Design and Experimental Verification of a 72/48 Switched Reluctance Motor for Low-Speed Direct-Drive Mining Applications
Abstract
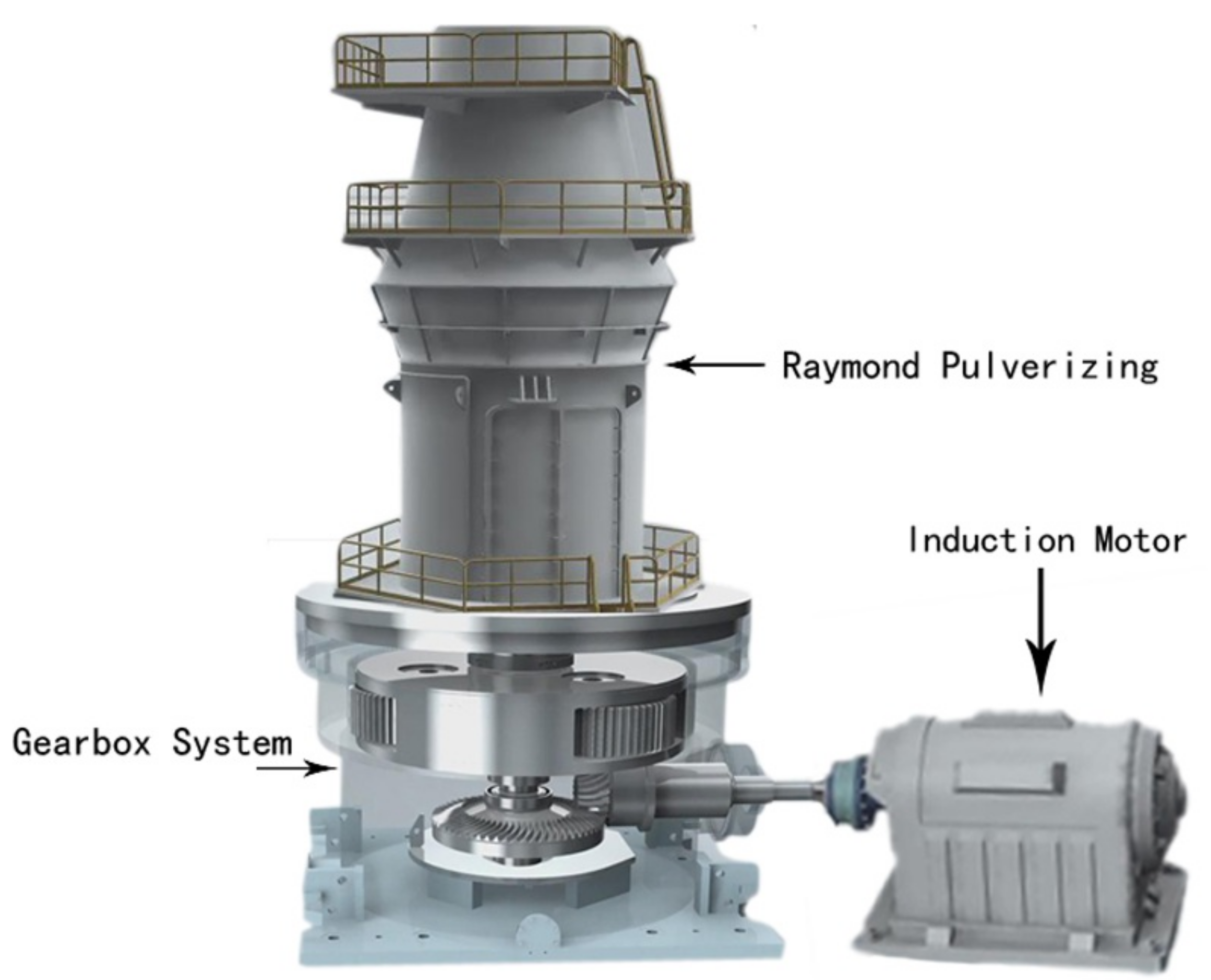
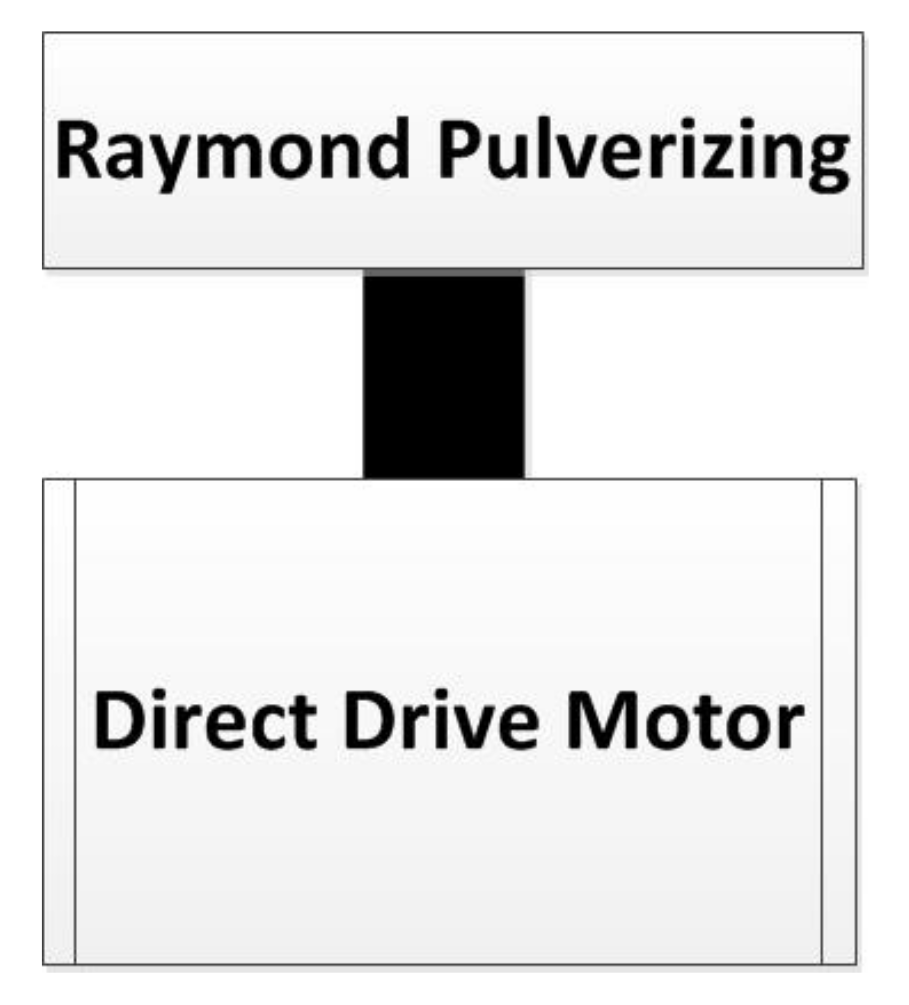
1. Introduction
2. Design of a Switched Reluctance Motor
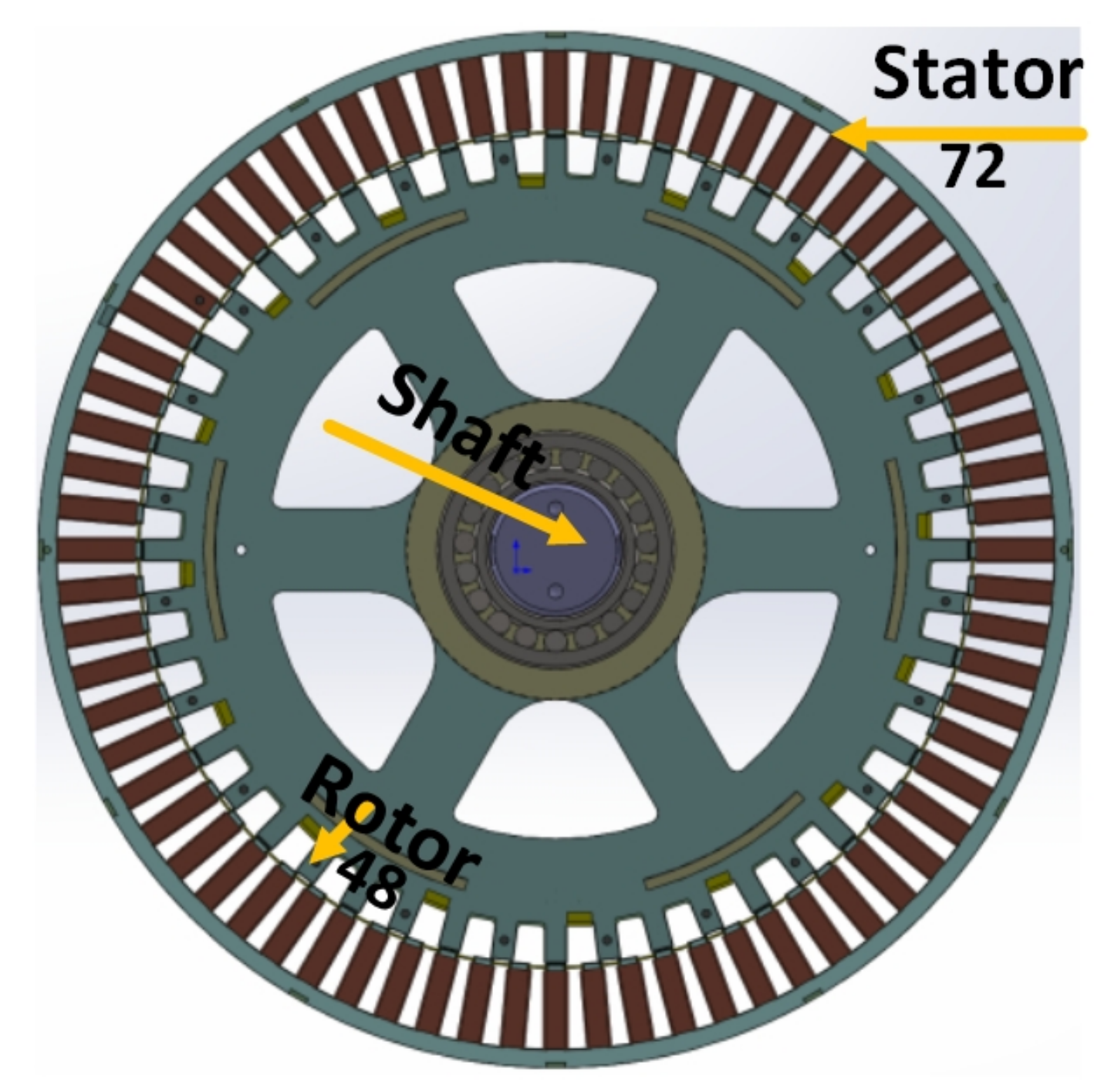
2.1. Step 1 Initial Design
2.2. Step 2 Optimization of the Parameters
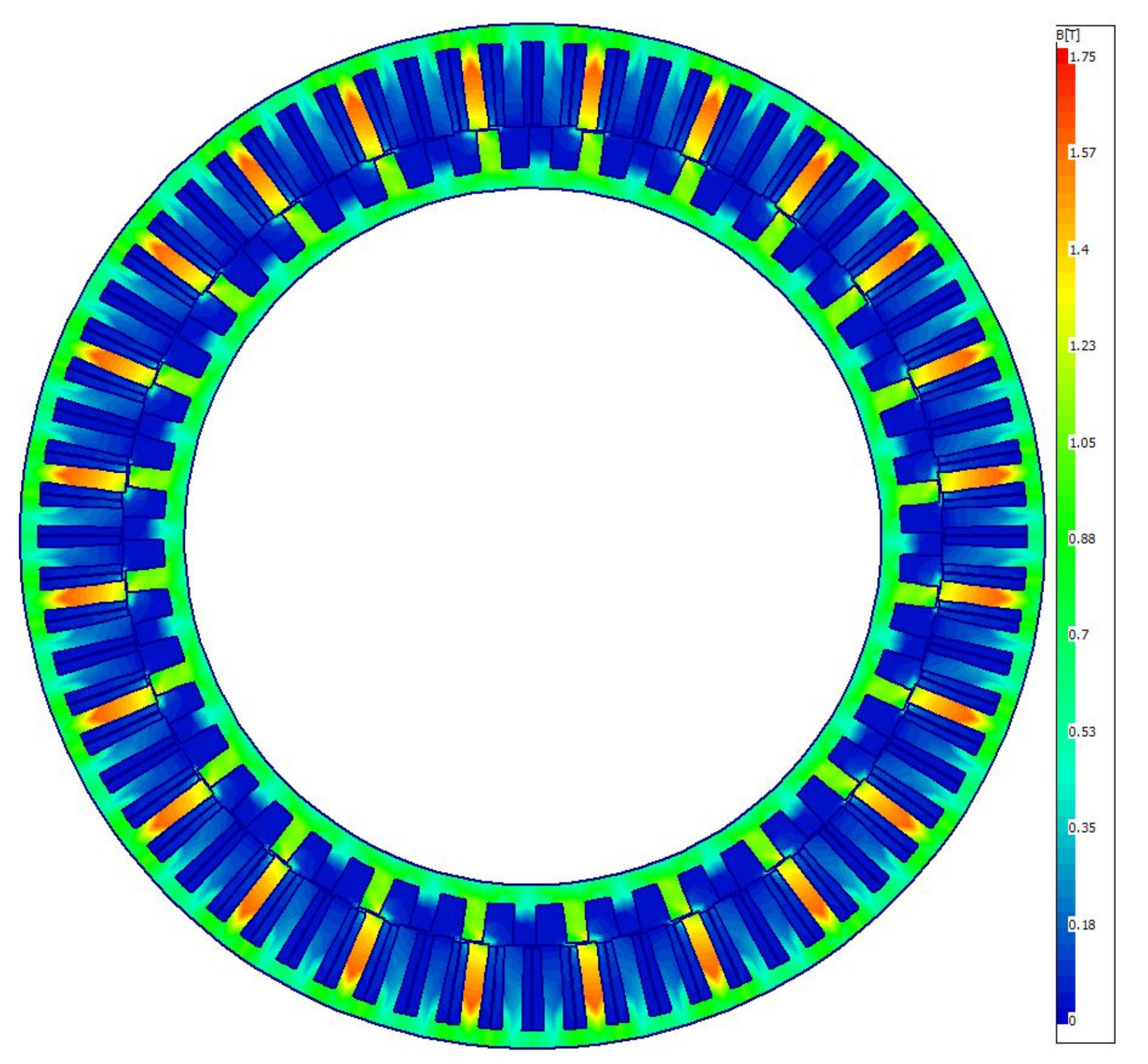
3. Investigation of Losses
3.1. Stator Copper Loss
3.2. Core Loss
3.3. Mechanical Loss
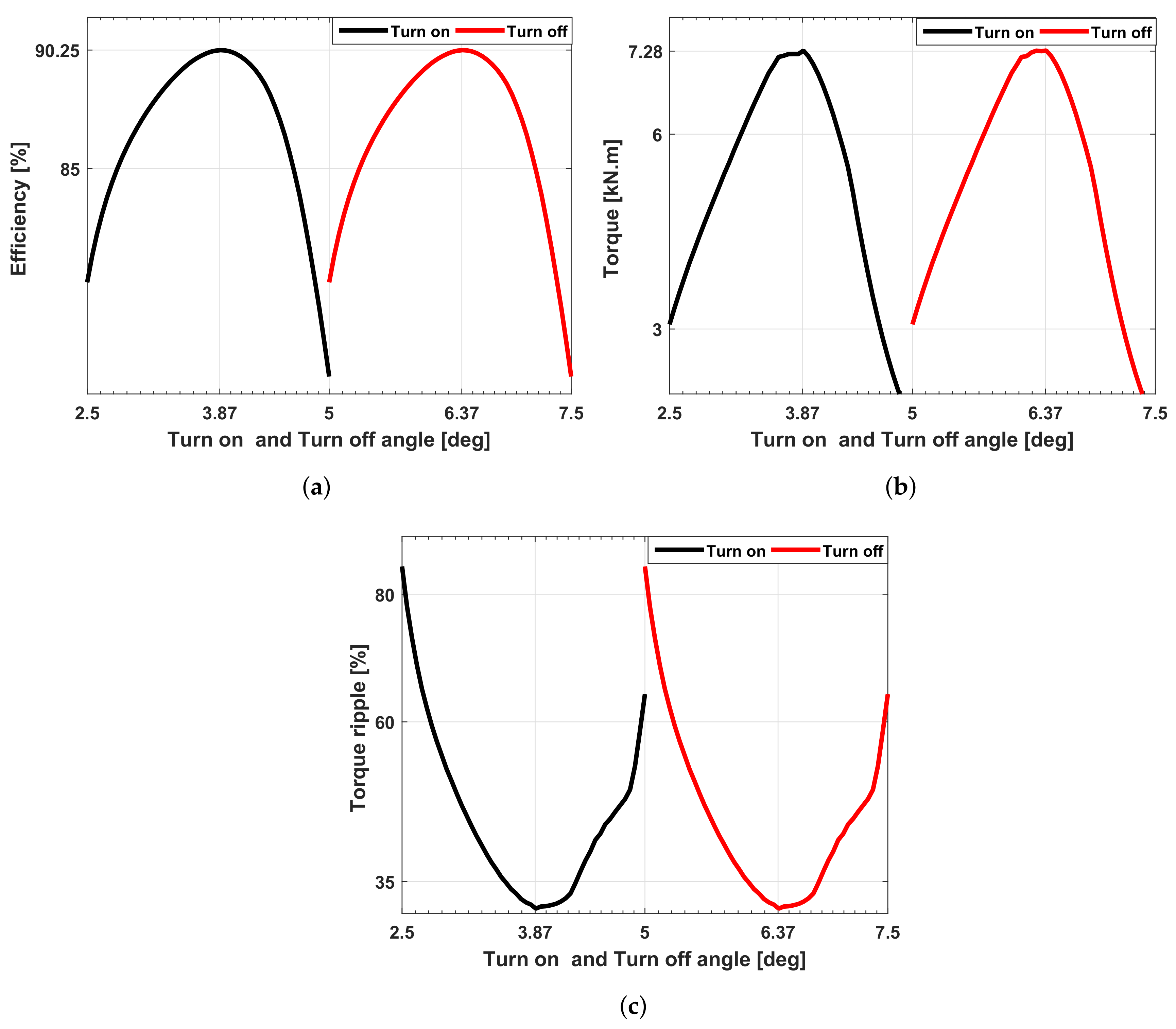
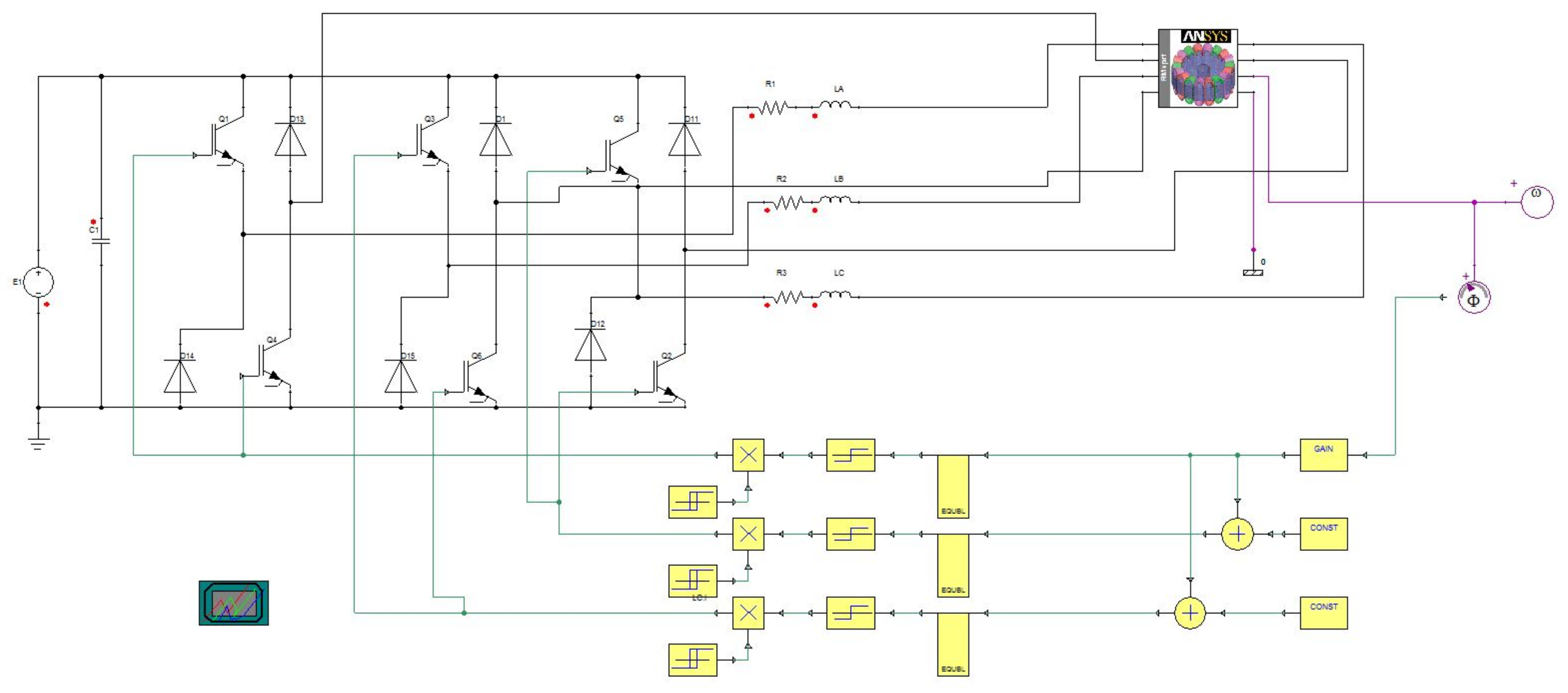
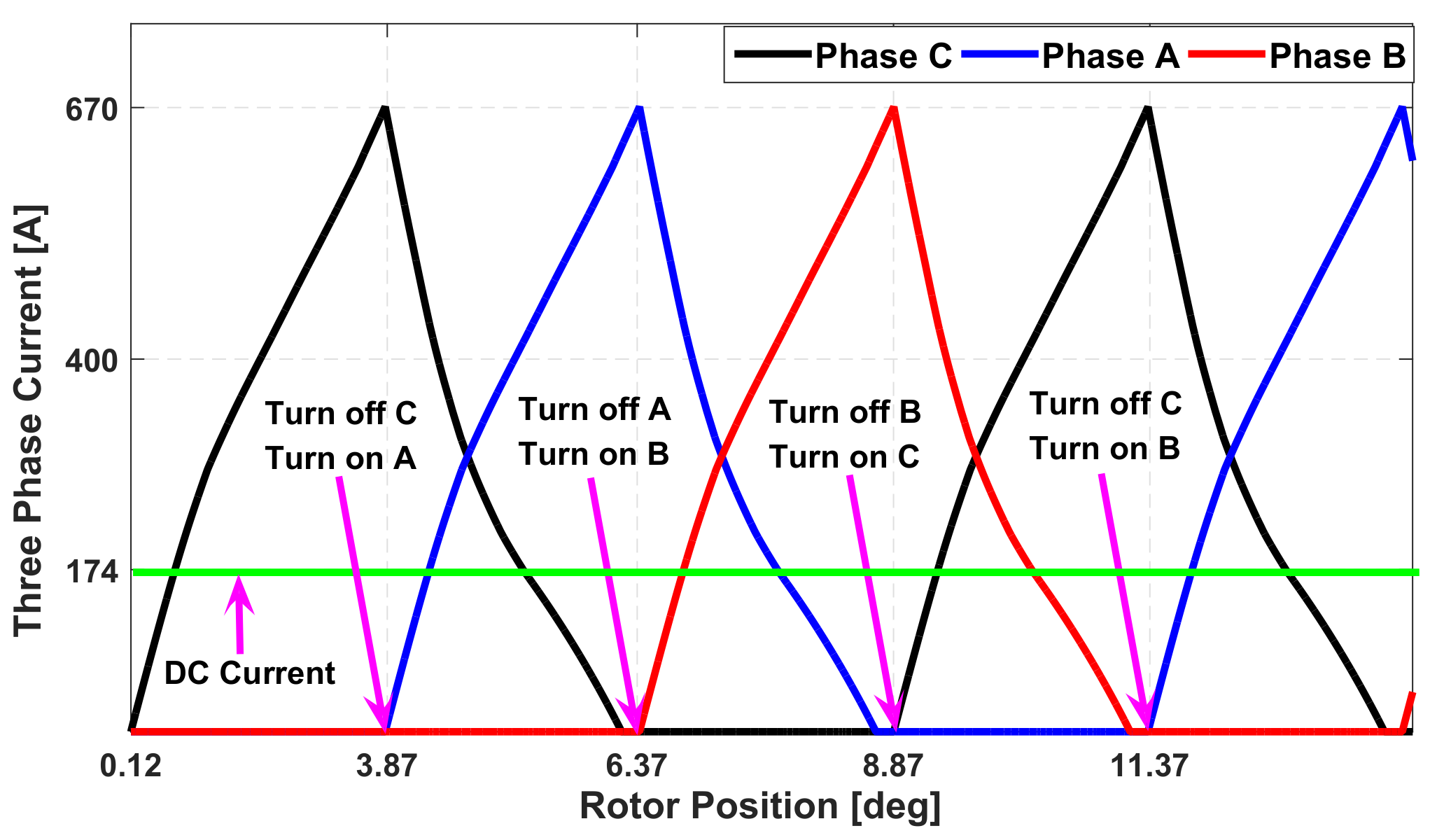
4. Converter Topology and Optimization Turn-on and Turn-off Angle
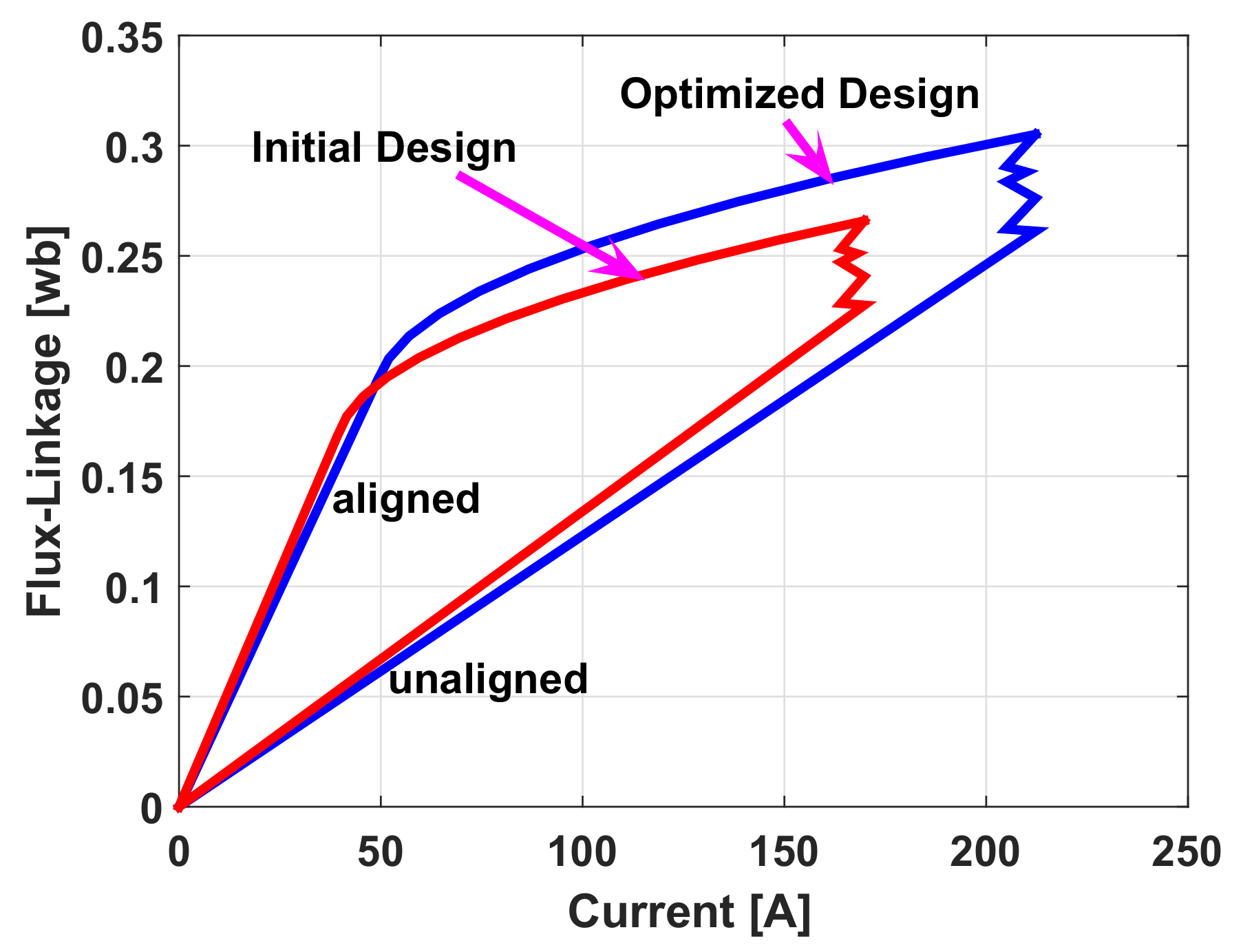
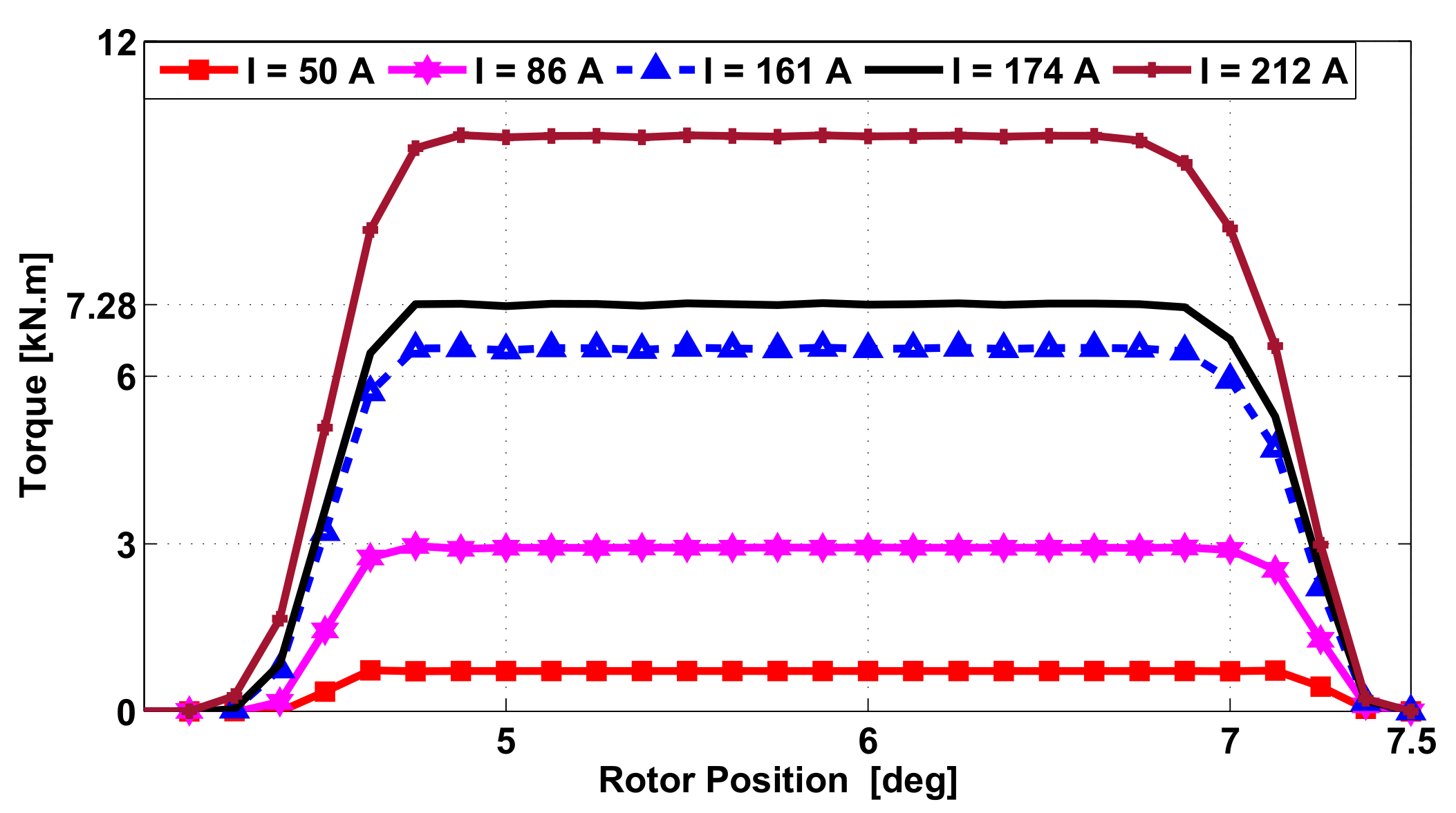
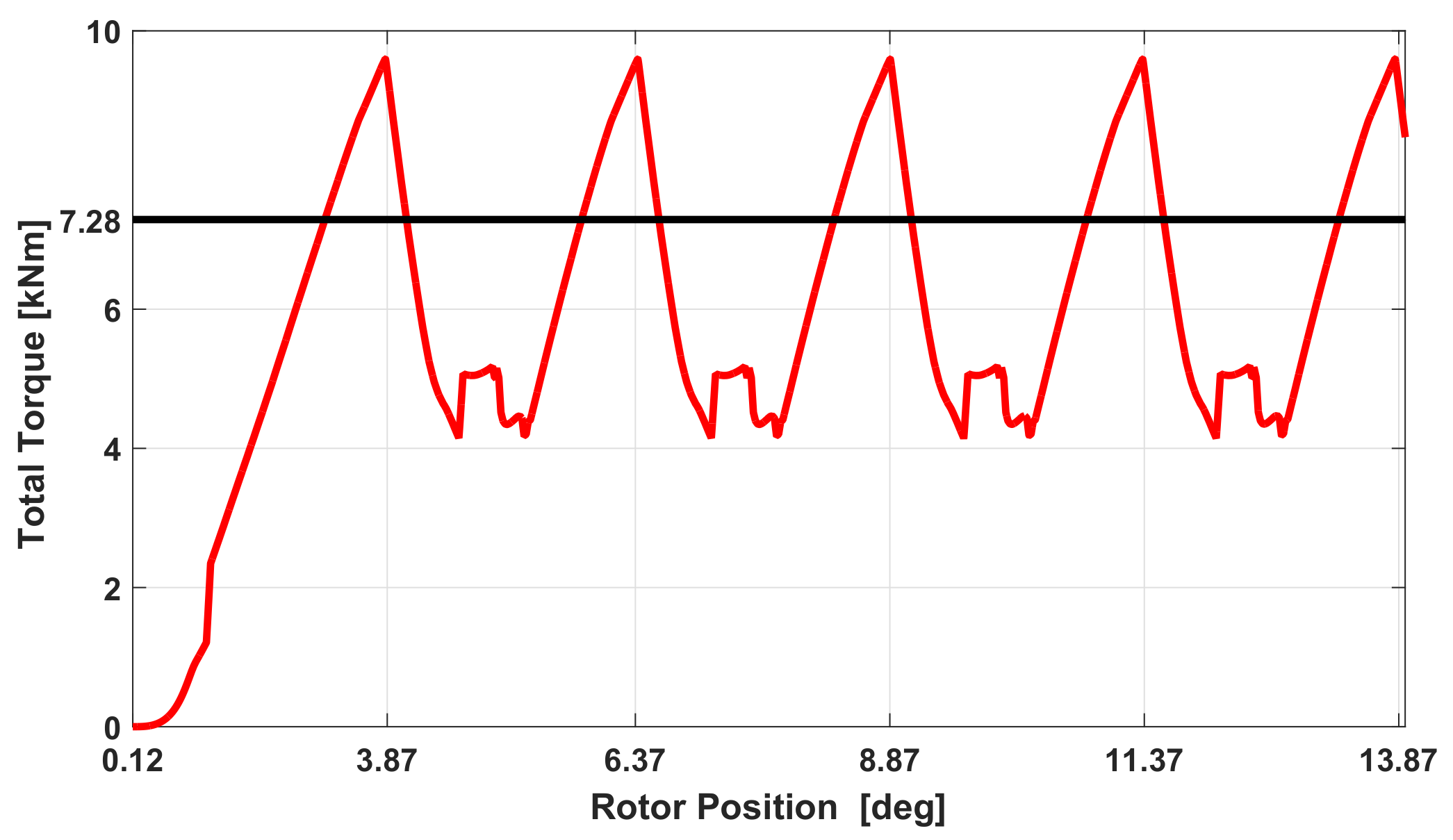
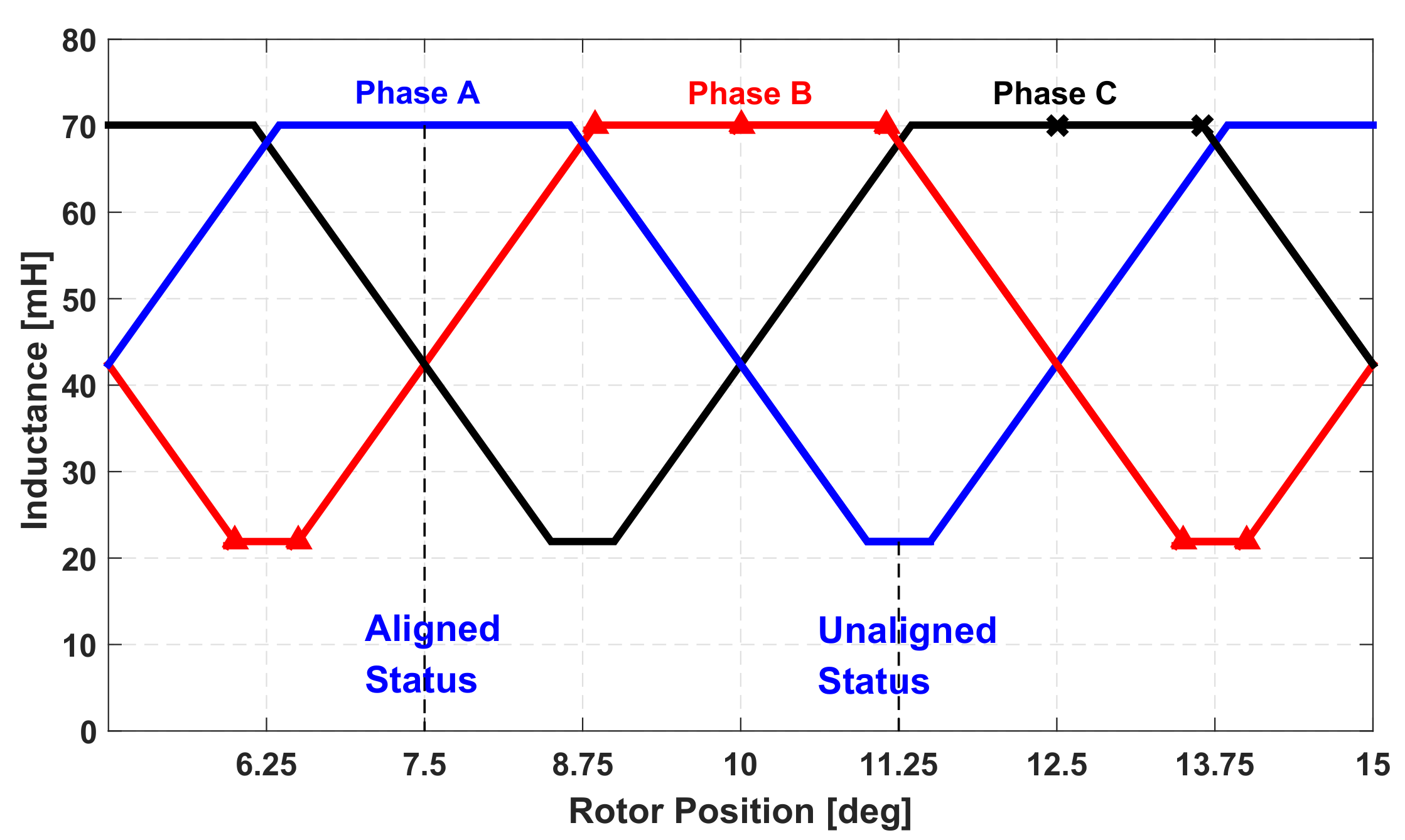
5. Static Characteristics of the SRM
6. Simulation Results
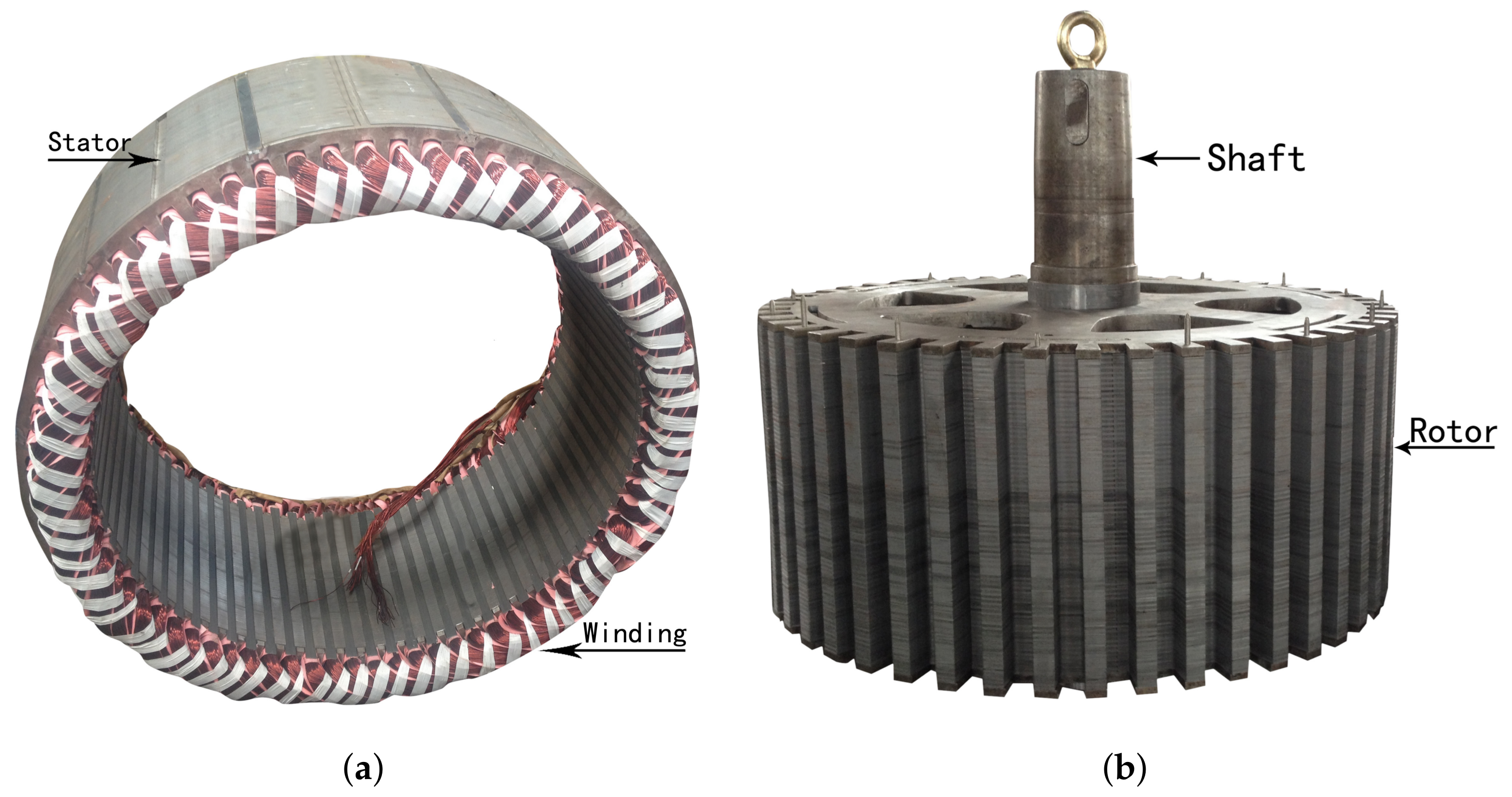
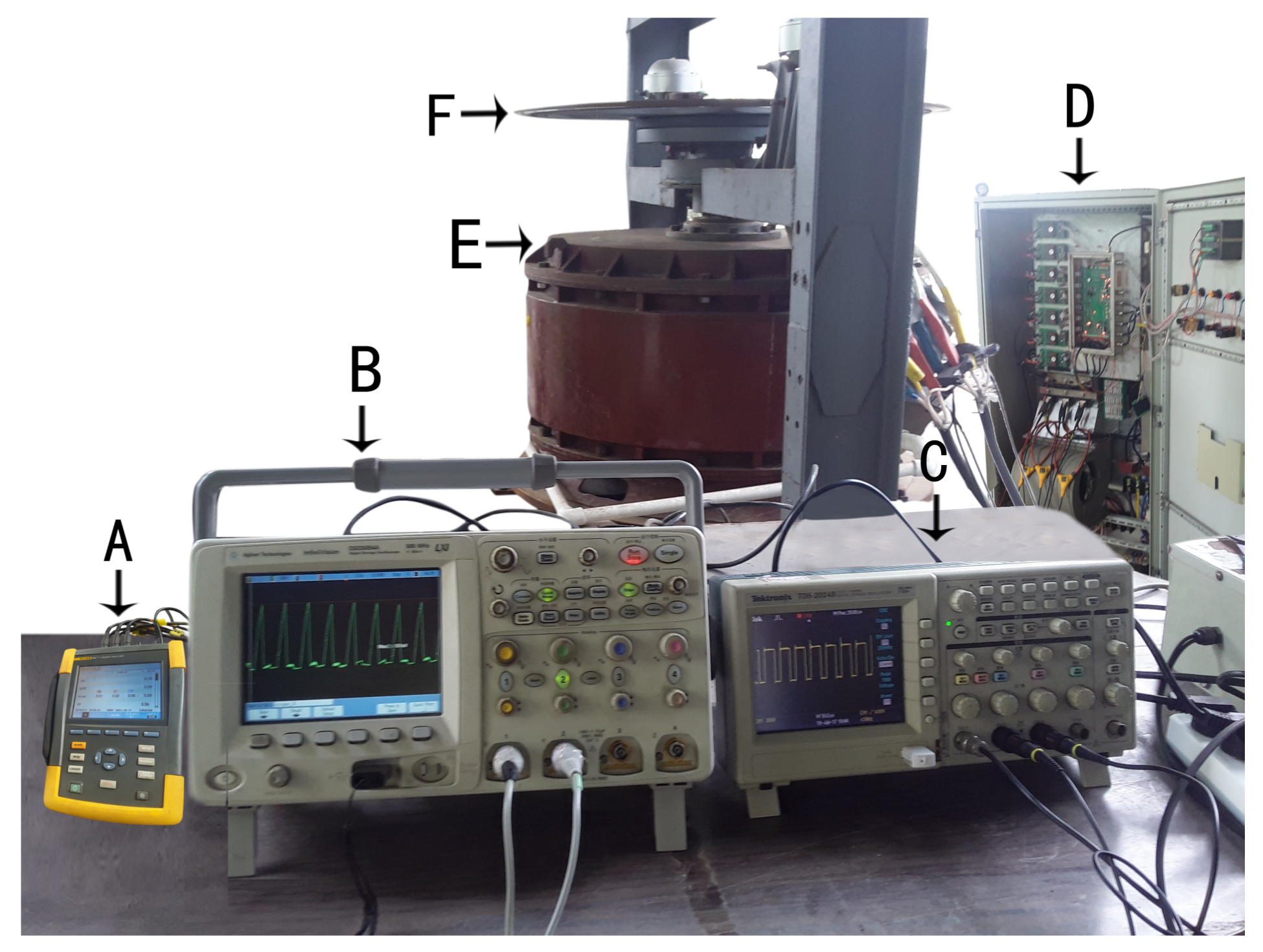
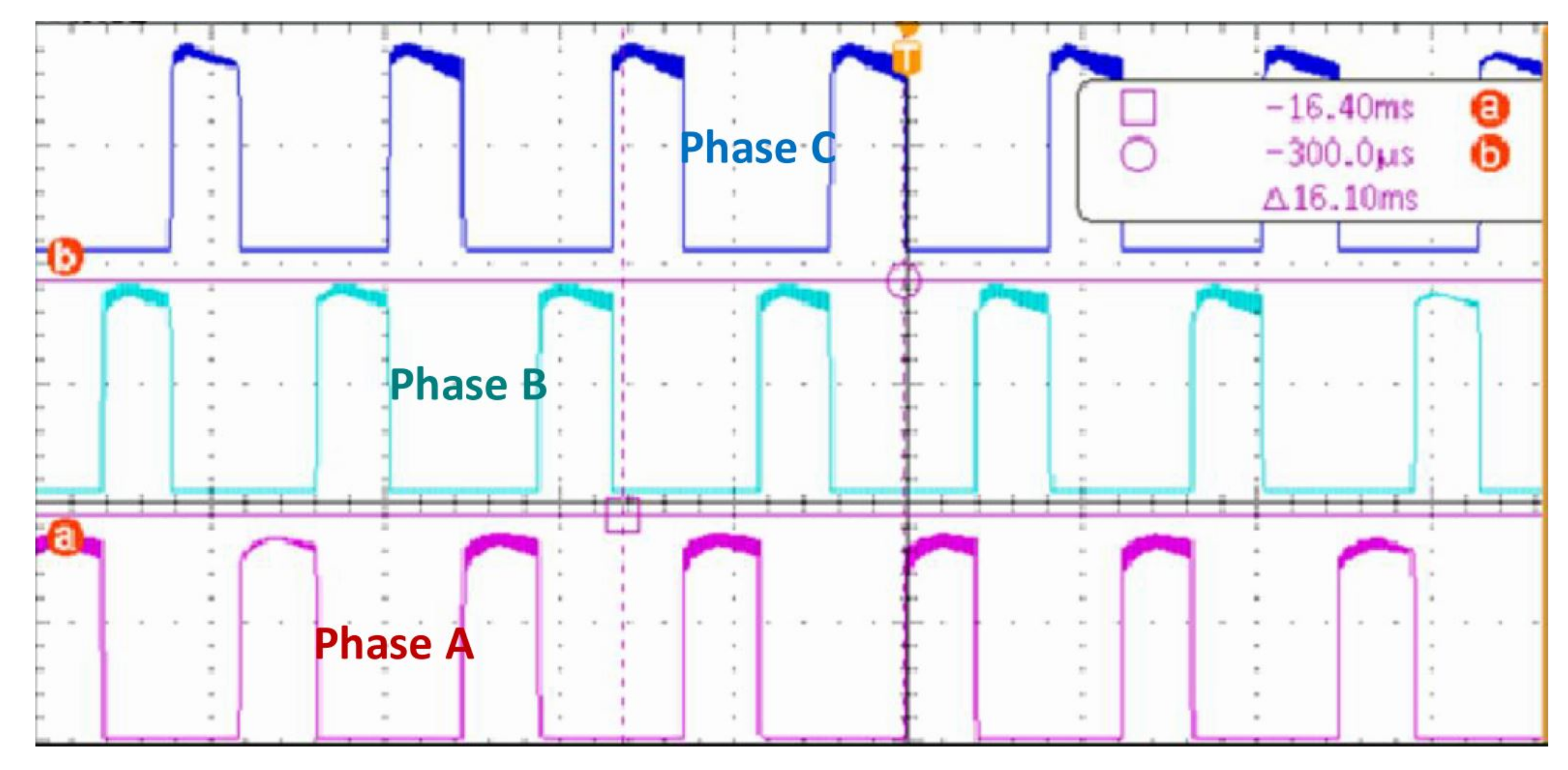
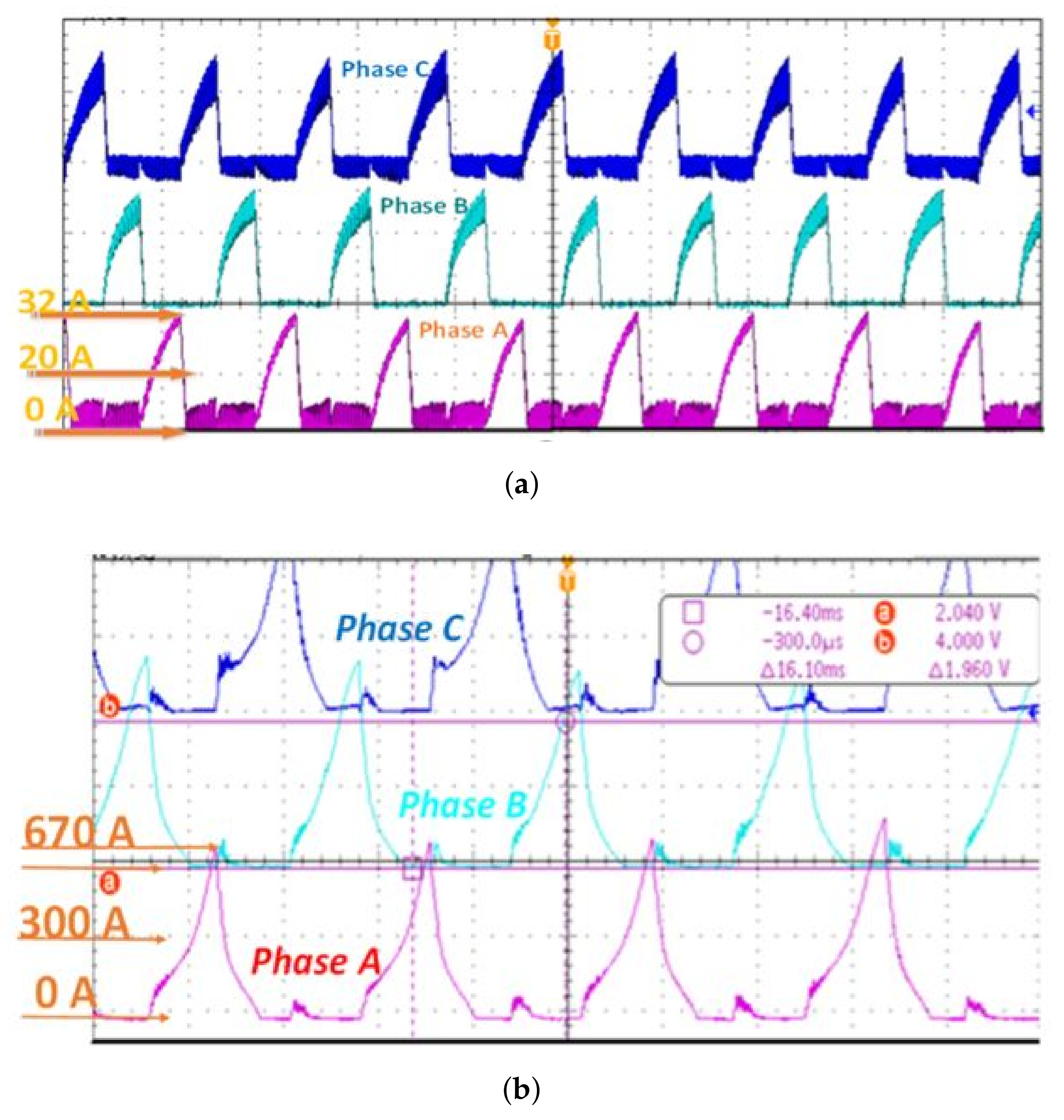
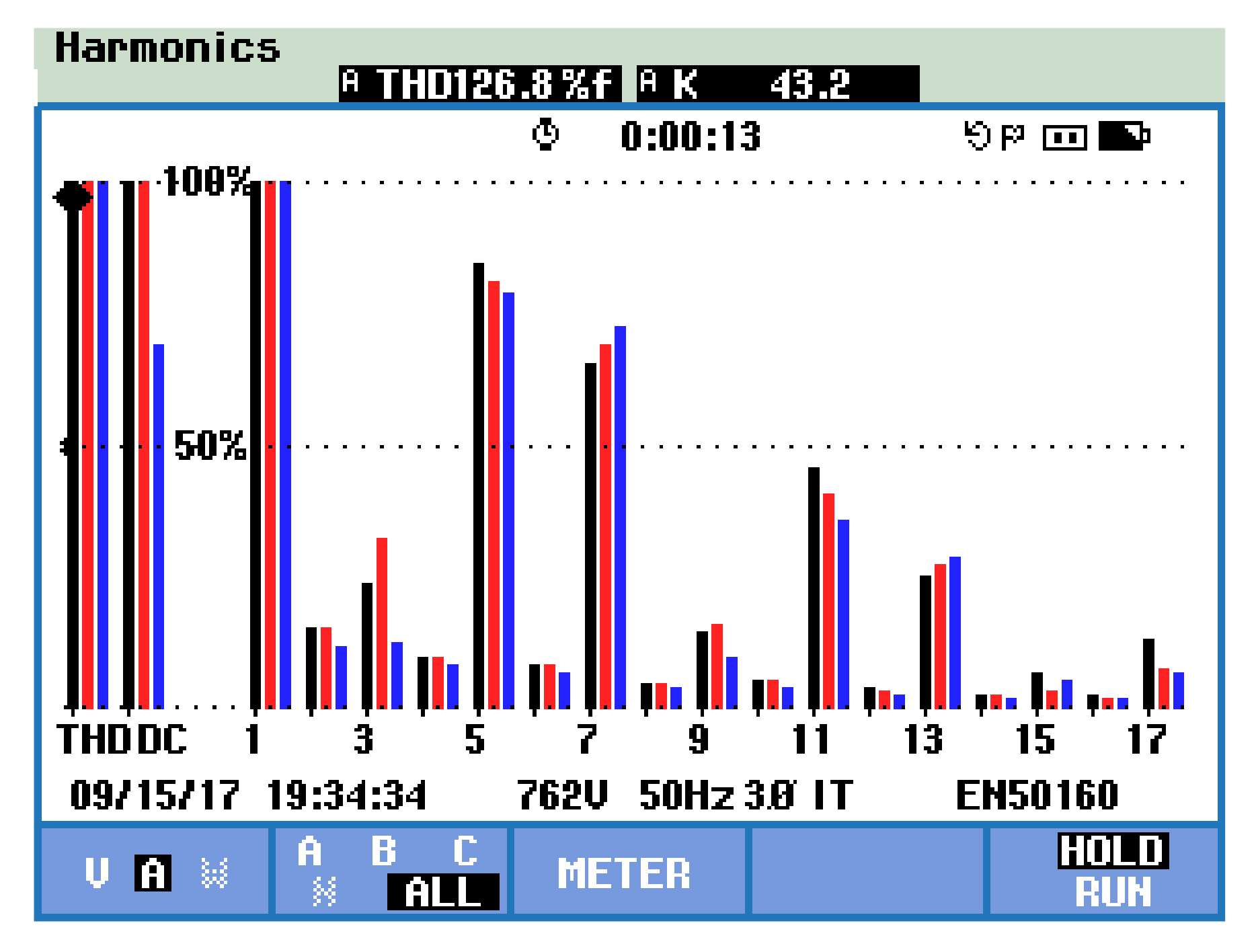
7. Experimental Setup and Its Verification
- (A)
- Three-Phase Power Quality Analyzer Fluke 434,
- (B)
- Digital Oscilloscope (Measured Current),
- (C)
- Digital Oscilloscope (Measured Voltage),
- (D)
- Power Supply and Control System,
- (E)
- Prototype SRM,
- (F)
- The Load Disc is Connected Directly to SRM.
8. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suzuki, M. Direct Drive Technology and Its Impact on Gearmotor Business. Available online: http://www.powertransmission.com (accessed on 8 September 2017).
- Raymond Mills. Available online: http://www.arvos-group.com (accessed on 1 September 2017).
- Three-PhaseInduction Motors-2SIE280S4. Available online: http://www.cantonigroup.com (accessed on 3 September 2017).
- Mahdavian, H. A smart motor drive system for domestic and industrial applications. Ph.D. Thesis, Victoria University of Technology, Victoria, Australia, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hashemnia, N.; Asaei, B. Comparative study of using different electric motors in the electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2008 18th International Conference on Electrical Machines, Vilamoura, Portugal, 6–9 September 2008; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, M.; Polat, M.; Kürüm, H. A survey on comparison of electric motor types and drives used for electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2014 16th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference and Exposition, Antalya, Turkey, 21–24 September 2014; pp. 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Ulbrich, S.; Hofmann, W. Design process of a high torque density direct drive involving a transverse flux machine. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Berlin, Germany, 2–5 September 2014; pp. 1096–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilic, M.; Marino, R.; Peresada, S.; Taylor, D. Feedback linearizing control of switched reluctance motors. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1987, 32, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, R.S.; Taylor, D.G. Low-torque-ripple switched reluctance motors for direct-drive robotics. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1991, 7, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A. Design and Performance Evaluation of Switched Reluctance Machines with Higher Number of Rotor Poles for Low Power Propulsion Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, Illinois Institute of Technology, Chicago, IL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Raj, M.A.; Kavitha, A. Effect of Rotor Geometry on Peak and Average Torque of External Rotor Synchronous Reluctance Motor (Ex-R SynRM) in comparison with Switched Reluctance Motor for Low Speed Direct Drive Domestic Application. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, D. The Switched Reluctance Motor Drive for the Direct-Drive Joint of the Robot. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2001, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, R. Switched Reluctance Motor Drives: Modeling, Simulation, Analysis, Design, and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001; ISBN 0849308380. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, M.; Miller, T.E. Comparison of design and performance parameters in switched reluctance and induction motors. In Proceedings of the 1989 Fourth International Conference on Electrical Machines and Drives, London, UK, 13–15 September 1989; pp. 303–307. [Google Scholar]
- Shoujun, S.; Weiguo, L.; Peitsch, D.; Schaefer, U. Detailed design of a high speed switched reluctance starter/generator for more/all electric aircraft. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2010, 23, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, G.I.; Xu, Z.; Ahn, J.W. Design of SRM considering dual drive modes. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Busan, Korea, 26 February–1 March 2014; pp. 872–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, R.; Arumugan, R.; Lindsay, J.F. Design procedure for switched-reluctance motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1988, 24, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.J.E. Switched Reluctance Motors and Their Control; Magna Physics Pub.: Oxford, UK, 1993; ISBN 1881855023. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, T.J.E. Brushless Permanent-Magnet and Reluctance Motor Drives; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1989; ISBN 0198593694. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, T.J.E. Electronic Control of Switched Reluctance Machines; Newnes: Oxford, UK, 2001; ISBN 9780750650731. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, T.J.E. Optimal design of switched reluctance motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2002, 49, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Doncker, R.; Pulle, D.W.; Veltman, A. Advanced Electrical Drives: Analysis, Modeling, Control; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2010; ISBN 9400701799. [Google Scholar]
- Nakano, S.; Kiyota, K.; Chiba, A. Design consideration of high torque-density switched reluctance motor for hybrid electrical vehicle. In Proceedings of the 2016 19th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Chiba, Japan, 13–16 November 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi, H.; Nakamura, K.; Chiba, A.; Fukao, T.; Tungpimolrut, K.; Dorrell, D.G. Efficiency improvements of switched reluctance motors with high-quality iron steel and enhanced conductor slot fill. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2009, 24, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichert, T. Design and construction modifications of switched reluctance machines. Ph.D. Thesis, Warsaw University of Technology, Warszawa, Poland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Pillay, P. An improved formula for lamination core loss calculations in machines operating with high frequency and high flux density excitation. In Proceedings of the 37th IAS Annual Meeting, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 13–18 October 2002; Volume 2, pp. 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampen, D.; Owzareck, M.; Beyer, S.; Parspour, N.; Schmitt, S. Analytical core loss models for electrical steel in power electronic applications. In Proceedings of the 2012 13th International Conference on Optimization of Electrical and Electronic Equipment (OPTIM), Brasov, Romania, 24–26 May 2012; pp. 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyrhonen, J.; Jokinen, T.; Hrabovcova, V. Design of Rotating Electrical Machines; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-118-58157-5. [Google Scholar]
- Gieras, J.F. Permanent Magnet Motor Technology: Design and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; ISBN 1420064401. [Google Scholar]
- Krings, A. Iron Losses in Electrical Machines-Influence of Material Properties, Manufacturing Processes, and Inverter Operation. Ph.D. Thesis, KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, Sweden, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, S.M.; El-Sherif, M.Z.; Abdel-Aliem, E.S.; Nashed, M.N. Studying different types of power converters fed switched reluctance motor. Int. J. Electron. Electr. Eng. 2013, 1, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nie, Z.; Schofield, N. Analysis and comparison of power electronic converters for conventional and toroidal switched reluctance machines. In Proceedings of the 8th IET International Conference on Power Electronics, Machines and Drives (PEMD 2016), Glasgow, UK, 19–21 April 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, X.; Huo, Y.; Gu, J. Optimization research of turn-on angle and turn-off angle based on switched reluctance starter/generator system. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 28th Canadian Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering (CCECE), Halifax, NS, Canada, 3–6 May 2015; pp. 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borujeni, M.M.; Rashidi, A.; Nejad, S.M.S. Optimal four quadrant speed control of switched reluctance motor with torque ripple reduction based on EM-MOPSO. In Proceedings of the The 6th Power Electronics, Drive Systems & Technologies Conference (PEDSTC2015), Tehran, Iran, 3–4 February 2015; pp. 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.W.; Bilgin, B.; Howey, B.; Emadi, A. Design optimization of switched reluctance machine using genetic algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Electric Machines & Drives Conference (IEMDC), Coeur d’Alene, ID, USA, 10–13 May 2015; pp. 1671–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radun, A.V. Design considerations for the switched reluctance motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1995, 31, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power [kW] | 75 | Weight [Kg] | 678 |
| Voltage [V] | 400 | The gear system outer diameter [mm] | 1000 |
| Current [A] | 128 | The gear system stack length [mm] | 340 |
| Frequency [Hz] | 50 | The output speed of a gear system [rpm] | 105 |
| Power factor at full load | The efficiency of a gear system [%] | ||
| Rate Speed [rpm] | 1488 | The total weight of a gear drive system [kg] | 1050 |
| Rate torque [N·m] | 481 | The total efficiency of a gear drive system [%] | |
| Efficiency at full load [%] |
| Construction | Geared Drive System | Direct-Drive System | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gear Ratio | About 14.28:1 | —– | |
| Balance | Poor | Good | |
| Noise | High | Low | |
| Efficiency | Low | High | |
| Reliability | Moderate | High | |
| Lubrication System | Significant | No Significant | |
| Maintainability | Longer time | Short time | |
| Motor | Induction Motor | Brushless DC | Switched Reluctance Motor |
| Torque | Small | Larger | Larger |
| Cost | Cheap | Expensive | Cheaper |
| Weight | Medium | Medium | Larger |
| Limiting thermal | Winding insulation | Winding insulation andpermanent magnet | Winding insulation |
| Coolant system | Stator and rotor | Stator and Rotor | Stator (Only) |
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of stator poles | 72 | Stack length [mm] | 340 |
| Number of rotor poles | 48 | Air gap length [mm] | 1 |
| Stator out diameter [mm] | 1000 | Rotor out diameter [mm] | 798 |
| Stator pole arc angle [deg] | 2.95 | Rotor pole arc angle [deg] | 3.05 |
| Stator pole width [mm] | 20.59 | Rotor pole width [mm] | 21.23 |
| Stator yoke thickness [mm] | 15.45 | Rotor yoke thickness [mm] | 15.71 |
| Stator slot depth [mm] | 84.55 | Rotor slot depth [mm] | 29 |
| Number of turns per pole [Turns] | 12 | Shaft diameter [mm] | 708.58 |
| Number of coils per slot | 2 | Slot fill factor [%] | 56.3 |
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of stator poles | 72 | Stack length [mm] | 340 |
| Number of rotor poles | 48 | Air gap length [mm] | 1 |
| Stator out diameter [mm] | 1000 | Rotor out diameter [mm] | 798 |
| Stator pole arc angle [deg] | 2.85 | Rotor pole arc angle [deg] | 3.15 |
| Stator pole width [mm] | 19.89 | Rotor pole width [mm] | 21.93 |
| Stator yoke thickness [mm] | 18 | Rotor yoke thickness [mm] | 20 |
| Stator slot depth [mm] | 82 | Rotor slot depth [mm] | 39 |
| Number of turns per pole [Turns] | 15 | Shaft diameter [mm] | 680 |
| Number of coils per slot | 2 | Slot fill factor [%] | 70.3 |
| Angle [deg] | Values |
|---|---|
| stroke angle | |
| Stator pole pitch | 5 |
| Rotor pole pitch | |
| Aligned rotor position | |
| Unaligned rotor position | |
| The electrical period |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Efficiency [%] | |
| Torque [kN·m] | |
| Torque ripple [%] |
| Phase | [deg] | [deg] | [deg] | [deg] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phase A | 3.75 | 7.5 | 3.87 | 6.37 |
| Phase B | 6.25 | 10 | 6.37 | 8.87 |
| Phase C | 8.75 | 12.5 | 8.87 | 11.37 |
| Parameters | Test (1) | Test (2) | Test (3) | Test (4) | Test (5) | Test (6) | Test (7) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Speed [rpm] | 105 | ||||||
| DC Voltage [V] | 510 | ||||||
| DC Current [A] | |||||||
| Total Loss [kW] | |||||||
| Torque [kN·m] | |||||||
| Efficiency [%] |
| Parameters | 72/48 SRM | IM (2SIE 280 S4) | Gear Drive System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power [kW] | 75 | 75 | 75 |
| Rate speed [rpm] | 105 | 1488 | 105 |
| Torque [kN·m] | 7.28 | 0.481 | 7 |
| Efficiency at full load [%] | 90.19 | 94.2 | 59.32 |
| Weight [kg] | 1180 | 678 | 1050 |
| Price of motor [USD] | 12,000 | 9000 | 1350 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elhomdy, E.; Li, G.; Liu, J.; Bukhari, S.A.; Cao, W.-P. Design and Experimental Verification of a 72/48 Switched Reluctance Motor for Low-Speed Direct-Drive Mining Applications. Energies 2018, 11, 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11010192
Elhomdy E, Li G, Liu J, Bukhari SA, Cao W-P. Design and Experimental Verification of a 72/48 Switched Reluctance Motor for Low-Speed Direct-Drive Mining Applications. Energies. 2018; 11(1):192. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11010192
Chicago/Turabian StyleElhomdy, Esmail, Guofeng Li, Jiang Liu, Syed Abid Bukhari, and Wen-Ping Cao. 2018. "Design and Experimental Verification of a 72/48 Switched Reluctance Motor for Low-Speed Direct-Drive Mining Applications" Energies 11, no. 1: 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11010192
APA StyleElhomdy, E., Li, G., Liu, J., Bukhari, S. A., & Cao, W.-P. (2018). Design and Experimental Verification of a 72/48 Switched Reluctance Motor for Low-Speed Direct-Drive Mining Applications. Energies, 11(1), 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11010192






