Wind Turbulence Intensity at La Ventosa, Mexico: A Comparative Study with the IEC61400 Standards
Abstract
:1. Introduction
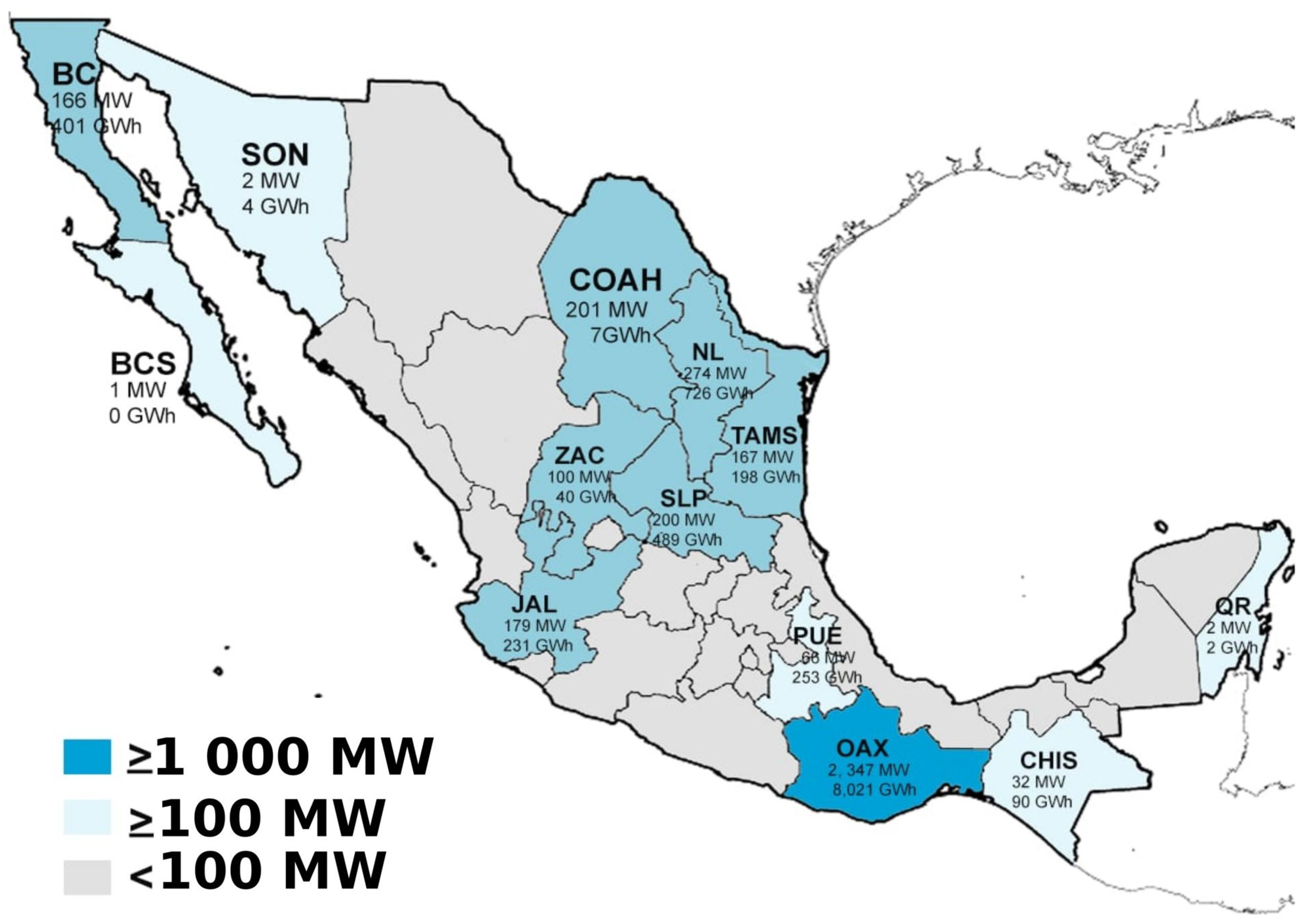
1.1. Wind Power Status Internationally and in Mexico
1.2. Small Wind Turbine Design: Normal Turbulence Model and Turbulence Intensity
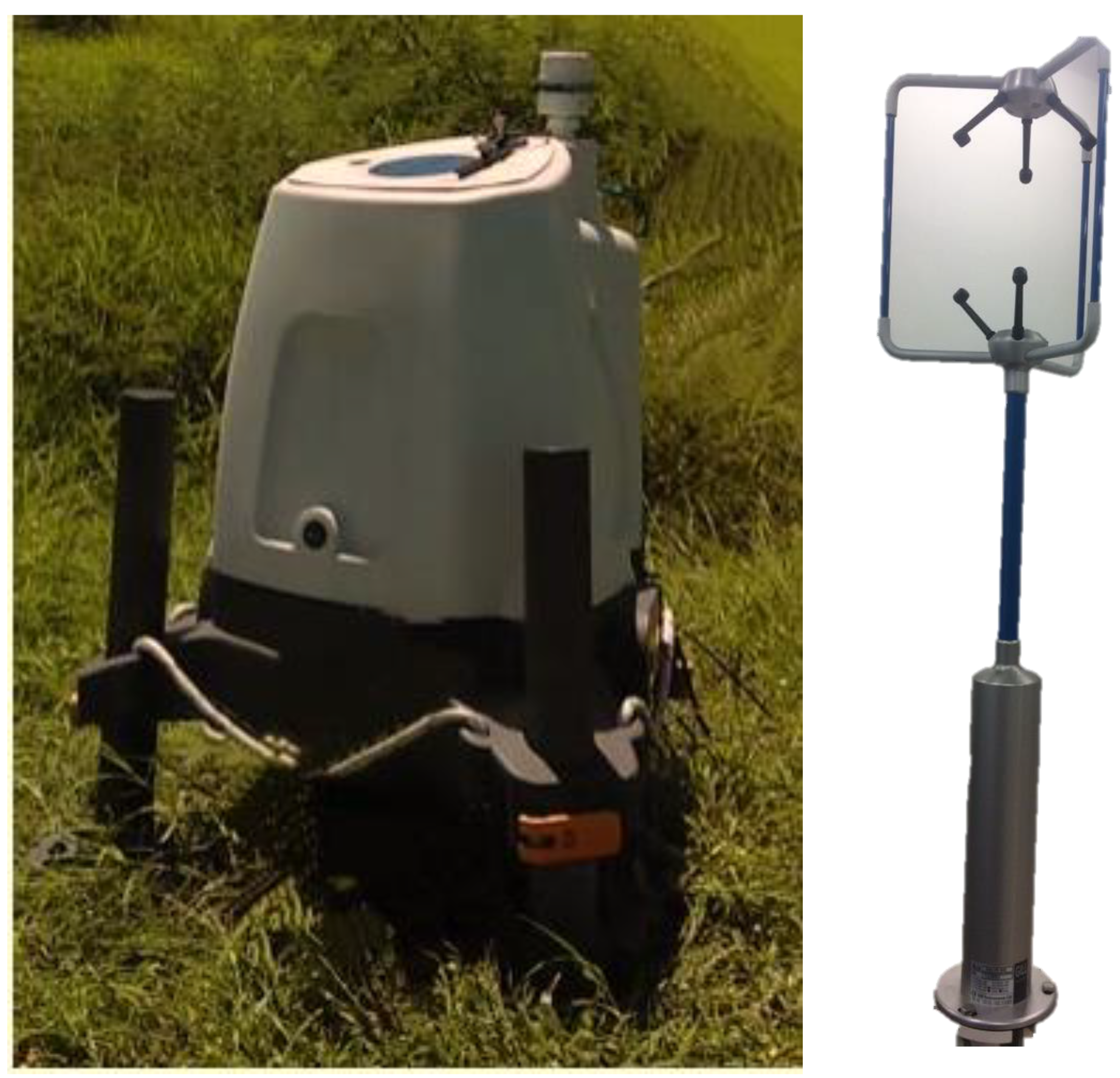
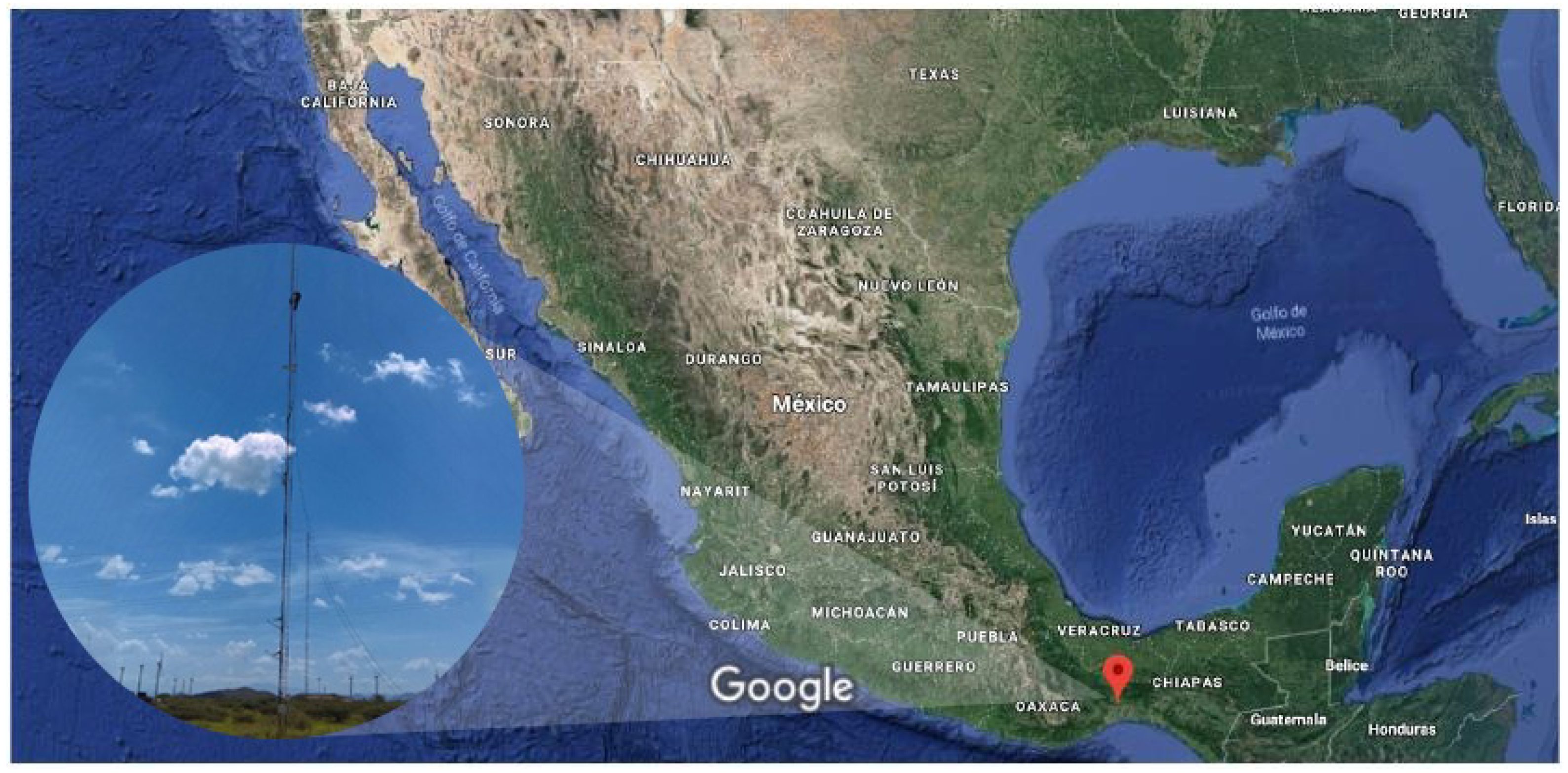
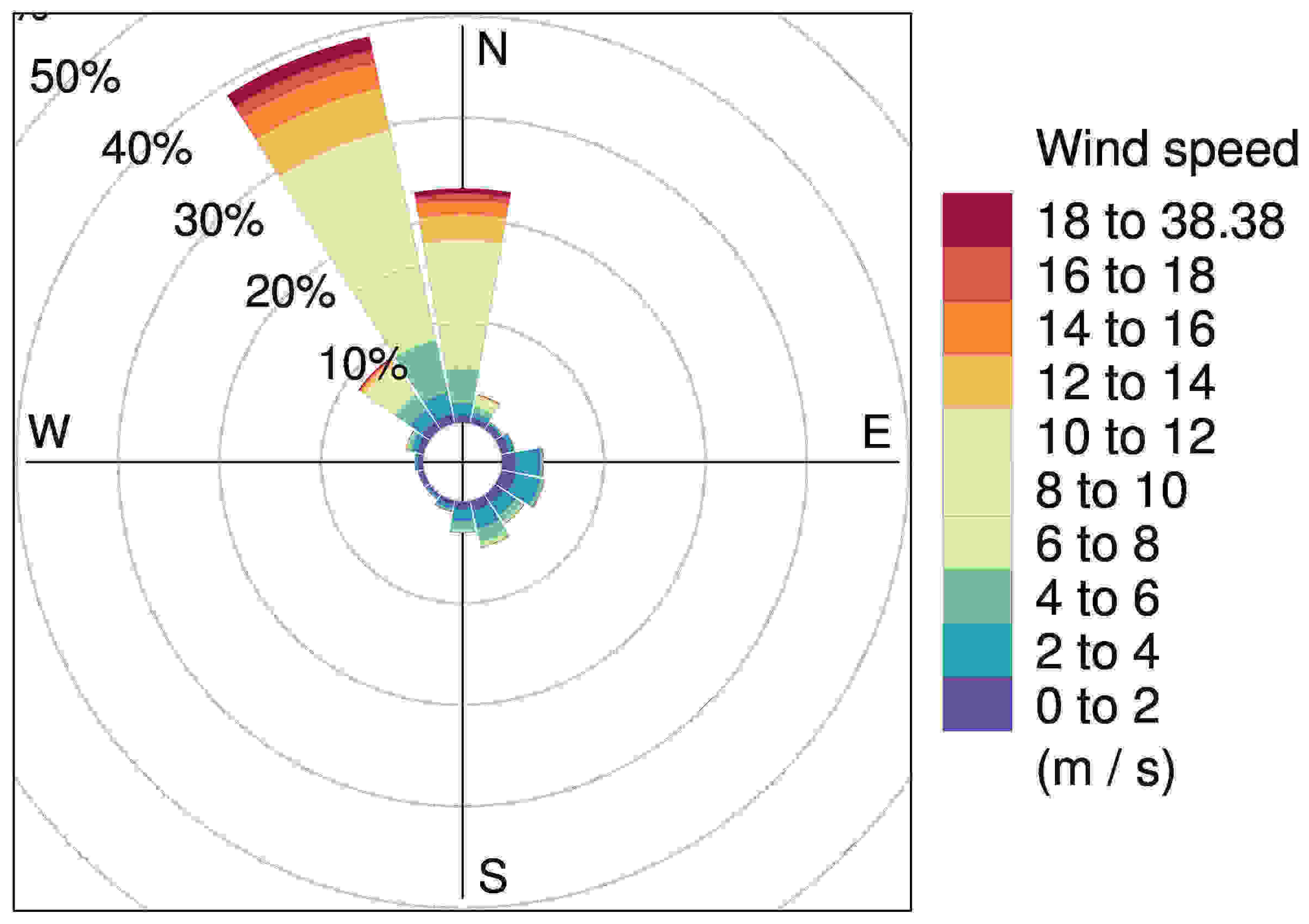
2. Site Measurements and Data Processing
3. Turbulence Intensity
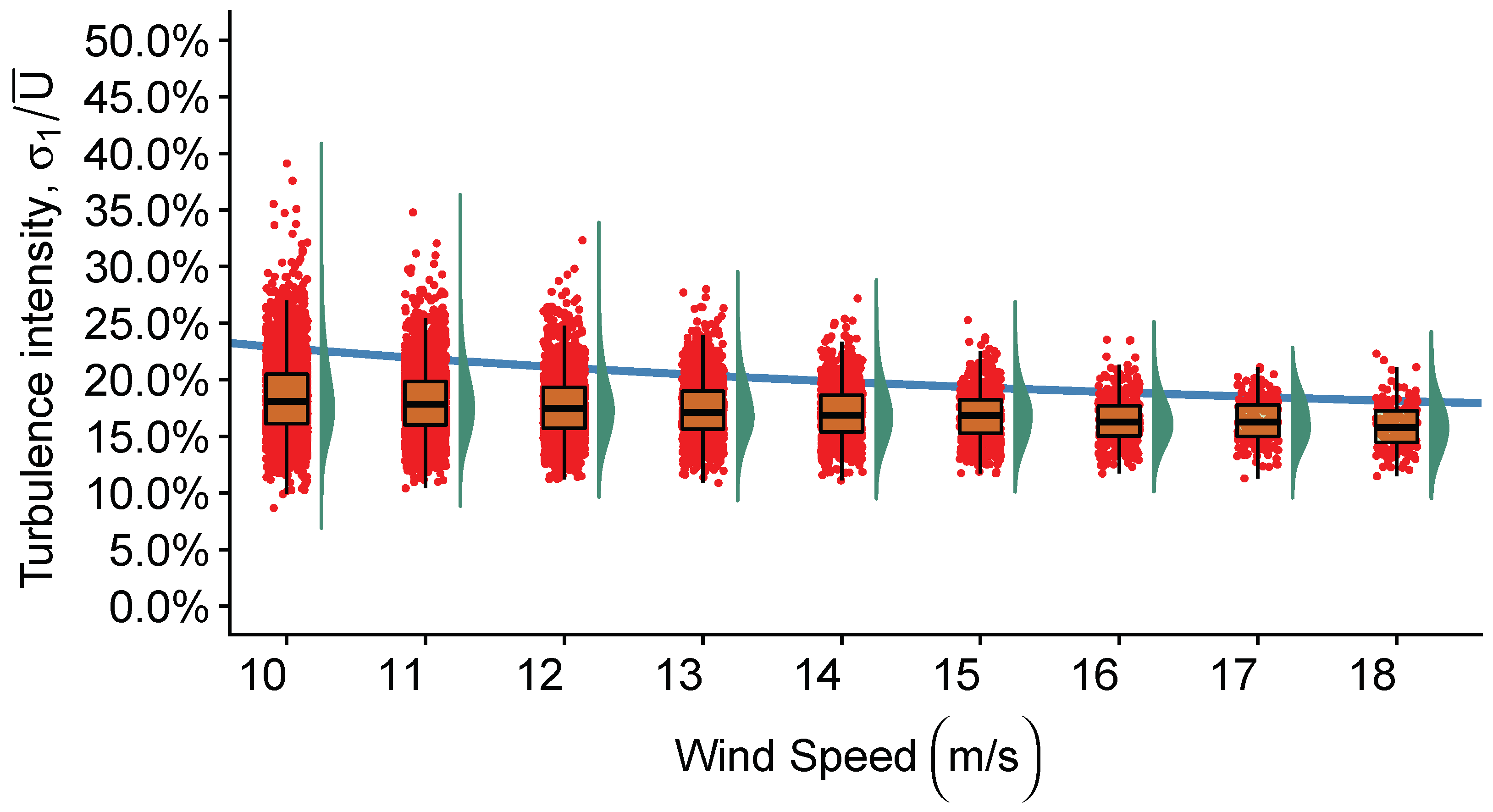
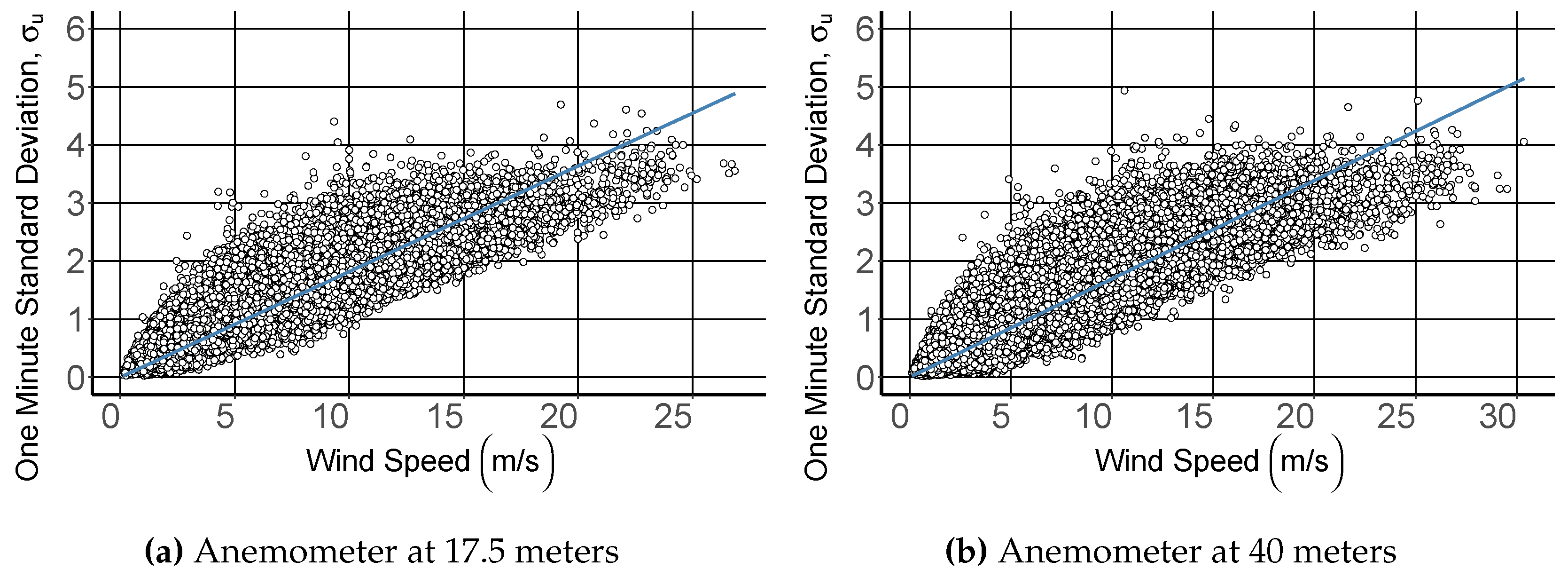
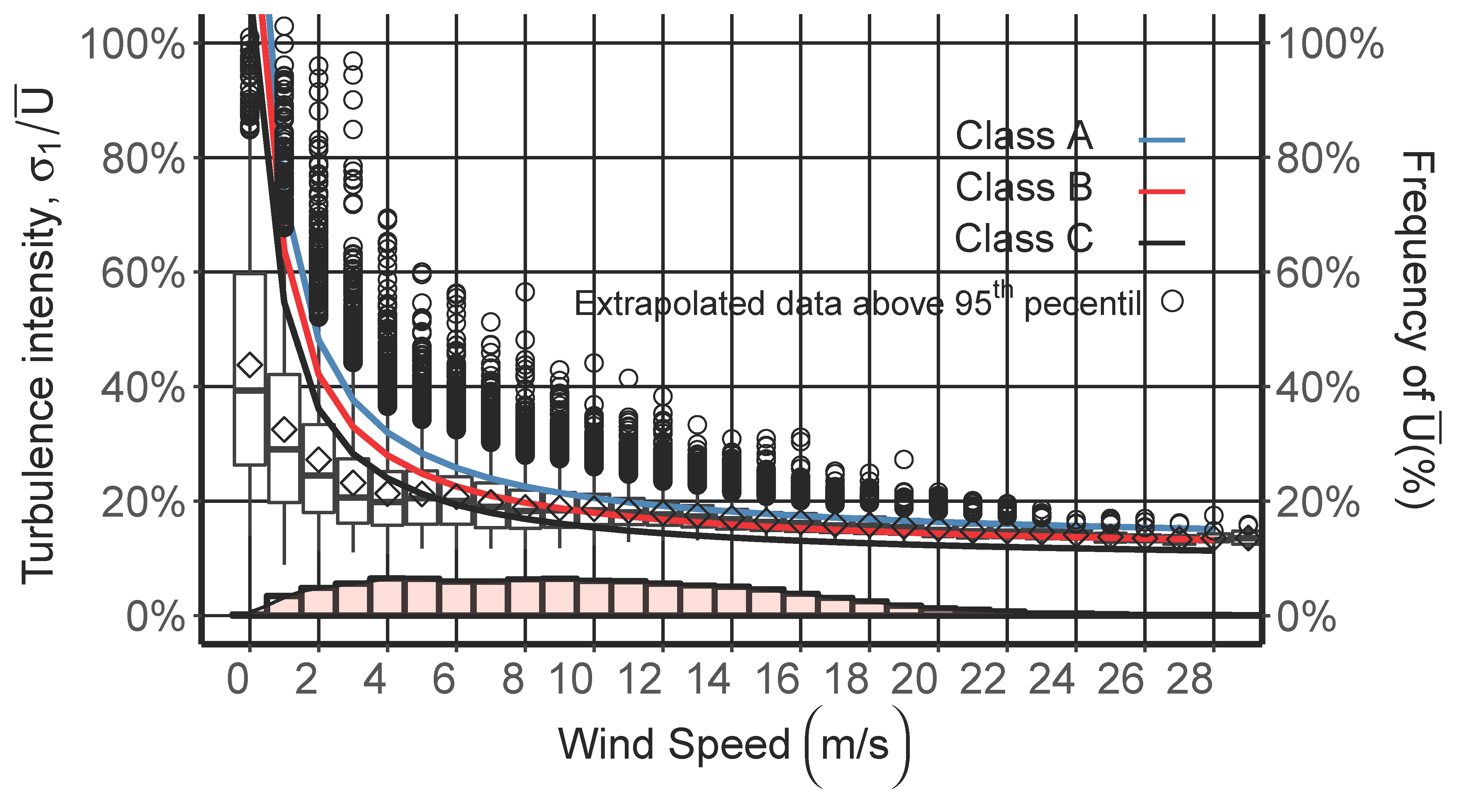
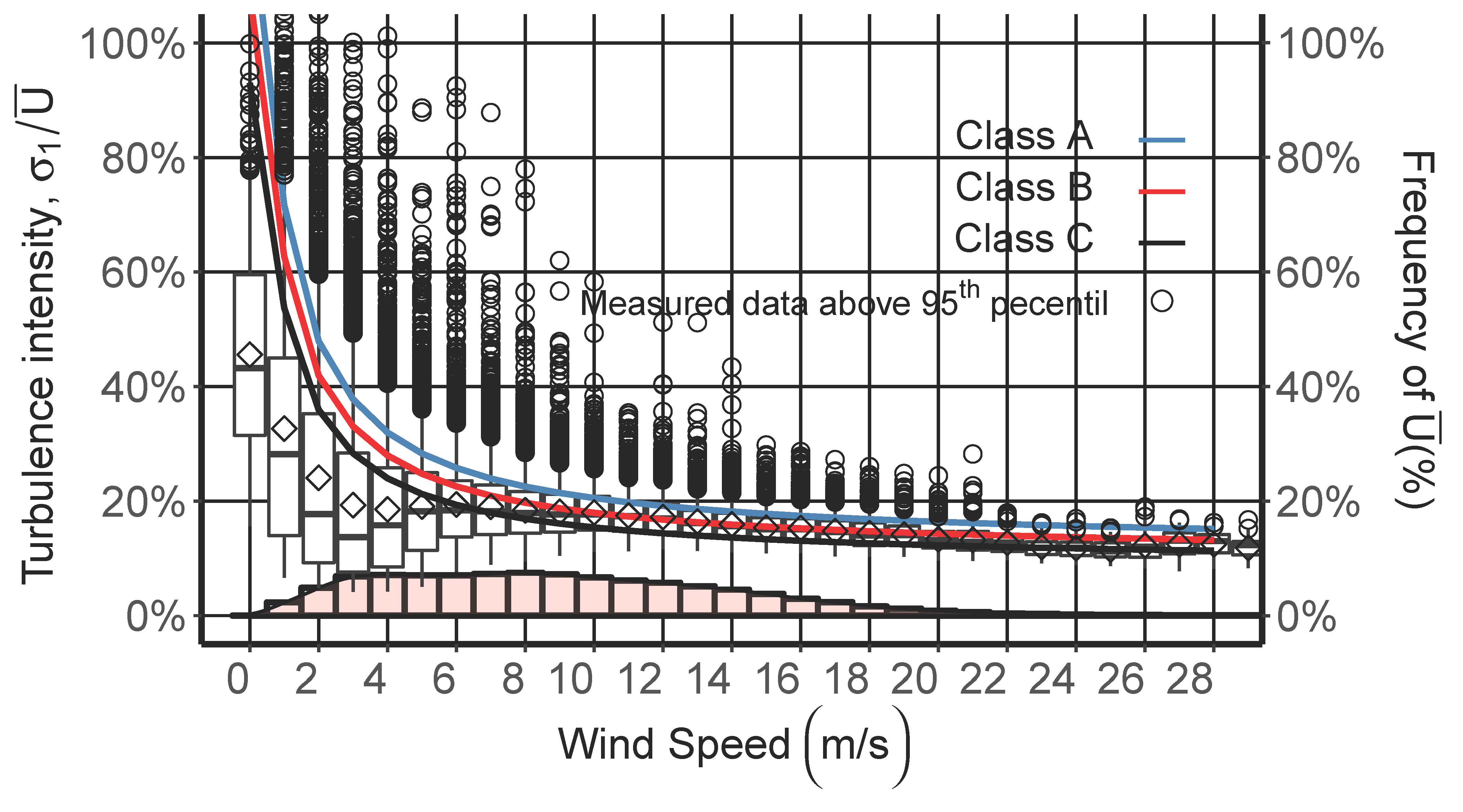
4. Results and Discussion
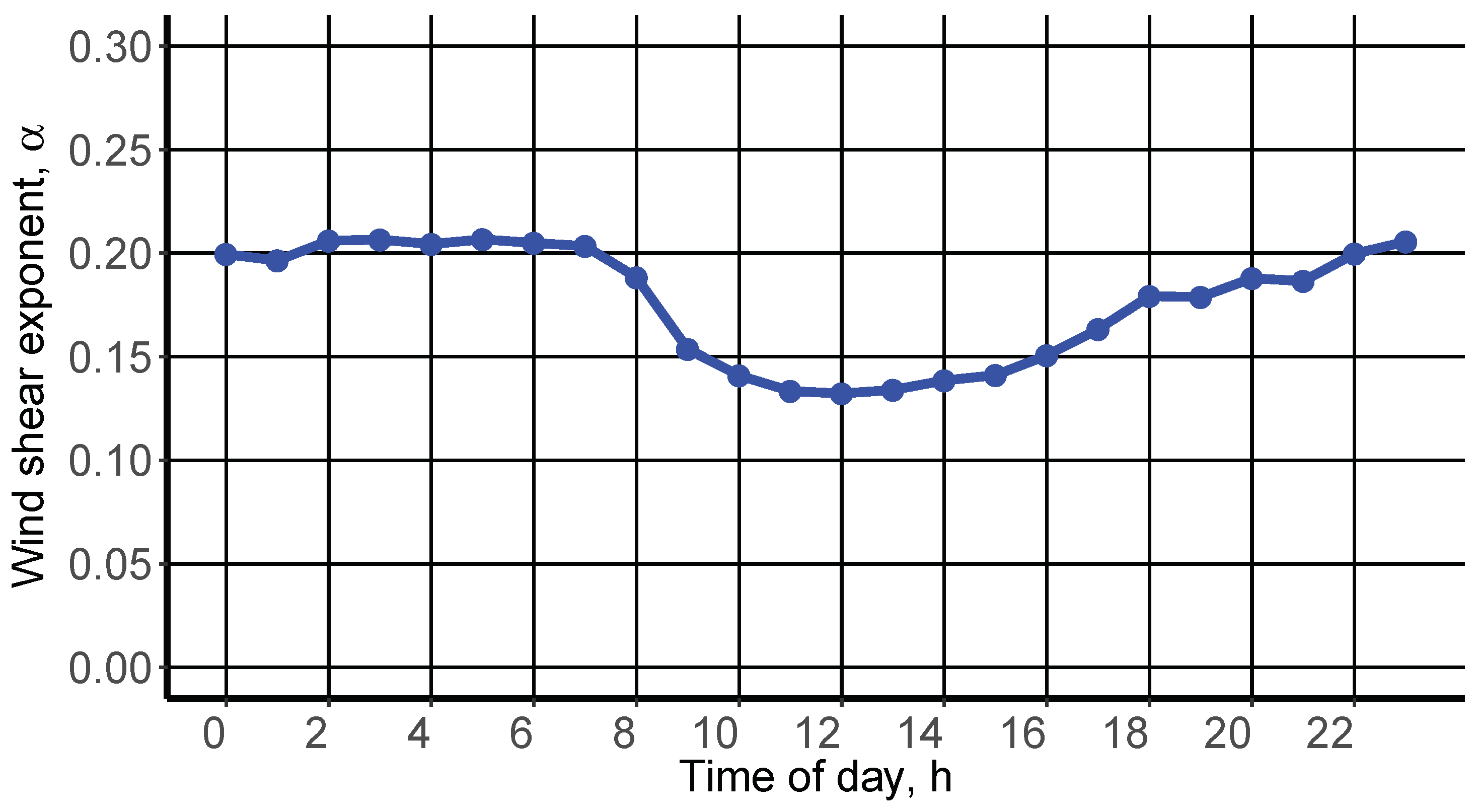
4.1. Power Law Extrapolation
4.2. Characterization of Turbulence Intensity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
References
- GWEC, G.W.E.C. Global Wind Report: Annual Market Update 2017. Available online: http://files.gwec.net/files/GWR2017.pdf?ref=Website (accessed on 25 April 2018).
- De Innovación en Energía, C.M. Documento del Mapa de Ruta Tecnológica Energía eólica en tierra. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/sener/documentos/mapas-de-ruta-tecnologica-de-energias-renovables (accessed on 8 May 2018).
- Juárez-Hernández, S.; León, G. Energía eólica en el istmo de Tehuantepec: desarrollo, actores y oposición social. Problemas del desarrollo 2014, 45, 139–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wharton, S.; Lundquist, J.K. Atmospheric stability affects wind turbine power collection. Environ. Res. Lett. 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, C.J.; Dragt, D.J. Accuracy of Power Curve Measurements (M-2632); Technical Report for Risø National Laboratory: Roskilde, Denmark, November 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, G.; Liu, J.; Wan, J.; Li, F.; Guo, Y.; Yu, D. The analysis of turbulence intensity based on wind speed data in onshore wind farms. Renew. Energy 2018, 123, 756–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedevang, E. Wind turbine power curves incorporating turbulence intensity. Wind Energy 2014, 17, 173–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.T.; Porté-Agel, F. Atmospheric turbulence effects on wind-turbine wakes: An LES study. Energies 2012, 5, 5340–5362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtslag, M.; Bierbooms, W.; Van Bussel, G. Estimating atmospheric stability from observations and correcting wind shear models accordingly. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2014, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iungo, G.V.; Porté-Agel, F. Volumetric scans of wind turbine wakes performed with three simultaneous wind LiDARs under different atmospheric stability regimes. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2014, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hand, M.M.; Kelley, N.D.; Balas, M.J. Identification of Wind Turbine Response to Turbulent Inflow Structures. In Proceedings of the ASME/JSME 2003 4th Joint Fluids Summer Engineering Conference, Honolulu, HI, USA, 6–10 July 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Bhaganagar, K.; Debnath, M. Implications of stably stratified atmospheric boundary layer turbulence on the near-wake structure of wind turbines. Energies 2014, 7, 5740–5763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, T. Numerical Investigation of Terrain-Induced Turbulence in Complex Terrain by Large-Eddy Simulation (LES) Technique. Energies 2018, 11, 2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Churchfield, M.; Moriarty, P.; Jonkman, J.; Michalakes, J. Atmospheric and Wake Turbulence Impacts on Wind Turbine Fatigue Loadings. In Proceedings of the 50th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting Including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition, Nashville, TN, USA, 9–12 January 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lavely, A.; Vijayakumar, G.; Kinzel, M.; Brasseur, J.; Paterson, E. Space-time loadings on wind turbine blades driven by atmospheric boundary layer turbulence. In Proceedings of the 49th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition, Orlando, FL, USA, 4–7 January 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Carpman, N. Turbulence Intensity in Complex Environments and Its Influence on Small Wind Turbines. Master’s Thesis, Department of Earth Sciences, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden, 10 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- IEC61400-2. Wind Turbines-Part 2. Small Wind Turbines, 2nd ed.; International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- IEC61400-1. Wind Turbines Part 1: Design Requirements, 3rd ed.; International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chamorro, L.P.; Porte-Agel, F. Turbulent flow inside and above a wind farm: a wind-tunnel study. Energies 2011, 4, 1916–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, D.; Niezrecki, C.; Kuchma, D.; Hines, E.; Arwade, S.; Barthelmie, R.; DiPaola, M.; Drane, P.; Hansen, C.; Inalpolat, M. Wind energy research: State-of-the-art and future research directions. Renew. Energy 2018, 125, 133–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamorro, L.; Hill, C.; Morton, S.; Ellis, C.; Arndt, R.; Sotiropoulos, F. On the interaction between a turbulent open channel flow and an axial-flow turbine. J. Fluid Mechan. 2013, 716, 658–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamorro, L.P.; Lee, S.J.; Olsen, D.; Milliren, C.; Marr, J.; Arndt, R.; Sotiropoulos, F. Turbulence effects on a full-scale 2.5 MW horizontal-axis wind turbine under neutrally stratified conditions. Wind Energy 2015, 18, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, N.; Zhu, H.; Chamorro, L. Spectral behaviour of the turbulence-driven power fluctuations of wind turbines. J. Turbulence 2015, 16, 832–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertényi, T.; Wickins, C.; McIntosh, S. Enhanced energy capture through gust-tracking in the urban wind environment. In Proceedings of the 48th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting Including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition, Orlando, FL, USA, 4–7 January 2010; p. 1376. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, K.S.; Larsen, G.C. Characterising turbulence intensity for fatigue load analysis of wind turbines. Wind Eng. 2005, 29, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellani, F.; Astolfi, D.; Becchetti, M.; Berno, F.; Cianetti, F.; Cetrini, A. Experimental and Numerical Vibrational Analysis of a Horizontal-Axis Micro-Wind Turbine. Energies 2018, 11, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, M.; Santoni, C.; Leonardi, S.; Iungo, G. Towards reduced order modelling for predicting the dynamics of coherent vorticity structures within wind turbine wakes. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2017, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaramillo, O.A.; Borja, M.A. Wind speed analysis in La Ventosa, Mexico: A bimodal probability distribution case. Renew. Energy 2004, 29, 1613–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berny-Brandt, E.A.; Ruiz, S.E. Reliability over time of wind turbines steel towers subjected to fatigue. Wind Struct. 2016, 23, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg, G. Effects of the wind profile at night on wind turbine sound. J. Sound Vib. 2004, 277, 955–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emejeamara, F.; Tomlin, A.; Millward-Hopkins, J. Urban wind: Characterisation of useful gust and energy capture. Renew. Energy 2015, 81, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagner, S.; Bareiss, R.; Guidati, G. Wind Turbine Noise; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mathew, S.; Philip, G.S. Advances in Wind Energy and Conversion Technology; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; Volume 20. [Google Scholar]
- Stork, C.; Butterfield, C.; Holley, W.; Madsen, P.H.; Jensen, P.H. Wind conditions for wind turbine design proposals for revision of the IEC 1400-1 standard. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerod. 1998, 74, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stull, R.B. An Introduction to Boundary Layer Meteorology; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wharton, S.; Lundquist, J.K. Assessing atmospheric stability and its impacts on rotor-disk wind characteristics at an onshore wind farm. Wind Energy 2012, 15, 525–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabrizi, A.B.; Whale, J.; Lyons, T.; Urmee, T. Rooftop wind monitoring campaigns for small wind turbine applications: Effect of sampling rate and averaging period. Renew. Energy 2015, 77, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


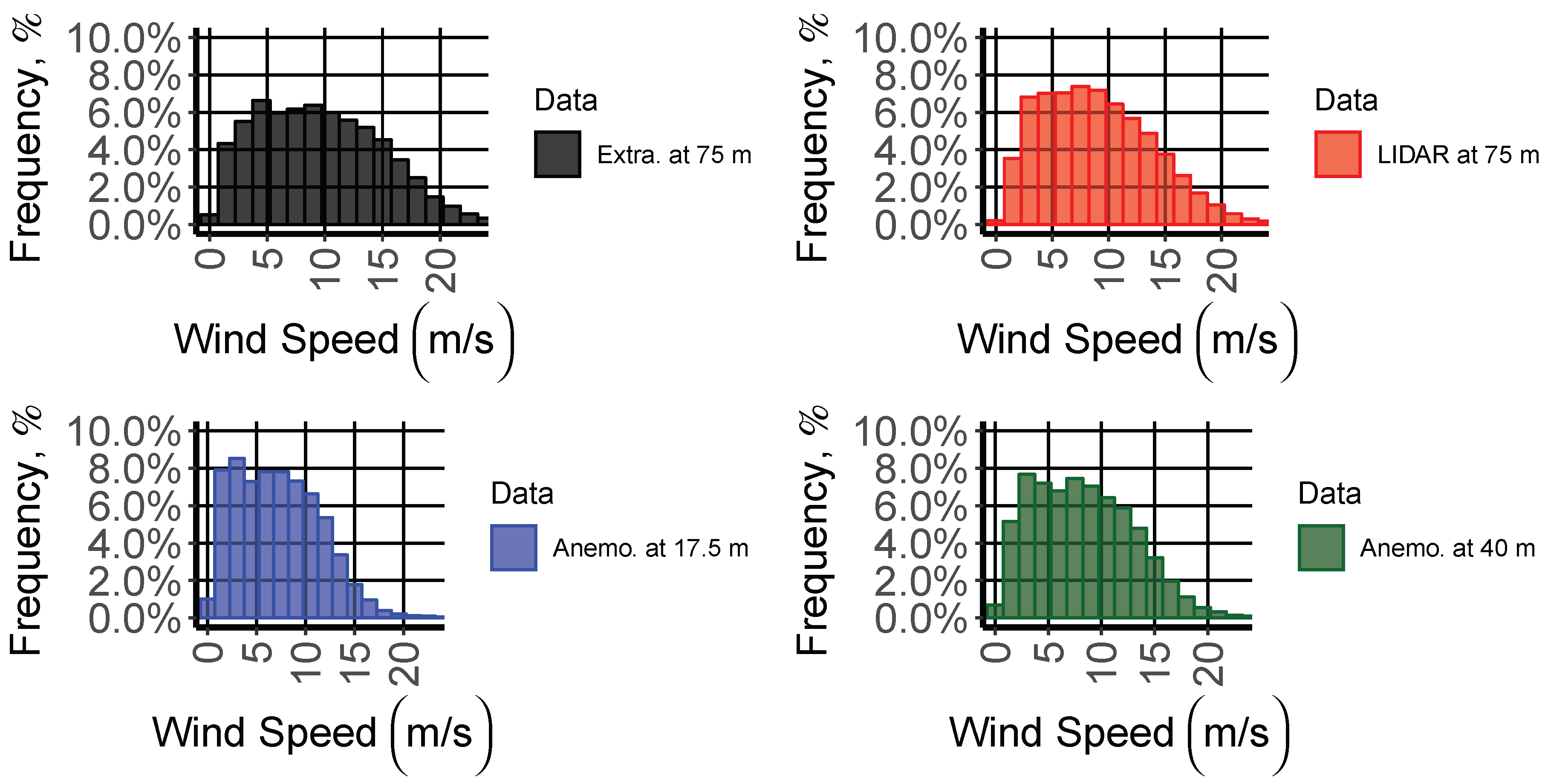

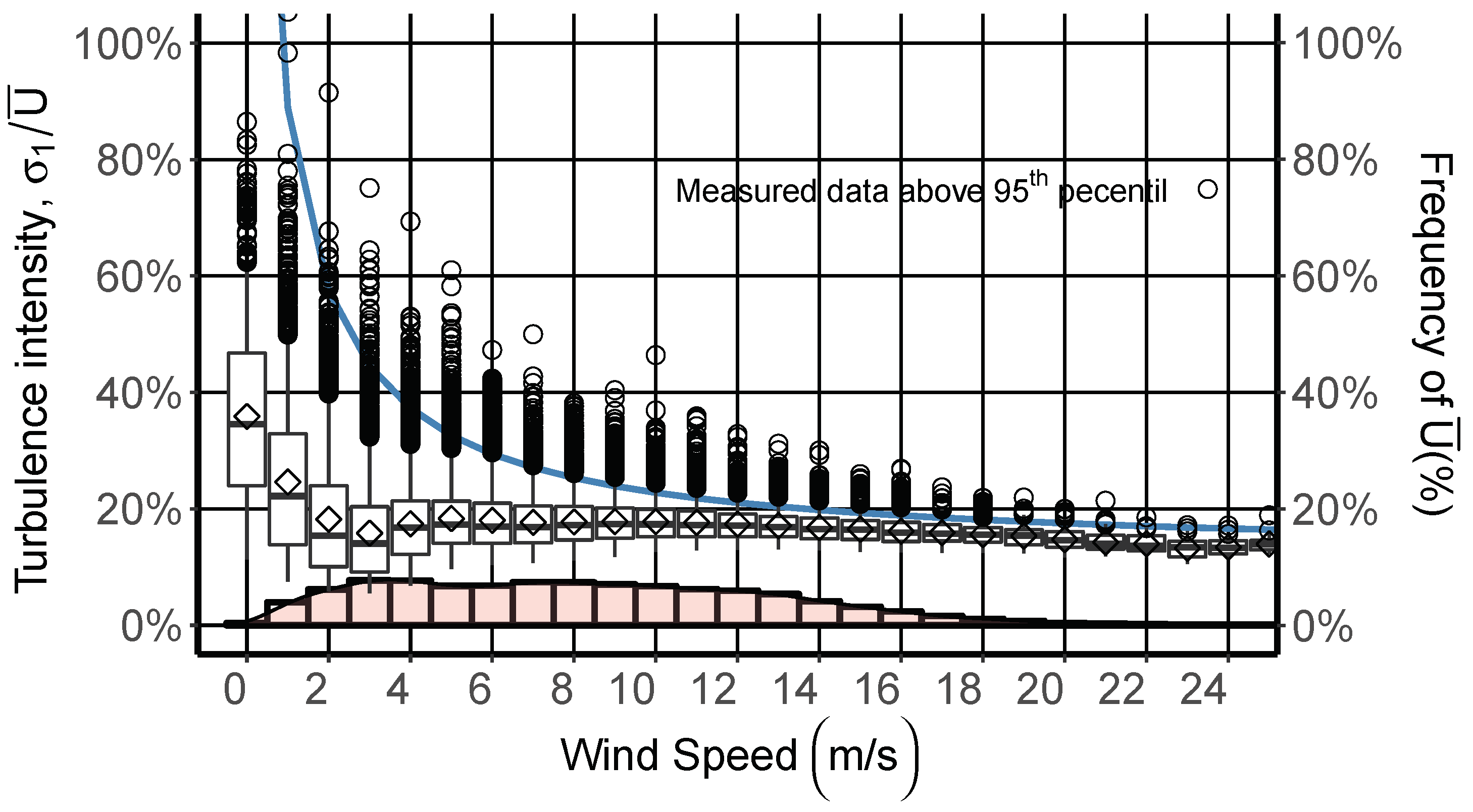
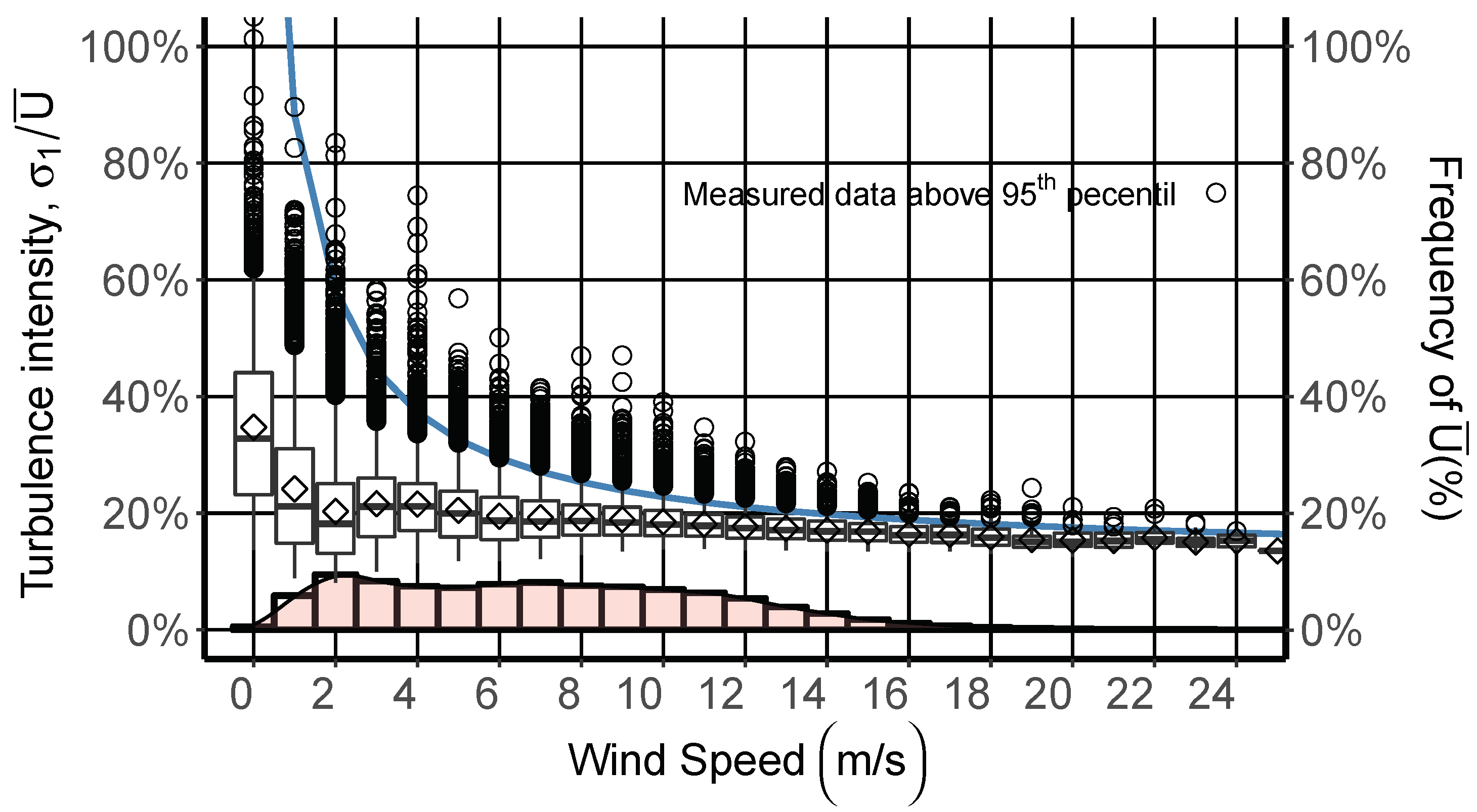
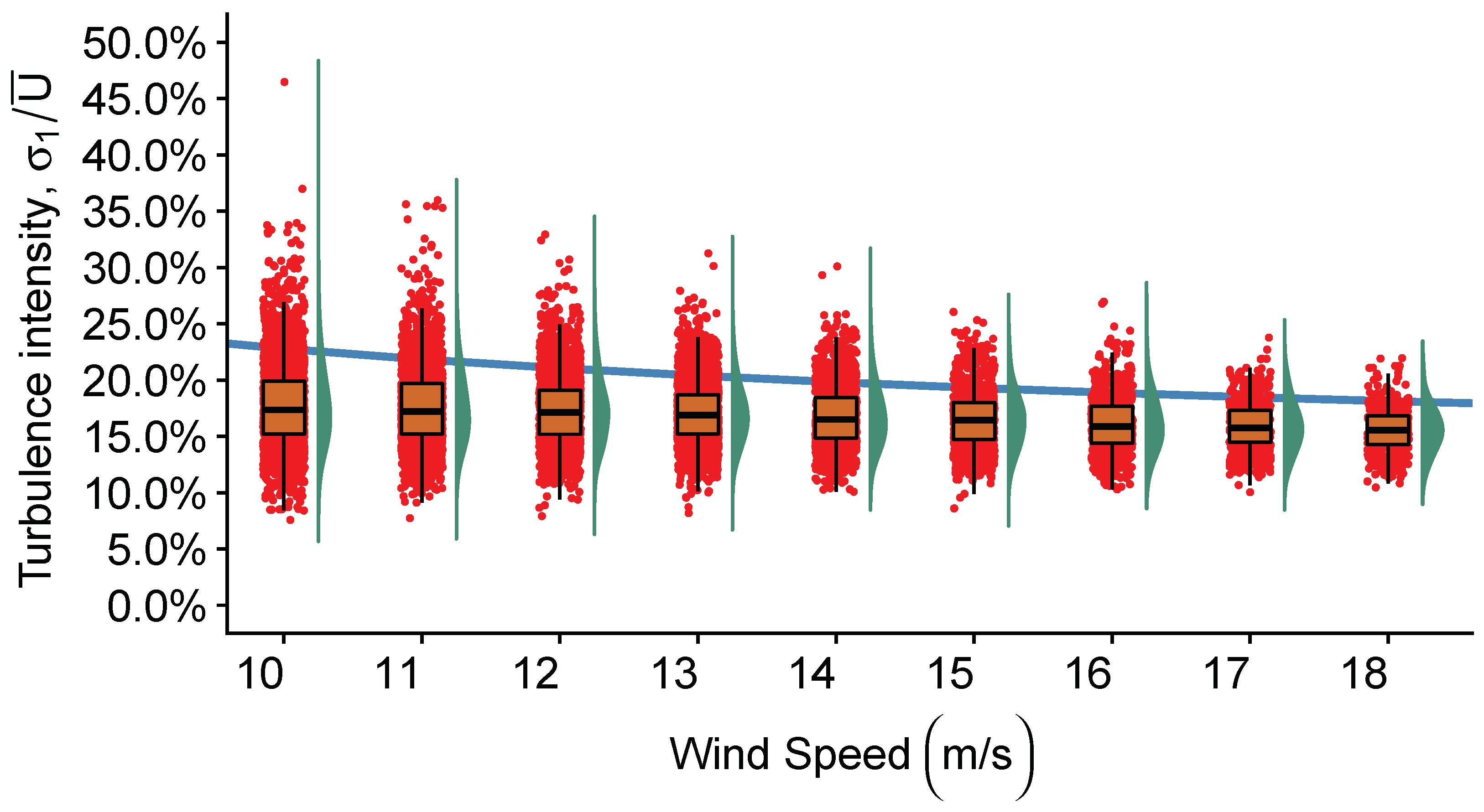
| Equipment | Height (m) | Variable | Mean | Median | SD | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anemometer 1 | 17.5 | (m/s) | 7.21 | 6.68 | 4.51 | 0.0 | 38.38 |
| Anemometer 2 | 40 | (m/s) | 8.30 | 7.69 | 4.10 | 0.0 | 41.760 |
| LIDAR | 75 | (m/s) | 9.05 | 8.301 | 5.28 | 0.46 | 40.062 |
| Extrapolated | 75 | (m/s) | 9.70 | 8.63 | 6.29 | 0.0 | 61.66 |
| a | b | β | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IEC Class A | 0.16 | ||||
| IEC Class B | 0.14 | 0.75 | 3.8 | 0 | 1.4 |
| IEC Class C | 0.12 |
| Stability Class | |
|---|---|
| Strongly stable (Ss) | |
| Stable (S) | |
| Neutral (N) | |
| Convective (C) | |
| Strongly convective (Sc) |
| Parameter | Ss | S | N | C | Sc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.14 | 0.09 | −0.01 |
| Equipment | Height (m) | Average in Period (min) | Correlation Coefficient | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anemometer 1 | 17.5 | 1 | 0.135 | 0.908 |
| 10 | 0.181 | 0.952 | ||
| Anemometer 2 | 40 | 1 | 0.123 | 0.899 |
| 10 | 0.169 | 0.949 | ||
| LIDAR | 75 | 1 | 0.124 | 0.753 |
| 10 | 0.168 | 0.931 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lopez-Villalobos, C.A.; Rodriguez-Hernandez, O.; Campos-Amezcua, R.; Hernandez-Cruz, G.; Jaramillo, O.A.; Mendoza, J.L. Wind Turbulence Intensity at La Ventosa, Mexico: A Comparative Study with the IEC61400 Standards. Energies 2018, 11, 3007. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11113007
Lopez-Villalobos CA, Rodriguez-Hernandez O, Campos-Amezcua R, Hernandez-Cruz G, Jaramillo OA, Mendoza JL. Wind Turbulence Intensity at La Ventosa, Mexico: A Comparative Study with the IEC61400 Standards. Energies. 2018; 11(11):3007. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11113007
Chicago/Turabian StyleLopez-Villalobos, C. A., O. Rodriguez-Hernandez, R. Campos-Amezcua, Guillermo Hernandez-Cruz, O. A. Jaramillo, and J. L. Mendoza. 2018. "Wind Turbulence Intensity at La Ventosa, Mexico: A Comparative Study with the IEC61400 Standards" Energies 11, no. 11: 3007. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11113007
APA StyleLopez-Villalobos, C. A., Rodriguez-Hernandez, O., Campos-Amezcua, R., Hernandez-Cruz, G., Jaramillo, O. A., & Mendoza, J. L. (2018). Wind Turbulence Intensity at La Ventosa, Mexico: A Comparative Study with the IEC61400 Standards. Energies, 11(11), 3007. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11113007






