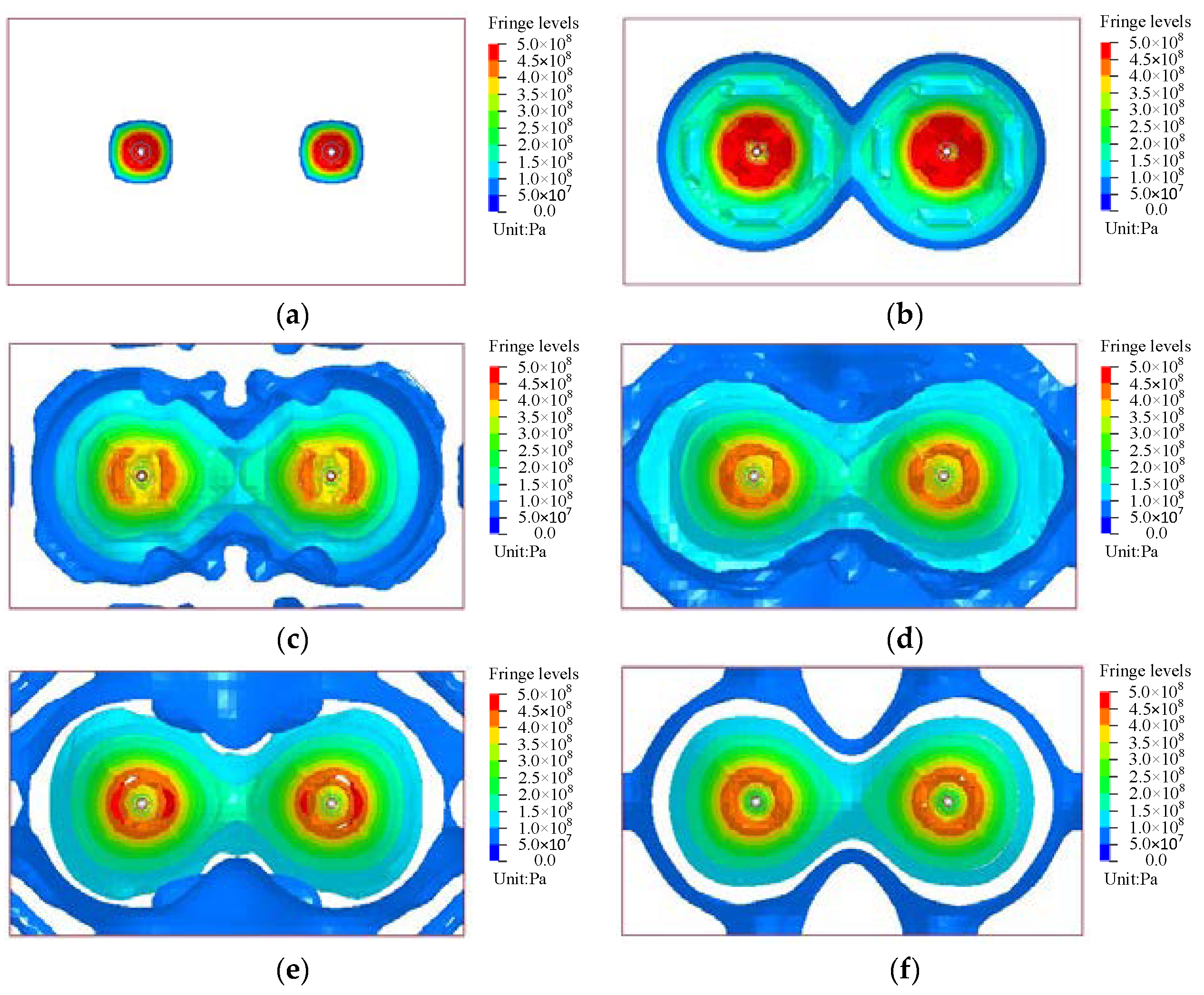
3.2.1. Shallow-Hole Blasting Range Law
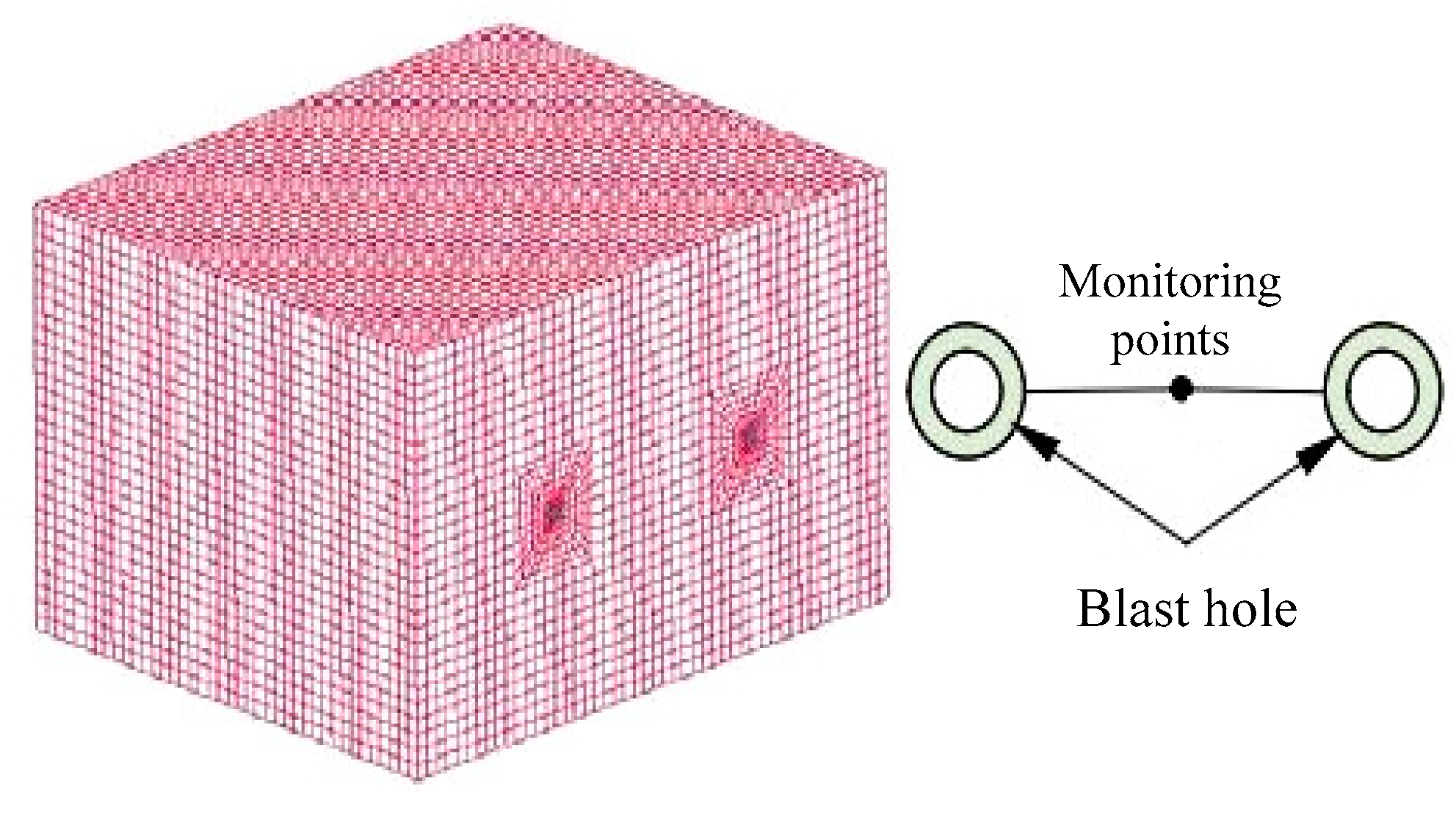
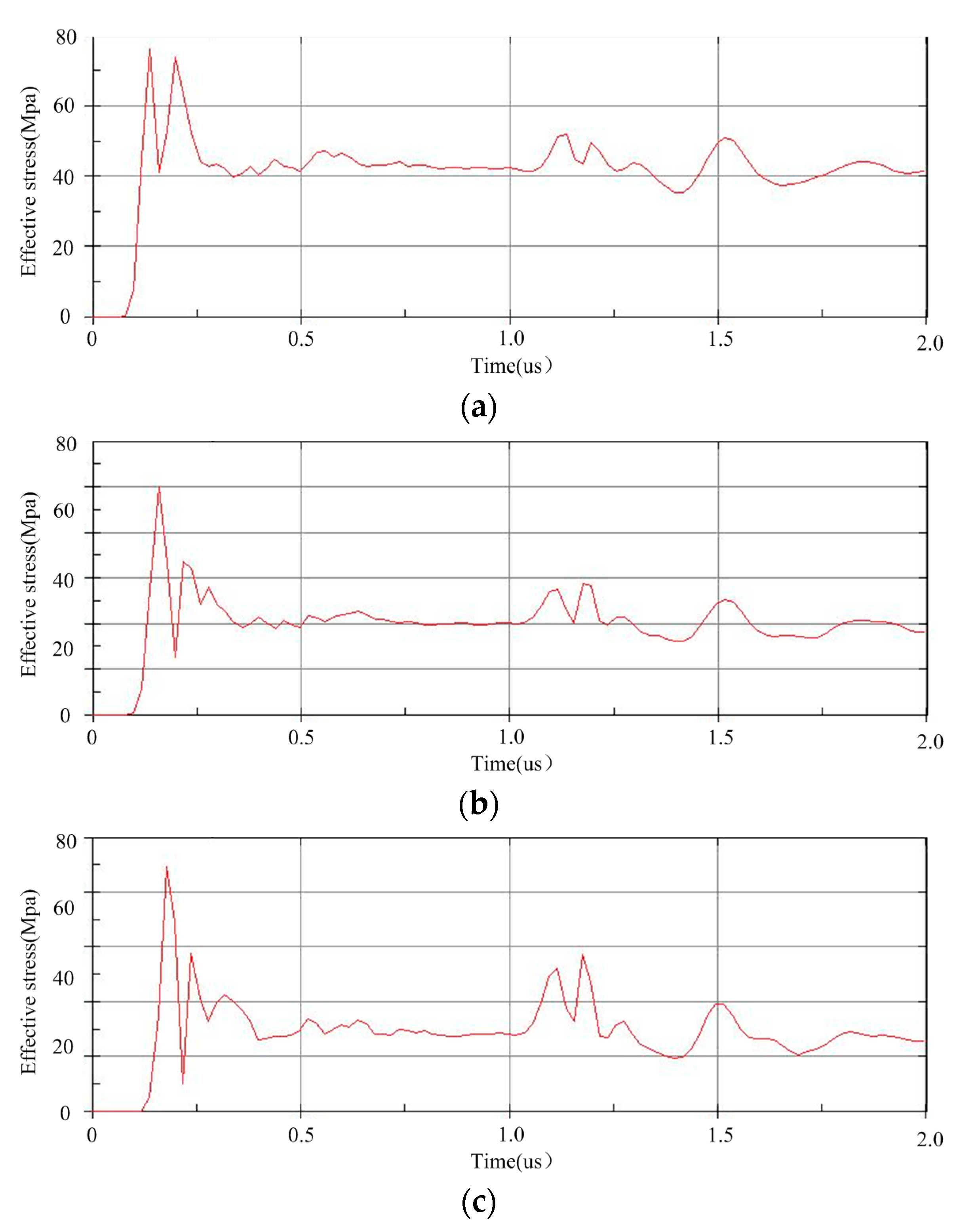
3.2.2. Determination of Critical Parameters for Shallow Blasting
4. Engineering Application
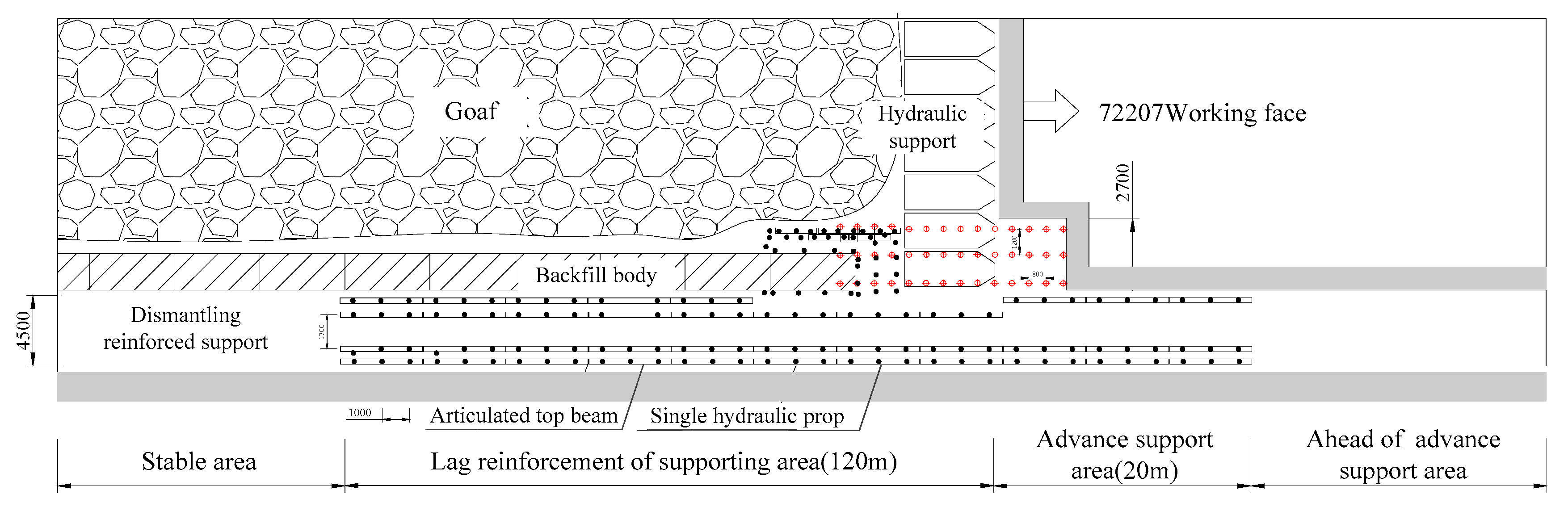
4.1. Roadway Support
4.1.1. Roadway Primary Support
4.1.2. Roadway Strengthening Support
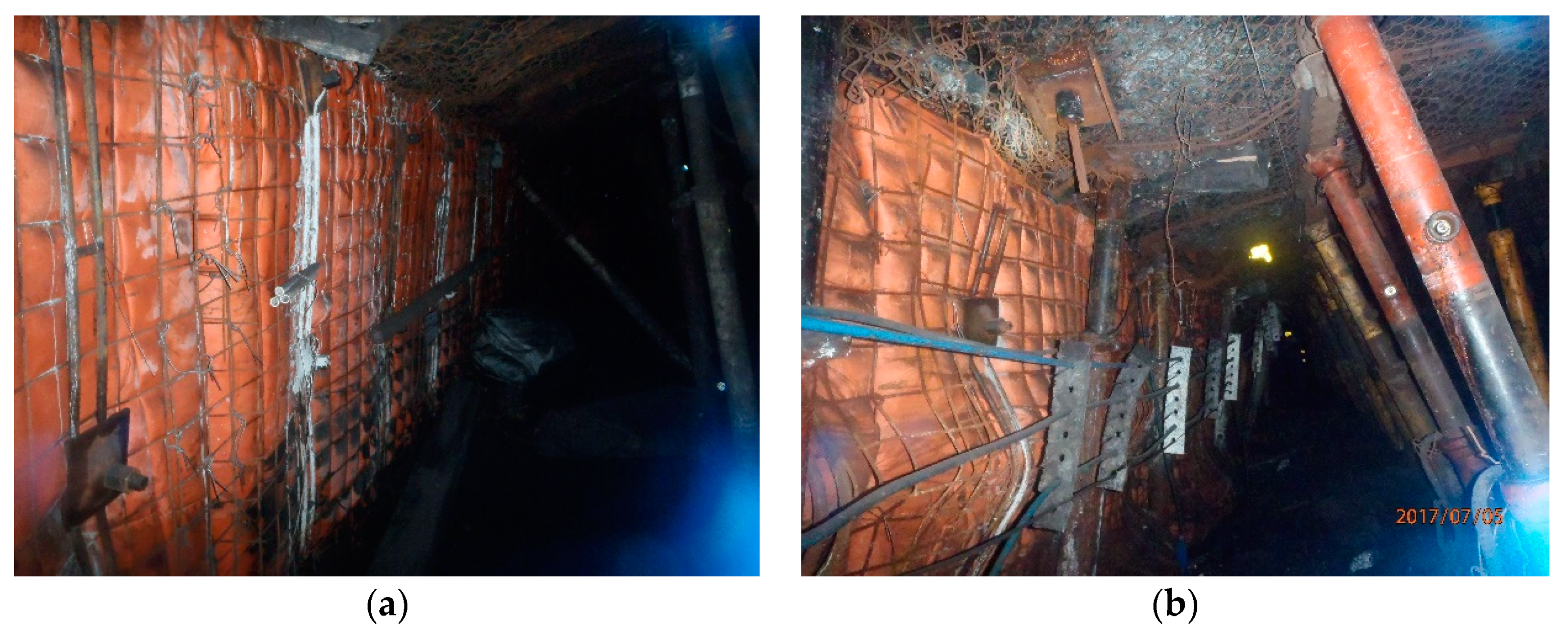
4.1.3. The Support of A Safe Working Space
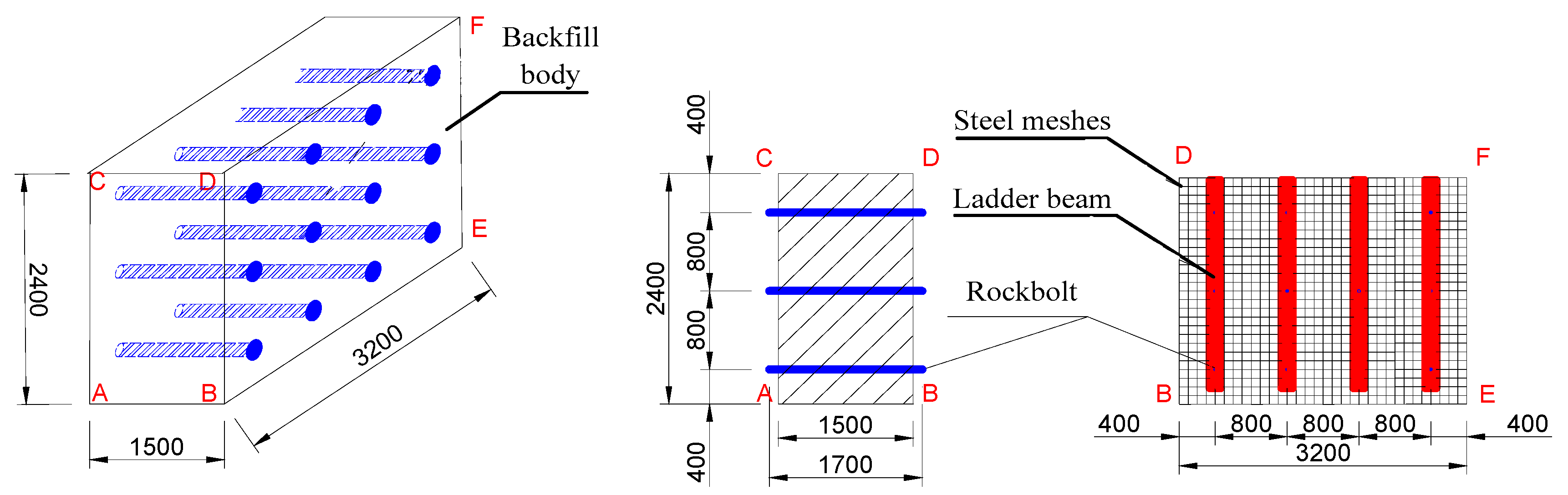
4.2. Backfill Body
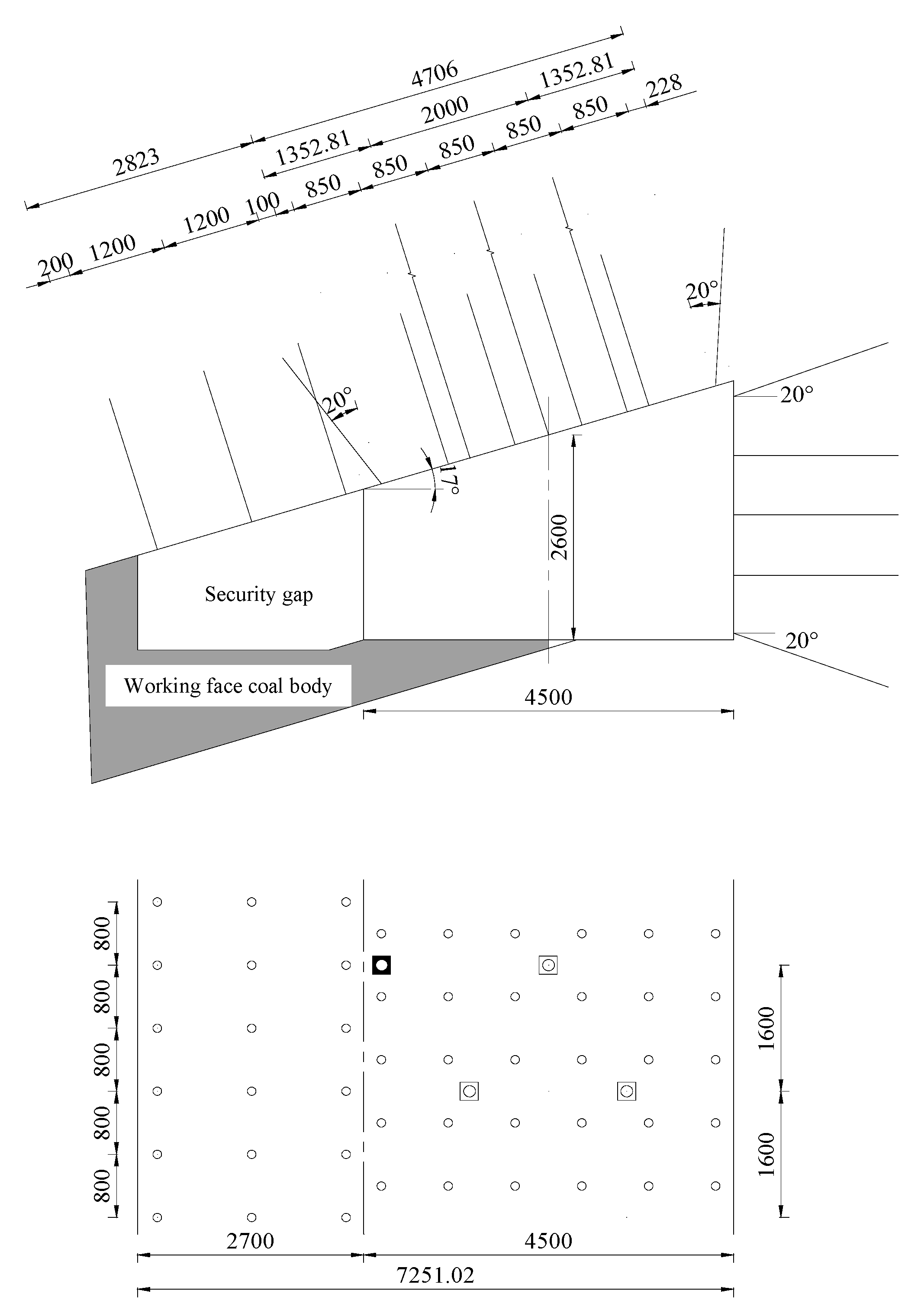
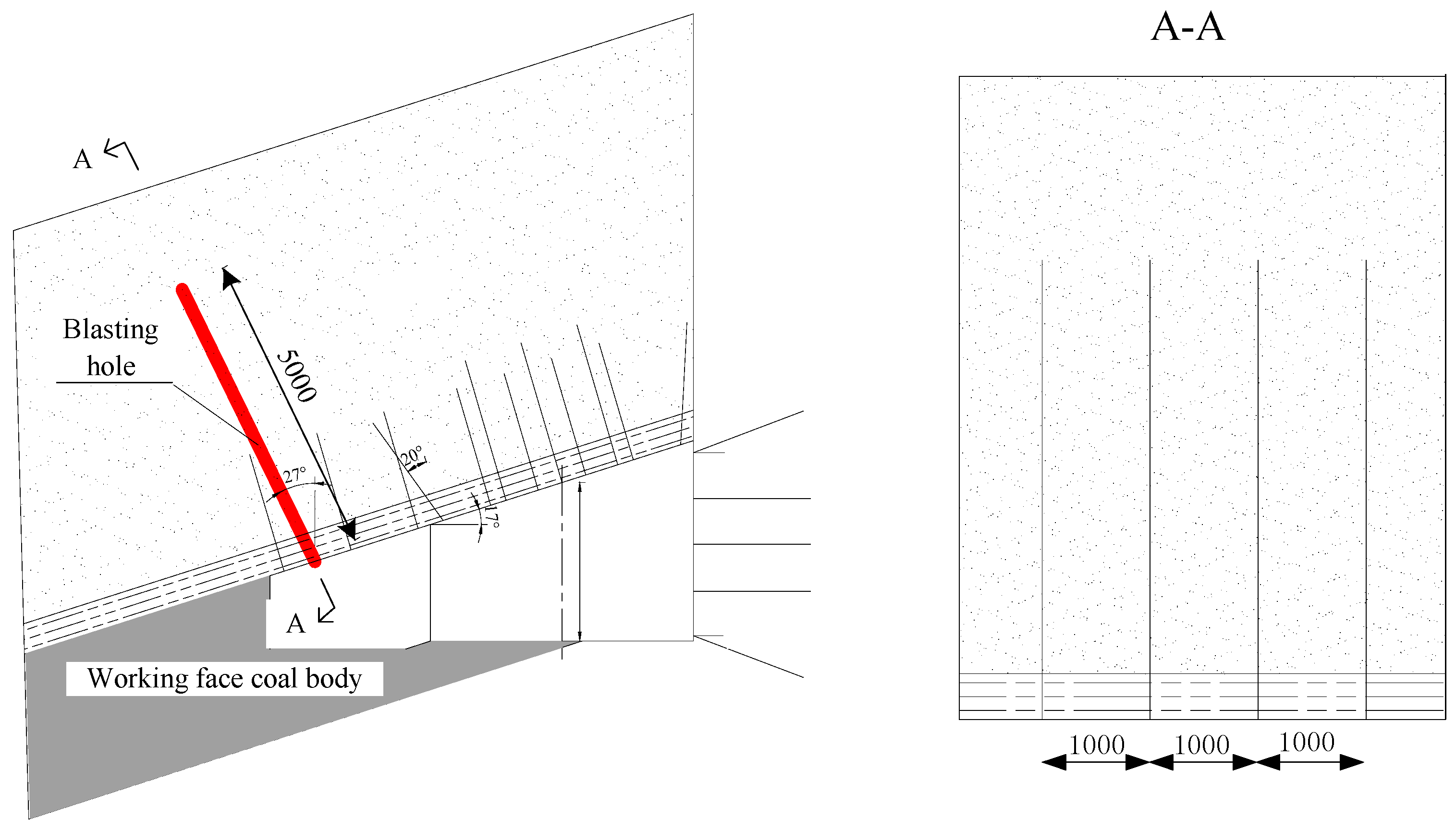
4.3. The Design of the Shallow-Hole Blasting
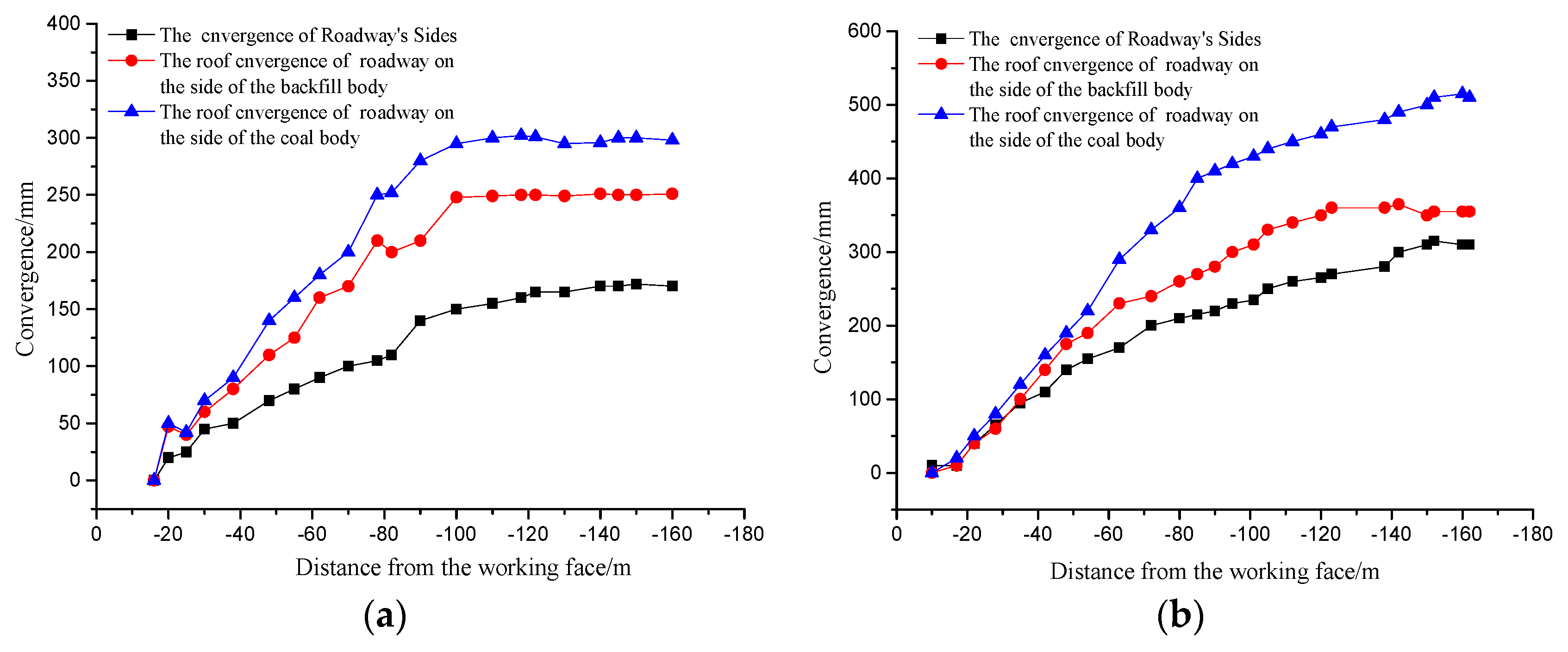
5. Discussions on the Field Measurements
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, H.; Zhao, B. Surrounding Rock Control of Entry Driven Aong Next Goaf; China Coal Industry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Zhang, X.; Li, J. Practices on gateway retaining along goaf side in thin seam with hard roof. Coal Sci. Technol. 2011, 39, 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Tang, J.; Zhu, X. Industrial test of concrete packing for gob-side entry retained in gently-inclined medium-thickness coal seam. J. Southwest Jiaotong Univ. 2011, 46, 523–528. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, X. Development status and improved proposals on gob-side entry retaining support technology in China. Coal Sci. Technol. 2006, 34, 78–81. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Bai, J.; Hou, C. Study on the main parameters of gateside packs in gateways maintained along gob-edges. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 1992, 21, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Bu, T.; Feng, G.; Jia, K. Gateway side backfilling support technology of goaf side gateway in fully mechanized high cutting longwall mining face. Coal Sci. Technol. 2010, 38, 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, H.; Niu, D.; Zhang, Z. Deformation characteristics of surrounding rock and supporting technology of gob-side entry retaining in deep coal mine. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2010, 29, 1977–1987. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Bai, J.; Wang, X. Support technology research and application inside roadway of gob-side entry retaining. J. China Coal Soc. 2012, 37, 903–910. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, G.; An, X. Numerical simulation of blasting-induced rock fractures. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2008, 45, 966–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Da, J.; Feng, G. Mechanism of controlling surrounding rock around gob-side entry retaining in top-coal caving mining face. J. Cent. South Univ. 2004, 35, 657–661. [Google Scholar]
- Han, C. Stress Optimization and Structure Stability Control for the Surrounding Rock of Gob-Side Entry Retainin; China University of Mining and Technology: Xuzhou, China, 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Wang, M.; Du, H. Gateway retained technology along goaf of coalmining face with thick and hard roo. Coal Sci. Technol. 2013, 41, 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Tu, S.; Yuang, Y. Deep-hole pre-split blasting mechanism and its application for controlled roof caving in shallow depth seams. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2013, 64, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Ma, P.; Liu, X. Supporting mechanism of “yielding-supporting” beside roadway maintained along the goaf under hard rocks. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 2013, 30, 369–374. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, F.; Zhou, T.; Jing, Y. Forced roof caving technology and application to goaf-side entry retaining. Coal Sci. Technol. 2006, 34, 16–24. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, K.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J. Application of deep borehole blasting to gob-side entry retaining forced roof caving in hard and compound roof deep well. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2013, 32, 1588–1594. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.; Liu, C.; Fu, J. Hydraulic fracturing after water pressure control blasting for increased fracturing. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2011, 48, 976–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S. Application of pre-splitting blasting hard roof in retaining roadway along gob. Coal Min. Technol. 2013, 18, 79–81. [Google Scholar]
- Sim, Y.; Cho, G.; Song, K. Prediction of Fragmentation Zone Induced by Blasting in Rock. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2017, 50, 2177–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Hu, Y.; Lu, W. Numerical simulation of blasting excavation induced damage to deep tunnel. Rock Soil Mech. 2011, 32, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Xu, G.; Wang, W. Numerical simulation of fan-hole blasting-induced rock fracture. China Min. Mag. 2014, 23, 84–99. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.; Zhao, Z.; Gu, J. Numerical simulations of rock mass damage induced by underground explosion. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2009, 46, 1206–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Administration of Work Safety, Coal Mine Safety Regulations; Coal Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Zhu, Z.; Mohanty, B.; Xie, H. Numerical investigation of blasting-induced crack initiation and propagation in rocks. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2007, 44, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Silberschmidt, V. Damage response of steel plate to underwater explosion: Effect of shaped charge liner. Int. J. Impact. Eng. 2017, 103, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample Name | Sample Number | Sample Size: Diameter (mm) × Height (mm) | Uniaxial Compressive Strength (MPa) | Uniaxial Tensile Strength (MPa) | Cohesion (MPa) | Internal Friction Angle (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main roof | 1-1-1 | 49.86 × 101.26 | 65.43 | 5.86 | 7.7 | 42 |
| 1-1-2 | 50.20 × 100.30 | |||||
| 1-1-3 | 50.00 × 101.20 | |||||
| Immediate roof | 2-1-1 | 49.58 × 101.56 | 33.65 | 4.475 | 2.51 | 40 |
| 2-1-2 | 49.20 × 100.36 | |||||
| 2-1-3 | 49.30 × 100.46 | |||||
| #7 coal | 3-1-1 | 50.60 × 102.34 | 8.82 | 2.17 | 2.0 | 26.72 |
| 3-1-2 | 50.08 × 100.20 | |||||
| 3-1-3 | 50.20 × 100.30 | |||||
| Floor | 4-1-1 | 49.86 × 102.36 | 40.6 | 6.986 | 2.8 | 46.46 |
| 4-1-2 | 50.20 × 101.14 | |||||
| 4-1-3 | 50.10 × 101.20 |
| Sample Name | Hard (>60 MPa) | Harder (60–30 MPa) | Softer (30–15 MPa) | Soft (15–5 MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main roof | √ | - | - | - |
| Immediate roof | - | √ | - | - |
| #7 coal | - | - | - | √ |
| Floor | - | √ | - | - |
| Explosive Density (kg/m3) | Explosive Detonation (m/s) | A (GPa) | B (GPa) | E0 (GPa) | R1 | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1200 | 3600 | 214.4 | 0.182 | 4.192 | 4.2 | 0.9 | 0.15 |
| Density (kg/m3) | Shear Modulus (GPa) | Bulk Modulus (GPa) | Poisson’s Ratio | Yield Strength (MPa) | Cohesion (MPa) | Internal Friction Angle (°) | Dynamic Tensile Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2700 | 10.5 | 15 | 0.22 | 90 | 7.7 | 42 | 18 |
| Water Cement Ratio | Cementing Dosage (kg∙m−1) | Water Dosage (kg∙m−1) | Gelation Time (min) | Compressive Strength (MPa) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 h | 24 h | 7 days | 28 days | ||||
| 0.8 | 873 | 698 | 7 | 14.40 | 19.0 | 21.32 | 22.55 |
| 1.0 | 744 | 744 | 8 | 10.2 | 15.8 | 17.90 | 19.10 |
| 1.2 | 647 | 776 | 8 | 8.40 | 14.0 | 15.22 | 16.97 |
| 1.5 | 542 | 813 | 10 | 4.48 | 9.14 | 10.36 | 11.51 |
| 2.0 | 426 | 850 | 12 | 3.33 | 6.26 | 7.92 | 8.70 |
| 2.25 | 385 | 866 | 14 | 2.42 | 4.74 | 6.19 | 7.08 |
| 2.5 | 352 | 880 | 16 | 2.05 | 3.97 | 5.08 | 5.44 |
| Depth of Blasting Hole (m) | Angle (°) | Hole Size (mm) | Explosive Charge in Per Hole | Sealing Mud Length (m) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Rolls/Branches | Weight (kg) | ||||
| 5.0 | 10 | 42 | 8 | 2.4 | 2.0 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Ma, S.; Yang, Y.; Meng, N.; Bai, J. Application of Shallow-Hole Blasting in Improving the Stability of Gob-Side Retaining Entry in Deep Mines: A Case Study. Energies 2019, 12, 3623. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12193623
Chen Y, Ma S, Yang Y, Meng N, Bai J. Application of Shallow-Hole Blasting in Improving the Stability of Gob-Side Retaining Entry in Deep Mines: A Case Study. Energies. 2019; 12(19):3623. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12193623
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yong, Shuqi Ma, Yugui Yang, Ningkang Meng, and Jianbiao Bai. 2019. "Application of Shallow-Hole Blasting in Improving the Stability of Gob-Side Retaining Entry in Deep Mines: A Case Study" Energies 12, no. 19: 3623. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12193623
APA StyleChen, Y., Ma, S., Yang, Y., Meng, N., & Bai, J. (2019). Application of Shallow-Hole Blasting in Improving the Stability of Gob-Side Retaining Entry in Deep Mines: A Case Study. Energies, 12(19), 3623. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12193623





