Peak Operation Problem Solving for Hydropower Reservoirs by Elite-Guide Sine Cosine Algorithm with Gaussian Local Search and Random Mutation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Hybrid Sine Cosine Algorithm (HSCA)
2.1. Optimization Problem
2.2. Sine Cosine Algorithm (SCA)
2.3. Elite-Guide Evolution Strategy to Improve the Convergence Speed
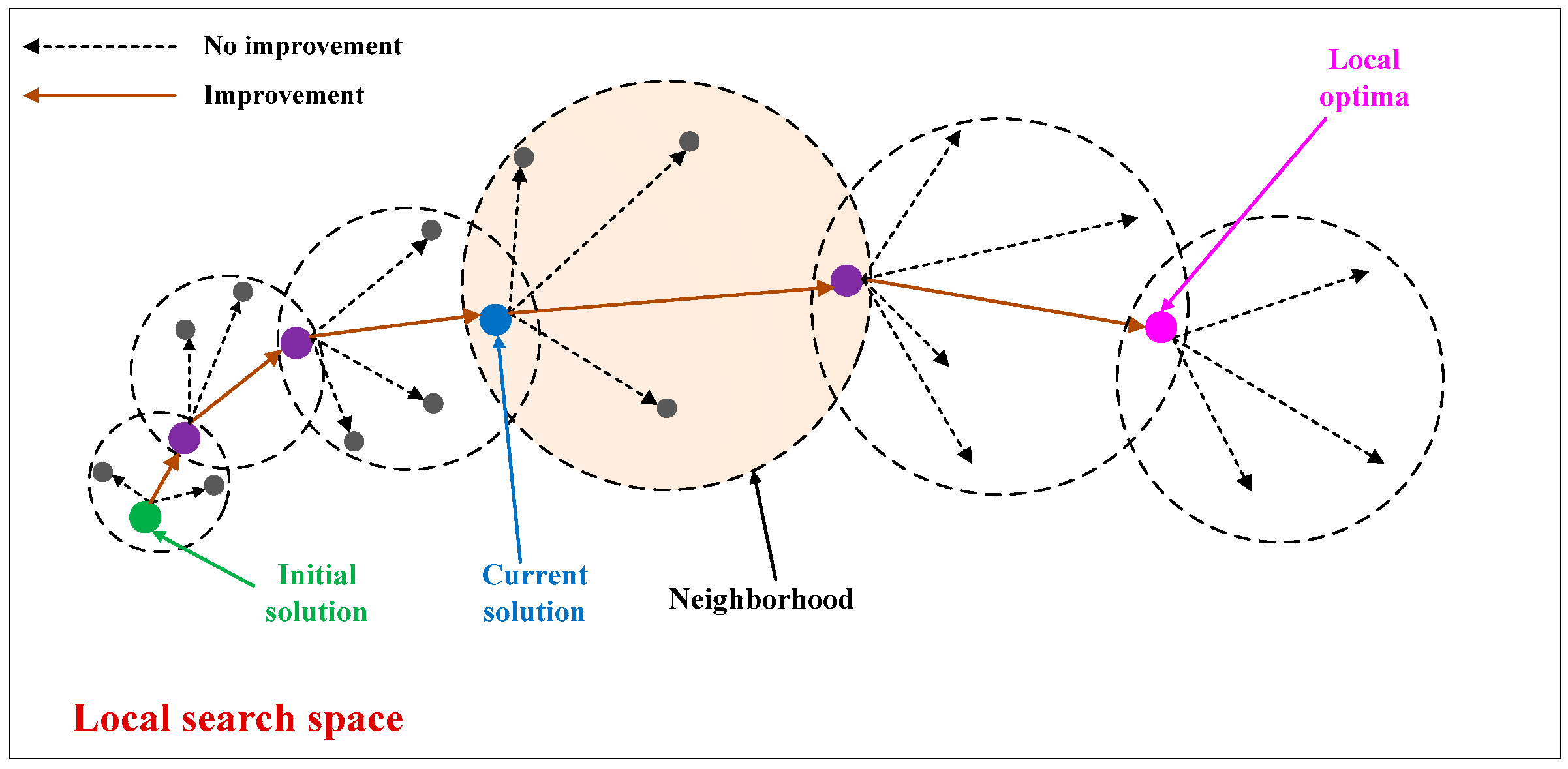
2.4. Gaussian Local Search Strategy to Improve the Individuals’ Search Capability
2.5. Random Mutation Strategy to Increase the Population Diversity
2.6. Execution Procedure of the Proposed HSCA Method
3. Numerical Experiments to Verify the Feasibility of the HSCA Method
3.1. Benchmark Functions
3.2. Parameter Settings
3.3. Performances of the HSCA Method
4. HSCA for the Peak Operation of Cascade Hydropower Reservoirs
4.1. Mathematical Model
4.1.1. Objective Function
4.1.2. Operation Constraints
4.2. Details of HSCA for Peak Operation of Cascade Hydropower Reservoirs
4.2.1. Individual Encoding and Swarm Initiation Strategies
4.2.2. Constraint Handling Method
4.2.3. Overall Execution Procedures
5. Case Studies
5.1. Mature Multi-Reservoir System
5.1.1. Convergence Process Analysis
5.1.2. Simulation and Result Analysis
5.1.3. Robustness Performance of the HSCA Method
5.2. Real-World Multi-Reservoir System
5.2.1. Engineering Background
5.2.2. Simulation and Analysis of the HSCA Method
5.2.3. Robustness Performance of the HSCA Method
5.2.4. Performances of the HSCA Method in Different Cases
5.3. Result Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, Z.K.; Niu, W.J.; Cheng, C.T. China’s large-scale hydropower system: Operation characteristics, modeling challenge and dimensionality reduction possibilities. Renew. Energy 2019, 136, 805–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Shen, J.; Wu, X.; Chau, K. Operation challenges for fast-growing China’s hydropower systems and respondence to energy saving and emission reduction. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 2386–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Li, Y.P.; Huang, G.H. A fuzzy-stochastic simulation-optimization model for planning electric power systems with considering peak-electricity demand: A case study of Qingdao, China. Energy 2016, 98, 190–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Li, Y.P.; Huang, G.H.; An, C.J. A robust flexible-probabilistic programming method for planning municipal energy system with considering peak-electricity price and electric vehicle. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 137, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Niu, W.; Wang, W.; Zhou, J.; Cheng, C. A mixed integer linear programming model for unit commitment of thermal plants with peak shaving operation aspect in regional power grid lack of flexible hydropower energy. Energy 2019, 175, 618–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Zhong, P.A.; Wan, X.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X. Dynamic feasible region genetic algorithm for optimal operation of a multi-reservoir system. Energies 2012, 5, 2894–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Liu, S.; Ma, X. Modeling, nonlinear dynamical analysis of a novel power system with random wind power and it’s control. Energy 2013, 53, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, W.J.; Feng, Z.K.; Feng, B.F.; Min, Y.W.; Cheng, C.T.; Zhou, J.Z. Comparison of multiple linear regression, artificial neural network, extreme learning machine, and support vector machine in deriving operation rule of hydropower reservoir. Water 2019, 11, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, M.; Riahi-Madvar, H.; Hooshyaripor, F.; Mosavi, A.; Shamshirband, S.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Chau, K.W. Prediction of hydropower generation using grey Wolf optimization adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system. Energies 2019, 12, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y. Optimization of guide vane closing schemes of pumped storage hydro unit using an enhanced multi-objective gravitational search algorithm. Energies 2017, 10, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Li, C.; Wang, B.; Liu, M.; Wang, L. Multi-Stage dynamic programming method for Short-Term cascade reservoirs optimal operation with flow attenuation. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 31, 4571–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Ding, W.; Zeng, X.; Xin, Z.; Wu, J.; Zhang, C. Inherent relationship between flow duration curves at different time scales: A perspective on monthly flow data utilization in daily flow duration curve estimation. Water 2018, 10, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Zhang, C.; Peng, Y.; Zeng, R.; Zhou, H.; Cai, X. An analytical framework for flood water conservation considering forecast uncertainty and acceptable risk. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 4702–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.K.; Niu, W.J.; Cheng, C.T.; Zhou, J.Z. Peak shaving operation of hydro-thermal-nuclear plants serving multiple power grids by linear programming. Energy 2017, 135, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, K.; Lund, J.R. Modeling California’s high-elevation hydropower systems in energy units. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, W09413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, K. Game theory and water resources. J. Hydrol. 2010, 381, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Cai, X.; Wang, Z. Optimality conditions for a two-stage reservoir operation problem. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W08503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, Y.P.; Huang, G.H.; Zeng, X.T. A dual-interval fixed-mix stochastic programming method for water resources management under uncertainty. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2014, 88, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Zhao, J.; Liu, P.; Lei, X. Evaluating the marginal utility principle for long-term hydropower scheduling. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 106, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, P.; Li, T. Joint operation of the multi-reservoir system of the Three Gorges and the Qingjiang cascade reservoirs. Energies 2011, 4, 1036–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.K.; Niu, W.J.; Wang, S.; Cheng, C.T.; Jiang, Z.Q.; Qin, H.; Liu, Y. Developing a successive linear programming model for head-sensitive hydropower system operation considering power shortage aspect. Energy 2018, 115, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.K.; Niu, W.J.; Cheng, C.T.; Wu, X.Y. Optimization of hydropower system operation by uniform dynamic programming for dimensionality reduction. Energy 2017, 134, 718–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Simpson, A.R.; Zecchin, A.C. A combined NLP-differential evolution algorithm approach for the optimization of looped water distribution systems. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W08531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, T.; Kan, Y.B.; Chang, J.X.; Huang, Q.; Chang, F.J. Fusing feasible search space into PSO for multi-objective cascade reservoir optimization. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 2017, 51, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Lian, J.; Wang, J. Short-term optimal operation of Three-gorge and Gezhouba cascade hydropower stations in non-flood season with operation rules from data mining. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 65, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; McKinney, D.C.; Lasdon, L.S. Solving nonlinear water management models using a combined genetic algorithm and linear programming approach. Adv. Water Resour. 2001, 24, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.K.; Niu, W.J.; Cheng, C.T. Optimization of hydropower reservoirs operation balancing generation benefit and ecological requirement with parallel multi-objective genetic algorithm. Energy 2018, 153, 706–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osório, G.J.; Gonçalves, J.N.D.L.; Lujano-Rojas, J.M.; Catalão, J.P.S. Enhanced forecasting approach for electricity market prices and wind power data series in the short-term. Energies 2016, 9, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.K.; Niu, W.J.; Cheng, C.T. Multi-objective quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization for economic environmental hydrothermal energy system scheduling. Energy 2017, 131, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vašcák, J. Adaptation of fuzzy cognitive maps by migration algorithms. Kybernetes 2012, 41, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, M.; Rashedi, E.; Dashti, S.M.; Hakimi, A. Ideal gas optimization algorithm. Int. J. Artif. Intell. 2017, 15, 116–130. [Google Scholar]
- Vrkalovic, S.; Lunca, E.-C.; Borlea, I.-D. Model-free sliding mode and fuzzy controllers for reverse osmosis desalination plants. Int. J. Artif. Intell. 2018, 16, 208–222. [Google Scholar]
- Precup, R.E.; David, R.C. Nature-Inspired Optimization Algorithms for Fuzzy Controlled Servo Systems; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yang, W.; Du, P.; Niu, T. A novel hybrid forecasting system of wind speed based on a newly developed multi-objective sine cosine algorithm. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 163, 134–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Deep, K. A hybrid self-adaptive sine cosine algorithm with opposition based learning. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 119, 210–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Elaziz, M.; Oliva, D.; Xiong, S. An improved Opposition-Based Sine Cosine Algorithm for global optimization. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 90, 484–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Fang, H.; Liu, X. Parameter optimization of support vector regression based on sine cosine algorithm. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 91, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Tan, J.; Li, C.; Zou, Z.; Li, Q.; Chen, T. A hybrid fault diagnosis approach for rotating machinery with the fusion of entropy-based feature extraction and SVM optimized by a chaos quantum sine cosine algorithm. Entropy 2018, 20, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Tian, H.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, X. Multi-objective artificial physical optimization algorithm for daily economic environmental dispatch of hydrothermal systems. Electr. Power Compon. Syst. 2016, 44, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, N.; Zhou, J. A multi-objective artificial sheep algorithm. Neural Comput. Appl. 2018, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizk-Allah, R.M. Hybridizing sine cosine algorithm with multi-orthogonal search strategy for engineering design problems. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 2018, 5, 249–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Deep, K. Improved sine cosine algorithm with crossover scheme for global optimization. Knowl. Based Syst. 2019, 165, 374–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nenavath, H.; Kumar Jatoth, D.R.; Das, D.S. A synergy of the sine-cosine algorithm and particle swarm optimizer for improved global optimization and object tracking. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2018, 43, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhou, J.; Ouyang, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H. Optimal operation of multi-reservoir system by multi-elite guide particle swarm optimization. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2013, 48, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, C.; Jiao, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y. Multiobjective nondominated neighbor coevolutionary algorithm with elite population. Soft Comput. 2015, 19, 1329–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tan, H.; Zhang, Y. Efficient artificial immune network with elite-learning inspired from PSO for optimization. J. Comput. Inf. Syst. 2008, 4, 1331–1338. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.X.; Huang, Q.; Wang, Y.M. Genetic algorithms for optimal reservoir dispatching. Water Resour. Manag. 2005, 19, 321–331. [Google Scholar]
- Coelho, L.D.S. Gaussian quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization approaches for constrained engineering design problems. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 1676–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, F.; Han, S.; Salgado, R.; Li, J. System probabilistic stability analysis of soil slopes using Gaussian process regression with Latin hypercube sampling. Comput. Geotech. 2015, 63, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, W.; Feng, Z.; Cheng, C.; Zhou, J. Forecasting daily runoff by extreme learning machine based on quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2018, 23, 4018002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, W.; Wu, T.; Liang, X.; Xu, S. Solving high-dimensional global optimization problems using an improved sine cosine algorithm. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 123, 108–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, R.; Wang, C. Chaotic differential bee colony optimization algorithm for dynamic economic dispatch problem with valve-point effects. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2014, 62, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, W.J.; Feng, Z.K.; Cheng, C.T.; Wu, X.Y. A parallel multi-objective particle swarm optimization for cascade hydropower reservoir operation in southwest China. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 2018, 70, 562–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S. SCA: A Sine Cosine Algorithm for solving optimization problems. Knowl. Based Syst. 2016, 96, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.F.; Qiu, J. Multi-objective reservoir optimization balancing energy generation and firm power. Energies 2015, 8, 6962–6976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, T.; Wang, P.; Gooi, H.B.; Wu, L.; Liu, Y.; Ye, J. Optimal operation of multimicrogrids via cooperative energy and reserve scheduling. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 3459–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.K.; Niu, W.J.; Cheng, C.T. Optimizing electrical power production of hydropower system by uniform progressive optimality algorithm based on two-stage search mechanism and uniform design. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 190, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.K.; Niu, W.J.; Cheng, C.T.; Lund, J.R. Optimizing hydropower reservoirs operation via an orthogonal progressive optimality algorithm. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2018, 144, 4018001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Tian, H.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, Y.; Ikram, R.M. An extended NSGA-III for solution multi-objective hydro-thermal-wind scheduling considering wind power cost. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 96, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Niu, W.; Wang, S.; Cheng, C.; Song, Z. Mixed integer linear programming model for peak operation of gas-fired generating units with disjoint-prohibited operating zones. Energies 2019, 12, 2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.Z.; Gooi, H.B.; Ye, J.; Xin, H.; Jiang, X.; Pan, J. Distributed Robust Energy Management of a Multi-Microgrid System in the Real-Time Energy Market. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2019, 10, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Tan, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, T.; Wang, K. Blind parameter identification of MAR model and mutation hybrid GWO-SCA optimized SVM for fault diagnosis of rotating machinery. Complexity 2019, 2019, 3264969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














|
| Function | Range | Best Function |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | ||
| 0 | ||
| 0 | ||
| 0 | ||
| 0 | ||
| 0 |
| Function | Item | GA | DE | PSO | SCA | HSCA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | Best | 3.52 × 100 | 6.73 × 10−2 | 1.14 × 10−3 | 1.32 × 10−19 | 0 |
| Average | 1.13 × 101 | 1.12 × 10−1 | 4.36 × 10−3 | 1.18 × 10−11 | 0 | |
| Std. | 7.94 × 100 | 3.02 × 10−2 | 3.26 × 10−3 | 5.69 × 10−11 | 0 | |
| F2 | Best | 3.65 × 10−1 | 5.64 × 10−2 | 1.86 × 10−2 | 1.85 × 10−16 | 0 |
| Average | 6.64 × 10−1 | 7.67 × 10−2 | 4.98 × 10−2 | 6.09 × 10−11 | 0 | |
| Std. | 1.89 × 10−1 | 9.83 × 10−3 | 2.02 × 10−2 | 2.25 × 10−10 | 0 | |
| F3 | Best | 6.88 × 107 | 1.48 × 103 | 3.70 × 106 | 8.66 × 103 | 8.76 × 10−133 |
| Average | 3.31 × 109 | 1.67 × 103 | 2.05 × 1010 | 5.31 × 104 | 9.35 × 10−19 | |
| Std. | 8.64 × 109 | 9.13 × 101 | 4.39 × 1010 | 5.88 × 104 | 3.87 × 10−18 | |
| F4 | Best | 1.56 × 102 | 2.16 × 102 | 3.46 × 101 | 3.66 × 101 | 2.91 × 101 |
| Average | 5.71 × 102 | 4.19 × 102 | 5.73 × 101 | 3.88 × 101 | 3.15 × 101 | |
| Std. | 3.73 × 102 | 1.07 × 102 | 3.73 × 101 | 3.35 × 100 | 9.31 × 10−1 | |
| F5 | Best | 6.75 × 101 | 1.44 × 102 | 1.70 × 101 | 0 | 0 |
| Average | 1.34 × 102 | 1.59 × 102 | 4.54 × 101 | 8.39 × 10−4 | 0 | |
| Std. | 3.84 × 101 | 8.07 × 100 | 1.51 × 101 | 3.17 × 10−3 | 0 | |
| F6 | Best | 6.51 × 10−1 | 6.78 × 10−2 | 1.43 × 10−2 | 6.05 × 10−12 | 4.44 × 10−16 |
| Average | 1.17 × 100 | 1.03 × 10−1 | 1.64 × 100 | 1.15 × 101 | 2.46 × 10−15 | |
| Std. | 4.35 × 10−1 | 1.82 × 10−2 | 1.56 × 100 | 1.02 × 101 | 1.79 × 10−15 |
| Function | Item | GA | DE | PSO | SCA | HSCA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | Best | 1.31 × 102 | 2.16 × 102 | 1.76 × 10−1 | 2.68 × 10−15 | 0 |
| Average | 2.44 × 102 | 3.18 × 102 | 1.29 × 101 | 6.25 × 10−9 | 0 | |
| Std. | 7.95 × 101 | 5.66 × 101 | 3.75 × 101 | 2.61 × 10−8 | 0 | |
| F2 | Best | 3.96 × 100 | 9.75 × 100 | 9.94 × 10−1 | 2.35 × 10−12 | 0 |
| Average | 5.84 × 100 | 1.13 × 101 | 1.34 × 100 | 1.36 × 10−9 | 0 | |
| Std. | 1.02 × 100 | 1.02 × 100 | 2.22 × 10−1 | 2.79 × 10−9 | 0 | |
| F3 | Best | 3.32 × 1019 | 6.08 × 103 | 1.21 × 1019 | 2.88 × 1015 | 8.72 × 10−131 |
| Average | 9.05 × 1020 | 6.28 × 103 | 7.90 × 1021 | 3.44 × 1016 | 3.56 × 10−14 | |
| Std. | 9.68 × 1020 | 9.53 × 101 | 1.49 × 1022 | 7.40 × 1016 | 1.95 × 10−13 | |
| F4 | Best | 1.74 × 104 | 1.33 × 105 | 9.27 × 101 | 7.74 × 101 | 7.24 × 101 |
| Average | 7.51 × 104 | 1.87 × 105 | 1.56 × 102 | 9.53 × 101 | 7.37 × 101 | |
| Std. | 5.06 × 104 | 3.09 × 104 | 5.52 × 101 | 6.19 × 101 | 8.26 × 10−1 | |
| F5 | Best | 2.31 × 102 | 5.17 × 102 | 7.50 × 101 | 3.02 × 10−14 | 0 |
| Average | 4.26 × 102 | 5.61 × 102 | 1.02 × 102 | 1.70 × 100 | 0 | |
| Std. | 8.22 × 101 | 1.92 × 101 | 1.56 × 101 | 5.25 × 100 | 0 | |
| F6 | Best | 3.53 × 10−1 | 7.58 × 10−1 | 1.48 × 10−1 | 1.18 × 10−9 | 4.44 × 10−16 |
| Average | 5.49 × 10−1 | 9.22 × 10−1 | 4.93 × 10−1 | 2.60 × 10−7 | 3.52 × 10−15 | |
| Std. | 1.19 × 10−1 | 9.03 × 10−2 | 4.47 × 10−1 | 4.73 × 10−7 | 1.23 × 10−15 |
| Item (No unit) | Plant 1 | Plant 2 | Plant 3 | Plant 4 | Plant 5 | Plant 6 | Plant 7 | Plant 8 | Plant 9 | Plant 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum storage Vup | 12.00 | 17.00 | 6.00 | 19.00 | 19.10 | 14.00 | 30.10 | 13.16 | 7.90 | 30.00 |
| Minimum storage Vdown | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 1.0 |
| Maximum discharge qup | 4.00 | 4.50 | 2.12 | 7.00 | 6.43 | 4.21 | 17.10 | 3.10 | 4.20 | 18.90 |
| Minimum discharge qdown | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.010 | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.010 |
| Generation coefficient C0 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.0 | 1.1 | 1.0 | 1.4 | 2.6 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 2.7 |
| Initial storage Vbegin | 6.0 | 6.0 | 3.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 7.0 | 15.0 | 6.0 | 5.0 | 15.0 |
| Period | I1 | I2 | I3 | I5 | I6 | I8 | Load Lt |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.50 | 0.40 | 0.80 | 1.50 | 0.32 | 0.71 | 80 |
| 2 | 1.00 | 0.70 | 0.80 | 2.00 | 0.81 | 0.83 | 90 |
| 3 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 0.80 | 2.50 | 1.53 | 1.00 | 100 |
| 4 | 3.00 | 2.00 | 0.80 | 2.50 | 2.16 | 1.25 | 90 |
| 5 | 3.50 | 4.00 | 0.80 | 3.00 | 2.31 | 1.67 | 80 |
| 6 | 2.50 | 3.50 | 0.80 | 3.50 | 4.32 | 2.50 | 70 |
| 7 | 2.00 | 3.00 | 0.80 | 3.50 | 4.81 | 2.80 | 60 |
| 8 | 1.25 | 2.50 | 0.80 | 3.00 | 2.24 | 1.87 | 50 |
| 9 | 1.25 | 1.30 | 0.80 | 2.50 | 1.63 | 1.45 | 40 |
| 10 | 0.75 | 1.20 | 0.80 | 2.50 | 1.91 | 1.20 | 50 |
| 11 | 1.75 | 1.00 | 0.80 | 2.00 | 0.80 | 0.93 | 60 |
| 12 | 1.00 | 0.70 | 0.80 | 1.50 | 0.46 | 0.81 | 70 |
| 13 | 0.50 | 0.40 | 0.80 | 1.50 | 0.32 | 0.71 | 80 |
| 14 | 1.00 | 0.70 | 0.80 | 2.00 | 0.81 | 0.83 | 90 |
| 15 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 0.80 | 2.50 | 1.53 | 1.00 | 100 |
| 16 | 3.00 | 2.00 | 0.80 | 2.50 | 2.16 | 1.25 | 90 |
| 17 | 3.50 | 4.00 | 0.80 | 3.00 | 2.31 | 1.67 | 80 |
| 18 | 2.50 | 3.50 | 0.80 | 3.50 | 4.32 | 2.50 | 70 |
| 19 | 2.00 | 3.00 | 0.80 | 3.50 | 4.81 | 2.80 | 60 |
| 20 | 1.25 | 2.50 | 0.80 | 3.00 | 2.24 | 1.87 | 50 |
| Case | Plant 1 | Plant 2 | Plant 3 | Plant 4 | Plant 5 | Plant 6 | Plant 7 | Plant 8 | Plant 9 | Plant 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6.00 | 6.00 | 3.00 | 8.00 | 8.00 | 7.00 | 15.00 | 6.00 | 5.00 | 15.00 |
| 2 | 5.99 | 5.99 | 2.99 | 7.99 | 7.99 | 6.99 | 14.99 | 5.99 | 4.99 | 15.00 |
| 3 | 5.98 | 5.98 | 2.98 | 7.98 | 7.98 | 6.98 | 14.99 | 5.99 | 4.99 | 14.99 |
| 4 | 5.99 | 5.99 | 2.99 | 7.99 | 7.99 | 6.99 | 14.99 | 5.99 | 4.99 | 14.99 |
| Reservoir | HJD | DF | SFY | WJD | GPT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Generation coefficient | 8.00 | 8.35 | 8.30 | 8.00 | 8.50 |
| Installed capacity (MW) | 600 | 695 | 600 | 1250 | 3000 |
| Normal water level (m) | 1140 | 970 | 837 | 760 | 630 |
| Dead water level (m) | 1076 | 936 | 822 | 720 | 590 |
| Maximum power flow (m3/s) | 490.50 | 632.10 | 994.50 | 1087 | 1909 |
| Method | Item | Peak (MW) | Valley (MW) | Peak-Valley Difference (MW) | Average (MW) | Std. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original load | 13,477.93 | 10,101.60 | 3376.33 | 11,910.93 | 1281.95 | |
| GA | Optimization load | 11,259.51 | 8020.04 | 3239.47 | 9662.40 | 890.25 |
| Reduction | 2218.42 | 2081.56 | 136.86 | 2248.53 | 391.70 | |
| Improvement (%) | 16.46 | 20.61 | 4.05 | 18.88 | 30.56 | |
| DE | Optimization load | 10,586.69 | 8512.56 | 2074.13 | 9649.85 | 585.83 |
| Reduction | 2891.24 | 1589.04 | 1302.20 | 2261.08 | 696.12 | |
| Improvement (%) | 21.45 | 15.73 | 38.57 | 18.98 | 54.30 | |
| PSO | Optimization load | 10,149.54 | 9185.88 | 963.66 | 9637.28 | 255.12 |
| Reduction | 3328.39 | 915.72 | 2412.67 | 2273.65 | 1026.83 | |
| Improvement (%) | 24.70 | 9.07 | 71.46 | 19.09 | 80.10 | |
| SCA | Optimization load | 11,106.73 | 8214.05 | 2892.68 | 9668.49 | 769.43 |
| Reduction | 2371.20 | 1887.55 | 483.65 | 2242.44 | 512.52 | |
| Improvement (%) | 17.59 | 18.69 | 14.32 | 18.83 | 39.98 | |
| HSCA | Optimization load | 9958.69 | 9255.71 | 702.98 | 9637.55 | 166.16 |
| Reduction | 3519.24 | 845.89 | 2673.35 | 2273.38 | 1115.79 | |
| Improvement (%) | 26.11 | 8.37 | 79.18 | 19.09 | 87.04 |
| Case | Item | Peak (MW) | Valley (MW) | Peak-Valley Difference (MW) | Average | Std. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | Original load | 13,477.93 | 10,101.60 | 3376.33 | 11,910.93 | 1281.95 |
| Optimization load | 9958.69 | 9255.71 | 702.98 | 9637.55 | 166.16 | |
| Reduction | 3519.24 | 845.89 | 2673.35 | 2273.38 | 1115.79 | |
| Improvement (%) | 26.11 | 8.37 | 79.18 | 19.09 | 87.04 | |
| Summer | Original load | 14,119.78 | 10,342.98 | 3776.80 | 12,170.94 | 1302.21 |
| Optimization load | 10,337.67 | 9451.54 | 886.13 | 9896.81 | 192.12 | |
| Reduction | 3782.11 | 891.44 | 2890.67 | 2274.13 | 1110.09 | |
| Improvement (%) | 26.79 | 8.62 | 76.54 | 18.68 | 85.25 | |
| Autumn | Original load | 14,773.84 | 10,786.00 | 3987.84 | 13,220.16 | 1528.83 |
| Optimization load | 11,570.46 | 10,338.56 | 1231.90 | 10,946.91 | 300.48 | |
| Reduction | 3203.38 | 447.44 | 2755.94 | 2273.25 | 1228.35 | |
| Improvement (%) | 21.68 | 4.15 | 69.11 | 17.20 | 80.35 | |
| Winter | Original load | 14,913.26 | 11,028.24 | 3885.02 | 12,971.28 | 1489.76 |
| Optimization load | 11,078.99 | 10,179.92 | 899.07 | 10,695.26 | 256.41 | |
| Reduction | 3834.27 | 848.32 | 2985.95 | 2276.02 | 1233.35 | |
| Improvement (%) | 25.71 | 7.69 | 76.86 | 17.55 | 82.79 |
| Name | Item | Swarm Size | Maximum Iterations | Mutation Probability | Combination Coefficient | Accepted Accuracy | Constraint Adjustment Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level | 1 | 100 | 300 | 0.005 | 0.3 | 1.00 × 10−6 | 3 |
| 2 | 150 | 500 | 0.01 | 0.5 | 1.00 × 10−5 | 5 | |
| 3 | 200 | 700 | 0.015 | 0.7 | 1.00 × 10−4 | 7 | |
| Average | 1 | 238.0 | 243.1 | 225.4 | 226.7 | 218.6 | 241.1 |
| standard | 2 | 207.6 | 208.5 | 215.0 | 212.6 | 214.0 | 205.3 |
| deviation | 3 | 204.6 | 198.6 | 209.7 | 210.9 | 217.7 | 203.8 |
| Maximum | 238.0 | 243.1 | 225.4 | 226.7 | 218.6 | 241.1 | |
| Minimum | 204.6 | 198.6 | 209.7 | 210.9 | 214.0 | 203.8 | |
| Range | 33.4 | 44.4 | 15.7 | 15.9 | 4.5 | 37.4 | |
| Rank | 3 | 1 | 5 | 4 | 6 | 2 |
| List | Item | Peak (MW) | Peak-Valley Difference (MW) | Standard Deviation (MW) | Load Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | Original load | 13,827.26 | 3943.26 | 1421.64 | 86.56 |
| SCA | 10,946.80 | 2899.19 | 987.40 | 88.78 | |
| HSCA | 10,039.14 | 719.99 | 202.27 | 96.53 | |
| Case 2 | Original load | 13,870.88 | 4124.86 | 1369.89 | 86.70 |
| SCA | 11,808.02 | 3418.09 | 1001.09 | 82.79 | |
| HSCA | 10,099.36 | 781.20 | 197.96 | 96.52 | |
| Case 3 | Original load | 14,156.40 | 4659.78 | 1390.02 | 85.35 |
| SCA | 11,278.18 | 3835.12 | 818.93 | 86.14 | |
| HSCA | 10,075.19 | 966.85 | 217.19 | 96.07 | |
| Case 4 | Original load | 13,680.52 | 3882.49 | 1323.51 | 85.89 |
| SCA | 10,678.87 | 2847.26 | 785.43 | 88.97 | |
| HSCA | 9909.46 | 875.16 | 213.04 | 95.57 | |
| Case 5 | Original load | 13,490.69 | 3745.08 | 1243.21 | 86.60 |
| SCA | 10,792.23 | 3006.65 | 766.72 | 87.41 | |
| HSCA | 9756.73 | 809.19 | 176.62 | 96.38 | |
| Case 6 | Original load | 14,676.75 | 3874.80 | 1332.25 | 86.11 |
| SCA | 12,064.70 | 3226.63 | 851.15 | 86.11 | |
| HSCA | 10,774.41 | 983.04 | 196.86 | 96.14 | |
| Case 7 | Original load | 15,543.89 | 5045.08 | 1659.78 | 86.24 |
| SCA | 12,934.25 | 4181.35 | 1146.98 | 86.34 | |
| HSCA | 11,536.46 | 1299.87 | 369.48 | 96.47 | |
| Case 8 | Original load | 15,123.05 | 4589.19 | 1618.46 | 87.04 |
| SCA | 12,298.81 | 3595.05 | 1021.03 | 88.74 | |
| HSCA | 11,336.99 | 1212.21 | 335.52 | 96.03 | |
| Case 9 | Original load | 15,431.76 | 5058.47 | 1745.89 | 85.78 |
| SCA | 12,771.31 | 4229.12 | 1239.81 | 86.02 | |
| HSCA | 11,593.51 | 1402.37 | 415.48 | 94.60 | |
| Case 10 | Original load | 15,409.61 | 4436.59 | 1526.04 | 85.36 |
| SCA | 13,206.72 | 3934.85 | 946.33 | 82.62 | |
| HSCA | 11,222.26 | 874.62 | 245.55 | 96.93 | |
| Case 11 | Original load | 14,878.13 | 4156.90 | 1498.37 | 88.17 |
| SCA | 12,524.05 | 4050.02 | 949.40 | 86.82 | |
| HSCA | 11,288.57 | 1279.77 | 249.69 | 96.04 | |
| Case 12 | Original load | 14,949.36 | 4434.51 | 1522.37 | 87.62 |
| SCA | 12,863.87 | 3417.11 | 878.54 | 84.41 | |
| HSCA | 11,271.75 | 1194.92 | 317.28 | 96.01 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Feng, Z.-K.; Niu, W.-J.; Zhang, H.-R.; Song, Z.-G. Peak Operation Problem Solving for Hydropower Reservoirs by Elite-Guide Sine Cosine Algorithm with Gaussian Local Search and Random Mutation. Energies 2019, 12, 2189. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12112189
Liu S, Feng Z-K, Niu W-J, Zhang H-R, Song Z-G. Peak Operation Problem Solving for Hydropower Reservoirs by Elite-Guide Sine Cosine Algorithm with Gaussian Local Search and Random Mutation. Energies. 2019; 12(11):2189. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12112189
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shuai, Zhong-Kai Feng, Wen-Jing Niu, Hai-Rong Zhang, and Zhen-Guo Song. 2019. "Peak Operation Problem Solving for Hydropower Reservoirs by Elite-Guide Sine Cosine Algorithm with Gaussian Local Search and Random Mutation" Energies 12, no. 11: 2189. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12112189
APA StyleLiu, S., Feng, Z.-K., Niu, W.-J., Zhang, H.-R., & Song, Z.-G. (2019). Peak Operation Problem Solving for Hydropower Reservoirs by Elite-Guide Sine Cosine Algorithm with Gaussian Local Search and Random Mutation. Energies, 12(11), 2189. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12112189





