Energy Recovery Efficiency of Poultry Slaughterhouse Sludge Cake by Hydrothermal Carbonization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
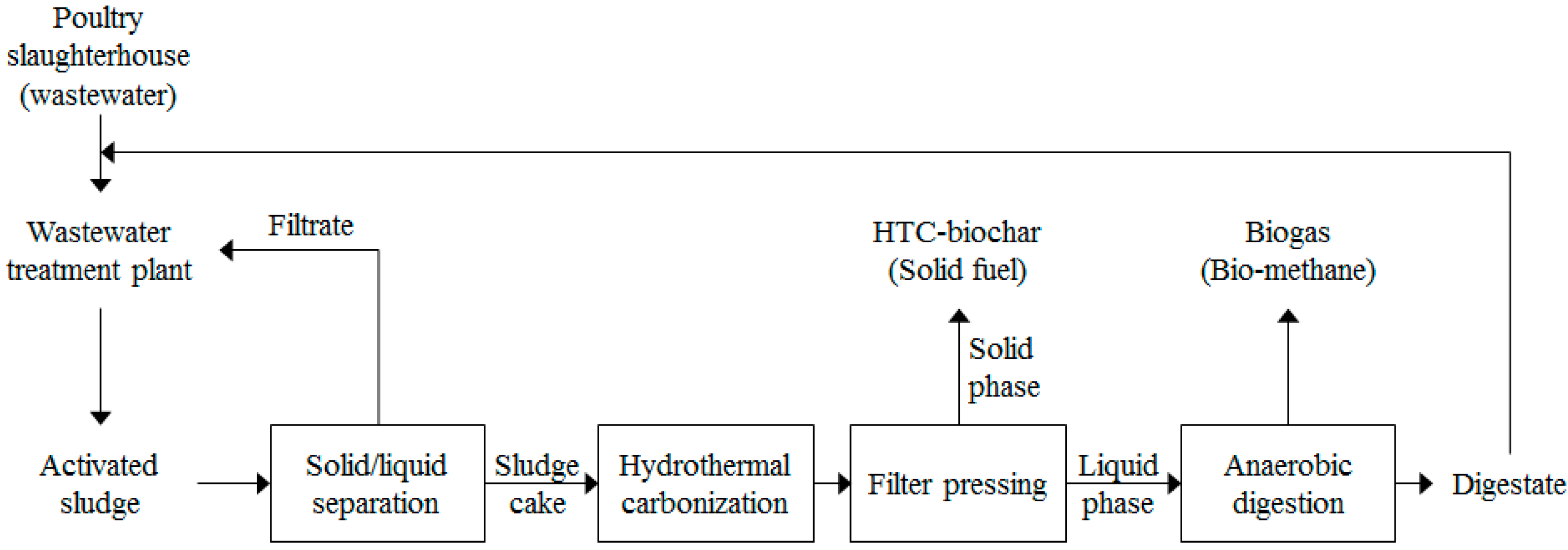
2.2. Proposed Energy Conversion System
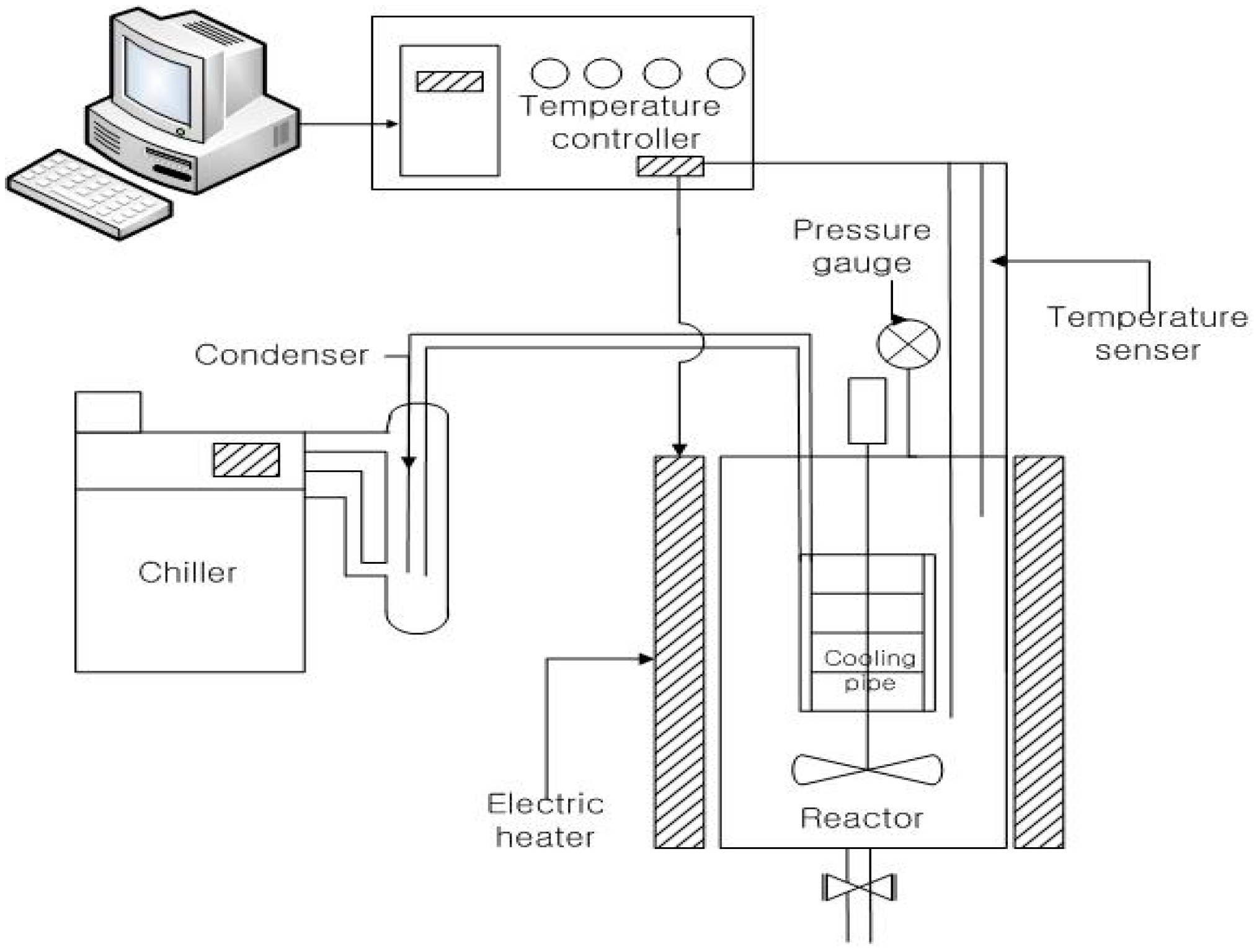
2.3. Hydrothermal Carbonization
2.4. Methane Production Potential of HTC-Hydrolysate
2.5. Analysis
2.6. Efficiency Parameters
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Properties of Sludge Cake
3.2. Physicochemical Properties of HTC-Biochar and HTC-Hydrolysate
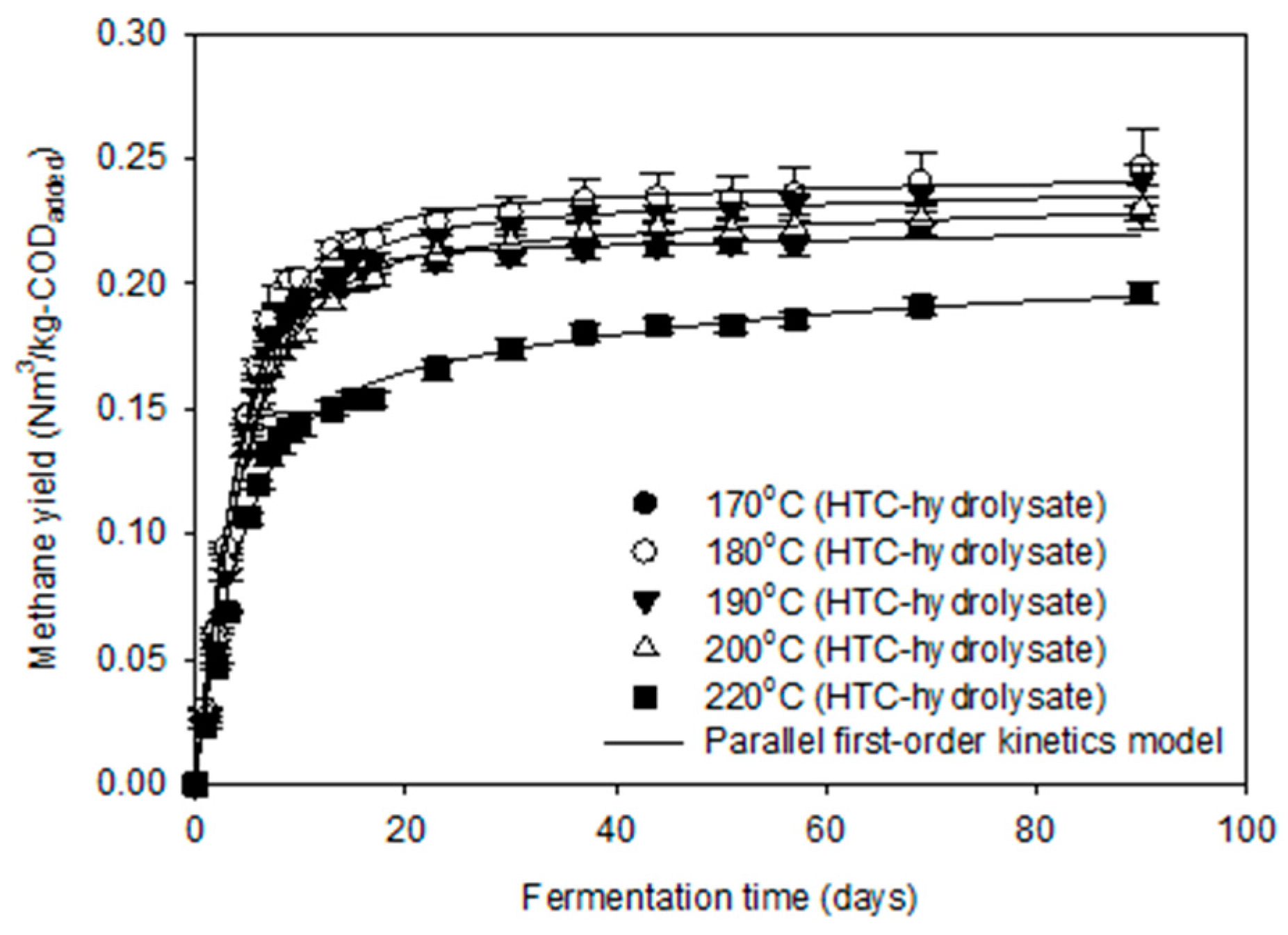
3.3. Methane Production Potential of HTC-Hydrolysate
3.4. Energy Recovery Efficiency
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeon, Y.-W.; Kang, J.-W.; Kim, H.; Yoon, Y.-M.; Lee, D.-H. Unit mass estimation and characterization of litter generated in the broiler house and slaughter house. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2013, 85, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-H.; Kim, H.; Kim, C.-H.; Yoon, Y.-M. Effect of the pretreatment by thermal hydrolysis on biochemical methane potential of piggery sludge. Korean J. Soil Sci. Fertil. 2012, 45, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Abalde, A.; Fernández, B.; Silvestre, G.; Flotats, X. Effects of thermal pre-treatments on solid slaughterhouse waste methane potential. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 1488–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salminen, E.; Einola, J.; Rintala, J. The methane production of poultry slaughtering residues and effects of pre-treatments on the methane production of poultry feather. Environ. Technol. 2003, 24, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salminen, E.; Rintala, J. Anaerobic digestion of organic solid poultry slaughterhouse waste—A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 83, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelidaki, I.; Ahring, B. Thermophilic anaerobic digestion of livestock waste: The effect of ammonia. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1993, 38, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinert, M.; Wittmann, T. Carbonisation of biomass using hydrothermal approach: State-of-the-art and recent developments. In Proceedings of the 17th European Biomass Conference and Exhibition, Hamburg, Germany, 29 June–3 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Funke, A.; Ziegler, F. Hydrothermal carbonization of biomass: A summary and discussion of chemical mechanisms for process engineering. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefin. 2010, 4, 160–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titirici, M.-M.; Thomas, A.; Antonietti, M. Back in the black: Hydrothermal carbonization of plant material as an efficient chemical process to treat the co 2 problem? New J. Chem. 2007, 31, 787–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libra, J.A.; Ro, K.S.; Kammann, C.; Funke, A.; Berge, N.D.; Neubauer, Y.; Titirici, M.-M.; Fühner, C.; Bens, O.; Kern, J. Hydrothermal carbonization of biomass residuals: A comparative review of the chemistry, processes and applications of wet and dry pyrolysis. Biofuels 2011, 2, 71–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Quek, A.; Hoekman, S.K.; Balasubramanian, R. Production of solid biochar fuel from waste biomass by hydrothermal carbonization. Fuel 2013, 103, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manara, P.; Zabaniotou, A. Towards sewage sludge based biofuels via thermochemical conversion—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 2566–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, D.; Patuzzi, F.; Castello, D.; Baratieri, M.; Rada, E.C.; Weiss-Hortala, E.; Fiori, L. Agro-industrial waste to solid biofuel through hydrothermal carbonization. Waste Manag. 2016, 47, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Yoshikawa, K.; Park, K. Characteristics of biochar obtained by hydrothermal carbonization of cellulose for renewable energy. Energies 2015, 8, 14040–14048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekman, S.K.; Broch, A.; Robbins, C. Hydrothermal carbonization (htc) of lignocellulosic biomass. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 1802–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramke, H.-G.; Blöhse, D.; Lehmann, H.-J.; Fettig, J. Hydrothermal carbonization of organic waste. In Proceedings of the Twelfth International Waste Management and Landfill Symposium, Sardinia, Italy, 5–9 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, J.C.; Barbosa, S.G.; Alves, M.M.; Sousa, D.Z. Thermochemical pre- and biological co-treatments to improve hydrolysis and methane production from poultry litter. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 111, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mäkelä, M.; Kwong, C.W.; Broström, M.; Yoshikawa, K. Hydrothermal treatment of grape marc for solid fuel applications. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 145, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, M.; Fiori, L. From olive waste to solid biofuel through hydrothermal carbonisation: The role of temperature and solid load on secondary char formation and hydrochar energy properties. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2017, 124, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.; Singh, S. Bioenergy conversion studies of organic fraction of msw: Kinetic studies and gas yield–organic loading relationships for process optimisation. Bioresour. Technol. 2004, 95, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.Y.; Yoon, Y.M. Assessment of methane potential in hydro-thermal carbonization reaction of organic sludge using parallel first order kinetics. Korean J. Environ. Agric. 2016, 35, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VDI Standard. VDI 4630: Fermentation of Organic Materials—Characterization of the Substrate, Sampling, Collection of Material Data, Fermentation Tests; VDI: Düsseldorf, Germany, 2006; Volume 92. [Google Scholar]
- Association, A.P.H.; Water Environment Federation (1998). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA; American Water Works Association: Denver, CO, USA; Water Environment Federation: Alexandria, VA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Beuvink, J.; Spoelstra, S.; Hogendorp, R. An automated method for measuring time-course of gas production of feed-stuffs incubated with buffered rumen fluid. Neth. J. Agric. Sci. 1992, 40, 401. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, I.; Blöhse, D.; Ramke, H.-G. Hydrothermal carbonization of agricultural residues. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 142, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronsse, F.; van Hecke, S.; Dickinson, D.; Prins, W. Production and characterization of slow pyrolysis biochar: Influence of feedstock type and pyrolysis conditions. GCB Bioenergy 2013, 5, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brassard, P.; Godbout, S.; Raghavan, V.; Palacios, J.; Grenier, M.; Zegan, D. The production of engineered biochars in a vertical auger pyrolysis reactor for carbon sequestration. Energies 2017, 10, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrappa, K.; Adschiri, T. Hydrothermal technology for nanotechnology. Prog. Cryst. Growth Charact. Mater. 2007, 53, 117–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevilla, M.; Fuertes, A.B. The production of carbon materials by hydrothermal carbonization of cellulose. Carbon 2009, 47, 2281–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quitain, A.T.; Faisal, M.; Kang, K.; Daimon, H.; Fujie, K. Low-molecular-weight carboxylic acids produced from hydrothermal treatment of organic wastes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2002, 93, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, K.; Kumar, A.; Patil, K.; Bellmer, D.; Wang, D.; Yuan, W.; Huhnke, R. Effects of biomass feedstocks and gasification conditions on the physiochemical properties of char. Energies 2013, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, N.; Jones, J.; Page-Dumroese, D.; McCollum, D.; Baker, S.; Loeffler, D.; Chung, W. A comparison of producer gas, biochar, and activated carbon from two distributed scale thermochemical conversion systems used to process forest biomass. Energies 2013, 6, 164–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, H.; Strong, P.; Xu, S.; Liu, S.; Lu, K.; Sheng, K.; Guo, J.; Che, L.; He, L.; et al. Thermal properties of biochars derived from waste biomass generated by agricultural and forestry sectors. Energies 2017, 10, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuckey, D.C.; McCarty, P.L. The effect of thermal pretreatment on the anaerobic biodegradability and toxicity of waste activated sludge. Water Res. 1984, 18, 1343–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lee, K.; Park, K.Y. Hydrothermal carbonization of anaerobically digested sludge for solid fuel production and energy recovery. Fuel 2014, 130, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahirul, M.; Rasul, M.; Chowdhury, A.; Ashwath, N. Biofuels production through biomass pyrolysis—A technological review. Energies 2012, 5, 4952–5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottet, A.; Steyer, J.; Déléris, S.; Vedrenne, F.; Chauzy, J.; Carrère, H. Kinetics of thermophilic batch anaerobic digestion of thermal hydrolysed waste activated sludge. Biochem. Eng. J. 2009, 46, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, S.I.; Jongen, W.M.; Van Boekel, M.A. A review of maillard reaction in food and implications to kinetic modelling. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2000, 11, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougrier, C.; Delgenes, J.P.; Carrère, H. Effects of thermal treatments on five different waste activated sludge samples solubilisation, physical properties and anaerobic digestion. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 139, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucian, M.; Fiori, L. Hydrothermal carbonization of waste biomass: Process design, modeling, energy efficiency and cost analysis. Energies 2017, 10, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample | pH | TS 1 | VS 2 | CODCr 3 | TN 4 | NH4+-N | Alkalinity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (-) | (wt. %, w.b. 5) | (wt. %, w.b.) | (g/L) | (wt. %, w.b.) | (wt. %, w.b.) | (g/L as CaCO3) | |
| Inoculum | 8.2 (0.0) 6 | 2.6 (0.0) | 1.4 (0.0) | 25.2 (0.1) | 0.4 (0.0) | 0.3 (0.0) | 19.2 (0.3) |
| Parameters | Sludge Cake | |
|---|---|---|
| Elemental composition (wt. %, d.b. 1) | C | 61.9 |
| H | 7.2 | |
| O | 5.3 | |
| N | 6.5 | |
| S | 0.0 | |
| Ash | 19.1 | |
| pH (-) | 7.1 (0.0) 8 | |
| TS 2 (wt. %, w.b. 3) | 16.4 (0.4) | |
| VS 4 (wt. %, w.b.) | 13.9 (0.1) | |
| VS/TS (%) | 84.8 (0.1) | |
| CODCr 5 (g/L) | 208.2 (30.4) | |
| TN 6 (wt. %, w.b.) | 11.0 (0.3) | |
| NH4+-N (wt. %, w.b.) | 2.6 (0.2) | |
| Calorific value 7 (MJ/kg, d.b.) | 27.7 (1.1) | |
| Parameters | HTC Reaction Temperatures | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 170 °C | 180 °C | 190 °C | 200 °C | 220 °C | ||
| Output yield 1 (wt. %, w.b. 2) | 37.7 (0.1) 10 | 30.5 (0.1) | 31.0 (0.1) | 25.4 (0.1) | 23.8 (0.1) | |
| Solid yield 3 (wt. %, d.b. 4) | 75.9 (0.2) | 73.5 (0.2) | 72.4 (0.2) | 69.6 (0.2) | 66.8 (0.3) | |
| Elemental composition (wt. %, d.b.) | C | 59.9 | 58.9 | 57.9 | 59.2 | 60.8 |
| H | 9.4 | 8.9 | 8.4 | 8.6 | 8.7 | |
| O | 7.0 | 6.2 | 6.9 | 6.7 | 5.0 | |
| N | 4.1 | 3.9 | 4.4 | 3.7 | 3.8 | |
| S | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| Ash | 19.6 | 22.1 | 22.4 | 21.8 | 21.7 | |
| Atomic ratio (-) | O/C | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.06 |
| H/C | 1.87 | 1.81 | 1.73 | 1.73 | 1.70 | |
| pH (-) | 6.2 (0.0) | 5.9 (0.0) | 5.6 (0.0) | 6.0 (0.0) | 6.1 (0.0) | |
| TS 5 (wt. %, w.b.) | 33.0 (0.7) | 39.5 (0.1) | 38.3 (0.1) | 44.8 (0.7) | 46.1 (0.4) | |
| VS 6 (wt. %, w.b.) | 29.1 (0.8) | 34.5 (0.0) | 33.5 (0.0) | 39.0 (0.5) | 39.5 (0.1) | |
| VS/TS (%) | 88.2 (0.5) | 87.4 (0.3) | 87.4 (0.2) | 87.0 (0.1) | 85.7 (0.3) | |
| TN 7 (g/kg) | 14.0 (0.7) | 11.5 (0.7) | 10.5 (0.5) | 12.0 (1.6) | 12.5 (1.5) | |
| NH4+-N (g/kg) | 3.2 (0.1) | 3.2 (0.3) | 3.8 (0.2) | 3.6 (0.1) | 3.8 (0.0) | |
| Calorific value 8 (MJ/kg, d.b.) | 29.6 (0.4) | 30.1 (0.1) | 30.2 (0.2) | 30.8 (0.1) | 31.3 (0.4) | |
| Energy densification 9 | 1.07 (0.02) | 1.09 (0.01) | 1.09 (0.01) | 1.11 (0.00) | 1.13 (0.01) | |
| Parameters | HTC Reaction Temperatures | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 170 °C | 180 °C | 190 °C | 200 °C | 220 °C | |
| Product yield 1 (wt. %, w.b. 2) | 62.3 (0.1) 8 | 69.5 (0.2) | 69.0 (0.2) | 74.6 (0.2) | 76.2 (0.4) |
| pH | 6.2 (0.0) | 5.9 (0.0) | 5.6 (0.0) | 6.0 (0.0) | 6.1 (0.0) |
| TS 3 (wt. %, w.b.) | 6.1 (0.1) | 6.6 (0.1) | 6.2 (0.01) | 6.9 (0.1) | 7.2 (0.2) |
| VS 4 (wt. %, w.b.) | 5.9 (0.1) | 6.3 (0.1) | 6.0 (0.0) | 6.7 (0.1) | 6.9 (0.1) |
| VS/TS (%) | 96.7 (0.1) | 95.5 (0.2) | 96.8 (0.2) | 97.1 (0.0) | 95.8 (0.9) |
| TN 5 (g/L) | 9.7 (0.5) | 10.5 (0.8) | 9.8 (0.3) | 10.9 (0.5) | 11.5 (0.5) |
| NH4+-N (g/L) | 3.2 (0.5) | 2.9 (0.0) | 3.3 (0.0) | 3.5 (0.3) | 5.3 (0.1) |
| CODCr 6 (g/L) | 99.3 (1.6) | 103.4 (1.3) | 101.1 (3.7) | 103.0 (1.6) | 97.9 (1.9) |
| VFAs 7 (mg/L) | 188.2 (3.3) | 195.7 (2.2) | 204.3 (1.5) | 191.4 (5.1) | 251.6 (2.7) |
| Alkalinity (g/L) | 9.5 (0.0) | 9.1 (0.0) | 8.6 (0.0) | 9.6 (0.4) | 12.1 (0.3) |
| Parameters | HTC Reaction Temperatures | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 170 °C | 180 °C | 190 °C | 200 °C | 220 °C | |
| Bu 1 (Nm3/kg-CODadded) | 0.222 | 0.242 | 0.237 | 0.228 | 0.197 |
| fe 2 (-) | 0.927 | 0.903 | 0.903 | 0.873 | 0.717 |
| k1 3 (1/day) | 0.228 | 0.215 | 0.190 | 0.203 | 0.230 |
| k2 3 (1/day) | 0.011 | 0.028 | 0.019 | 0.020 | 0.024 |
| CODDeg 4 (%) | 70.6 | 75.6 | 74.7 | 72.8 | 62.8 |
| Parameters | Sludge Cake | HTC Reaction Temperature (°C) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 170 | 180 | 190 | 200 | 220 | |||
| Feedstock | Solid product (kg/kginput) | 0.164 | - | - | - | - | - |
| GEPfeedstock 1 (MJ/kginput) | 4.541 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| HTC-biochar | Solid product (kg/kginput) | - | 0.125 | 0.121 | 0.119 | 0.114 | 0.11 |
| GERbiochar 2 (MJ/kginput) | - | 3.689 | 3.627 | 3.583 | 3.516 | 3.432 | |
| GERbiochar efficiency 3 (%) | - | 81.2 | 79.9 | 78.9 | 77.4 | 75.6 | |
| HTC-hydrolysate | Methane yield (NL/kginput) | - | 12.0 | 15.2 | 14.5 | 15.3 | 12.9 |
| GERmethane 4 (MJ/kginput) | - | 0.546 | 0.691 | 0.657 | 0.696 | 0.584 | |
| GERmethane efficiency 5 (%) | - | 12.0 | 15.2 | 14.5 | 15.3 | 12.9 | |
| GERtotal 6 (MJ/kginput) | - | 4.234 | 4.318 | 4.240 | 4.212 | 4.016 | |
| GERtotal efficiency 7 (%) | - | 93.2 | 95.1 | 93.4 | 92.7 | 88.5 | |
| Parameters | Sludge Cake (Simple Drying) | HTC (180 °C) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biochar | Hydrolysate | ||
| Input and output (kg) | 1.000 | 0.305 | 0.695 |
| Moisture content (kg) | 0.836 | 0.185 | - |
| HTC thermal energy 1 (MJ/kginput) | - | 0.183 | |
| Drying energy 2 (MJ/kginput) | 1.885 | 0.416 | - |
| GER 3 (MJ/kginput) | 4.541 | 3.627 | 0.691 |
| NER 4 (MJ/kginput) | 2.656 | 3.628 | |
| NER efficiency 5 (%) | 58.5 | 79.9 | |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, S.-Y.; Yoon, Y.-M. Energy Recovery Efficiency of Poultry Slaughterhouse Sludge Cake by Hydrothermal Carbonization. Energies 2017, 10, 1876. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10111876
Oh S-Y, Yoon Y-M. Energy Recovery Efficiency of Poultry Slaughterhouse Sludge Cake by Hydrothermal Carbonization. Energies. 2017; 10(11):1876. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10111876
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Seung-Yong, and Young-Man Yoon. 2017. "Energy Recovery Efficiency of Poultry Slaughterhouse Sludge Cake by Hydrothermal Carbonization" Energies 10, no. 11: 1876. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10111876
APA StyleOh, S.-Y., & Yoon, Y.-M. (2017). Energy Recovery Efficiency of Poultry Slaughterhouse Sludge Cake by Hydrothermal Carbonization. Energies, 10(11), 1876. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10111876




