A Non-Standard Characteristic Based Protection Scheme for Distribution Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Motivation
1.2. Relevant Literature
1.3. Contributions and Organization of the Paper
- Devising a novel non-standard characteristic that depends on both current and voltage measurements during the fault in order to mitigate the effect of DG connection.
- Constructing a new protection scheme based on a double characteristic aiming to obtain a coordination-free primary operation time of the relays.
- Providing comparative results between the proposed characteristic and the IEC normal standard characteristic taking into account the size and the location of DG units.
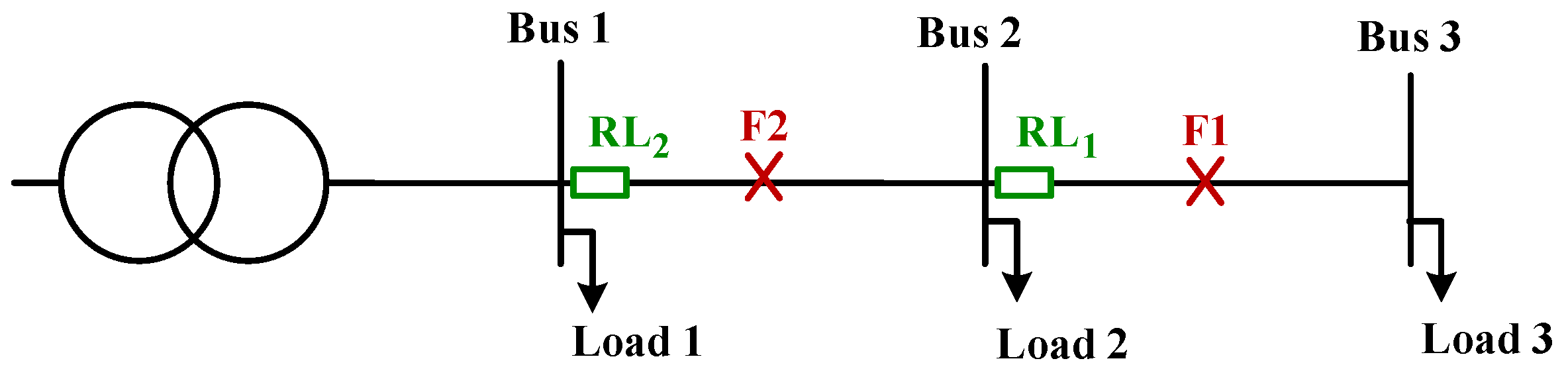
2. Proposed Protection Approach
2.1. Standard Characteristics
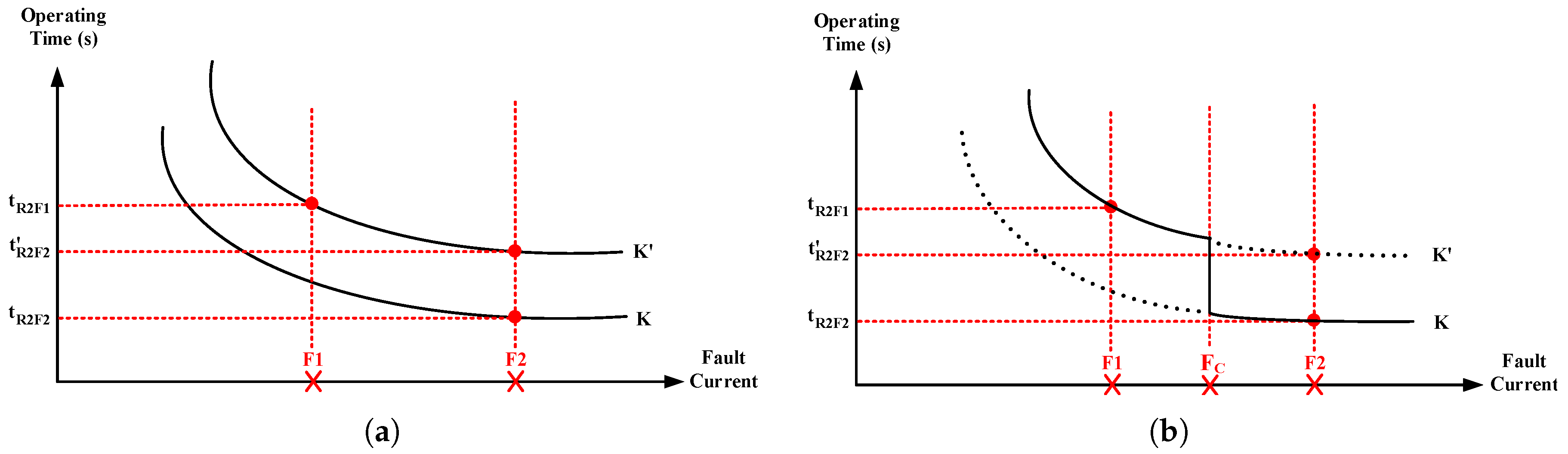
2.2. Devised Relay Characteristic
2.3. Proposed Coordination Scheme
3. Optimization of Protection Coordination
3.1. Problem Formulation and Evaluated Cases
- T denotes the total operating time of the relays,
- Y symbolizes the total number of the relays while i is the relay indicator,
- G represents the total number of the faults considered while j is the fault type indicator,
- states the total number of the backup relays for each primary relay,
- and express the primary and backup operating time of i th relay for fault type j, respectively.
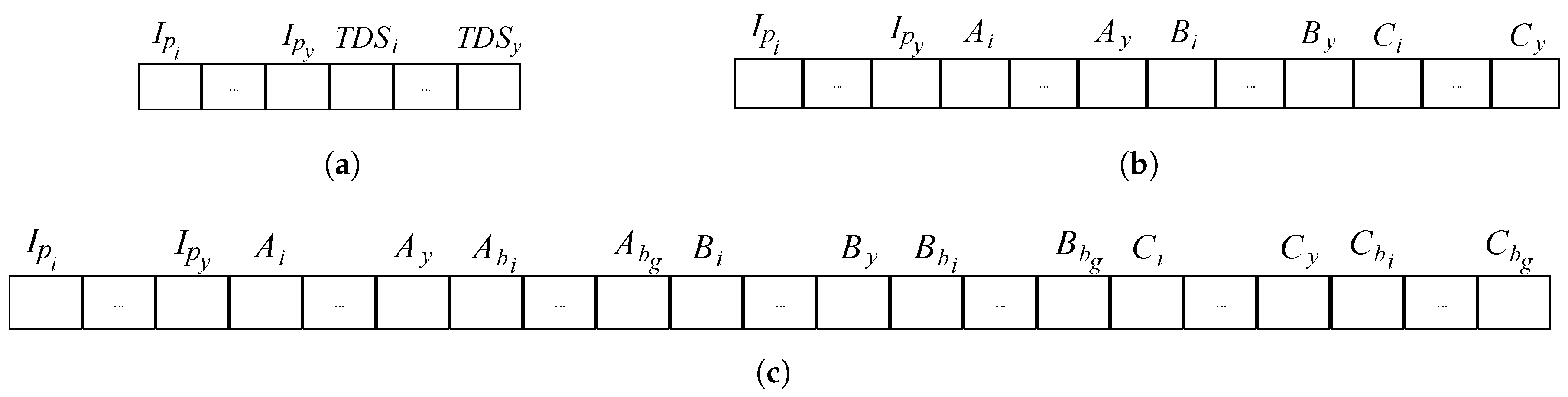
3.2. Solution Method
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Test System and Scenarios
4.2. Results
4.3. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anderson, P.M. Power System Protection; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, T.; Li, Y.; Duan, X.; Zhu, J. Simplified Analytic Approach of Pole-to-Pole Faults in MMC-HVDC for AC System Backup Protection Setting Calculation. Energies 2018, 11, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.; Son, D.H.; Kang, S.H.; Nam, S.R. A novel protection method for single line-to-ground faults in ungrounded low-inertia microgrids. Energies 2016, 9, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norshahrani, M.; Mokhlis, H.; Abu Bakar, A.H.; Jamian, J.J.; Sukumar, S. Progress on Protection Strategies to Mitigate the Impact of Renewable Distributed Generation on Distribution Systems. Energies 2017, 10, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ok, Y.; Lee, J.; Choi, J. Analysis and solution for operations of overcurrent relay in wind power system. Energies 2016, 9, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Salam, M.; Kamel, R.; Sayed, K.; Khalaf, M. Design and implementation of a multifunction DSP-based-numerical relay. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2017, 143, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phadke, A.G.; Thorp, J.S. Computer Relaying for Power Systems; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Brahma, S.M.; Girgis, A.A. Development of adaptive protection scheme for distribution systems with high penetration of distributed generation. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2004, 19, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Phadke, A. A novel adaptive current protection scheme for distribution systems with distributed generation. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2012, 43, 1460–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Khattam, W.; Sidhu, T.S. Restoration of directional overcurrent relay coordination in distributed generation systems utilizing fault current limiter. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2008, 23, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, O.A.; Enríquez, A.C.; Guajardo, L.T. Overcurrent relay with unconventional curves and its application in industrial power systems. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2014, 110, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, K.A.; Zeineldin, H.; Al-Hinai, A.; El-Saadany, E.F. Optimal coordination of directional overcurrent relays using a new time–current–voltage characteristic. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2015, 30, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, K.A.; El Moursi, M.S.; Zeineldin, H.H. A new protection scheme considering fault ride through requirements for transmission level interconnected wind parks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2015, 11, 1324–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewadasa, M.; Ghosh, A.; Ledwich, G. Fold back current control and admittance protection scheme for a distribution network containing distributed generators. IET Gene. Transm. Distrib. 2010, 4, 952–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewadasa, M.; Ghosh, A.; Ledwich, G. An inverse time admittance relay for fault detection in distribution networks containing DGs. In Proceedings of the TENCON 2009—2009 IEEE Region 10 Conference, Singapore, 23–26 January 2009; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yazdaninejadi, A.; Jannati, J.; Farsadi, M. A New Formulation for Coordination of Directional Overcurrent Relays in Interconnected Networks for Better Miscoordination Suppression. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. 2017, 18, 169–175. [Google Scholar]
- Alkaran, D.S.; Vatani, M.R.; Sanjari, M.J.; Gharehpetian, G.B.; Naderi, M.S. Optimal Overcurrent Relay Coordination in Interconnected Networks by Using Fuzzy-Based GA Method. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.; Karami, H.; Sanjari, M.; Tarimoradi, H.; Gharehpetian, G. Application of hyper-spherical search algorithm for optimal coordination of overcurrent relays considering different relay characteristics. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2016, 83, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrão, D.L.; Vieira, J.C. The Local Fit Method for Coordinating Directional Overcurrent Relays. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2016, 31, 1464–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karegar, H.K.; Aghdam, T.S. Relay Curve Selection Approach for Microgrid Optimal Protection. Int. J. Renew. Energy Res. 2017, 7, 636–642. [Google Scholar]
- Keil, T.; Jager, J. Advanced coordination method for overcurrent protection relays using nonstandard tripping characteristics. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2008, 23, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojaghi, M.; Ghahremani, R. Piece–wise Linear Characteristic for Coordinating Numerical Overcurrent Relays. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2017, 32, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEC. Electrical Relays-Part 3: Single Input Energizing Quantity Measuring Relays with Dependent or Independent Time, 60255-3; IEC: Geneva, Switzerland, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- IEEE. Standard Inverse-Time Characteristic Equations for Overcurrent Relays, Std C37.112-1996; IEEE: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, D.E.; Holland, J.H. Genetic algorithms and machine learning. Mach. Learn. 1988, 3, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storn, R. On the usage of differential evolution for function optimization. In Proceedings of the 1996 Biennial Conference of the North American NAFIPS Fuzzy Information Processing Society, Berkeley, CA, USA, 19–22 June 1996; pp. 519–523. [Google Scholar]
- University of Washington. Power Systems Test Case Archive. 1993. Available online: https://www2.ee.washington.edu/research/pstca/ (accessed on 5 February 2018).
- Talaat, H.E.A.; Abdelaziz, A.Y.; Nosseir, A.I.; Hajjar, A.A. Optimal coordination of overcurrent relays by linear programming: An enhanced problem formulation. In Proceedings of the 1999 Arab Countries IEEE 3rd CIGRE Regional Conference, Douha, Qatar, 25–27 May 1999. [Google Scholar]
- DIgSILENT GmbH. DIgSILENT/PowerFactory Software. Available online: https://www.digsilent.de/en/ (accessed on 5 March 2018).


| Relay Name | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | R7 | R8 |
| Current Tr. Ratio | 400/5 | 100/5 | 200/5 | 300/5 | 100/5 | 300/5 | 200/5 | 100/5 |
| Relay Name | R9 | R10 | R11 | R12 | R13 | R14 | R15 | R16 |
| Current Tr. Ratio | 400/5 | 300/5 | 100/5 | 300/5 | 300/5 | 200/5 | 400/5 | 400/5 |
| Scenarios | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| Connection Bus(es) | - | 10 | 10,11 | 10,11,12 | 10,11,12,13 | 10,11,12,13,14 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 14 | 14 | 14 |
| DG Size(s) | 3.3 | 3.3* | 3.3* | 3.3* | 3.3* | 3.3* | 3.3 | 5.5 | 9.9 | 3.3 | 5.5 | 9.9 | 3.3 | 5.5 | 9.9 |
| Case | Variable | Relay Name | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | R7 | R8 | R9 | R10 | R11 | R12 | R13 | R14 | R15 | R16 | ||
| 1 | Ip (A) | 3.48 | 2.21 | 2.48 | 1.35 | 1.33 | 2.06 | 2.79 | 1.96 | 4.60 | 3.64 | 0.26 | 3.93 | 3.68 | 1.82 | 3.23 | 4.83 |
| TDS | 0.72 | 0.06 | 0.30 | 0.27 | 0.09 | 0.29 | 0.92 | 0.22 | 0.90 | 0.84 | 0.83 | 0.63 | 0.59 | 0.25 | 0.95 | 0.32 | |
| 2 | Ip (A) | 3.66 | 4.20 | 1.76 | 2.83 | 0.33 | 2.77 | 0.58 | 1.71 | 2.19 | 3.00 | 2.86 | 2.74 | 3.69 | 1.78 | 2.92 | 3.10 |
| A | 1.07 | 1.01 | 1.03 | 1.04 | 1.01 | 1.00 | 1.08 | 1.04 | 1.02 | 1.06 | 1.06 | 1.02 | 1.09 | 1.02 | 1.07 | 1.01 | |
| B | 0.11 | 0.75 | 0.06 | 0.81 | 0.61 | 0.39 | 0.12 | 0.54 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.45 | 0.15 | 0.46 | 0.93 | 0.21 | 0.12 | |
| C | 0.31 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.36 | 0.12 | 0.40 | 0.34 | 0.13 | 0.29 | 0.38 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.40 | 0.14 | 0.48 | 0.29 | |
| 3 | Ip (A) | 1.61 | 3.53 | 0.95 | 3.11 | 0.66 | 1.69 | 0.59 | 0.69 | 1.68 | 3.61 | 2.17 | 1.11 | 4.59 | 1.15 | 4.55 | 3.62 |
| A | 1.02 | 1.08 | 1.03 | 1.09 | 1.03 | 1.07 | 1.04 | 1.00 | 1.07 | 1.02 | 1.06 | 1.01 | 1.03 | 1.09 | 1.08 | 1.02 | |
| Ab | 1.03 | 1.01 | 1.02 | 1.03 | 1.01 | 1.07 | 1.10 | 1.02 | 1.05 | 1.04 | 1.00 | ||||||
| B | 0.90 | 0.64 | 0.91 | 0.88 | 0.81 | 0.29 | 0.43 | 0.62 | 0.71 | 0.92 | 0.96 | 0.17 | 0.50 | 0.64 | 0.48 | 0.76 | |
| Bb | 0.17 | 0.06 | 0.44 | 0.46 | 0.09 | 0.20 | 0.76 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.14 | 0.15 | ||||||
| C | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.34 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.25 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.25 | 0.08 | 0.32 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.13 | 0.19 | |
| Cb | 0.33 | 0.00 | 0.46 | 0.43 | 0.16 | 0.44 | 0.45 | 0.48 | 0.40 | 0.30 | 0.33 | ||||||
| Operation Time of Relay(s) against Three Phase Fault (pr = primary, bc = backup) (s) | Operation Time of Relay(s) against Double-Phase-to- Ground Fault (pr = primary, bc = backup) (s) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fault Location | Conventional Characteristic | Proposed Characteristic | Fault Location | Conventional Characteristic | Proposed Characteristic | ||||||||
| pr | bc1 | bc2 | pr | bc1 | bc2 | pr | bc1 | bc2 | pr | bc1 | bc2 | ||
| L1 | R1: 1.09 | R1: 0.07 | L1 | R1: 1.04 | R1: 0.07 | ||||||||
| R2: 0.05 | R4: 0.36 | R2: 0.21 | R4: 0.54 | R2: 0.05 | R4: 0.35 | R2: 0.21 | R4: 0.55 | ||||||
| L2 | R3: 0.92 | R1: 1.47 | R3: 0.09 | R1: 0.74 | L2 | R3: 0.89 | R1: 1.39 | R3: 0.10 | R1: 0.74 | ||||
| R4: 0.33 | R16: 0.97 | R7: 0.87 | R4: 0.04 | R16: 0.44 | R7: 0.58 | R4: 0.32 | R16: 0.91 | R7: 0.86 | R4: 0.04 | R16: 0.44 | R7: 0.60 | ||
| L3 | R16: 0.68 | R16:0.14 | L3 | R16: 0.63 | R16: 0.14 | ||||||||
| R5: 0.10 | R3: 1.16 | R7: 0.81 | R5: 0.01 | R3: 0.55 | R7: 0.54 | R5: 0.10 | R3: 1.16 | R7: 0.79 | R5: 0.02 | R3: 0.58 | R7: 0.56 | ||
| L4 | R6: 0.50 | R16: 0.98 | R3: 1.28 | R6: 0.07 | R16: 0.48 | R3: 0.65 | L4 | R6: 0.49 | R16: 0.94 | R3: 1.24 | R6: 0.08 | R16: 0.48 | R3: 0.66 |
| R7: 0.70 | R9: 1.93 | R7: 0.01 | R9: 0.73 | R7: 0.68 | R9: 1.85 | R7: 0.01 | R9: 0.74 | ||||||
| L5 | R15: 1.35 | R15: 0.06 | L5 | R15: 1.27 | R15: 0.06 | ||||||||
| R14: 0.30 | R12: 0.73 | R14: 0.01 | R12: 0.41 | R14: 0.29 | R12: 0.72 | R14: 0.02 | R12: 0.44 | ||||||
| L6 | R12: 0.66 | R10: 1.48 | R12: 0.01 | R10: 0.40 | L6 | R12: 0.64 | R10: 1.40 | R12: 0.01 | R10: 0.42 | ||||
| R13: 1.28 | R15: 1.77 | R13: 0.21 | R15: 0.94 | R13: 1.24 | R15: 1.70 | R13: 0.22 | R15: 0.99 | ||||||
| L7 | R10: 1.28 | R10: 0.05 | L7 | R10: 1.18 | R10: 0.05 | ||||||||
| R11: 0.52 | R13: 1.45 | R11: 0.01 | R13: 0.61 | R11: 0.52 | R13: 1.42 | R11: 0.01 | R13: 0.71 | ||||||
| L8 | R8: 0.11 | R6: 0.62 | R8: 0.07 | R6: 0.71 | L8 | R8: 0.10 | R6: 0.61 | R8: 0.07 | R6: 0.73 | ||||
| R9: 1.48 | R9: 0.06 | R9: 1.40 | R9: 0.06 | ||||||||||
| L1 | R1: 1.04 | R1: 0.07 | L1 | R1: 1.14 | R1: 0.08 | ||||||||
| R2: 0.05 | R4: 0.35 | R2: 0.22 | R4: 0.59 | R2: 0.05 | R4: 0.38 | R2: 0.22 | R4: 0.61 | ||||||
| L2 | R3: 0.89 | R1: 1.39 | R3: 0.10 | R1: 0.77 | L2 | R3: 0.95 | R1: 1.55 | R3: 0.11 | R1: 0.80 | ||||
| R4: 0.32 | R16: 0.91 | R7: 0.86 | R4: 0.05 | R16: 0.49 | R7: 0.62 | R4: 0.34 | R16: 1.04 | R7: 0.90 | R4: 0.05 | R16: 0.54 | R7: 0.62 | ||
| L3 | R16: 0.63 | R16: 0.15 | L3 | R16: 0.71 | R16: 0.15 | ||||||||
| R5: 0.10 | R3: 1.15 | R7: 0.69 | R5: 0.02 | R3: 0.64 | R7: 0.59 | R5: 0.10 | R3: 1.31 | R7: 0.84 | R5: 0.02 | R3: 0.66 | R7: 0.59 | ||
| L4 | R6: 0.49 | R16: 0.94 | R3: 1.24 | R6: 0.09 | R16: 0.51 | R3: 0.69 | L4 | R6: 0.52 | R16: 1.05 | R3: 1.34 | R6: 0.09 | R16: 0.57 | R3: 0.71 |
| R7: 0.69 | R9: 1.86 | R7: 0.01 | R9: 0.76 | R7: 0.72 | R9: 2.03 | R7: 0.01 | R9: 0.79 | ||||||
| L5 | R15: 1.27 | R15: 0.06 | L5 | R15: 1.42 | R15: 0.07 | ||||||||
| R14: 0.29 | R12: 0.72 | R14: 0.03 | R12: 0.49 | R14: 0.32 | R12: 0.75 | R14: 0.03 | R12: 0.49 | ||||||
| L6 | R12: 0.64 | R10: 1.40 | R12: 0.01 | R10: 0.46 | L6 | R12: 0.68 | R10: 1.32 | R12: 0.01 | R10: 0.48 | ||||
| R13: 1.24 | R15: 1.70 | R13: 0.23 | R15: 1.08 | R13: 1.34 | R15: 1.89 | R13: 0.24 | R15: 1.16 | ||||||
| L7 | R10: 1.17 | R10: 0.06 | L7 | R10: 1.32 | R10: 0.07 | ||||||||
| R11: 0.52 | R13: 1.42 | R11: 0.01 | R13: 0.93 | R11: 0.54 | R13: 1.52 | R11: 0.01 | R13: 0.95 | ||||||
| L8 | R8: 0.10 | R6: 0.61 | R8: 0.08 | R6: 0.76 | L8 | R8: 0.11 | R6: 0.65 | R8: 0.08 | R6: 0.79 | ||||
| R9: 1.40 | R9: 0.06 | R9: 1.54 | R9: 0.07 | ||||||||||
| Case | Pop. Data | Scenario | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | ||
| 1 | Mean Value (s) | 103.08 | 133.64 | 111.48 | 113.40 | 121.51 | 112.66 | 199.00 | 148.87 | 127.26 | 133.38 | 121.55 | 155.09 | 112.76 | 106.75 | 107.24 |
| Variance (s) | 0.78 | 3.78 | 3.50 | 2.72 | 1.32 | 2.38 | 5.21 | 2.31 | 6.00 | 3.46 | 6.19 | 4.92 | 2.99 | 4.09 | 2.11 | |
| Best Ind. (s) | 101.41 | 127.69 | 105.90 | 108.30 | 118.39 | 108.27 | 111.02 | 143.23 | 119.54 | 128.96 | 113.58 | 147.40 | 107.48 | 99.73 | 103.25 | |
| 2 | Mean (s) | 86.64 | 85.70 | 75.43 | 76.19 | 80.92 | 83.12 | 75.04 | 81.74 | 80.99 | 92.73 | 89.58 | 90.47 | 91.27 | 86.40 | 81.80 |
| Variance (s) | 2.81 | 1.59 | 0.88 | 1.34 | 1.41 | 1.09 | 3.00 | 1.57 | 0.80 | 3.16 | 1.83 | 0.91 | 1.21 | 1.59 | 1.23 | |
| Best Ind. (s) | 80.19 | 81.11 | 71.52 | 72.50 | 76.60 | 79.65 | 70.39 | 77.45 | 75.55 | 86.52 | 85.25 | 87.08 | 87.71 | 82.28 | 76.84 | |
| Decrese in T (%) | 20.92 | 36.48 | 32.46 | 33.06 | 35.30 | 26.43 | 36.60 | 45.93 | 36.80 | 32.91 | 24.94 | 40.93 | 18.40 | 17.50 | 25.58 | |
| 3 | Mean (s) | 49.30 | 48.91 | 44.78 | 48.12 | 43.62 | 44.70 | 53.69 | 61.63 | 56.20 | 65.81 | 43.04 | 51.85 | 57.17 | 53.78 | 52.36 |
| Variance (s) | 1.06 | 0.89 | 0.61 | 0.52 | 2.90 | 0.96 | 0.89 | 0.35 | 0.61 | 1.37 | 0.63 | 0.28 | 1.29 | 0.73 | 0.39 | |
| Best Ind. (s) | 46.12 | 45.23 | 42.16 | 45.65 | 40.51 | 40.92 | 50.26 | 59.44 | 53.61 | 61.84 | 40.39 | 50.06 | 52.78 | 50.77 | 50.38 | |
| Decrese in T (%) | 54.52 | 64.58 | 60.19 | 57.85 | 65.78 | 62.21 | 54.73 | 58.50 | 55.15 | 52.05 | 64.44 | 66.04 | 50.89 | 49.09 | 51.21 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kılıçkıran, H.C.; Akdemir, H.; Şengör, İ.; Kekezoğlu, B.; Paterakis, N.G. A Non-Standard Characteristic Based Protection Scheme for Distribution Networks. Energies 2018, 11, 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11051241
Kılıçkıran HC, Akdemir H, Şengör İ, Kekezoğlu B, Paterakis NG. A Non-Standard Characteristic Based Protection Scheme for Distribution Networks. Energies. 2018; 11(5):1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11051241
Chicago/Turabian StyleKılıçkıran, Hasan Can, Hüseyin Akdemir, İbrahim Şengör, Bedri Kekezoğlu, and Nikolaos G. Paterakis. 2018. "A Non-Standard Characteristic Based Protection Scheme for Distribution Networks" Energies 11, no. 5: 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11051241
APA StyleKılıçkıran, H. C., Akdemir, H., Şengör, İ., Kekezoğlu, B., & Paterakis, N. G. (2018). A Non-Standard Characteristic Based Protection Scheme for Distribution Networks. Energies, 11(5), 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11051241






