Combined Ball Milling and Ethanol Organosolv Pretreatment to Improve the Enzymatic Digestibility of Three Types of Herbaceous Biomass
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Combined Physicochemical Pretreatment
2.3. Enzymatic Digestibility
2.4. Compositional Analysis of the Solid and Liquid Phases
3. Results
3.1. Compositions of Herbaceous Biomasses Used in This Study
3.2. Composition Changes after Combined Physicochemical Pretreatment
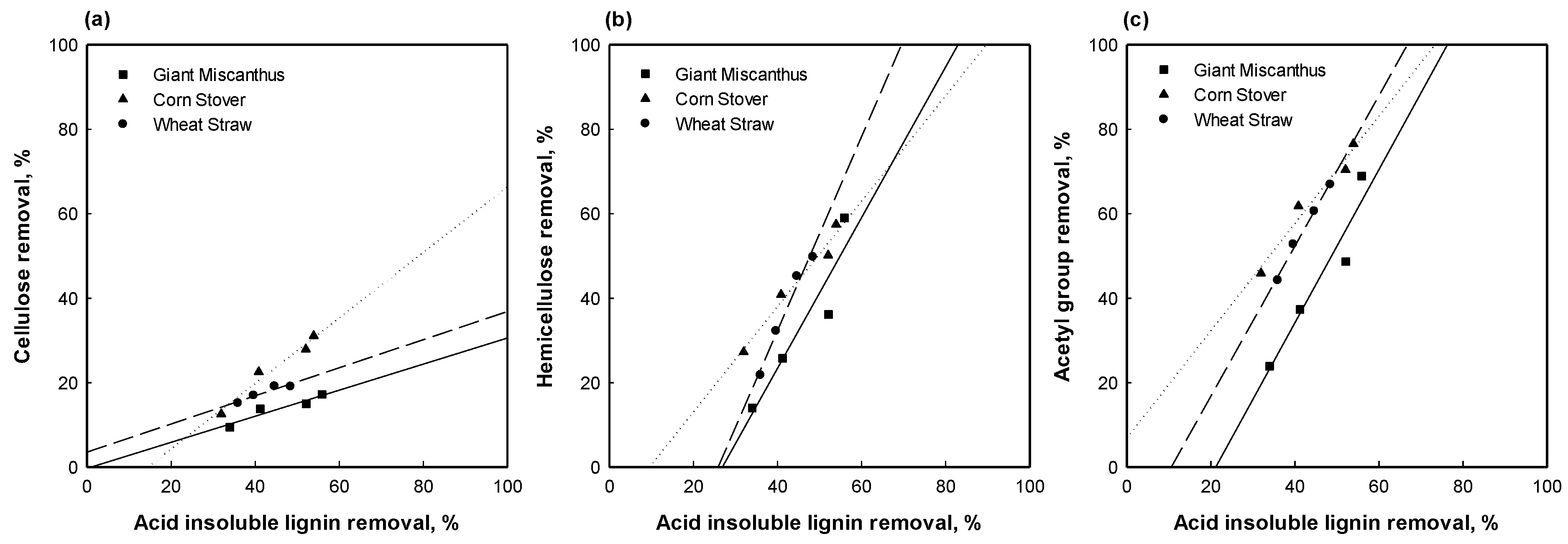
3.3. Correlation of Lignin Removal with the Removal of Other Compounds
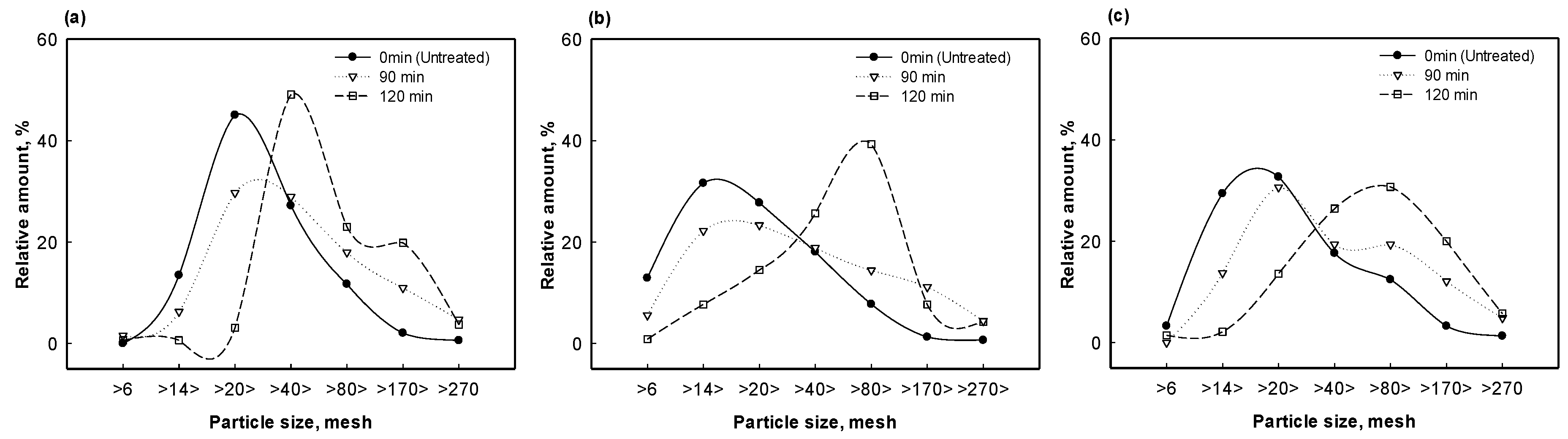
3.4. Changes in Biomass Particle Size
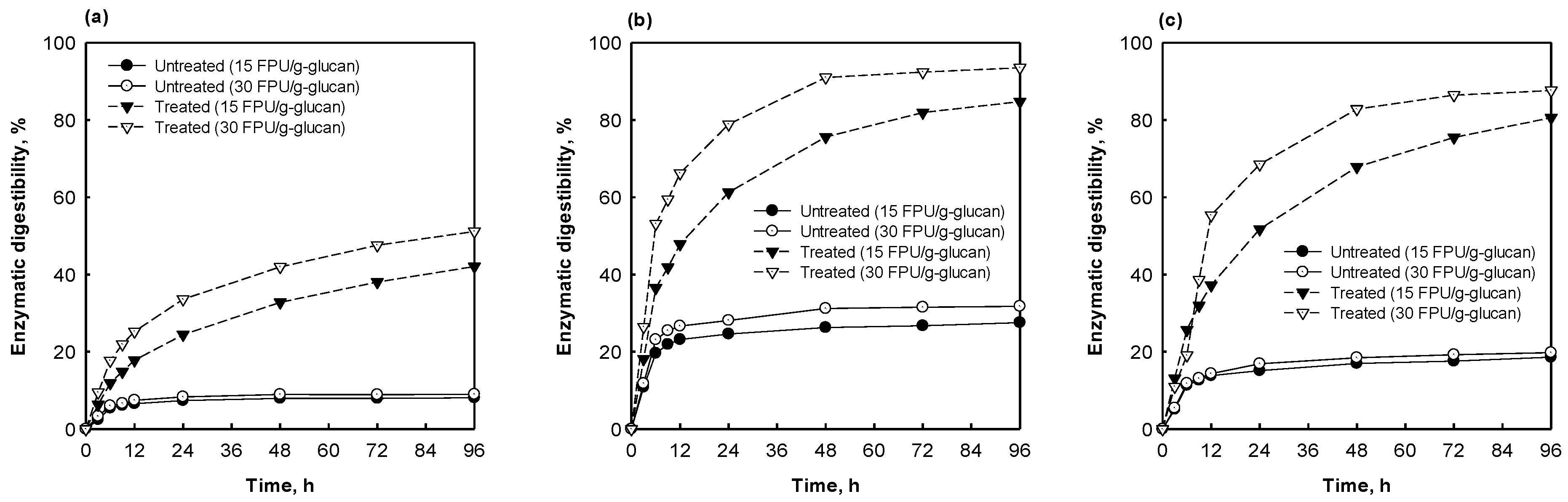
3.5. Enzymatic Digestibility of Pretreated Herbaceous Biomasses
3.6. Composition of Recovered Lignin from the Black Liquor
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wettstein, S.G.; Alonso, D.M.; Gürbüz, E.I.; Dumesic, J.A. A roadmap for conversion of lignocellulosic biomass to chemicals and fuels. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2012, 1, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R.A. Green and sustainable manufacture of chemicals from biomass: State of the art. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 950–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Cheng, J. Hydrolysis of lignocellulosic materials for ethanol production: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 83, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Barrett, D.M.; Delwiche, M.J.; Stroeve, P. Methods for pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for efficient hydrolysis and biofuel production. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 3713–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazacu, G.; Capraru, M.; Popa, V.I. Advances concerning lignin utilization in new materials. In Advances in Natural Polymers; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 255–312. [Google Scholar]
- Menon, V.; Rao, M. Trends in bioconversion of lignocellulose: Biofuels, platform chemicals & biorefinery concept. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2012, 38, 522–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherzadeh, M.J.; Karimi, K. Pretreatment of lignocellulosic wastes to improve ethanol and biogas production: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2008, 9, 1621–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakaria, M.R.; Hirata, S.; Hassan, M.A. Combined pretreatment using alkaline hydrothermal and ball milling to enhance enzymatic hydrolysis of oil palm mesocarp fiber. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 169, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.M.; Dien, B.S.; Tumbleson, M.E.; Rausch, K.D.; Singh, V. Improvement of sugar yields from corn stover using sequential hot water pretreatment and disk milling. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 216, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barakat, A.; Chuetor, S.; Monlau, F.; Solhy, A.; Rouau, X. Eco-friendly dry chemo-mechanical pretreatments of lignocellulosic biomass: Impact on energy and yield of the enzymatic hydrolysis. Appl. Energy 2014, 113, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Long, J.; Wang, T.; Shu, R.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, L. Process intensification effect of ball milling on the hydrothermal pretreatment for corn straw enzymolysis. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 101, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, A.; Ren, J.; Wang, W.; Li, H.; Lin, Q.; Yan, Y.; Sun, R.; Liu, G. Production of xylo-sugars from corncob by oxalic acid-assisted ball milling and microwave-induced hydrothermal treatments. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 79, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, D.; Fang, G.; Yang, Q.; Han, S.; Deng, Y.; Shen, K.; Lin, Y. Enhancement of eucalypt chips’ enzymolysis efficiency by a combination method of alkali impregnation and refining pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 150, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, A.S.; Inoue, H.; Endo, T.; Yano, S.; Bon, E.P.S. Milling pretreatment of sugarcane bagasse and straw for enzymatic hydrolysis and ethanol fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 7402–7409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, H.; Yano, S.; Endo, T.; Sakaki, T.; Sawayama, S. Combining hot-compressed water and ball milling pretreatments to improve the efficiency of the enzymatic hydrolysis of eucalyptus. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2008, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Huang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Yan, L.; Chen, J. Ball milling pretreatment of corn stover for enhancing the efficiency of enzymatic hydrolysis. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 162, 1872–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, G.G.D.; Couturier, M.; Berrin, J.-G.; Buléon, A.; Rouau, X. Effects of grinding processes on enzymatic degradation of wheat straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 103, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kwon, J.H.; Kim, T.H.; Choi, W. Impact of planetary ball mills on corn stover characteristics and enzymatic digestibility depending on grinding ball properties. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 241, 1094–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Pei, Z.; Wang, D. Organic solvent pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for biofuels and biochemicals: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 199, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Arato, C.; Gilkes, N.; Gregg, D.; Mabee, W.; Pye, K.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Saddler, J. Biorefining of softwoods using ethanol organosolv pulping: Preliminary evaluation of process streams for manufacture of fuel-grade ethanol and co-products. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2005, 90, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Cheng, K.; Liu, D. Organosolv pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for enzymatic hydrolysis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 82, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakzeski, J.; Bruijnincx, P.C.A.; Jongerius, A.L.; Weckhuysen, B.M. The catalytic valorization of lignin for the production of renewable chemicals. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 3552–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Torre, M.; Moral, A.; Hernández, M.; Cabeza, E.; Tijero, A. Organosolv lignin for biofuel. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 45, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, V.S.; Holtzapple, M.T. Fundamental factors affecting biomass enzymatic reactivity. In Twenty-first Symposium on Biotechnology for Fuels and Chemicals; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2000; pp. 5–37. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.; Yu, A.H.C.; Saddler, J.N. Evaluation of cellulase recycling strategies for the hydrolysis of lignocellulosic substrates. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1995, 45, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öhgren, K.; Bura, R.; Saddler, J.; Zacchi, G. Effect of hemicellulose and lignin removal on enzymatic hydrolysis of steam pretreated corn stover. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 2503–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Miao, S.; Su, Z.; Wang, P. Temperature sensitivity of cellulase adsorption on lignin and its impact on enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 166, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, B.-W.; Kim, H.-Y.; Park, N.; Lee, S.-M.; Yeo, H.; Choi, I.-G. Organosolv pretreatment of Liriodendron tulipifera and simultaneous saccharification and fermentation for bioethanol production. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 1833–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, A.; De Vries, H.; Rouau, X. Dry fractionation process as an important step in current and future lignocellulose biorefineries: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 134, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, A.K.; Chaney, K.; Crook, M.; Humphries, A.C. Alkaline pre-treatment of oilseed rape straw for bioethanol production: Evaluation of glucose yield and pre-treatment energy consumption. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 6547–6553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-H.; Teramoto, Y.; Endo, T. Enzymatic saccharification of woody biomass micro/nanofibrillated by continuous extrusion process I—Effect of additives with cellulose affinity. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hideno, A.; Inoue, H.; Tsukahara, K.; Fujimoto, S.; Minowa, T.; Inoue, S.; Endo, T.; Sawayama, S. Wet disk milling pretreatment without sulfuric acid for enzymatic hydrolysis of rice straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 2706–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Pan, X.J. Woody biomass pretreatment for cellulosic ethanol production: Technology and energy consumption evaluation. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 4992–5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selig, M.; Weiss, N.; Ji, Y. Enzymatic Saccharification of Lignocellulosic Biomass: Laboratory Analytical Procedure; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Yan, L.; Wang, Z.; Laskar, D.D.; Swita, M.S.; Cort, J.R.; Yang, B. Characterization of lignin derived from water only and dilute acid flowthrough pretreatment of poplar wood at elevated tempeatures. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2015, 8, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sluiter, A.; Hames, B.; Ruiz, R.; Scarlata, C.; Sluiter, J.; Templeton, D.; Crocker, D. Determination of Structural Carbohydrates and Lignin in Biomass: Laboratory Analytical Procedure; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sluiter, A.; Hames, B.; Ruiz, R.; Scarlata, C.; Sluiter, J.; Templeton, D. Determination of Sugars, Byproducts, and Degradation Products in Liquid Fraction Process Samples: Laboratory Analytical Procedure; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sluiter, A.; Hames, B.; Ruiz, R.; Scarlata, C.; Sluiter, J.; Templeton, D. Determination of Ash in Biomass: Laboratory Analytical Procedure; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- El Hage, R.; Chrusciel, L.; Desharnais, L.; Brosse, N. Effect of autohydrolysis of Miscanthus x giganteus on lignin structure and organosolv delignification. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 9321–9329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huijgen, W.J.J.; Smit, A.T.; De Wild, P.J.; Den Uil, H. Fractionation of wheat straw by prehydrolysis, organosolv delignification and enzymatic hydrolysis for production of sugars and lignin. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 114, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffries, T.W. Biodegradation of lignin-carbohydrate complexes. In Physiology of Biodegradative Microorganisms; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1991; pp. 163–176. [Google Scholar]
- Zadeh, E.M.; O’Keefe, S.F.; Kim, Y.-T. Utilization of lignin in biopolymeric packaging films. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 7388–7398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compositions (%) | GM | CS | WS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | Glucan | 43.77 ± 0.07 | 30.30 ± 0.26 | 31.42 ± 0.44 |
| Xylan | 21.22 ± 0.08 | 16.58 ± 0.19 | 21.38 ± 0.09 | |
| Mannan | - | 0.60 ± 0.21 | - | |
| Galactan | - | 1.53 ± 0.47 | 1.56 ± 0.14 | |
| Arabinan | 0.50 ± 0.01 | 0.82 ± 0.02 | 1.00 ± 0.02 | |
| Sub Total | 65.49 | 49.83 | 55.36 | |
| Lignin | Acid soluble | 0.96 ± 0.01 | 1.47 ± 0.03 | 1.11 ± 0.02 |
| Acid insoluble | 19.55 ± 0.01 | 12.38 ± 0.09 | 13.47 ± 0.24 | |
| Sub Total | 20.51 | 13.85 | 14.58 | |
| Extractive | Water | 4.96 ± 0.71 | 21.14 ± 0.12 | 17.11 ± 0.33 |
| Ethanol | 1.47 ± 0.11 | 3.71 ± 0.22 | 2.77 ± 0.27 | |
| Sub Total | 6.43 | 24.85 | 19.88 | |
| Acetyl group | 3.88 ± 0.02 | 2.76 ± 0.06 | 3.02 ± 0.06 | |
| Ash | 2.18 ± 0.03 | 7.92 ± 0.05 | 7.36 ± 0.10 | |
| Total | 98.49 | 99.21 | 100.2 | |
| Time (min) | Solid Remaining (%) | Glucan (%) | XMG 1 (%) | Acetyl Group (%) | AIL (%) | AIL Removal Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | 100 | 43.77 | 21.22 | 3.88 | 19.53 | |
| 30 | 79.25 | 50.01 | 23.03 | 3.73 | 16.28 | 33.95 |
| 60 | 72.29 | 52.22 | 21.79 | 3.36 | 15.89 | 41.18 |
| 90 | 65.41 | 56.90 | 20.72 | 3.04 | 14.30 | 52.11 |
| 120 | 57.44 | 63.09 | 15.14 | 2.10 | 15.00 | 55.89 |
| Time (min) | Solid Remaining (%) | Glucan (%) | XMG (%) | Acetyl Group (%) | AIL (%) | AIL Removal Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | 100 | 30.30 | 18.71 | 2.76 | 12.23 | |
| 30 | 56.98 | 46.51 | 23.89 | 2.62 | 14.61 | 31.92 |
| 60 | 48.32 | 48.58 | 22.91 | 2.18 | 14.97 | 40.84 |
| 90 | 42.24 | 51.73 | 22.08 | 1.93 | 13.89 | 52.04 |
| 120 | 39.28 | 53.16 | 20.27 | 1.65 | 14.35 | 53.91 |
| Time (min) | Solid Remaining (%) | Glucan (%) | XMG (%) | Acetyl Group (%) | AIL (%) | AIL Removal Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | 100 | 31.42 | 22.94 | 3.02 | 14.61 | |
| 30 | 64.47 | 41.36 | 27.83 | 2.61 | 14.53 | 35.90 |
| 60 | 58.07 | 44.93 | 26.76 | 2.45 | 15.19 | 39.62 |
| 90 | 52.06 | 48.78 | 24.13 | 2.29 | 15.55 | 44.58 |
| 120 | 50.70 | 50.15 | 22.71 | 1.97 | 14.87 | 48.39 |
| Biomass | Time (min) | AIL (%) | ASL (%) | AIA (%) | Glucan (%) | XMG (%) | Acetyl Group (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GM | 30 | 55.62 | 1.99 | 5.39 | 14.57 | 12.60 | 2.59 |
| 60 | 59.02 | 1.85 | 5.41 | 10.74 | 13.00 | 2.65 | |
| 90 | 62.27 | 2.06 | 6.57 | 11.34 | 13.96 | 2.71 | |
| 120 | 77.94 | 2.32 | 1.58 | 2.66 | 11.87 | 2.73 | |
| CS | 30 | 59.37 | 3.07 | 2.90 | 5.83 | 5.56 | 1.14 |
| 60 | 64.28 | 3.29 | 2.34 | 5.76 | 6.23 | 1.37 | |
| 90 | 56.34 | 3.78 | 2.32 | 6.14 | 7.28 | 1.42 | |
| 120 | 67.81 | 3.48 | 2.39 | 4.68 | 6.28 | 1.24 | |
| WS | 30 | 50.91 | 3.65 | 2.97 | 10.47 | 12.24 | 1.93 |
| 60 | 54.42 | 2.78 | 4.30 | 10.10 | 11.44 | 1.69 | |
| 90 | 55.38 | 3.03 | 3.22 | 8.16 | 12.97 | 1.97 | |
| 120 | 61.66 | 3.20 | 2.32 | 5.94 | 12.24 | 1.90 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.J.; Um, B.H.; Im, D.J.; Lee, J.H.; Oh, K.K. Combined Ball Milling and Ethanol Organosolv Pretreatment to Improve the Enzymatic Digestibility of Three Types of Herbaceous Biomass. Energies 2018, 11, 2457. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11092457
Kim SJ, Um BH, Im DJ, Lee JH, Oh KK. Combined Ball Milling and Ethanol Organosolv Pretreatment to Improve the Enzymatic Digestibility of Three Types of Herbaceous Biomass. Energies. 2018; 11(9):2457. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11092457
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Seong Ju, Byung Hwan Um, Dong Joong Im, Jin Hyung Lee, and Kyeong Keun Oh. 2018. "Combined Ball Milling and Ethanol Organosolv Pretreatment to Improve the Enzymatic Digestibility of Three Types of Herbaceous Biomass" Energies 11, no. 9: 2457. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11092457
APA StyleKim, S. J., Um, B. H., Im, D. J., Lee, J. H., & Oh, K. K. (2018). Combined Ball Milling and Ethanol Organosolv Pretreatment to Improve the Enzymatic Digestibility of Three Types of Herbaceous Biomass. Energies, 11(9), 2457. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11092457






