Influence of Water Immersion on Pore System and Methane Desorption of Shales: A Case Study of Batu Gajah and Kroh Shale Formations in Malaysia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Shale Sample Preparation
2.1.1. Shale Samples Collection
2.1.2. Shale Samples Preparations
2.2. Pore System Characteristics
2.3. Total Organic Carbon wt % Measurement
2.4. Mineral Content
2.5. Desorption Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Total Organic Carbon wt % Content
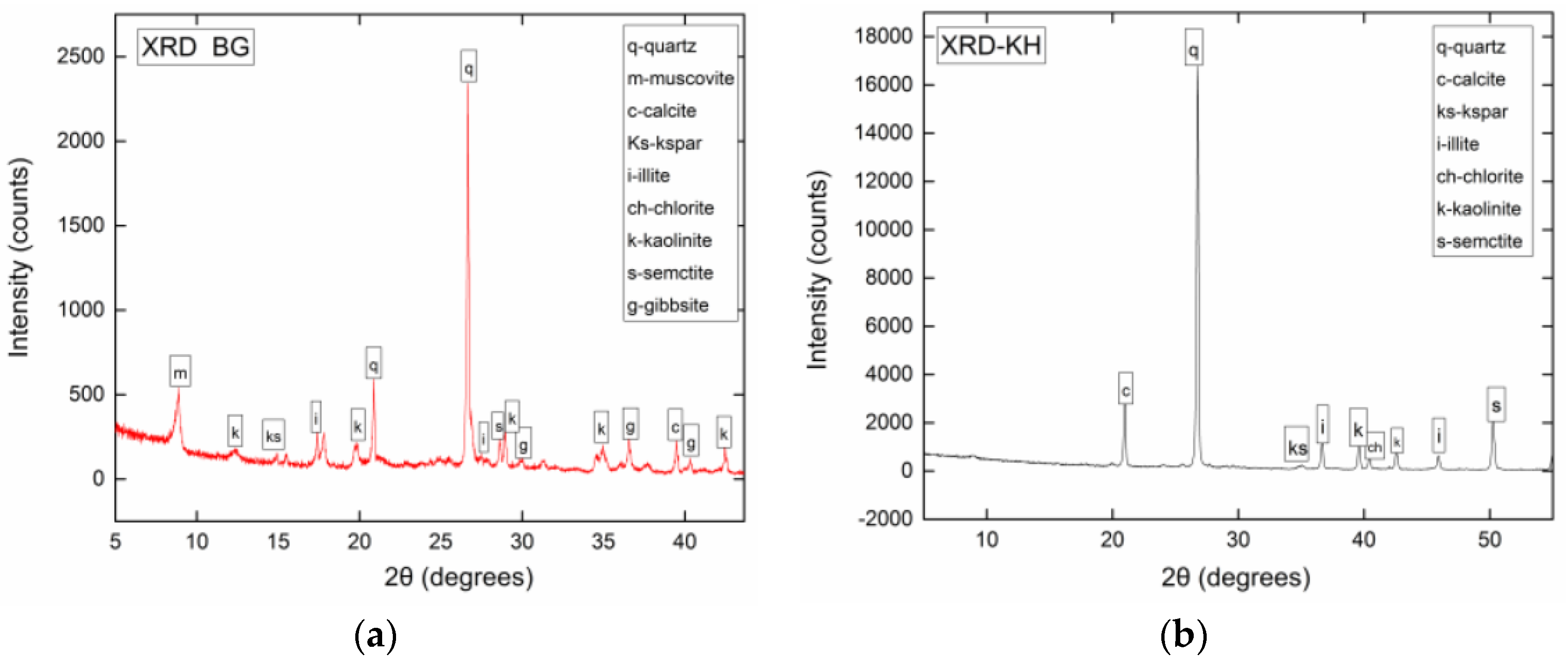
3.2. Mineralogy
3.3. Water Uptake
3.4. Pore System
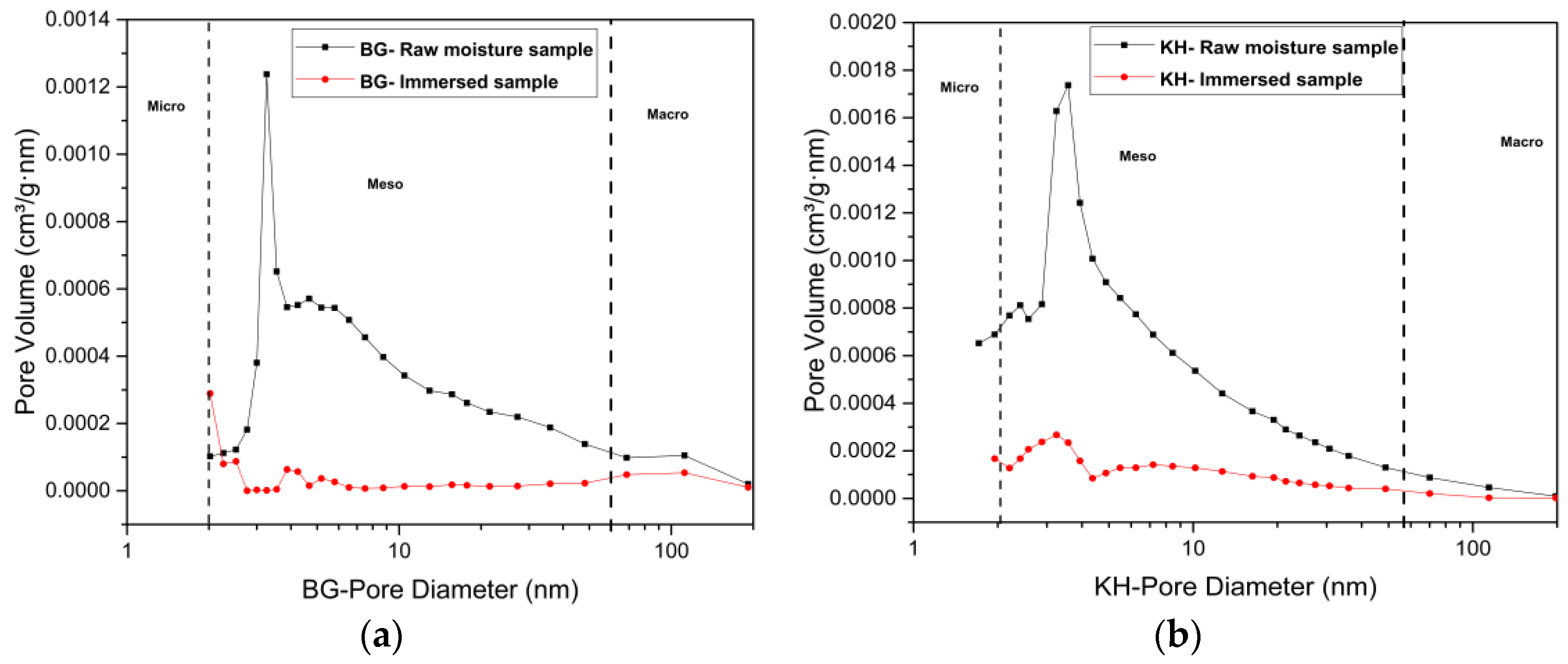
3.4.1. Low N2 Pressure Adsorption Results
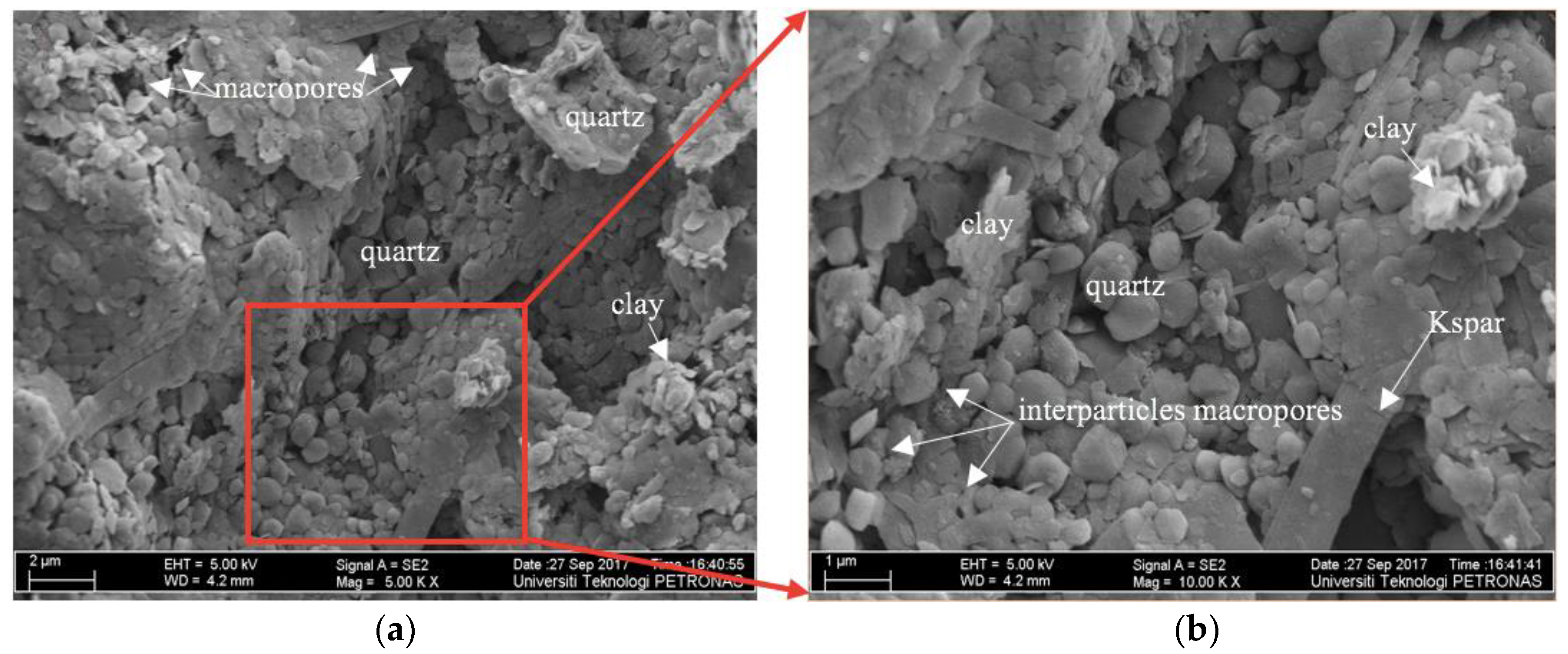
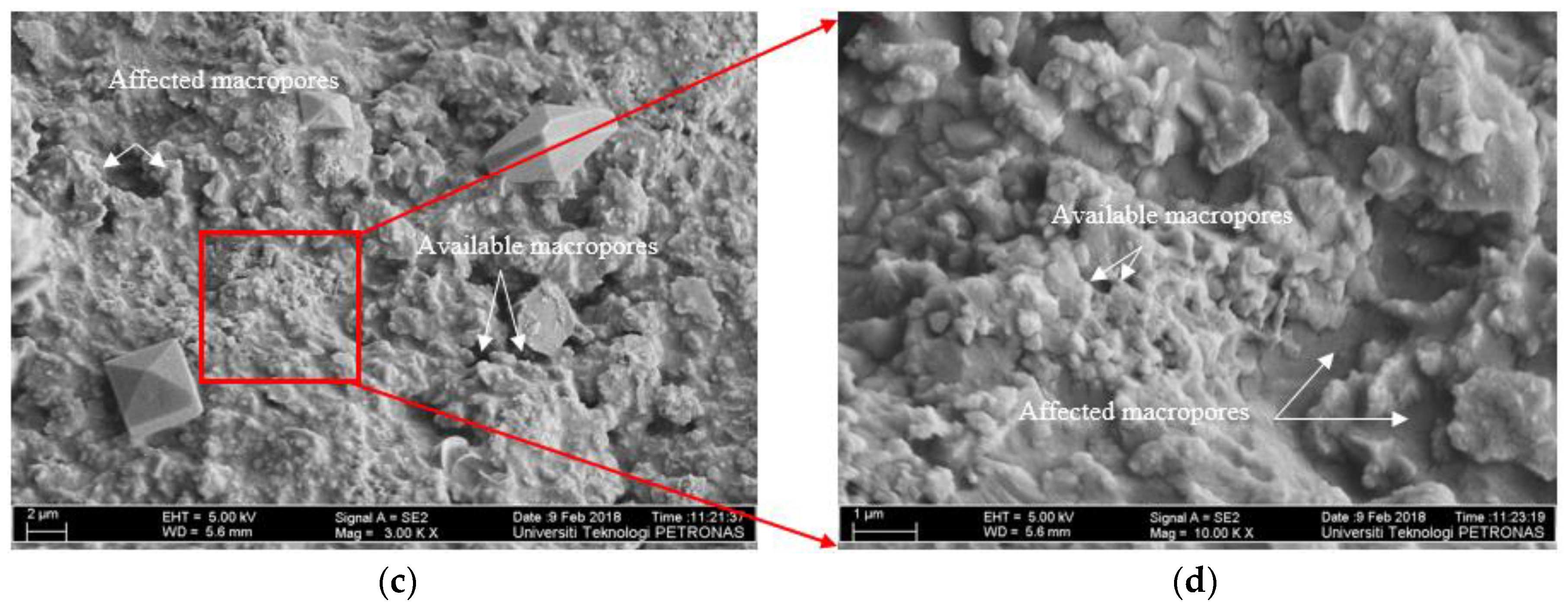
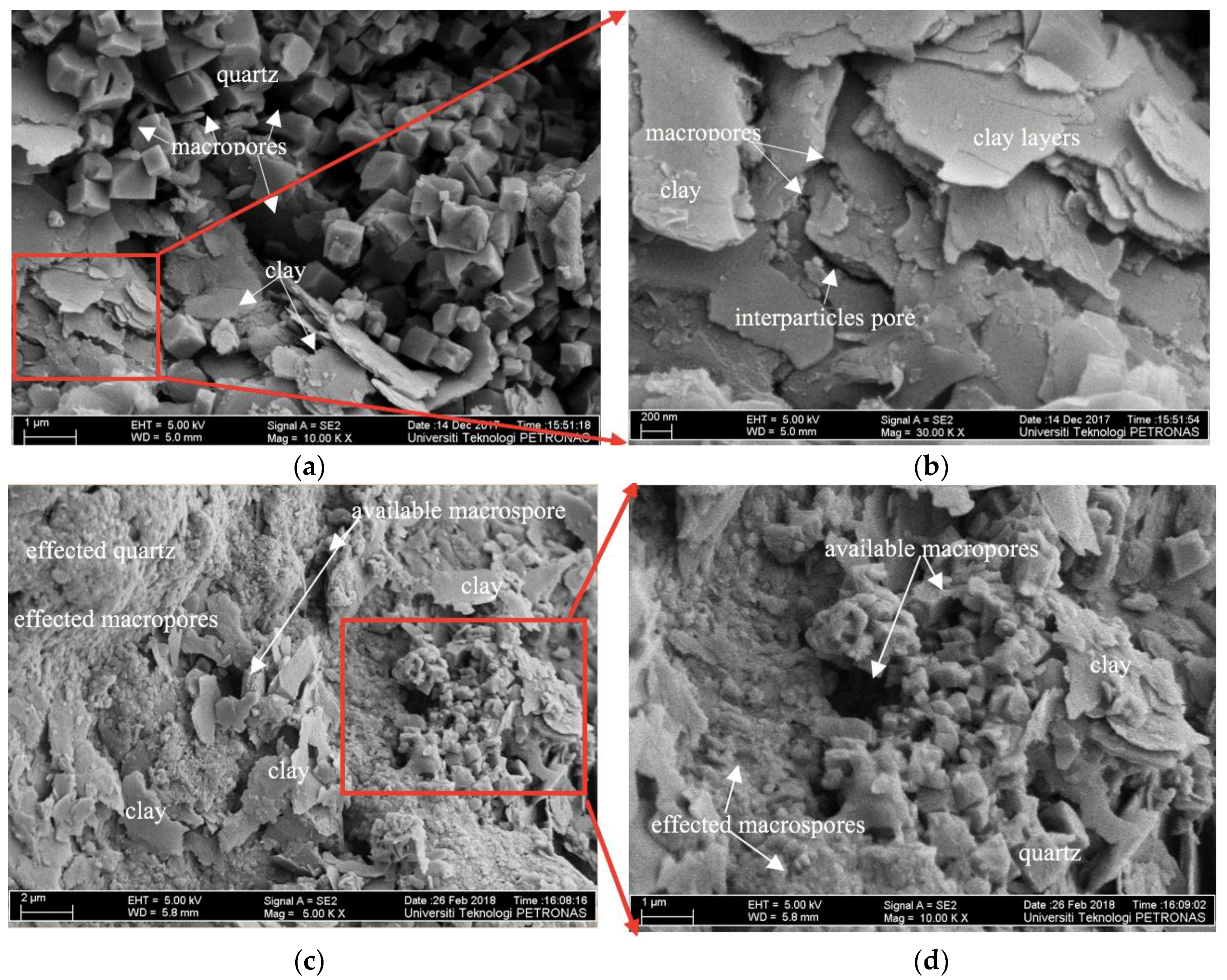
3.4.2. FE-SEM Images
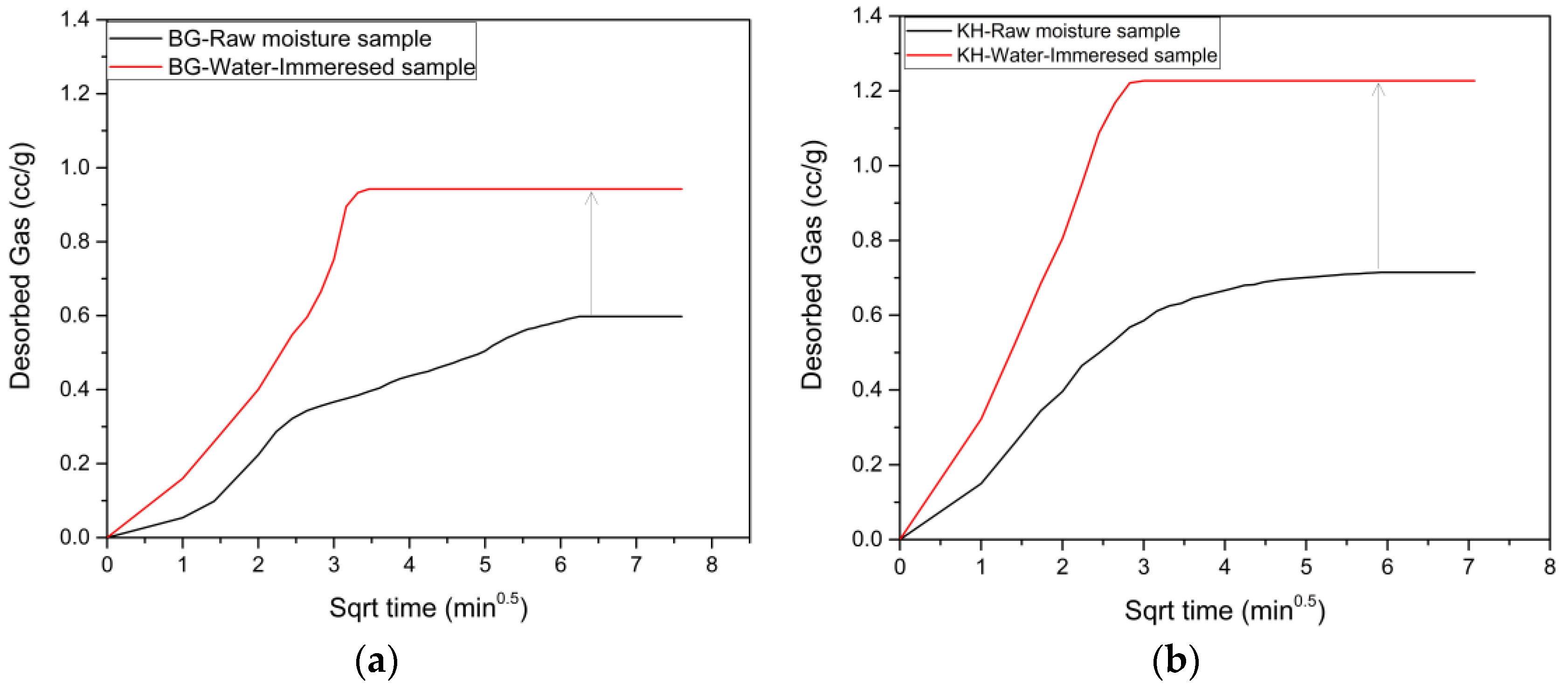
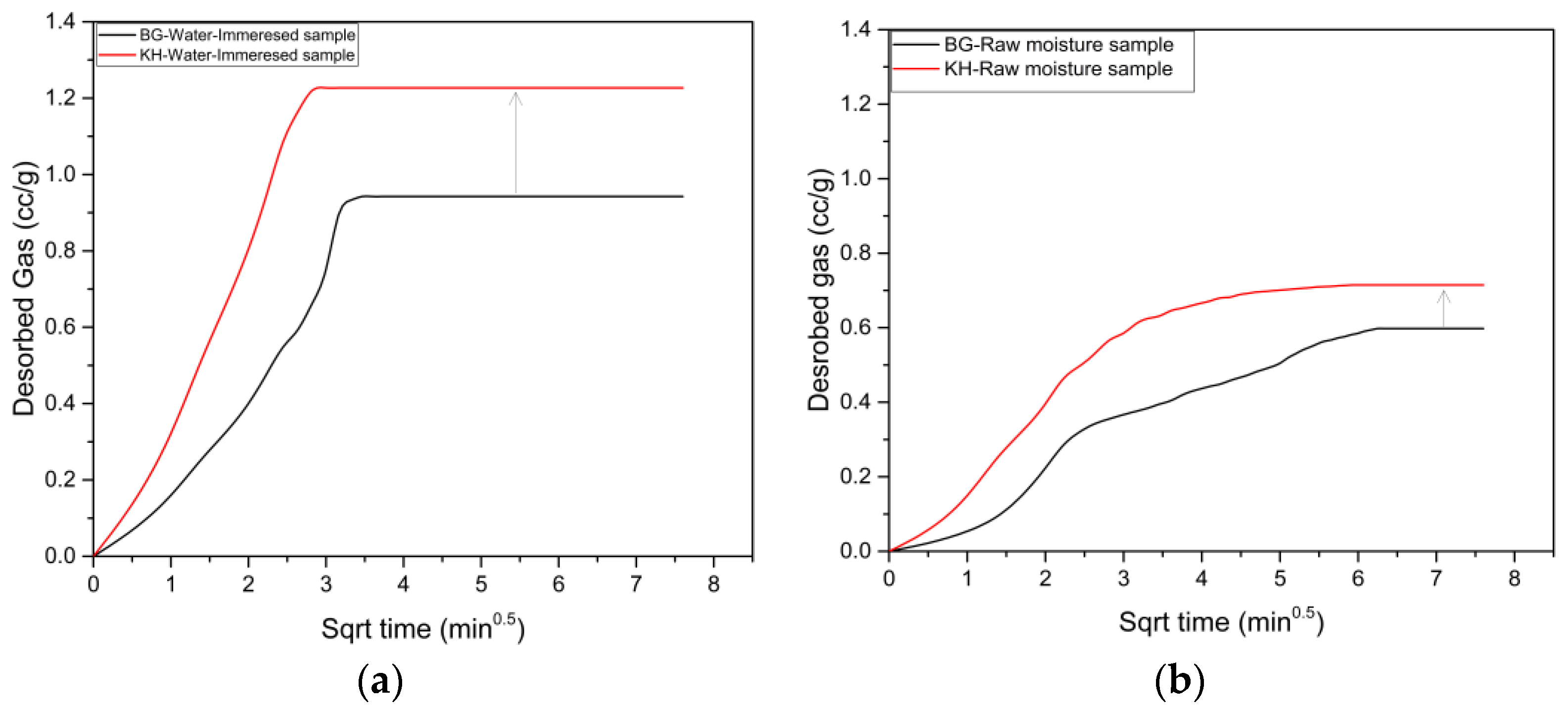
3.5. Desorption Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdulelah, H.; Mahmood, S.M.; Al-Mutarreb, A. The Effect of Anionic Surfactant on The Wettability of Shale and its Implication on Gas Adsorption/Desorption Behavior. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Dehghanpour, H. Advances in understanding wettability of gas shales. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 4362–4375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, R.G.; Qian, Y.; Raimi, D. Global energy outlook 2015. Natl. Bureau Econ. Res. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaee, R. Fundamentals of Gas Shale Reservoirs; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kuila, U.; Prasad, M. Specific surface area and pore-size distribution in clays and shales. Geophys. Prospect. 2013, 61, 341–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, F.; Zou, H.; Lu, Y. Mechanisms of shale gas storage: Implications for shale gas exploration in China. AAPG Bull. 2013, 97, 1325–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.-C.; Li, F.-C.; Watson, A.T. Adsorption measurements in Devonian shales. Fuel 1995, 74, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.; Jonk, R.; Schelble, R. Effect of multicomponent adsorption/desorption behavior on Gas-In-Place (GIP) and Estimated Ultimate Recovery (EUR) in shale gas systems. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, San Antonio, TX, USA, 8–10 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Heller, R.; Zoback, M. Adsorption of methane and carbon dioxide on gas shale and pure mineral samples. J. Unconv. Oil Gas Resour. 2014, 8, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, D.J.; Bustin, R.M. The importance of shale composition and pore structure upon gas storage potential of shale gas reservoirs. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2009, 26, 916–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmers, G.R.; Bustin, R.M. The organic matter distribution and methane capacity of the Lower Cretaceous strata of Northeastern British Columbia, Canada. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2007, 70, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Ellis, G.S.; Ruppel, S.C.; Milliken, K.; Yang, R. Effect of organic-matter type and thermal maturity on methane adsorption in shale-gas systems. Org. Geochem. 2012, 47, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkel, A.; Fink, R.; Littke, R. The role of pre-adsorbed water on methane sorption capacity of Bossier and Haynesville shales. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2015, 147, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, K.; Shi, J.; Yang, L.; Feng, D.; Zhang, T.; Yu, P. Water distribution characteristic and effect on methane adsorption capacity in shale clay. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2016, 159, 135–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yu, Q. The effect of moisture on the methane adsorption capacity of shales: A study case in the eastern Qaidam Basin in China. J. Hydrol. 2016, 542, 487–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Firoozabadi, A. Effect of water on methane and carbon dioxide sorption in clay minerals by Monte Carlo simulations. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2014, 382, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlumberger. Available online: https://www.slb.com/~/media/Files/stimulation/product_sheets/unconventionalgas/openfrac_ps.pdf (accessed on 23 December 2010).
- Singh, H. A critical review of water uptake by shales. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 34, 751–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y. Impact of water dynamics in fractures on the performance of hydraulically fractured wells in gas-shale reservoirs. J. Can. Pet. Technol. 2012, 51, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennion, D.B.; Bietz, R.F.; Thomas, F.B.; Cimolai, M.P. Reductions in the productivity of oil and low permeability gas reservoirs due to aqueous phase trapping. J. Can. Pet. Technol. 1994, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevan, J.; Sharma, M.M. Factors affecting clean-up of water-blocks: A laboratory investigation. Spe J. 2005, 10, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, D.H.; Hoang, H.N.; Mahadevan, J. Gas recovery from tight sands: Impact of capillarity. Spe J. 2012, 17, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Thompson, J.W.; Robinson, J.R. Understanding gas production mechanism and effectiveness of well stimulation in the Haynesville Shale through reservoir simulation. In Proceedings of the Canadian Unconventional Resources and International Petroleum Conference, Calgary, AB, Canada, 19–21 October 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Baioumy, H.; Ulfa, Y.; Nawawi, M.; Padmanabhan, E.; Anuar, M.N.A. Mineralogy and geochemistry of Palaeozoic black shales from Peninsular Malaysia: Implications for their origin and maturation. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2016, 165, 90–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Han, Y.; Fu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Zuo, Z. Micro and nano-size pores of clay minerals in shale reservoirs: Implication for the accumulation of shale gas. Sediment. Geol. 2016, 342, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavor, M.; Owen, L.; Pratt, T. Measurement and evaluation of coal sorption isotherm data. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 23–26 September 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Rouquerol, J.; Avnir, D.; Fairbridge, C.; Everett, D.; Haynes, J.; Pernicone, N.; Ramsay, J.D.F.; Sing, K.S.W.; Unger, K.K. Recommendations for the characterization of porous solids (Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 1994, 66, 1739–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmers, G.R.; Bustin, R.M.; Power, I.M. Characterization of gas shale pore systems by porosimetry, pycnometry, surface area, and field emission scanning electron microscopy/transmission electron microscopy image analyses: Examples from the Barnett, Woodford, Haynesville, Marcellus, and Doig units. AAPG Bull. 2012, 96, 1099–1119. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett, E.P.; Joyner, L.G.; Halenda, P.P. The determination of pore volume and area distributions in porous substances. I. Computations from nitrogen isotherms. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1951, 73, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.H.; Teller, E. Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvie, D.M. Total Organic Carbon (TOC) Analysis: Chapter 11: Geochemical Methods and Exploration; American Association of Petroleum Geologists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Gao, Y.; Dong, S.; Wang, D. GB/T 19145-2003, Determination of Total Organic Carbon in Sedimentary Rock; Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- McMurdie, H.F.; Morris, M.C.; Evans, E.H.; Paretzkin, B.; Wong-Ng, W.; Ettlinger, L.; Hubbard, C.R. Standard X-ray diffraction powder patterns from the JCPDS research associateship. Powder Diffr. 1986, 1, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zektser, I.S.; Marker, B.; Ridgway, J.; Rogachevskaya, L.; Vartanyan, G. Geology and Ecosystems; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Tuttle, M.L.; Breit, G.N. Weathering of the New Albany Shale, Kentucky, USA: I. Weathering zones defined by mineralogy and major-element composition. Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 1549–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosen, A. Mineralogical Analysis of Upper Devonian Black Shales in Western New York; Geological Society of America Abstracts with Programs: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Eberl, D. User Guide to RockJock—A Program for Determining Quantitative Mineralogy from X-Ray Diffraction Data; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2003.
- Tang, X.; Jiang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, Y. Characteristics and origin of in-situ gas desorption of the Cambrian Shuijingtuo Formation shale gas reservoir in the Sichuan Basin, China. Fuel 2017, 187, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingqing, Y.; Jie, L.; Shoumai, R.; Zijian, H.; Fanyang, M.; Fei, W.; Guangyu, S. Application of rock desorbed gas determinator in shale gas exploration. China Pet. Explor. 2016, 21, 120–124. [Google Scholar]
- Matta, J.E.; LaScola, J.C.; Kissell, F.N. Methane Absorption in Oil Shale and Its Potential Mine Hazard; United States Department of Interior, Bureau of Mines: Washington D.C., WA, USA, 1977.
- Jinchuan, Z. Favorable Zone Optimization Standard of Shale Gas. In Proceedings of the Guizhou: Symposium on Investigation and Evaluation of National Shale Gas Resources Potential and Favorable Zone Optimization. Guizhou, China. 2011. Available online: http://www.mlr.gov.cn/xwdt/jrxw/201203/t20120302_1069466.htm (accessed on 8 June 2018).
- Shuangfang, L.; Huang, W.; Chen, F.; Li, J.; Wang, M.; Xue, H.; Wang, W.; Cai, X. Classification and evaluation criteria of shale oil and gas resources: Discussion and application. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2012, 39, 268–276. [Google Scholar]
- Passey, Q.R.; Bohacs, K.; Esch, W.L.; Klimentidis, R.; Sinha, S. From oil-prone source rock to gas-producing shale reservoir-geologic and petrophysical characterization of unconventional shale gas reservoirs. In Proceedings of the International oil and Gas Conference and Exhibition in China, Beijing, China, 8–10 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, Q.; Dehghanpour, H.; Wood, J.; Sanei, H. Wettability of the Montney tight gas formation. SPE Reserv. Eval. Eng. 2015, 18, 417–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfaghari, A.; Dehghanpour, H. Pore size distribution from water adsorption isotherm. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Houston, TX, USA, 28–30 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zolfaghari, A.; Dehghanpour, H.; Holyk, J. Water sorption behaviour of gas shales: I. Role of clays. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2017, 179, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinz, D.; Littke, R. Development of the micro-and ultramicroporous structure of coals with rank as deduced from the accessibility to water. Fuel 2005, 84, 1645–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzi, M.; Rupp, E.C.; Liu, C.W.; Wilcox, J. Molecular simulation and experimental characterization of the nanoporous structures of coal and gas shale. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2014, 121, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassin, M.R.; Begum, M.; Dehghanpour, H. Organic shale wettability and its relationship to other petrophysical properties: A Duvernay case study. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2017, 169, 74–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenevert, M.E. Shale alteration by water adsorption. J. Pet. Technol. 1970, 22, 1141–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Ge, H.; Li, C.; Yang, X.; Ren, K.; Yang, Z.; Su, S. Water imbibition of shale and its potential influence on shale gas recovery—A comparative study of marine and continental shale formations. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 35, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


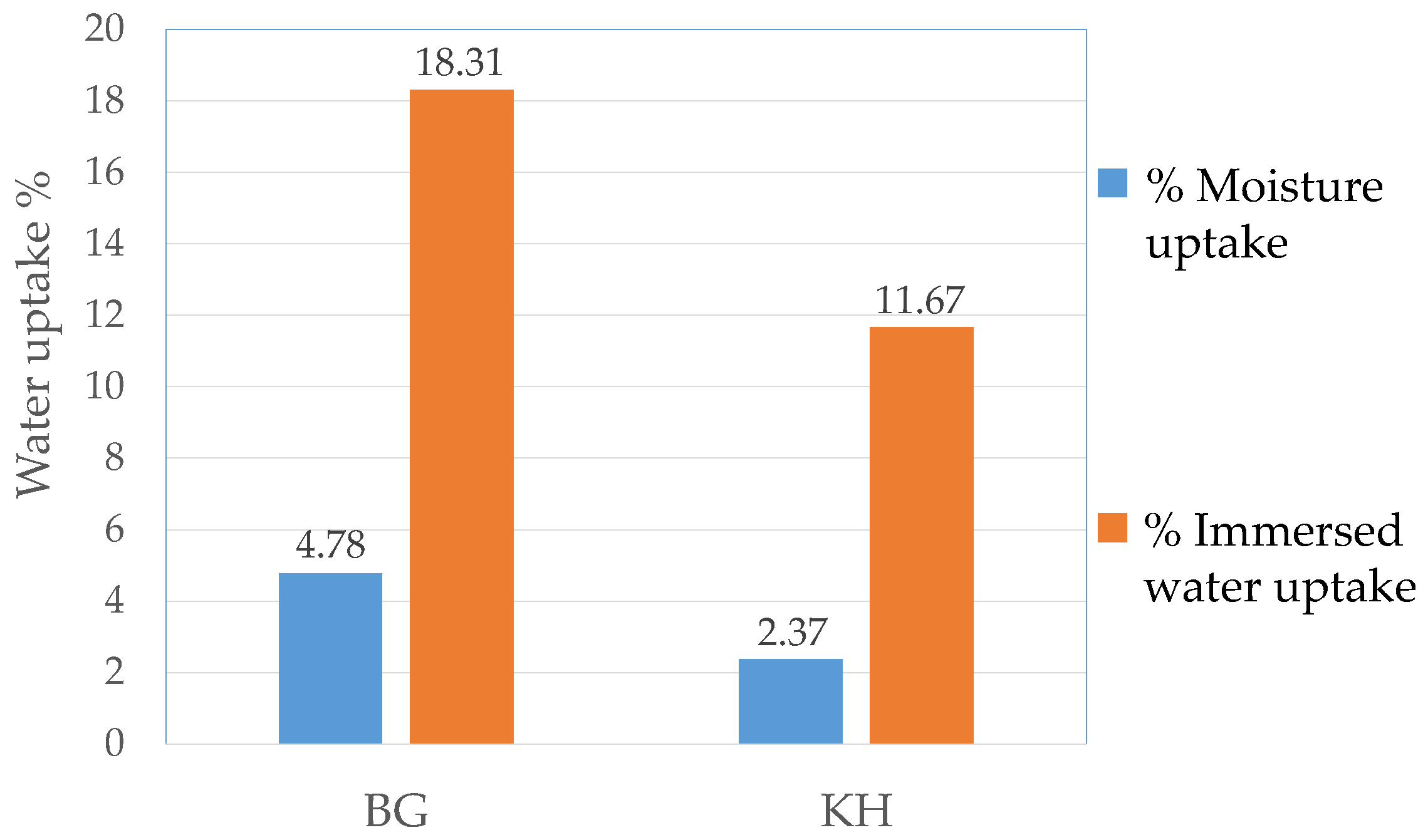

| Sample ID | Longitude | Latitude | Formation |
|---|---|---|---|
| BG | 101°0′7.32″ | 4°47′36.27″ | Batu Gajah |
| KH | 05°36′50″ | 101°01′ 49″ | Kroh |
| Sample ID | Non-clay Minerals (wt %) | Clay Minerals (wt %) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quartz | Kpsar | Clacite | Total (%) | Kaolinite | Smectite | Illite | Chlorite | Muscovite | Biotite | Dickite | Total (%) | |
| BG | 29.3 | 12.8 | 1.3 | 43.4 | 6.3 | 12.7 | 23.1 | 5 | 9.3 | 0.1 | NA | 56.6 |
| KH | 66 | 7.2 | 0.8 | 74.5 | 2.8 | 9.7 | 9.7 | 1.9 | NA | 0.9 | 0.5 | 25.5 |
| Sample ID | SSA BET m²/g | Reduction in SSA % | Pore Volume BJH cm3/g | Reduction in Pore Volume % | Avg. Pore Diameter nm | Increase in Pore Diameter Size % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BG-immersed | 0.7945 | 88.34 | 0.009011 | 64.83 | 29.896 | 95.76 |
| BG-raw moisture | 6.8147 | 0.025625 | 15.271 | |||
| KH-immersed | 2.9468 | 59.63 | 0.016449 | 44.12 | 19.851 | 54.41 |
| KH-raw moisture | 7.2999 | 0.029441 | 12.856 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Mutarreb, A.; Jufar, S.R.; Abdulelah, H.; Padmanabhan, E. Influence of Water Immersion on Pore System and Methane Desorption of Shales: A Case Study of Batu Gajah and Kroh Shale Formations in Malaysia. Energies 2018, 11, 1511. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11061511
Al-Mutarreb A, Jufar SR, Abdulelah H, Padmanabhan E. Influence of Water Immersion on Pore System and Methane Desorption of Shales: A Case Study of Batu Gajah and Kroh Shale Formations in Malaysia. Energies. 2018; 11(6):1511. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11061511
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Mutarreb, Ahmed, Shiferaw Regassa Jufar, Hesham Abdulelah, and Eswaran Padmanabhan. 2018. "Influence of Water Immersion on Pore System and Methane Desorption of Shales: A Case Study of Batu Gajah and Kroh Shale Formations in Malaysia" Energies 11, no. 6: 1511. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11061511
APA StyleAl-Mutarreb, A., Jufar, S. R., Abdulelah, H., & Padmanabhan, E. (2018). Influence of Water Immersion on Pore System and Methane Desorption of Shales: A Case Study of Batu Gajah and Kroh Shale Formations in Malaysia. Energies, 11(6), 1511. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11061511





