A Review of Green Building Development in China from the Perspective of Energy Saving
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Development of Green Building Policies in China
2.1. The Initiation of Green Building in China
2.2. Policy Support for Green Building in China
3. Scientific Research on Green Building in China
4. Development of Assessment Standards for Green Building in China
4.1. Emergence of Assessment Standards for Green Building in China
4.2. Effectiveness of the Assessment Standards System for Green Building in China
5. Development of Green Building Technologies in China
5.1. Research Progress of the Basic Theory
5.2. Technological Innovations in Energy Conservation and Energy Utilization in Green Building in China
5.3. Other Technical Innovations of Green Building in China
5.4. Practical Projects of Green Building Technology in China
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wei, J.Y.; Yan, W.G.; Yao, Z.M. Present situation of energy consumption and potentiality saving on energy of building in China. J. Shenyang Archit. Civ. Eng. Inst. 1994, 4, 185. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, Y.Y. Green Building and Energy Saving Technology; Qingdao Technological University: Qingdao, China, 2014; p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, A.Q.; Liu, N. A review of the simple green ideas of Chinese ancient architecture. J. Xi’an Univ. Archit. Technol. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2010, 3, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Thinking about China’s Energy Structure. Available online: http://xianhuo.hexun.com/2012-10-25/147224682.htm (accessed on 20 September 2017).
- Yang, J.B. Comparative analysis of China’s first five year plan and the Soviet Union first five year plan. Stat. Commun. 1955, 8, 5–11. [Google Scholar]
- The first academic meeting summary of the Architectural Society of Chinese cave and adobe building. Archit. J. 1981, 10, 29–30.
- Wang, Q.Q. Promoting green building development. Learn. Times 2017, 7, 1. [Google Scholar]
- China Academy of Building Research. Review and Prospect of Green Building Standard in China; China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2017; Volume 7, pp. 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.J. A new subject of eco architecture in the development of modern cities. Archit. J. 1981, 2, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, R.S. Agenda 21: Action and prospect. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2012, 5, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, W.Y. The theoretical connotation of sustainable development—The 20th anniversary of UN conference on environment and development in Rio de Janeiro. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2012, 5, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Editorial Department. China green building decade. Constr. Sci. Technol. 2014, 6, 1.
- Notice of the State Council and the State Council on printing and Distributing the Plan of Energy Saving and Emission Reduction in 12th Five-Year ([2012] 40). Available online: http://www.nea.gov.cn/2012-08/22/c_131800277.htm (accessed on 8 October 2017).
- Qin, Y.G. Chinese Condition Must Be Considered on Developing Green Building in China; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 6, p. 15. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Housing and Urban Rural Development, Ministry of Finance. Opinions on Accelerating the Development of Green Building in China (Financial Construction [2012] 167). Available online: http://www.mohurd.gov.cn/zcfg/xgbwgz/201205/t20120510_209831.html (accessed on 8 October 2017).
- Qiu, B.X. Development prospects and countermeasure suggestions of green building in China. Constr. Technol. 2011, 6, 10–12. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.J. Sustainable development of population and environment in China. Univ. Forum 2013, 173–174. [Google Scholar]
- State Council of the People’s Republic of China. The National Plan for Medium and Long-Term Science and Technology Development (2006–2020); State Council of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2006; p. 2.
- People’s Republic of China. The Outline of the Tenth Five-Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development; Theory and Contemporary: Guizhou, China, 2001; pp. 31–48.
- The Twelfth Five-Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development of People’s Republic of China. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/2011lh/content_1825838.htm (accessed on 10 October 2017).
- People’s Republic of China. The thirteenth five-year plan for national economic and social development. In People’s Daily; 2016; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Qin, Y.G.; Zhu, Y.X. Assessment system for green building of the Beijing Olympics for green positioning. Constr. Sci. Technol. 2003, 12, 68–69. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.N.; Yang, L.; He, B.J.; Zhao, D.D. Green building in China: Needs great promotion. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2014, 11, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.R. Assessment standard for green building: Indoor environmental quality. Constr. Sci. Technol. 2015, 4, 30–33. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.Y.; Cheng, Z.J.; Ye, L. Interpretation of assessment standard for green building. Constr. Sci. Technol. 2013, 6, 64–66. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y.G.; Lin, B.R.; Zhu, Y.X. Research on assessment standard for green building. Archit. J. 2007, 3, 68. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.G.; Gu, L.J. Challenges and policy recommendations of the green building development in China. China’s Energy 2012, 12, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Notice of the Ministry of Urban and Rural Construction on Issue of the 13th Five-year Plan for the Development of Building Energy Conservation and Green Buildings JianKe [2017] No. 53. Available online: http://www.mohurd.gov.cn/wjfb/201703/t20170314_230978.html (accessed on 10 October 2017)).
- Wang, Q.Q.; Meng, C.; Li, G.Z. Development demands and prospect of healthy buildings. Heat. Vent. Air Cond. 2017, 7, 32–35. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics of the People’s Republic of China. Available online: http://data.stats.gov.cn/index.htm (accessed on 1 November 2017).
- Green Building Map Network. Available online: http://www.gbmap.org/ (accessed on 1 November 2017).
- Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Construction of Building Energy-Saving and Notification of Division on Elements of a Published Work in 2017 JianKe Comprehensive Letter [2017] No. 17. Available online: http://www.mohurd.gov.cn/wjfb/201703/t20170323_231232.html (accessed on 1 November 2017).
- Lan, K.; Li, Q.M. A study of the development of UK’s green architecture. J. Xi’an Univ. Archit. Technol. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2012, 6, 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.M. The Study on the Green Building Assessment System; Tianjin University: Tianjin, China, 2003; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.Q.; Deng, X. The first of strategies of Chinese green building: Overall Composition of the Straegy. Urban Hous. 2008, 4, 66–69. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.Q.; Deng, X. The second of strategies of Chinese green building: Formation process. Urban Hous. 2008, 4, 66–69. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y.G. Green buildings under China’s actual conditions. Chin. Foreign Constr. 2005, 3, 4–5. [Google Scholar]
- Gou, Z.H.; Shen, J. Intelligent building envelope with integrated green technology. Huazhong Archit. 2007, 9, 78–80. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.Y.; Wang, Q.Q. Enhancing technology research and promoting scale development of green building in China. Constr. Technol. 2014, 5, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.P.; Wu, L.Y. New energy utilization in architectural energy conservation and design. New Energy Technol. 2001, 2, 12–15. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.Y.; Yang, F. Two strategies of adaptive transformation of old buildings: Renewal of building functions and innovation of energy consumption technology. Archit. J. 2007, 6, 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.L. Passive house:ideal buildings with high comfort and ultra-low energy consumption. Constr. Technol. 2012, 10, 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, J.Q.; Chen, B.; Chen, T.D.; Song, L.; Kang, J. Design of whole life cycle green buildings and human living environment. Urban Dev. Stud. 2015, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.J.; Jin, H.; Zhao, Y.D. Details of insulation wall. J. Harbin Univ. Civil Eng. Archit. 2002, 8, 84–86. [Google Scholar]
- Gou, Z.H.; Lau, S.S.Y.; Chen, F.N. Subjective and objective evaluation of the thermal environment in a three-Star green office building in China. Indoor Built Environ. 2012, 21, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, Z.H.; Prasad, D.; Lau, S.S.Y. Are green buildings more satisfactory and comfortable? Habitat Int. 2013, 39, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, Z.H.; Xie, X.H. Evolving green building: Triple bottom line or regenerative design? J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 153, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Urban Science Research Association. Green Building in China (2013); China Architecture and Building Press: Beijing, China, 2013; Volume 4, pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.Y. Research on Whole Life Appraisal of Green Building; Tianjin University of Technology: Tianjin, China, 2008; p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.K.; Luo, F. Research on building energy consumption based on whole life cycle theory. Build. Sci. 2008, 10, 26–27. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, B.X. From green building to low carbon eco-city. Urban Stud. 2009, 7, 2–10. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, B.X. Six fields with the largest building energy-saving potential and their outlooking in China. Archit. Technol. 2011, 1, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Y.X. Architecture vision for the 21st century. Archit. J. 1997, 2, 38–40. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.C. Green building system and research. New Archit. 1997, 4, 8–10. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.H. The first five-year plan on the several problems of urban construction. Archit. J. 1955, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, N. 60 years of Chinese architecture: Analysis of the development of the architectural creation I. Archicreation 2009, 6, 153–157. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.Q. Energy Efficiency Design of Residential Building’s External Window in Cold North Area; Tianjin University: Tianjin, China, 2007; p. 14. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.X.; Dang, R. Building Energy Conservation; China Construction Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2009; pp. 92, 115, 138. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.L.; Hu, C.Y.; Bo, D.S.; Li, W.F. Building energy conservation technology status and development trend in China. Build. Energy Conserv. 2015, 3, 118. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.X. Key points of green building technology and suggestions for implementing green building. Archit. J. 2011, 9, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.G.; Gu, L.J. Development status, challenges and policy suggestions of green building in China. Energy China 2012, 12, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.X.; Zhao, Y.Z. Advancing green buildings, promoting energy saving and CO2 emission reduction and improving human inhabitation environment. Dynamic (Eco-City Green Build.) 2011, 12, 21–22. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, L.; Cheng, Z.J. Overview on green building standards development. Build. Sci. 2016, 12, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.Z.; Mo, W.; Qian, Y.M. Application of measures for water saving and water resources utilization in design of green buildings. China Water Waste Water 2009, 7, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.L.; Sun, H.; Peng, B. Green building materials and utilization technologies of material resources. Green Technol. Summ. 2013, 1, 30–31. [Google Scholar]
- Su, D.X.; Zhou, Z.N. Interpretation of ultra low energy consumption demonstration building of Tsinghua University. Archit. J. 2005, 9, 16–17. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.K. Introduction of ecological and energy-efficient office demonstration building in Shanghai. Inaug. Semin. China’s Energy-Sav. Refrig. Air Cond. Eng. Technol. 2006, 2, 82–89. [Google Scholar]
- Fraser: Science and technology gave birth to green homes. Urban Hous. 2009, 2, 34–35.
- Zou, S.W.; Yu, Z. China architecture won the first international green building gold award. China Inf. News 2006, 4, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.M. The challenges of the green building development in China. Urban Dev. Stud. 2015, 22, 3, 6. [Google Scholar]
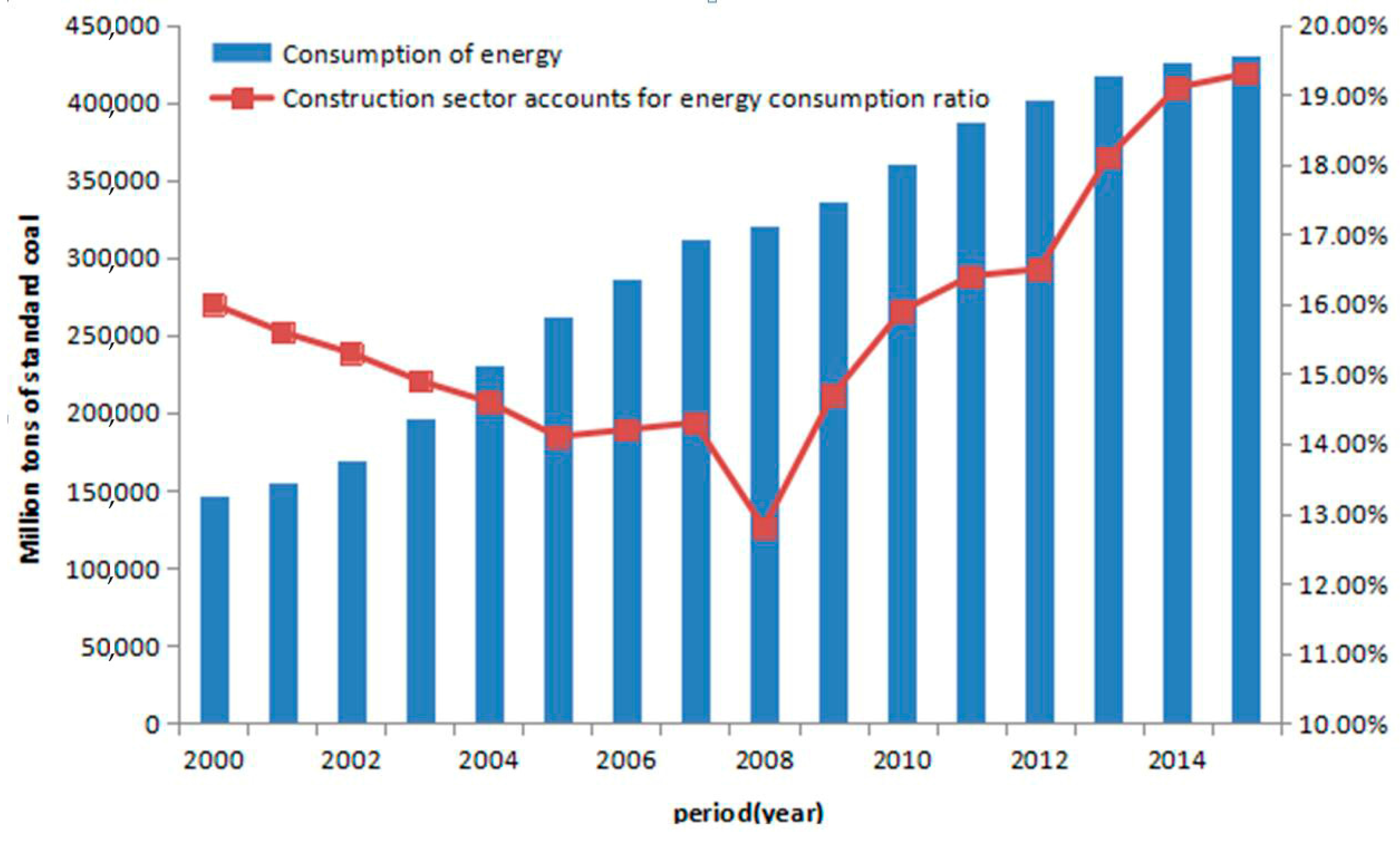
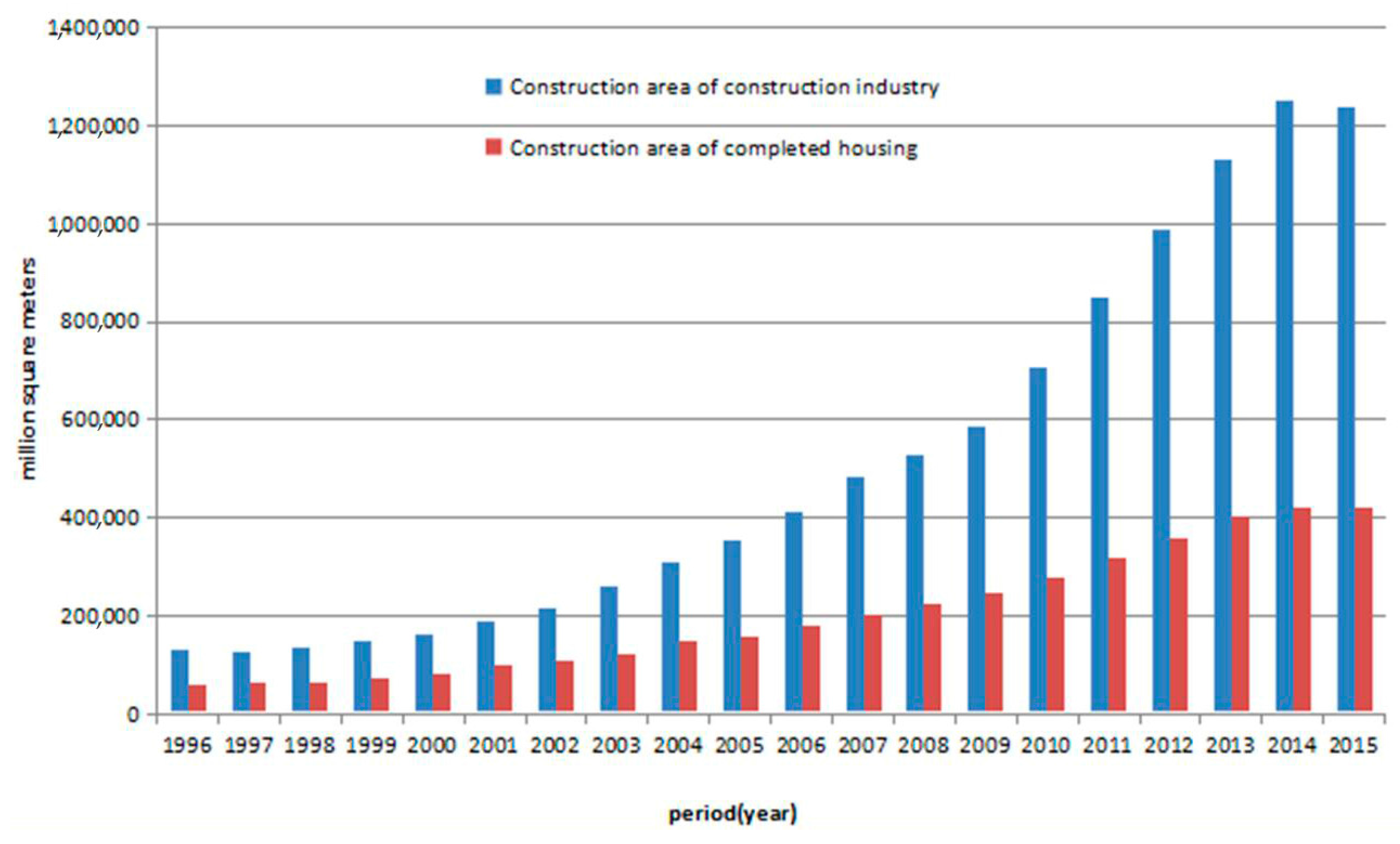
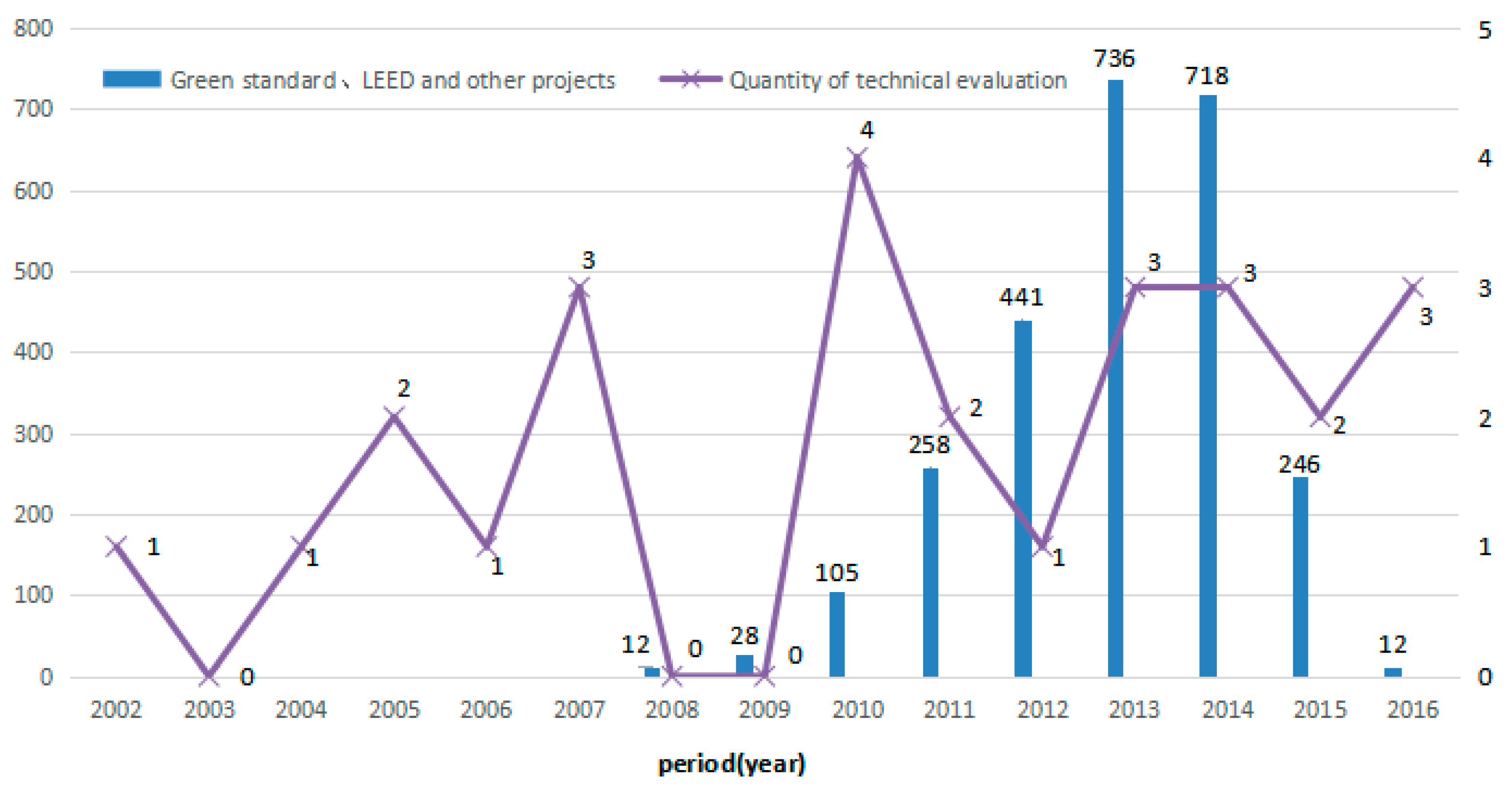
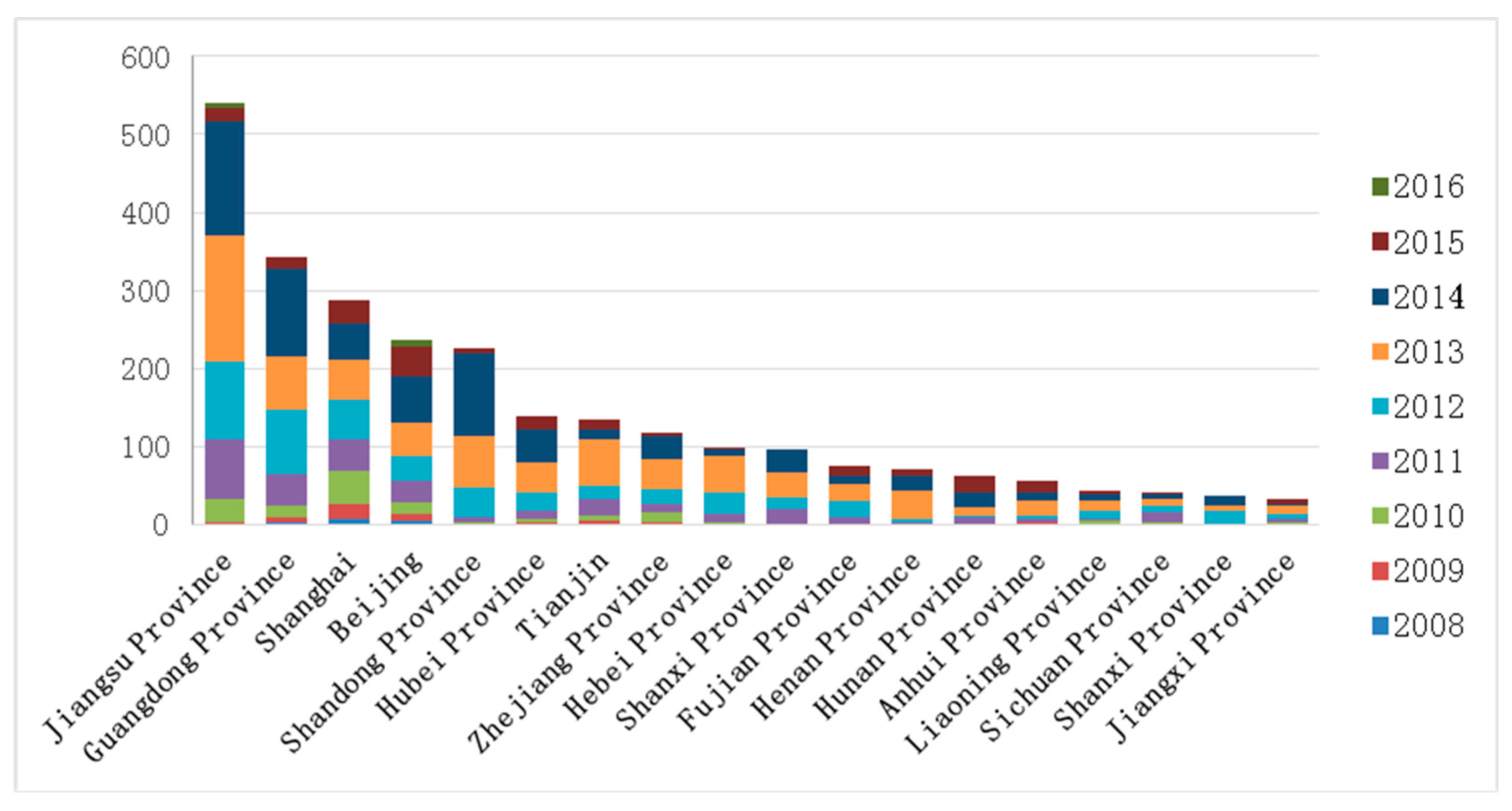
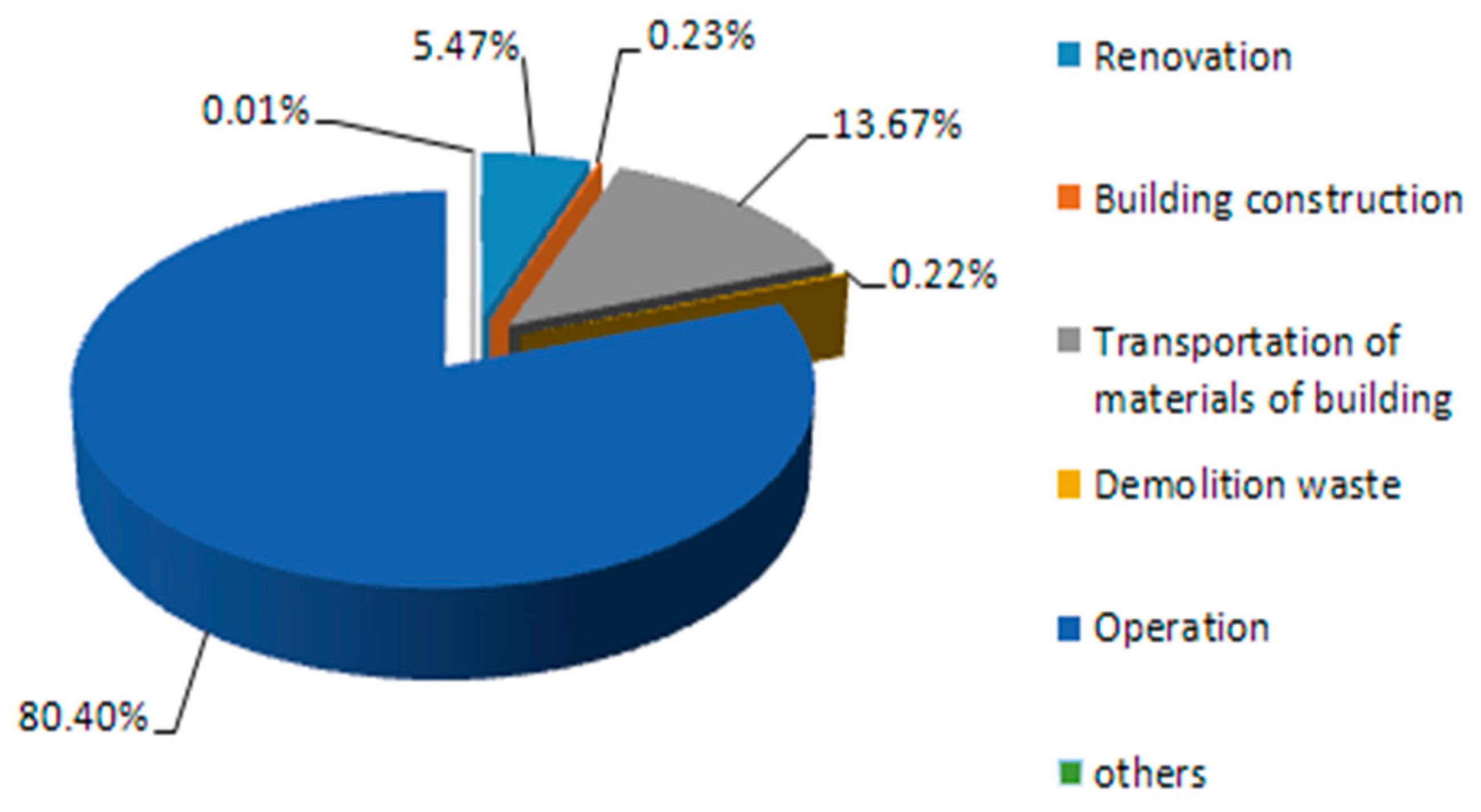
| No. | Types | Standard or Code | The Role of Standard or Code |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Guidance | Chinese Ecological Residential Technology Assessment Handbook (2001) | To supplement, improve, and guide the standards or codes issued during each period. |
| 2 | The Technical Essentials for Construction of Healthy Housing (2001) | ||
| 3 | Green Building Evaluation Technology Conditions (2007) | ||
| 4 | Green Building Evaluation Identity Management Method (2007) | ||
| 5 | For Beijing Olympics | Assessment System for Green Building of Beijing Olympic (GOBAS) | To guide the construction of the Beijing Olympic Games. |
| 6 | Implementation Manual of Green Building for Beijing Olympics | ||
| 7 | For every link in the building | Code for Green Building of Civil Building (2010) | Design is a key link in the whole life cycle of architecture. It dominates the influence of each stage of building on resources and environment. It is of great significance to promote the development of energy-saving and land-saving residential buildings and public buildings. |
| 8 | Evaluation Standard for Green Construction of Building (2010) | Promote green construction, standardize the evaluation method of green construction for building engineering, and develop the standard. | |
| 9 | Code for Green Construction of Building (2014) | Improve the utilization rate of building materials, promote the improvement of construction engineering management level, and promote the benign development of construction enterprises. | |
| 10 | Technical Code for Operation and Maintenance of Green Building (2016) | Operation and maintenance, as the longest stage of construction, is an important link in the life of the building. The code is effective and profitable. | |
| 11 | For different types of buildings | Evaluation Standard for Green Industrial Building (2013) | The development of green industrial buildings and assessment of green industrial buildings can collect important basic information of building energy consumption and water consumption, and provide important data support for formulating more comprehensive energy saving indicators. |
| 12 | Evaluation Standard for Green Office Building (2013) | Improve the assessment system of green building in China, and guide and promote the development of green office building. | |
| 13 | Assessment Standard for Green Store Building (2015) | Improve the assessment system of green building in China, and guide and promote the development of green store building. | |
| 14 | Evaluation Standard for Green Hospital Building (2016) | Compared with other types of buildings, hospital buildings have high performance requirements, strict environmental requirements, and different functional requirements. It is necessary to compile green building evaluation standard specifically for hospital buildings. | |
| 15 | Assessment Standard for Green Hotel Building (2016) | Improve the assessment system of green building in China, and guide and promote the development of green hotel building. | |
| 16 | Assessment Standard for Green Museum and Exhibition Building (2016) | It is of great significance and promotion for the whole society to pay attention to energy saving and environmental protection by promoting the development of green expo building. | |
| 17 | For existing building | Assessment Standard for Green Retrofitting of Existing Building (2015) | Improve the technology of green transformation and the system of products, and promote the development of green reconstruction of existing buildings. |
| 18 | For green building and healthy building | Assessment Standard for Green Building (2006) | The first national standard on green building. With the green building work step by step, the connotation and extension of green building have been continuously enriched. Various industries, various places, and various types of construction demand for green ideas to be put forward. However, this standard cannot fully meet the needs of green building practice and assessment work at the present stage. |
| 19 | Assessment Standard for Green Building (2014) | On the basis of old standards, the scope of evaluation objects is extended, the evaluation stage is clear, the evaluation method is more scientific and reasonable, and it is synchronized with the international community. The evaluation index is more systematic and perfect, taking full account of China’s national conditions. | |
| 20 | Assessment Standard for Healthy Building (2016) | China’s healthy building is based on green building. With the green building as the starting point, balance the performance, outstanding health is the optimal choice. |
| Material | Example Diagram | Thickness (mm) | Thermal Resistance (m2·K/W) | Heat Transmission Coefficient (W/m2·K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Harbin old building: ordinary brick wall 490 mm |  | 510 | 0.797 | 1.056 |
| Harbin old building: ordinary brick wall 370 mm (no heat preservation) | 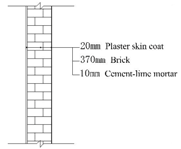 | 400 | 0.641 | 1.264 |
| Modern method of heat preservation: thermal insulating wall |  | 360 | 3.134 | 0.304 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Kang, J.; Jin, H. A Review of Green Building Development in China from the Perspective of Energy Saving. Energies 2018, 11, 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11020334
Zhang Y, Kang J, Jin H. A Review of Green Building Development in China from the Perspective of Energy Saving. Energies. 2018; 11(2):334. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11020334
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ying, Jian Kang, and Hong Jin. 2018. "A Review of Green Building Development in China from the Perspective of Energy Saving" Energies 11, no. 2: 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11020334
APA StyleZhang, Y., Kang, J., & Jin, H. (2018). A Review of Green Building Development in China from the Perspective of Energy Saving. Energies, 11(2), 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11020334






