Application of Hybrid Meta-Heuristic Techniques for Optimal Load Shedding Planning and Operation in an Islanded Distribution Network Integrated with Distributed Generation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Optimal Load Shedding Planning
2.1. Voltage Stability Index
2.2. Proposed Load Shedding Scheme
2.2.1. Formulation of Objective Function
2.2.2. Constraints
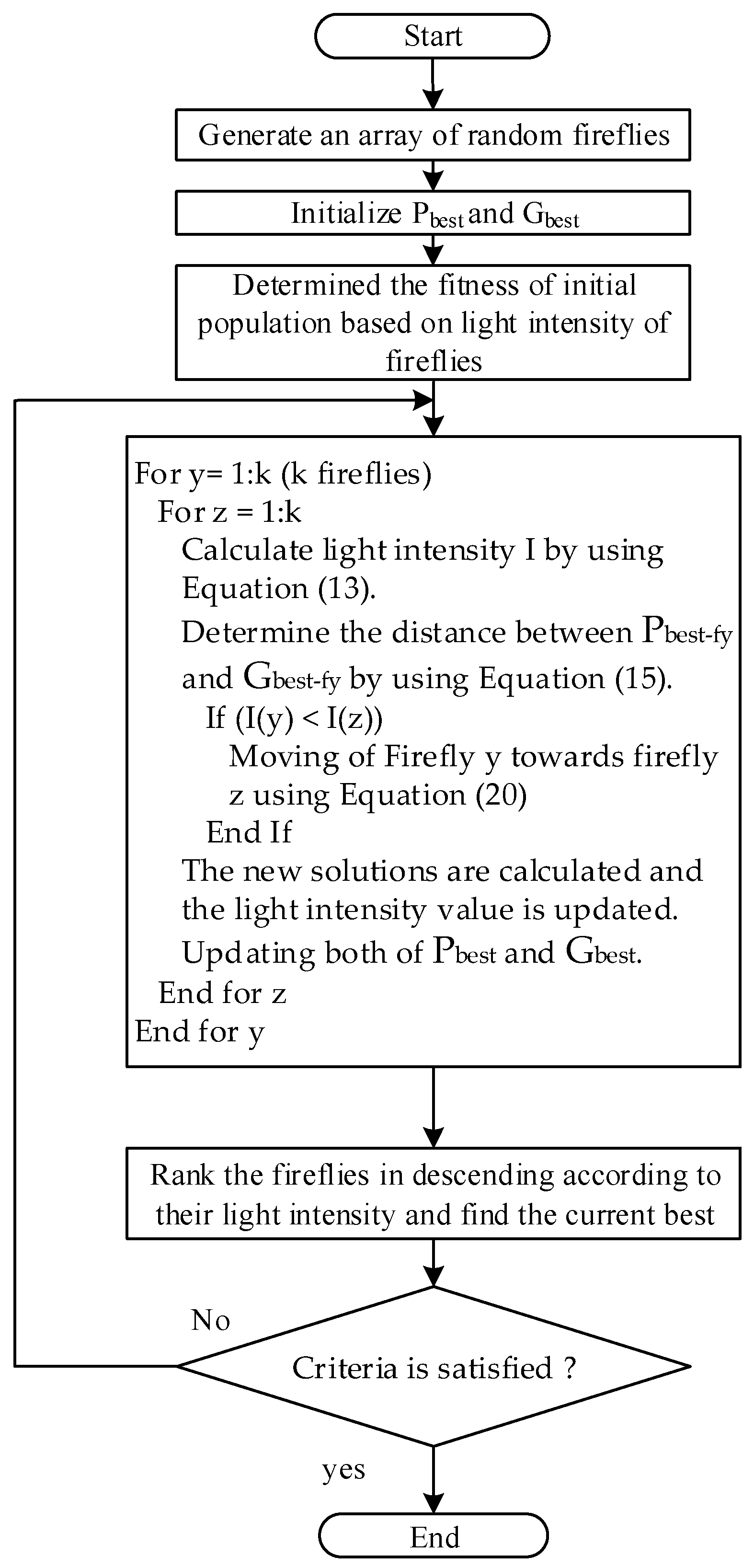
2.2.3. Load Shedding Optimization Algorithm
2.2.4. Procedure
3. Proposed UFLS Scheme Using FAPSO Algorithm
- (i)
- Event-based strategy—when one or more of generator supply like Renewable Energy Source (RES) are disconnected from distribution network and/or the decreasing in output power generated by RESs (such as wind turbine and Photovoltaic).
- (ii)
- Response based strategy—when suddenly load increased in the islanded distribution network.
4. Test System for Planning Load Shedding
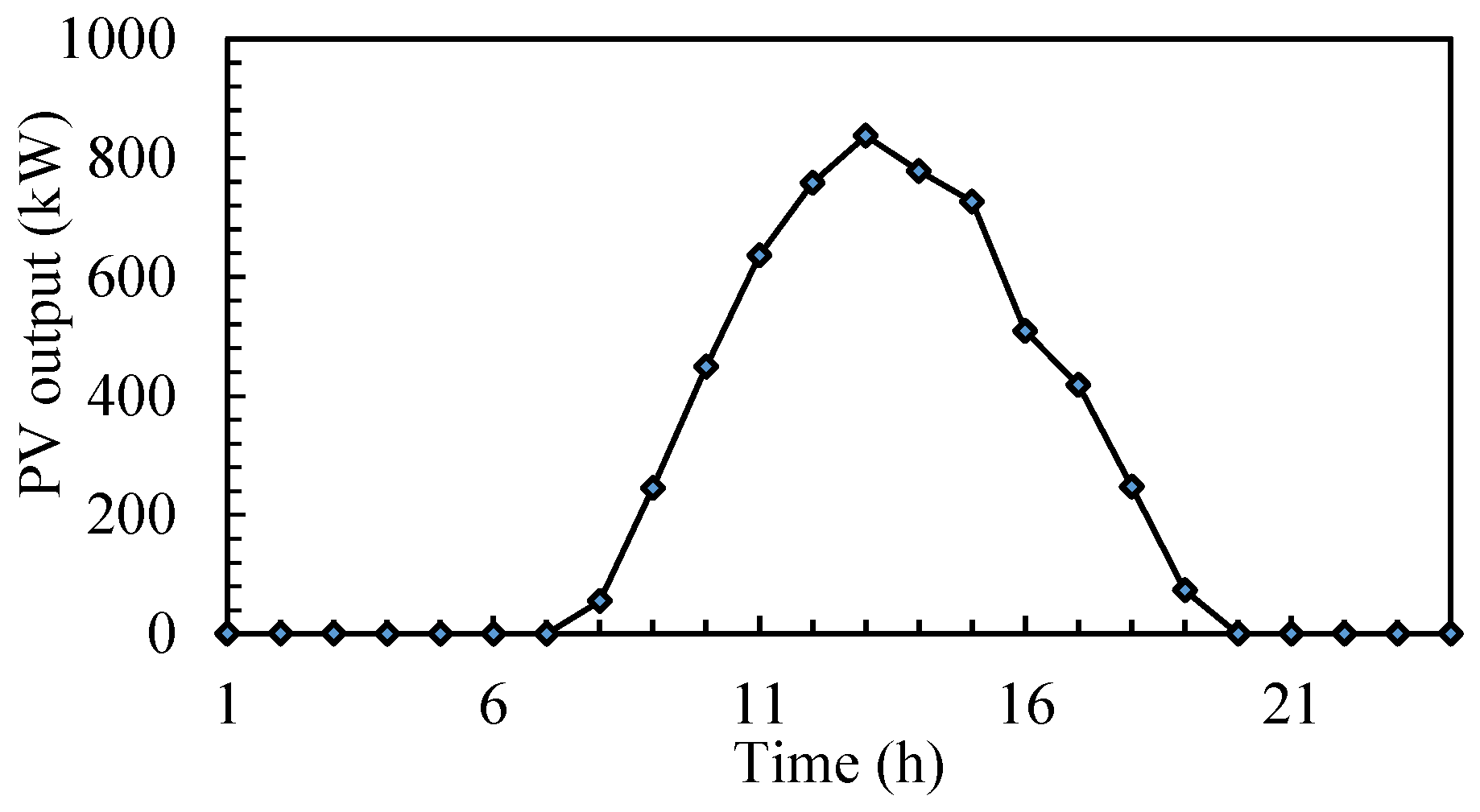
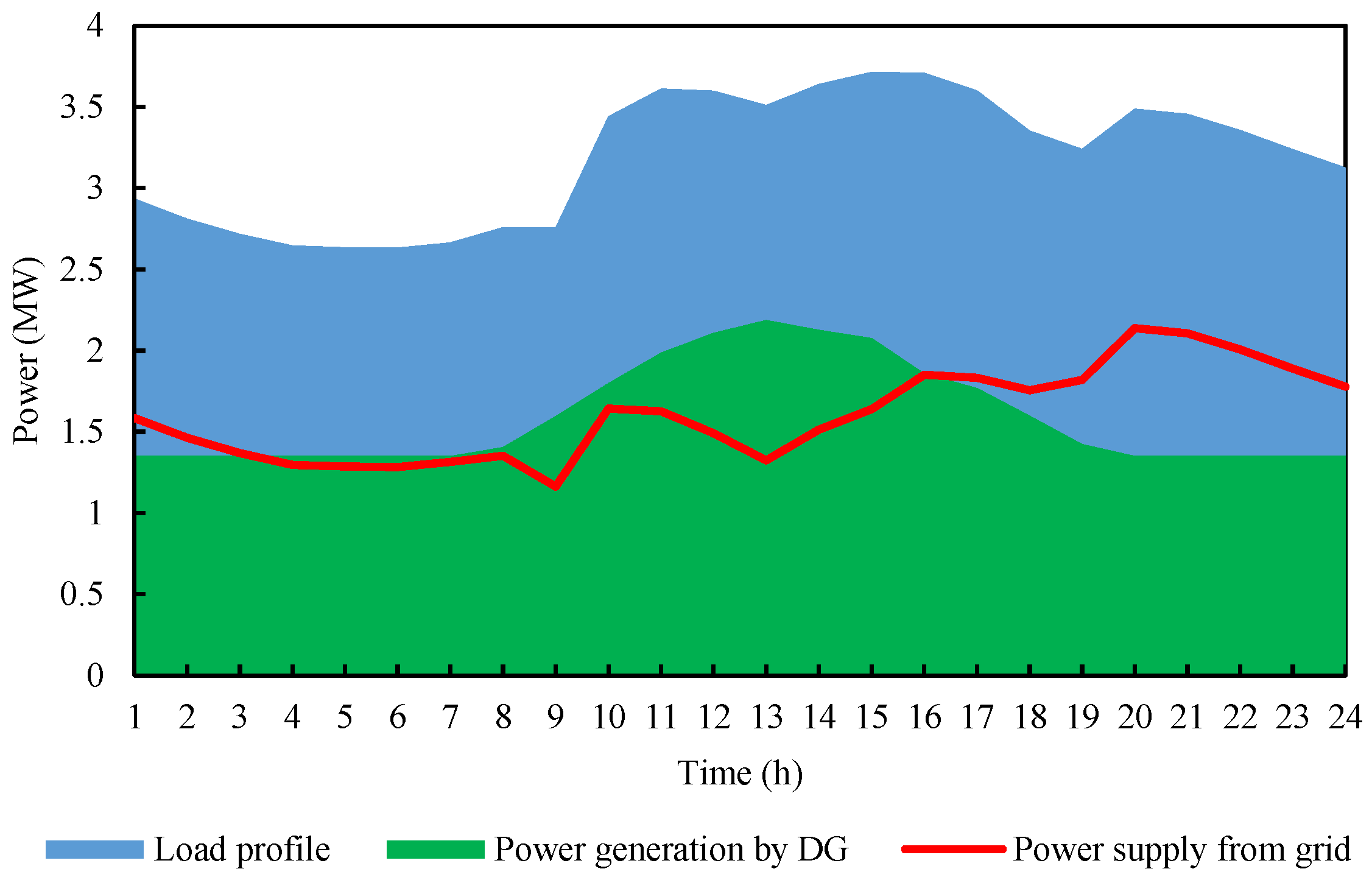
5. Simulation Results and Discussion of the Planning Load Shedding Scheme
6. Test System for Proposed UFLS Scheme
7. Simulation Study of UFLS Scheme Using BFAPSO, BEP, BGSA, BPSO Techniques, and UFLS-FRPL
- The first case represents a comparative simulation study between, FA, PSO, GSA, EP, UFLS method proposed in [24], and FAPSO in terms of execution time.
- The second and third case study represent the simulation study of UFLS scheme for islanding case and adding extra load using FAPSO, FA, PSO, EP and GSA techniques, and UFLS method proposed in [24].
7.1. Comparison Between Different Metaheuristic Techniques in Term of Execution Time
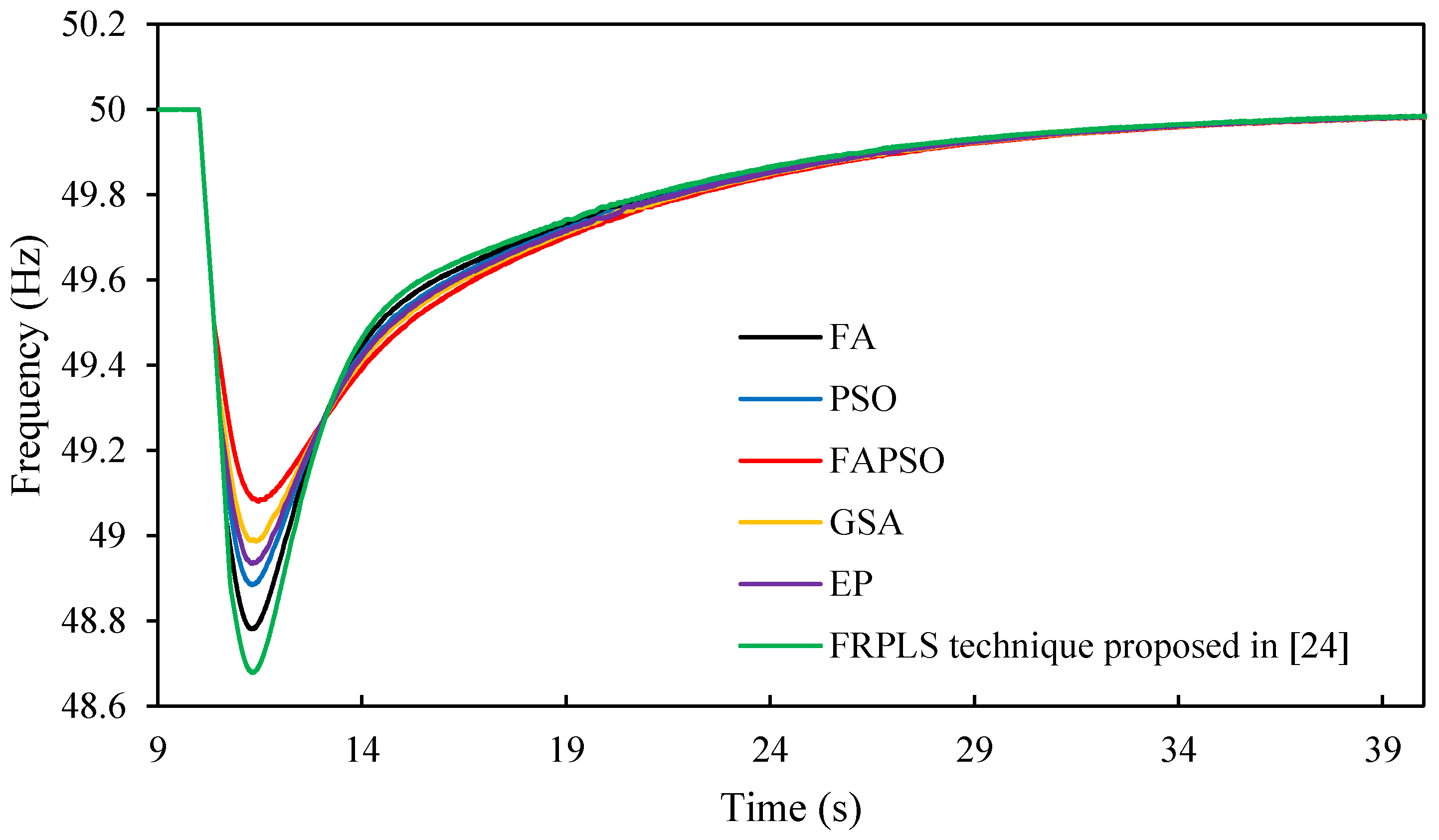
7.2. Intentional Islanding at 0.6 MW Imbalance Power
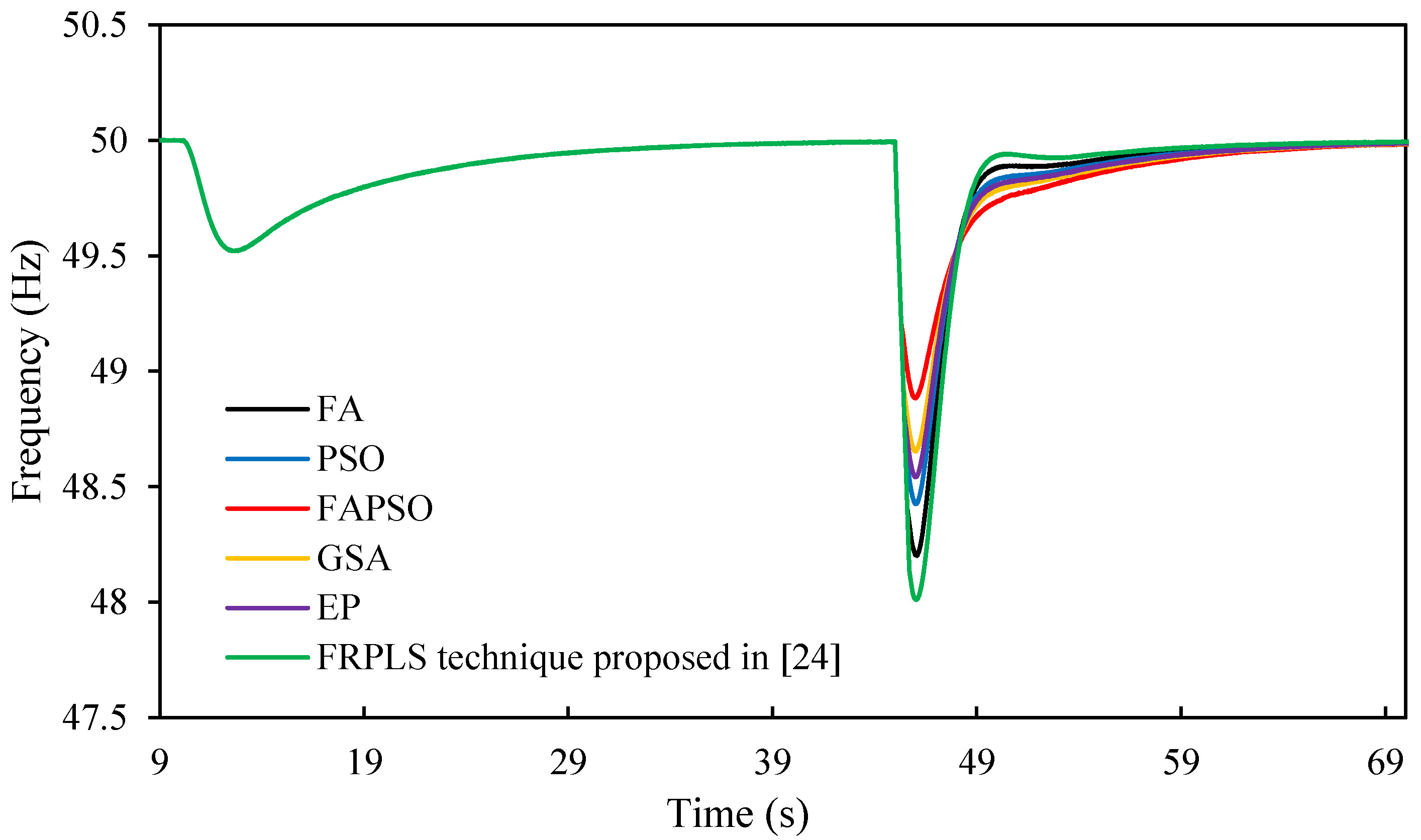
7.3. Load Increment of 0.9 MW
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eurostat: “Electricity Production and Supply Statistics”. Available online: http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/statistics_explained/index.php/Electricity_pproductio_and_supply_statiss (2012) (accessed on 20 September 2016).
- Hashim, H.; Ho, W.S. Renewable energy policies and initiatives for a sustainable energy future in Malaysia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 4780–4787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, M.; Bevrani, H. Statistical cooperative power dispatching in interconnected microgrids. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2013, 4, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagnano, A.; Bugliari, A.C.; De Tuglie, E. A cooperative control for the reserve management of isolated microgrids. Appl. Energy 2018, 218, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashiesh, F.; Mostafa, H.E.; Khatib, A.-R.; Helal, I.; Mansour, M.M. An intelligent wide area synchrophasor based system for predicting and mitigating transient instabilities. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2012, 3, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Xiao, S. Generalized congestion of power systems: Insights from the massive blackouts in India. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2013, 1, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-T.; Chuang, H.-J.; Chen, C.-S. Adaptive load shedding for an industrial petroleum cogeneration system. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 13967–13974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-T.; Kang, M.-S.; Chen, C.-S. Design of adaptive load shedding by artificial neural networks. IEE Proc.-Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2005, 152, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooshmand, R.; Moazzami, M. Optimal design of adaptive under frequency load shedding using artificial neural networks in isolated power system. Int. J. Electr. Power 2012, 42, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallam, A.; Khafaga, A. Fuzzy expert system using load shedding for voltage instability control. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Power Engineering Large Engineering Systems, LESCOPE 02, Halifax, NS, Canada, 26–28 June 2002; pp. 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Mokhlis, H.; Laghari, J.; Bakar, A.; Karimi, M. A fuzzy based under-frequency load shedding scheme for islanded distribution network connected with DG. Int. Rev. Electr. Eng. 2012, 7, 4992–5000. [Google Scholar]
- Ketabi, A.; Fini, M.H. Adaptive underfrequency load shedding using particle swarm optimization algorithm. J. Appl. Res. Technol. 2017, 15, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanaye-Pasand, M.; Davarpanah, M. A new adaptive multidimensioanal load shedding scheme using genetic algorithm. In Proceedings of the Canadian Conference on IEEE Electrical and Computer Engineering, Saskatoon, SK, Canada, 1–4 May 2005; pp. 1974–1977. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.-R.; Tsai, W.-T.; Chen, H.-Y.; Lee, C.-Y.; Chen, C.-J.; Lan, H.-W. Optimal load shedding planning with genetic algorithm. In Proceedings of the Conference on IEEE Industry Applications Society Annual Meeting (IAS), Orlando, FL, USA, 9–13 October 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Amraee, T.; Mozafari, B.; Ranjbar, A. An improved model for optimal under voltage load shedding: Particle swarm approach. In Proceedings of the Conference on IEEE Power India, New Delhi, India, 10–12 April 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sadati, N.; Amraee, T.; Ranjbar, A. A global particle swarm-based-simulated annealing optimization technique for under-voltage load shedding problem. Appl. Soft Comput. 2009, 9, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.K.; Rai, C.; Singh, A.P. Comparative study of firefly algorithm and particle swarm optimization for noisy non-linear optimization problems. IJISA 2012, 4, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niknam, T.; Narimani, M.R.; Jabbari, M. Dynamic optimal power flow using hybrid particle swarm optimization and simulated annealing. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy 2013, 23, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Kao, W.-S.; Chen, Y.-T. Study of applying load shedding scheme with dynamic D-factor values of various dynamic load models to Taiwan power system. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2005, 20, 1976–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundur, P.; Balu, N.J.; Lauby, M.G. Power System Stability and Control; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1994; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Maliszewski, R.; Dunlop, R.; Wilson, G. Frequency actuated load shedding and restoration part I-Philosophy. IEEE Trans. Power App. Syst. 1971, PAS-90, 1452–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seethalekshmi, K.; Singh, S.N.; Srivastava, S.C. A synchrophasor assisted frequency and voltage stability based load shedding scheme for self-healing of power system. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2011, 2, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, D.; Elmersson, P.; Juntti, A.; Gajic, Z.; Karlsson, D.; Fabiano, L. Intelligent load shedding to counteract power system instability. In Proceedings of the IEEE/PES Transmission and Distribution Conference and Exposition: Latin America, Sao Paulo, Brazil, 8–11 November 2004; pp. 570–574. [Google Scholar]
- Laghari, J.; Mokhlis, H.; Karimi, M.; Bakar, A.H.A.; Mohamad, H. A new under-frequency load shedding technique based on combination of fixed and random priority of loads for smart grid applications. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2015, 30, 2507–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudez, U.; Mihalic, R. Monitoring the first frequency derivative to improve adaptive underfrequency load-shedding schemes. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2011, 26, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, P.; Mirheydar, M. An adaptive method for setting underfrequency load shedding relays. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1992, 7, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Liu, C.-C.; Tanimoto, S.L.; Vittal, V. Adaptation in load shedding under vulnerable operating conditions. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2002, 17, 1199–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghari, J.; Mokhlis, H.; Bakar, A.H.A.; Karimi, M.; Shahriari, A. An intelligent under frequency load shedding scheme for islanded distribution network. In Proceedings of the Power Engineering and Optimization Conference (PEDCO), Melaka, Malaysia, 6–7 June 2012; pp. 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.-Y.; Wei, S.-F. Multiobjective underfrequency load shedding in an autonomous system using hierarchical genetic algorithms. IEEE Trans. Power Del. 2010, 25, 1355–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahat, P.; Chen, Z.; Bak-Jensen, B. Underfrequency load shedding for an islanded distribution system with distributed generators. IEEE Trans. Power Del. 2010, 25, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zin, A.M.; Hafiz, H.M.; Wong, W. Static and dynamic under-frequency load shedding. In Proceedings of the International IEEE Conference on Power System Technology, Singapore, Singapore, 21–24 November 2004; pp. 941–945. [Google Scholar]
- Chakravorty, M.; Das, D. Voltage stability analysis of radial distribution networks. Int. J. Electr. Power 2001, 23, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Kothari, D.; Kalam, A. Simple and efficient method for load flow solution of radial distribution networks. Int. J. Electr. Power 1995, 17, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, J.; Swami, P. Calculating voltage instability using index analysis in radial distribution system. Int. J. Mod. Eng. Res. 2014, 4, 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, N.I.A.; Sulaiman, S.I.; Musirin, I.; Shaari, S. Assessment of evolutionary programming models for single-objective optimization. In Proceedings of the 7th International IEEE Power Engineering and Optimization Conference (PEOCO), Langkawi, Malaysia, 3–4 June 2013; pp. 304–308. [Google Scholar]
- Rahim, S.A.; Rahman, T.A.; Musirin, I.; Azmi, S.; Mohammed, M.; Hussain, M.; Faridun, M. Comparing the network performance between the installation of DG and compensating capacitor using EP. Int. J. Power Energy Artif. Intell. 2008, 1, 14–21. [Google Scholar]
- Rashedi, E.; Nezamabadi-Pour, H.; Saryazdi, S. GSA: A gravitational search algorithm. Inf. Sci. 2009, 179, 2232–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-S. Nature-Inspired Metaheuristic Algorithms; Luniver Press: Bristol, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gandomi, A.H.; Yang, X.-S.; Alavi, A.H. Mixed variable structural optimization using firefly algorithm. Comput. Struct. 2011, 89, 2325–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhart, R.; Kennedy, J. A new optimizer using particle swarm theory. In Proceedings of the IEEE Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium on Micro Machine and Human Science (MHS’95), Nagoya, Japan, 4–6 October 1995; pp. 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Chen, Z. Contribution of VSC-HVDC to frequency regulation of power systems with offshore wind generation. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2015, 30, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aponte, E.E.; Nelson, J.K. Time optimal load shedding for distributed power systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2006, 21, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, M.E.; Wu, F.F. Network reconfiguration in distribution systems for loss reduction and load balancing. IEEE Trans. Power Del. 1989, 4, 1401–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Eberhart, R.C. Empirical study of particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC 99), Washington, DC, USA, 6–9 July 1999; pp. 1945–1950. [Google Scholar]
- Badran, O.; Mokhlis, H.; Mekhilef, S.; Dahalan, W. Multi-Objective Network Reconfiguration with Optimal DG Output Using Meta-Heuristic Search Algorithms. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2017, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Ye, L.; Sun, B.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, T. A New Hybrid Prediction Method of Ultra-Short-Term Wind Power Forecasting Based on EEMD-PE and LSSVM Optimized by the GSA. Energies 2018, 11, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreidy, M.; Mokhlis, H.; Mekhilef, S. Application of Meta-Heuristic Techniques for Optimal Load Shedding in Islanded Distribution Network with High Penetration of Solar PV Generation. Energies 2017, 10, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
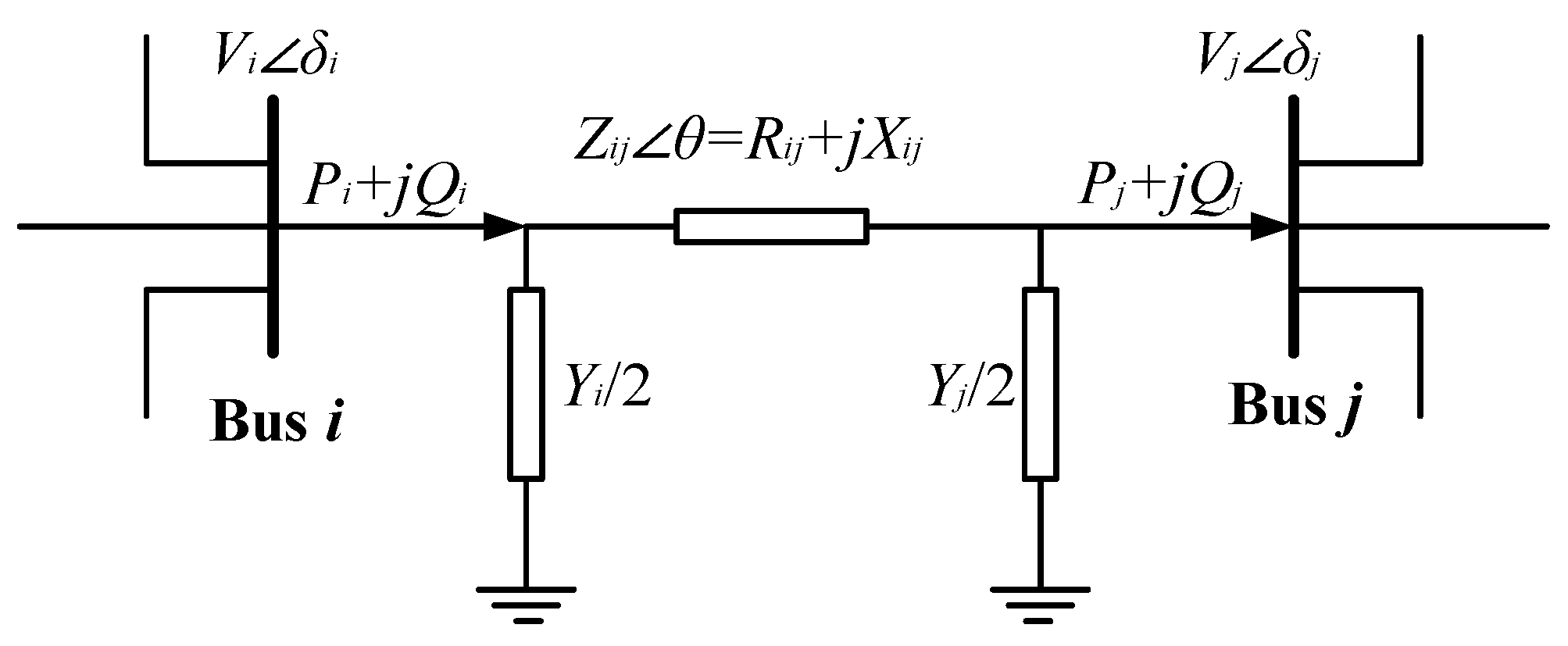



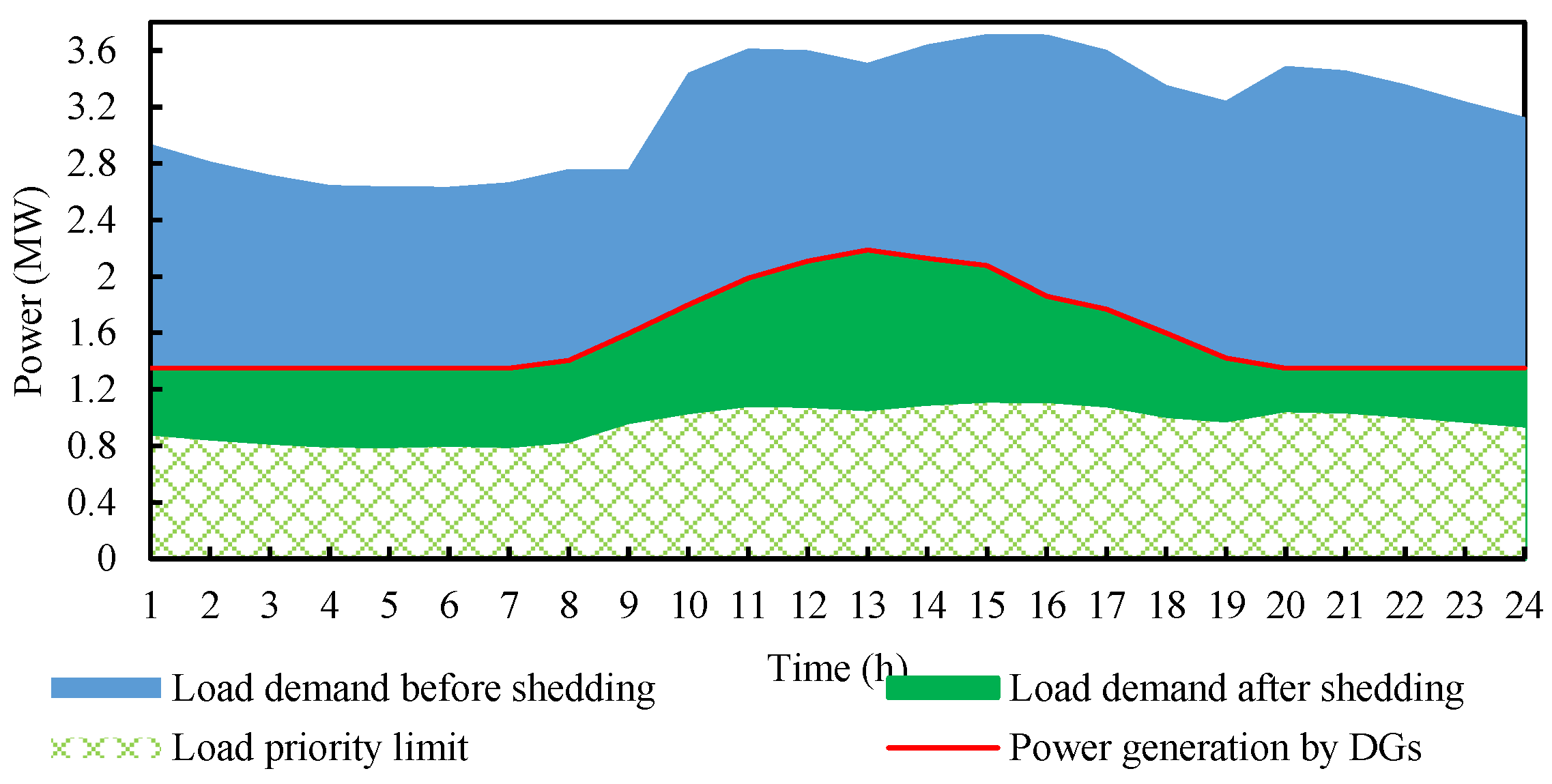

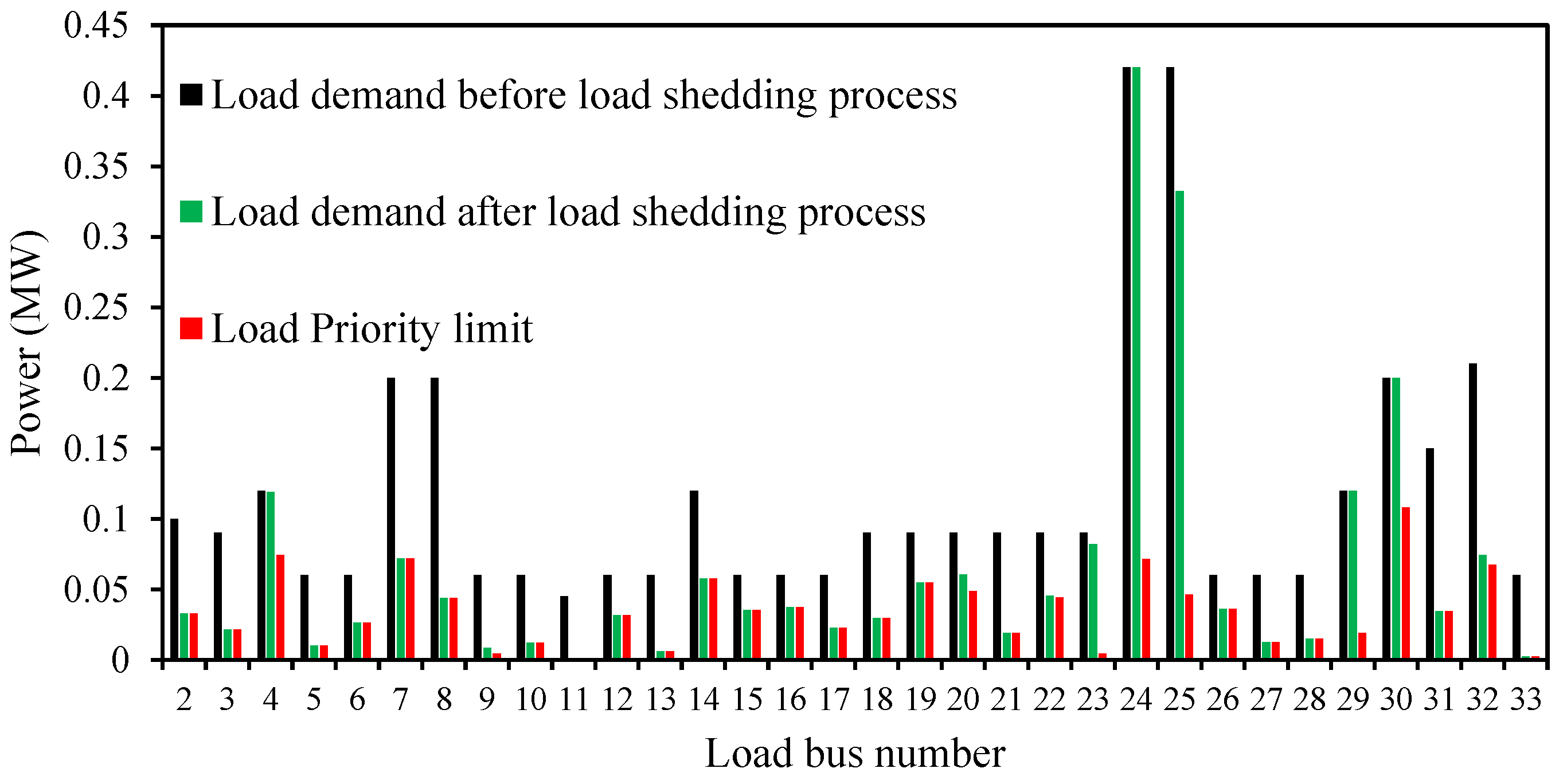
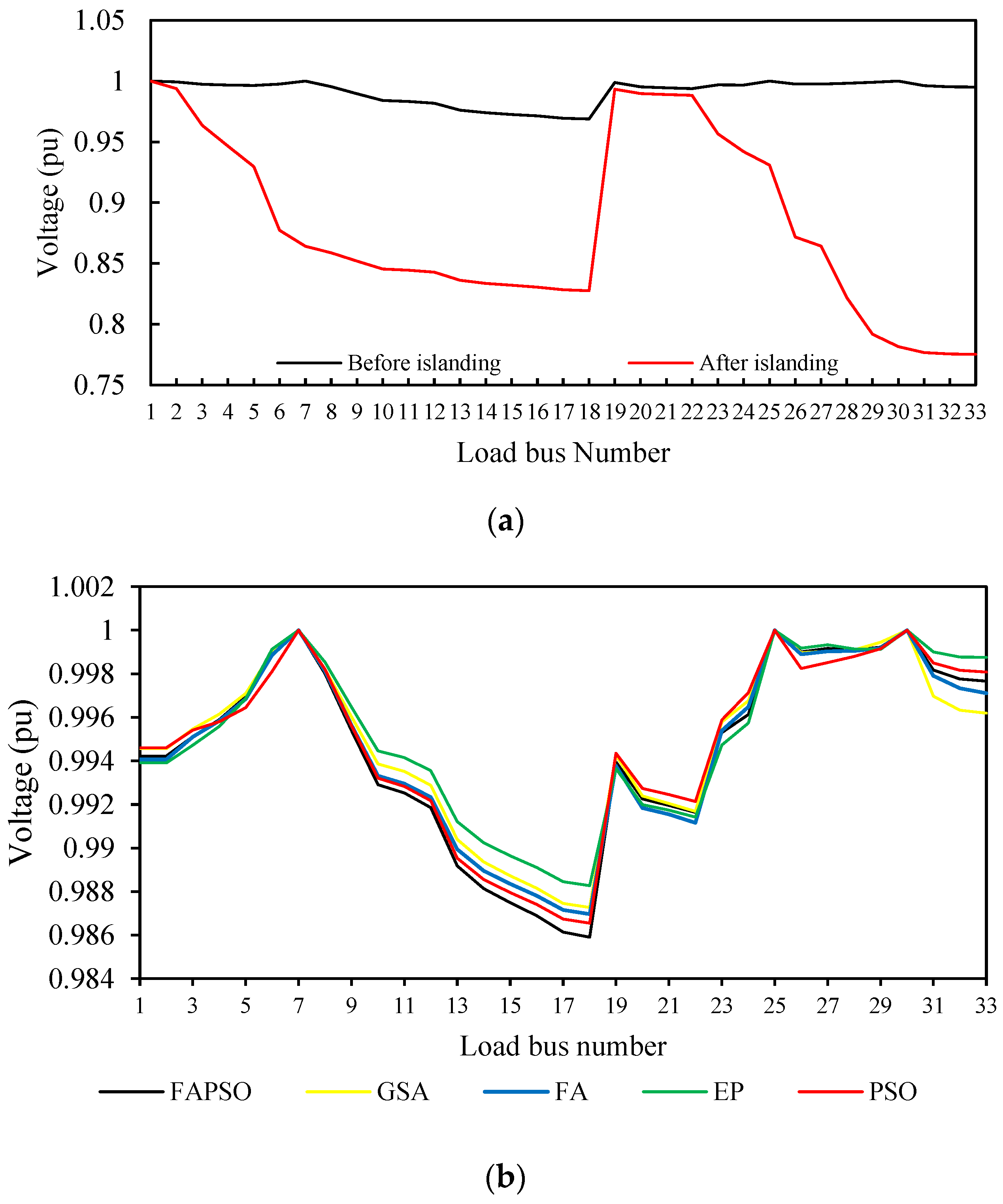
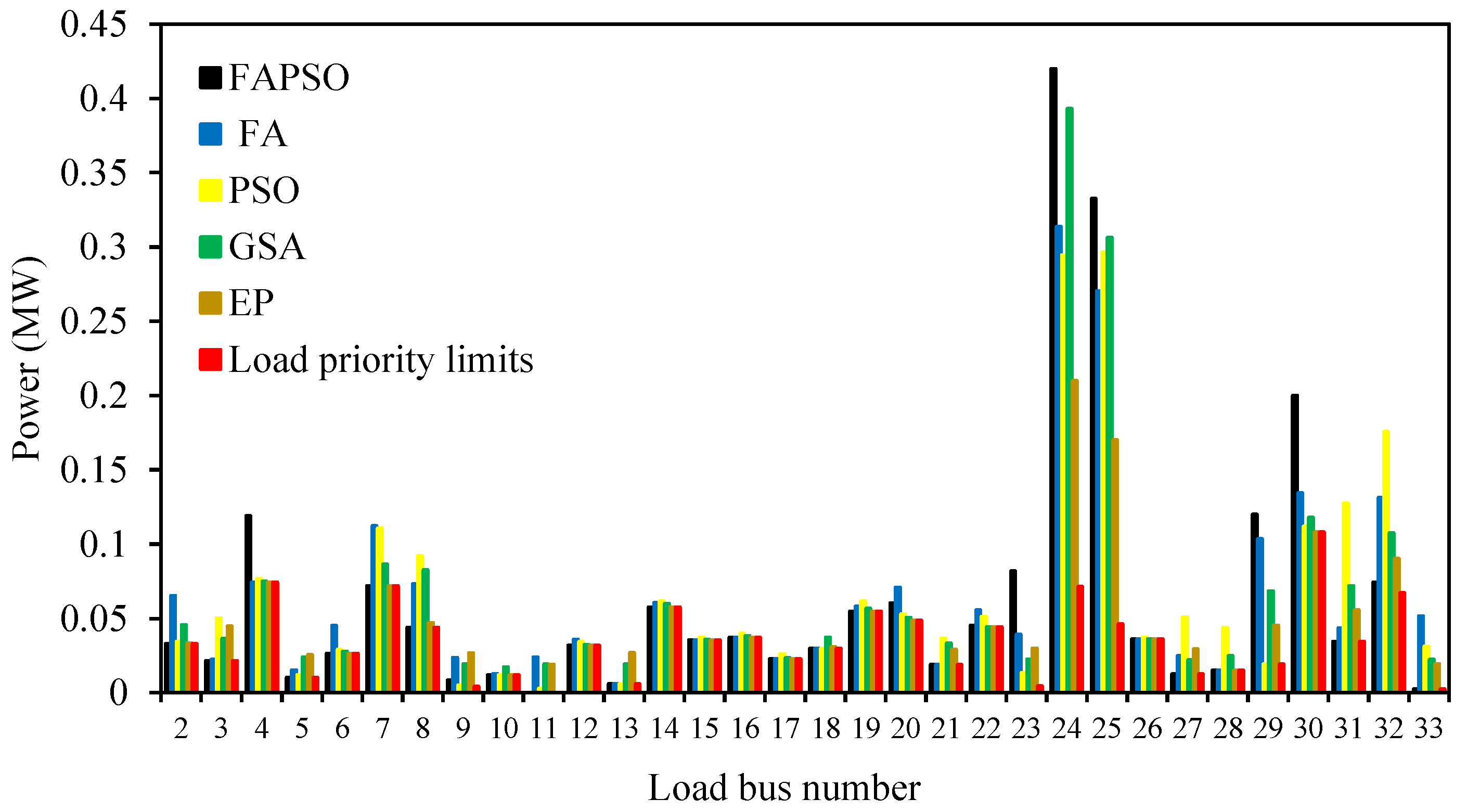

| DG Number | Bus Number | Type of DG | Maximum Output Power (MW) | Power Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7 | Mini-Hydro | 0.85 | 0.8 |
| 2 | 25 | Mini-Hydro | 0.5 | 0.8 |
| 3 | 30 | PV | 0.837 | 1 |
| Bus No. | Percentage (%) | Bus No. | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 33 | 19 | 61 |
| 3 | 24 | 20 | 54 |
| 4 | 62 | 21 | 21 |
| 5 | 17 | 22 | 49 |
| 6 | 44 | 23 | 5 |
| 7 | 36 | 24 | 17 |
| 8 | 22 | 25 | 11 |
| 9 | 7 | 26 | 60 |
| 10 | 20 | 27 | 21 |
| 11 | 0 | 28 | 25 |
| 12 | 53 | 29 | 16 |
| 13 | 10 | 30 | 54 |
| 14 | 48 | 31 | 23 |
| 15 | 59 | 32 | 32 |
| 16 | 62 | 33 | 4 |
| 17 | 38 | - | - |
| 18 | 33 | - | - |
| Parameter | PSO | FA | FAPSO | EP | GSA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population size (N) | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Maximum iteration (n) | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 |
| Parameters values that used for algorithm | wmax = 0.9 wmin = 0.4 c1 = 2 c2 = 2 | β0 = 0.2 γ = 1 α = 0.8 | β0 = 0.2 γ = 1 α = 0.8 c1 = 2 | - | G0 = 100 α = 10 |
| No. | w1 | w2 | Remaining Load (MW) | Minimum Value of SI | ηLAV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1.974802 | 0.951475 | 34.86 |
| 2 | 0.9 | 0.1 | 2.03936 | 0.950209 | 78.63 |
| 3 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 2.07637 | 0.956846 | 4178.4 |
| 4 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 2.034878 | 0.952472 | 79.10 |
| 5 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 1.890752 | 0.941886 | 17.49 |
| 6 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 2.068509 | 0.944912 | 119.49 |
| 7 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 2.031323 | 0.940203 | 49.77 |
| 8 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 2.03376 | 0.95338 | 80.36 |
| 9 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 1.987242 | 0.95048 | 38.57 |
| 10 | 0.1 | 0.9 | 1.784058 | 0.957304 | 12.22 |
| 11 | 0 | 1 | 1.114939 | 0.957304 | 2.32 |
| Algorithms | Applying Optimal Load Shedding with Consideration Priority Limit at Time 15:00 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Fitness | Minimum Voltage of Load Bus | Load Curtailment % | |
| PSO | 0.59719 | 0.98654 | 44.43 |
| FA | 0.59759 | 0.98696 | 44.46 |
| FAPSO | 0.59424 | 0.98590 | 44.11 |
| GSA | 0.59929 | 0.987271 | 44.56 |
| EP | 0.70726 | 0.988271 | 56.66 |
| Population Size/Max Iteration | Indices | Algorithms | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP | GSA | FA | PSO | FAPSO | ||
| 50/300 | Average fitness | 0.77924 | 0.59988 | 0.59939 | 0.59904 | 0.59468 |
| Best solution | 0.70726 | 0.59929 | 0.59760 | 0.59719 | 0.59419 | |
| Standard deviation | 0.031476 | 0.00039588 | 0.00050378 | 0.0008866 | 0.00032375 | |
| Average computational time (seconds) | 661.21 | 330.01 | 760.58 | 655.7 | 708.11 | |
| Load Ranked | Bus No. | P (MW) | Load Priority |
|---|---|---|---|
| Load 1 | 1050 | 0.044 | Random |
| Load 2 | 1013 | 0.069 | Random |
| Load 3 | 1047,1026 | 0.15 | Random |
| Load 4 | 1012 | 0.314 | Random |
| Load 5 | 1151 | 0.5 | Random |
| Load 6 | 1029 | 0.55 | Random |
| Load 7 | 1010,1039 | 0.583 | Random |
| Load 8 | 1075 | 0.645 | Random |
| Load 9 | 1018–1020, 1046 | 0.7 | Random |
| Load 10 | 1144 | 0.119 | Random |
| Trial Number | Execution Time (Second) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FA | PSO | FAPSO | GSA | EP | FRPLS Technique Proposed in [24] | |
| 1 | 0.723 | 0.609 | 0.122 | 0.13 | 0.155 | 0.5 |
| 2 | 0.712 | 0.607 | 0.06 | 0.143 | 0.153 | 0.5 |
| 3 | 0.703 | 0.605 | 0.11 | 0.109 | 0.153 | 0.5 |
| 4 | 0.787 | 0.646 | 0.145 | 0.25 | 0.152 | 0.5 |
| 5 | 0.657 | 0.657 | 0.05 | 0.15 | 0.162 | 0.5 |
| 6 | 0.741 | 0.626 | 0.101 | 0.09 | 0.15 | 0.5 |
| Average | 0.7205 | 0.625 | 0.098 | 0.145 | 0.154 | 0.5 |
| Parameter | FA | PSO | FAPSO | GSA | EP | UFLS Technique Proposed in [24] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔP (MW) | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| Reserve (MW) | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.18 |
| Total Load Shed Power (MW) | 0.427 | 0.427 | 0.427 | 0.427 | 0.427 | 0.427 |
| Shedding loads | Loads 1,2,4 | Loads 1,2,4 | Loads 1,2,4 | Loads 1,2,4 | Loads 1,2,4 | Loads 1,2,4 |
| Nadir Frequency (Hz) | 48.2 | 48.42 | 48.88 | 48.65 | 48.54 | 48.01 |
| Parameter | FA | PSO | FAPSO | GSA | EP | FRPLS Technique Proposed in [24] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔP (MW) | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| Reserve (MW) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total Load Shed Power (MW) | 0.897 | 0.897 | 0.897 | 0.897 | 0.897 | 0.897 |
| Shedding loads | Loads 4,7 | Loads 4,7 | Loads 4,7 | Loads 4,7 | Loads 4,7 | Loads 4,7 |
| Nadir Frequency (Hz) | 48.2 | 48.42 | 48.88 | 48.65 | 48.54 | 48.01 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jallad, J.; Mekhilef, S.; Mokhlis, H.; Laghari, J.; Badran, O. Application of Hybrid Meta-Heuristic Techniques for Optimal Load Shedding Planning and Operation in an Islanded Distribution Network Integrated with Distributed Generation. Energies 2018, 11, 1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11051134
Jallad J, Mekhilef S, Mokhlis H, Laghari J, Badran O. Application of Hybrid Meta-Heuristic Techniques for Optimal Load Shedding Planning and Operation in an Islanded Distribution Network Integrated with Distributed Generation. Energies. 2018; 11(5):1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11051134
Chicago/Turabian StyleJallad, Jafar, Saad Mekhilef, Hazlie Mokhlis, Javed Laghari, and Ola Badran. 2018. "Application of Hybrid Meta-Heuristic Techniques for Optimal Load Shedding Planning and Operation in an Islanded Distribution Network Integrated with Distributed Generation" Energies 11, no. 5: 1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11051134
APA StyleJallad, J., Mekhilef, S., Mokhlis, H., Laghari, J., & Badran, O. (2018). Application of Hybrid Meta-Heuristic Techniques for Optimal Load Shedding Planning and Operation in an Islanded Distribution Network Integrated with Distributed Generation. Energies, 11(5), 1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11051134







