Loading History Effect on Creep Deformation of Rock
Abstract
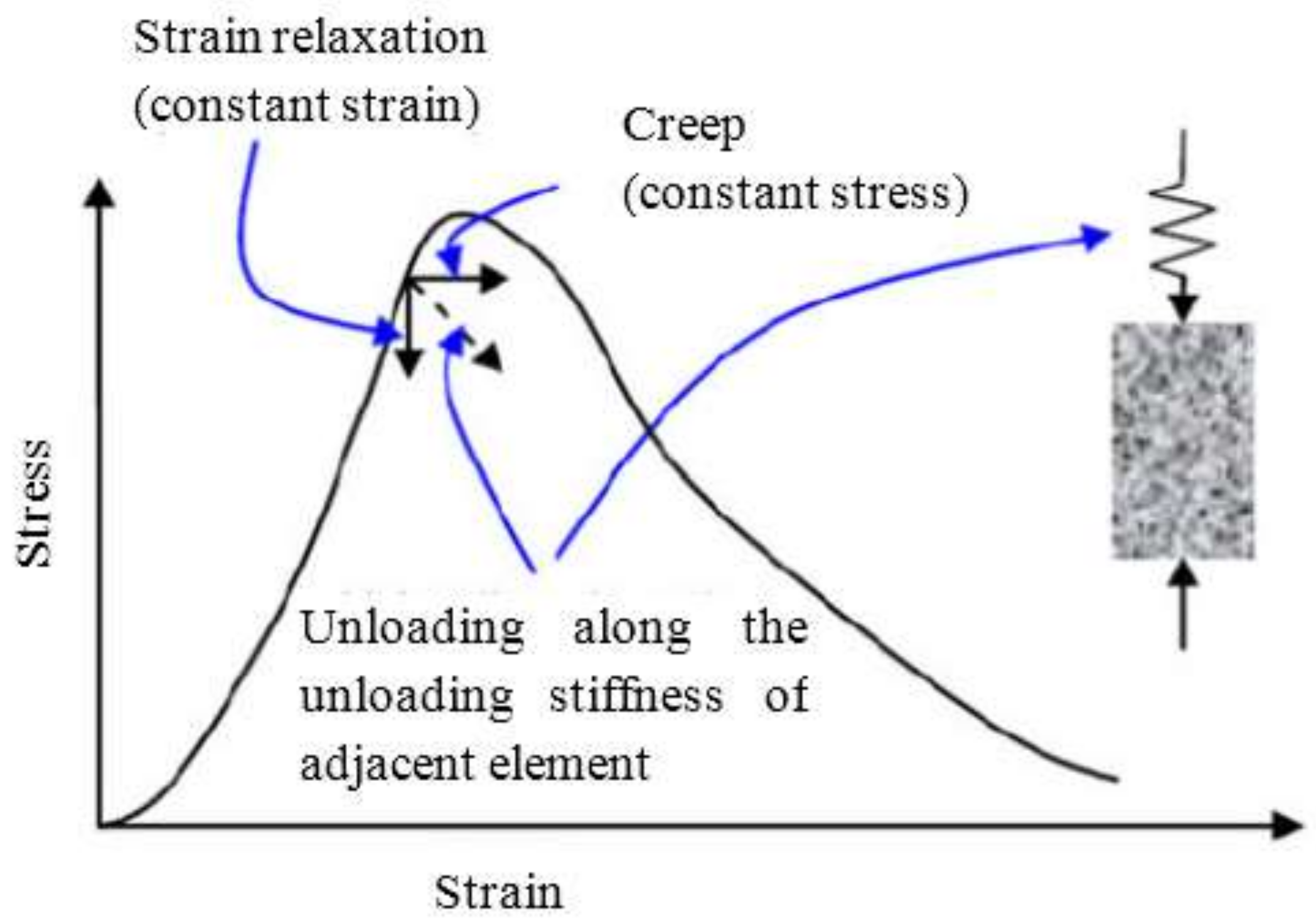
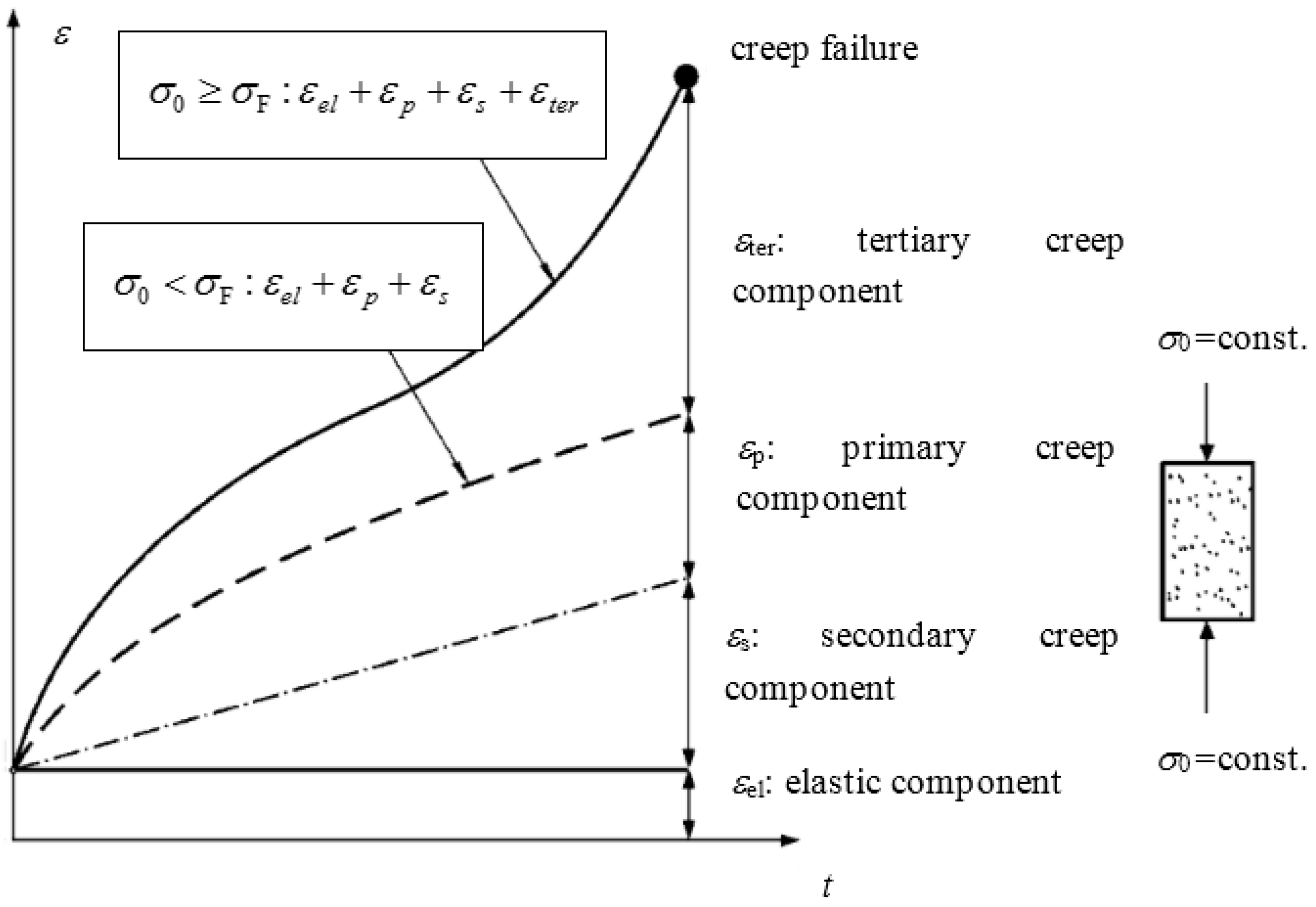
:1. Introduction
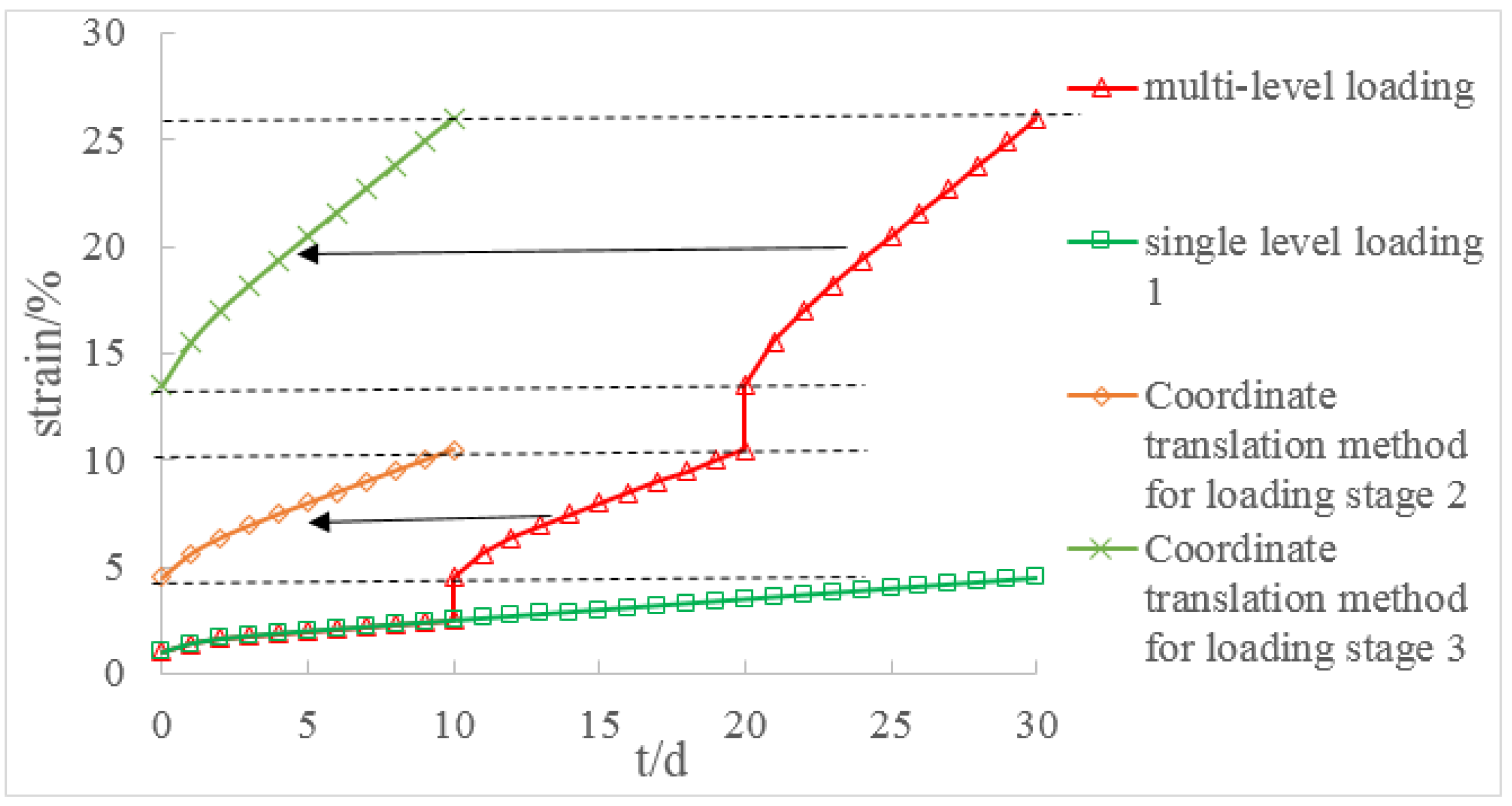
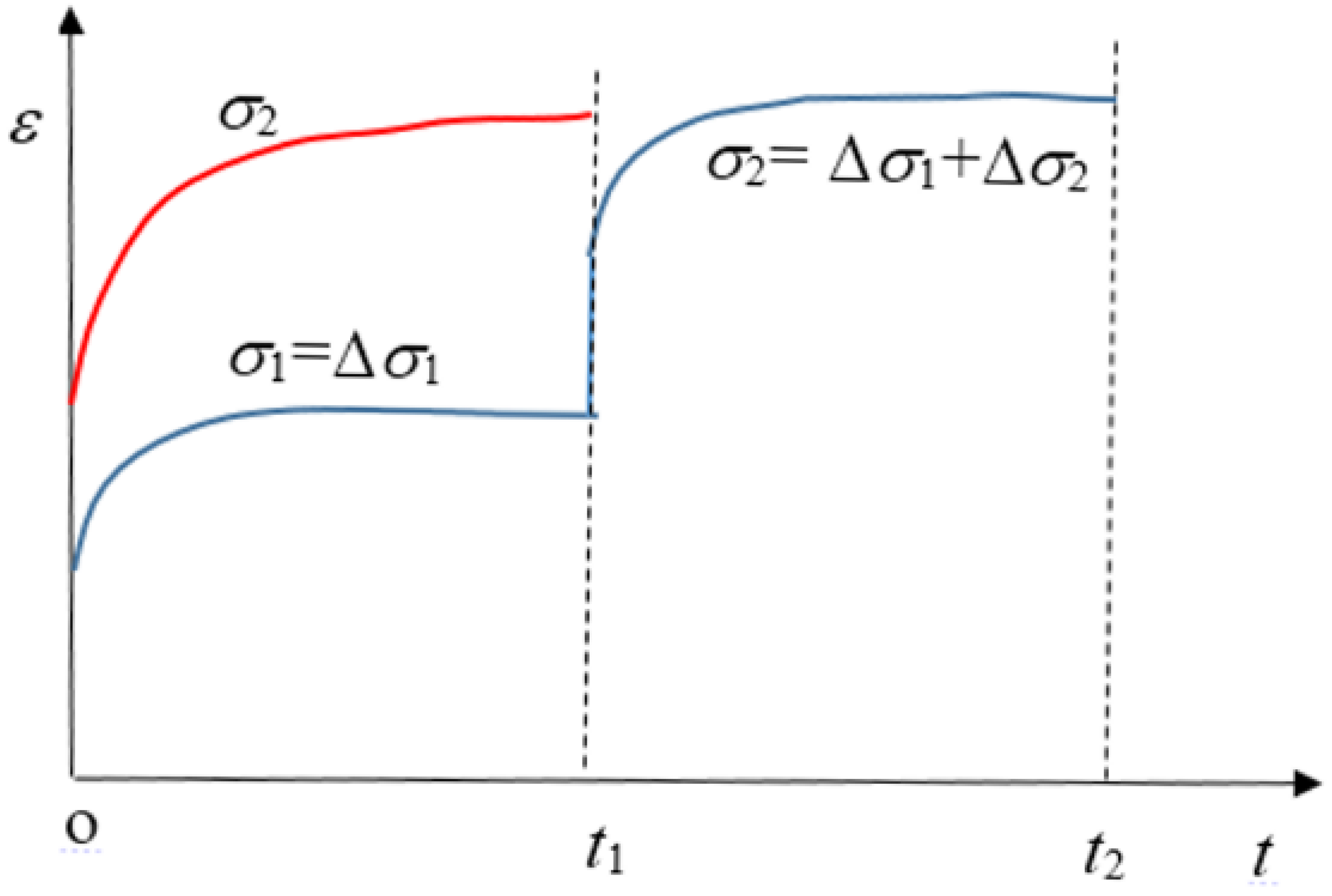
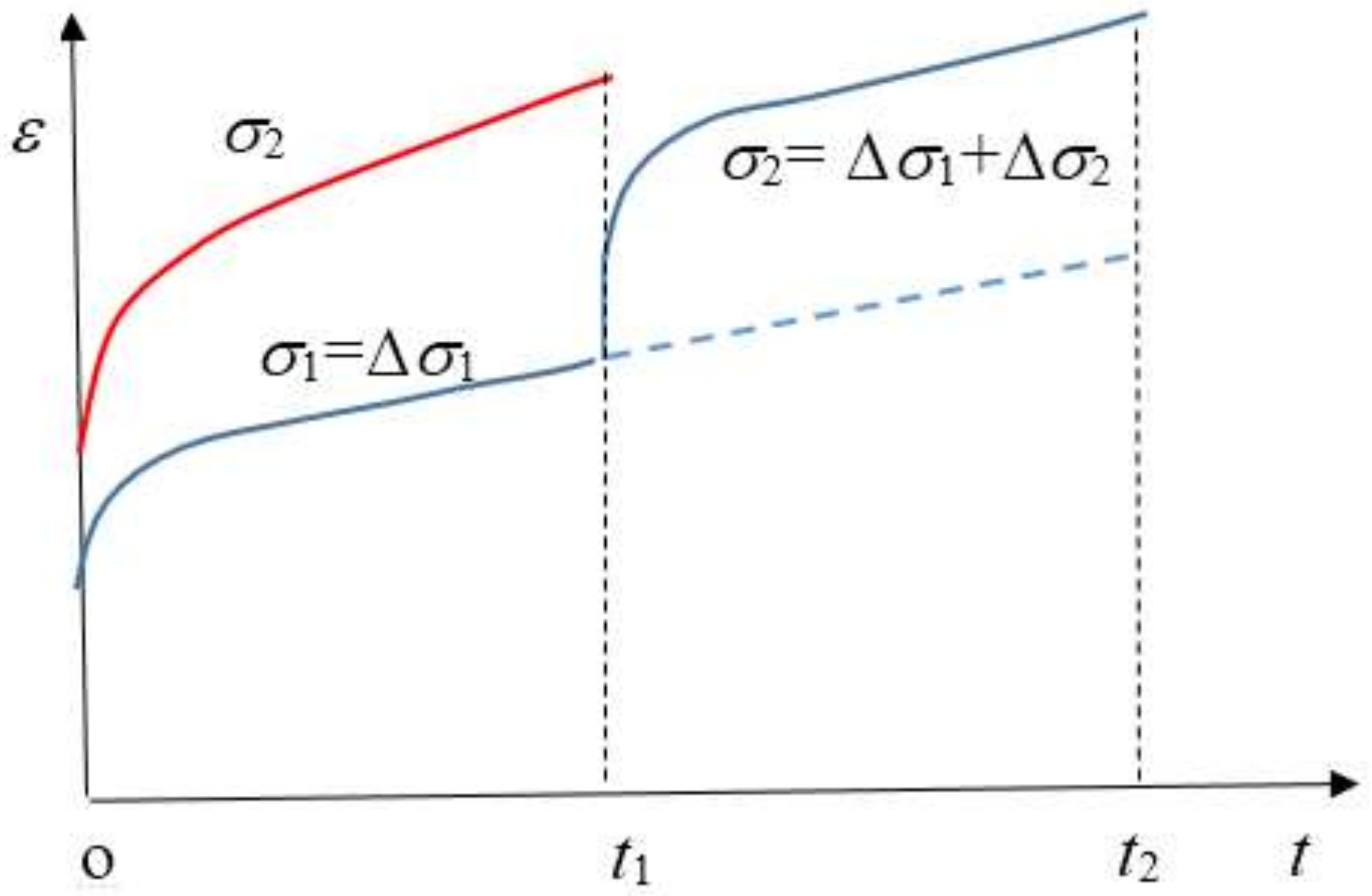
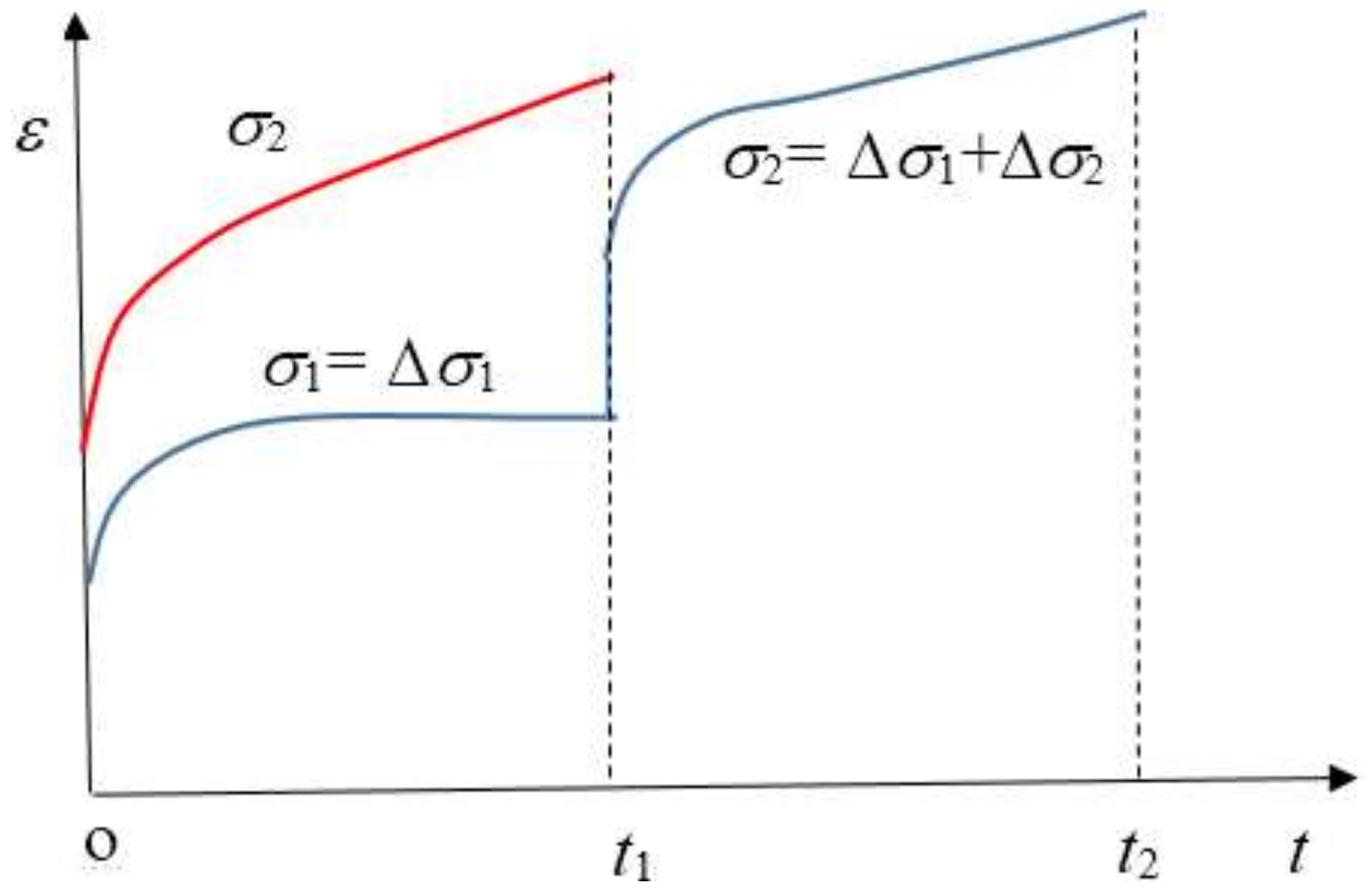
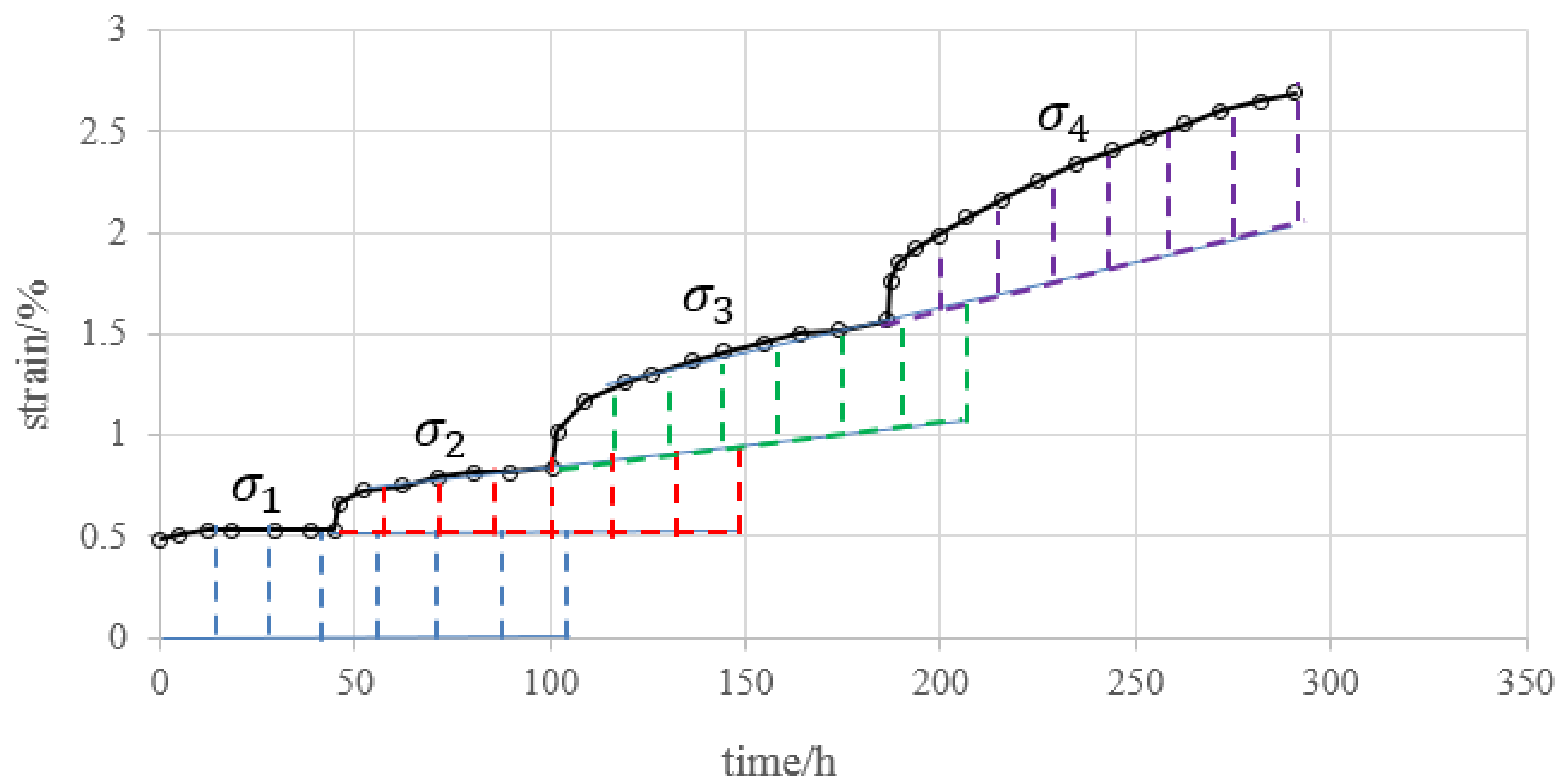
2. Coordinate Translation Method
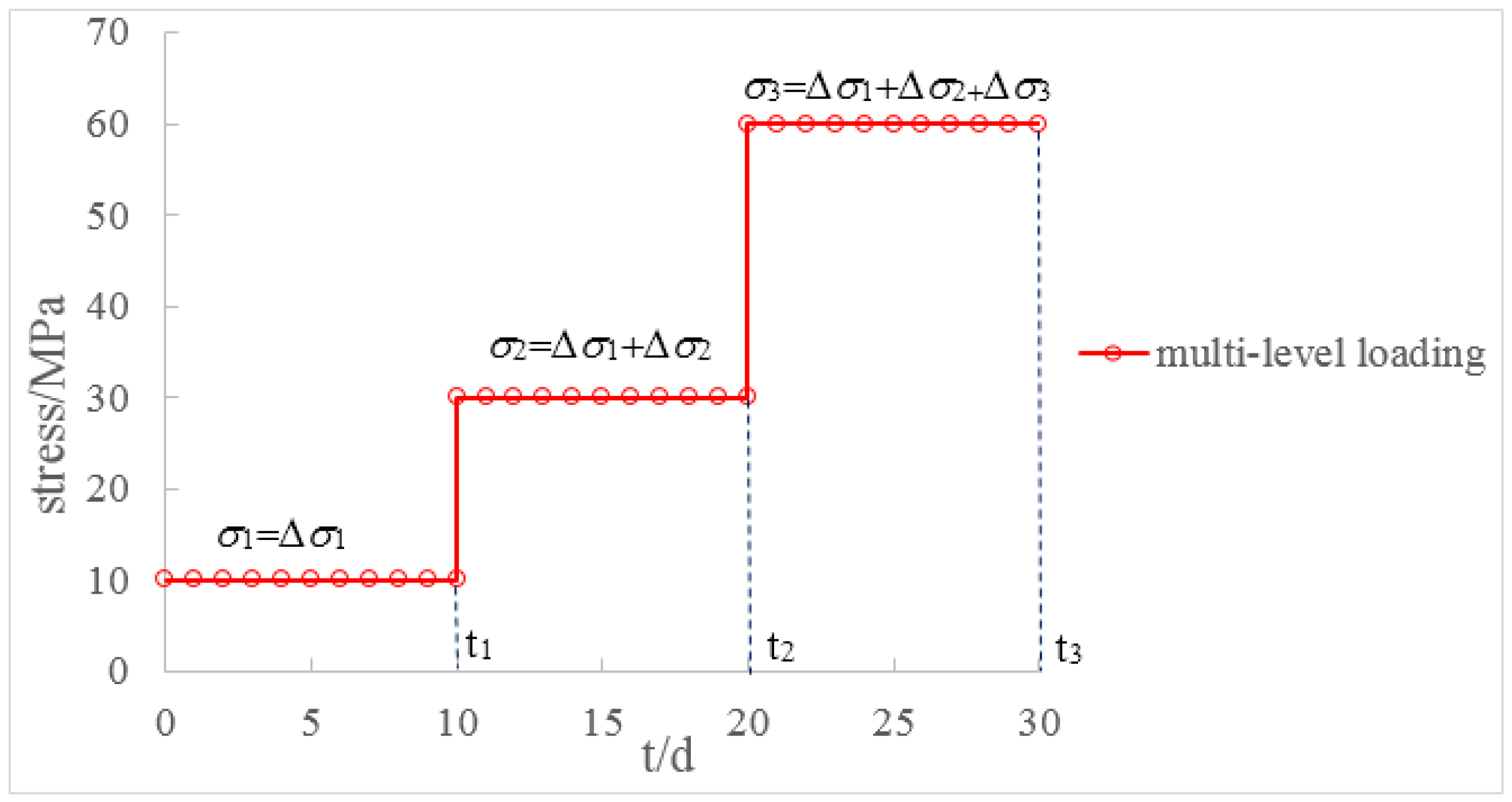
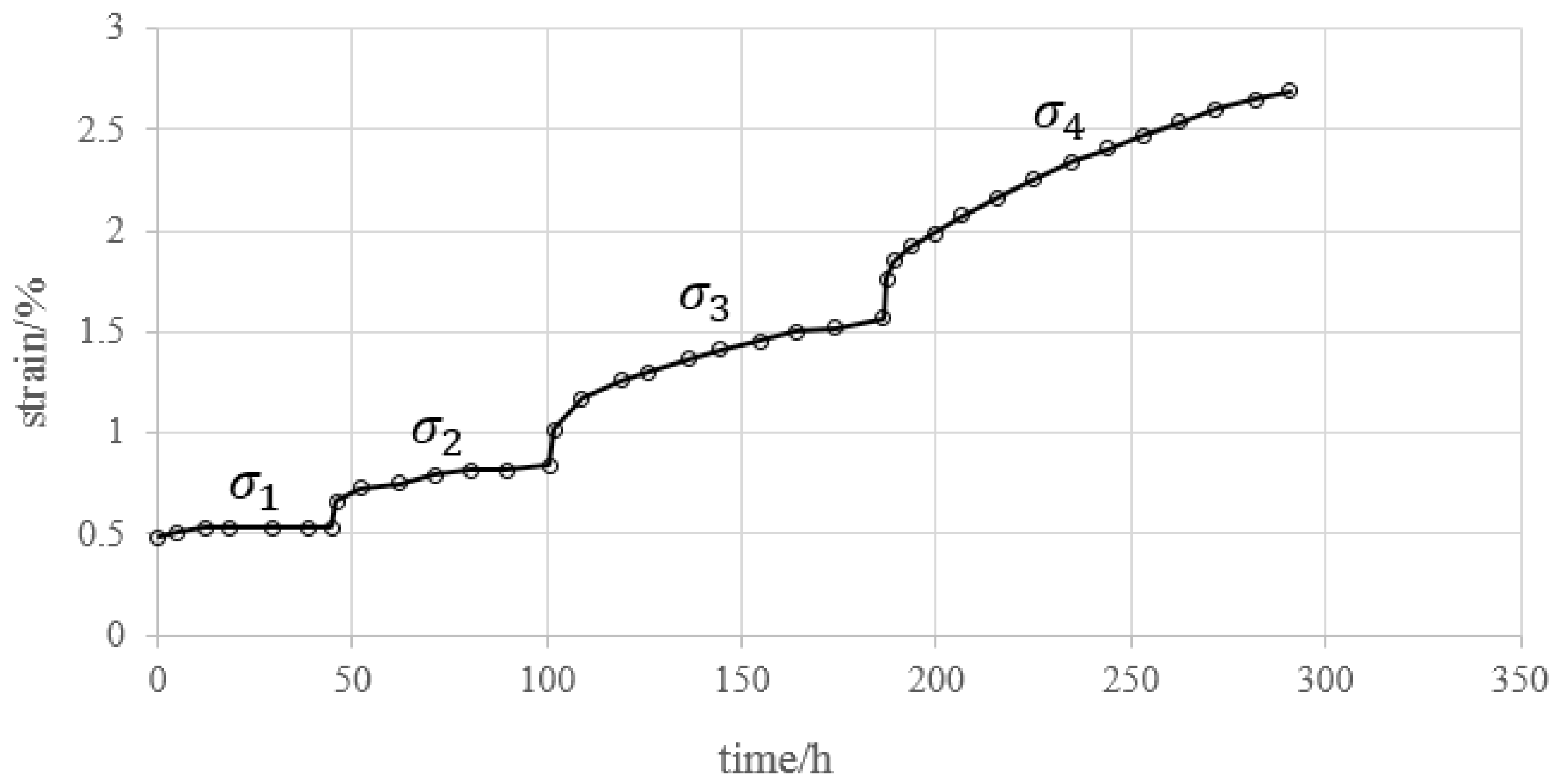
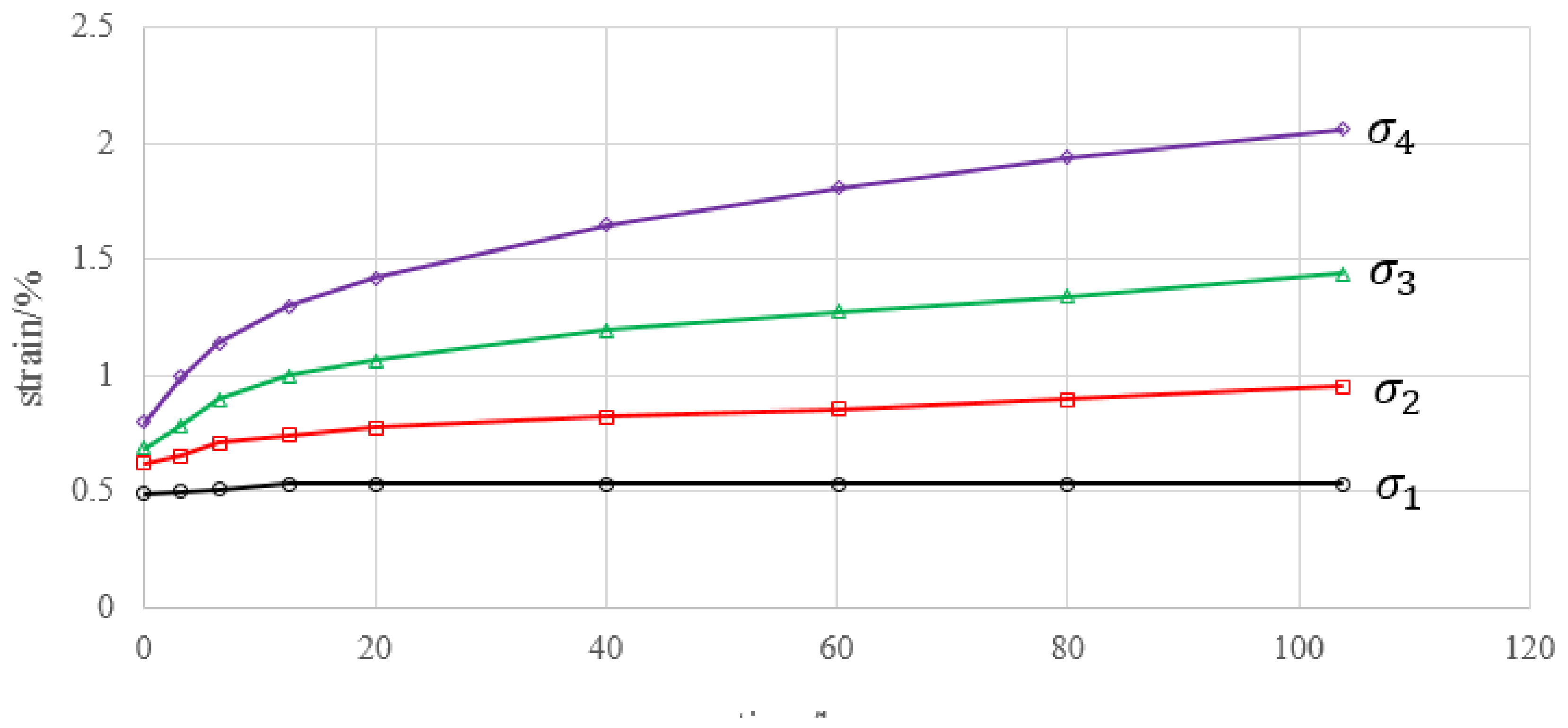
3. Data Analysis of Creep Deformation Considering Loading History
- (1)
- Ensure that creep is in the steady-state creep stage (the creep rate becomes zero or a positive constant).
- (2)
- Obtain the incremental creep deformation ∆εi under each loading increment ∆σi The loading increment ∆σi does not necessarily have to be the same for every loading stage.
- (3)
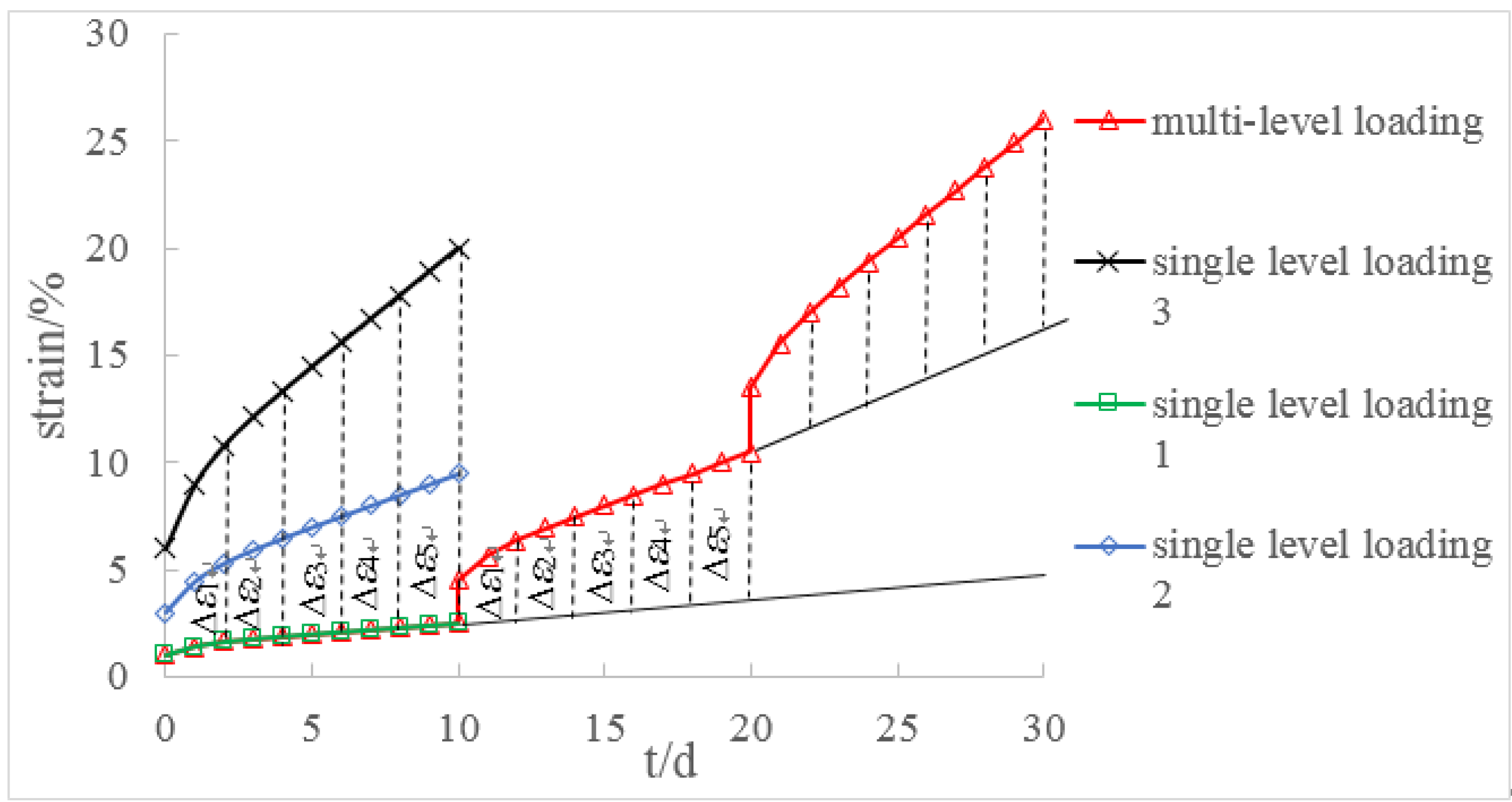
- The creep deformation under loading applied to the specimen in one step can be obtained by superimposing the incremental creep deformation in every step.
- (4)
- If the creep loading time ∆ti is not the same for every step, we extend the deformation trend by using the creep rate at the end of the shorter stage to make each creep time equal for every loading step.
4. Creep Strain Expression Considering Time Effect for Several Creep Models
4.1. H-K Model
4.2. Burgers Model
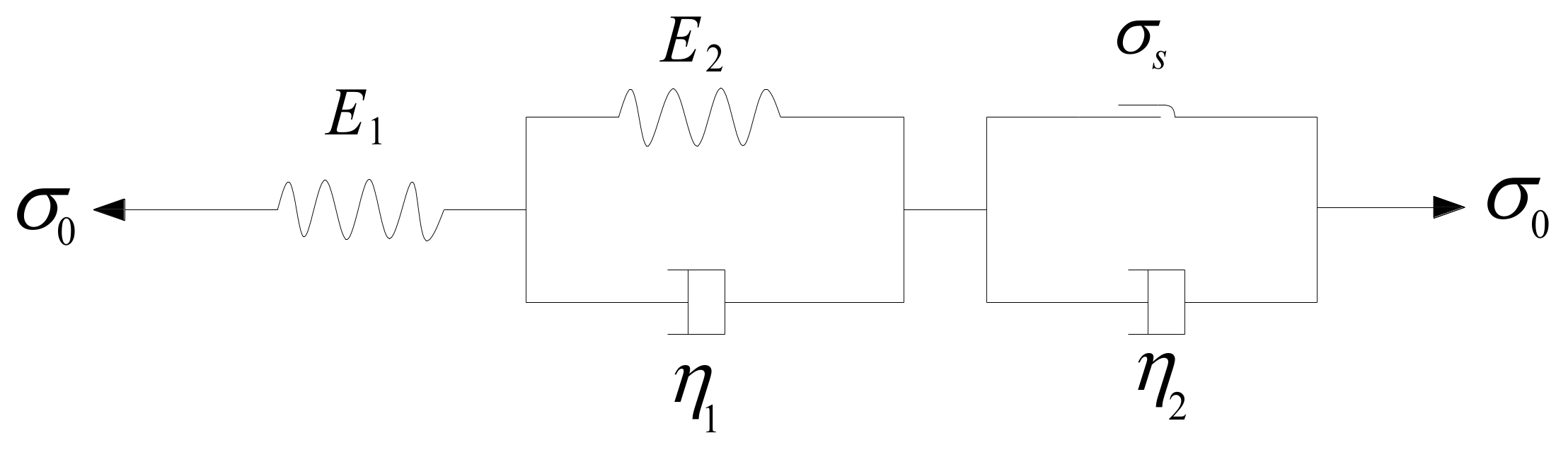
4.3. Nishihara Model
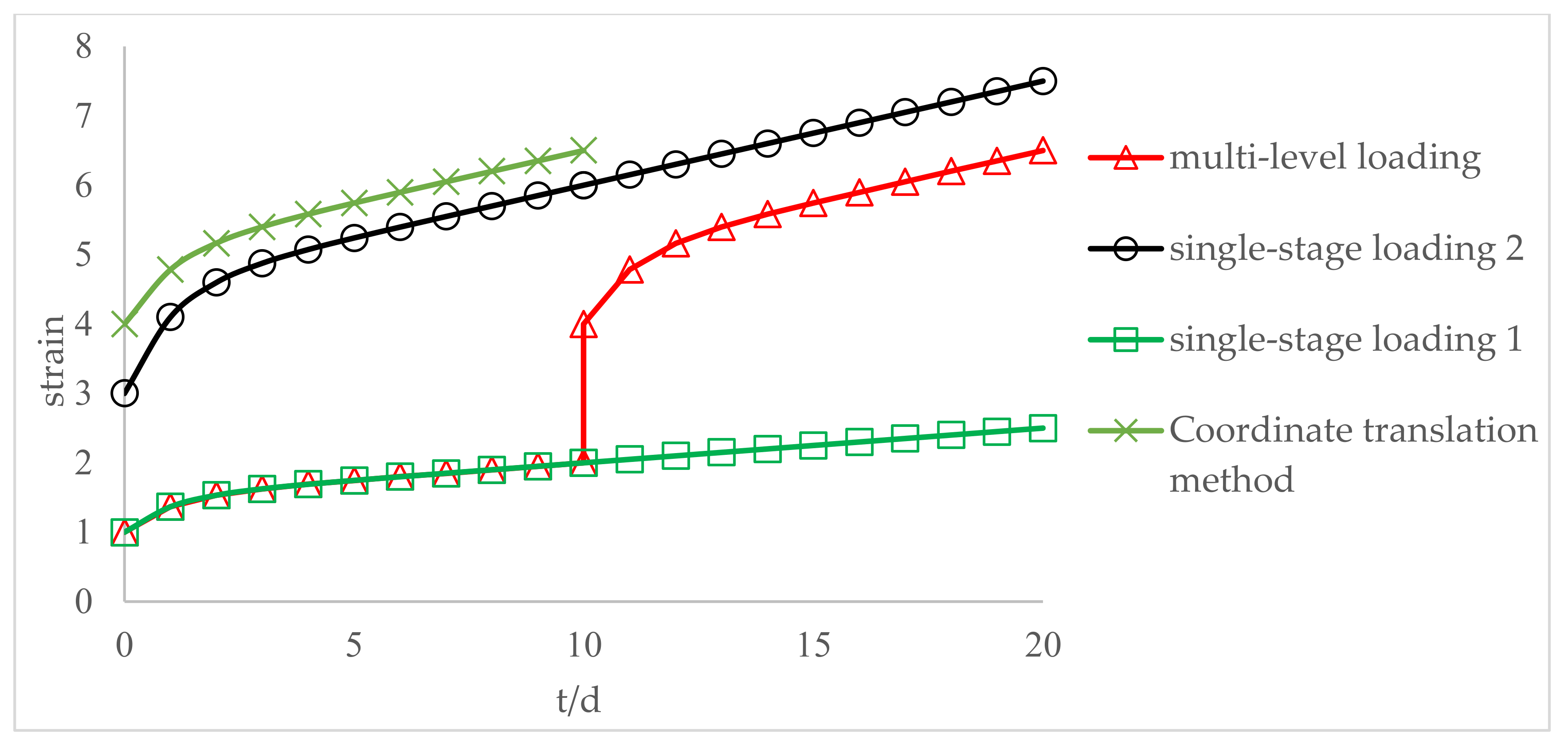
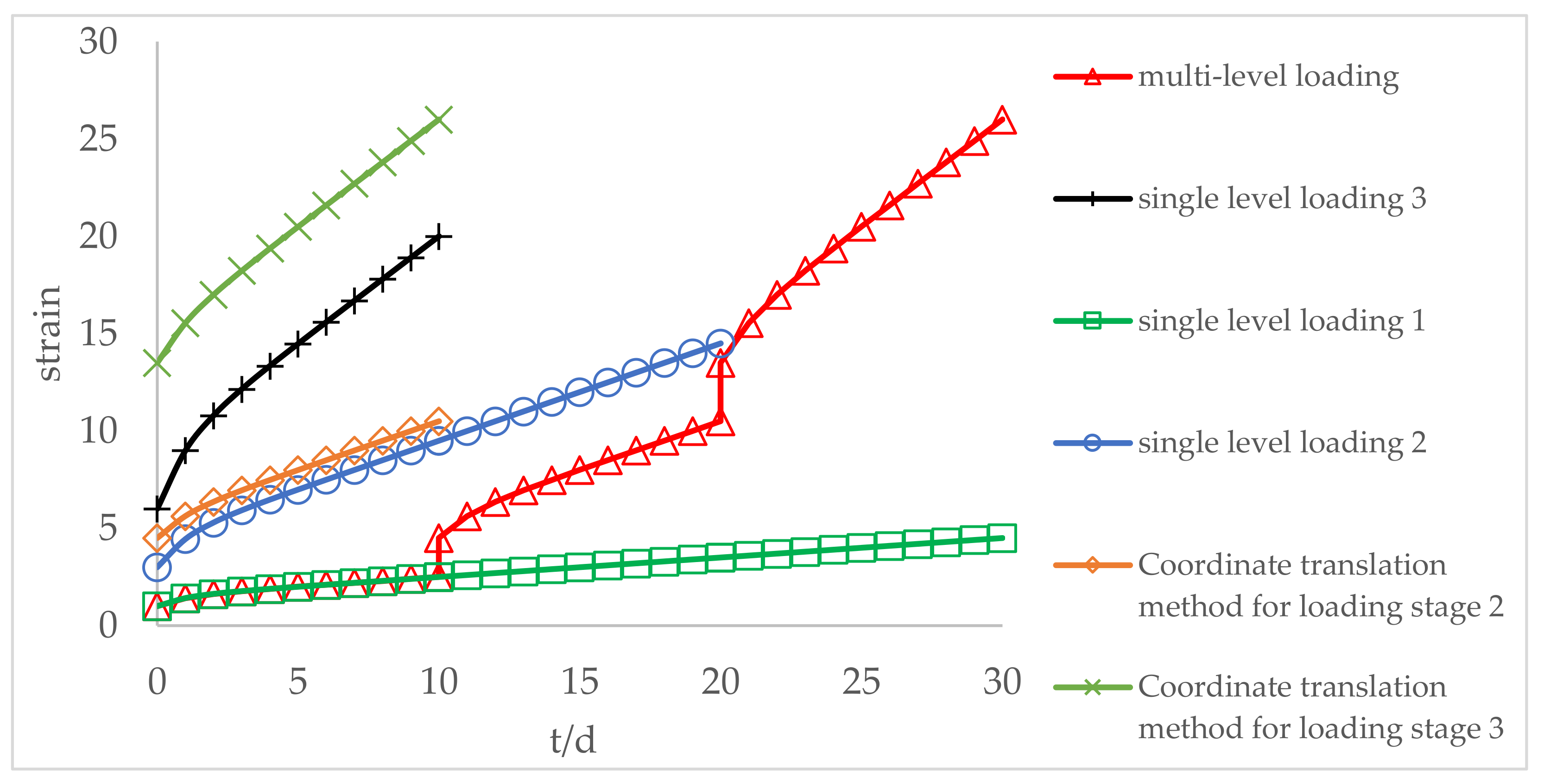
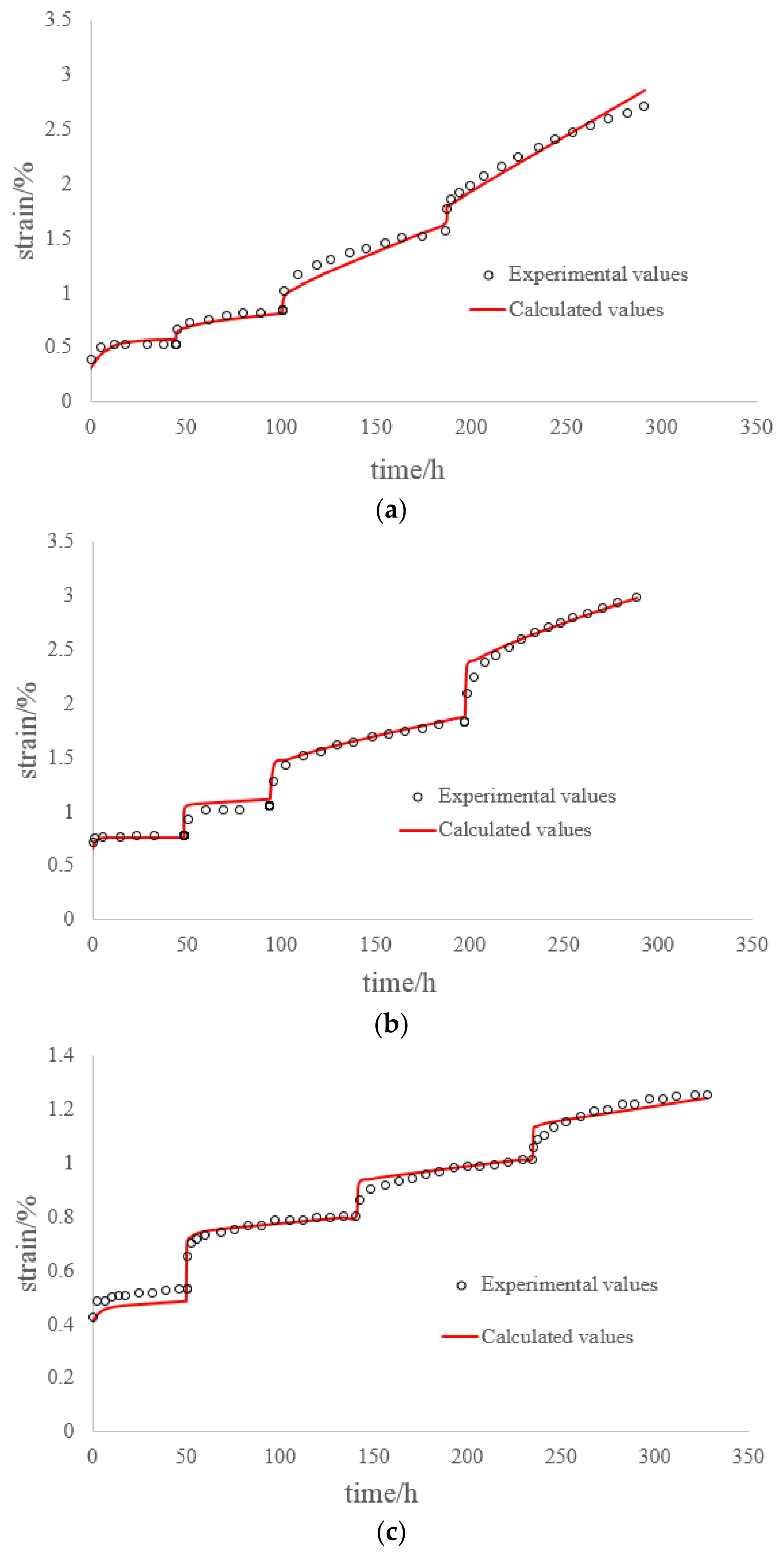
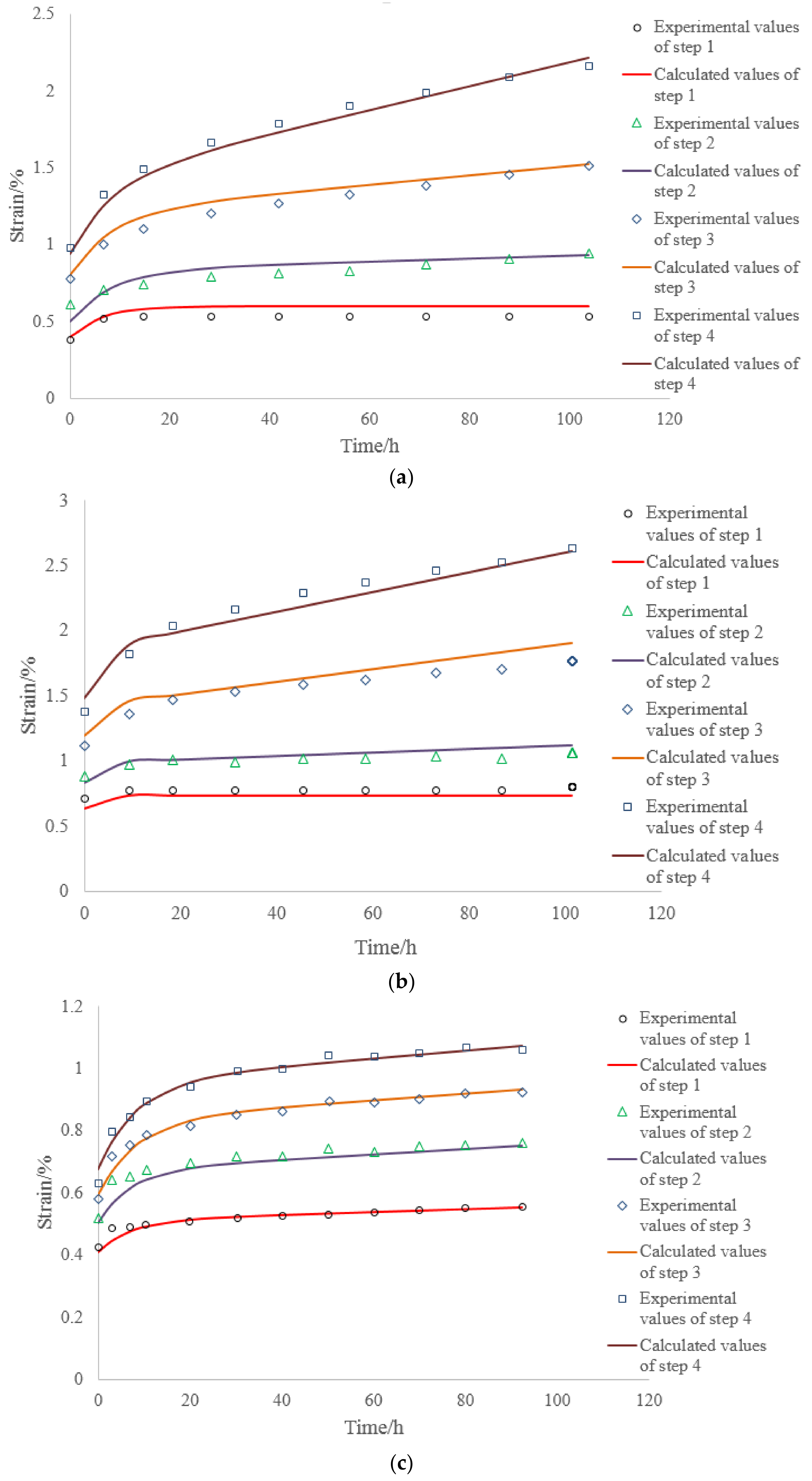
5. Analysis of Creep Test Data
6. Conclusions
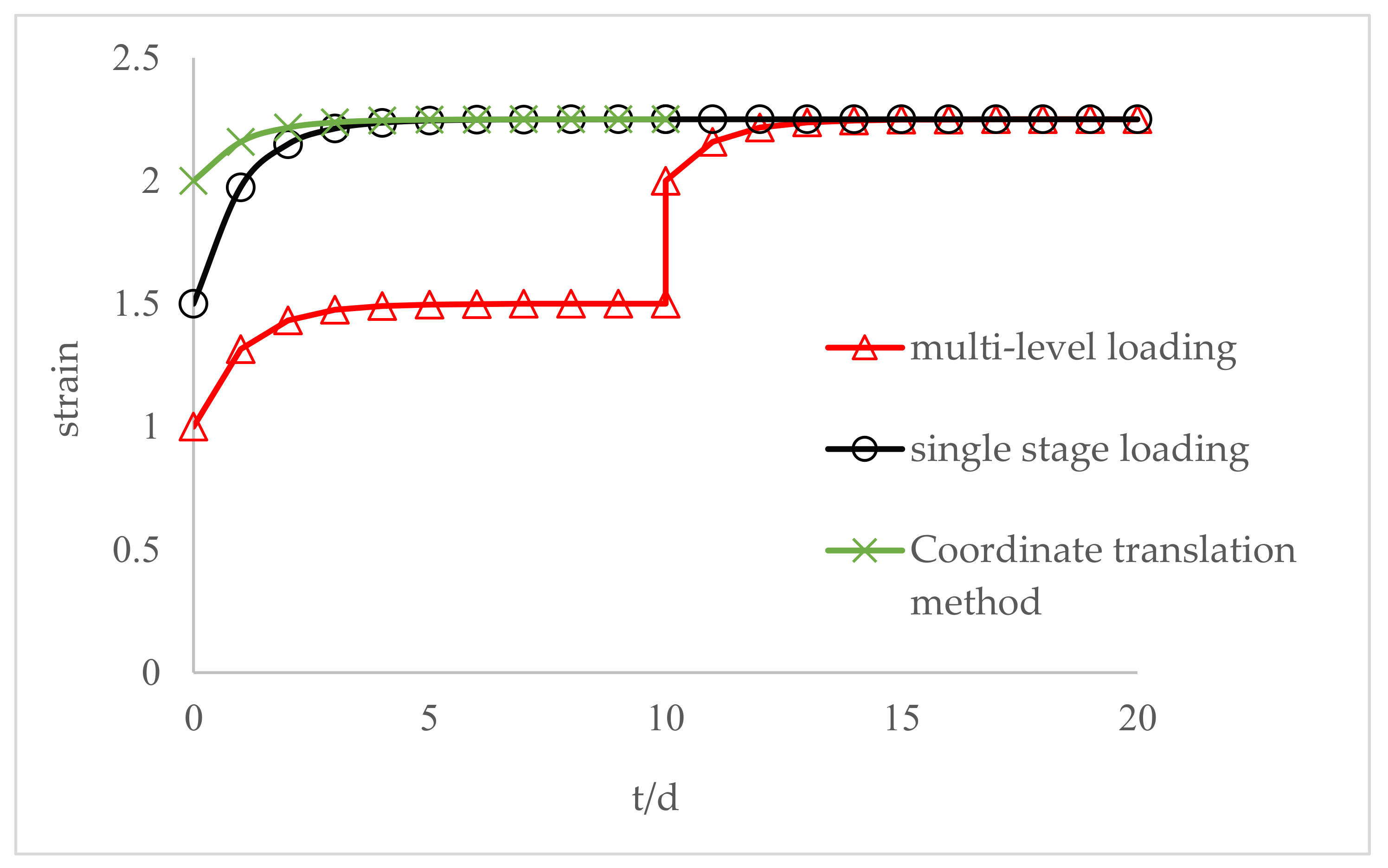
- The multi-step loading method is more efficient than single-step loading method for creep test. We could estimate the creep strain under single-step loading from the results of multi-step loading creep test unless we consider the loading history. The creep deformation under single-step loading can be estimated by the super-position of creeps obtained by the dissolution of a multi-step creep. The proposed time-affected correction method is effective for all types of rock and for various loading sequences and time intervals.
- A mathematical creep strain equation considering the loading history effect is proposed, which is the mathematical explanation of this correction method.
- By comparing the time-affected correction method with the coordinate translation method, the results showed that the former results are more consistent with the experimental results. Because the coordinate translation method ignores the influence of loading history which produces a large error.
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aydan, Ö.; Ito, T.; Özbay, U.; Kwasniewski, M.; Shariar, K.; Okuno, T.; Özğenoğlu, A.; Malan, D.F.; Okada, T. ISRM suggested methods for determining the creep characteristics of rock. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2014, 47, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagros, A.; Johanson, E.; Hudson, J.A. Time Dependency in the Mechanical Properties of Crystalline Rocks: A Literature Survey; Possiva OY: Eurajoki, Finland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Malan, D.F. Time-dependent behaviour of deep level tabular excavations. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 1999, 32, 123–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malan, D.F. Simulating the time-dependent behavior of excavations in hard rock. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2002, 35, 225–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perzyna, P. Fundamental problems in viscoplasticity. Adv. Appl. Mech. 1966, 9, 244–368. [Google Scholar]
- Lade, P.V.; Liu, C.T. Experimental study of drained creep behavior of sand. J. Eng. Mech. 1998, 124, 912–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.J.; Chen, X.P. Experimental study on creep characteristics of soft soils. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2006, 28, 626–630. [Google Scholar]
- Akagi, T.; Ichikawa, Y.; Kuroda, T.; Kawamoto, T. A non-linear rheological analysis of deeply located tunnels. Int. J. Num. Anal. Meth. Geomech. 1984, 8, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okubo, S.; Nishimatsu, Y.; Fukui, K. Complete creep curves under uniaxial compression. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 1991, 28, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okubo, S.; Fukui, K.; Nishimatsu, Y. Control performance of servocontrolled testing machines in compression and creep tests. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 1993, 30, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabre, G.; Pellet, F. Creep and time-dependent damage in rgillaceous rocks. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2006, 43, 950–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukharov, G.N.; Chandi, M.W.; Boukharov, N.G. The three processes of brittle crystalline rock creep. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 1995, 32, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.B.; Shao, J.F. Strength Behavior, Creep failure and permeability change of a tight marble under triaxial compression. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2017, 50, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baud, P.; Meredith, P.G. Damage accumulation during triaxial creep of Darley Dale sandstone from pore volumometry and acoustic emission. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 1997, 34, 24.e1–24.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heap, M.J.; Baud, P.; Meredith, P.G.; Vinciguerra, S.; Bell, A.F.; Main, I.G. Brittle creep in basalt and its application to time-dependent volcano deformation. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2011, 307, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Q.; Jiang, Y. Triaxial mechanical creep behavior of sandstone. Min. Sci. Technol. 2010, 20, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.S. A damage mechanics treatment of creep failure in rock salt. Int. J. Damage Mech. 1997, 6, 122–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.H.; Daemen, J.J.K.; Yin, J.H. Experimental investigation of creep behavior of salt rock. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 1999, 36, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunsche, U.; Hampel, A. Rock salt—The mechanical properties of the host rock material for a radioactive waste repository. Eng. Geol. 1999, 52, 271–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slizowski, J.; Lankof, L. Salt-mudstones and rock-salt suitabilities for radioactive-waste storage systems: Rheological properties. Appl. Energy 2003, 75, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berest, P.; Blum, P.; Charpentier, J.; Gharbi, H.; Vales, F. Very slow creep tests on rock samples. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2005, 42, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lomnitz, C. Creep measurements in igneous rocks. J. Geol. 1956, 64, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockner, D.A.; Byerlee, J.D. Acoustic emission and creep in rock at high confining pressure and differential stress. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1977, 67, 247–258. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Molen, I.; Paterson, M.S. Experimental deformation of partially-melted granite. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1979, 70, 299–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, H.; Sasajima, S. A ten year creep experiment on small rock specimens. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 1987, 24, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, K.; Mizutani, H.; Yamada, I. Experimental study of strain-rate dependence and pressure dependence of failure properties of granite. J. Phys. Earth 1987, 35, 37–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, K.; Mizutani, H.; Yamada, I.; Imanishi, Y. Effects of water on time-dependent behavior of granite. J. Phys. Earth 1988, 36, 291–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.D.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Li, S.C.; Wang, S.G. Estimation of in situ viscoelastic parameters of a weak rock layer by time-dependent plate-loading tests. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2014, 66, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.D.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Li, S.C.; Wang, S.G. Time-dependent behavior of diabase and a nonlinear creep model. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2014, 47, 1211–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heap, M.J.; Baud, P.; Meredith, P.G.; Bell, A.F.; Main, I.G. Time-dependent brittle creep in Darley Dale sandstone. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brantut, N.; Heap, M.J.; Meredith, P.G.; Baud, P. Time-dependent cracking and brittle creep in crustal rocks: A review. J. Struct. Geol. 2013, 52, 17–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brantut, N.; Baud, P.; Heap, M.J.; Meredith, P.G. Micromechanics of brittle creep in rocks. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atkinson, B.K.; Meredith, P.G. The theory of subcritical crack growth with applications to minerals and rocks. Fract. Mech. Rock 1987, 2, 111–166. [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger, J.C.; Cook, N.G.W. Fundamentals of Rock Mechanics; Chapman and hall Ltd. and Science Paperbacks: London, UK, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Cristescu, N.D. Rock Rheolgy; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Cristescu, N.D.; Hunsche, U. Time Effects in Rock Mechanics; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Q.L.; Zhu, W.C.; Ranjith, P.G.; Shao, S.S. Numerical simulation and interpretation of the grain size effect on rock strength. Geomech. Geophys. Geo-Energ. Geo-Resour. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Q.; Xu, P.; Xu, T. Nonlinear visco-elastic and accelerating creep model for coal under conventional triaxial compression. Geomech. Geophys. Geo-Energ. Geo-Resour. 2015, 1, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.B.; Xie, S.Y.; Shao, J.F.; Conil, N. Effects of deviatoric stress and structural anisotropy on compressive creep behavior of a clayey rock. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 114, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.M.; Wang, Z.Y. Experimental study on rheological deformation and stress properties of limestone. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 2008, 15 (Suppl. 1), 475–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, P.; Wen, Y.D.; Wang, Y.X.; Yuan, H.P.; Yuan, B.X. Study on nonlinear damage creep constitutive model for high-stress soft rock. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.K.; Kang, W.F. Locked in stresses, creep and dilatancy of rocks, and constitutive equations. Rock Mech. 1980, 13, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.C.; Zhong, S.Q. Experimental data processing method in consideration of influence of loading history on rock specimen deformation. J. Cent. South. Univ. 1989, 20, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Kolařík, J.; Pegoretti, A. Proposal of the Boltzmann-like superposition principle for nonlinear tensile creep of thermoplastics. Polym. Test. 2008, 27, 596–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.; Verma, P. Uniaxial and triaxial single and multistage creep tests on coal-measure shale rocks. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2015, 137, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.L.; Xu, W.Y.; Yan, L.; Meng, Q.X.; Wang, R.B.; Zhao, H.B.; Xie, W.C. Investigation on time-dependent behaviour and long-term stability of underground water-sealed cavern. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2015, 19 (Suppl. 1), 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.G.; Hu, B.; Tang, H.M.; Hu, X.L.; Wang, J.D.; Huang, L. A constitutive model of granite shear creep under moisture. J. Earth Sci. 2016, 27, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Y.; Zhu, W.C.; Xu, T.; Niu, L.L.; Wei, J. Numerical simulation of rock creep behavior with a damage-based constitutive law. Int. J. Geomech. 2017, 17, 04016044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.B.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zheng, Y.L.; Duan, P.J.; Ding, S.L. Study on tri-axial creep experiment and constitutive relation of different rock salt. Saf. Sci. 2012, 50, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shao, J.F.; Xu, W.Y.; Jia, Y. Time-dependent behavior of cataclastic rocks in a multi-loading triaxial creep test. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2016, 49, 3793–3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakes, R.S. Viscoelastic Solids; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J. Rheological Behavior of Geomaterials and Its Engineering Applications; China Architecture and Building Press: Beijing, China, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.S.; Xia, C.C. Time-dependent tests on intact rocks in uniaxial compression. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2000, 37, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomanovic, Z. Rheological model of soft rock creep based on the tests on marls. Mech. Time-Depend. Mater. 2006, 10, 135–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Rheological Model | Constitutive Equation | Creep Equation |
|---|---|---|
| Maxwell | ||
| Kelvin | ||
| H-K | ||
| H|M | ||
| Burgers | ||
| Bingham | ||
| Nishihara |
| Rheological Properties | Creep | Transient Deformation | Relaxation | Elastic After-Effect | Viscous Flow | Deformation Limit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maxwell | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | NO |
| Kelvin | YES | NO | NO | YES | NO | YES |
| H-K | YES | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES |
| H|M | YES | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES |
| Burgers | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | NO |
| Bingham | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | NO |
| Nishihara | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | NO |
| σ0 (MPa) | E1 (MPa) | E2 (MPa) | η1 (MPa·d) | η2 (MPa·d) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| σ1 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | - |
| σ2 | 15.0 | 10.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | - |
| σ0 (MPa) | E1 (MPa) | E2 (MPa) | η1 (MPa·d) | η2 (MPa·d) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| σ1 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 200.0 |
| σ2 | 30.0 | 10.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 200.0 |
| σ0 (MPa) | E1 (MPa) | E2 (MPa) | η1 (MPa·d) | η2 (MPa·d) | σs (MPa) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| σ1 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 20.0 | 50.0 | 15.0 |
| σ2 | 30.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 20.0 | 50.0 | 15.0 |
| σ3 | 60.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 20.0 | 50.0 | 15.0 |
| Rock Type | G0 (GPa) | G1 (GPa) | η1 (GPa·h) | η2 (GPa·h) | K (GPa) | τs (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anhydrite rock salt | 3.5 | 3.0 | 25.5 | 52.1 | 7.6 | 27.0 |
| Glauberite rock salt | 0.94 | 4.2 | 5.6 | 76.3 | 2.0 | 15.1 |
| Argillaceous rock salt | 2.1 | 10.9 | 42.6 | 1003.5 | 4.6 | 4.1 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, W.; Gamage, R.P.; Huang, C.; Luo, G.; Guo, J.; Wang, S. Loading History Effect on Creep Deformation of Rock. Energies 2018, 11, 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11061462
Yang W, Gamage RP, Huang C, Luo G, Guo J, Wang S. Loading History Effect on Creep Deformation of Rock. Energies. 2018; 11(6):1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11061462
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Wendong, Ranjith Pathegama Gamage, Chenchen Huang, Guangyu Luo, Jingjing Guo, and Shugang Wang. 2018. "Loading History Effect on Creep Deformation of Rock" Energies 11, no. 6: 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11061462
APA StyleYang, W., Gamage, R. P., Huang, C., Luo, G., Guo, J., & Wang, S. (2018). Loading History Effect on Creep Deformation of Rock. Energies, 11(6), 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11061462






