Abstract
This study compared the electrolytic refining process using different commercial Pd-based electrodes. The Pd-based electrode had an Ir:Sn molar ratio of 1:1 and contained 10% tantalum on a titanium substrate. The palladium weight ratio varied from 0 g to 1.8 g, 4.7 g, 8.6 g, and 15.4 g. Electrolytic refining was investigated for the Pd-based electrode in 3 M of H2SO4. The interfacial microstructure and components of the substrate were investigated using energy-dispersive X-ray analysis, and the electrochemical properties of the materials were measured using cyclic voltammetry, linear scan voltammetry, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, and accelerated life tests. Of all the tested Pd-based electrodes, those with a palladium loading weight of 8.6 g showed the highest and most stable electrode activity at 3 M of H2SO4, with a capacitance retention of 96% of its initial value. The accelerated life test results for the 8.6 g Pd-Ir-Sn-Ta/TiO2 electrode showed a gradual slope with an efficiency of almost 100% at 1000 h in an aqueous solution of 3 M of H2SO4. After the test, the dissolved elements that caused resistance in the electrolyte increased with increasing palladium loading content. Thus, the 8.6 g Pd-Ir-Sn-Ta/TiO2 electrode demonstrated the optimum composition in 3 M of H2SO4 for electrolyte refining.
1. Introduction
Rare metals are characterized by restricted deposits and are difficult to extract, yet their industrial demand is currently increasing. Because of the limited supply, significant efforts are being made to secure related resources, especially for businesses and countries that consume large quantities of rare metals. Unlike developed countries, however, developing countries fail to achieve efficient resource use through recycling, as their recycling processes are not technologically advanced nor industrialized. Among the various types of recycling, electrowinning (electrolytic refining) is typically very energy efficient [1,2,3,4,5].
Recently, mixed-metal oxide electrodes have been designed to reduce electricity costs and solve the problems related to first-generation electrodes composed of only noble metals, such as their high price, short life time, and difficulties with impurities [6,7,8,9]. To overcome this, many researchers have focused on improving the short-lived and impure nature of the electrodes, and on increasing the tightness of the electrode layer to reduce the penetration of the electrolyte into the parent metal. [10,11,12,13].
Titanium is widely used as the substrate during this process because of its good corrosion resistance and excellent electrochemical properties [14,15,16]. To date, several electrodes have been shown to be active for surface-active coating materials including tantalum, iridium, zirconium, and other rare noble metals [17,18,19,20]. Among them, the co-existence of IrO2 and SnO2 leads to good stability in highly acidic environments for electro-oxidation [21,22,23,24,25]. However, electrode activity has recovery limitations. Despite this, several studies have reported that Pd-based electrodes exhibit high durability and superior electrical conductivity [26,27,28]. The advantage of four-component electrodes is that they involve a smaller amount of the precious metal Pd, which forms the binary system, and the other three components play a role in reducing the dispersion and stability of Pd.
Considering this, we analyzed the influence of Pd loading weight on the interlayer (Ir-Sn-Ta/TiO2) of the electrode, used as a buffer component to reduce distortion of the electrode and to increase the affinity between the substrate and the surface layer. Moreover, we evaluated the accelerated life testing of the electrode at a current density of 10,000 mA/cm2 for 3 M of H2SO4 for electrolyte refining applications.
2. Experimental
2.1. Electrode
The commercial electrode was purchased from West Co.(Changwon-si, Republic of Korea) The substrate was a titanium (TiO2) plate, containing an Ir and Sn manufacturing ratio of 1:1, a Ta coating weight of 10%, and 4% of different electrodes. Pd-IST/TiO2 denotes that the Pd-Ir-Sn-Ta/TiO2 electrode contained PdOx, IrOx, SnOx, and TaOx on a TiO2 substrate. The surface texture of the commercial Pd-based electrode was characterized using energy-dispersive X-ray analysis (EDAX, Inspect F50, ThermoFisher).
2.2. Electrochemical Characterization
The electrochemical behavior of the electrodes was tested on a ZIVE electrochemical workstation (BP2C) from WonA Tech. (Seoul, Republic of Korea), using a three-electrode system. The Pd-based electrode was used as the working electrode with a test area of 20 mm × 10 mm. The platinum electrode was employed as the counter-electrode and the silver/silver chloride electrode was the reference electrode. Electrochemical degradation experiments were conducted using a 3 M H2SO4 solution using ZIVE (MP2C) from WonA Tech. (Seoul, Republic of Korea). The gravimetric capacitive performance and equivalent series resistance were evaluated using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) in a frequency range between 10 mHz and 1 kHz. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) is an effective experimental technique for evaluating the characteristic capacitive behavior of electrode materials; therefore, the CV of the Pd-based electrode in 3 M of H2SO4 was detected for a sweep frequency from 10–200 mV/s within 0.5–1.0 V.
2.3. Accelerated Life Test
Accelerated life testing (ALT) was performed for all electrodes using a multi-channel device that allowed for simultaneous life assessment of multiple specimens, under the conditions shown in Table 1 and constant current application. The life expectancy of the insoluble electrodes was shown several years earlier using the ALT method, which assesses lifespan under the operating conditions typically applied in actual environments.

Table 1.
Accelerated life test conditions.
In this study, it was desirable that the life of the electrodes ended at the point where the operating voltage reached 4 V, considering that the operating voltage was increased by 20–40%. ALT was performed by applying a current density of 10,000 A/dm2 with 3 M of H2SO4 at 293 K. The lifetime of the commercial Pd-based electrodes was assessed based on the voltage phase. After the ALT test, the electrolyte was analyzed using inductively coupled plasma-mass spectroscopy (ICP-MS, iCAP6000, Thermo) to determine the decomposed electrode composition.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Pd-Based Electrode
The typical atomic and metal composition obtained using EDAX is shown in Table 2. The EDAX results of the electrode without Pd reveal a Ta content of 6.5% and an Ir/Sn weight ratio of almost 1/1. For the electrodes with Pd, the Ta contents ranged from 18–33%. The Ir and Sn contents were 40–48% and 20–30%, respectively. Abnormally higher Ir contents were observed in several regions of the 15.4 g Pd-IST/TiO2 electrode.

Table 2.
EDAX analysis and resistance of commercial Pd-based electrodes.
3.2. Electroactive Properties of the Pd-Based Electrode
The resistances of Pd-based electrodes were measured at 293 K in a three-electrode system. As shown in Table 2, the resistance of the 0 g Pd-IST/TiO2 electrode was 0.28 Ω, while that of the 15.4 g Pd-IST/TiO2 electrode was 0.60 Ω, indicating that the ion conductivity of the former was much higher at the same concentration of H2SO4. The resistances of 1.8 g Pd-IST/TiO2, 4.7 g Pd-IST/TiO2, and 8.6 g Pd-IST/TiO2 electrodes showed similar values. The resistance of the relative standard deviation (R.S.D) was less than 5%, which shows good repeatability.
To investigate the influence of electrode composition, we compared the potential differences with the same current density of 500 mA/cm2 in 3 M of H2SO4. Under the experimental conditions, the initial potential in 0 g Pd-IST/TiO2 was 1.80 V, indicating a higher positive potential (Figure 1a). Generally, the initial and final potential differences were approximately 0.5 V. The initial potential decreased with increasing palladium loading content until 8.6 g Pd-IST/TiO2. Otherwise, the 15.4 g Pd-IST/TiO2 electrode showed a higher potential than the 8.6 g Pd-IST/TiO2 electrode. We believe that a large amount of Pd led to Pd aggregation and reduced the electrode activity.
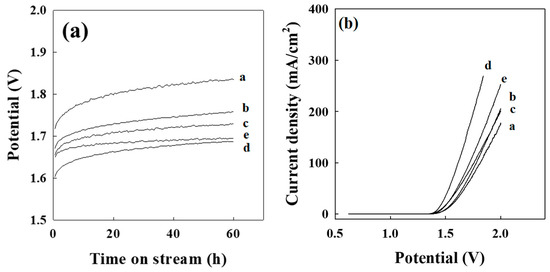
Figure 1.
Electrode properties: (a) potential curve; (b) linear scan voltammograms of Pd-based electrodes viz., a: 0 g Pd-IST/TiO2, b: 1.8 g Pd-IST/TiO2, c: 4.7 g Pd-IST/TiO2, d: 8.6 g Pd-IST/TiO2, and e: 15.4 g Pd-IST/TiO2.
A better understanding of the electroactive properties of the Pd-based electrodes toward the oxygen evolution was obtained using linear scan voltammogram (LSV) measurements [29]. The polarization curves are displayed in Figure 1b and their potential slopes are listed in Table 3. The overvoltage of Pd-based electrodes increased with increasing current density. The potential slope was evaluated by repeating five experiments in the same standard condition. The R.S.D are given as shown in Table 3. The potential slope of Pd-based electrodes at 3 M of H2SO4 decreased in the following order: 8.6 g Pd-IST/TiO2 > 15.4 g Pd-IST/TiO2 > 4.7 g Pd-IST/TiO2 > 1.8 g Pd-IST/TiO2 > 0 g Pd-IST/TiO2. Thus, the potential slope typically increased with increasing Pd content, except for 15.4 g Pd-IST/TiO2.

Table 3.
Overvoltage and the potential slope for Pd-based electrodes.
To highlight the advantages of Pd as an electrode material for electrolyte refining, its electrochemical performance was investigated using cyclic voltammetry (CV) in a three-electrode system. Figure 2 shows the typical CV curves of the Pd-based electrode in the potential range of 0.5–1.0 V (vs Ag/AgCl) at a scan rate of 100 mV/s in 3 M of H2SO4. Typical CV curves were observed for all Pd-based electrodes. Generally, the potential wave was attributed to the overlapping redox couple peaks of the Ir3+/Ir4+ transition at ≈ 0.68, and the anodic oxidation metallic iridium could occur at ≈0.93 V, which led to the formation of a different oxidative phase. As the Pd content increased, the current decreased at a low potential state but increased at a high potential state. The calculated current efficiencies of Pd-based electrodes in 3 M of H2SO4 solution are presented in Figure 2b. They decreased in the following order: 15.4 g Pd-IST/TiO2 ≈ 8.6 g Pd-IST/TiO2 ≈ 4.7 g Pd-IST/TiO2 ≈ 1.8 g Pd-IST/TiO2 > 0 g Pd-IST/TiO2, indicating that Pd affected the current efficiency, but there was no effect over 1.8 g of Pd loading content.
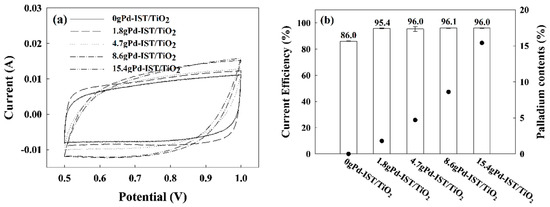
Figure 2.
(a) CVs for Pd-based electrodes of different palladium loading weights with sweep rates from 100 mV/s in 3M of H2SO4 solution; (b) Comparison of current efficiency (left bar) and palladium contents (right bar, dots) at different palladium contents.
Figure 3a shows the typical CV curves of the Pd-based electrodes in the potential range of 0–1.0 V (vs Ag/AgCl) at scan rates from 10–200 mV/s. The CV curves show that H2SO4 was very stable, and there was no reduction reaction of H2SO4 during the electrolytic process. Moreover, there was no reduction peak between 0.5 and 1.0 V for the H2SO4 solution. Figure 3b shows the cell voltage in the complete electrolysis course at different current densities. The increase in cell voltage was approximately directly proportional to the increase in current density. When the scan rate was 10 mV/s, the potential was 0.75 V. However, when the scan rate reached 200 mV/s, the potential was 0.78 V.
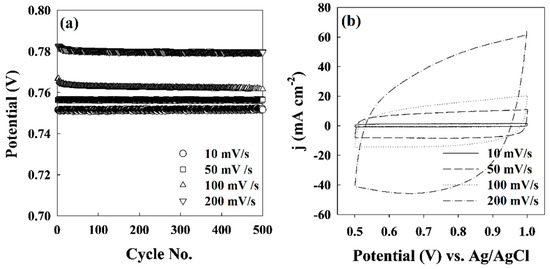
Figure 3.
Electrochemical performance of an 8.6 g Pd-IST/TiO2 electrode: (a) CV behavior; (b) the cell voltage at four different scan rates of 10, 50, 100, and 200 mV/s in a 3 M H2SO4 solution.
These results indicate the cell voltages after 500 cycles were all maintained around the initial voltage; that is, the cell voltage was steady for all 500 cycles. The charge–discharge potential of the 8.6 g Pd-IST/TiO2 electrode was very stable, and there was no reduction of H2SO4 during the electrolytic process (not shown).
3.3. ALT Results
The multi-channel accelerated life assessment device used in this study was designed so that the operating voltage of each cell was stored in real time [30]. As shown in Figure 4 and Table 4, the accelerated life evaluation experiment was conducted on the following Pd-based electrodes: 1.8 g Pd-IST/TiO2, 4.7 g Pd-IST/TiO2, 8.6 g Pd-IST/TiO2, and 15.4 g Pd-IST/TiO2. For a current density of 10,000 mA/cm2, the ALT tended to gradually increase with the applied voltage of 3.84 V, 3.98 V, 3.74 V, and 3.24 V, respectively. Thus, the initial voltage gradually increased with decreasing palladium loading weight.
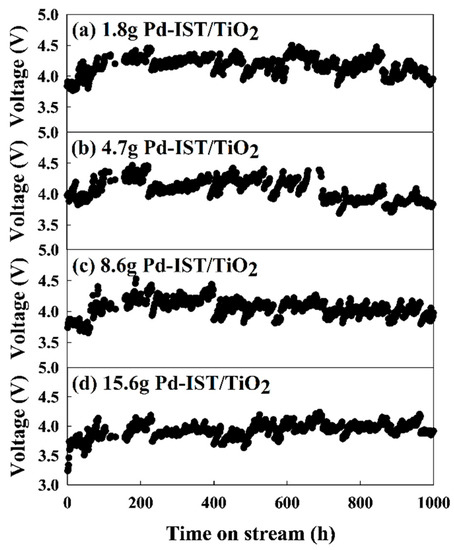
Figure 4.
Accelerated life test of Pd-based electrodes viz: (a) 1.8 g Pd-IST/TiO2; (b) 4.7 g Pd-IST/TiO2; (c) 8.6 g Pd-IST/TiO2; (d) 15.4 g Pd-IST/TiO2.

Table 4.
The results of accelerated life test.
As shown in Figure 5, the slope of the Pd-based electrode was stable even though it was 20 times that of the acceleration experiment. In addition, the slope of the Pd-based electrodes tended to decrease from 0.10 V/h to 0.01 V/h in acceleration multiples until the 8.6 g Pd-IST/TiO2 electrode. The slope of the 15.4 g Pd-IST/TiO2 electrode was 0.05 V/h. After ALT for 1000 h, the average voltage decreased from 4.28 V to 3.85 V with increasing Pd content. Therefore, the 8.6 g Pd-IST/TiO2 electrode was the optimum electrode for electron refining due to its initial voltage and slope.
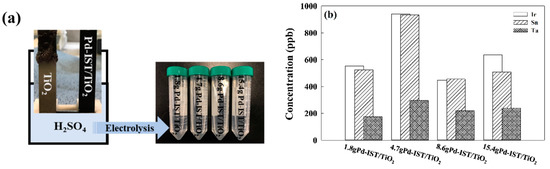
Figure 5.
(a) The scheme of the accelerated life test; (b) The impurity concentration in 3 M of H2SO4 after ALT using ICP-MS.
As shown in Figure 5a, the electrolyte was discolored due to oxidation of the parent of the electrodes, and the production of purple matter on the surface of the cathode produced an increase in the voltage. Therefore, we analyzed the electrolyte after ALT using ICP-MS. The concentration of Ir and Sn in the electrolyte increased in the following order: 8.6 g Pd-IST/TiO2 > 1.8 g Pd-IST/TiO2 > 15.6 g Pd-IST/TiO2 > 4.7 g Pd-IST/TiO2. The concentration of Ta in the electrolyte was approximately 200 ppb for all Pd-based electrodes. This means that the 8.6 g Pd-IST/TiO2 electrode had good electron activity due to the suppression of oxidation reactions and decomposition of the electrode after ALT.
4. Conclusions
Electrochemical analyses, including electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), linear scan voltammetry (LSV), cyclic voltammetry (CV), and accelerated life testing (ALT), were performed on Pd-based electrodes with different palladium loading contents: 0 g Pd-IST/TiO2, 1.8 g Pd-IST/TiO2, 4.7 g Pd-IST/TiO2, 8.6 g Pd-IST/TiO2, and 15.4 g Pd-IST/TiO2 at 3 M of H2SO4. The results show that EIS decreased with increasing palladium content. The 8.6 g Pd-IST/TiO2 electrode was shown to be a superior electrode because of the high current efficiency and low initial voltage. After the accelerated life testing for 1000 h at 10,000 mA/cm2, the voltage slope decreased in the following order: 8.6 g Pd-IST/TiO2 > 15.4 g Pd-IST/TiO2 > 4.7 g Pd-IST/TiO2 > 1.8 g Pd-IST/TiO2.
The electrolyte after ALT exhibited isolated elements that, when analyzed using ICP-MS, exhibited three of the electrode elements: Ir, Sn, and Ta, but not Pd. Among all Pd-based electrodes after ALT, the electrolyte of the 8.6 g Pd-IST/TiO2 electrode had the lowest concentration of these elements, which indicated electrode stability and resistance to oxidation. Therefore, for applications in electron refining, we suggest mixed oxides with an 8.6 g Pd electrode as a promising anode material.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, J.E.P. and E.S.L.; Methodology, S.K.Y. and J.H.K.; Investigation, J.E.P.; Data Curation, S.K.Y. and J.E.P.; Writing-Original Draft Preparation, J.E.P. and E.S.L.; Writing-Review & Editing, J.E.P.; Supervision, E.S.L.; Project Administration, M.J.P.; Funding Acquisition, E.S.L.
Funding
This study was supported by the Energy Development Technology Program of the Korea Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning (KETEP) granted financial resources from the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy, Republic of Korea (20172010105220) and also the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) and the Center for Women In Science, Engineering and Technology (WISET) Grant funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT under the Program for Returners into R&D.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ojebuoboh, F.; Wang, S.; Maccagni, M. Refining primary lead by granulation-leaching-electrowining. J. Miner. Met. Mater. Soc. 2003, 55, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Pan, J.; Sun, Y.; Feng, Y.; Niu, H. An Energy saving and fluorine-free Electrorefining process for Ultrahigh Purity Lead Refining. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Kirchhoff, M. Promoting sustainability through green chemistry. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 2005, 44, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owais, A. Effect of electrolyte characteristics on electrowinning of copper powder. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2009, 39, 1587–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Atrens, A. Influence of lead dioxide surface films on anodic oxidation of a lead alloy under conditions typical of copper electrowinning. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2008, 38, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulandaisamy, S.; Rethinaraj, J.P.; Chockalingam, S.C.; Visvanathan, S.; Venkateswaran, K.V.; Ramachandran, P.; Nandakumar, V. Performance of catalytically activated anodes in the electrowinning of metals. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1997, 27, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, Z.; Yu, Q.; Zhu, W.; Cui, W. Electrocatalytic Activity of Ti/Al/Ti/PbO2-WC Rod Composite Electrodes During Zinc Electrowinning. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2018, 13, 4367–4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amadelli, R.; Maldotti, A.; Molinari, A.; Danilov, F.I.; Velichenko, A.B. Influence of the electrode history and effects of the electrolyte composition and temperature on O2 evolution at β-PbO2 anodes in acid media. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2002, 534, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrussanova, A.; Mirkova, L.; Dobrev, T. Anodic behaviour of the Pb–Co3O4 composite coating in copper electrowinning. Hydrometallurgy 2001, 60, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Chen, Z.; Yu, Q.; Zhu, W.; Li, H.; Wang, H. Preparation of Ti/PbO2-ZrO2 Composite Anode for Zn Electrowinnig. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 13, 1400–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Zhu, P.; Xu, L.; Kannan, C.S.; Guo, S.; Liu, J.; Koppala, S.; Ju, S. Electrochemical properties of the IrO2-Ta2O5 coated anodes with Al/Ti and Cu/Ti layered composites substrates. J. Alloys Compd. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.A.; Yang, S.W.; Chen, C.Z.; Hsu, F.-Y. Electrochemical behavior of IrO2-Ta2O5/Ti anodes prepared with different surface pretreatments of Ti substrate. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 320, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y. Surface determination and electrochemical behavior of IrO2-RuO2-SiO2 ternary oxide coatings in oxygen evolution reaction application. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 264, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Lai, Y.; Jiang, L.; Lü, X.; Chen, P.; Li, J.; Liu, Y. Fabrication and anodic polarization behavior of lead-based porous anodes in zinc electrowinning. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 2008, 15, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherevko, S.; Geiger, S.; Kasian, O.; Kulyk, N.; Grote, J.-P.; Savan, A.; Shrestha, B.R.; Merzlikin, S.; Breitbach, B.; Ludwig, A.; Mayrhofer, K.J.J. Oxygen and hydrogen evolution reactions on Ru, RuO2, Ir, and IrO2 thin film electrodes in acidic and alkaline electrolytes: A comparative study on activity and stability. Catal. Today 2016, 262, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurung, K.; Ncibi, M.C.; Shestakova, M.; Sillanpää, M. Removal of carbamazepine from MBR effluent by electrochemical oxidation (EO) using a Ti/Ta2O5-SnO2 electrode. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2018, 221, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ghali, E.; Houlachi, G. Review of oxide coated catalytic titanium anodes performance for metal electrowinning. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 169, 456–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Robichaud, M.; Ghali, E.; Houlachi, G. Electrochemical behavior of mesh and plate oxide coated anodes during zinc electrowinning. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2016, 26, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Wang, S.; Liu, J.; Huang, H.; Dong, C.; He, Y.; Yan, W.; Guo, Z.; Xu, R.; Yang, H. Corrosion resistance mechanism of a novel porous Ti/Sn-Sb-RuOx/β-PbO2 anode for zinc electrowinning. Corros. Sci. 2018, 144, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mraz, R.; Krysa, J. Long service life IrO2/Ta2O5 electrodes for electroflotation. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1994, 24, 1262–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayal, J.; Rawat, B.; Basu, S. Bi-metallic and tri-metallic Pt–Sn/C, Pt–Ir/C, Pt–Ir–Sn/C catalysts for electro-oxidation of ethanol in direct ethanol fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 14884–14897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, F.H.; Osugi, M.E.; Paschoal, F.M.M.; Profeti, D.; Olivi, P.; Zanoni, M.V.B. Electrochemical oxidation of an acid dye by active chlorine generated using Ti/Sn(1−x)IrxO2 electrodes. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2007, 37, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-M. Oxygen Evolution on Ir-Ru-Sn Ternary Oxide-Coated Electrodes in H2SO4 Solution. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1993, 140, 2265–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Chen, X.; Yue, P.L. Electrochemical Behavior of Novel Ti/IrOx−Sb2O5−SnO2 Anodes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 4364–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, G.; Yue, P.L. Stable Ti/IrOx−Sb2O5−SnO2 Anode for O2 Evolution with Low Ir Content. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 4623–4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grdeń, M.; Łukaszewski, M.; Jerkiewicz, G.; Czerwiński, A. Electrochemical behaviour of palladium electrode: Oxidation, electrodissolution and ionic adsorption. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 7583–7598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, E.J.; Kim, Y.; Choi, S.M.; Lee, S.; Noh, Y.; Kim, W.B. Binary PdM catalysts (M = Ru, Sn, or Ir) over a reduced graphene oxide support for electro-oxidation of primary alcohols (methanol, ethanol, 1-propanol) under alkaline conditions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 5491–5500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, L.D. An Examination of the Electrochemical Behavior of Palladium Electrodes in Acid. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1993, 140, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Xu, L.; Kannan, C.S.; Liu, J.; Koppala, S.; Ju, S.; Zhang, L. Preparation and electrochemical properties of Al/TiB2/β-PbO2 layered composite electrode materials for electrowinning of nonferrous metals. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 18420–18428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Kang, D.-K.; Lee, K.; Chang, D. An Investigation on the Electrochemical Characteristics of Ta2O5-IrO2 Anodes for the Application of Electrolysis Process. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2011, 2, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).