Design and Optimization of a Brushless Wound-Rotor Vernier Machine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
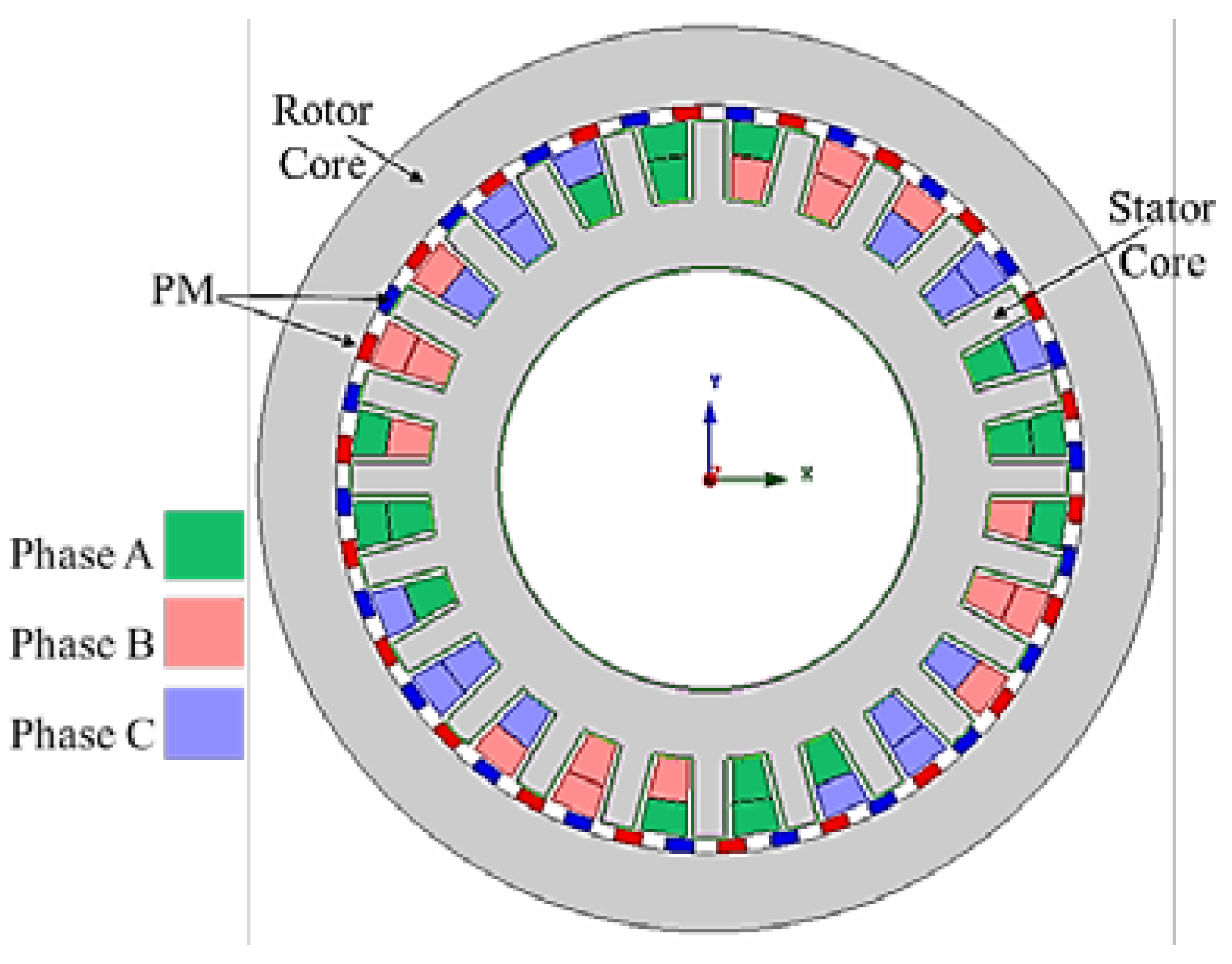
2. Brushless Wound-Rotor Topology and Proposed Configuration
2.1. Brushless Wound-Rotor Topology
2.2. Proposed Vernier Machine Configuration
3. Design and Performance of Proposed BL-WRVM
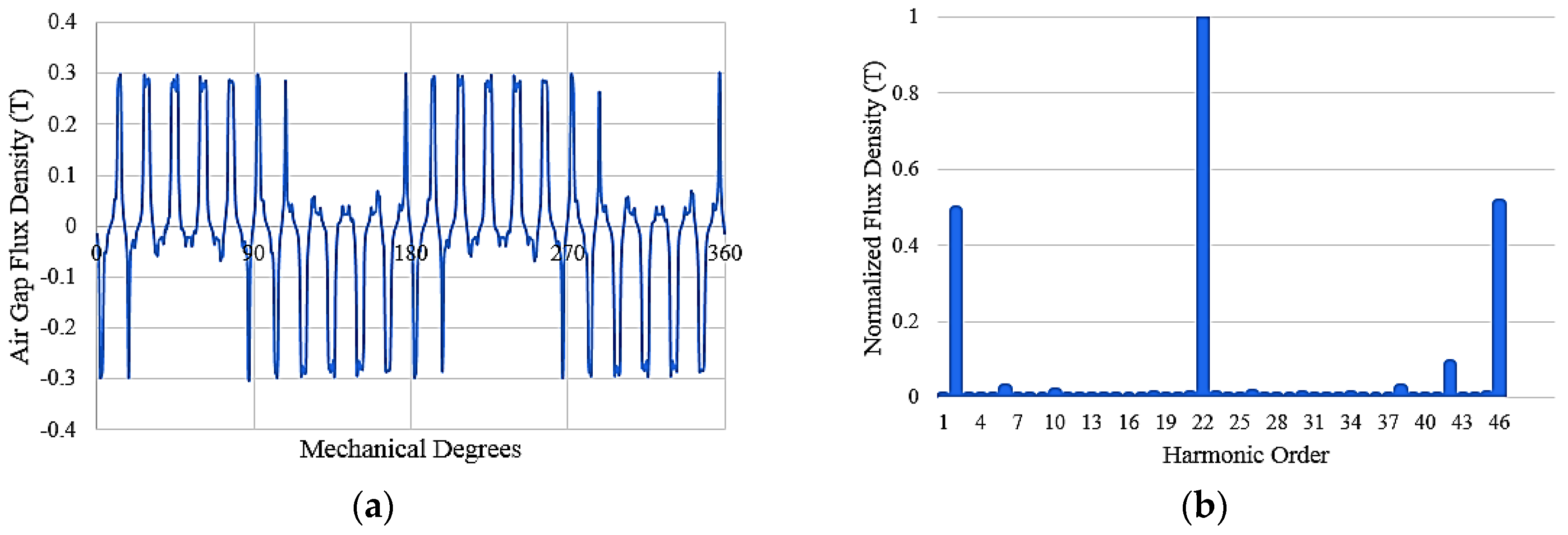
3.1. Design Considerations
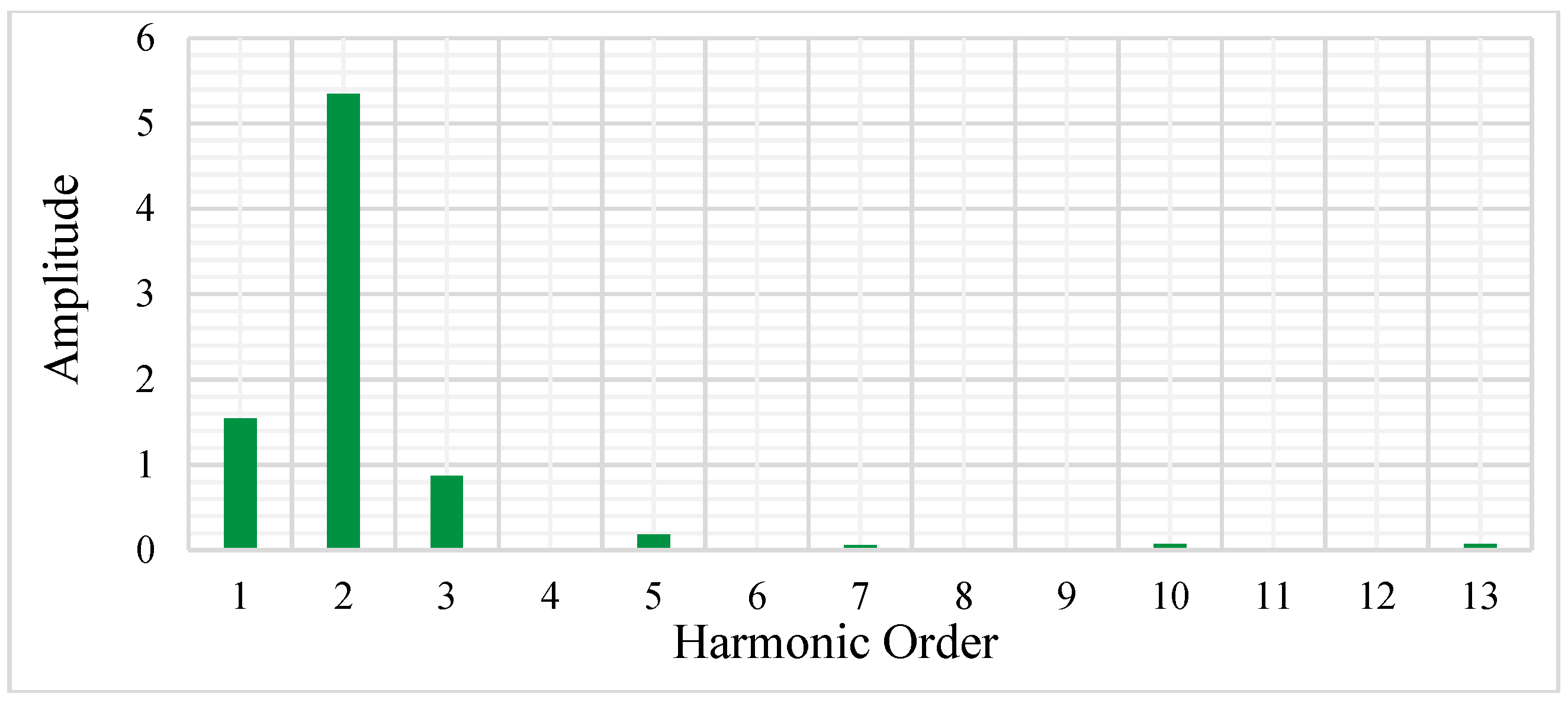
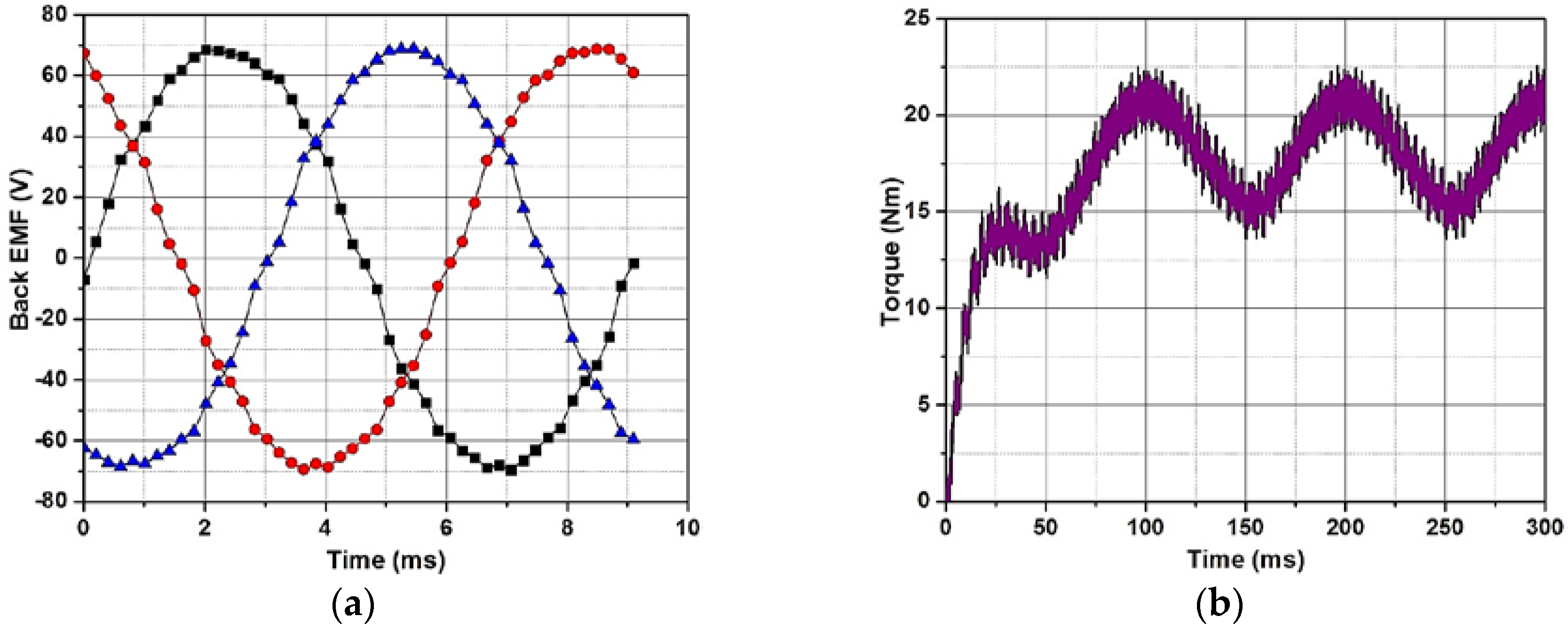
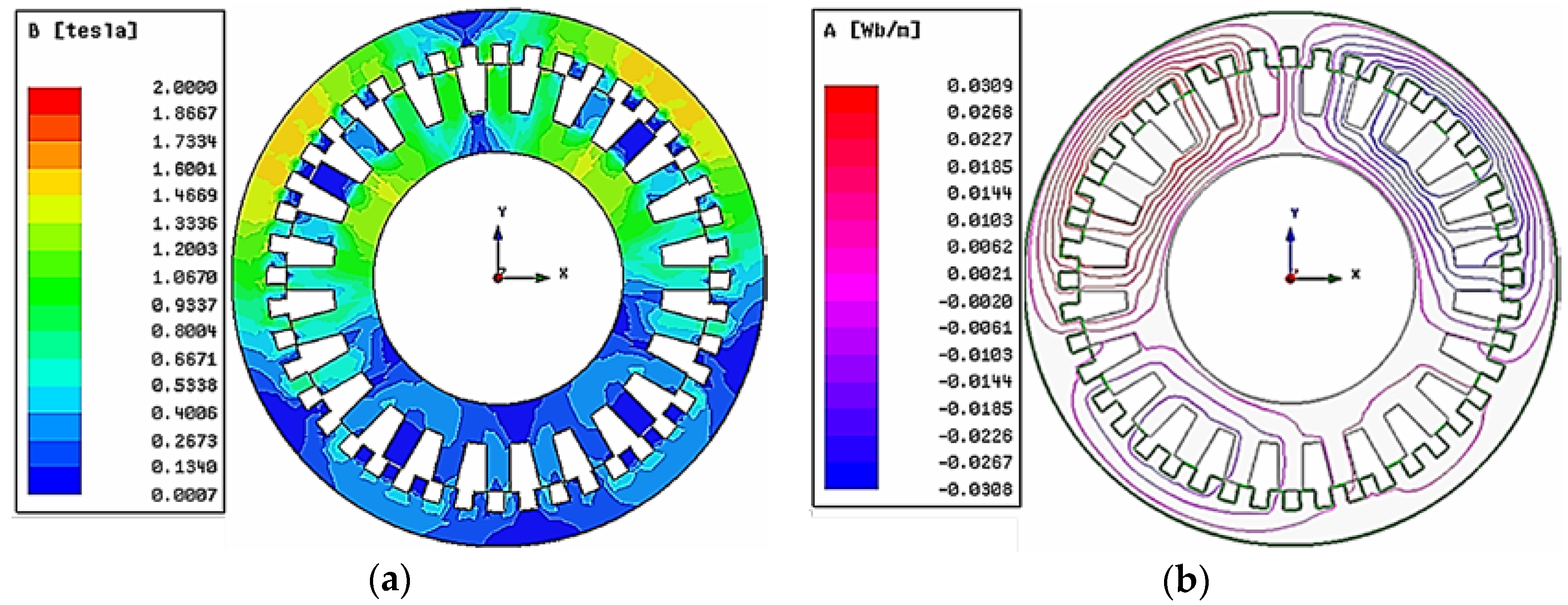
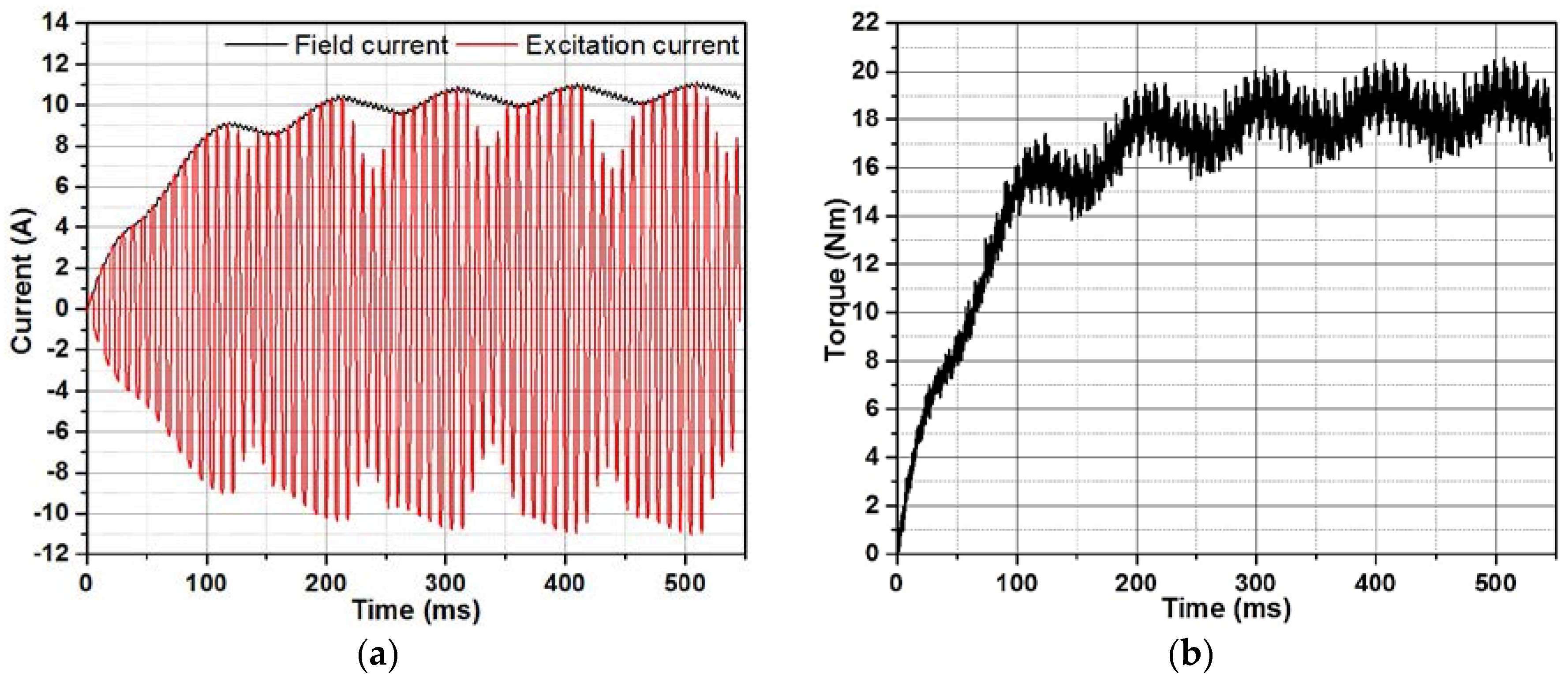
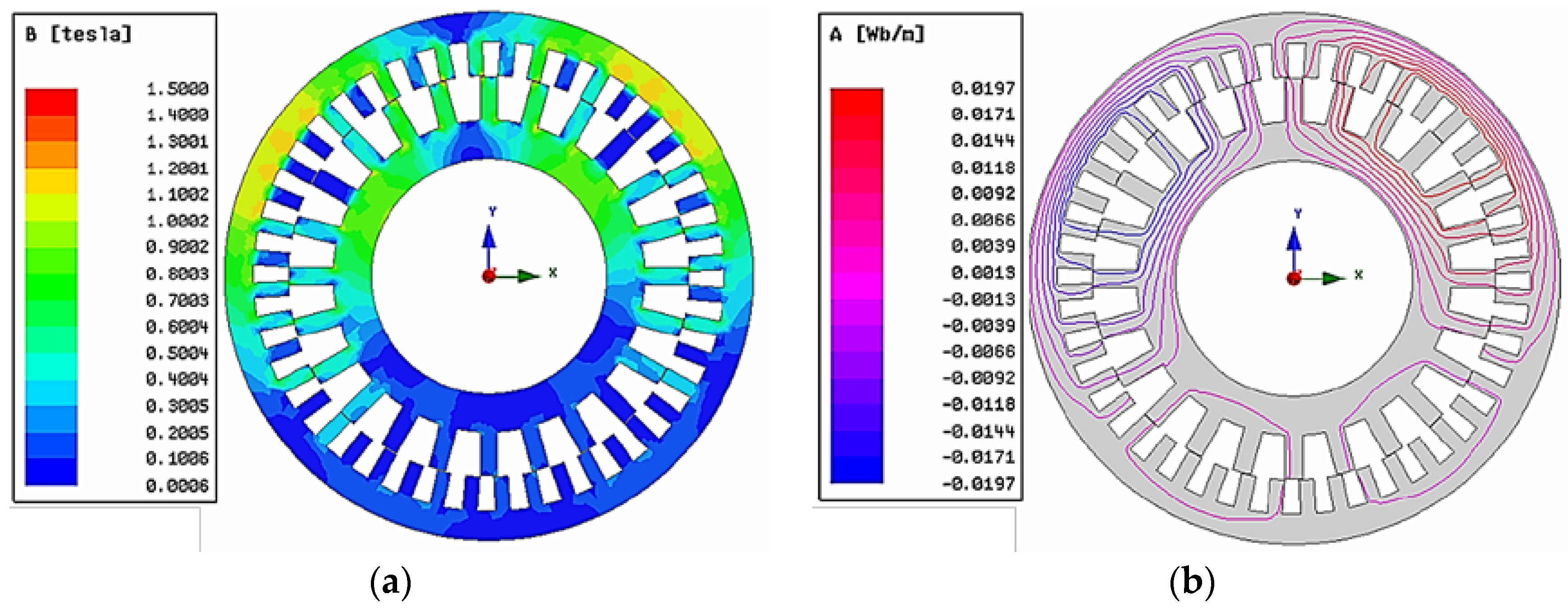
3.2. Performance Analysis
4. Machine Sensitivity Analysis and Optimization
4.1. Sensitivity Analysis
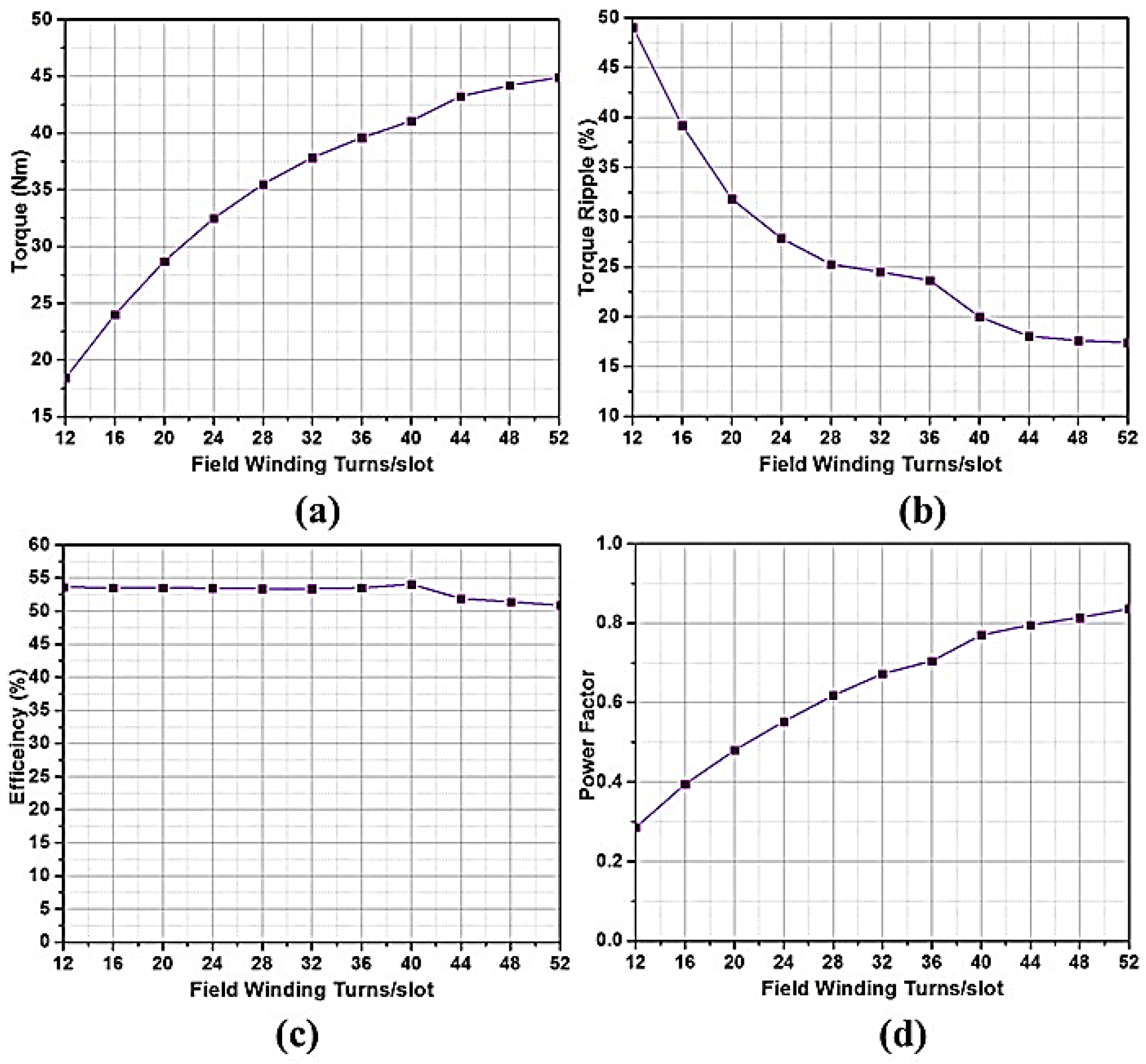
4.1.1. Effect of Variation of Field Winding Turns on the Machine Performance
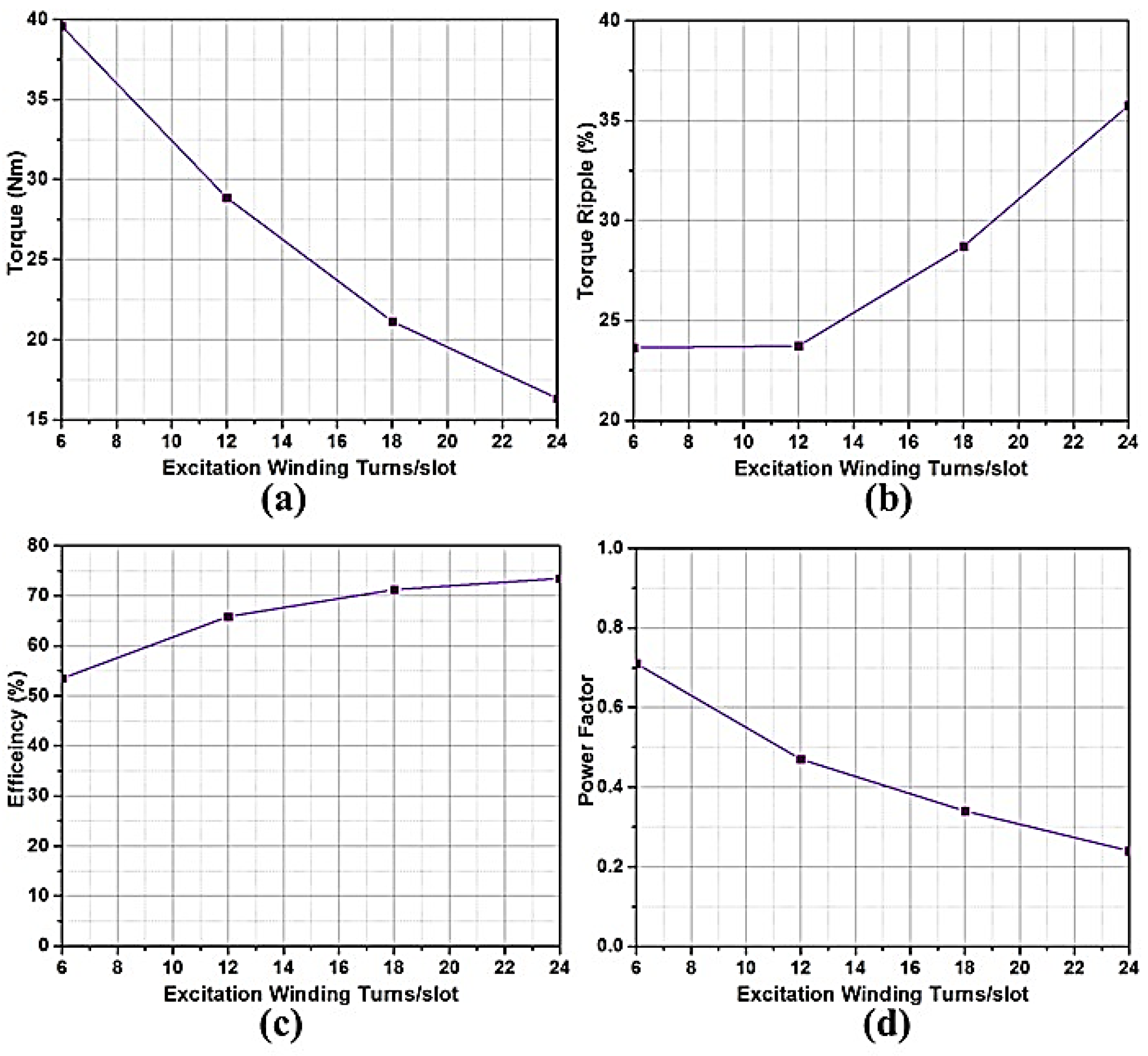
4.1.2. Effect of Variation of Excitation Winding Turns on the Machine Performance
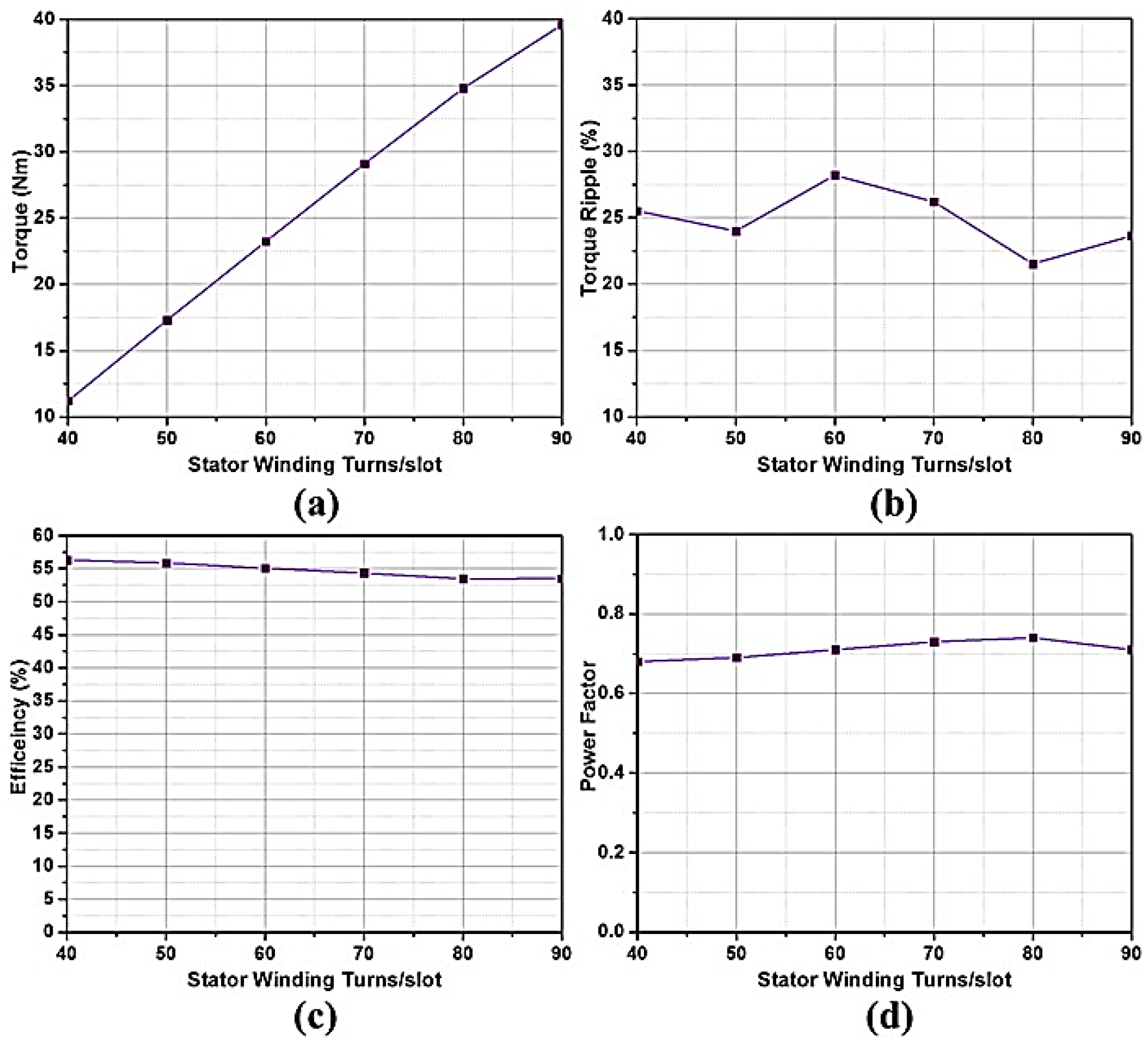
4.1.3. Effect of Variation of Stator Winding Turns on the Machine Performance
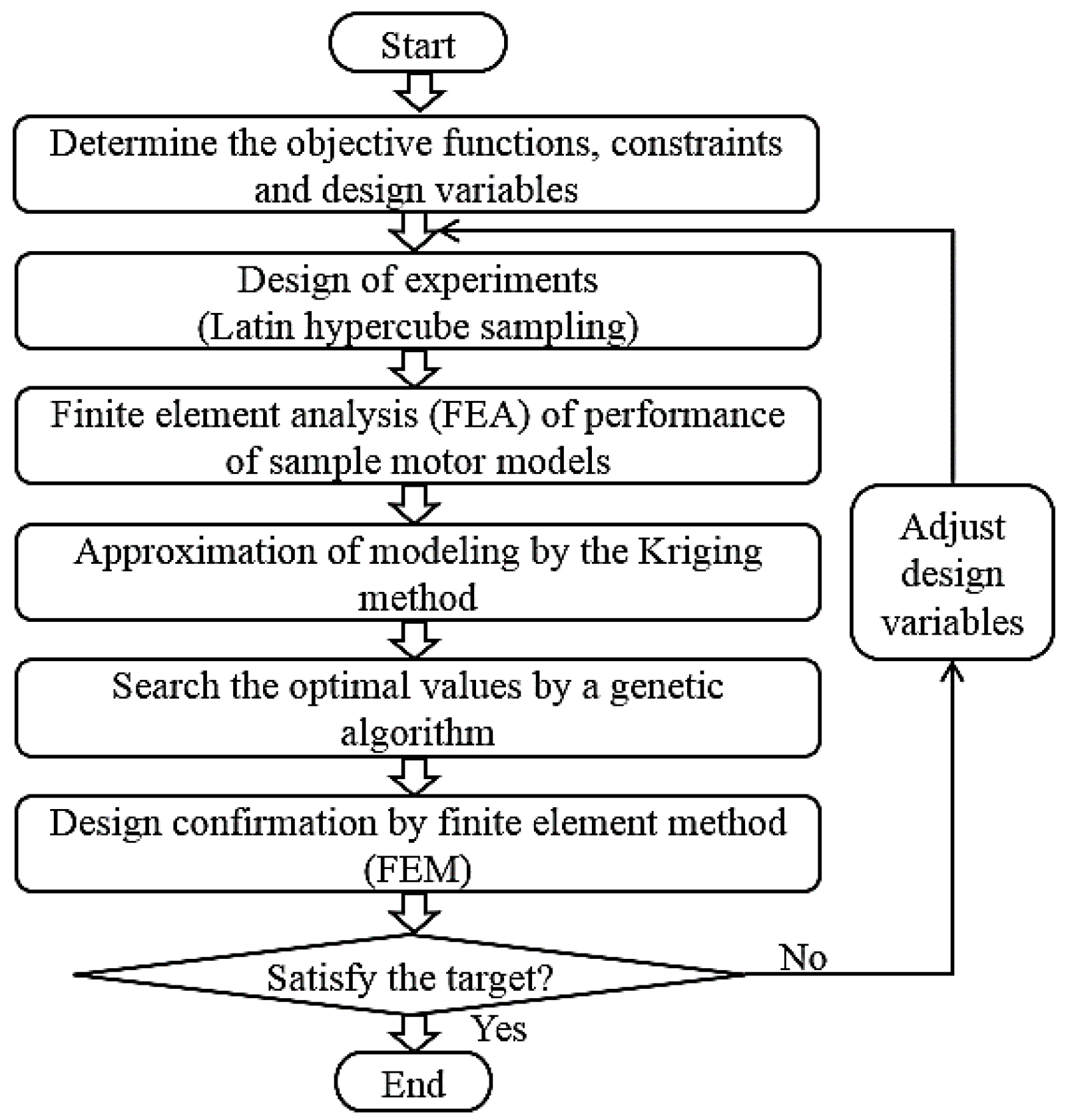
4.2. Design Optimization
- Objective functionMaximize the power factor
Minimize the torque ripple - ConstraintsEfficiency ≥ 55%
Torque ≥ 18.33 Nm - Design variables
5. Wide-Speed Operation and Performance Comparison
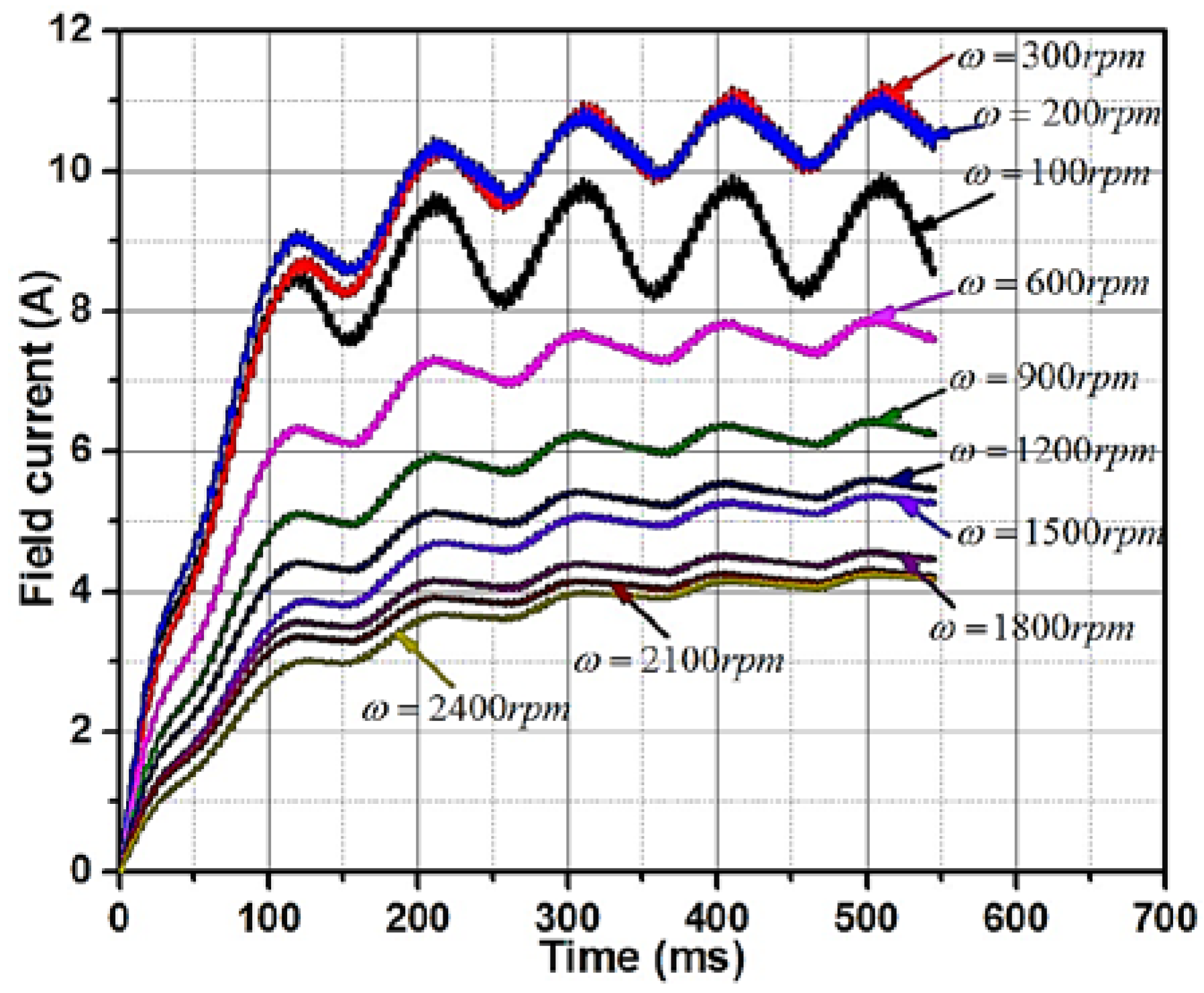
5.1. Wide-Speed Operation
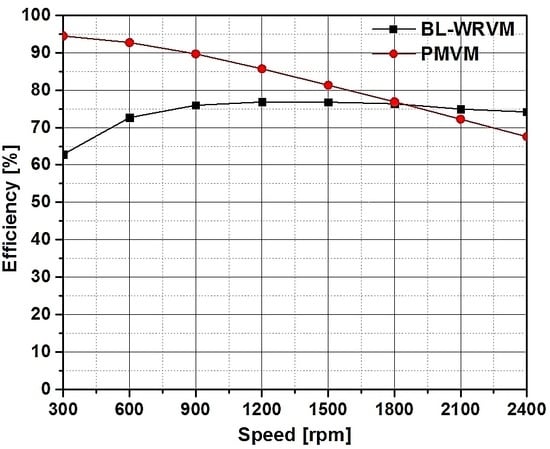
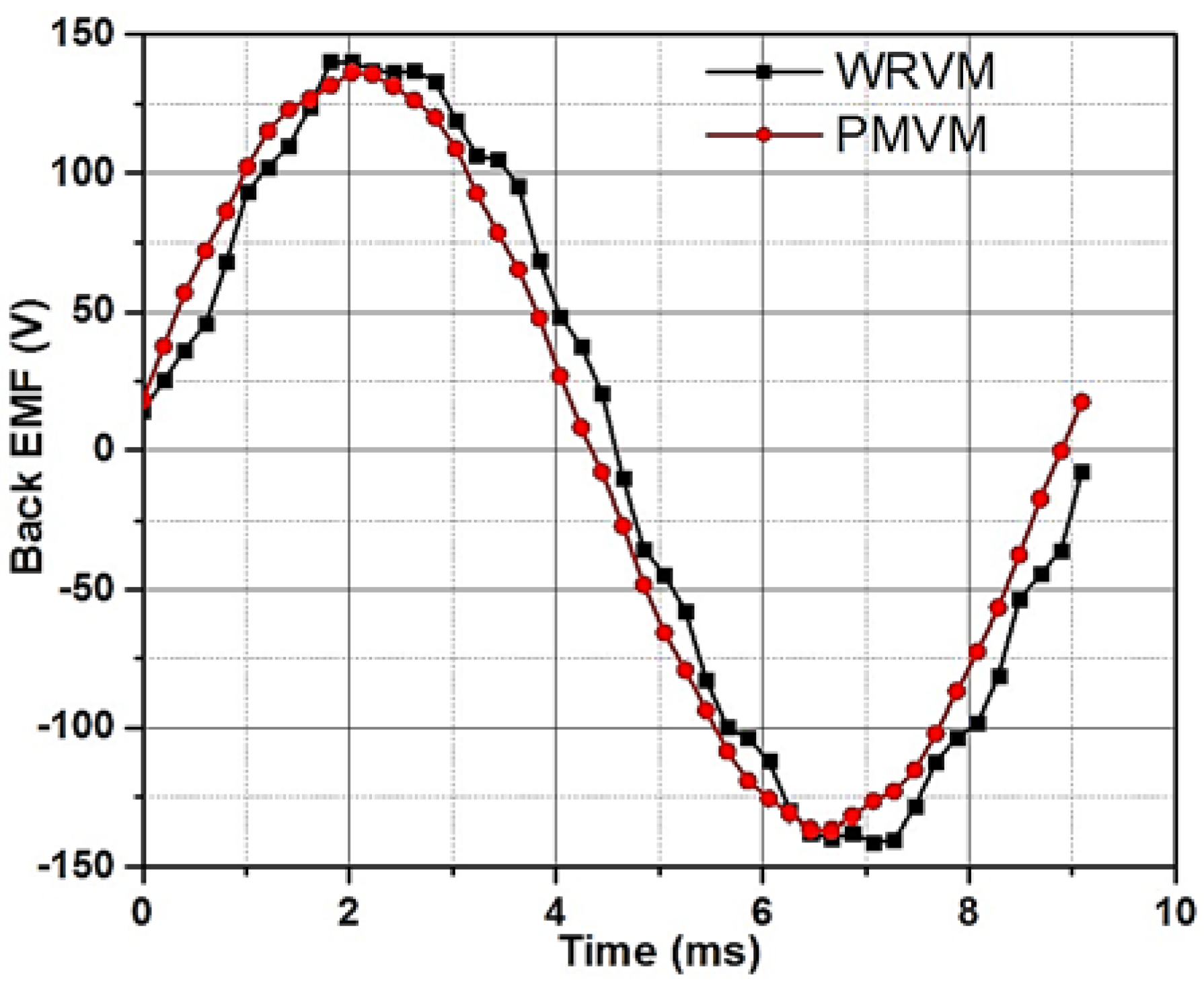
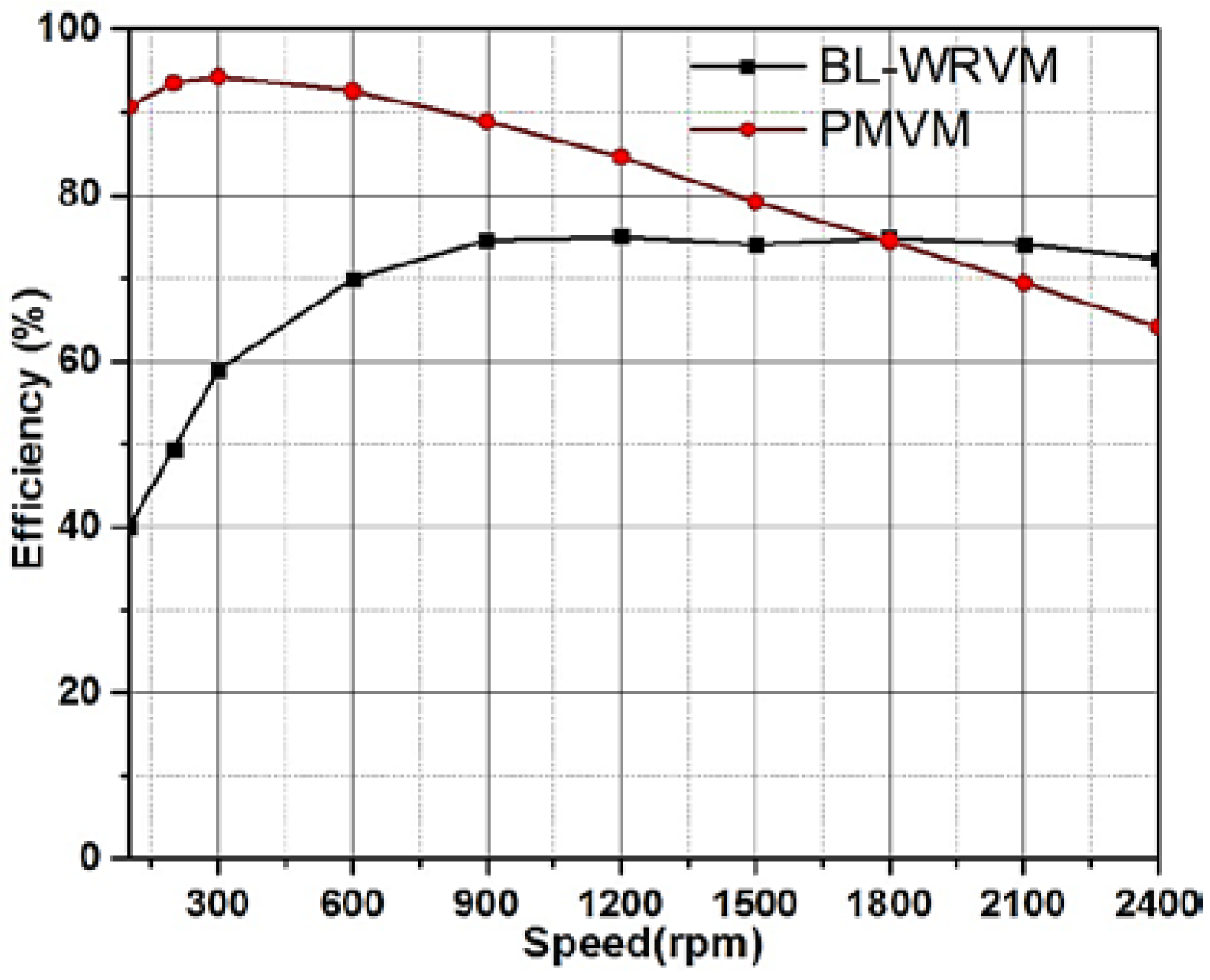
5.2. Performance Comparison with PMVM
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, B.; Thomas, A.L. Operation and Design Principles of a PM Vernier Motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 3656–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B. Characteristic Analysis of a Vernier PM motor Considering Adjustable Speed Control. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference and Expo Transportation Electrification Asia-Pacific (ITEC Asia-Pacific), Busan, Korea, 1–4 June 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Thomas, A.L. Design of a Surface PM Vernier Motor for a Practical Variable Speed Application. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 September 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ching, T.W.; Chau, K.T. A Hybrid-Excited Vernier Permanent Magnet Machine Using Homopolar Topology. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Thomas, A.L.; Byung, I.K. A Novel Dual-Stator Axial-Flux Spoke-Type Permanent Magnet Vernier Machine for Direct-Drive Applications. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherji, K.C.; Tustin, A. Vernier reluctance motor. Proc. Inst. Electr. Eng. 1974, 121, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Qu, R.; Li, J.; Li, D.; Lu, X. Comparison of Stator DC Current Excited Vernier Reluctance Machines with Different Field Winding Configurations. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Qu, R.; Li, J.; Li, D. Principles of Stator DC Winding Excited Vernier Reluctance Machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2016, 31, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhu, Z.Q. Influence of rotor pole number on electromagnetic performance of novel variable flux reluctance machine with DC-field coil in stator. In Proceedings of the 2012 7th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference (IPEMC), Harbin, China, 2–5 June 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tounzi, A.M.; Ramdane, B.; Zaïm, M.E. Study and experimentation of a rotor current excited Vernier reluctance machine aimed to direct-driven applications. Eur. Phys. J. 2010, 52, 11102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Q.; Lipo, T.A.; Kwon, B. Design and Analysis of a Novel Brushless Wound Rotor Synchronous Machine. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Magnetics Conference (INTERMAG), Beijing, China, 11–15 May 2015. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Qu, R.; Li, D.; Gao, Y. Influence of Pole Ratio and Winding Pole Numbers on Performance and Optimal Design Parameters of Surface Permanent-Magnet Vernier Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 3707–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Qu, R.; Li, J. Analysis of the Power Factor of Stator DC-Excited Vernier Reluctance Machines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipo, T.A.; Du, Z.S. Synchronous Motor Drives—A Forgotten Option. In Proceedings of the 2015 Intl Aegean Conference on Electrical Machines & Power Electronics (ACEMP), Side, Turkey, 2–4 September 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Units | Vernier Machine |
|---|---|---|
| Stator Poles | - | 4 |
| Stator Slots | - | 24 |
| Rotor Field Poles | - | 44 |
| Rotor Slots | - | 44 |
| Operating speed | rpm | 300 |
| Stator outer diameter | mm | 238 |
| Stator inner diameter | mm | 140 |
| Air gap length | mm | 0.5 |
| Rotor inner diameter | mm | 239 |
| Rotor outer diameter | mm | 300 |
| Machine axial length | mm | 30 |
| Parameter | Units | Vernier Machine (Basic Model) |
|---|---|---|
| Torque | Nm | 18.33 |
| Torque ripple | % | 49 |
| Efficiency | % | 55 |
| Power Factor | - | 0.28 |
| Parameter | Units | BL-WRVM (Basic Model) | BL-WRVM (Optimized Model) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FEA | Algorithm | FEA | |||
| Design variable | Turns/slot | 6 | 8 | ||
| Turns/slot | 90 | 60 | |||
| Torque | - | Nm | 18.42 | 18.81 | 18.44 |
| Torque ripple | % | 49.0 | 22.34 | 23.25 | |
| Efficiency | % | 55.0 | 57.83 | 58.93 | |
| Power factor | - | 0.28 | 0.68 | 0.62 | |
| Parameter | 100 rpm | 200 rpm | 300 rpm | 600 rpm | 900 rpm | 1200 rpm | 1500 rpm | 1800 rpm | 2100 rpm | 2400 rpm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input Current (A) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.67 | 0.54 | 0.46 | 0.39 | 0.37 | 0.35 | 0.31 |
| Field Current (A) | 9.09 | 10.63 | 10.56 | 7.68 | 6.05 | 5.49 | 5.26 | 4.47 | 4.23 | 4.17 |
| Torque (Nm) | 17.94 | 18.21 | 18.44 | 9.31 | 6.11 | 4.57 | 3.75 | 2.98 | 2.65 | 2.30 |
| Copper Loss (W) | 271.22 | 365.33 | 360.83 | 189.55 | 117.97 | 96.83 | 88.42 | 63.99 | 57.38 | 55.40 |
| Core Loss (W) | 11.03 | 24.6 | 43.06 | 62.67 | 78.67 | 95.16 | 118.05 | 125.47 | 146.19 | 166.43 |
| Efficiency (%) | 39.97 | 49.45 | 58.93 | 69.89 | 74.56 | 74.98 | 74.05 | 74.83 | 74.11 | 72.29 |
| Parameter | 100 rpm | 200 rpm | 300 rpm | 600 rpm | 900 rpm | 1200 rpm | 1500 rpm | 1800 rpm | 2100 rpm | 2400 rpm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Core Loss (W) | 5.06 | 11.85 | 20.22 | 32.78 | 59.14 | 93 | 135.42 | 186.07 | 245 | 310.14 |
| Efficiency (%) | 90.69 | 93.54 | 94.29 | 92.57 | 88.92 | 84.62 | 79.17 | 74.44 | 69.42 | 64.13 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, Q.; Hussain, A.; Baloch, N.; Kwon, B.I. Design and Optimization of a Brushless Wound-Rotor Vernier Machine. Energies 2018, 11, 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11020317
Ali Q, Hussain A, Baloch N, Kwon BI. Design and Optimization of a Brushless Wound-Rotor Vernier Machine. Energies. 2018; 11(2):317. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11020317
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Qasim, Asif Hussain, Noman Baloch, and Byung Il Kwon. 2018. "Design and Optimization of a Brushless Wound-Rotor Vernier Machine" Energies 11, no. 2: 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11020317
APA StyleAli, Q., Hussain, A., Baloch, N., & Kwon, B. I. (2018). Design and Optimization of a Brushless Wound-Rotor Vernier Machine. Energies, 11(2), 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11020317