Optimal Scheduling Strategies of Distributed Energy Storage Aggregator in Energy and Reserve Markets Considering Wind Power Uncertainties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Problem and Method Statement
2.1. Problem Description
2.2. System Uncertainly Analysis
2.3. Scenario Reduction Strategy
3. Mathematical Modeling
3.1. Modeling DESA
3.2. Modeling in the Lower-Level Problem
3.2.1. Objective Function
3.2.2. Energy and Reserve Balance Constrains
3.2.3. Generator and WPP Operating Constrains
3.2.4. DESA Constraints
3.3. Modeling in the Upper-Level Problem
3.3.1. Objective Function of the Upper-Level Problem
3.3.2. DES Constraints
4. Simulation and Results
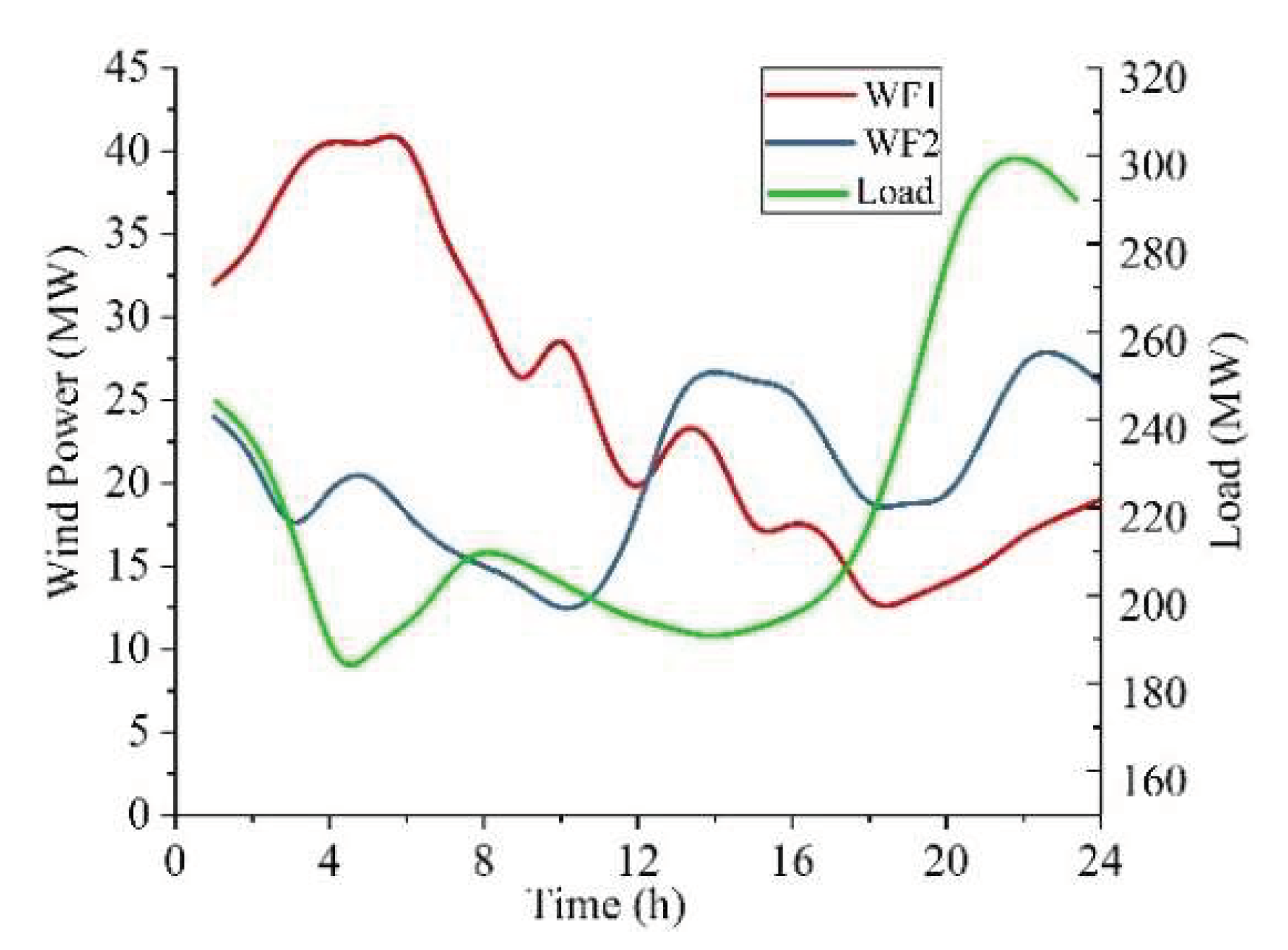
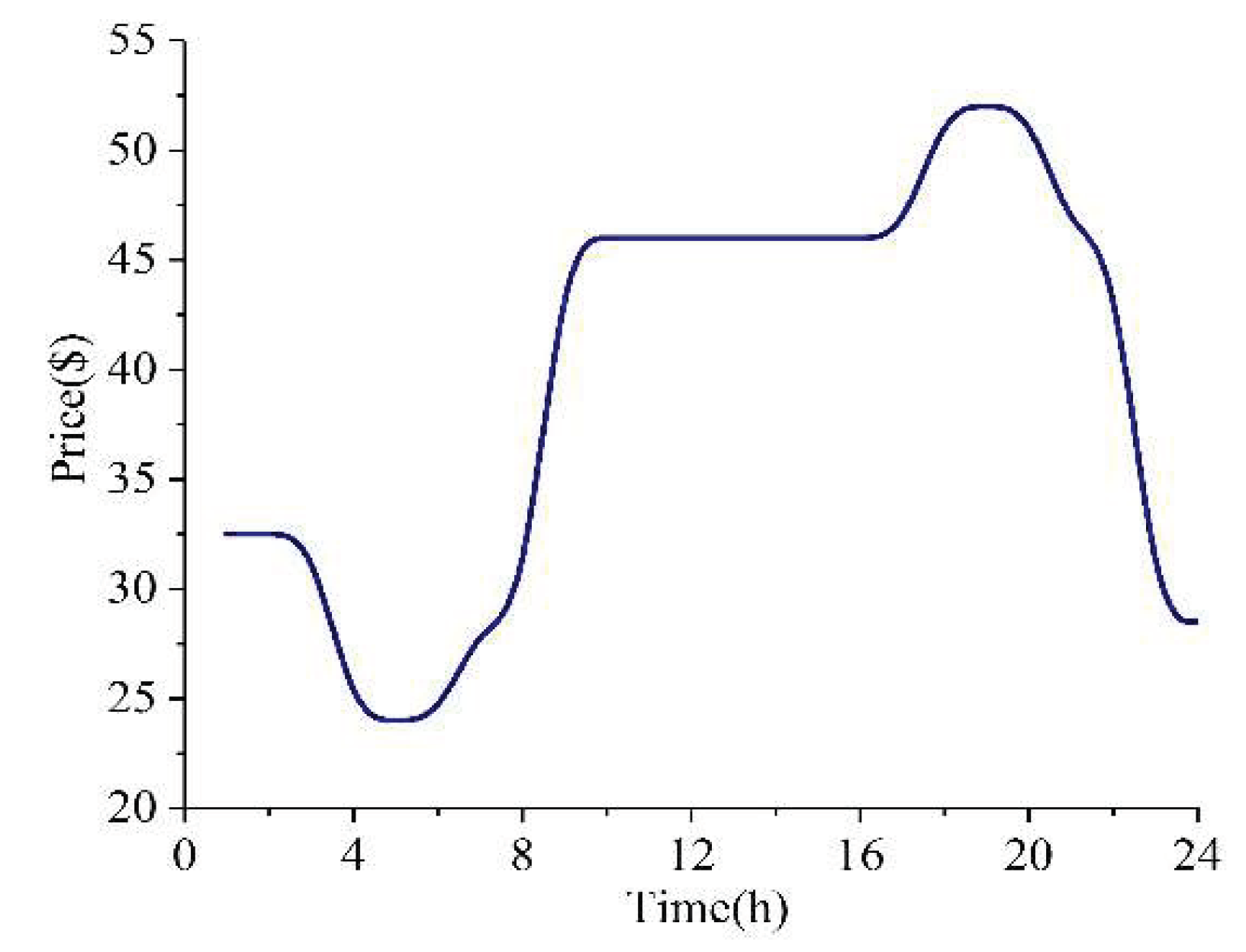
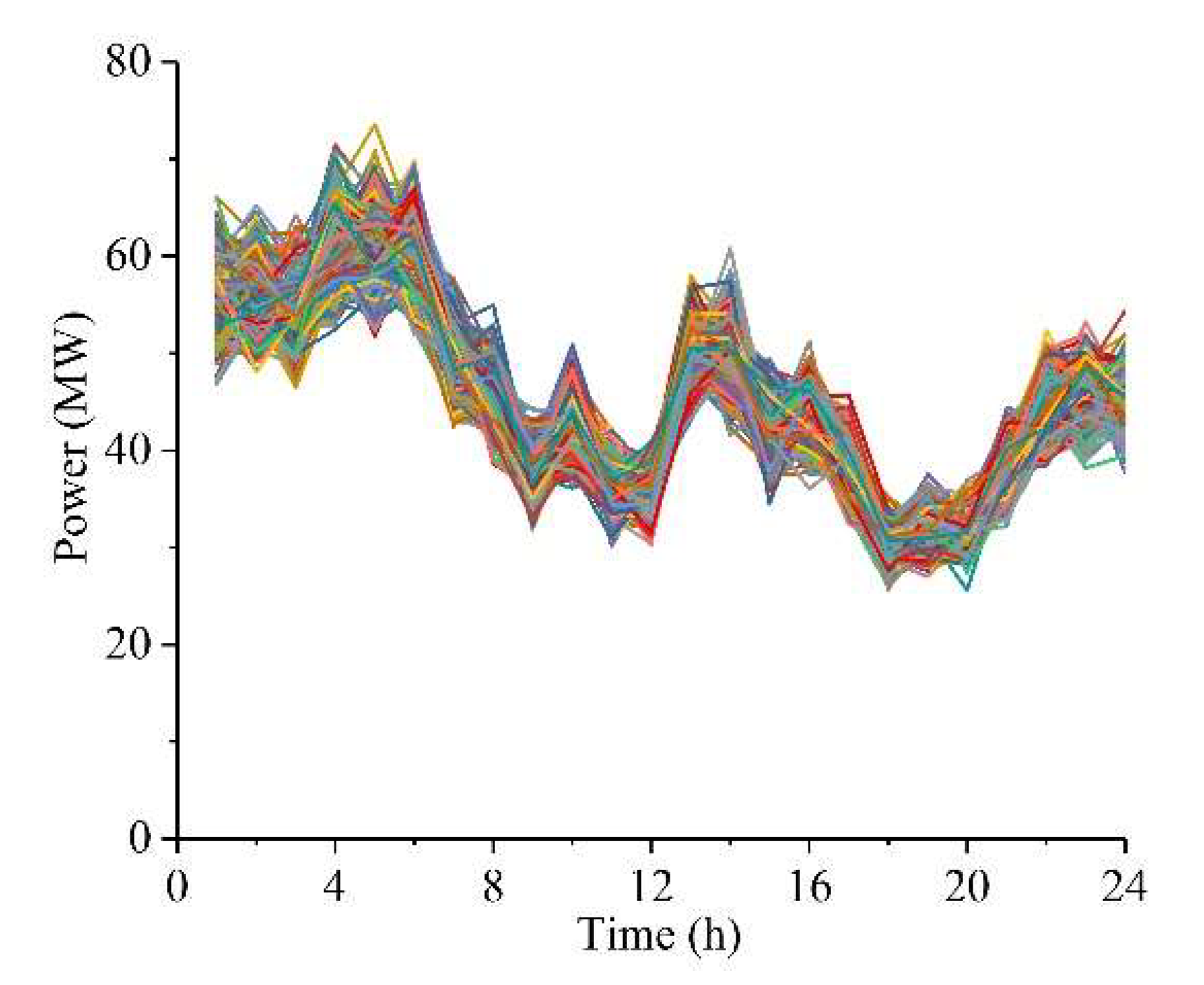
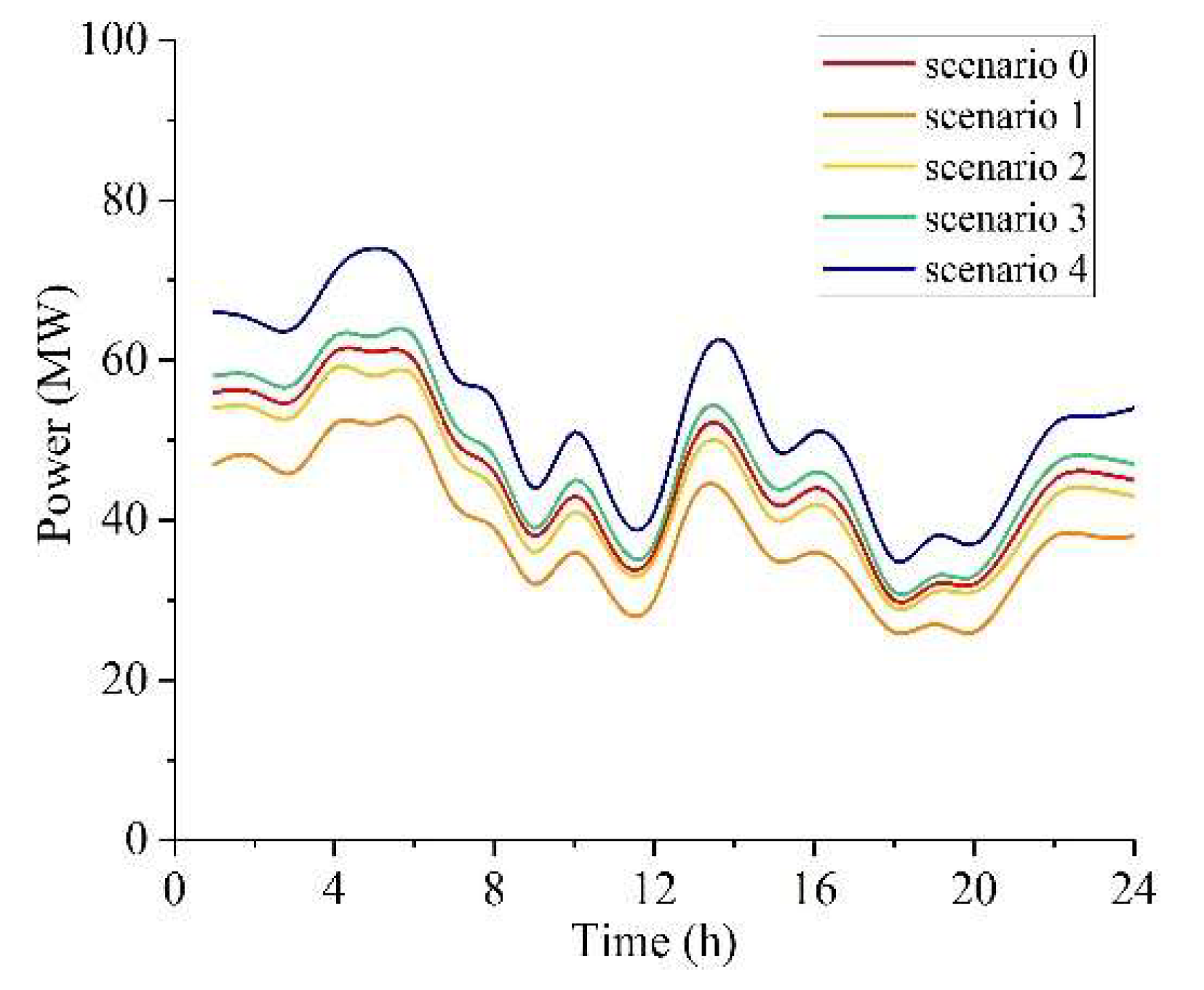
4.1. Test Description
4.2. Simulation Results
5. Conclusions and Future Studies
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
Sets and Indices
| a | Index of DESA |
| d(D) | Index (set) of DES |
| g(G) | Index (set) of generator unit |
| s(S) | Index (set) of wind power scenarios of WPP |
| t(T) | Index (set) of scheduling hour |
| w(W) | Index (set) of WPP |
| i(I) | Index (set) of transmission network nodes |
| j | Index of distribution network nodes |
Parameters
| Operation cost of unit in hour | |
| Fixed running cost of unit in hour | |
| Maximum power generation of unit | |
| Minimum power generation of unit | |
| WPP forecast output (MW) | |
| Maximum wind power that can be scheduled from of hour | |
| Power output of in scenario s in hour (MW) | |
| Ramp-down rate of unit (MW/h) | |
| Ramp-up rate of unit (MW/h) | |
| Maximum energy storage of a DES unit (MW/h) | |
| Initial energy stored in a DES unit (MW/h) | |
| Maximum charging/discharging power of a DES unit (MW/h) | |
| Shut-down cost of unit | |
| Start-up cost of unit | |
| Energy demand of load i in hour | |
| Energy demand of load j in hour | |
| Maximum capacity of line l (MW) | |
| Minimum down-time of unit (h) | |
| Minimum up-time of unit (h) | |
| Day-ahead market price in | |
| Real-time market price in | |
| Offer cost by in for up-spinning reserves | |
| Offer cost by in for down-spinning reserves | |
| Offer cost in for up-spinning reserves | |
| Offer cost in for down-spinning reserves | |
| CO2 emissions penalty price ($/ton) | |
| CO2 emission deviated from generator (ton/MW) | |
| Demand of reserve capacity in in DA | |
| Probability of scenario s |
Variables
| Binary variable-1 if unit is starting up in hour | |
| Binary variable-1 if unit is shutting down in hour | |
| Binary variable indicating unit status | |
| Scheduled charging/discharging power of DES in hour | |
| Scheduled output of unit in hour | |
| Binary variable-1 indicating DES status | |
| Up- and down-spinning reserve contributions of unit in hour | |
| Reserve contributions of discharging/charging in DA market | |
| Reserve contributions of discharging/charging in balancing market | |
| Scheduled charging/discharging power of DESA in hour | |
| Reserve contributions of DESA discharging/charging in hour |
References
- ODwyer, C.; Ryan, L.; Flynn, D. Efficient Large-Scale Energy Storage Dispatch: Challenges in Future High Renewable Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2017, 32, 3439–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gevorgian, V.; Wang, C.; Lei, X.; Chou, E.; Yang, R. Grid-Level Application of Electrical Energy Storage: Example Use Cases in the United States and China. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 2017, 15, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Baker, S.; Benner, S.; Berner, A.; Liu, J. PJM Integrates Energy Storage: Their Technologies and Wholesale Products. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 2017, 15, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Du, W.; Wang, H.F. An Improved Corrective Security Constrained OPF With Distributed Energy Storage. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2016, 31, 1537–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Ocana, J.E.; Ortega-Vazquez, M.A.; Zhang, B. Participation of an Energy Storage Aggregator in Electricity Markets. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tan, K.T.; Peng, X.Y.; So, P.L. Coordinated Control of Distributed Energy-Storage Systems for Voltage Regulation in Distribution Networks. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2016, 31, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strbac, G.; Aunedi, M.; Konstantelos, I.; Moreira, R.; Teng, F.; Moreno, R. Opportunities for Energy Storage: Assessing Whole-System Economic Benefits of Energy Storage in Future Electricity Systems. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 2017, 15, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Parida, S.K. A review on distributed generation allocation and planning in deregulated electricity market. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 4132–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.; Romlie, M.F.; Abdullah, M.F.; Abd Halim, S.; Abu Bakar, A.H.; Chia Kwang, T. A review on peak load shaving strategies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 3323–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpinelli, G.; Celli, G.; Mocci, S.; Mottola, F.; Pilo, F.; Proto, D. Optimal Integration of Distributed Energy Storage Devices in Smart Grids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2013, 4, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebel, C.; Jacobsen, H. Bringing Distributed Energy Storage to Market. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2016, 31, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, A.S.A.; EL-Fouly, T.H.M.; Salama, M.M.A. Optimal ESS Allocation for Benefit Maximization in Distribution Networks. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 8, 1668–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasekara, N.; Masoum, M.A.S.; Wolfs, P.J. Optimal Operation of Distributed Energy Storage Systems to Improve Distribution Network Load and Generation Hosting Capability. IEEE Trans Sustain Energy 2016, 7, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Niu, S.; Xu, H. Optimal Planning of Battery Energy Storage Considering Reliability Benefit and Operation Strategy in Active Distribution System. J. Mod. Power Syst. Cle. 2017, 5, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Shin, J.; Kim, J. Operation Strategy of Multi-Energy Storage System for Ancillary Service. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2017, 32, 4409–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, M.R.; Dvorkin, Y.; Ortega-Vazquez, M.A. Optimal Participation of an Electric Vehicle Aggregator in Day-Ahead Energy and Reserve Markets. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2016, 31, 3506–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Cao, J.; Chen, M.Z.Q.; Yu, J.; Yao, J.; Yang, S. Load Following of Multiple Heterogeneous TCL Aggregators by Centralized Control. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2017, 32, 3157–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.; Sanandaji, B.M.; Poolla, K.; Vincent, T.L. Aggregate Flexibility of Thermostatically Controlled Loads. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2015, 30, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayegan-Rad, A.; Badri, A.; Zangeneh, A. Day-ahead Scheduling of Virtual Power Plant in Joint Energy and Regulation Reserve Markets under Uncertainties. Energy 2017, 121, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konda, S.R.; Panwar, L.K.; Panigrahi, B.K.; Kumar, R. Optimal Offering of Demand Response Aggregation Company in Price-Based Energy and Reserve Market Participation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahramara, S.; Yazdani-Damavandi, M.; Contreras, J.; Shafie-khah, M.; Catalao, J.P.S. Modeling the Strategic Behavior of a Distribution Company in Wholesale Energy and Reserve Markets. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Wang, Y.; Dvorkin, Y.; Fernandez-Blanco, R.; Silva-Monroy, C.A.; Watson, J. Scalable Planning for Energy Storage in Energy and Reserve Markets. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2017, 32, 4515–4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrolahpour, E.; Kazempour, J.; Zareipour, H.; Rosehart, W.D. A Bilevel Model for Participation of a Storage System in Energy and Reserve Markets. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2018, 9, 582–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan-Hejazi, H.; Mohsenian-Rad, H. Optimal Operation of Independent Storage Systems in Energy and Reserve Markets with High Wind Penetration. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2014, 5, 1088–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruihuan, L.; Yajing, G.; Huaxin, C.; Haifeng, L. Two Step Optimal Dispatch Based on Multiple Scenarios Technique for Active Distribution System with the Uncertainties of Intermittent Distributed Generation and Load Considered. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Power System Technology, Chengdu, Sichuan, China, 20–22 October 2014; pp. 3303–3308. [Google Scholar]
- Bouffard, F.; Galiana, F.D. Stochastic Security for Operations Planning with Significant Wind Power Generation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2008, 23, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doostizadeh, M.; Aminifar, F.; Ghasemi, H.; Lesani, H. Energy and Reserve Scheduling Under Wind Power Uncertainty: An Adjustable Interval Approach. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2016, 7, 2943–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caves-Avila, J.P.; Hakvoort, R.A.; Ramos, A. The Impact of European Balancing Rules on Wind Power Economics and on Short-term Bidding Strategies. Energy Policy 2014, 68, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


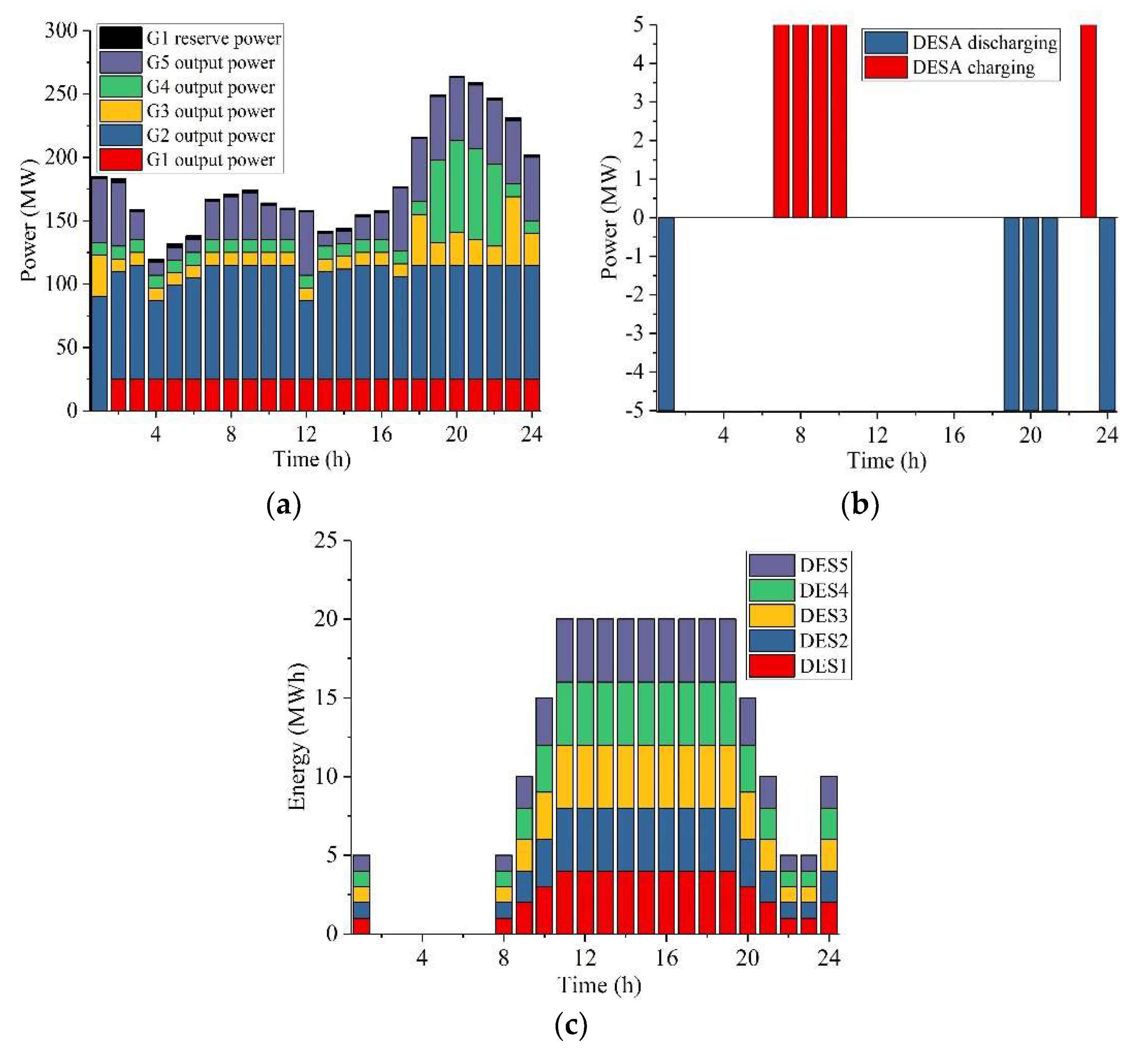
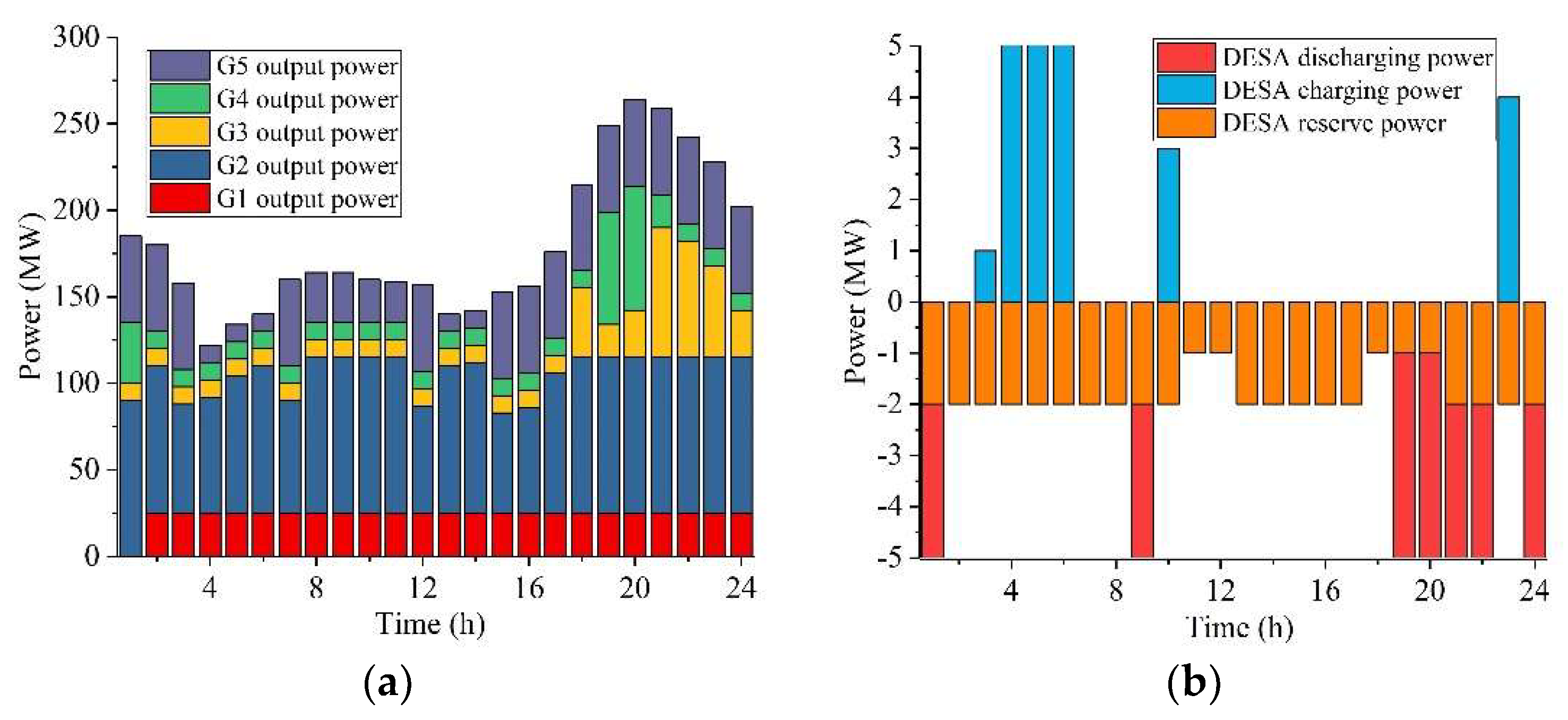
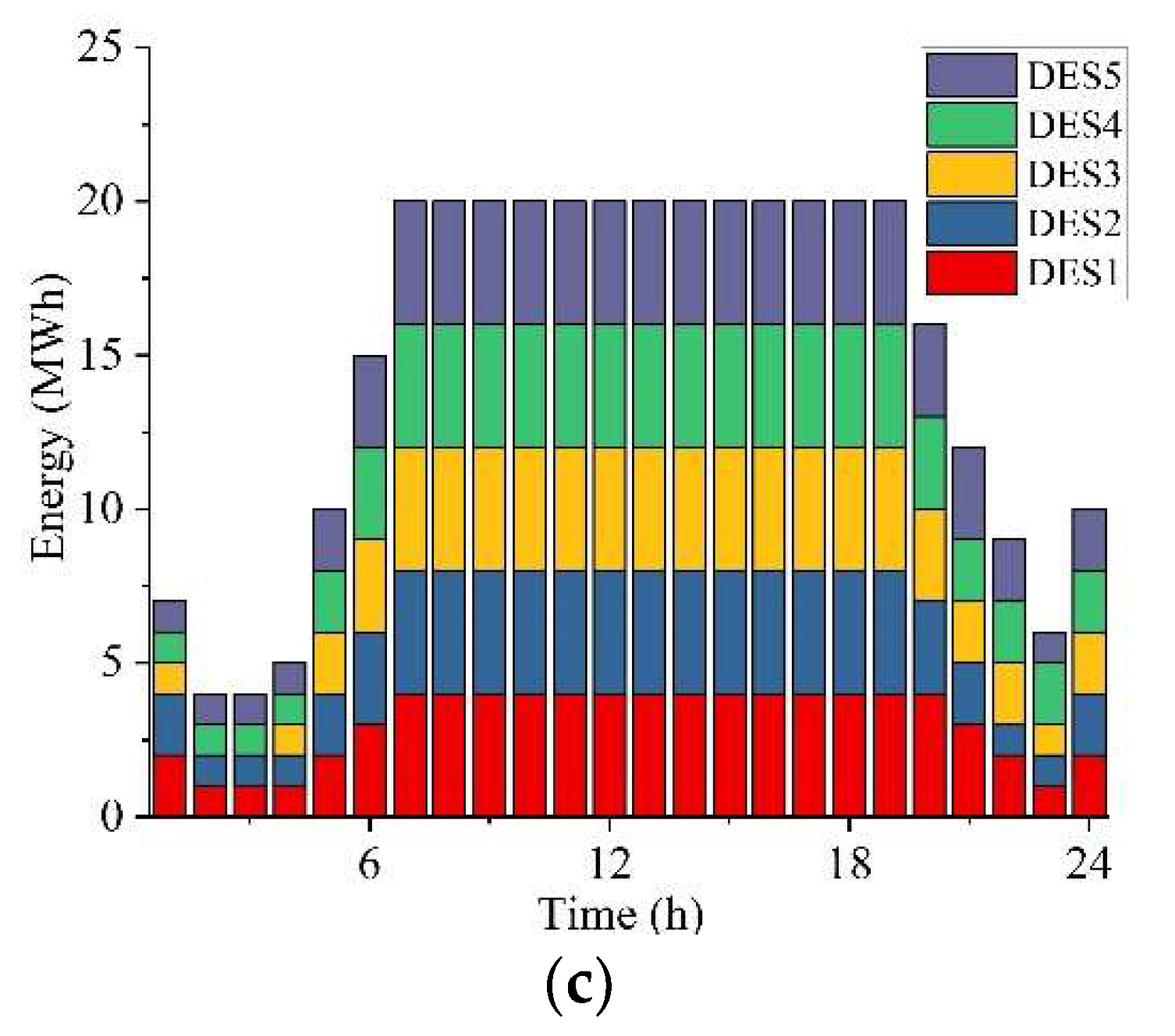

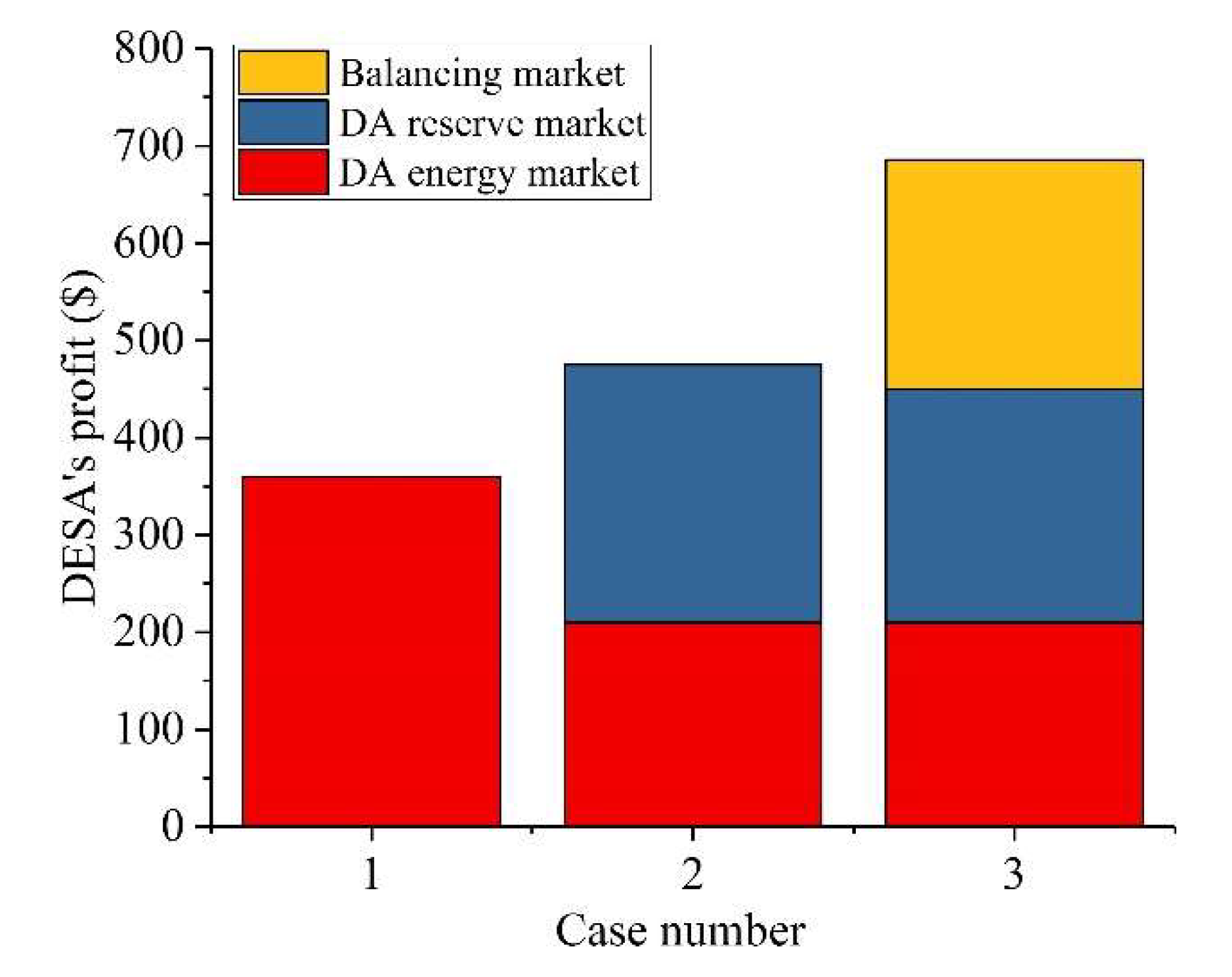
| Unit | (MW) | (MW) | (h) | (MW/h) | ($) | ($) | (MW) | ($)/MWh | ($)/h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | 100 | 25 | 5 | 30 | 2550 | 1200 | 5 | 500 | 32 |
| G2 | 90 | 15 | 4 | 40 | 2250 | 1100 | 8 | 400 | 34 |
| G3 | 75 | 10 | 3 | 50 | 2100 | 1050 | 10 | 450 | 36 |
| G4 | 72 | 10 | 3 | 55 | 2000 | 1000 | 12 | 450 | 36 |
| G5 | 50 | 10 | 2 | 50 | 2000 | 750 | 10 | 400 | 38 |
| From Bus | To Bus | X (p.u.) | Transmission Limit (MW) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 0.12 | 80 |
| 1 | 8 | 0.38 | 50 |
| 2 | 3 | 0.24 | 60 |
| 2 | 6 | 0.08 | 80 |
| 3 | 4 | 0.4 | 44 |
| 4 | 5 | 0.08 | 80 |
| 5 | 6 | 0.17 | 80 |
| 6 | 7 | 0.16 | 70 |
| 7 | 8 | 0.08 | 80 |
| Case | Scenario | DESA Up/Downward Reserve Capacity (MWh) | Generation Up/Downward Reserve Capacity (MWh) | DESA Capacity Utilization |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 1 | 120 | 61 | 100% |
| 2 | 45 | 0 | 75% | |
| 3 | 43 | 3 | 90% | |
| 4 | 119 | 65 | 100% |
| Case | Scenario | Total Generation Reserve Cost ($) | CO2 Emissions Penalty ($) | Total Generation Cost ($) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Provide upward reserve | 2840 | 43,582 | 1,848,142 |
| 2 | Provide upward reserve | 0 | 43,582 | 1,845,302 |
| 3 | 1 | 1620 | 42,952 | 1,835,142 |
| 2 | 0 | 41,815 | 1,829,792 | |
| 3 | 0 | 41,587 | 1,829,942 | |
| 4 | 1400 | 42,882 | 1,836,692 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mi, Z.; Jia, Y.; Wang, J.; Zheng, X. Optimal Scheduling Strategies of Distributed Energy Storage Aggregator in Energy and Reserve Markets Considering Wind Power Uncertainties. Energies 2018, 11, 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11051242
Mi Z, Jia Y, Wang J, Zheng X. Optimal Scheduling Strategies of Distributed Energy Storage Aggregator in Energy and Reserve Markets Considering Wind Power Uncertainties. Energies. 2018; 11(5):1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11051242
Chicago/Turabian StyleMi, Zengqiang, Yulong Jia, Junjie Wang, and Xiaoming Zheng. 2018. "Optimal Scheduling Strategies of Distributed Energy Storage Aggregator in Energy and Reserve Markets Considering Wind Power Uncertainties" Energies 11, no. 5: 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11051242
APA StyleMi, Z., Jia, Y., Wang, J., & Zheng, X. (2018). Optimal Scheduling Strategies of Distributed Energy Storage Aggregator in Energy and Reserve Markets Considering Wind Power Uncertainties. Energies, 11(5), 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11051242




