Stochastic Dynamic AC Optimal Power Flow Based on a Multivariate Short-Term Wind Power Scenario Forecasting Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We simultaneously forecast future wind power scenarios of multiple wind farms through the GDFM.
- We forecast the future wind power scenarios as the input to the stochastic OPF to reduce the computational cost by utilizing the common characteristics of correlated scenarios.
- The forecasted future scenarios through the GDFM can represent the spatial and temporal correlations among wind power and can fully capture the uncertainty information of the wind power.
- We modify the ABC algorithm to quickly find the optimal solution of the stochastic dynamic AC OPF problem.
2. Generalized Dynamic Factor Model
2.1. Derivation of the GDFM
2.2. Estimation of the GDFM
2.3. Forecast Using the GDFM
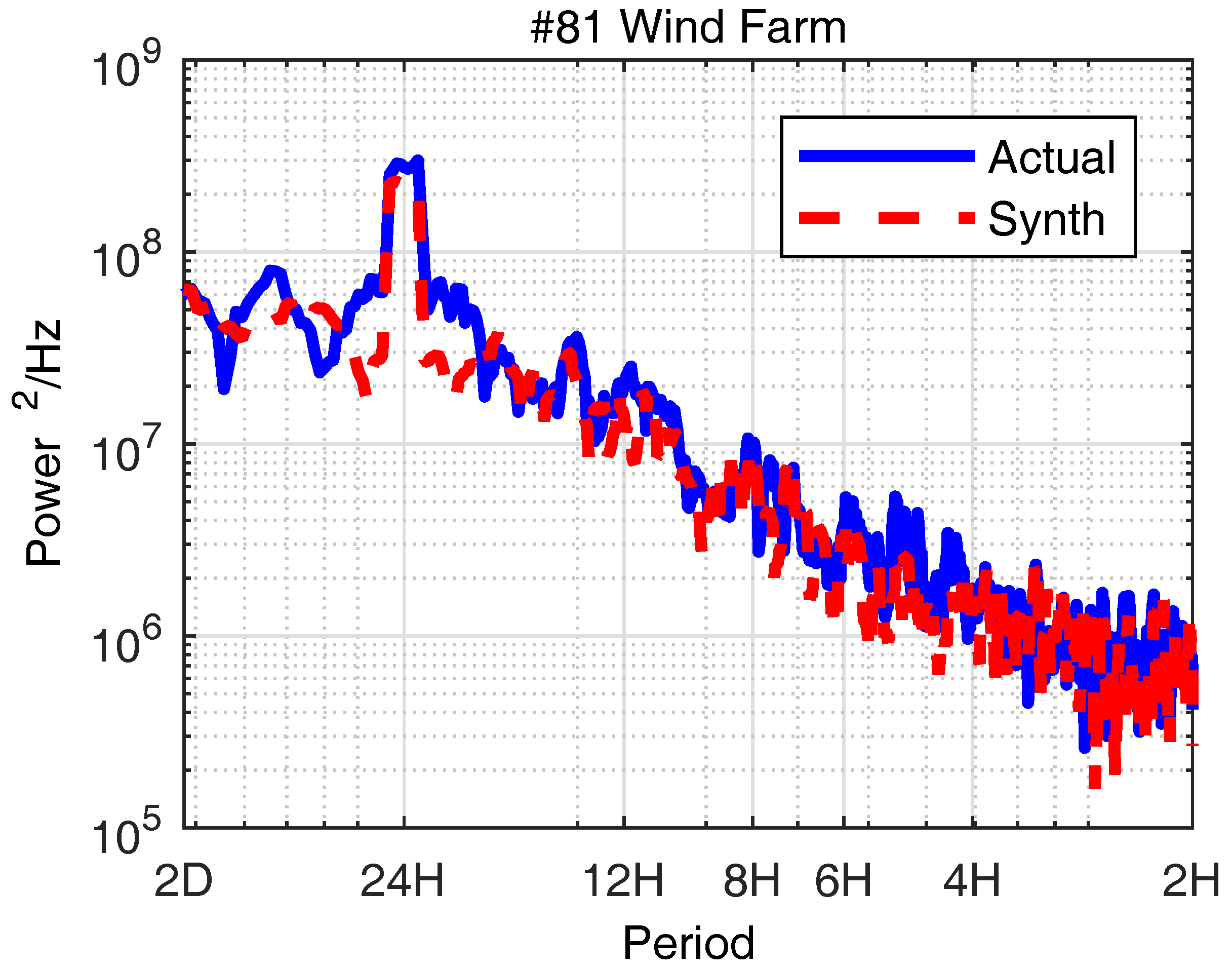
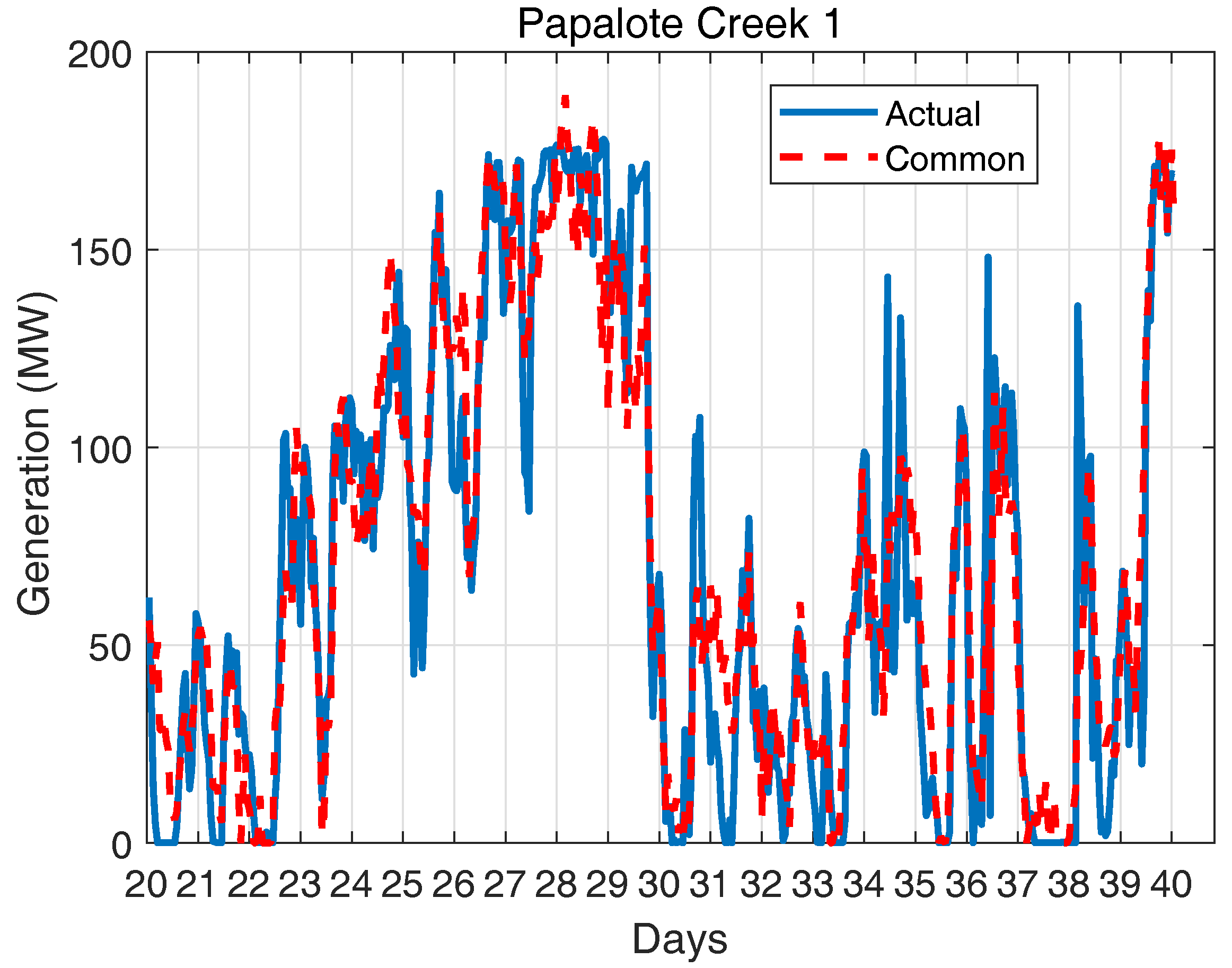
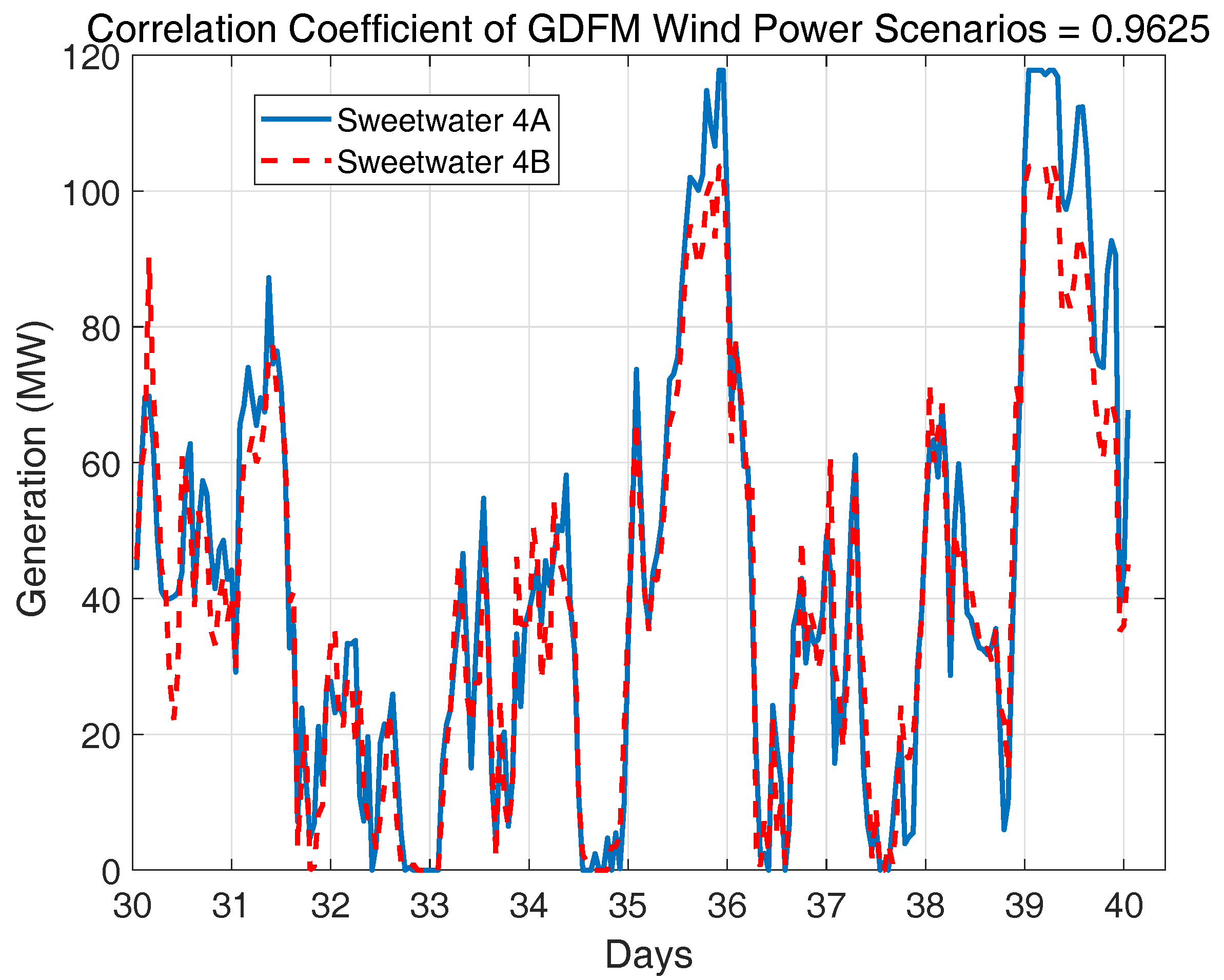
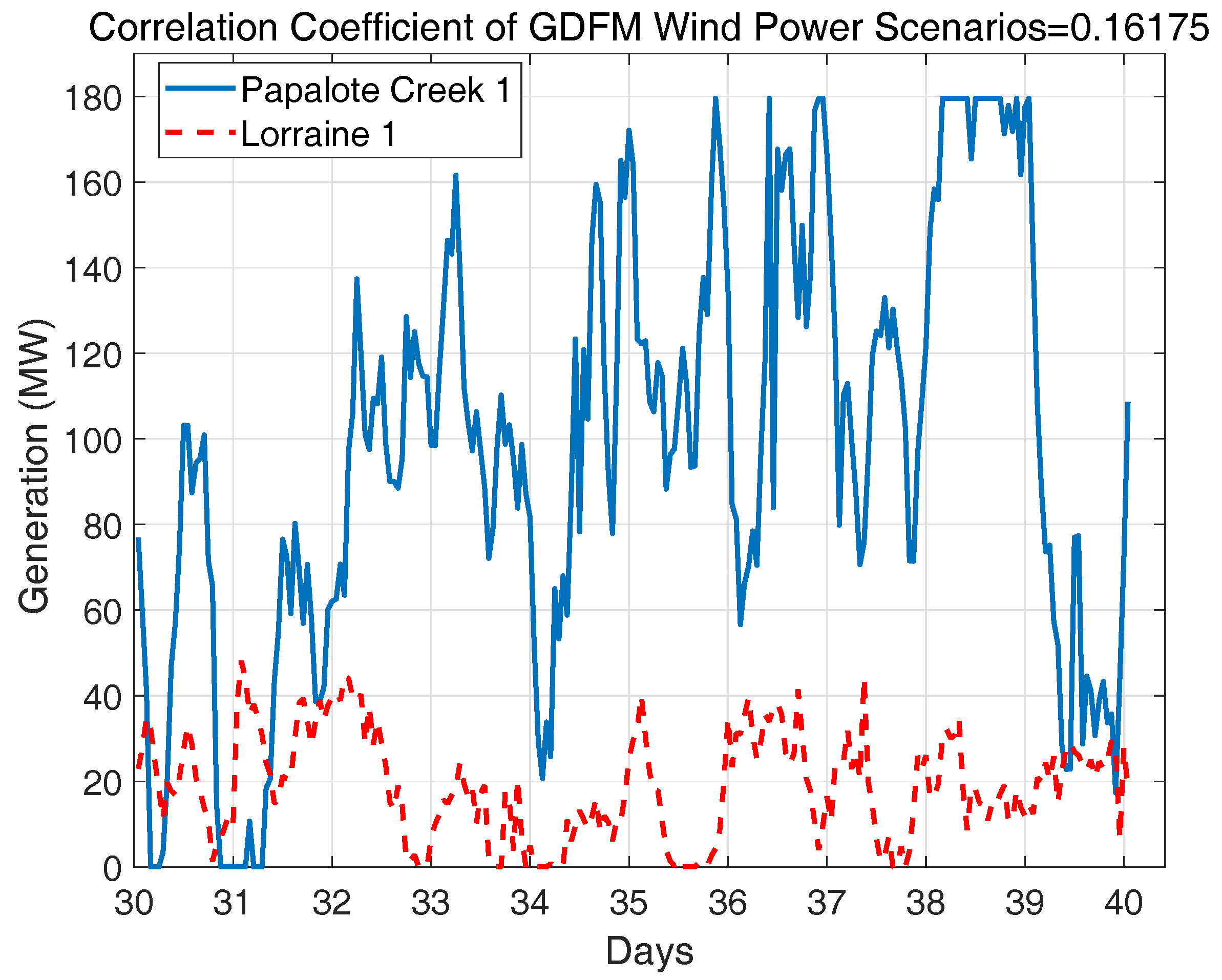
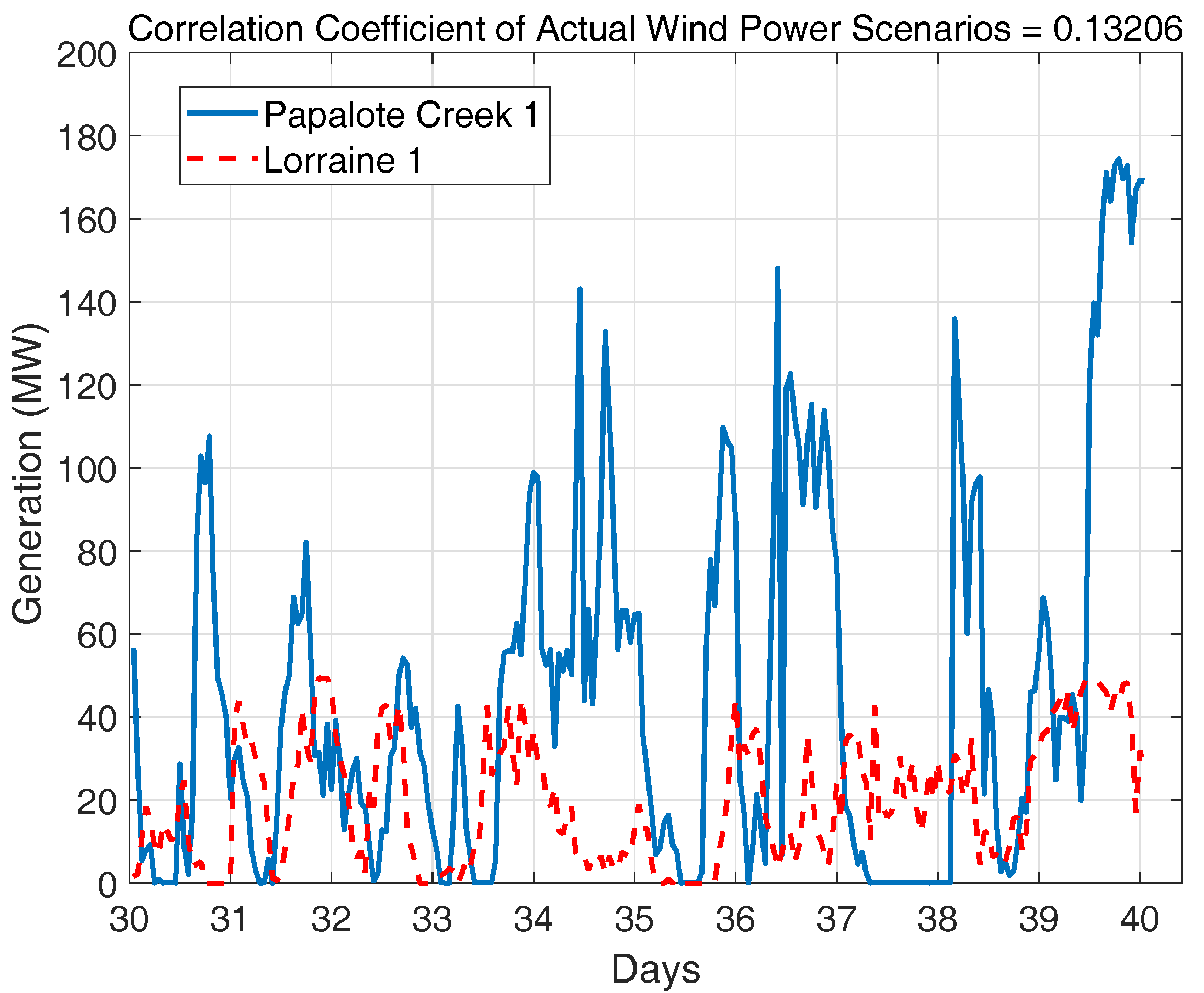
2.4. Verification of the Spatially and Temporally Correlated Scenarios
3. Stochastic Dynamic Optimal Power Flow
4. Solution Methodology
4.1. Original ABC Algorithm
4.2. Modified ABC for the Stochastic Dynamic AC OPF
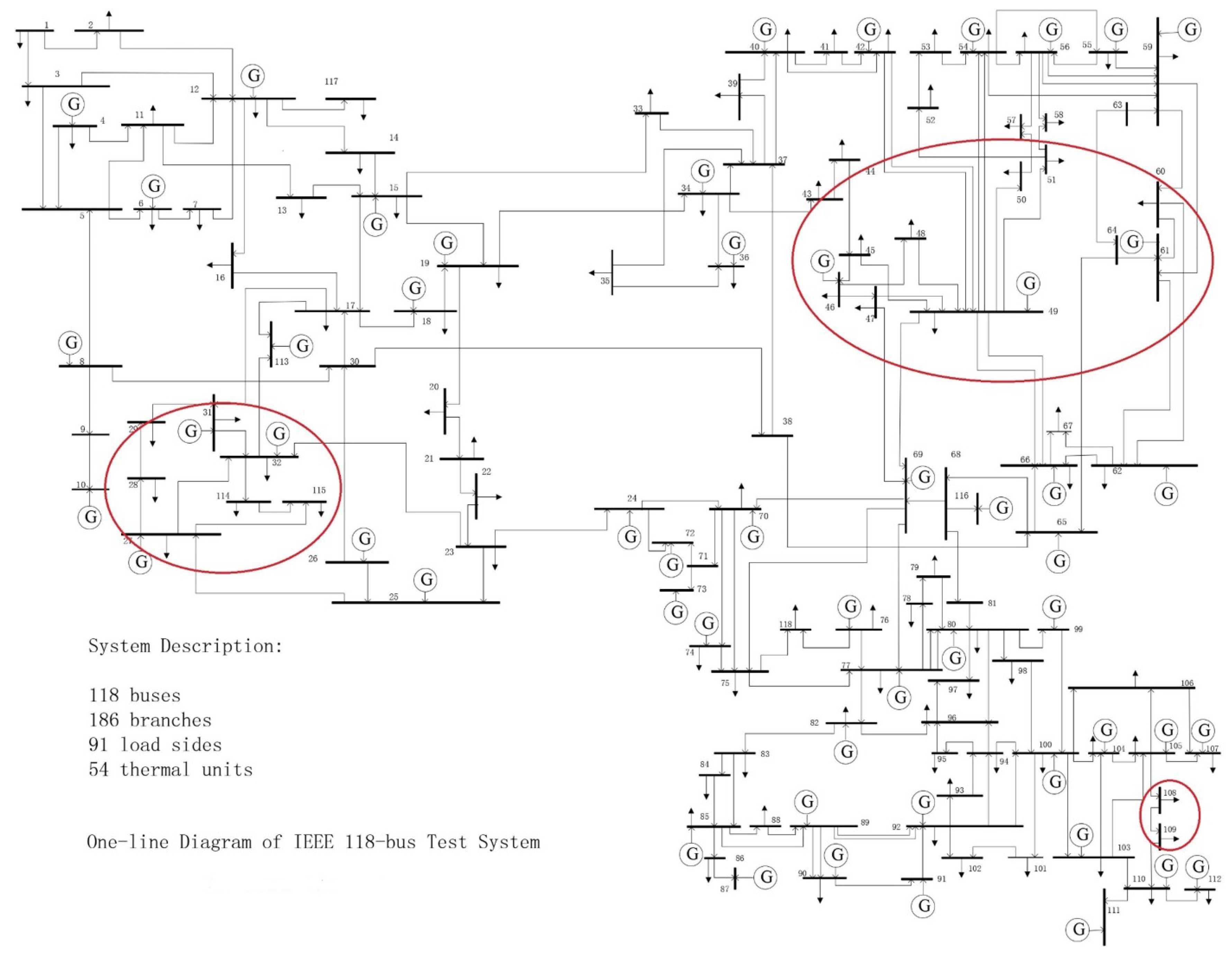
5. Case Studies
5.1. Case 1: Quadratic Fuel Cost Minimization
5.2. Case 2: Loss Minimization
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Calif, R.; Schmitt, F.G. Multiscaling and joint multiscaling of the atmospheric wind speed and the aggregate power output from a wind farm. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 2014, 21, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calif, R.; Schmitt, F.G.; Huang, Y. Multifractal description of wind power fluctuations using arbitrary order Hilbert spectral analysis. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2013, 392, 4106–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Sun, L.; Lee, K.Y. Disturbance rejection control of a fuel cell power plant in a grid-connected system. Control Eng. Pract. 2017, 60, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.; Eke, I.; Lee, K.Y. Heuristic optimization for wind energy integrated optimal power flow. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Power Energy Society General Meeting, Denver, CO, USA, 26–30 July 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, W.; Eke, I.; Lee, K.Y. Improved artificial bee colony based on orthogonal learning for optimal power flow. In Proceedings of the 2015 18th International Conference on Intelligent System Application to Power Systems (ISAP), Porto, Portugal, 11–16 September 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Botterud, A.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, J. Use of Wind Power Forecasting in Operational Decisions; Technical Report ANL/DIS-11-8; Argonne National Laboratory: Chicago, IL, USA, 2011.
- Zhu, X.; Genton, M.G. Short-Term Wind Speed Forecasting for Power System Operations. Int. Stat. Rev. 2012, 80, 2–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, C.; Bessa, R.; Miranda, V.; Botterud, A.; Wang, J. Wind Power Forecasting: State-of-the-Art; Technical Report ANL/DIS-10-1; Argonne National Laboratory: Chicago, IL, USA, 2009.
- Huang, Z.; Chalabi, Z. Use of time-series analysis to model and forecast wind speed. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 1995, 56, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Gu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Genton, M.G. Short-Term Spatio-Temporal Wind Power Forecast in Robust Look-ahead Power System Dispatch. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2014, 5, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, J.; Mínguez, R.; Conejo, A. A methodology to generate statistically dependent wind speed scenarios. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 843–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Baldick, R. Load and Wind Power Scenario Generation Through the Generalized Dynamic Factor Model. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2017, 32, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shahidehpour, M.; Li, Z. Security-Constrained Unit Commitment With Volatile Wind Power Generation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2008, 23, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; El-Sharkawi, A.M. Mordern Heuristic Optimization Techniques: Theory and Applications to Power Systems; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.; Lee, J.; Baldick, R. Wind power scenario generation for stochastic wind power generation and transmission expansion planning. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE PES General Meeting | Conference Exposition, National Harbor, MD, USA, 27–31 July 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Forni, M.; Gambetti, L. The dynamic effects of monetary policy: A structural factor model approach. J. Monetary Econ. 2010, 57, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nieuwenhuyze, C. A Generalised Dynamic Factor Model for the Belgian Economy—Useful Business Cycle Indicators and GDP Growth Forecasts; Technical Report 80; National Bank of Belgium Working Paper; National Bank of Belgium: Brussels, Belgium, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Forni, M.; Hallin, M.; Lippi, M.; Reichlin, L. The Generalized Dynamic Factor Model. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2005, 100, 830–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brillinger, D.R. Time Series: Data Analysis and Theory; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Reinsel, G.C. Elements of Multivariate Time Series Analysis; Spinger and Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Karaboga, D. An Idea Based on Honey Bee Swarm for Numerical optimization; Erciyes University: Kayseri, Turkey, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, W.; Lee, K.Y. Modified optimal power flow on storage devices and wind power integrated system. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), Boston, MA, USA, 17–21 July 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, W.; Abedi, M.R.; Lee, K.Y. Distributed generation system control strategies with PV and fuel cell in microgrid operation. Control Eng. Pract. 2016, 53, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, R.D.; Murillo-Sanchez, C.E.; Thomas, R.J. MATPOWER: Steady-State Operations, Planning, and Analysis Tools for Power Systems Research and Education. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2011, 26, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Park, Y.M.; Ortiz, J.L. A United Approach to Optimal Real and Reactive Power Dispatch. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 1985, PAS-104, 1147–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Electric Reliability Council of Texas. Technical Report. Available online: http://www.ercot.com/gridinfo/load/load_hist/ (accessed on 21 November 2017).
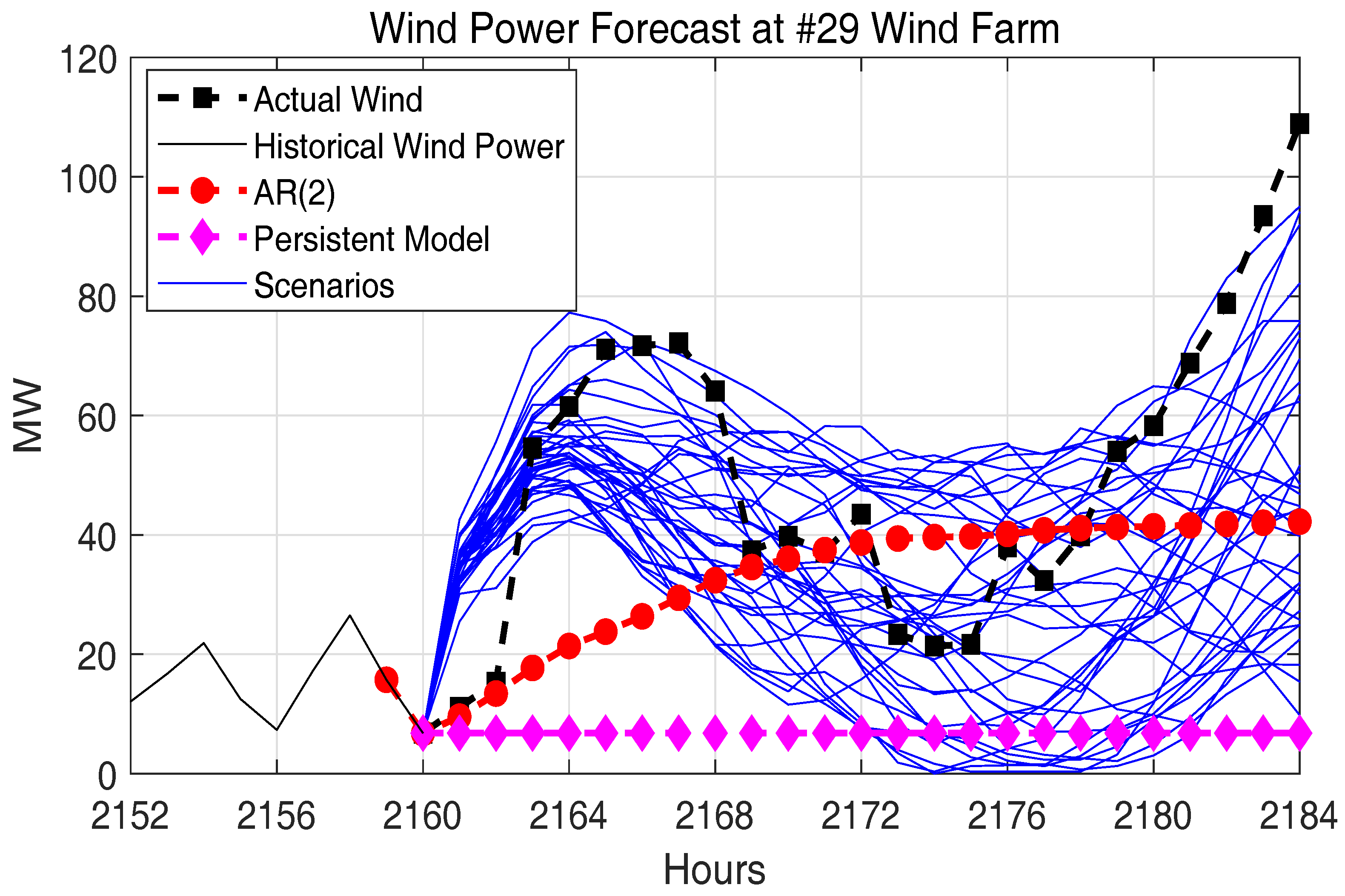
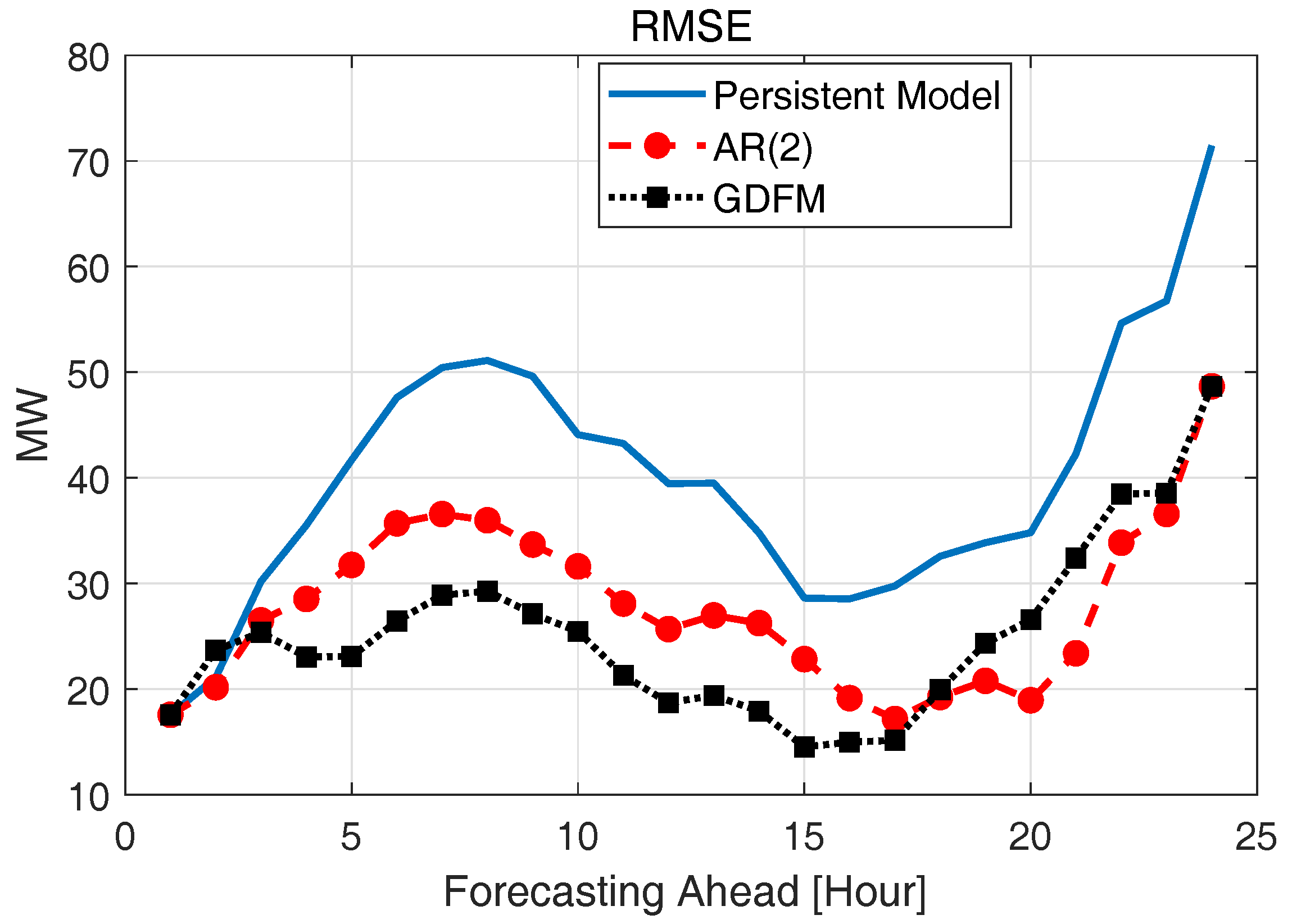
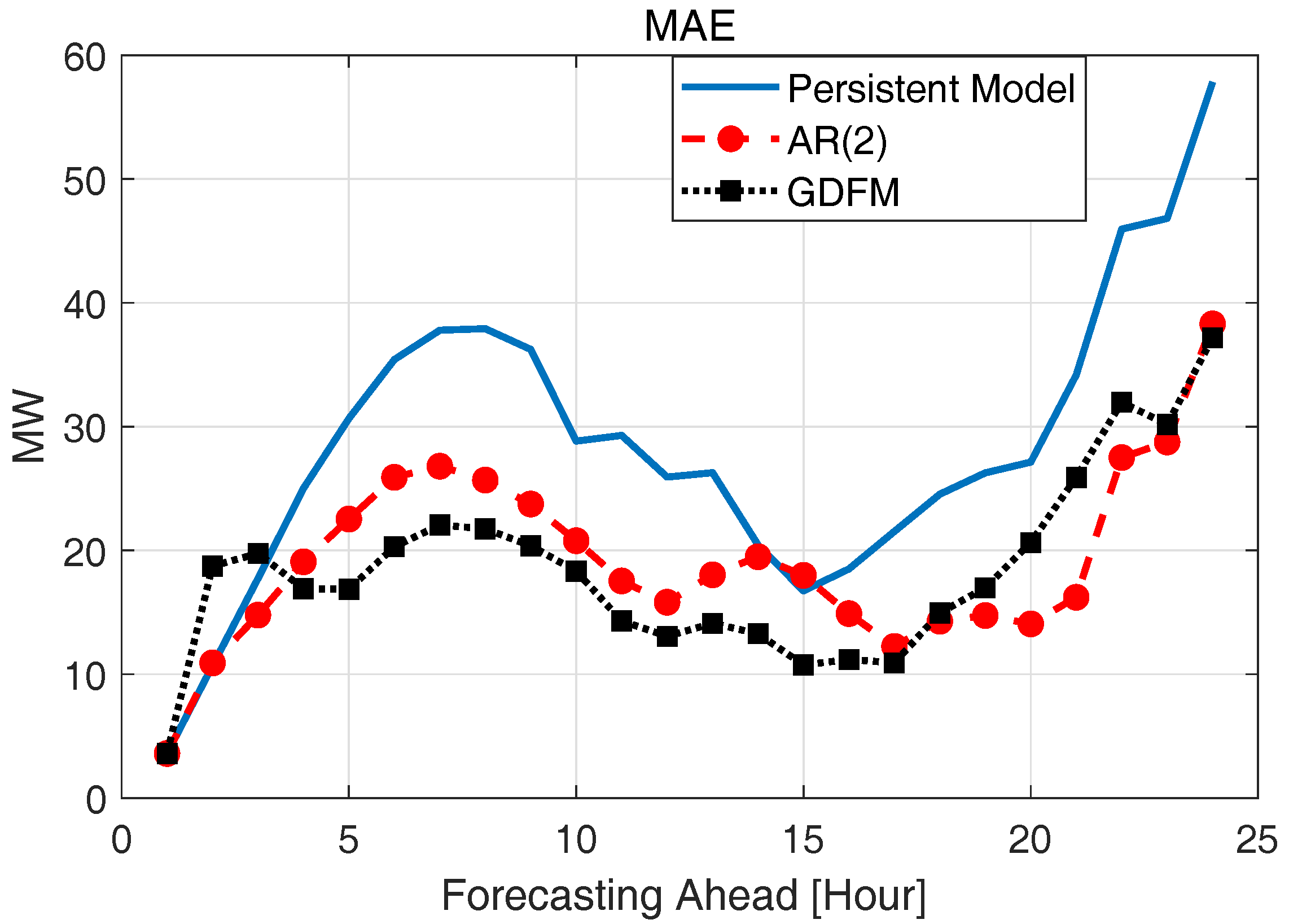


| Methods | Persistent Model | AR(2) | GDFM |
|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE [MW] | 39.9734 | 27.7461 | 25.0448 |
| MAE [MW] | 28.5546 | 19.32 | 18.05 |
| Methods | Random | GDFM | Random | GDFM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Minute) | (Minute) | ($) | ($) | |
| ABC | 305.6 | 56.7 | 3,284,856 | 3,264,344 |
| MABC | 120.3 | 30.3 | 3,254,221 | 3,120,322 |
| Methods | Random | GDFM | Random | GDFM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Minute) | (Minute) | (MW) | (MW) | |
| ABC | 250.4 | 80.5 | 1201.4 | 1193.8 |
| MABC | 110.3 | 42.5 | 1178.5 | 1128.4 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, W.; Lee, D.; Lee, K.Y. Stochastic Dynamic AC Optimal Power Flow Based on a Multivariate Short-Term Wind Power Scenario Forecasting Model. Energies 2017, 10, 2138. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10122138
Bai W, Lee D, Lee KY. Stochastic Dynamic AC Optimal Power Flow Based on a Multivariate Short-Term Wind Power Scenario Forecasting Model. Energies. 2017; 10(12):2138. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10122138
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Wenlei, Duehee Lee, and Kwang Y. Lee. 2017. "Stochastic Dynamic AC Optimal Power Flow Based on a Multivariate Short-Term Wind Power Scenario Forecasting Model" Energies 10, no. 12: 2138. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10122138
APA StyleBai, W., Lee, D., & Lee, K. Y. (2017). Stochastic Dynamic AC Optimal Power Flow Based on a Multivariate Short-Term Wind Power Scenario Forecasting Model. Energies, 10(12), 2138. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10122138






