A Study on Urea-Water Solution Spray-Wall Impingement Process and Solid Deposit Formation in Urea-SCR de-NOx System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup and Method
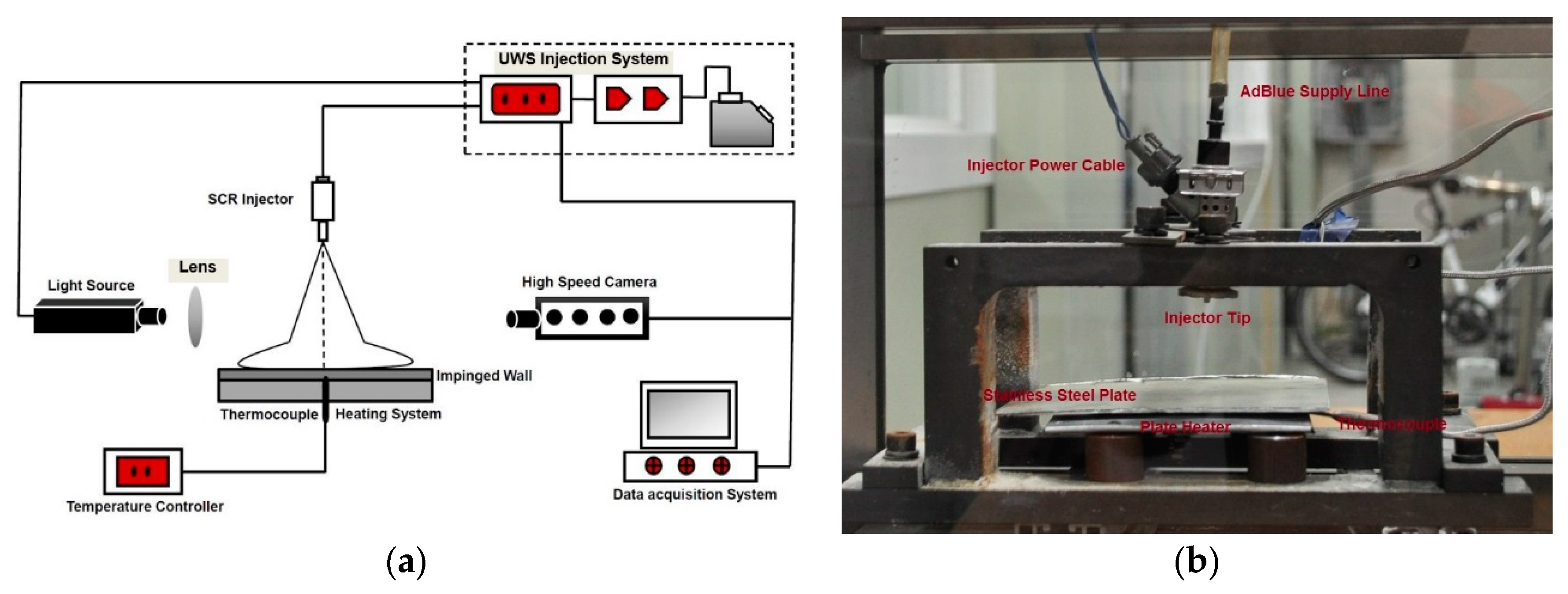
2.1. Optical Chamber and Heating Arrangement
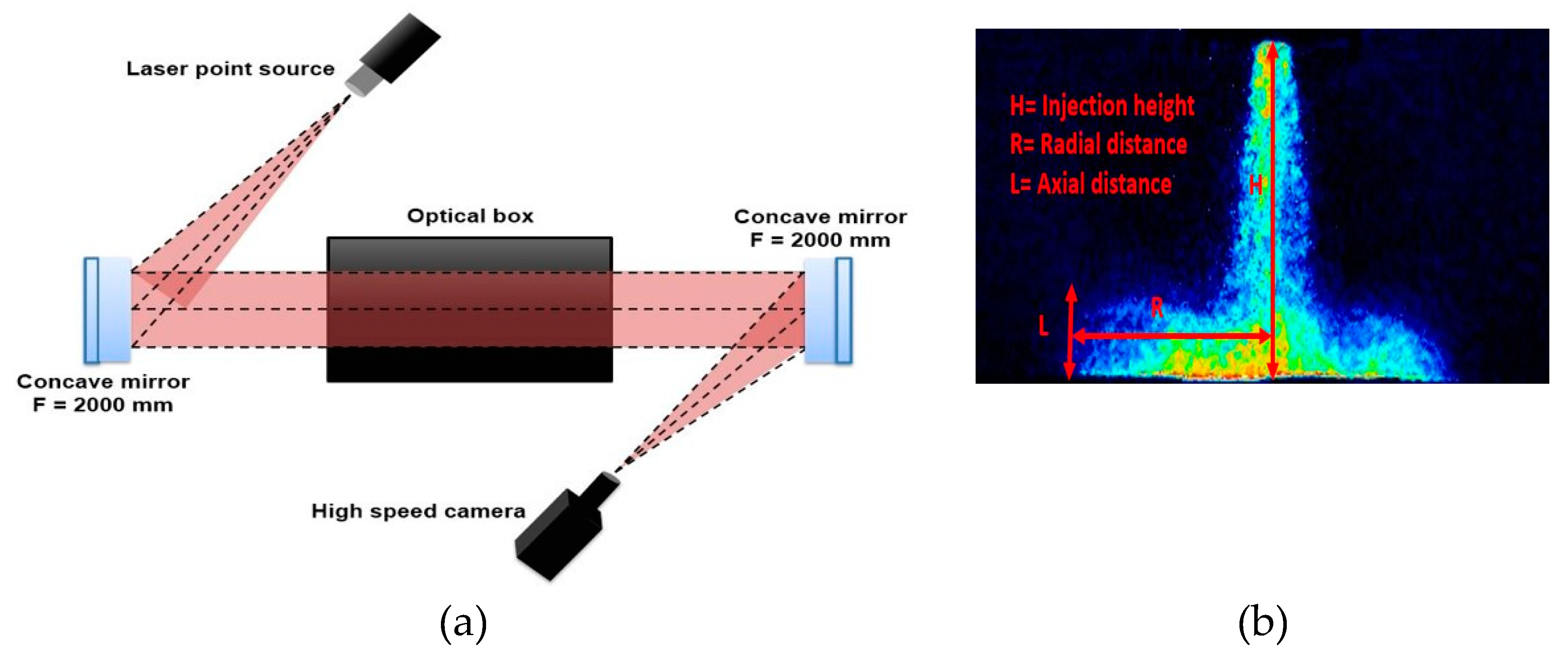
2.2. Optical and Imaging Arrangement
2.3. Experimental Conditions and Method
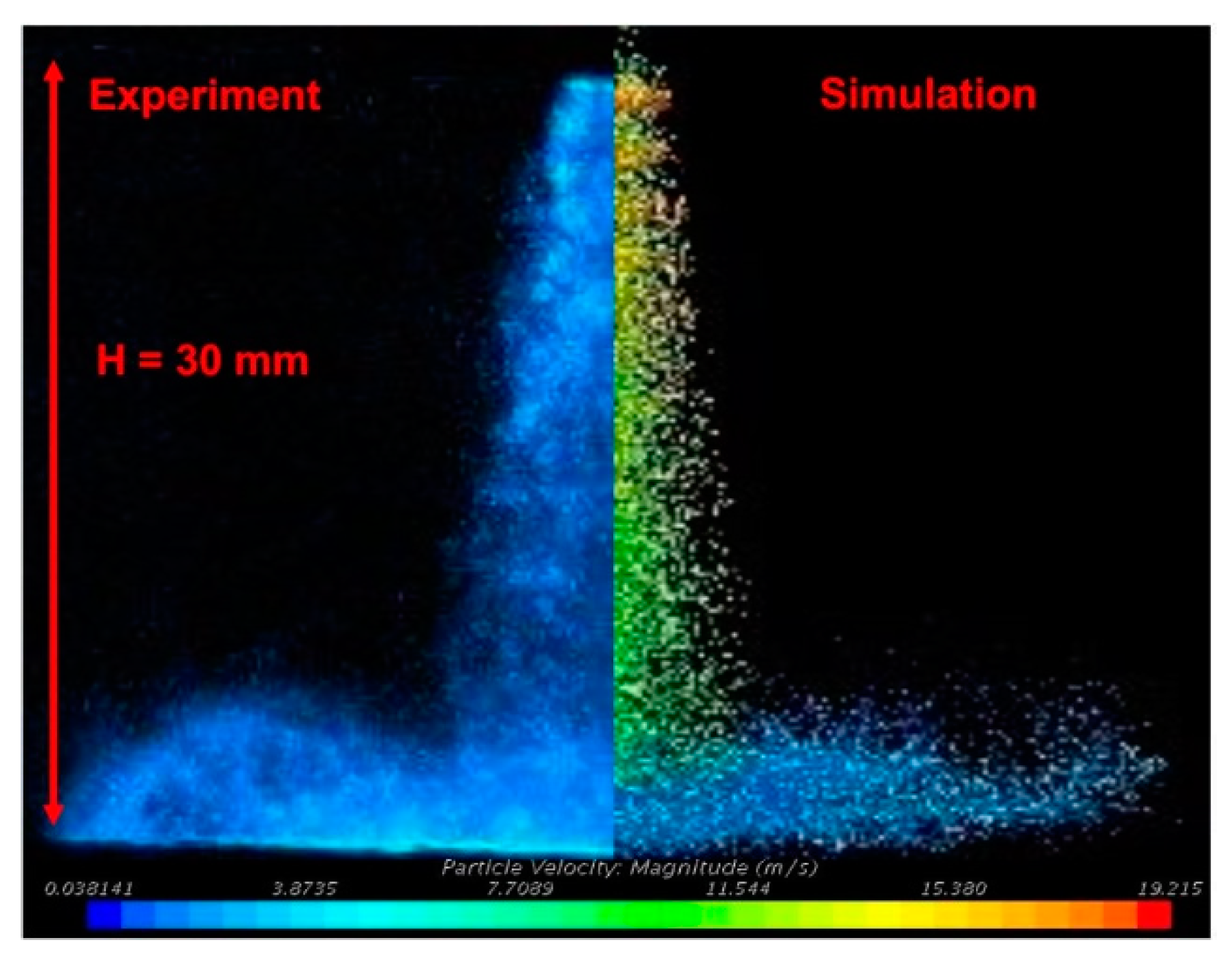
3. Numerical Modeling
4. Results and Discussion
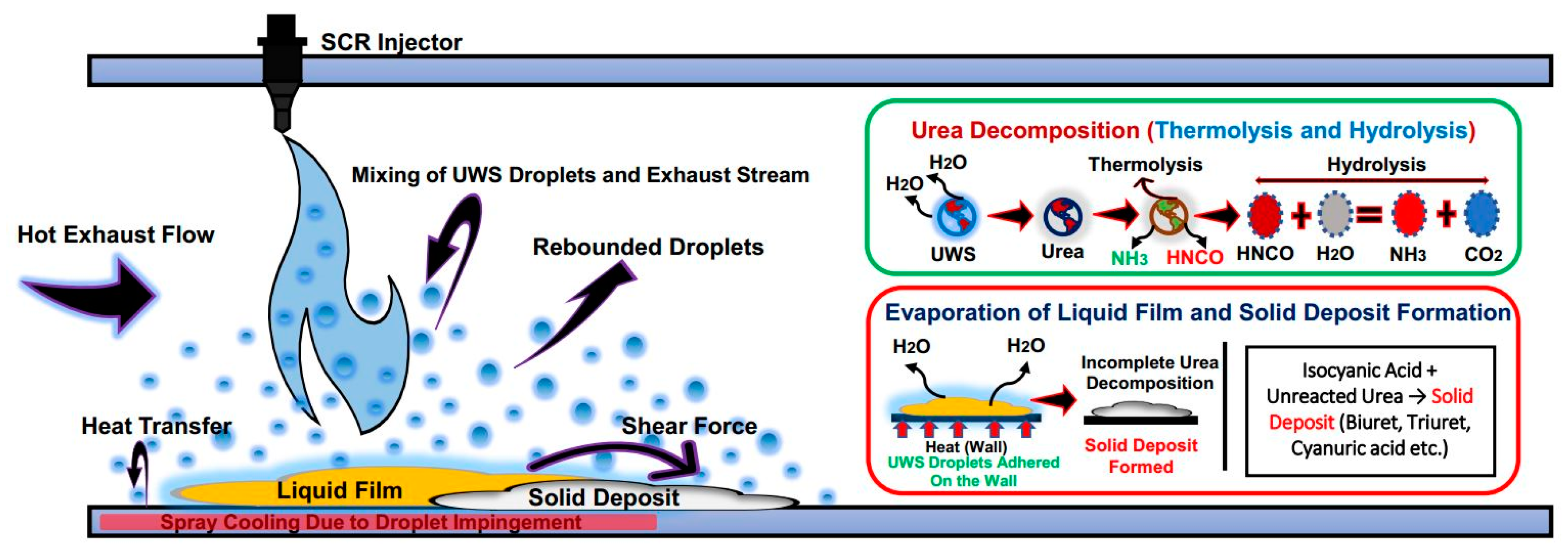
4.1. UWS Spray-Wall Impingement Phenomena
4.2. Effects of UWS Spray-Wall Impingement
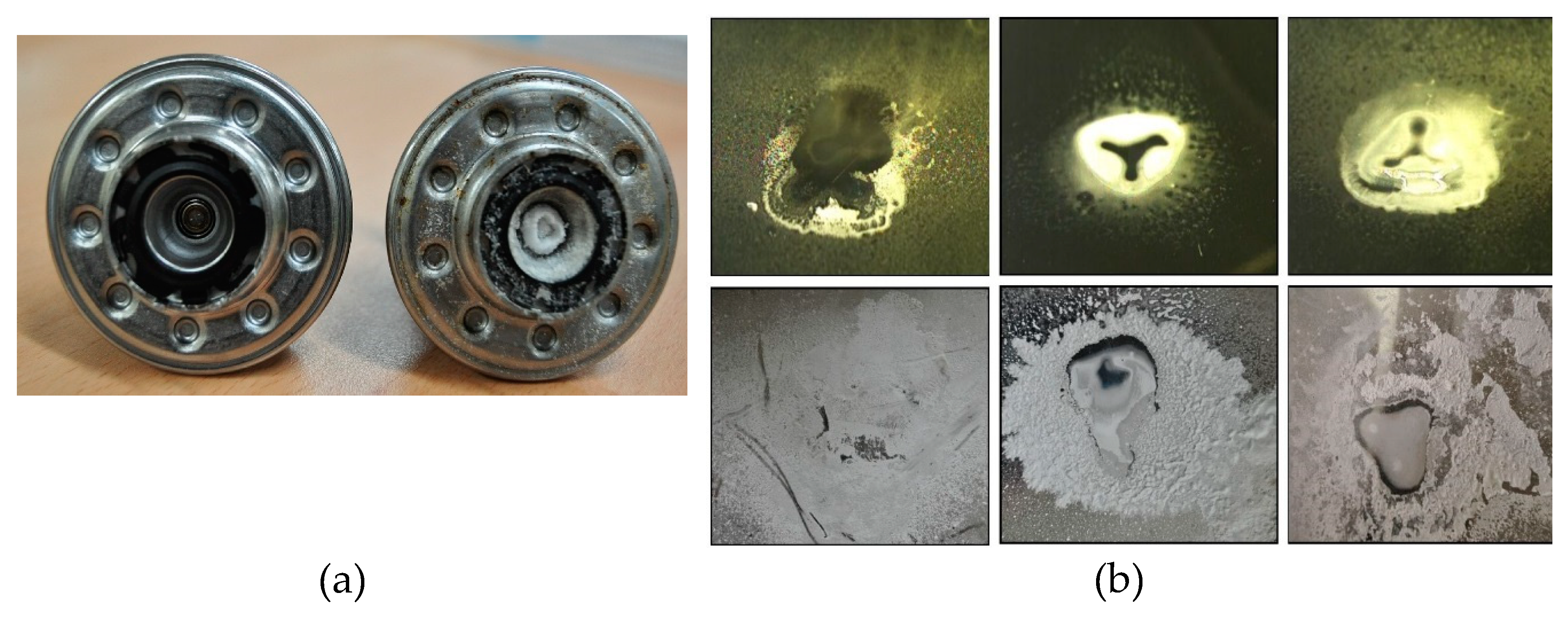
4.3. Characterization of Urea Deposits
5. Conclusions
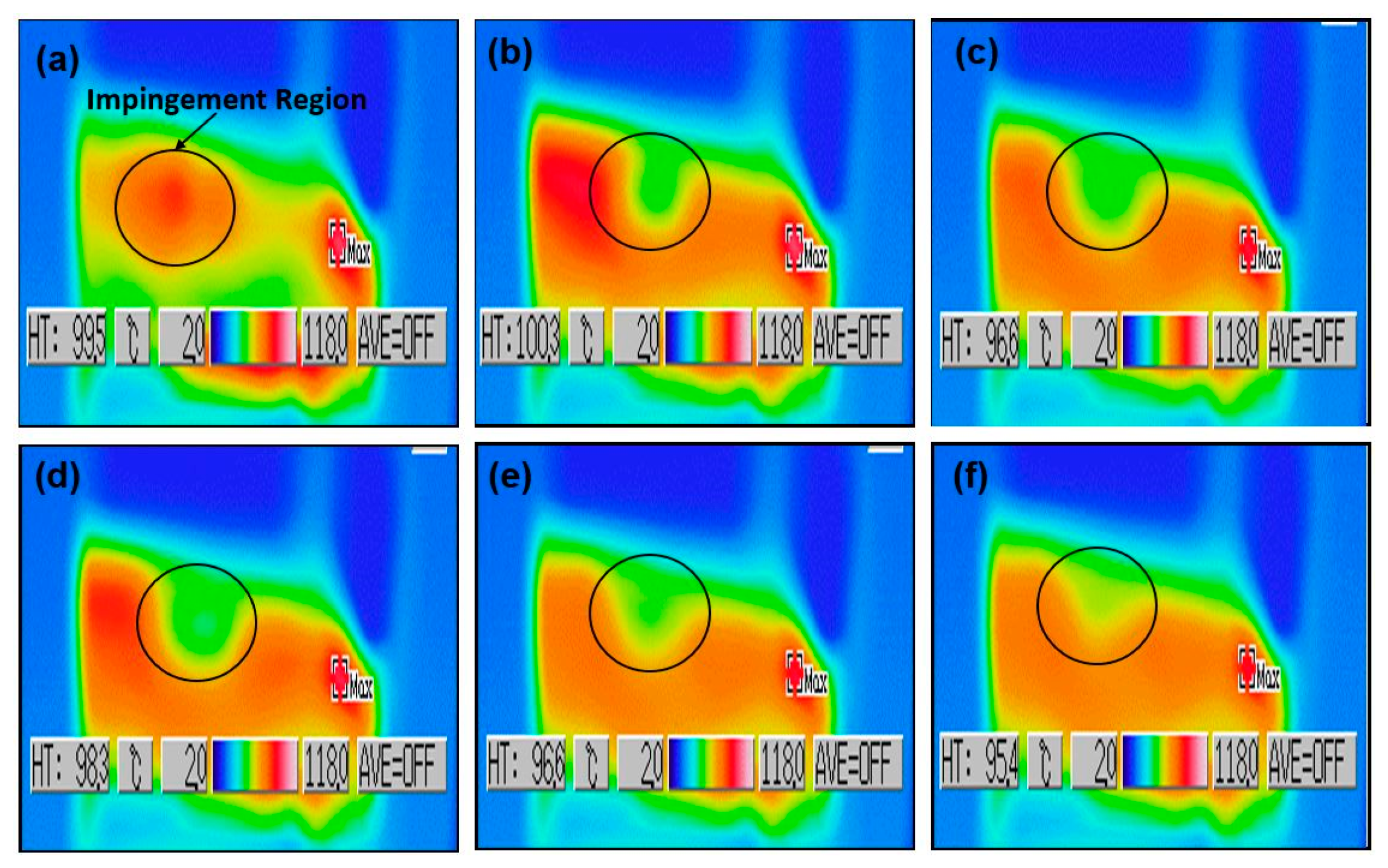
- Because of the droplet entrainment and evaporation, spray-wall impingement has significant effects on SCR performance. At a low temperature, droplets adhered on the wall increase wall wetting, which can maximize the deposit formation risk. On the other hand, at a high wall temperature, rebounding and thermal breakup occur, which increase the droplet evaporation. Rapid heat transfer between the droplets and wall surface causes enhanced urea decomposition, and a significant amount of gas is produced. As a result, a hot turbulence zone is formed by curl and bouncing, and the chance of wall wetting, as well as the risk of deposit formation reduced significantly.
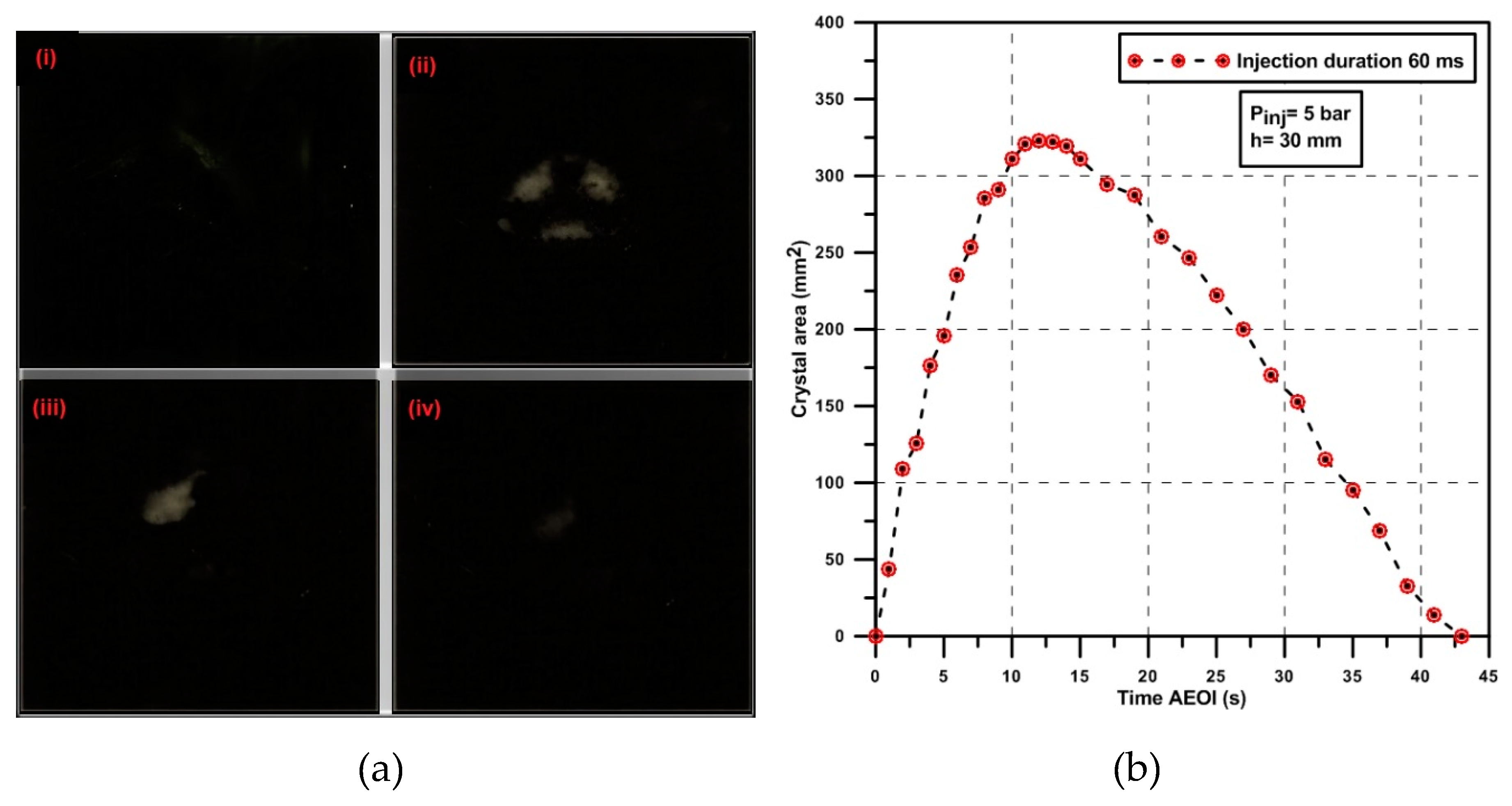
- The liquid film formed on the wall due to droplet spray-wall impingement and the accumulated film was further transported and distributed by the momentum of the subsequent injections. This liquid film is a urea-enriched solution, and solid deposits are generated in the film accumulation area.
- The spray cooling first starts at the spray cone core region and then spreads radially to the periphery of the impingement region.
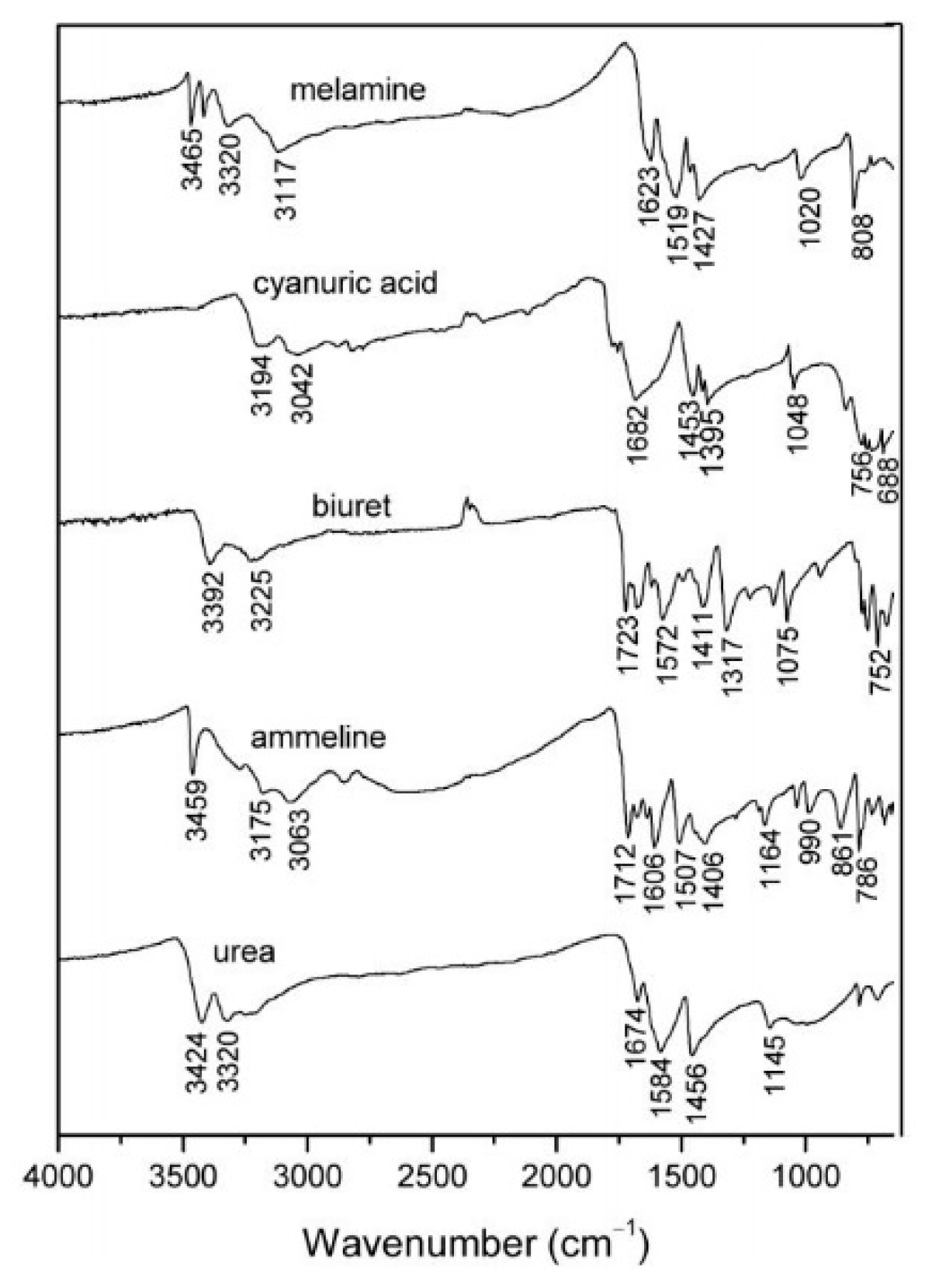
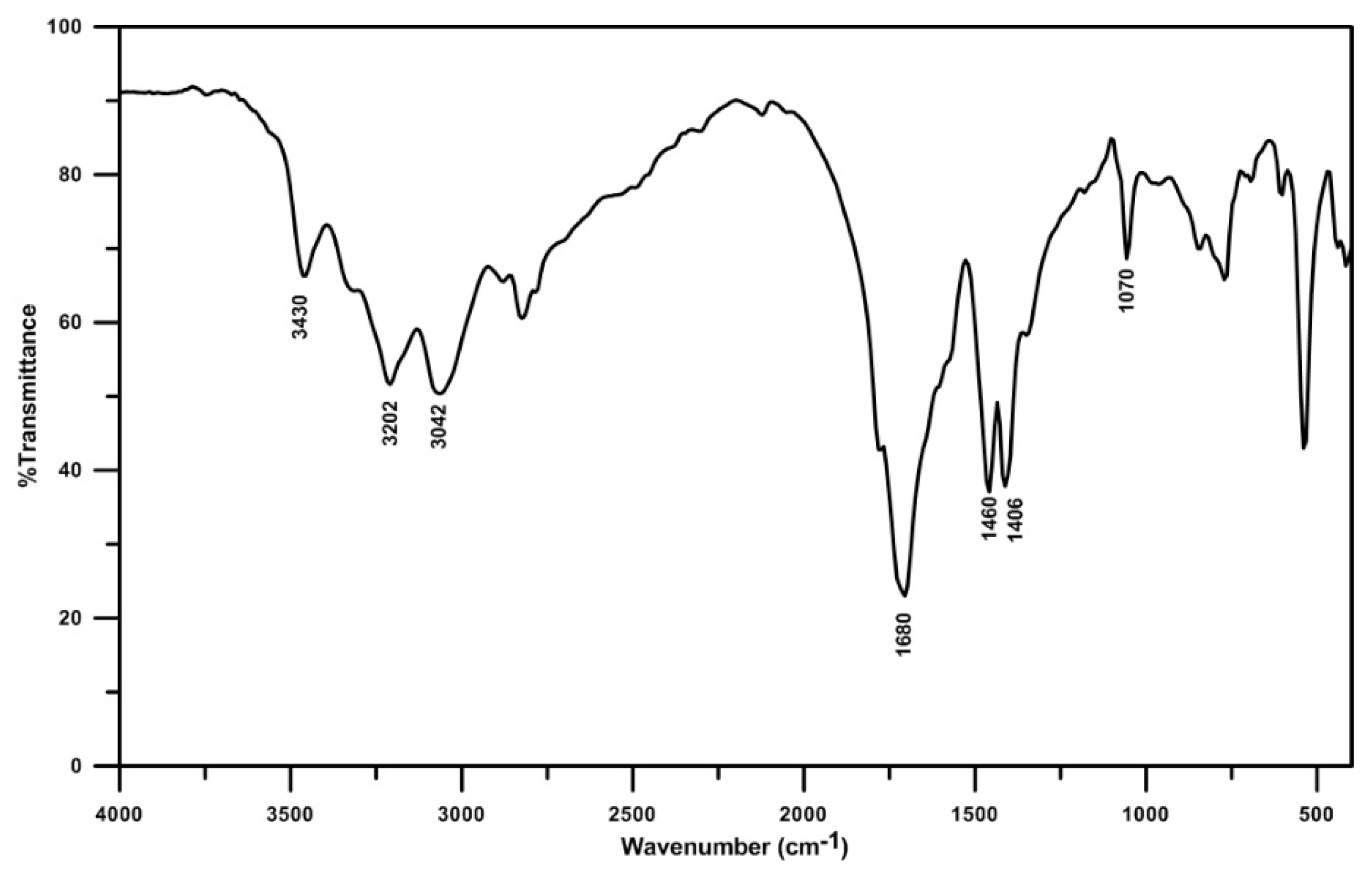
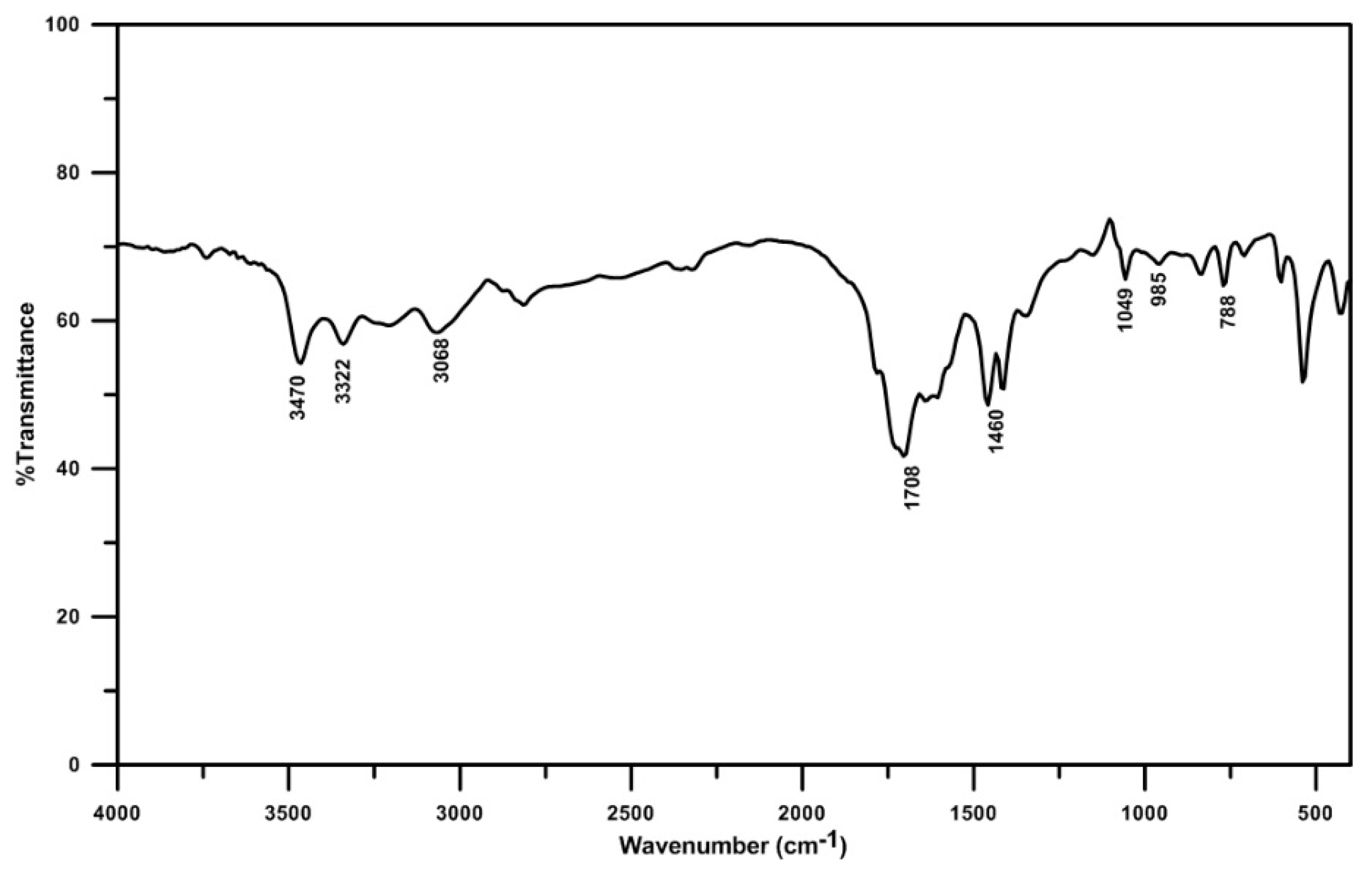
- The chemical composition of the solid deposit samples obtained from FTIR analysis significantly varies depending on the decomposition temperature. The major compounds found at different temperatures are unreacted urea, biuret, cyanuric acid, ammeline, and melamine.
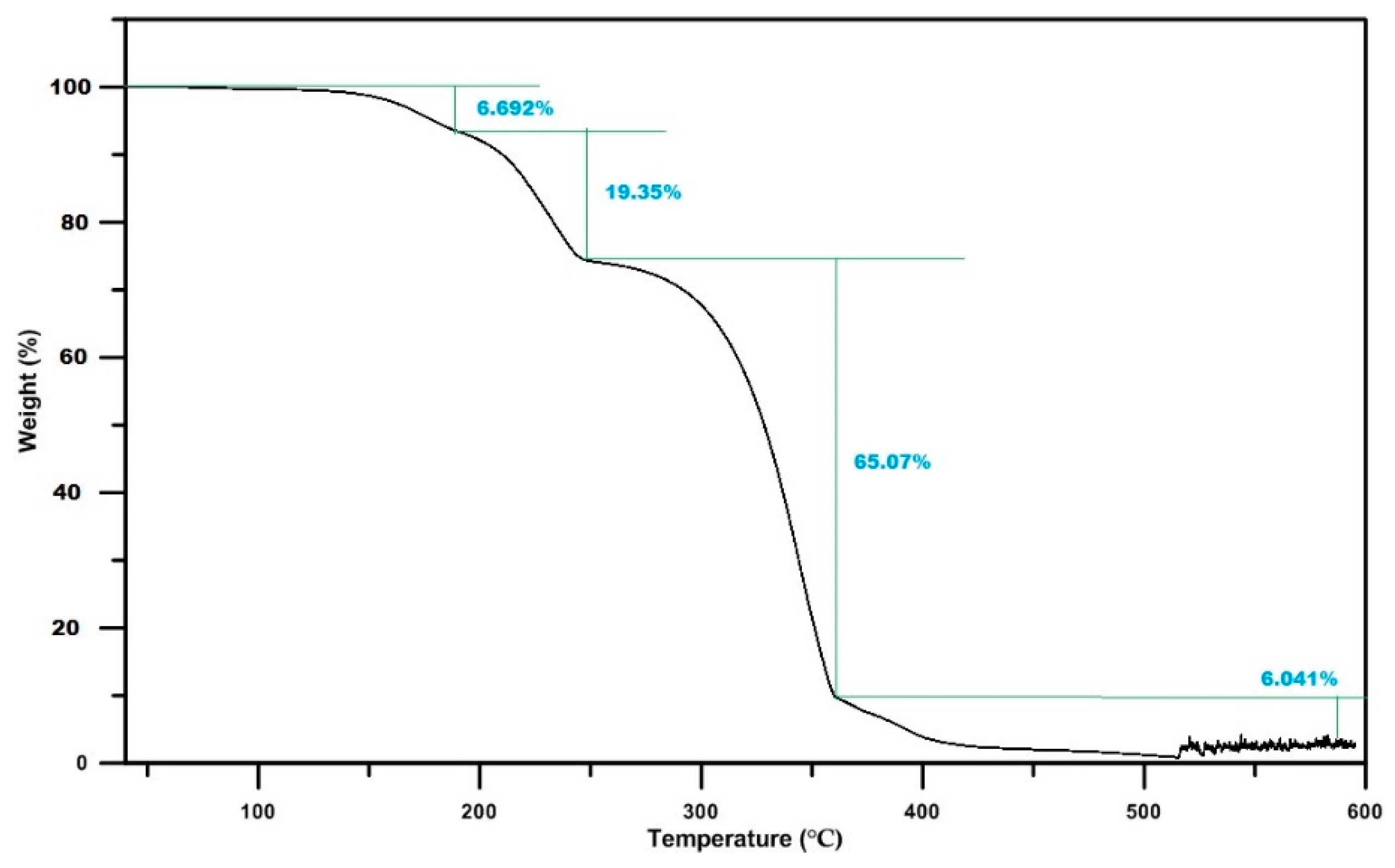
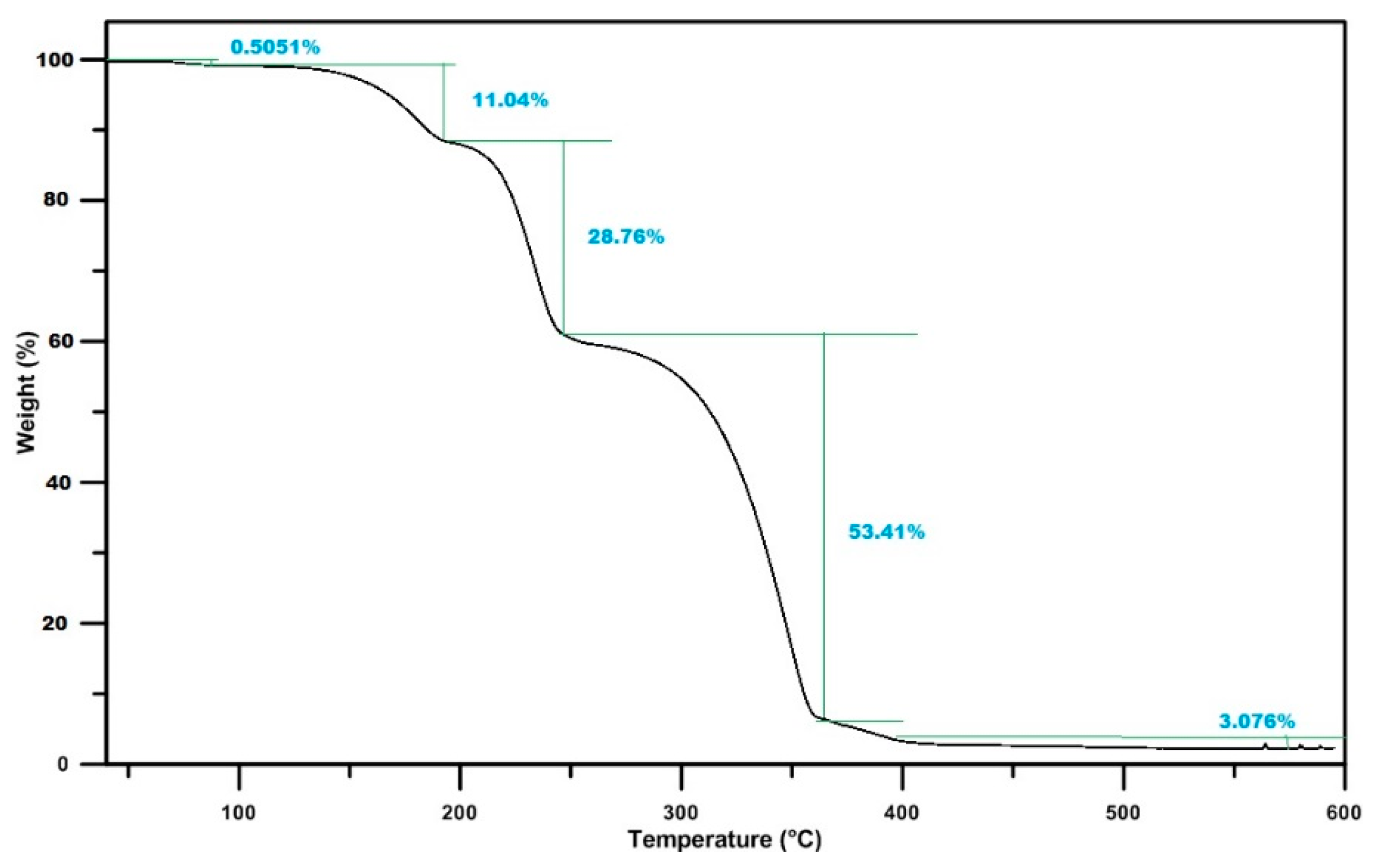
- TGA measurements show that the majority of the solid deposits thermally decompose around the 673 K temperature. Though this temperature can be achieved by the regular exhaust temperature condition, complete thermal decomposition takes a long time period, and the decomposition rate strongly depends on the mass percentage.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tartakovsky, L.; Mosyak, A.; Zvirin, Y. Energy analysis of ethanol steam reforming for hybrid electric vehicle. Int. J. Energy Res. 2013, 37, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Ha, T.; Choi, H. Experimental verification of optimized NOX reduction strategies in a decrepit Euro-3 diesel engine retrofitted with a cooled EGR system. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2016, 30, 2873–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, A.; Mandal, B.K. Numerical investigation of the performance and emission parameters of a diesel engine fuelled with diesel-biodiesel-methanol blends. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2016, 30, 1923–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grout, S.; Blaisot, J.-B.; Pajot, K.; Osbat, G. Experimental investigation on the injection of an urea–water solution in hot air stream for the SCR application: Evaporation and spray/wall interaction. Fuel 2013, 106, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.V. Vehicular emissions in review. SAE Int. J. Engines 2012, 5, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, A.; Pitchon, V. The current state of research on automotive lean NOx catalysis. Appl. Catal. B 1997, 13, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkhold, F.; Meingast, U.; Wassermann, P.; Deutschmann, O. Analysis of the Injection of Urea-Water-Solution for Automotive SCR DeNOx-Systems: Modeling of Two-Phase Flow and Spray/Wall-Interaction; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Yim, S.D.; Kim, S.J.; Baik, J.H.; Nam, I.-S.; Mok, Y.S.; Lee, J.-H.; Cho, B.K.; Oh, S.H. Decomposition of Urea into NH3 for the SCR Process. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2004, 43, 4856–4863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleemann, M.; Elsener, M.; Koebel, M.; Wokaun, A. Hydrolysis of isocyanic acid on SCR catalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2000, 39, 4120–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koebel, M.; Strutz, E.O. Thermal and hydrolytic decomposition of urea for automotive selective catalytic reduction systems: thermochemical and practical aspects. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2003, 42, 2093–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluder, C.S.; Storey, J.M.E.; Lewis, S.A.; Lewis, L.A. Low Temperature Urea Decomposition and SCR Performance; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Strots, V.O.; Santhanam, S.; Adelman, B.J.; Griffin, G.A.; Derybowski, E.M. Deposit formation in urea-SCR systems. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2010, 2, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munnannur, A.; Chiruta, M.; Liu, Z.G. Thermal and Fluid Dynamic Considerations in Aftertreatment System Design for SCR Solid Deposit Mitigation; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Spiteri, A.; Eggenschwiler, P.D.; Liao, Y.; Wigley, G.; Michalow-Mauke, K.A.; Elsener, M.; Kröcher, O.; Boulouchos, K. Comparative analysis on the performance of pressure and air-assisted urea injection for selective catalytic reduction of NOx. Fuel 2015, 161, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkhold, F.; Meingast, U.; Wassermann, P.; Deutschmann, O. Modeling and simulation of the injection of urea-water-solution for automotive SCR DeNOx-systems. Appl. Catal. B 2007, 70, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebelius, S.; Le, T.T.; Pettersson, L.J.; Lind, H. Identification of urea decomposition from an SCR perspective; A combination of experimental work and molecular modeling. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 231, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaber, P.M.; Colson, J.; Higgins, S.; Thielen, D.; Anspach, B.; Brauer, J. Thermal decomposition (pyrolysis) of urea in an open reaction vessel. Thermochim. Acta 2004, 424, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichelbaum, M.; Farrauto, R.J.; Castaldi, M.J. The impact of urea on the performance of metal exchanged zeolites for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx: Part I. Pyrolysis and hydrolysis of urea over zeolite catalysts. Appl. Catal. B 2010, 97, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahariar, G.M.H.; Wardana, M.K.A.; Lim, O.T. Investigation of urea-water solution spray impingement on the hot surface of automotive SCR system. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2018, 32, 2935–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Fila, A.; Kotrba, A.; Floyd, R. Investigation of Urea Deposits in Urea SCR Systems for Medium and Heavy Duty Trucks; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Weeks, C.L.; Ibeling, D.R.; Han, S.; Ludwig, L.; Ayyappan, P. Analytical investigation of urea deposits in SCR system. SAE Int. J. Engines 2015, 8, 1219–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.L.; DaCosta, H.F.M. Urea thermolysis and NOx reduction with and without SCR catalysts. Appl. Catal. B 2003, 46, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundström, A.; Andersson, B.; Olsson, L. Urea thermolysis studied under flow reactor conditions using DSC and FT-IR. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 150, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Shuai, S.; Wang, J. Effect of Urea Thermal Decomposition on Diesel NOx-SCR Aftertreatment Systems; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, S.-J.; Lee, S.-J.; Kim, W.-S. Numerical study on the optimum injection of urea–water solution for SCR DeNOx system of a heavy-duty diesel engine to improve DeNOx performance and reduce NH3 slip. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2008, 25, 1017–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Risi, A.; Donateo, T.; Sciolti, A.; Calò, M.; Gaballo, M.R. A New Energy-Based Model for the Prediction of Primary Atomization of Urea-Water Sprays; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Shahariar, G.M.H.; Lim, O.T. Investigation of urea aqueous solution injection, droplet breakup and urea decomposition of selective catalytic reduction systems. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2018, 32, 3473–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiteri, A.; Dimopoulos Eggenschwiler, P. Experimental Fluid Dynamic Investigation of Urea–Water Sprays for Diesel Selective Catalytic Reduction–DeNOx Applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 3047–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Lee, K. Spray characteristics of a urea solution injector and optimal mixer location to improve droplet uniformity and NOx conversion efficiency for selective catalytic reduction. Fuel 2014, 119, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Deng, J.; Wu, Z.; Li, L. Effect of injection parameters on spray characteristics of urea-SCR system. SAE Int. J. Engines 2013, 6, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, S.N.A.; Saito, M.; Furuhata, T.; Arai, M. Evaporation characteristics of a single aqueous urea solution droplet. In Proceedings of the ICLASS-2006, Kyoto, Japan, 27 August–1 September 2006. Paper ID ICLASS06-195. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.J.; Baek, S.W.; Lee, S.Y.; Kang, D.H.; Yeo, G.K. Experimental investigation on evaporation of urea-water-solution droplet for SCR applications. AIChE J. 2009, 55, 3267–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ding, H.; Ma, X.; Xu, H.; Wyszynski, M.L. Ultra-high speed imaging study of the diesel spray close to the injector tip at the initial opening stage with single injection. Appl. Energy 2016, 165, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Kim, K.; Lim, O. Experimental study on non-vaporizing spray characteristics of biodiesel-blended gasoline fuel in a constant volume chamber. Fuel Process. Technol. 2018, 178, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.Q.; Cader, T.; Schwarzkopf, J.; Okamoto, K.; Ramaprian, B. Spray angle effect during spray cooling of microelectronics: experimental measurements and comparison with inverse calculations. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2006, 26, 1788–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Ramadan, E.; Saha, K.; Li, X. Numerical Modeling of the Impingement Process of Urea-Water Solution Spray on the Heated Walls of SCR Systems; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Birkhold, F. Selektive katalytische Reduktion von Stickoxiden in Kraftfahrzeugen: Untersuchung der Einspritzung von Harnstoffwasserlösung; Shaker: Aachen, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Senecal, P.K.; Pomraning, E.; Richards, K.J.; Som, S. An investigation of Grid Convergence for Spray Simulations Using an LES Turbulence Model; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Drennan, S.; Kumar, G.; Quan, S.; Wang, M. Application of Automatic Meshing to Urea-Water Injection Simulation for Engine Aftertreatment; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, C.; Gosman, A.D. Development of Methodology for Spray Impingement Simulation; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, C.X.; Rusche, H.; Gosman, A.D. Modeling of gasoline spray impingement. Atomization Sprays 2002, 12, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhnke, D. Spray/Wall Interaction Modelling by Dimensionless Data Analysis; Shaker: Aachen, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Dan, H.J.; Lee, J.S. Modeling and measurement of boiling point elevation during water vaporization from aqueous urea for SCR applications. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2016, 30, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.; Lauer, T.; Mayer, M.; Pierson, S. Optical and numerical investigations on the mechanisms of deposit formation in SCR systems. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2014, 7, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.; Bitto, R.; Lauer, T.; Krenn, C.; Tauer, J.; Pessl, G. Impact of the Turbulence Model and Numerical Approach on the Prediction of the Ammonia Homogenization in an Automotive SCR System. SAE Int. J. Engines 2012, 5, 1443–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, L.; Cao, L.; Wu, Z. A Study on the Factors Affecting Heated Wall Impinging Characteristics of SCR Spray; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Shahariar, G.M.H.; Wardana, M.K.A.; Lim, O.T. A study on post impingement effects of urea-water solution spray on the heated wall of automotive SCR systems. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 133, 12025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaynor, P.D.; Reid, B.A.; Hargrave, G.K.; Lockyer, T.O.; Wilson, J. An experimental investigation into DEF dosing strategies for heavy duty vehicle applications. SAE Int. J. Engines 2015, 8, 1196–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowe, C.T.; Schwarzkopf, J.D.; Sommerfeld, M.; Tsuji, Y. Multiphase Flows With Droplets and Particles; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardin, J.D.; Mudawar, I. The Leidenfrost point: experimental study and assessment of existing models. J. Heat Transfer 1999, 121, 894–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunand, P.; Castanet, G.; Gradeck, M.; Maillet, D.; Lemoine, F. Energy balance of droplets impinging onto a wall heated above the Leidenfrost temperature. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2013, 44, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Eggenschwiler, P.D.; Rentsch, D.; Curto, F.; Boulouchos, K. Characterization of the urea-water spray impingement in diesel selective catalytic reduction systems. Appl. Energy 2017, 205, 964–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
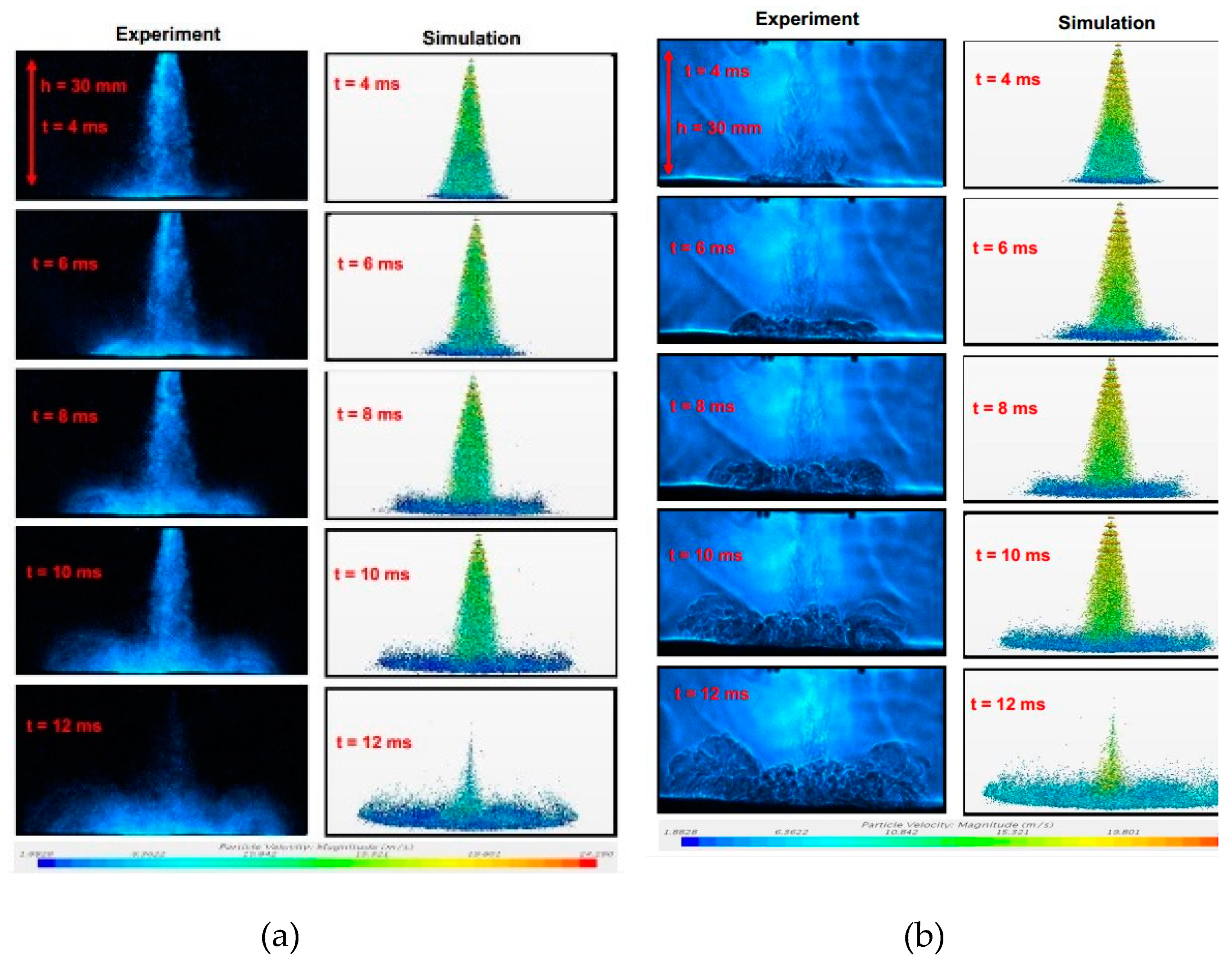
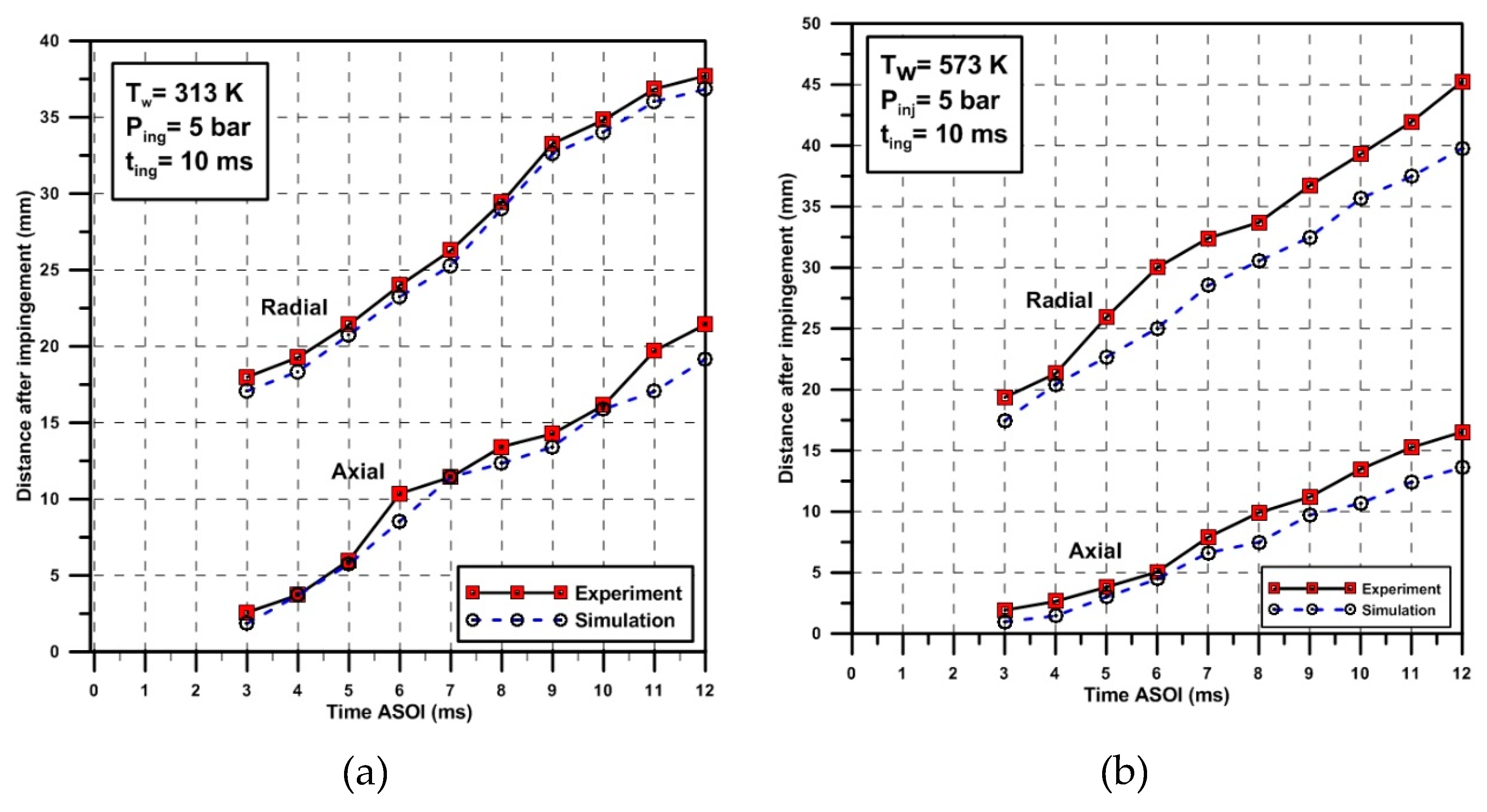
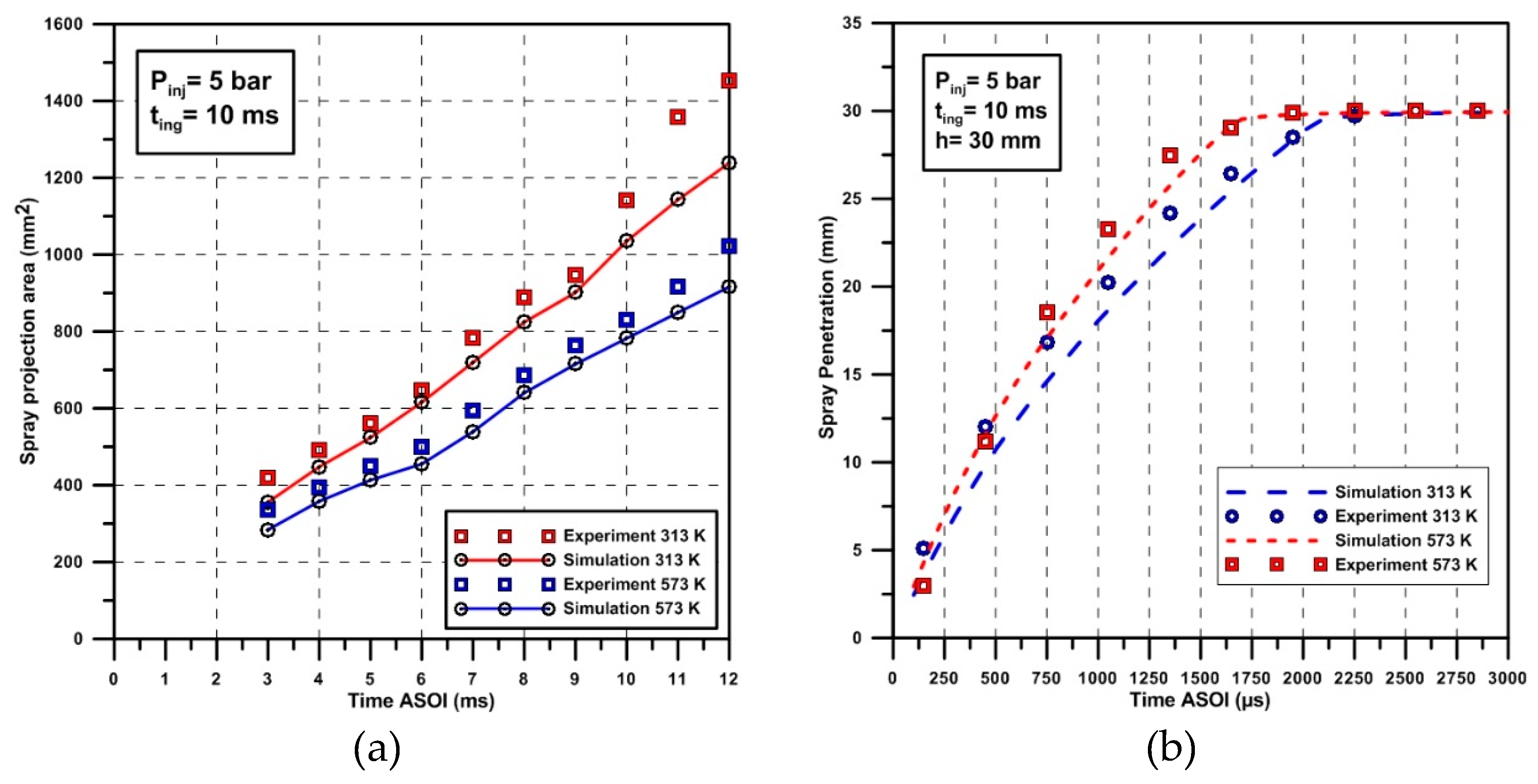
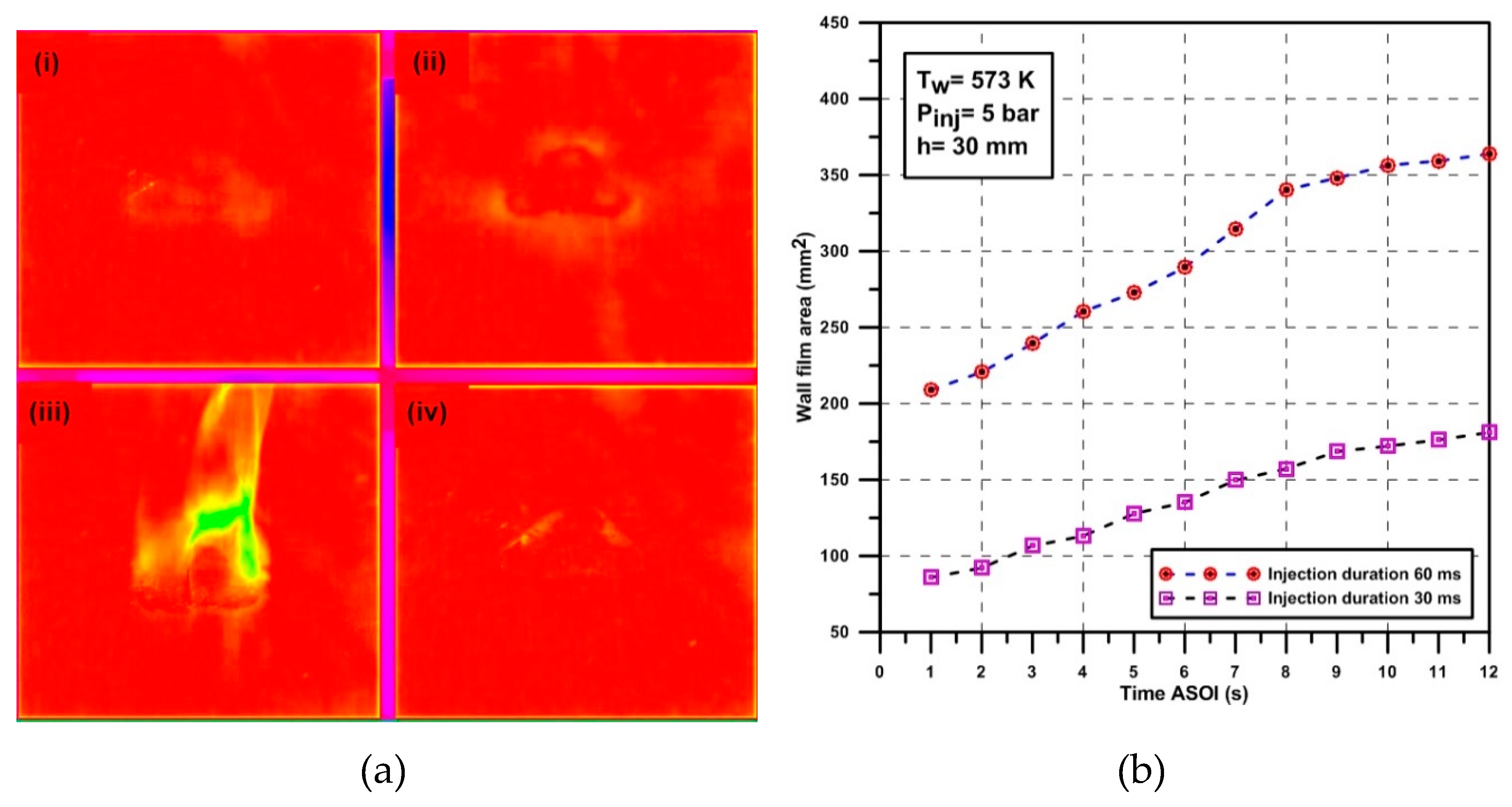

| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Frame rate | 7500 | fps |
| Resolution | 512 × 512 | Pixels |
| Aperture | f/2.8 | - |
| Shutter speed | 1/300,000 | Seconds |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Working fluid | UWS (32.5% urea by weight) |
| Injection duration, ting | 10, 30, 60 ms |
| Injection pressure, Ping | 5 bar |
| Injection rate, Ring | 40,824 kg/h |
| Nozzle diameter, d | 0.12 mm |
| Number of nozzle holes, n | 3 |
| Injection height, h | 30 mm |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shahariar, G.M.H.; Lim, O.T. A Study on Urea-Water Solution Spray-Wall Impingement Process and Solid Deposit Formation in Urea-SCR de-NOx System. Energies 2019, 12, 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12010125
Shahariar GMH, Lim OT. A Study on Urea-Water Solution Spray-Wall Impingement Process and Solid Deposit Formation in Urea-SCR de-NOx System. Energies. 2019; 12(1):125. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12010125
Chicago/Turabian StyleShahariar, G.M. Hasan, and Ock Taeck Lim. 2019. "A Study on Urea-Water Solution Spray-Wall Impingement Process and Solid Deposit Formation in Urea-SCR de-NOx System" Energies 12, no. 1: 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12010125
APA StyleShahariar, G. M. H., & Lim, O. T. (2019). A Study on Urea-Water Solution Spray-Wall Impingement Process and Solid Deposit Formation in Urea-SCR de-NOx System. Energies, 12(1), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12010125




