Numerical Analysis of the Combustion and Emission Characteristics of Diesel Engines with Multiple Injection Strategies Using a Modified 2-D Flamelet Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model Framework
2.1. Modified 2-D Flamelet Model
2.2. Further Modification of 2-D Flamelet Model
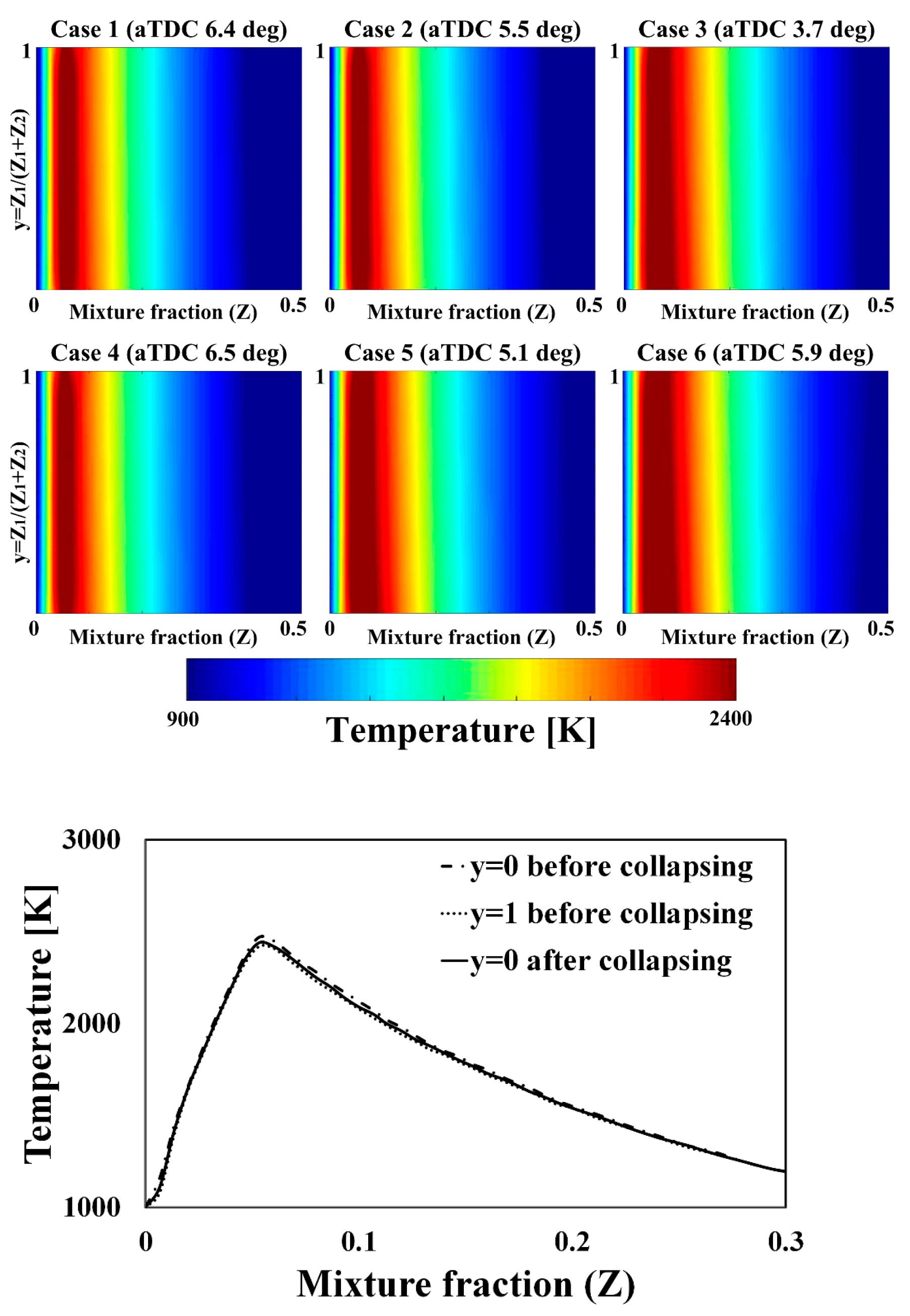
2.3. Collapse of 2-D Flamelet Solution
2.4. Linking with CFD Solver
2.5. Modeling Strategies for Diesel Engine Simulation
- From the start of the first injection until the start of the second injection
- From the start of the second injection until two mixture fields are merged
- From the start of the merging of mixture fields until the start of the third injection
- Moment just before the third injection
3. Experimental and Simulation Setup
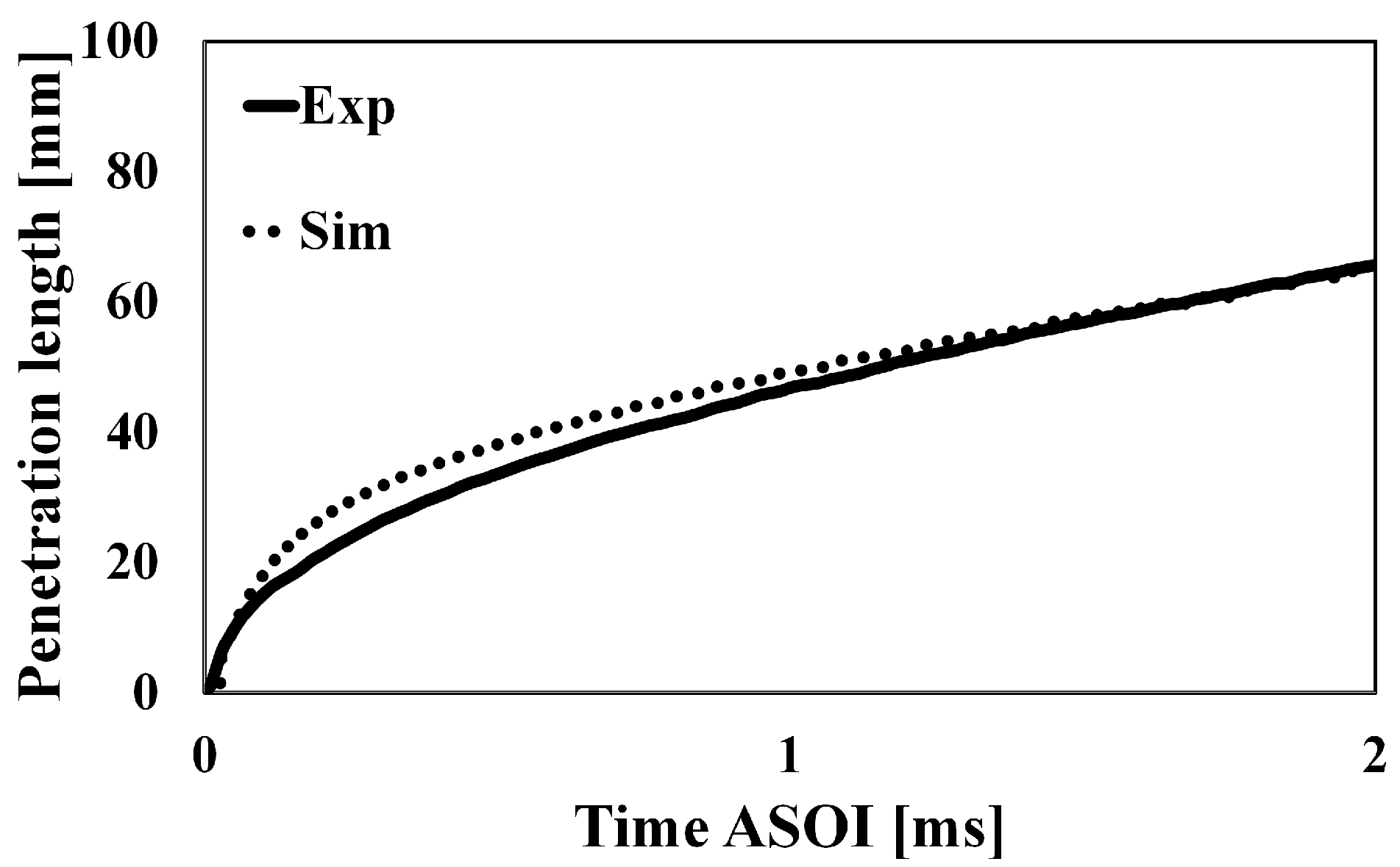
3.1. Experimental Setup
3.2. Numerical Implementation
4. Results and Discussion
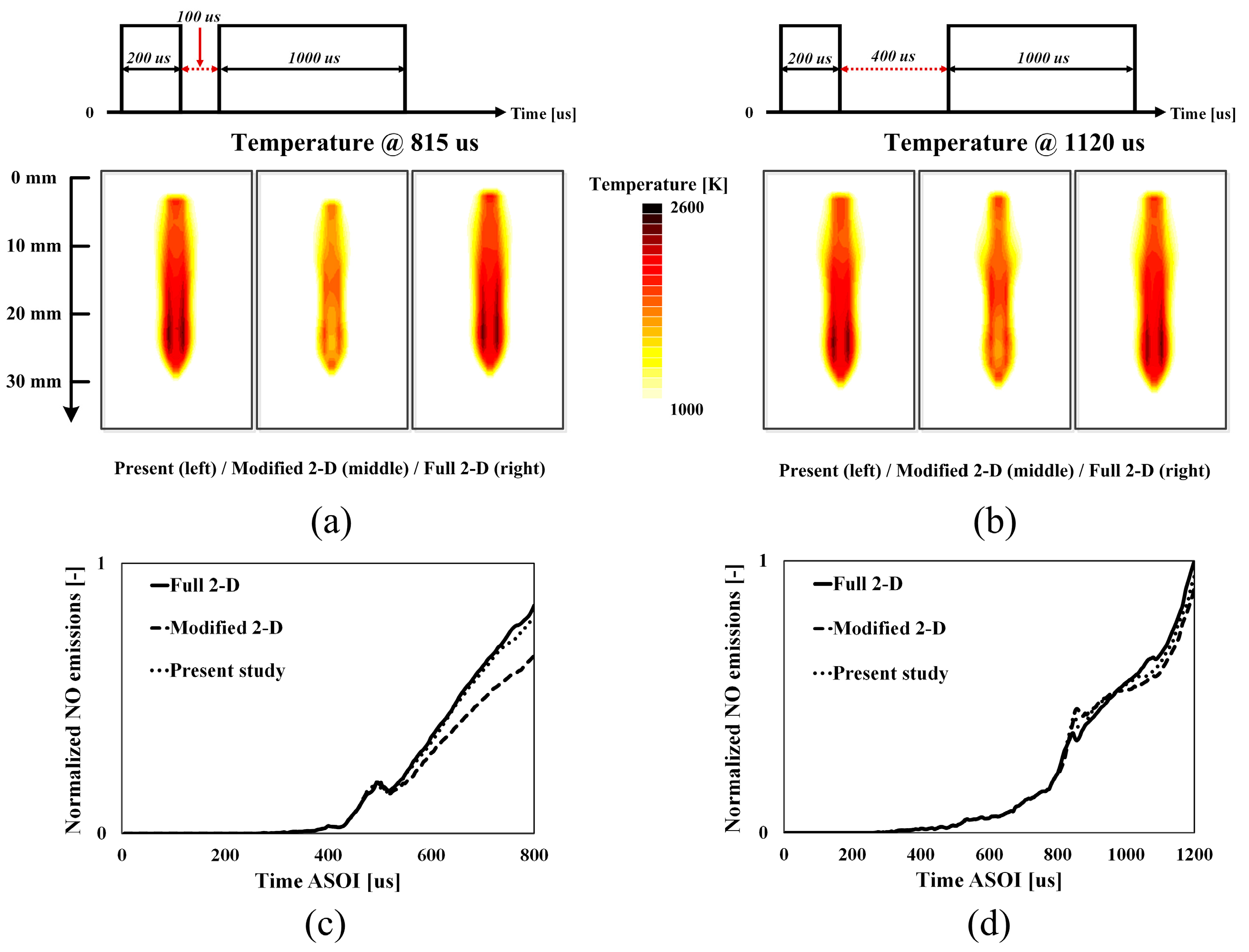
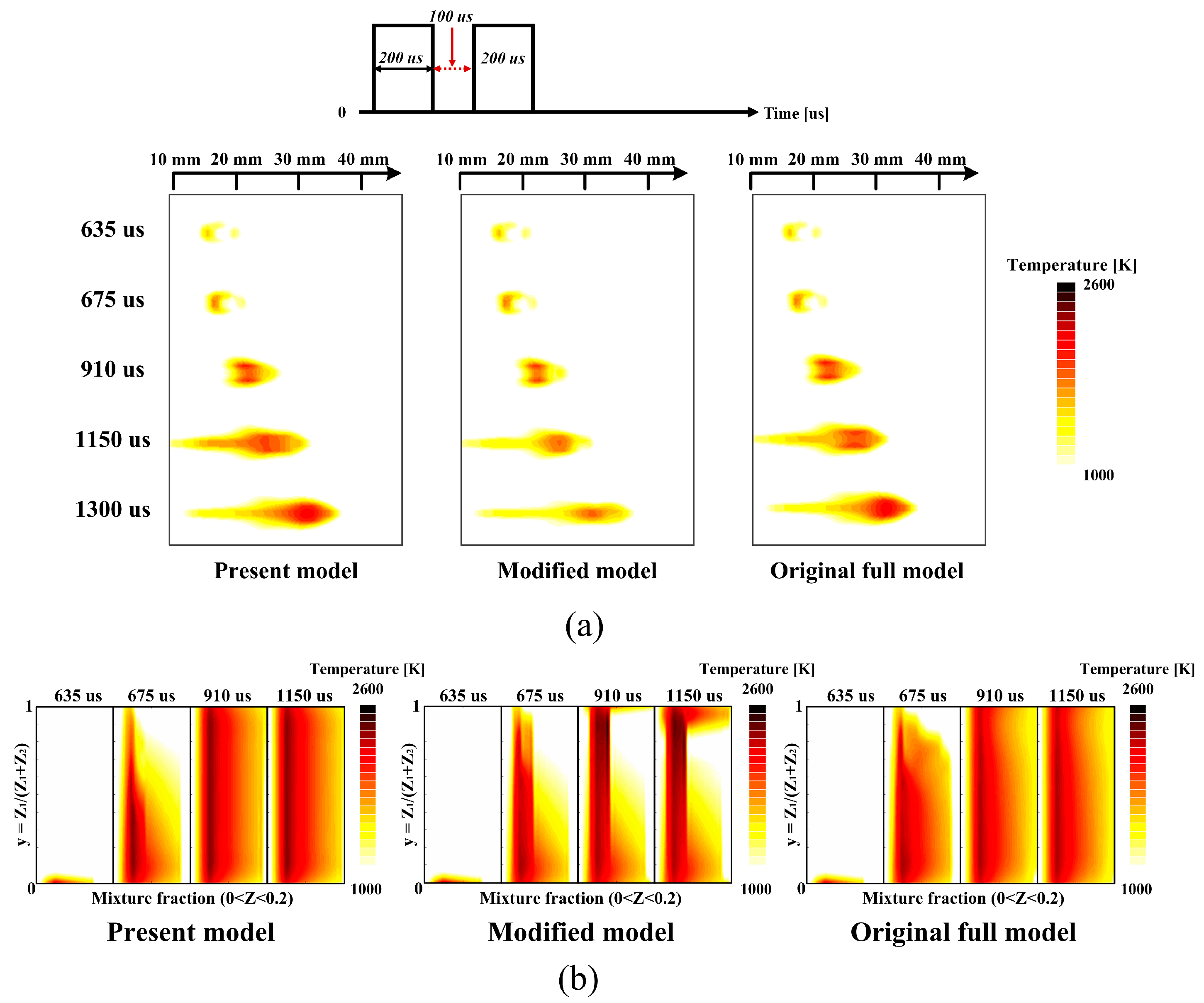
4.1. Validation of Modified 2-D Flamelet Model under Base Conditions
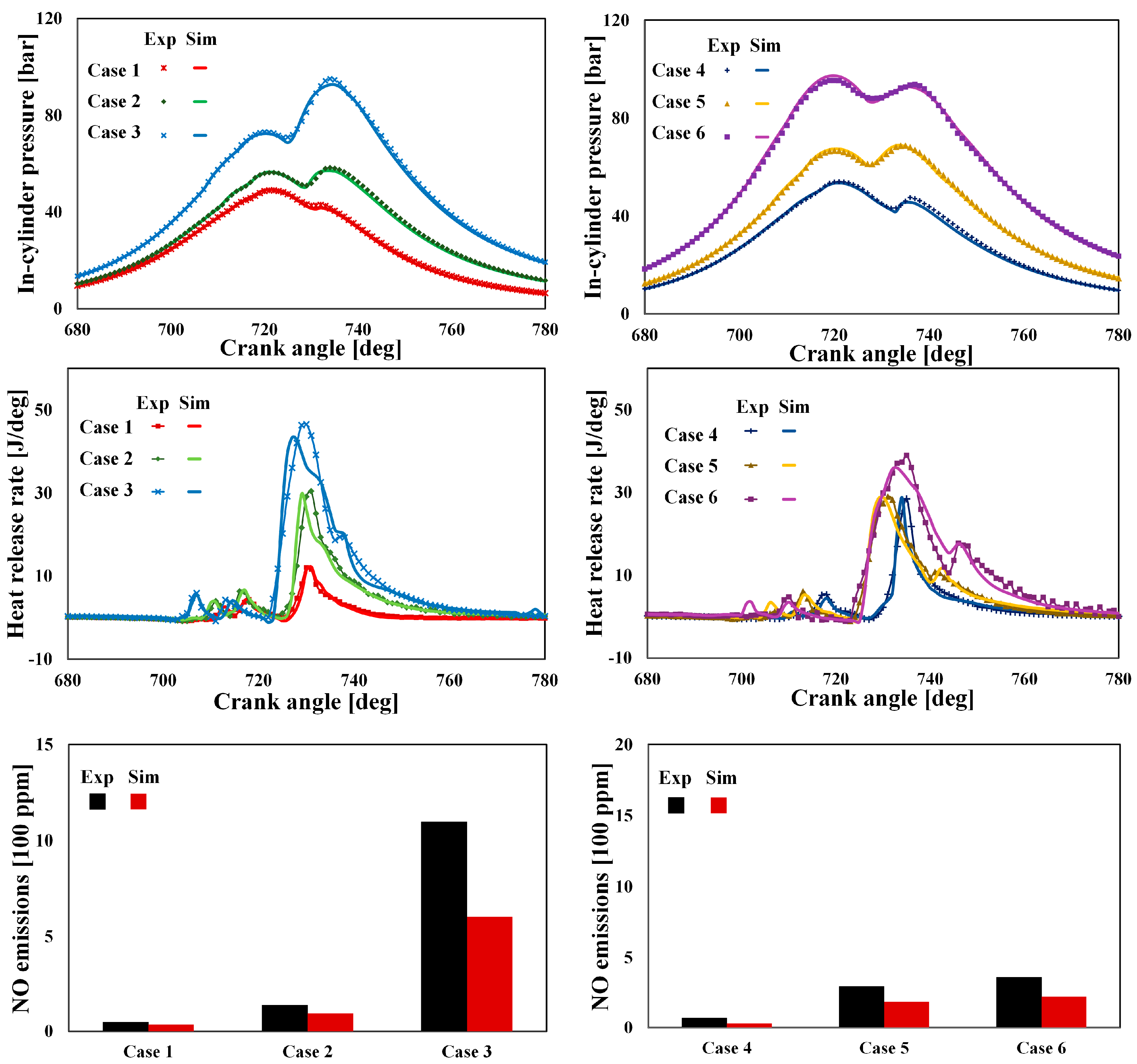
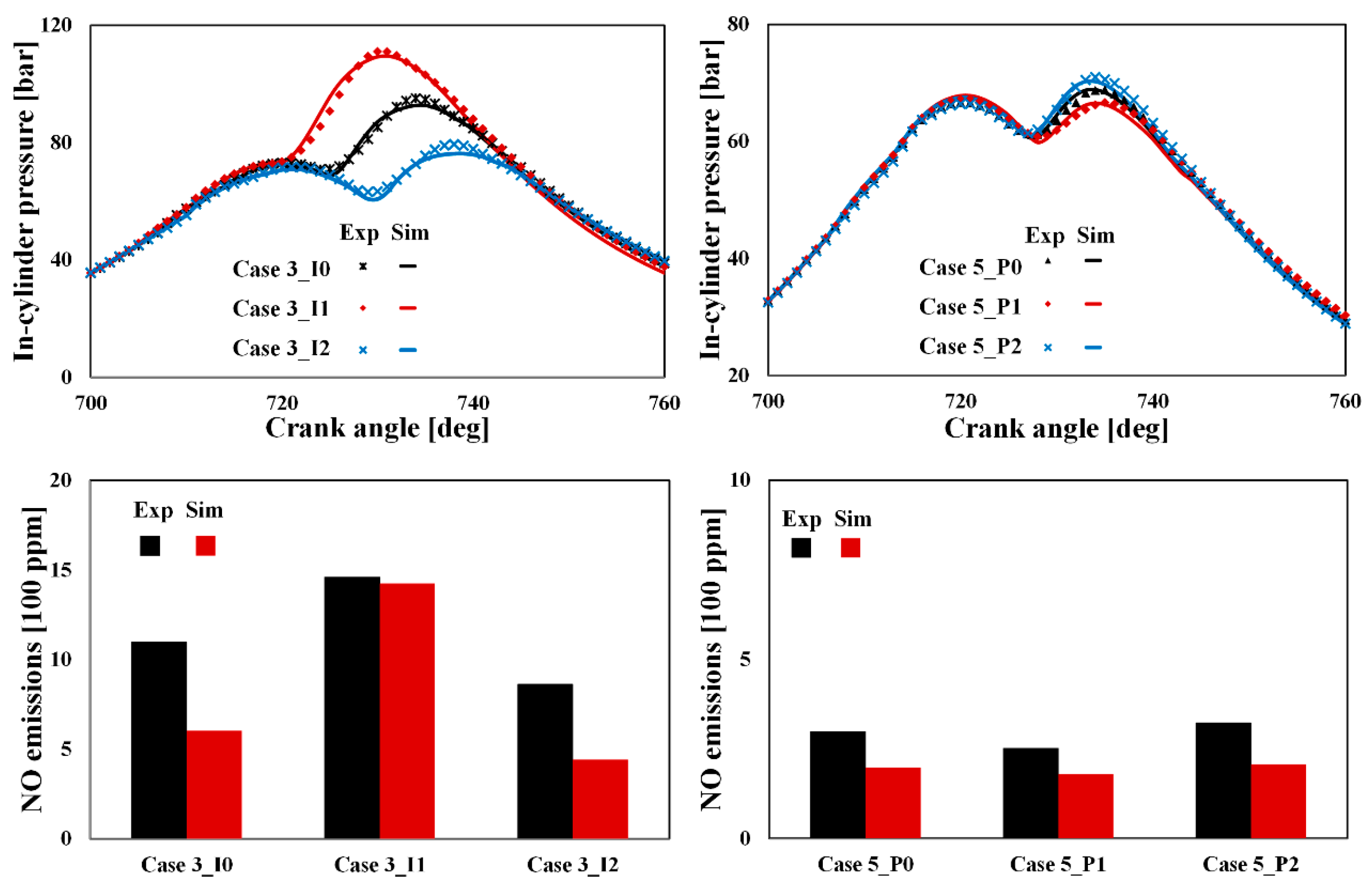
4.2. Validation of Injection Parameter Variations
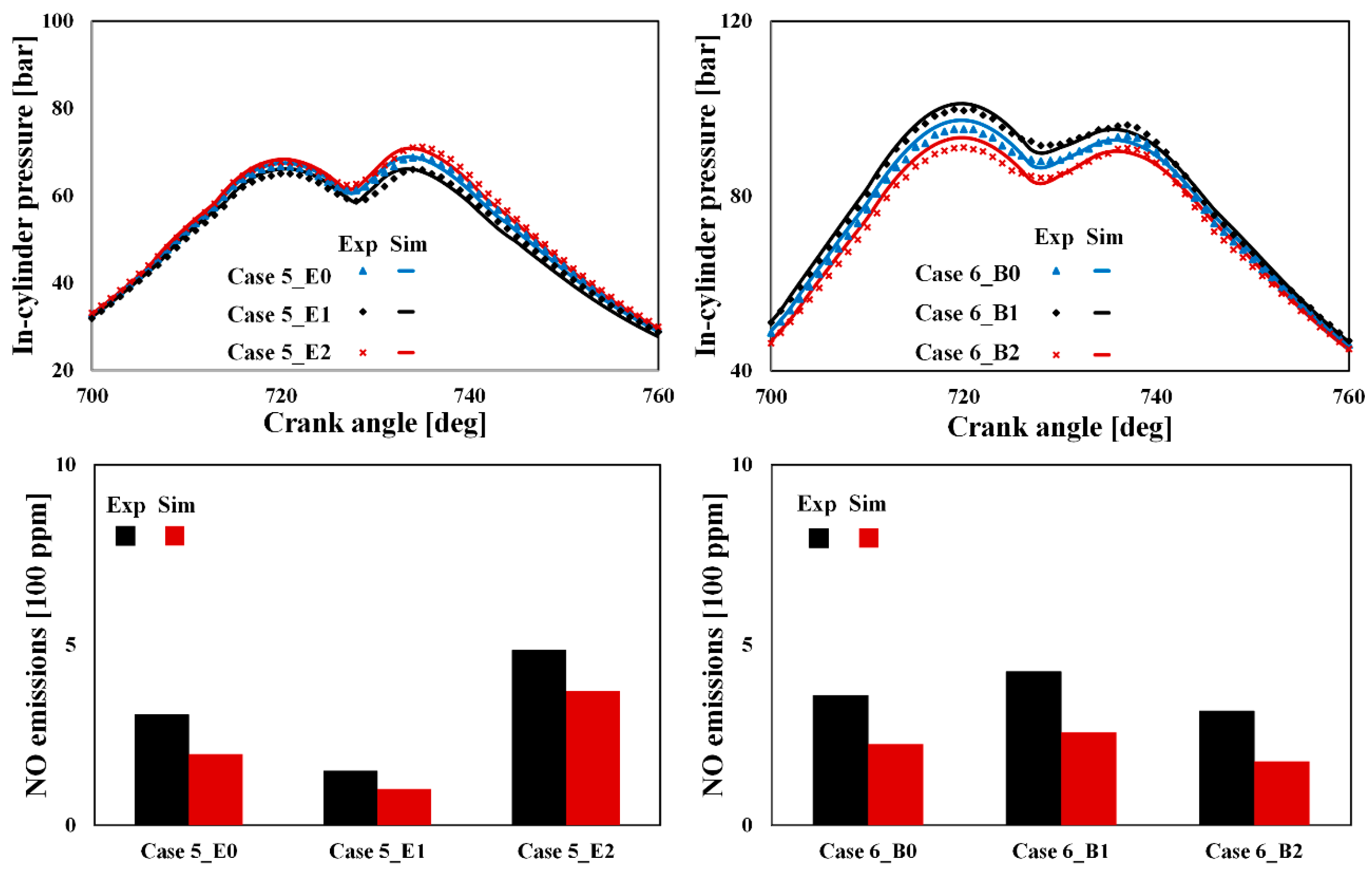
4.3. Validation of in-Cylinder Mixture Variations
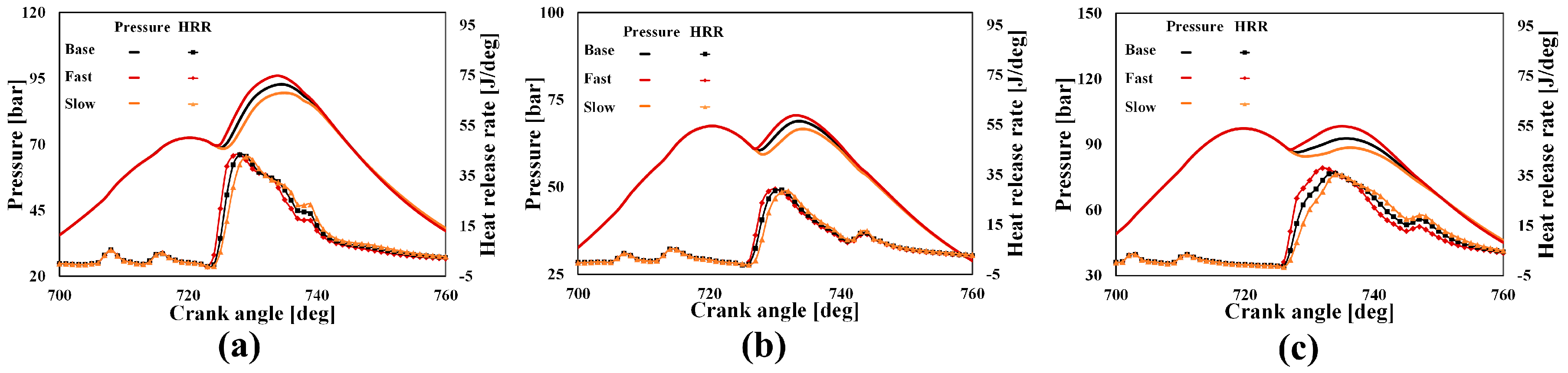
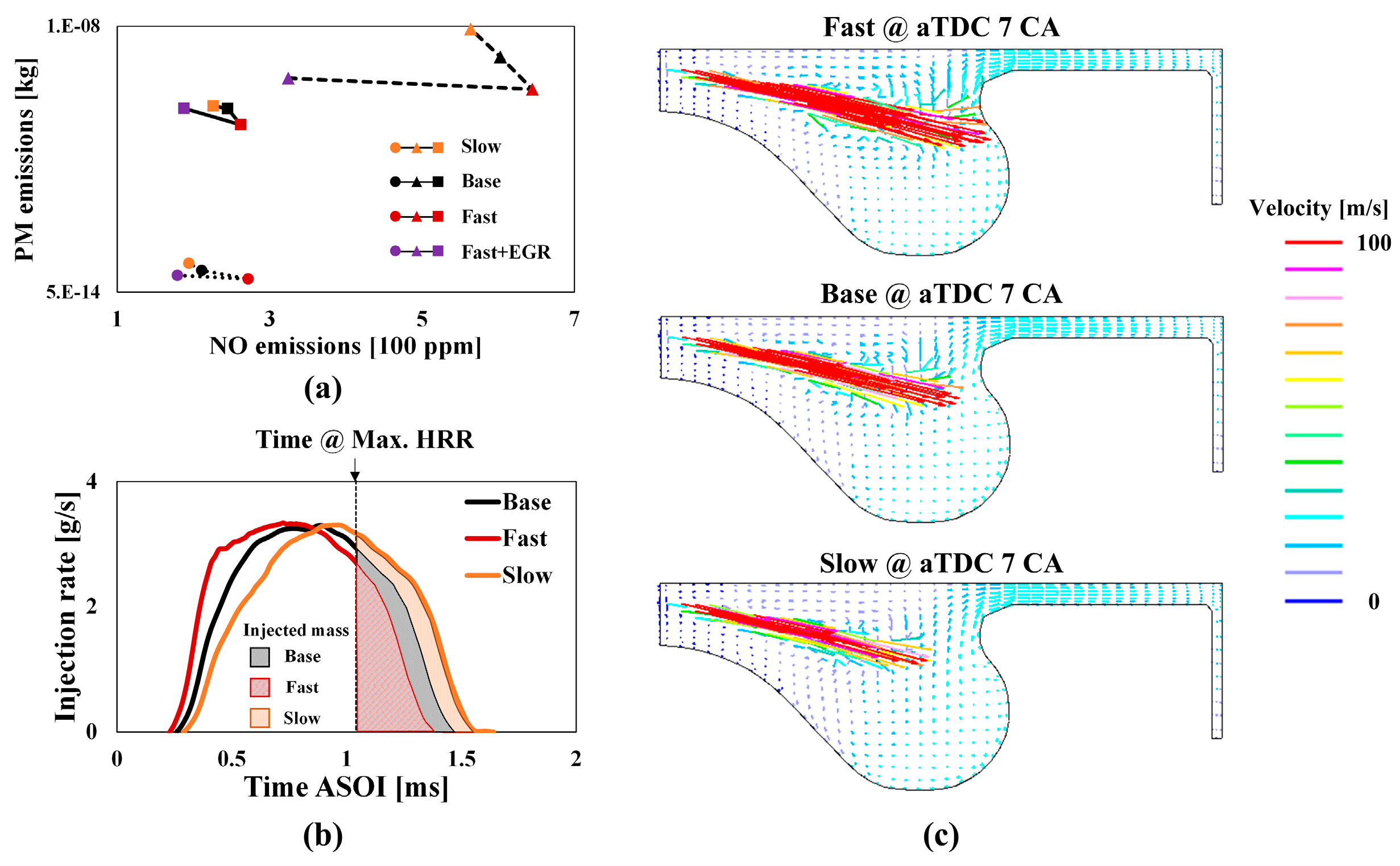
4.4. Numerical Analysis on the Effect of Injection Rate Shaping on Engine-Out Emissions
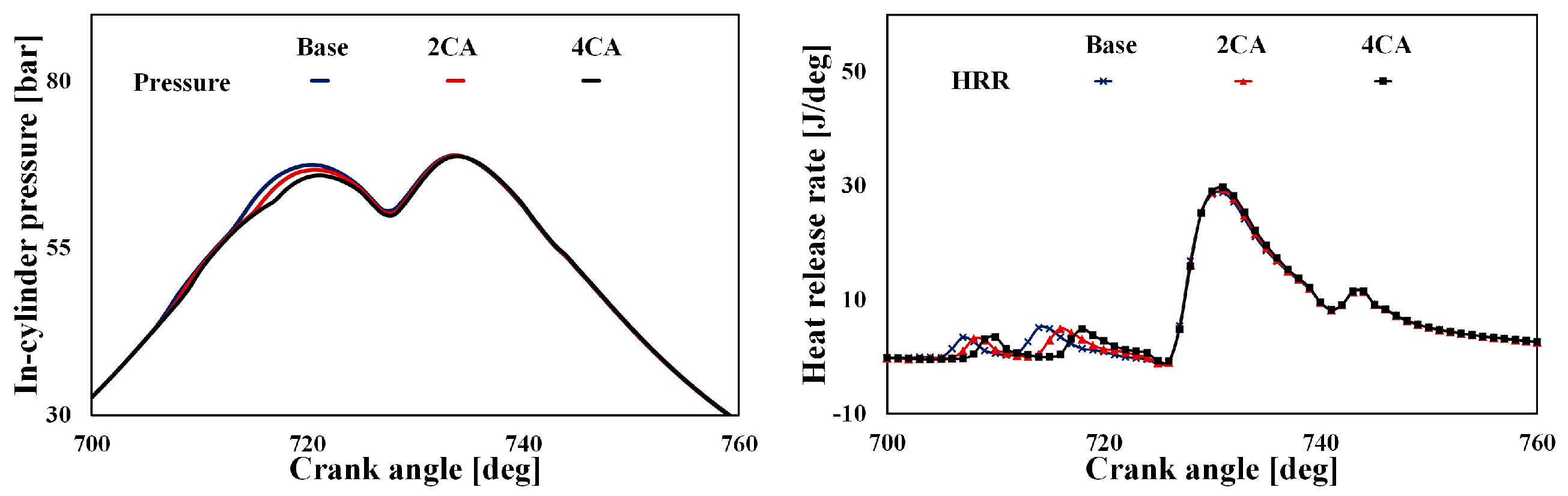
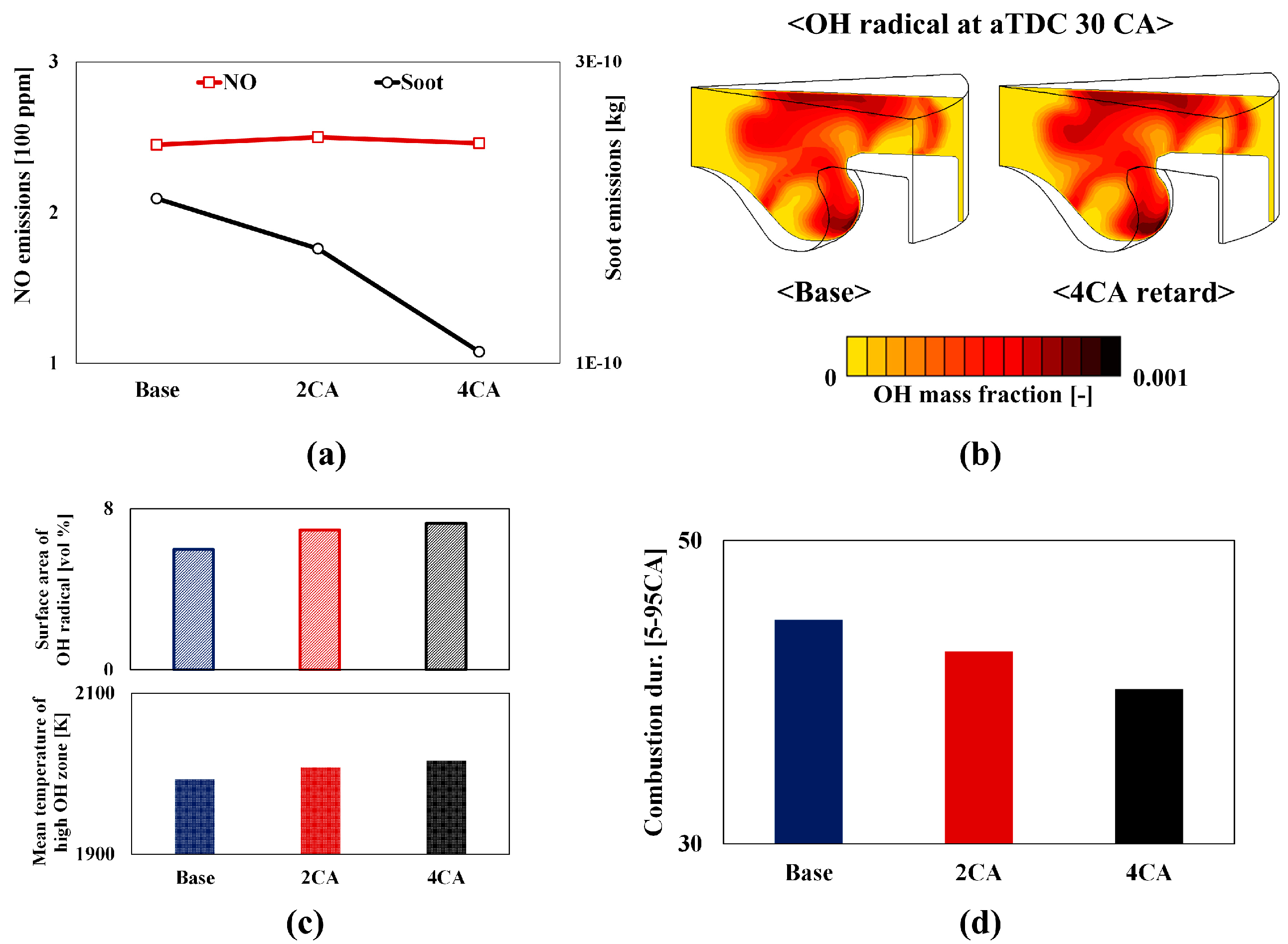
4.5. Numerical Analyses on the Effect of Dwell Time on NOx and Soot Emissions
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 1-D | One dimensional |
| 2-D | Two dimensional |
| 3-D | Three dimensional |
| a constant in Equation (10) | |
| a constant in Equation (10) | |
| aBDC | after Bottom Dead Center |
| aTDC | after Top Dead Center |
| bBDC | before Bottom Dead Center |
| BDC | Bottom Dead Center |
| bTDC | before Top Dead Center |
| CA | Crank Angle (degree) |
| CFD | Computational Fluid Dynamics |
| mean specific heat at constant pressure (J/kg·K) | |
| CPU | Central Processing Unit |
| D | scalar diffusion coefficient (m2/s) |
| DNS | Direct Numerical Simulation |
| EGR | Exhaust Gas Recirculation |
| erfc | complimentary error function in Equation (10) |
| EVC | exhaust valve close |
| EVO | exhaust valve open |
| exp | exponential function |
| h | enthalpy (J) |
| I | Interaction parameter |
| IVC | intake valve close |
| IVO | intake valve open |
| Le | Lewis number (-) |
| OH | hydroxide |
| RIF | Representative Interactive Flamelet |
| RNG | Re-Normalization Group |
| chemical production rate | |
| MI | Main injection |
| MFB | Mass fraction burned |
| N | Number of fuel streams |
| NO | nitric monoxide |
| NOx | nitric oxides |
| p | Pressure (bar) |
| probability density function | |
| Probability Density Function | |
| PI | Pilot Injection |
| PM | Particulate Matter |
| Po | Post injection |
| Radiative heat flux | |
| RANS | Reynolds-Averaged Navier-Stokes |
| RPM | Revolution per minute |
| t | time (s) |
| TDC | Top Dead Center |
| V | volume (m3) |
| spatial coordinate | |
| Y | species mass fraction |
| y | mixing parameter (-) |
| Z | overall mixture fraction (-) |
| mean mixture fraction | |
| Greek Symbols | |
| density (kg/m3) | |
| instantaneous scalar dissipation rate (1/s) | |
| joint scalar dissipation rate (1/s) | |
| domain averaged scalar dissipation rate conditioned on stoichiometric mixture (1/s) | |
| Subscripts | |
| 1 | fuel stream 1 |
| 2 | fuel stream 2 |
| i | ith species |
| j | jth fuel stream |
| k | kth species |
| st | stoichiometric mixture |
References
- Heywood, J.B. Combustion in compression-ignition engines. In Internal Combustion Engine Fundamentals; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 491–566. ISBN 0-07-100499-8. [Google Scholar]
- Stanglmaier, R.; Roberts, C. Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition (HCCI): Benefits, Compromises, and Future Engine Applications; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Reitz, R.D. Spray Targeting to Minimize Soot and CO Formation in Premixed Charge Compression Ignition (PCCI) Combustion with a HSDI Diesel Engine; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kokjohn, S.L.; Hanson, R.M.; Splitter, D.A.; Reitz, R.D. Fuel reactivity controlled compression ignition (RCCI): A pathway to controlled high-efficiency clean combustion. Int. J. Eng. Res. 2011, 12, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sarli, V.; Di Benedetto, A. Modeling and simulation of soot combustion dynamics in a catalytic diesel particulate filter. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 137, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sarli, V.; Landi, G.; Lisi, L.; Saliva, A.; Di Benedetto, A. Catalytic diesel particulate filters with highly dispersed ceria: Effect of the soot-catalyst contact on the regeneration performance. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 197, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tow, T.C.; Pierpont, D.A.; Reitz, R.D. Reducing Particulate and NOx Emissions by Using Multiple Injections in a Heavy Duty DI Diesel Engine; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Shundoh, S.; Komori, M.; Tsujimura, K.; Kobayashi, S. NOx Reduction from Diesel Combustion Using Pilot Injection with High Pressure Fuel Injection; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Nehmer, D.A.; Reitz, R.D. Measurement of the Effect of Injection Rate and Split Injections on Diesel Engine Soot and NOx Emissions; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S. Simultaneous Reduction of NOx and Particulate Emissions by Using Multiple Injections in a Small Diesel Engine; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Miyaki, M.; Fujisawa, H.; Masuda, A.; Yamamoto, Y. Development of New Electronically Controlled Fuel Injection System ECD-U2 for Diesel Engine; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Guerrassi, N.; Dupraz, P. A Common Rail Injection System for High Speed Direct Injection Diesel Engines; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Benajes, J.; Molina, S.; Garcia, J. Influence of Pre- and Post-Injection on the Performance and Pollutant Emissions in a HD Diesel Engine; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Payri, R.; Benajes, J.; Molina, S.; Soare, V. Investigation of the influence of injection rate shaping on the spray characteristics in a diesel common rail system equipped with a piston amplifier. J. Fluids Eng. 2005, 127, 1102–1110. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi, G.M.; Pelloni, P.; Corcione, F.E.; Luppino, F. Numerical Analysis of Passenger Car HSDI Diesel Engines with the 2nd Generation of Common Rail Injection Systems: The Effect of Multiple Injections on Emissions; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Corcione, F.E.; Vaglieco, B.M.; Corcione, G.E.; Lavorgna, M. Potential of Multiple Injection Strategy for Low Emission Diesel Engines; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid, M.; Leipertz, A.; Fettes, C. Influence of Nozzle Hole Geometry, Rail Pressure and Pre-Injection on Injection, Vaporisation and Combustion in a Single-Cylinder Transparent Passenger Car Common Rail Engine; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Patterson, M.A.; Kong, S.C.; Hampson, G.J.; Reitz, R.D. Modeling the Effects of Fuel Injection Characteristics on Diesel Engine Soot and NOx Emissions; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Z.; Uludogan, A.; Hampson, G.J.; Reitz, R.D. Mechanism of Soot and NOx Emission Reduction Using Multiple-Injection in a Diesel Engine; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y. A numerical study of multiple fuel injection strategies for NOx reduction from DI Diesel engines. Int. J. Green Energy 2007, 4, 453–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, N. Laminar diffusion flamelet models in a non-premixed turbulent combustion. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 1984, 10, 319–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasse, C.; Peters, N. A two mixture fraction flamelet model applied to split injections in a DI Diesel engine. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2005, 30, 2755–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitsch, H.; Wan, Y.P.; Peters, N. Numerical Investigation of Soot Formation and Oxidation under Diesel Engine Conditions; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, J.; Lee, S.; Min, K. Combustion modelling of split injection in HSDI Diesel engines. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2010, 183, 180–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Min, K. Numerical Study on the Multiple Injection Strategy in Diesel Engines Using a Modified 2-D Flamelet Model; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Felsch, C.; Gauding, M.; Hasse, C.; Vogel, S.; Peters, N. An extended flamelet model for multiple injections in DI Diesel engines. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2009, 32, 2775–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, V.; Cook, D.J.; Pitsch, H. An extended multi-regime flamelet model for IC engines. Combust. Flame 2012, 159, 2767–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doran, E.M.; Pitsch, H.; Cook, D.J. A priori testing of two-dimensional unsteady flamelet model for three-feed combustion systems. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2013, 34, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitsch, H.; Barths, H.; Peters, N. Three-Dimensional Modelling of NOx and Soot Formation in DI-Diesel Engines Using Detailed Chemistry Based on the Interactive Flamelet Approach; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Hergart, C.; Barths, H.; Peters, N. Modeling the Combustion in a Small-Bore Diesel Engine Using a Method Based on Representative Interactive Flamelets; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Pitsch, H.; Riesmeier, E.; Peters, N. Unsteady flamelet modelling of soot formation in turbulent diffusion flames. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2000, 158, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y. Numerical modelling for auto-ignition and combustion process of fuel sprays in high-pressure environment. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2001, 168, 85–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, W.P.; Whitelaw, J.H. Calculation methods for reacting turbulent flows: A review. Combust. Flame 1982, 48, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitsch, H.; Chen, M.; Peters, N. Unsteady flamelet modelling of turbulent hydrogen-air diffusion flames. Symposium (Int.) Combust. 1998, 27, 1057–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girimaji, S.S. Assumed β-pdf model for turbulent mixing: Validation and extension to multiple scalar mixing. Combust. Sci. Technol. 1991, 78, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kee, R.J.; Rupley, F.M.; Miller, J.A. The Chemkin Thermodynamic Data Base. No. SAND-87-8215B, Technical Report; USA, 1990. Available online: https://www.osti.gov/scitech/biblio/7073290-chemkin-thermodynamic-data-base/ (accessed on 28 August 2017).
- Yakhot, V.; Orszag, S.A. Renormalization group analysis of turbulence. I. Basic theory. J. Sci. Comput. 1986, 1, 3–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Kong, S.C.; Reitz, R.D. Development and Validation of a Reduced Reaction Mechanism for HCCI Engine Simulations; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- GRI-Mech 3.0. Available online: http://www.me.berkeley.edu/gri_mech/ (accessed on 17 July 2017).
- Reitz, R.D.; Diwakar, R. Effect of Drop Breakup on Fuel Sprays; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Bardi, M.; Payri, R.; Malbec, L.M.; Bruneaux, G.; Pickett, L.M.; Manin, J.; Bazyn, T.; Genzale, C.L. Engine combustion network: Comparison of spray development vaporization, and combustion in different combustion vessels. At. Sprays 2012, 22, 807–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, P.L.; Bürgler, L.; Winklhofer, E.; Zelenka, P.; Cartellieri, W. NOx Reduction Strategies for DI Diesel Engines; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Desantes, J.M.; Benajes, J.; Molina, S.; Gonzelez, C.A. The modification of the fuel injection rate in heavy-duty diesel engines. Part 1: Effect on engine performance and emissions. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2004, 24, 2701–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikemoto, M.; Omae, K.; Shimode, K.; Toda, N. Diesel spray and combustion development using nozzle flow visualization, spray and combustion analyses. In Proceedings of the International Conference: SIA Powertrain—Rouen 2016, Rouen, France, 1–2 June 2016; Available online: http://www.sia.fr/evenements/12-sia-powertrain-rouen-2016?calendrier=1#planning/ (accessed on 28 July 2017).
- Hardy, W.L.; Reitz, R.D. An Experimental Investigation of Partially Premixed Combustion Strategies Using Multiple Injections in a Heavy-Duty Diesel Engine; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Poorghasemi, K.; Ommi, F.; Yaghmaei, H.; Namaki, A. An investigation of high pressure post injection on soot and NO emissions in a DI diesel engine. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2012, 26, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diwakar, R.; Domenech-Llopis, V. Physics of Combustion Noise Reduction with Multiple Injections in a DI Diesel Engine—A Computational Study; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.; Yoon, S.; Lee, C. Impact of split injection strategy on the exhaust emissions and soot particulates from a compression ignition engine fueled with neat biodiesel. Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 1260–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Bore | 77.2 mm |
| Stroke | 84.5 mm |
| Connecting rod length | 140.0 mm |
| Displacement | 1592 cc (396 cc/cylinder) |
| Compression ratio | 17.3:1 |
| Piston bowl shape | ω-type |
| IVO/IVC | aTDC 17 CA/aBDC 14 CA |
| EVO/EVC | bBDC 23 CA/bTDC 20 CA |
| Injection system | Common-rail with solenoid injector |
| Spray angle | 156° |
| Injector hole diameter | 0.124 mm |
| Injector number of holes | 7 |
| Case | RPM | Fuel Mass (mg) | EGR Rate (%) | Injection Strategies | Equivalent Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1500 | 4 | 35.4 | Triple Injection (PI/PI/MI) | 0.29 |
| 2 | 1500 | 13.5 | 22.6 | 0.67 | |
| 3 | 1500 | 26.6 | 0 | Quadruple Injection (PI/PI/MI/Po) | 0.73 |
| 4 | 2000 | 8.85 | 33 | Triple Injection (PI/PI/MI) | 0.52 |
| 5 | 2000 | 17.1 | 16.1 | Quadruple Injection (PI/PI/MI/Po) | 0.62 |
| 6 | 2500 | 28.2 | 10.4 | 0.65 |
| Case | Details of Parametric Variations |
|---|---|
| 3-I1 | Injection timing Δ = −4 CA from case 3 |
| 3-I2 | Injection timing Δ = +4 CA from case 3 |
| 5-P1 | Injection pressure Δ = −100 bar from case 5 |
| 5-P2 | Injection pressure Δ = +100 bar from case 5 |
| 5-E1 | EGR rate Δ = −8% (abs.) from case 5 |
| 5-E2 | EGR rate Δ = +8% (abs.) from case 5 |
| 6-B1 | Boost pressure Δ = −4% (rel.) from case 6 |
| 6-B2 | Boost pressure Δ = +4% (rel.) from case 6 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, G.; Moon, S.; Lee, S.; Min, K. Numerical Analysis of the Combustion and Emission Characteristics of Diesel Engines with Multiple Injection Strategies Using a Modified 2-D Flamelet Model. Energies 2017, 10, 1292. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10091292
Kim G, Moon S, Lee S, Min K. Numerical Analysis of the Combustion and Emission Characteristics of Diesel Engines with Multiple Injection Strategies Using a Modified 2-D Flamelet Model. Energies. 2017; 10(9):1292. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10091292
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Gyujin, Sunyoung Moon, Seungha Lee, and Kyoungdoug Min. 2017. "Numerical Analysis of the Combustion and Emission Characteristics of Diesel Engines with Multiple Injection Strategies Using a Modified 2-D Flamelet Model" Energies 10, no. 9: 1292. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10091292
APA StyleKim, G., Moon, S., Lee, S., & Min, K. (2017). Numerical Analysis of the Combustion and Emission Characteristics of Diesel Engines with Multiple Injection Strategies Using a Modified 2-D Flamelet Model. Energies, 10(9), 1292. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10091292




