A Method to Improve the Response of a Speed Loop by Using a Reduced-Order Extended Kalman Filter
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Counting the number of encoder pulses m1 in a fixed period Tc.
- Recording the time interval ∆T of the next pulse edge after the fixed period.
- The calculated speed Nf (rpm) can be obtained as:
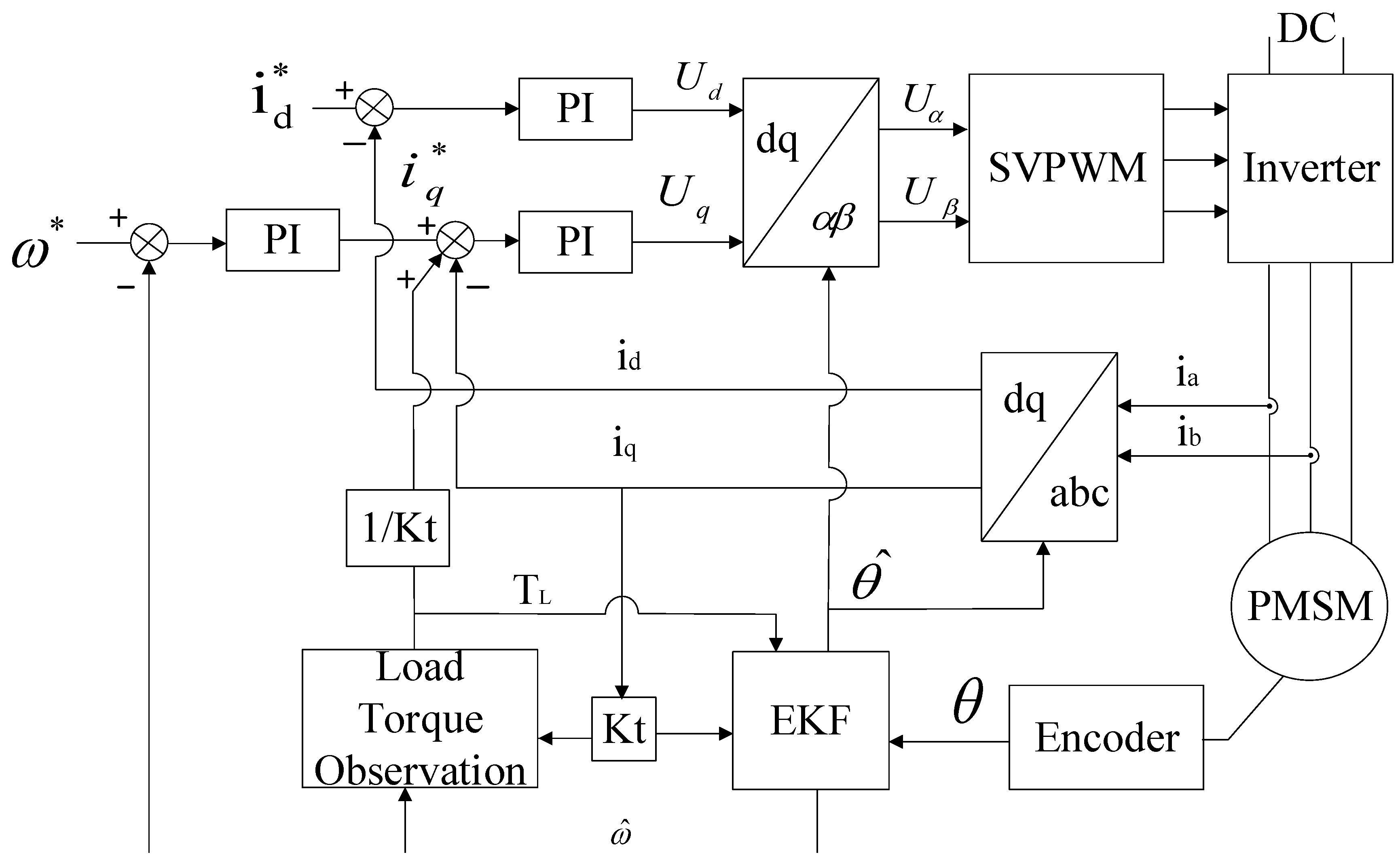
2. Speed Control Strategy Based on Filtered Speed Feedback by EKF
2.1. Overview of the Proposed Speed Loop Control Strategy
2.2. Mechanical Model of PMSM
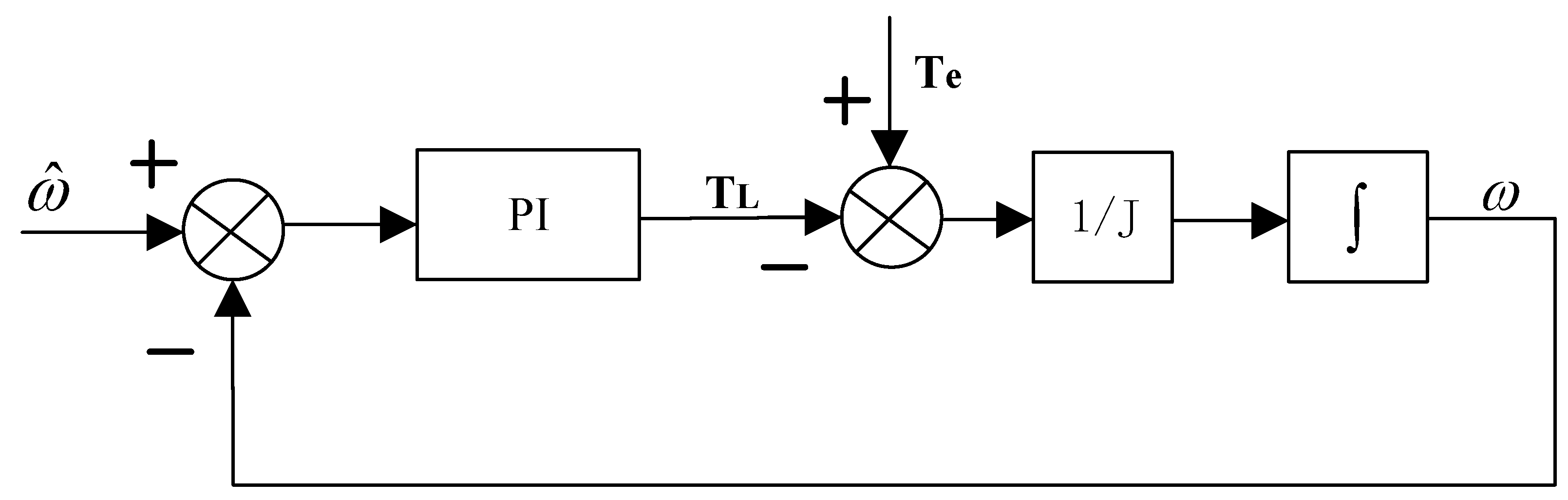
2.3. Composite Load Torque Observer
2.4. Reduced-Order EKF Equation
- Calculating the load torque using the load observer .
- State variables prediction and Kalman gain calculation:
- Calculating the optimal estimate values and update matrix:
3. Robustness Analysis
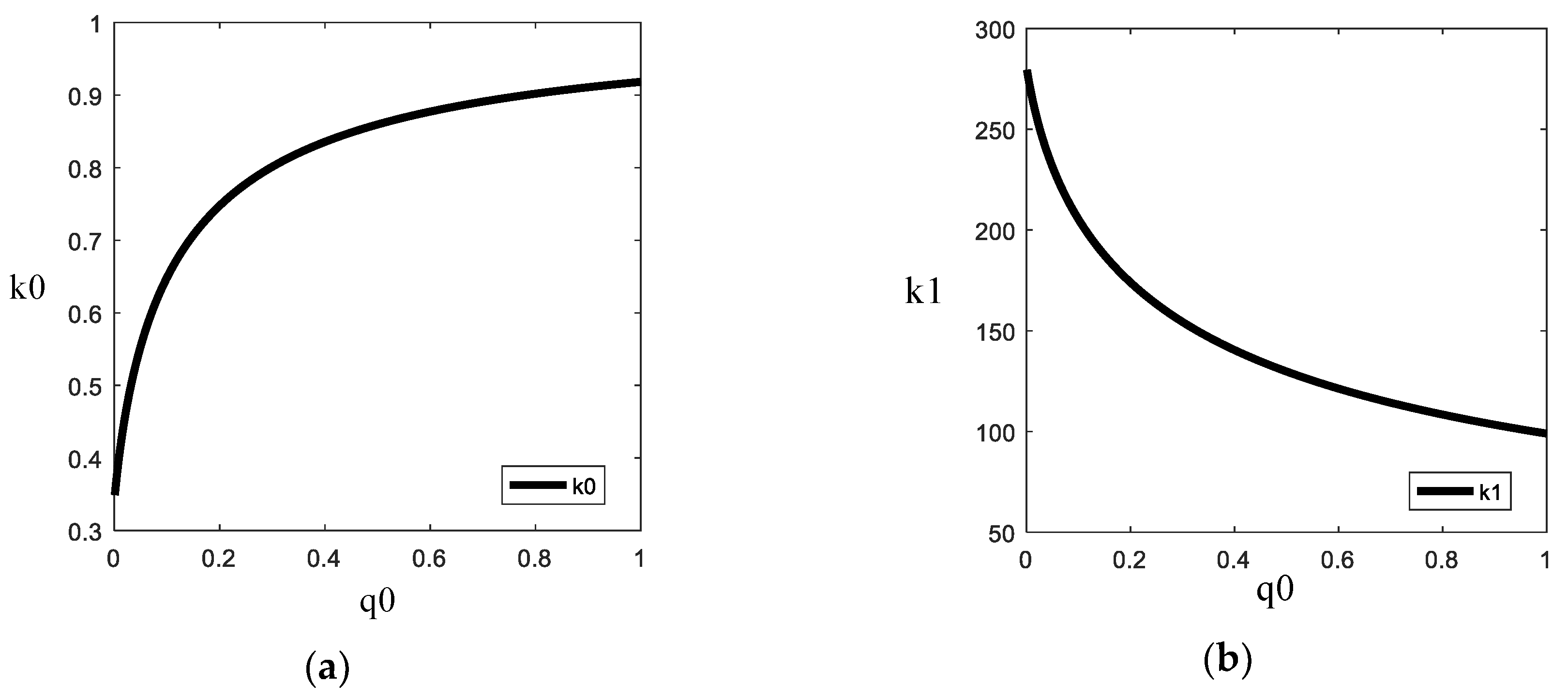
4. Design and Tuning of Q and R
5. Simulation and Analysis
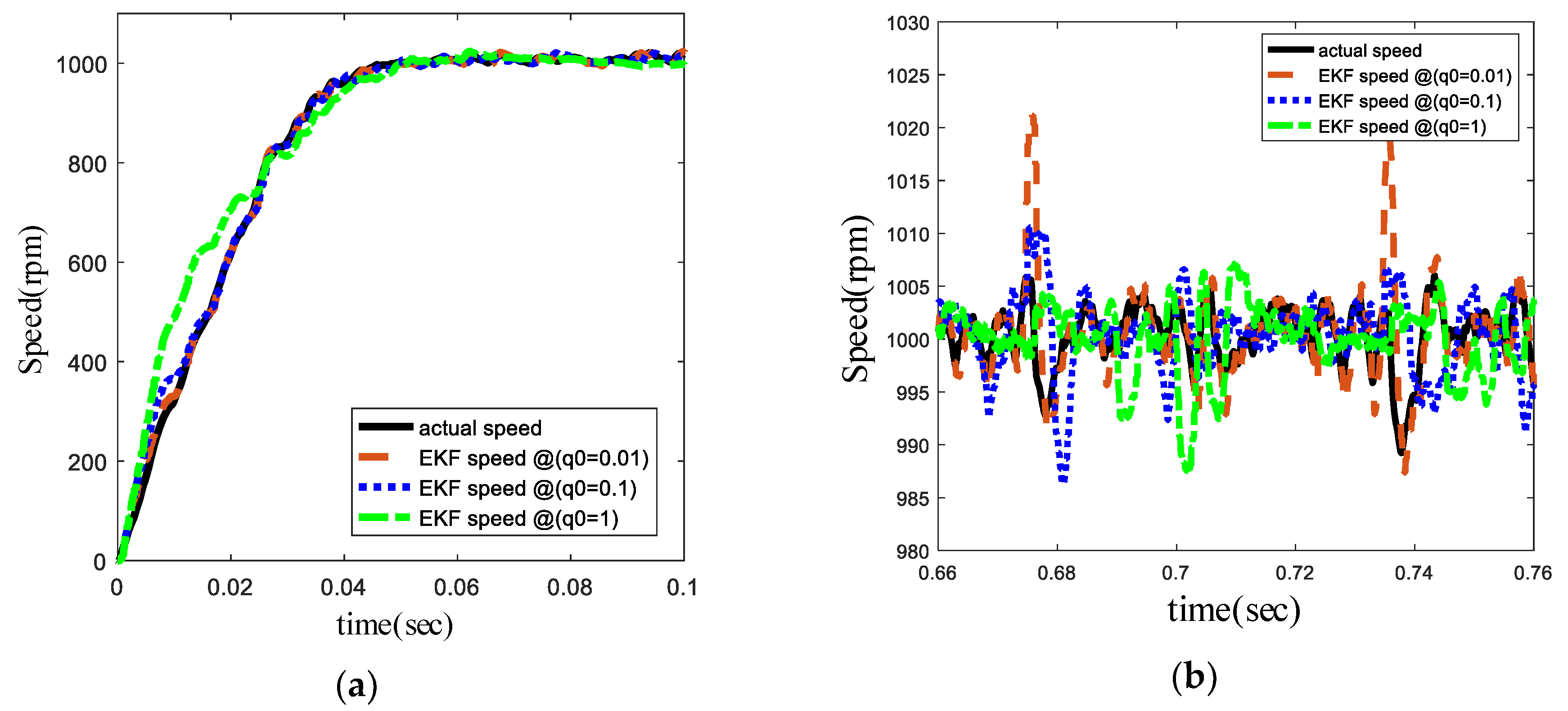
5.1. Step Excitation Simulation
5.2. Load Torque Simulation
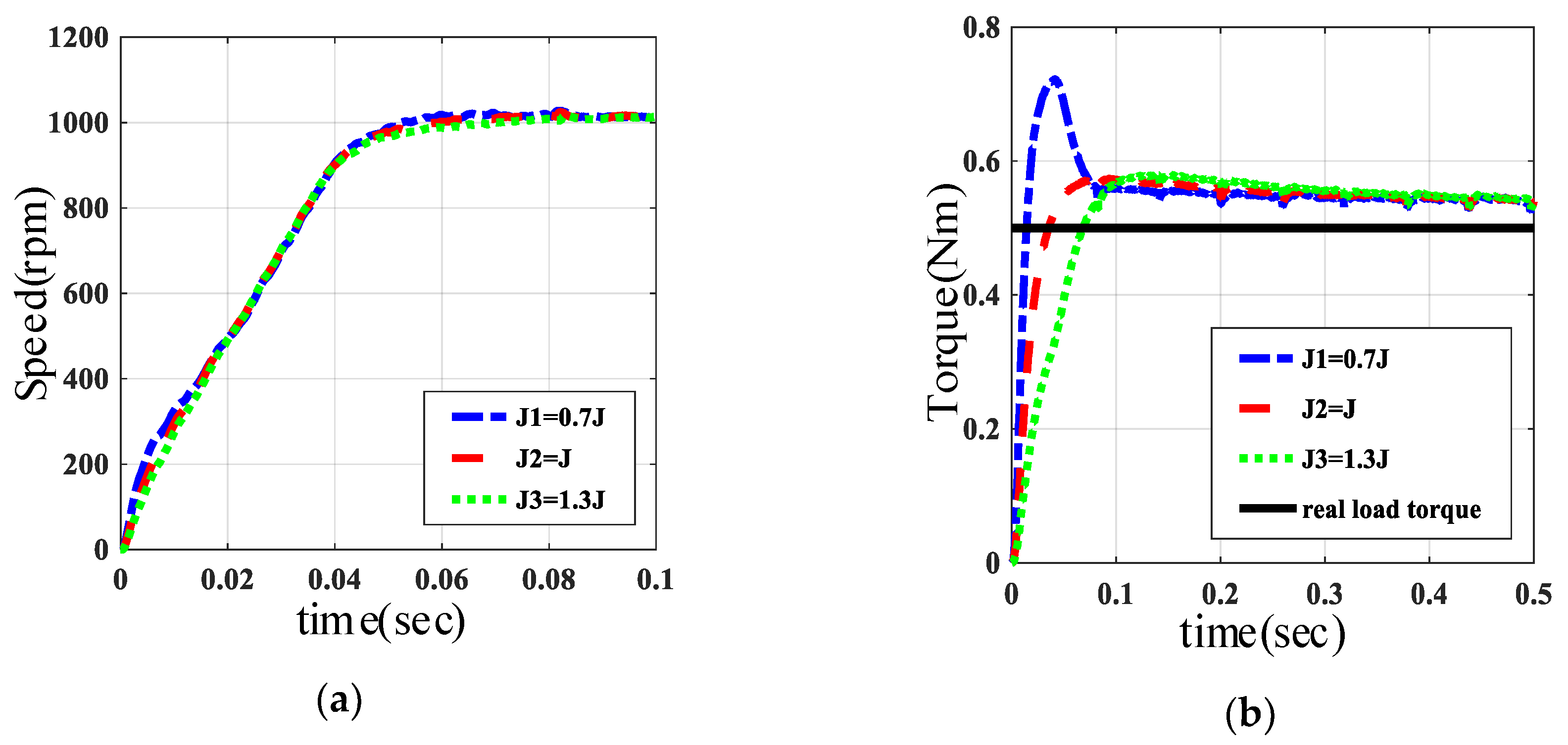
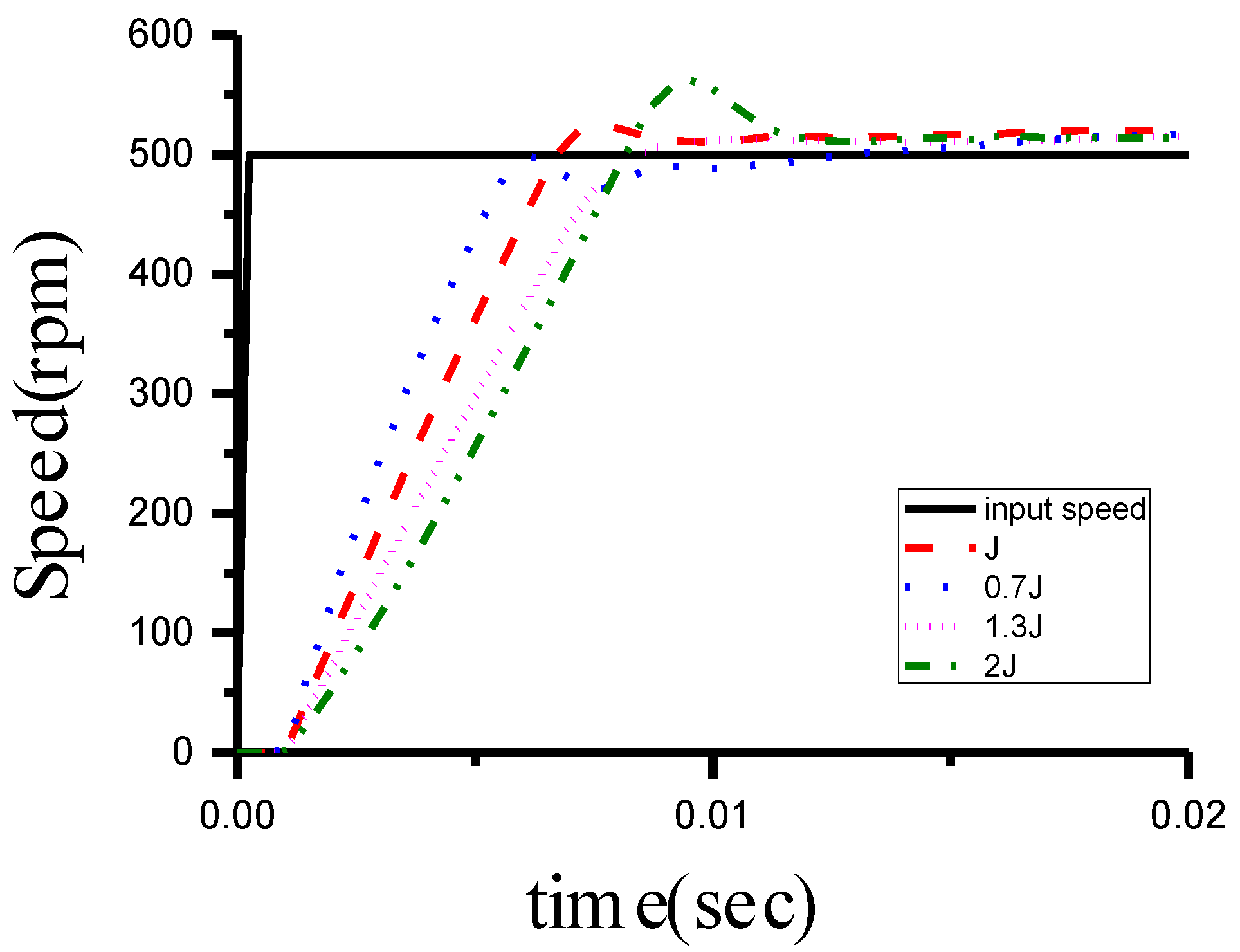
5.3. Inertia Simulation
6. Experiment and Analysis
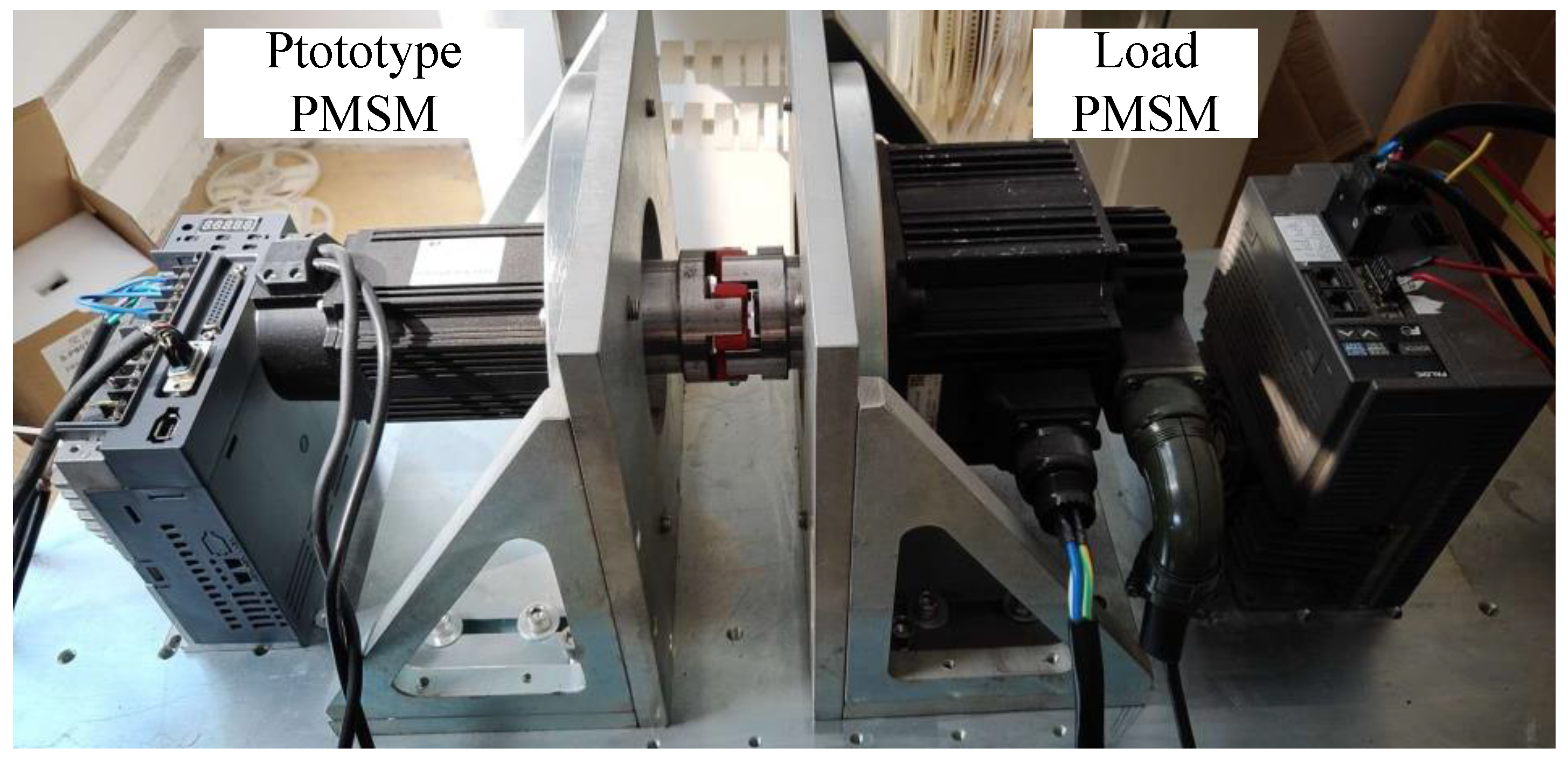
6.1. Experimental Platform Introduction
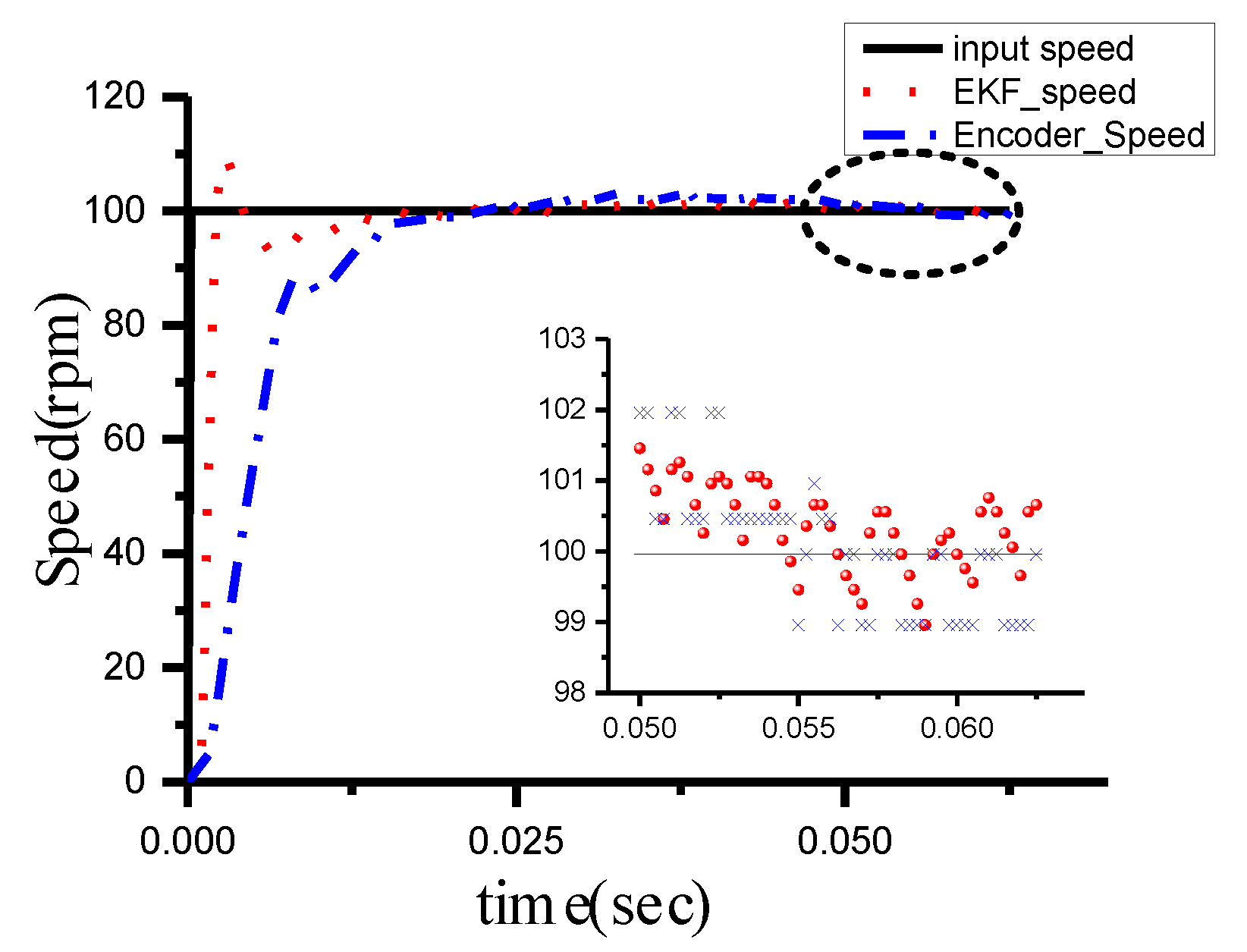
6.2. Step and Frequency Response Experiment
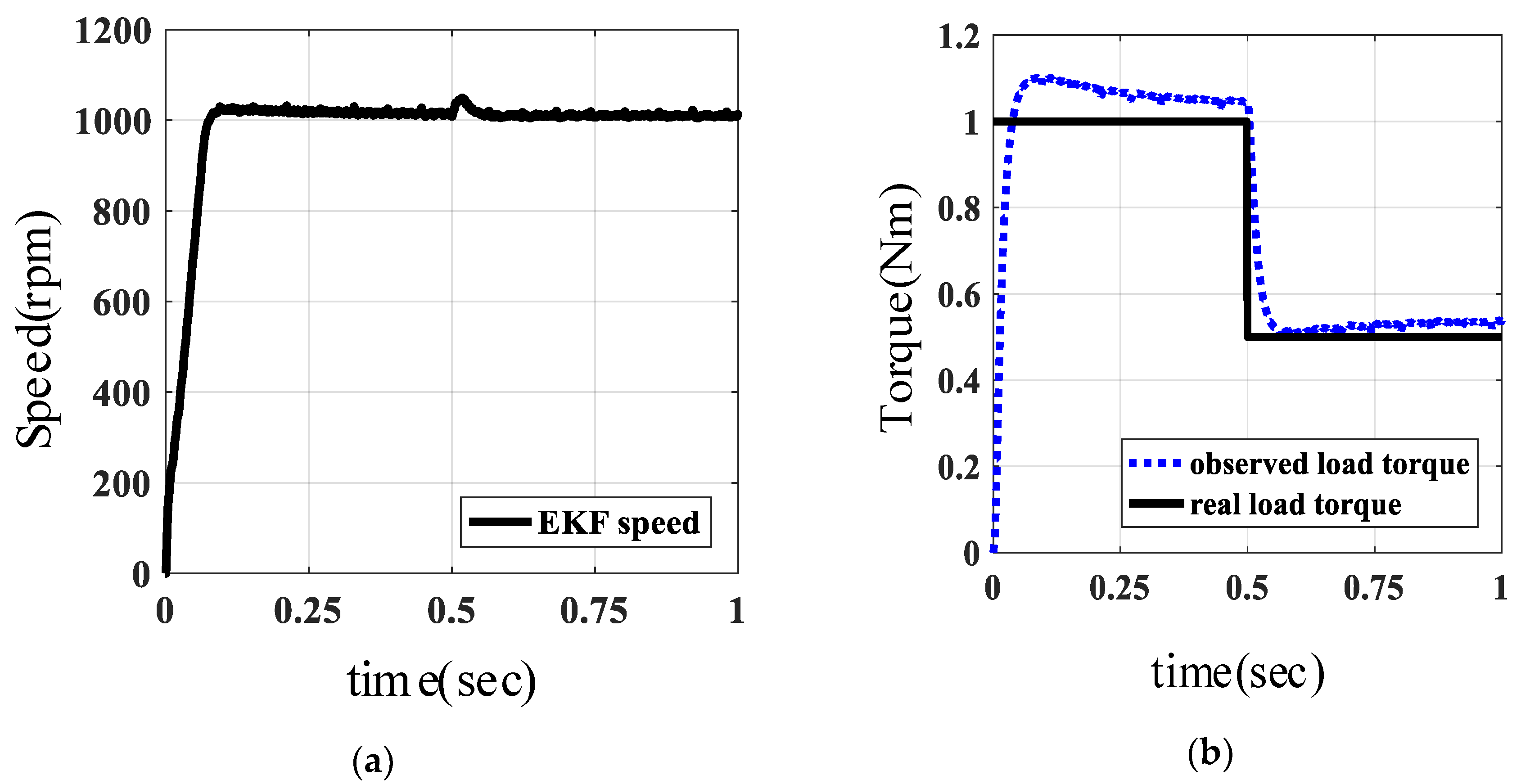
6.3. Load Torque Experiment
6.4. Inertia Experiment
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ohmae, T.; Matsuda, T.; Kamiyama, K. A microprocessor-controlled high-accuracy wide-range speed regulator for motor drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1982, 29, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, D.L.; Keith, W.V. High-resoolution velocity estimation for all-digital, ac servo drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1991, 27, 701–705. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.H.; Lasky, T.A.; Velinsky, S.A. Improved velocity estimation for low-speed and transient regimes using low-resolution encoders. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2004, 9, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Kamiyama, K.; Ohmae, T.; Matsuda, T. A microprocessor-controlled speed regulator with instantaneous speed estimation for motor drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1988, 35, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovaska, S.J. Improving the velocity sensing resolution of pulse encoders by FIR prediction. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 1991, 40, 657–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marc, B.; John, C.; Robert, T.N. Nonlinear speed observer for high-performance induction motor control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1995, 42, 337–343. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.H.; Song, J.B. Acceleration Estimator for low-velocity and low-acceleration regions based on encoder position data. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2001, 6, 337–343. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.X.; Zheng, C.H.; Sun, D.; Duan, B.Y. A simple nonlinear velocity estimator for high-performance motion control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2005, 52, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercorelli, P. A Motion-Sensorless Control for Intake Valves in Combustion Engines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 3402–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.M.; Ke, S.J. Performance evaluation of a velocity observer for accurate velocity estimation of servo motor drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2000, 36, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.W.; Sul, S.K. A new motor speed estimator using Kalman filter in low-speed range. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1996, 43, 498–504. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, W.H.; Gowda, M.; Cofie, P.; Fuller, J. Design of a speed controller using extended Kalman filter for PMSM. Trans. Int. Midwest Symp. Circuits Syst. 2014, 57, 1101–1104. [Google Scholar]
- Bolognani, S.; Tubiana, L.; Zigliotto, M. Extended Kalman filter tuning in sensorless PMSM drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2003, 39, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.D.; Fadel, M.; Li, Y.D. High performance PMSM sensorless control with load torque observation. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2007, 22, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Dhaouadi, R.; Mohan, N.; Norum, L. Design and implementation of an extended kalman filter for the state estimation of a permanent magnet synchronous motor. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 1991, 6, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognani, S.; Oboe, R.; Zigliotto, M. Sensorless full-digital PMSM drive with EKF estimation of speed and rotor position. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1999, 46, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognani, S.; Zigliotto, M.; Zordan, M. Extended-range PMSM sensorless speed drive based on stochastic filtering. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2001, 16, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.B.; Wang, X. Sensorless Direct Torque Control of Surface-Mounted Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors with Nonlinear Kalman Filtering. Energies 2018, 11, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Liu, Z.; Long, J.; Qu, W.; Xu, D. An Algorithm for Online Inertia Identification and Load Torque Observation via Adaptive Kalman Observer-Recursive Least Squares. Energies 2018, 11, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Mu, F.; Shi, G.; Ji, W.; Zhu, H. State Estimation of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Using Improved Square Root UKF. Energies 2016, 9, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, S. A Kalman estimator for detecting repetitive disturbances. In Proceedings of the 2005, American Control Conference, Portland, OR, USA, 8–10 June 2005; Volume 3, pp. 1631–1636. [Google Scholar]
- Masi, A.; Butcher, M.; Martino, M.; Picatos, R. An application of the extended Kalman filter for a sensorless stepper motor drive working with long cables. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 4217–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonge, F.; D’Ippolito, F.; Sferlazza, A. Sensorless control of induction-motor drive based on robust Kalman filter and adaptive speed estimation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 1444–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, J.; Shokri, E. Convergence analysis of non-linear filtering based on cubature Kalman filter. IET Sci. Meas. Technol. 2015, 9, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yaz, E.E. Stochastically resilient extended Kalman filtering for discrete-time nonlinear systems with sensor failures. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2014, 45, 1393–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Stator resister R (Ω) | 1.86 |
| Stator inductance L (mH) | 2.8 |
| Pole-pairs number | 4 |
| J (kg m2) | 2.45 × 10−4 |
| ϕf (Wb) | 0.109 |
| Kp | 0.03 |
| Ki | 0.005 |
| Ts (ms) | 0.25 |
| Encoder (1/rev) | 10000 |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Rated Power (W) | 750 |
| Rated Torque (Nm) | 2.4 |
| Rated Speed (Rpm) | 3000 |
| Rated Current (A) | 4.5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, T.; Tong, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Q.; Li, L.; Wu, Z. A Method to Improve the Response of a Speed Loop by Using a Reduced-Order Extended Kalman Filter. Energies 2018, 11, 2886. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11112886
Liu T, Tong Q, Zhang Q, Li Q, Li L, Wu Z. A Method to Improve the Response of a Speed Loop by Using a Reduced-Order Extended Kalman Filter. Energies. 2018; 11(11):2886. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11112886
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Tao, Qiaoling Tong, Qiao Zhang, Qidong Li, Linkai Li, and Zhaoxuan Wu. 2018. "A Method to Improve the Response of a Speed Loop by Using a Reduced-Order Extended Kalman Filter" Energies 11, no. 11: 2886. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11112886
APA StyleLiu, T., Tong, Q., Zhang, Q., Li, Q., Li, L., & Wu, Z. (2018). A Method to Improve the Response of a Speed Loop by Using a Reduced-Order Extended Kalman Filter. Energies, 11(11), 2886. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11112886





