Combustion of Flax Shives, Beech Wood, Pure Woody Pseudo-Components and Their Chars: A Thermal and Kinetic Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Char
2.3. Thermogravimetric Experiments
2.4. Kinetic Modelling
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thermogravimetric and Differential Thermogravimetic (DTG) Characteristic Curves
3.1.1. Raw Materials Combustion
3.1.2. Char Combustion
3.2. Thermal Analysis
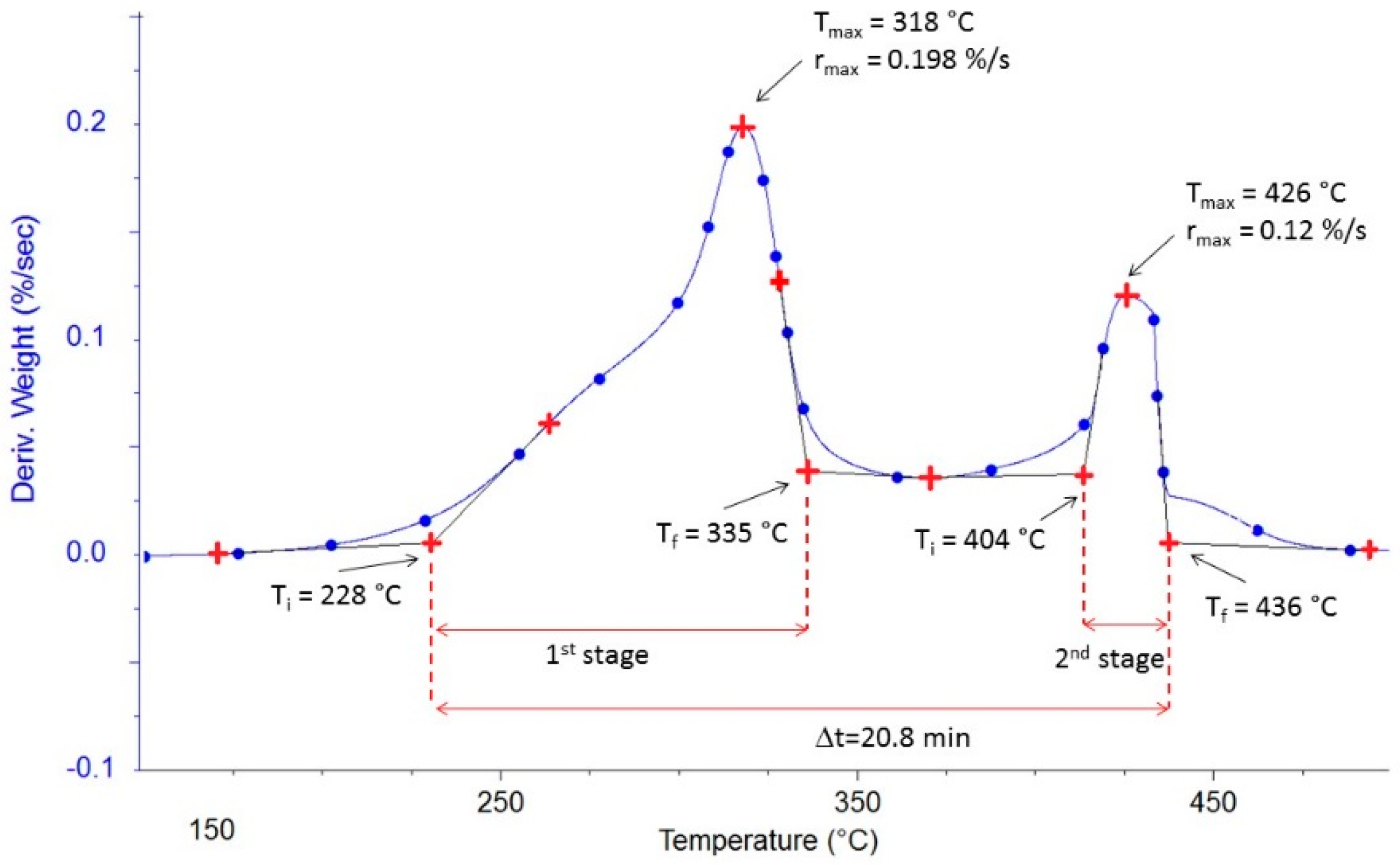
3.2.1. Ignition and Final Temperatures of Combustion Reaction
3.2.2. Burnout Time
3.2.3. Maximum Temperature
3.2.4. Maximum Rate
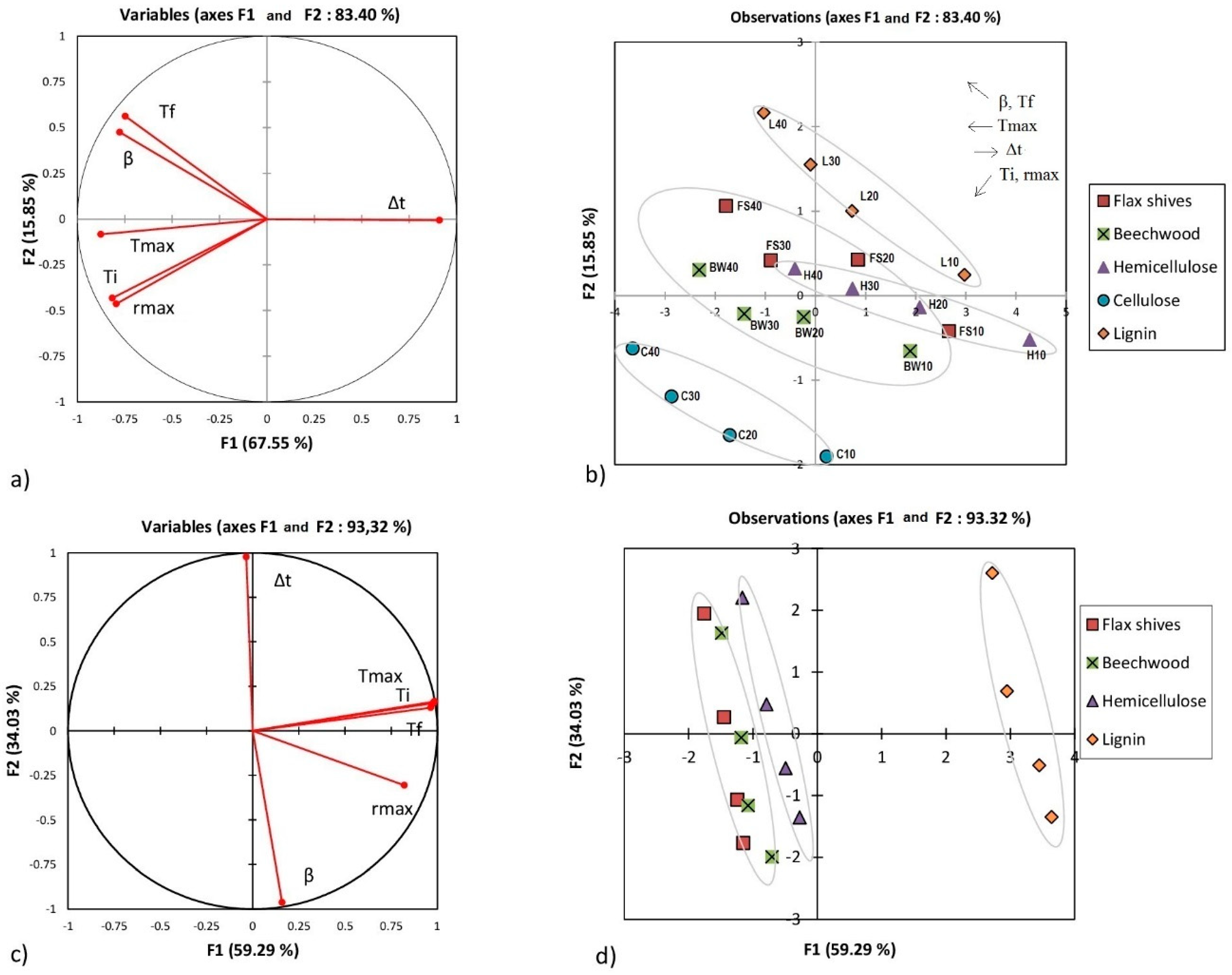
3.3. Principal Component Analysis
- Regarding the first stage of raw materials combustion:
- -
- A strong positive dependence between Ti, Tmax, and rmax.
- -
- A strong positive dependence between β and Tf.
- -
- Opposite evolution between Δt and the rest of the parameters.
- -
- Overall, there is no dependence between Ti, Tmax, and rmax.
- Regarding the second stage of raw materials combustion:
- -
- A clear opposite trend between Δt and β.
- -
- Δt and β seemed to be unrelated to Ti, Tf, Tmax, and rmax during this stage.
- -
- A strong positive dependence between Ti, Tmax, and Tf.
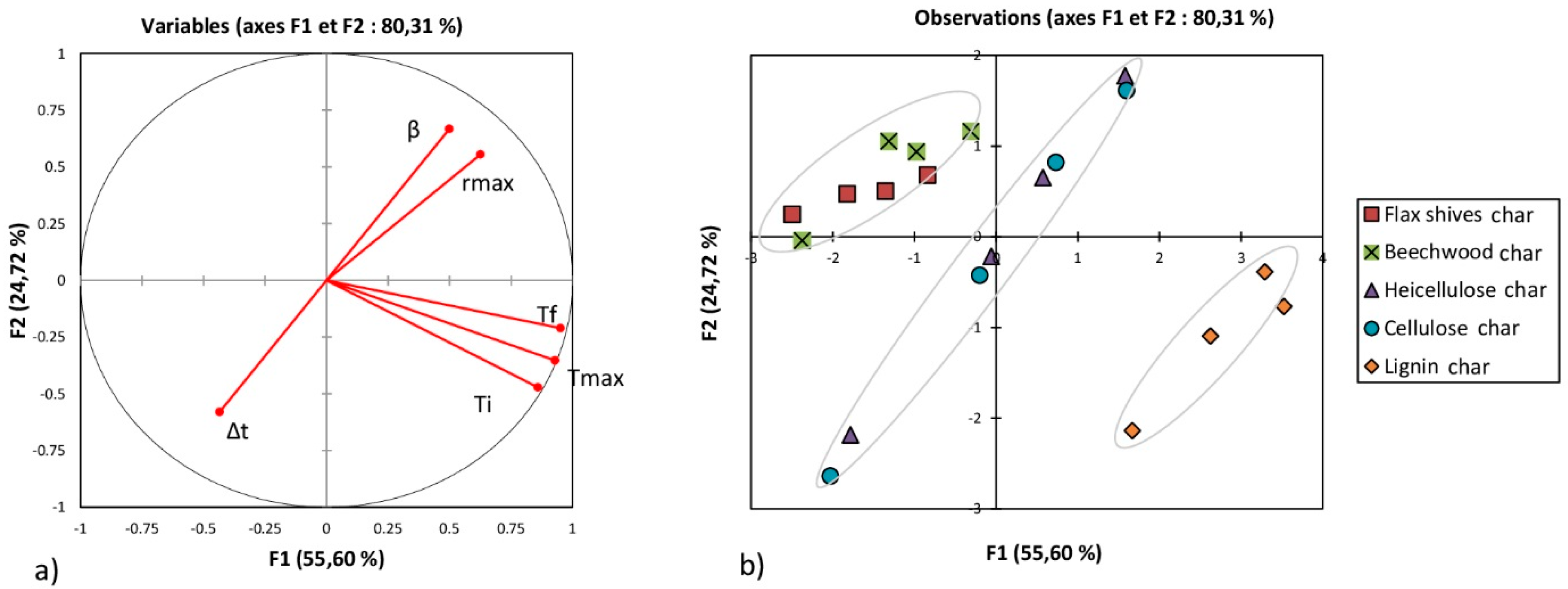
- Regarding the combustion of chars:
- -
- A strong positive dependence between Ti, Tmax, and Tf.
- -
- A strong positive dependence between β and rmax.
- -
- Surprisingly, no characteristic temperature seemed dependent on β.
3.4. Mechanism and Kinetic Parameters of Combustion
3.4.1. Mechanism
3.4.2. Kinetic Parameters
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| A | Pre-exponential factor (s−1) |
| dX/dt | The first derivative of conversion rate with respect to time |
| DTG | Differential thermogravimetry |
| Ea | Activation energy (kJ·mol−1) |
| mf | Final mass (kg) |
| mi | Initial mass (kg) |
| mt | Mass at temperature T (kg) |
| n | Reaction order (-) |
| R | Gas constant (8.314 J·K−1·mol−1) |
| R² | Correlation coefficient (-) |
| T | Temperature (K) |
| Tf | Final temperature (K) |
| TG | Thermogravimetry |
| TGA | Thermogravimetry analysis |
| Ti | Ignition temperature (K) |
| X | Conversion degree (-) |
| Greek symbols | |
| β | Heating rate (K·min−1) |
References
- International Energy Agency. Available online: http://www.iea.org/ (accessed on 23 March 2017).
- Nunes, L.J.R.; Matias, J.C.O.; Catalão, J.P.S. Biomass in the generation of electricity in Portugal: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 71, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.M.; Lea-Langton, A.R.; Ma, L.; Pourkashanian, M.; Williams, A. Combustion of Solid Biomass: Classification of Fuels. Pollutants Generated by the Combustion of Solid Biomass Fuels; Springer: London, UK, 2014; pp. 9–24. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-1-4471-6437-1_2 (accessed on 29 July 2018).
- van den Broek, R.; Faaij, A.; van Wijk, A. Biomass combustion for power generation. Biomass Bioenergy 1996, 11, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.M.; Lea-Langton, A.R.; Ma, L.; Pourkashanian, M.; Williams, A. Pollutants Generated by the Combustion of Solid Biomass Fuels; Springer: London, UK, 2014; Available online: https://www.springer.com/gb/book/9781447164364 (accessed on 29 July 2018).
- Sannigrahi, P.; Ragauskas, A.J.; Tuskan, G.A. Poplar as a feedstock for biofuels: A review of compositional characteristics. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefin. 2010, 4, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheer, A. Thermal Decomposition Mechanisms of Lignin Model Compounds: From Phenol to Vanillin. Physics Graduate Thesis & Dissertations. 2011. Available online: https://scholar.colorado.edu/phys_gradetds/55 (accessed on 15 August 2018).
- Yu, J.; Paterson, N.; Blamey, J.; Millan, M. Cellulose, xylan and lignin interactions during pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass. Fuel 2017, 191, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosoya, T.; Kawamoto, H.; Saka, S. Cellulose–hemicellulose and cellulose–lignin interactions in wood pyrolysis at gasification temperature. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2007, 80, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Matsumura, Y. Gasification of Cellulose, Xylan, and Lignin Mixtures in Supercritical Water. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2001, 40, 5469–5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gani, A.; Naruse, I. Effect of cellulose and lignin content on pyrolysis and combustion characteristics for several types of biomass. Renew. Energy 2007, 32, 649–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-García, S.; Luo, L.; Moreira, M.T.; Feijoo, G.; Huppes, G. Life cycle assessment of flax shives derived second generation ethanol fueled automobiles in Spain. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 1922–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daylan, B.; Ciliz, N. Life cycle assessment and environmental life cycle costing analysis of lignocellulosic bioethanol as an alternative transportation fuel. Renew. Energy 2016, 89, 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi Hamedani, S.; Villarini, M.; Colantoni, A.; Moretti, M.; Bocci, E. Life Cycle Performance of Hydrogen Production via Agro-Industrial Residue Gasification—A Small Scale Power Plant Study. Energies 2018, 11, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassner, M.; Maréchal, F. Thermodynamic comparison of the FICFB and Viking gasification concepts. Energy 2009, 34, 1744–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, K.; Kumar, A.; Patil, K.; Bellmer, D.; Wang, D.; Yuan, W.; Huhnke, R.L. Effects of Biomass Feedstocks and Gasification Conditions on the Physiochemical Properties of Char. Energies 2013, 6, 3972–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guizani, C.; Jeguirim, M.; Valin, S.; Limousy, L.; Salvador, S. Biomass Chars: The Effects of Pyrolysis Conditions on Their Morphology, Structure, Chemical Properties and Reactivity. Energies 2017, 10, 796. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Di Blasi, C. Modeling chemical and physical processes of wood and biomass pyrolysis. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2008, 34, 47–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El may, Y.; Jeguirim, M.; Dorge, S.; Trouvé, G.; Said, R. Study on the thermal behavior of different date palm residues: Characterization and devolatilization kinetics under inert and oxidative atmospheres. Energy 2012, 44, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia Torrent, J.; Fernandez Anez, N.; Medic Pejic, L.; Montenegro Mateos, L. Assessment of self-ignition risks of solid biofuels by thermal analysis. Fuel 2015, 143, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, M.V.; Casal, D.; Pevida, C.; Pis, J.J.; Rubiera, F. Thermal behaviour and kinetics of coal/biomass blends during co-combustion. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 5601–5608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kastanaki, E.; Vamvuka, D. A comparative reactivity and kinetic study on the combustion of coal–biomass char blends. Fuel 2006, 85, 1186–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haykırı-Açma, H. Combustion characteristics of different biomass materials. Energy Convers. Manag. 2003, 44, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Lin et le Chanvre Européen. Available online: http://www.europeanflax.com/ (accessed on 18 July 2018).
- Van de Velden, M.; Baeyens, J.; Brems, A.; Janssens, B.; Dewil, R. Fundamentals, kinetics and endothermicity of the biomass pyrolysis reaction. Renew. Energy 2010, 35, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohabeer, C.; Abdelouahed, L.; Marcotte, S.; Taouk, B. Comparative analysis of pyrolytic liquid products of beech wood, flax shives and woody biomass components. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2017, 127, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, R.; Pizarro, C.; Lavín, A.G.; Bueno, J.L. Biomass proximate analysis using thermogravimetry. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 139, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Channiwala, S.A.; Parikh, P.P. A unified correlation for estimating HHV of solid, liquid and gaseous fuels. Fuel 2002, 81, 1051–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdziarz, A.; Wilk, M.; Straka, R. Combustion process of torrefied wood biomass. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 127, 1339–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, B.; Karlström, O.; Backman, P.; Brink, A.; Zevenhoven, M.; Voglsam, S.; Winter, F.; Hupa, M. Mass transfer limitation in thermogravimetry of biomass gasification. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2012, 111, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelouahed, L.; Leveneur, S.; Vernieres-Hassimi, L.; Balland, L.; Taouk, B. Comparative investigation for the determination of kinetic parameters for biomass pyrolysis by thermogravimetric analysis. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 129, 1201–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lin, W.; Song, W.; Wu, X. Pyrolysis of the lignocellulose fermentation residue by fixed-bed micro reactor. Energy 2012, 43, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.E.; Catallo, W.J.; Legendre, B.L. Biomass pyrolysis kinetics: A comparative critical review with relevant agricultural residue case studies. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2011, 91, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, A.; Pizarro, C.; García, R.; Bueno, J.L.; Lavín, A.G. Determination of kinetic parameters for biomass combustion. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 216, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Maraver, A.; Perez-Jimenez, J.A.; Serrano-Bernardo, F.; Zamorano, M. Determination and comparison of combustion kinetics parameters of agricultural biomass from olive trees. Renew. Energy 2015, 83, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorulmaz, S.Y.; Atimtay, A. Investigation of Combustion Kinetics of Five Waste Wood Samples with Thermogravimetric Analysis. In Survival and Sustainability; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; p. 511. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-540-95991-5_46 (accessed on 5 July 2017).
- Islam, M.A.; Auta, M.; Kabir, G.; Hameed, B.H. A thermogravimetric analysis of the combustion kinetics of karanja (Pongamia pinnata) fruit hulls char. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coats, A.W.; Redfern, J.P. Kinetic Parameters from Thermogravimetric Data. Nature 1964, 201, 68–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damartzis, T.; Vamvuka, D.; Sfakiotakis, S.; Zabaniotou, A. Thermal degradation studies and kinetic modeling of cardoon (Cynara cardunculus) pyrolysis using thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 6230–6238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vamvuka, D.; Kastanaki, E.; Lasithiotakis, M. Devolatilization and Combustion Kinetics of Low-Rank Coal Blends from Dynamic Measurements. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2003, 42, 4732–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Long, Y.; Meng, A.; Chen, S.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y. A novel method for kinetics analysis of pyrolysis of hemicellulose, cellulose, and lignin in TGA and macro-TGA. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 26509–26516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Yuan, X.; Li, H.; Xiao, Z.; Liang, J.; Wang, H.; Wu, Z.; Chen, X.; Zeng, G. Pyrolysis and combustion kinetics of sludge–camphor pellet thermal decomposition using thermogravimetric analysis. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 106, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, S.; Daood, S.S.; Nimmo, W.; Cunliffe, A.M.; Gibbs, B.M. Thermal analysis and devolatilization kinetics of cotton stalk, sugar cane bagasse and shea meal under nitrogen and air atmospheres. Bioresour Technol. 2009, 100, 1413–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sait, H.H.; Hussain, A.; Salema, A.A.; Ani, F.N. Pyrolysis and combustion kinetics of date palm biomass using thermogravimetric analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 118, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gai, C.; Liu, Z.; Han, G.; Peng, N.; Fan, A. Combustion behavior and kinetics of low-lipid microalgae via thermogravimetric analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 181, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grønli, M.G.; Varhegyi, G.; Di Blasi, C. Thermogravimetric analysis and devolatilization kinetics of wood. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2002, 41, 4201–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhao, C.; Chen, X.; Wu, W.; Li, Y. Comparison of pulverized coal combustion in air and in O2/CO2 mixtures by thermo-gravimetric analysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2009, 85, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Yu, J.; Tahmasebi, A.; Han, Y. Pyrolysis and Combustion Behavior of Coal Gangue in O2/CO2 and O2/N2 Mixtures Using Thermogravimetric Analysis and a Drop Tube Furnace. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 2923–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Principal Component Analysis–Abdi–2010–Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Computational Statistics–Wiley Online Library. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/wics.101 (accessed on 19 July 2018).
- Dunteman, G.H. Principal Components Analysis; SAGE: Newcastle upon Tyne, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.A.; Fan, W.; Dobashi, R.; Huang, L. Kinetic modeling of thermal decomposition of natural cellulosic materials in air atmosphere. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2002, 63, 303–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorulmaz, S.Y.; Atimtay, A.T. Investigation of combustion kinetics of treated and untreated waste wood samples with thermogravimetric analysis. Fuel Process. Technol. 2009, 90, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capart, R.; Khezami, L.; Burnham, A.K. Assessment of various kinetic models for the pyrolysis of a microgranular cellulose. Thermochim. Acta 2004, 417, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyazovkin, S.; Burnham, A.K.; Criado, J.M.; Pérez-Maqueda, L.A.; Popescu, C.; Sbirrazzuoli, N. ICTAC Kinetics Committee recommendations for performing kinetic computations on thermal analysis data. Thermochim. Acta 2011, 520, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagini, E.; Lippi, F.; Petarca, L.; Tognotti, L. Devolatilization rate of biomasses and coal–biomass blends: An experimental investigation. Fuel 2002, 81, 1041–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Huang, Q. Thermogravimetric analysis and kinetics of coal/plastic blends during co-pyrolysis in nitrogen atmosphere. Fuel Process. Technol. 2008, 89, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, K.; Gökalp, I. Pyrolysis, combustion and gasification characteristics of miscanthus and sewage sludge. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 89, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Ma, H.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Ma, J. Thermal behavior and gaseous emission analysis during co-combustion of ethanol fermentation residue from food waste and coal using TG–FTIR. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2013, 99, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senneca, O. Kinetics of pyrolysis, combustion and gasification of three biomass fuels. Fuel Process. Technol. 2007, 88, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.G.; Sarkar, P.; Chakraborty, N.; Adak, A.K. Thermogravimetric assessment of combustion characteristics of blends of a coal with different biomass chars. Fuel Process. Technol. 2010, 91, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Wang, L.; Dzenis, Y.A.; Jones, D.D.; Hanna, M.A. Thermogravimetric characterization of corn stover as gasification and pyrolysis feedstock. Biomass Bioenergy 2008, 32, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurt, R.; Sun, J.-K.; Lunden, M. A Kinetic Model of Carbon Burnout in Pulverized Coal Combustion. Combust. Flame 1998, 113, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
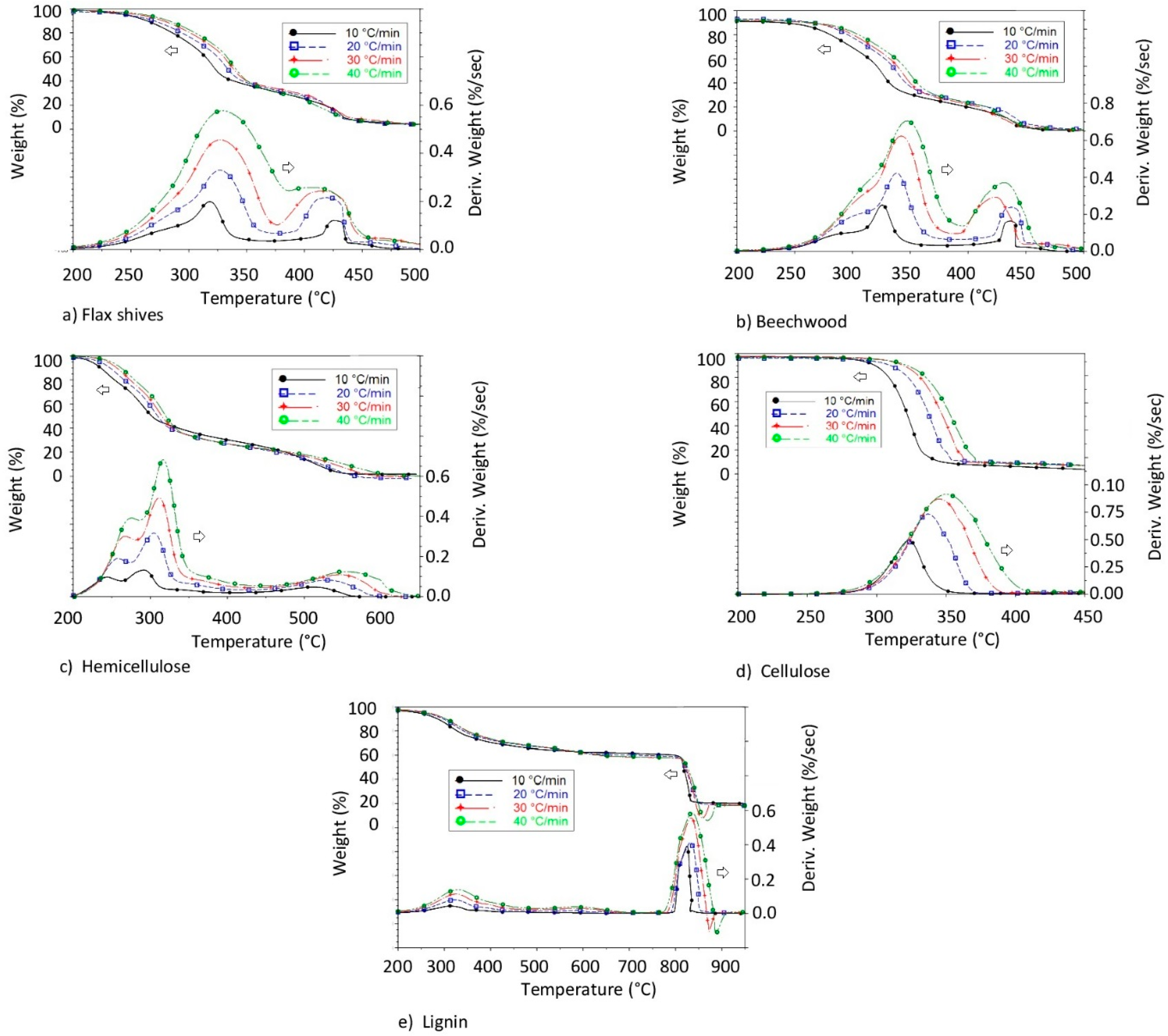
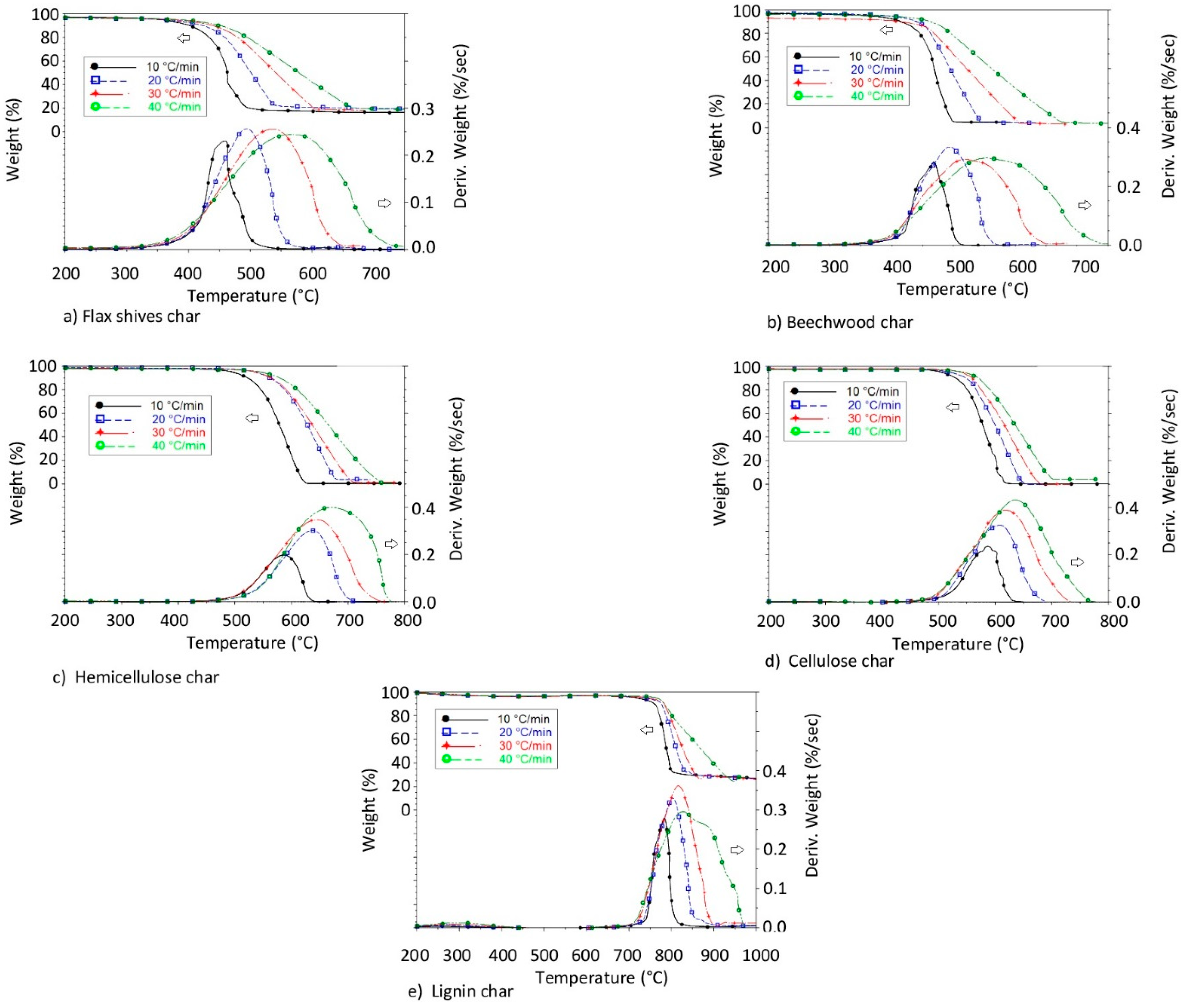
| Component | C (%) | H (%) | O (%) | N (%) | VM * (%) | FC ** (%) | Ash (%) | LHV (MJ·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flax shives | 45.7 | 5.77 | 48.12 | 0.41 | 75.47 | 21.77 | 2.76 | 17.71 |
| Beech wood | 47.38 | 6.11 | 46.51 | 0 | 80.15 | 18.92 | 0.92 | 18.91 |
| Cellulose | 41.74 | 6.08 | 52.18 | 0 | 96.26 | 3.74 | 0 | 16.34 |
| Hemicellulose | 41.47 | 6.48 | 52.05 | 0 | 80.18 | 19.57 | 0.25 | 16.72 |
| Lignin | 57.04 | 4.76 | 38.21 | 0 | 68.42 | 24.86 | 6.72 | 21.42 |
| Component | C (%) | H (%) | O (%) | N (%) | VM * (%) | FC ** (%) | Ash (%) | LHV (MJ·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flax shives char | 75.87 | 3.2 | 19.73 | 1.21 | 1.67 | 81.61 | 16.72 | 27.84 |
| Beech wood char | 78.24 | 3.13 | 18.63 | 0 | 1.59 | 93.83 | 4.58 | 28.97 |
| Cellulose char | 81.4 | 3.25 | 15.35 | 0 | 0.39 | 99.25 | 0.37 | 30.64 |
| Hemicellulose char | 71.19 | 3.2 | 25.61 | 0 | 0.74 | 98.83 | 0.43 | 25.96 |
| Lignin char | 58.04 | 2.65 | 39.3 | 0 | 2.75 | 71.67 | 25.58 | 18.78 |
| Raw Materials | First Stage | Second Stage | Δt (min) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti (°C) | Tf (°C) | Tmax (°C) | rmax (%·s−1) | Ti (°C) | Tf (°C) | Tmax (°C) | rmax (%·s−1) | ||
| Flax shives | 228 | 335 | 318 | 0.198 | 404 | 436 | 426 | 0.12 | 20.80 |
| Beech wood | 245 | 339 | 325 | 0.25 | 431 | 444 | 437 | 0.164 | 19.90 |
| Hemicellulose | 207 | 314 | 291 | 0.132 | 448 | 561 | 515 | 0.046 | 35.40 |
| Cellulose | 297 | 335 | 323 | 0.491 | - | - | - | - | 3.80 |
| Lignin | 227 | 346 | 314 | 0.043 | 806 | 837 | 823 | 0.389 | 61.00 |
| Chars | Ti (°C) | Tf (°C) | Tmax (°C) | rmax (%·s−1) | Δt (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flax shives char | 441 | 479 | 458 | 0.234 | 3.8 |
| Beech wood char | 441 | 501 | 468 | 0.282 | 6 |
| Hemicellulose char | 532 | 620 | 587 | 0.208 | 8.8 |
| Cellulose char | 513 | 627 | 587 | 0.235 | 11.4 |
| Lignin char | 748 | 801 | 784 | 0.279 | 5.3 |
| Samples | Raw Materials | Char Samples | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Stage | Second Stage | Only One Stage | ||||
| Ea (kJ·mol−1) | logA | Ea (kJ·mol−1) | logA | Ea (kJ·mol−1) | logA | |
| Flax shives | 82.54 ± 2.49 | 9.06 ± 0.51 | 66.89 ± 2.73 | 5.26 ± 0.32 | 134.90 ± 22.32 | 17.33 ± 0.63 |
| Beech wood | 99.26 ± 3.10 | 11.53 ± 0.32 | 79.51 ± 1.90 | 10.17 ± 0.67 | 151.68 ± 26.3 | 14.86 ± 6.21 |
| Hemicellulose | 172.33 ± 15.14 | 24.55 ± 2.08 | 66.08 ± 3.00 | 1.67 ± 0.08 | 180.32 ± 15.26 | 30.19 ± 1.14 |
| Cellulose | 212.21 ± 8.23 | 33.43 ± 2.30 | - | - | 218.37 ± 7.11 | 20.54 ± 2.61 |
| Lignin | 45.97 ± 0.82 | 1.36 ± 0.11 | 348.43 ± 15.57 | 25.09 ± 7.72 | 263.91 ± 32.49 | 20.54 ± 3.92 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boukaous, N.; Abdelouahed, L.; Chikhi, M.; Meniai, A.-H.; Mohabeer, C.; Bechara, T. Combustion of Flax Shives, Beech Wood, Pure Woody Pseudo-Components and Their Chars: A Thermal and Kinetic Study. Energies 2018, 11, 2146. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11082146
Boukaous N, Abdelouahed L, Chikhi M, Meniai A-H, Mohabeer C, Bechara T. Combustion of Flax Shives, Beech Wood, Pure Woody Pseudo-Components and Their Chars: A Thermal and Kinetic Study. Energies. 2018; 11(8):2146. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11082146
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoukaous, Nourelhouda, Lokmane Abdelouahed, Mustapha Chikhi, Abdeslam-Hassen Meniai, Chetna Mohabeer, and Taouk Bechara. 2018. "Combustion of Flax Shives, Beech Wood, Pure Woody Pseudo-Components and Their Chars: A Thermal and Kinetic Study" Energies 11, no. 8: 2146. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11082146
APA StyleBoukaous, N., Abdelouahed, L., Chikhi, M., Meniai, A.-H., Mohabeer, C., & Bechara, T. (2018). Combustion of Flax Shives, Beech Wood, Pure Woody Pseudo-Components and Their Chars: A Thermal and Kinetic Study. Energies, 11(8), 2146. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11082146






