A Simplified Top-Oil Temperature Model for Transformers Based on the Pathway of Energy Transfer Concept and the Thermal-Electrical Analogy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Heat Transfer Theory Application in Transformers
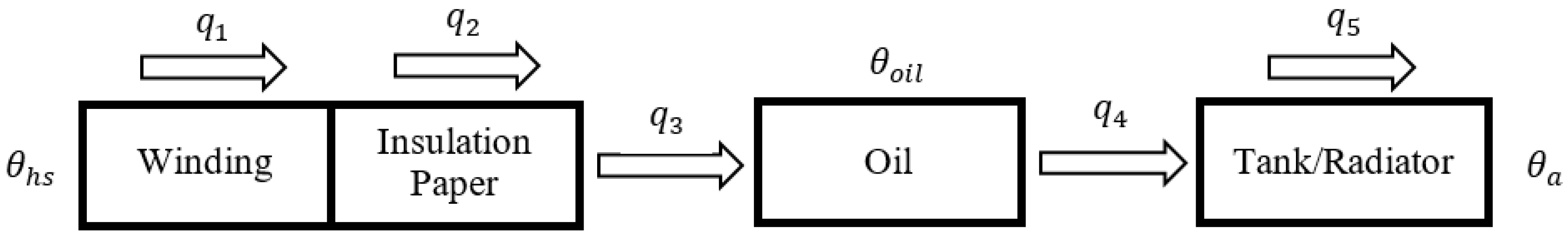
2.1. Concept of Heat Transfer in Transformers
2.2. Nonlinear Thermal Resistances
2.3. Lumped Capacitance
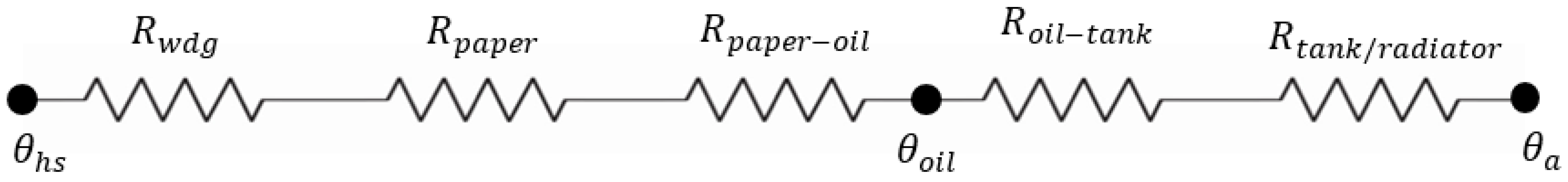
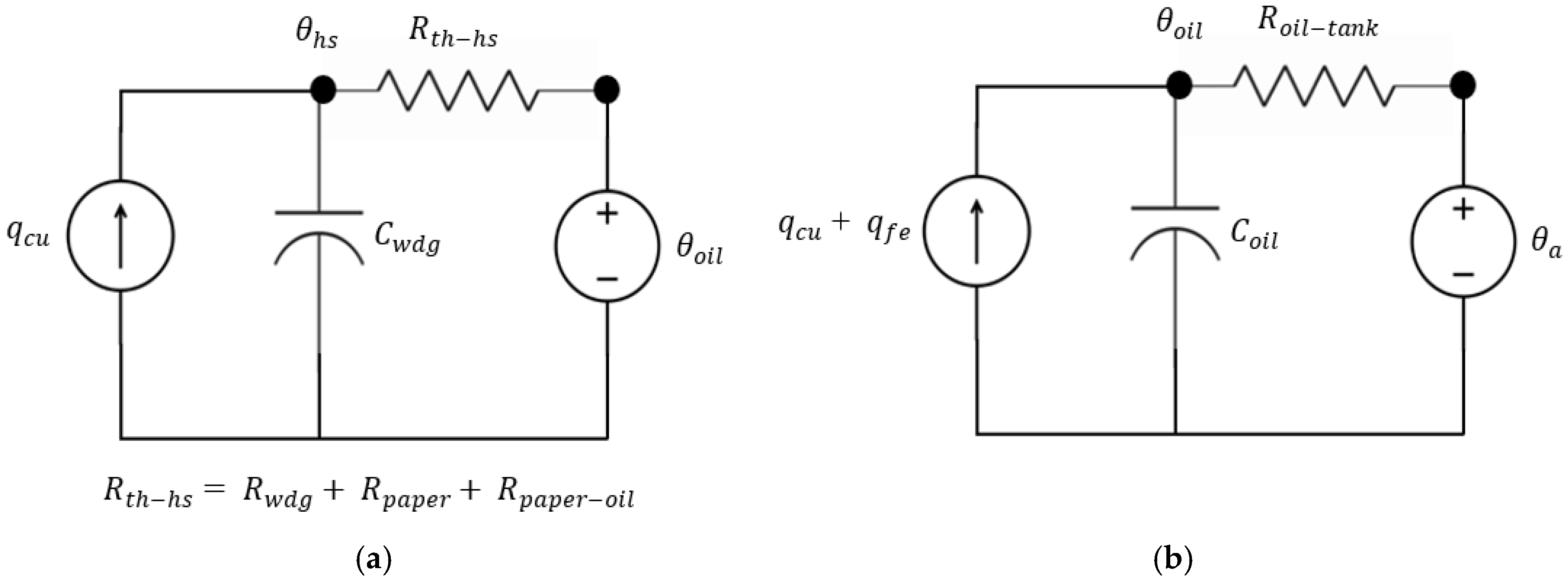
2.4. Thermal-Electrical Analogy
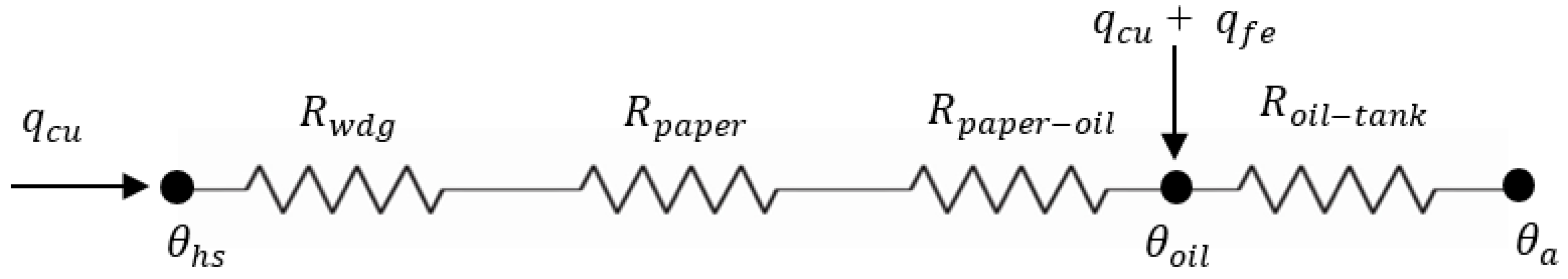
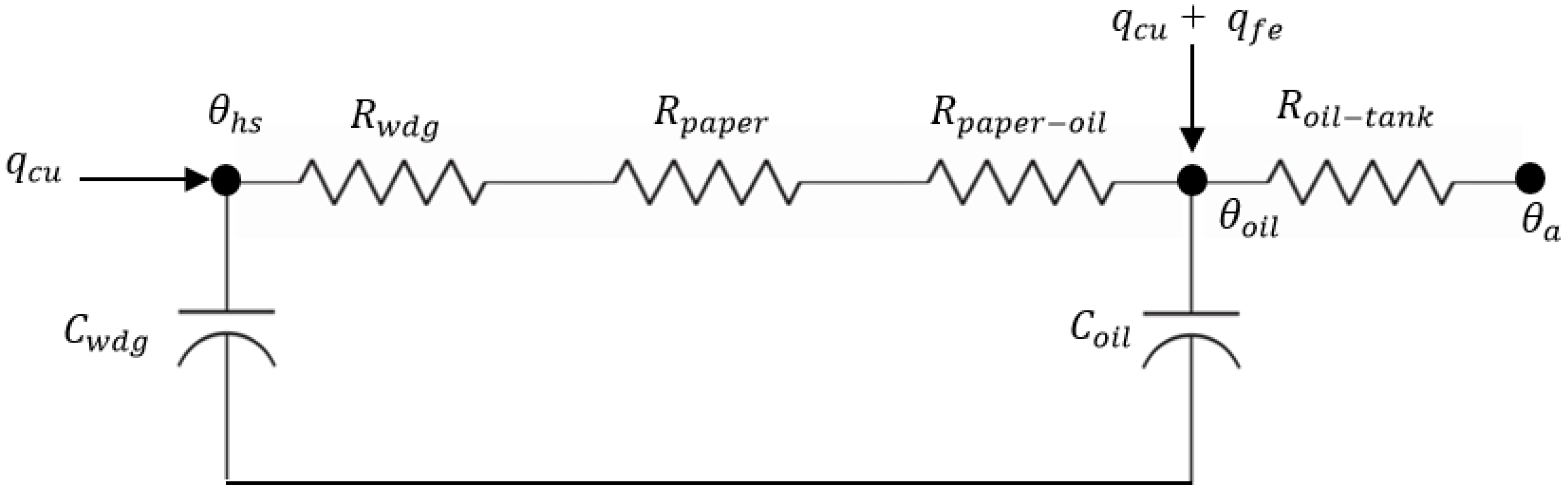
3. Top-Oil Temperature Thermal Model
3.1. Definition of Nonlinear Oil Thermal Resistance
3.2. Derivation of Top-Oil Temperature Thermal Model
3.3. Input Data
3.4. Comparison with Previous Thermal-Electrical and Standard Models
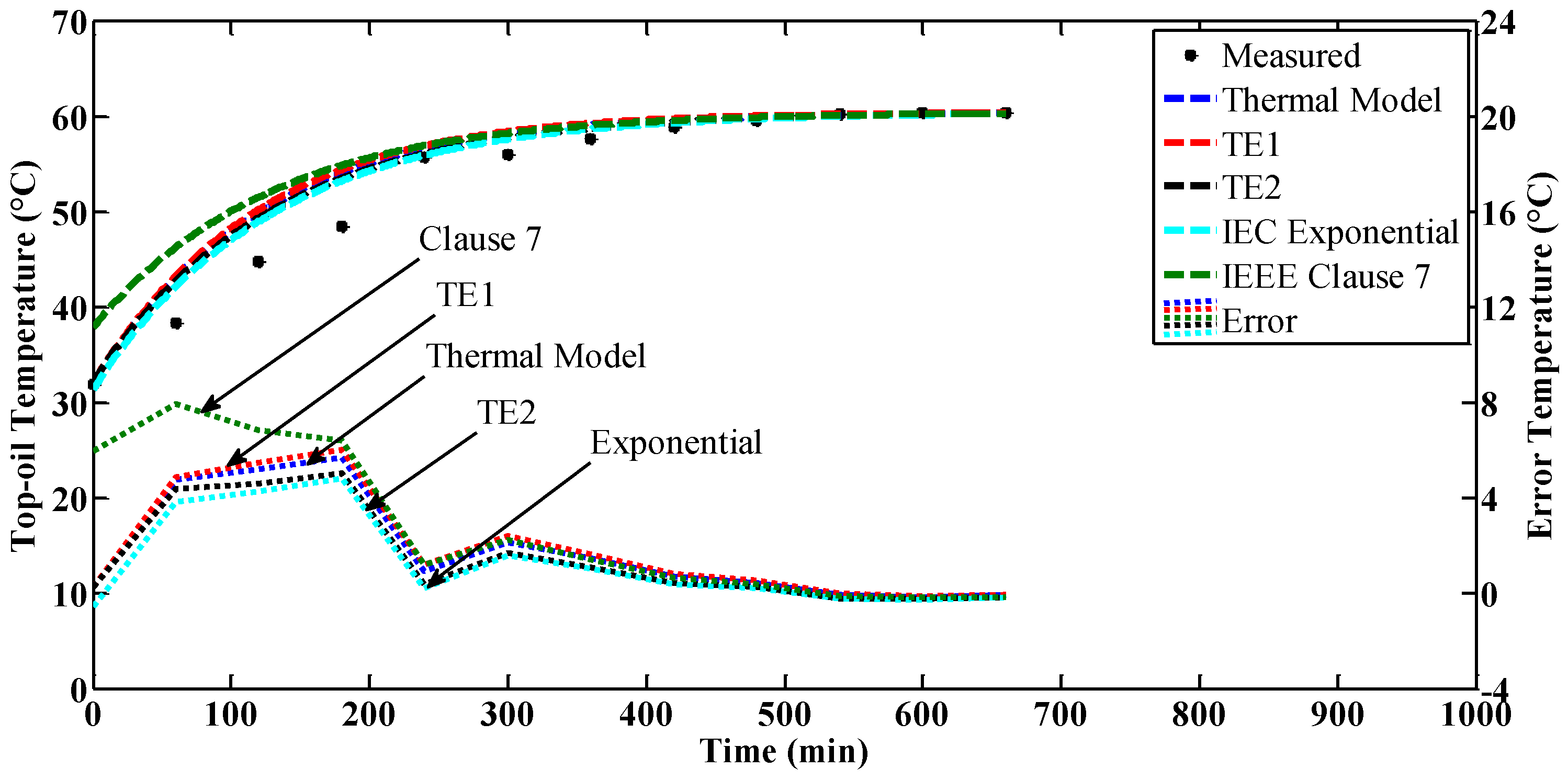
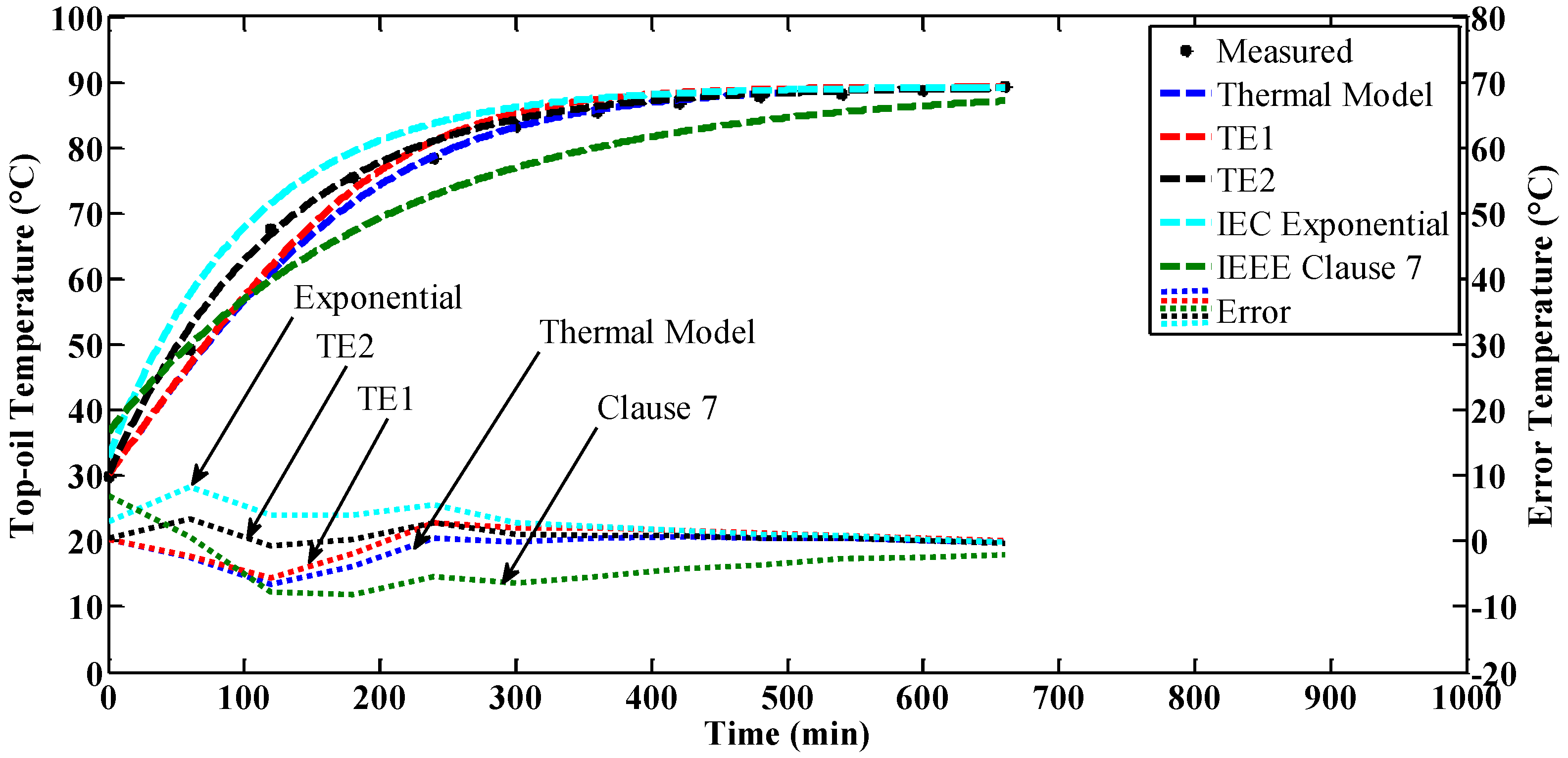
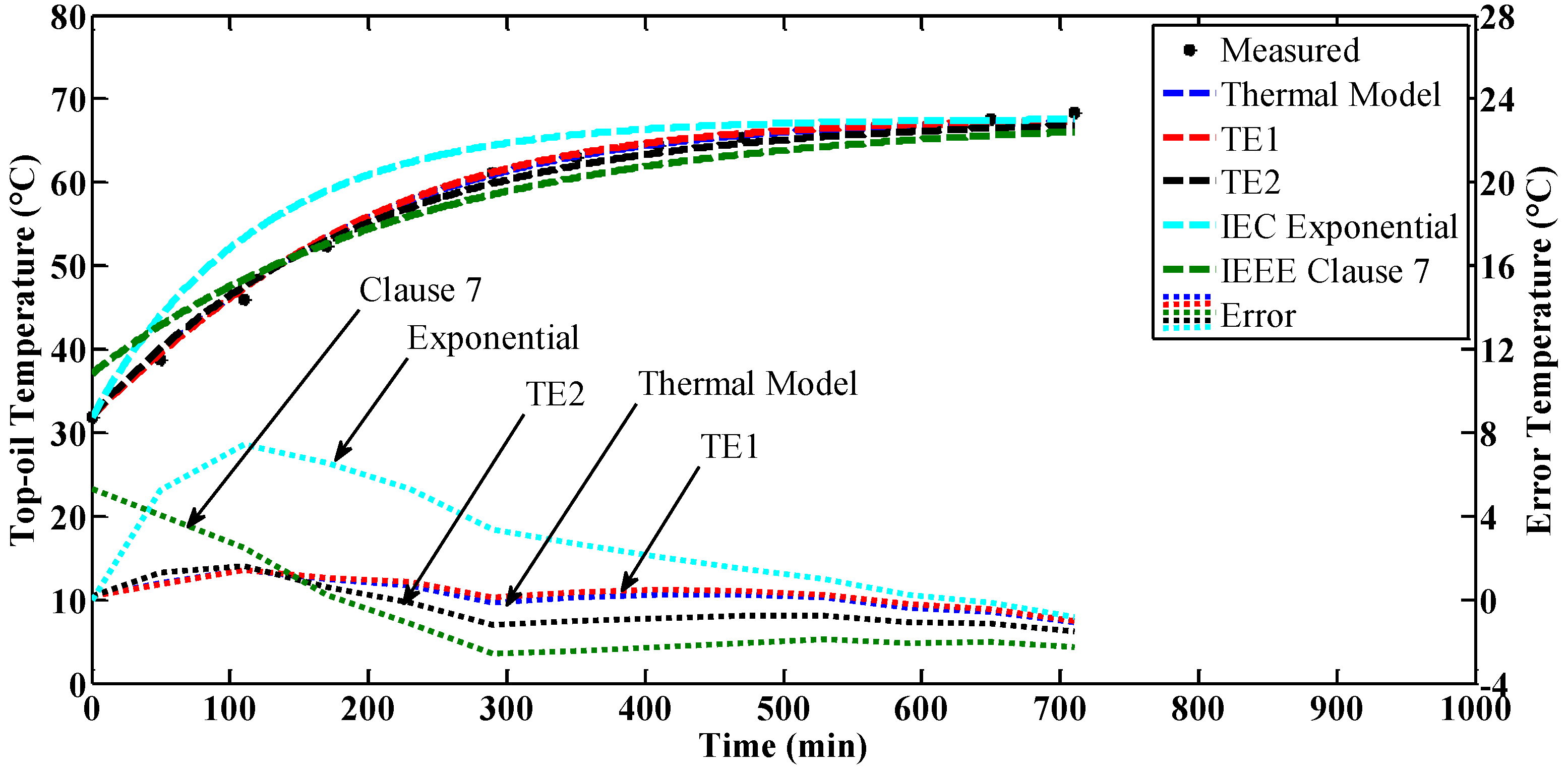
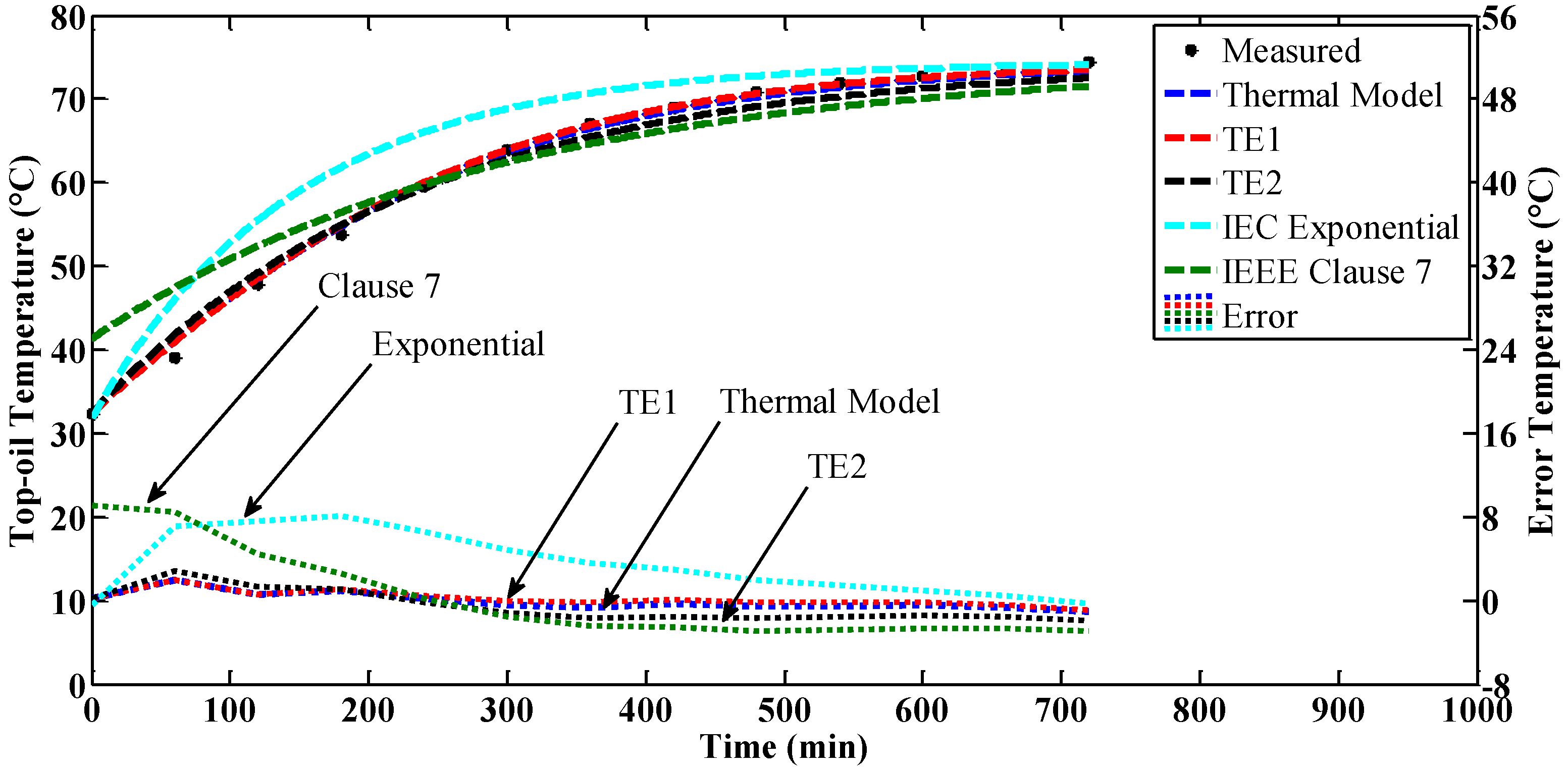
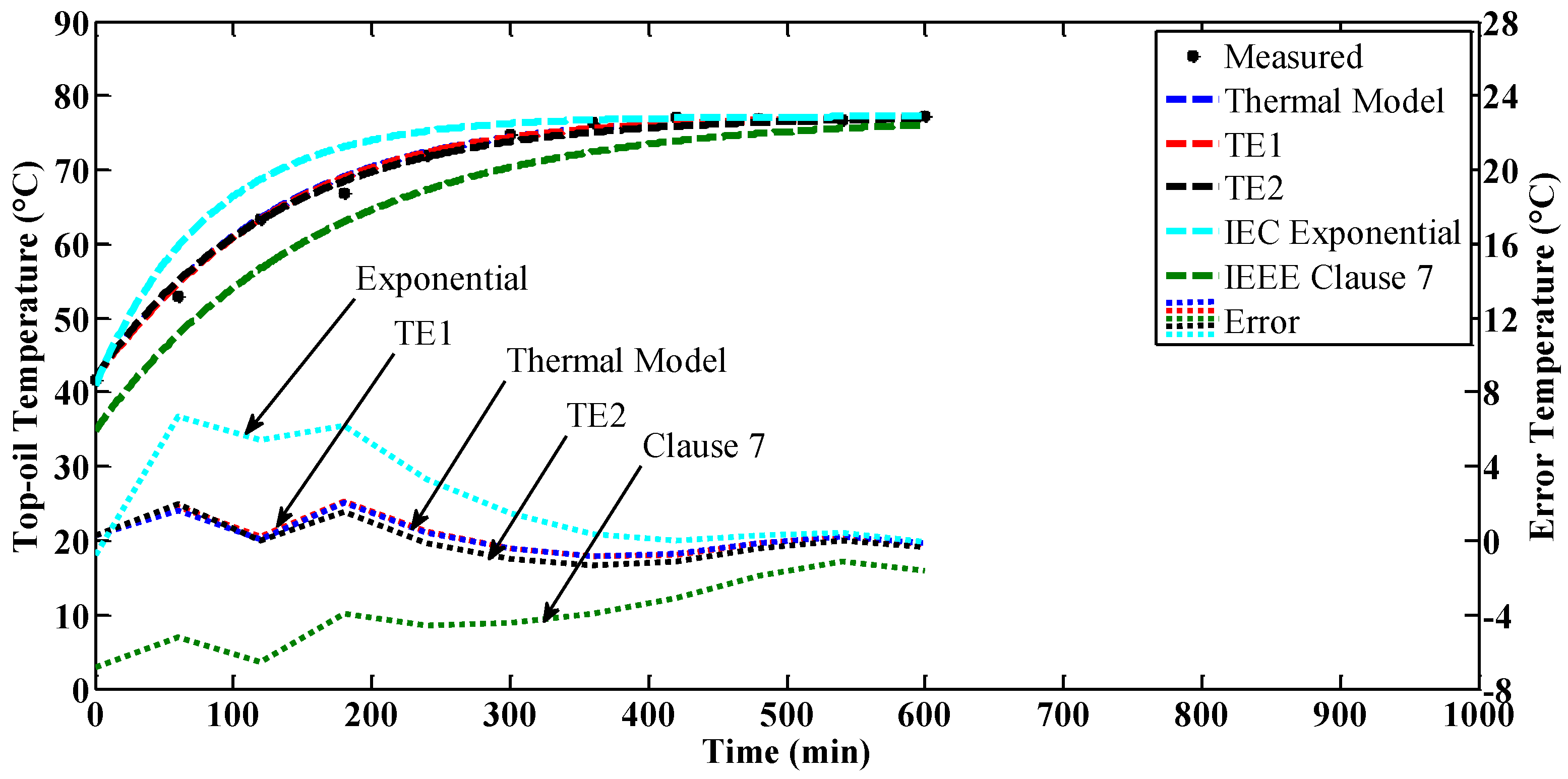
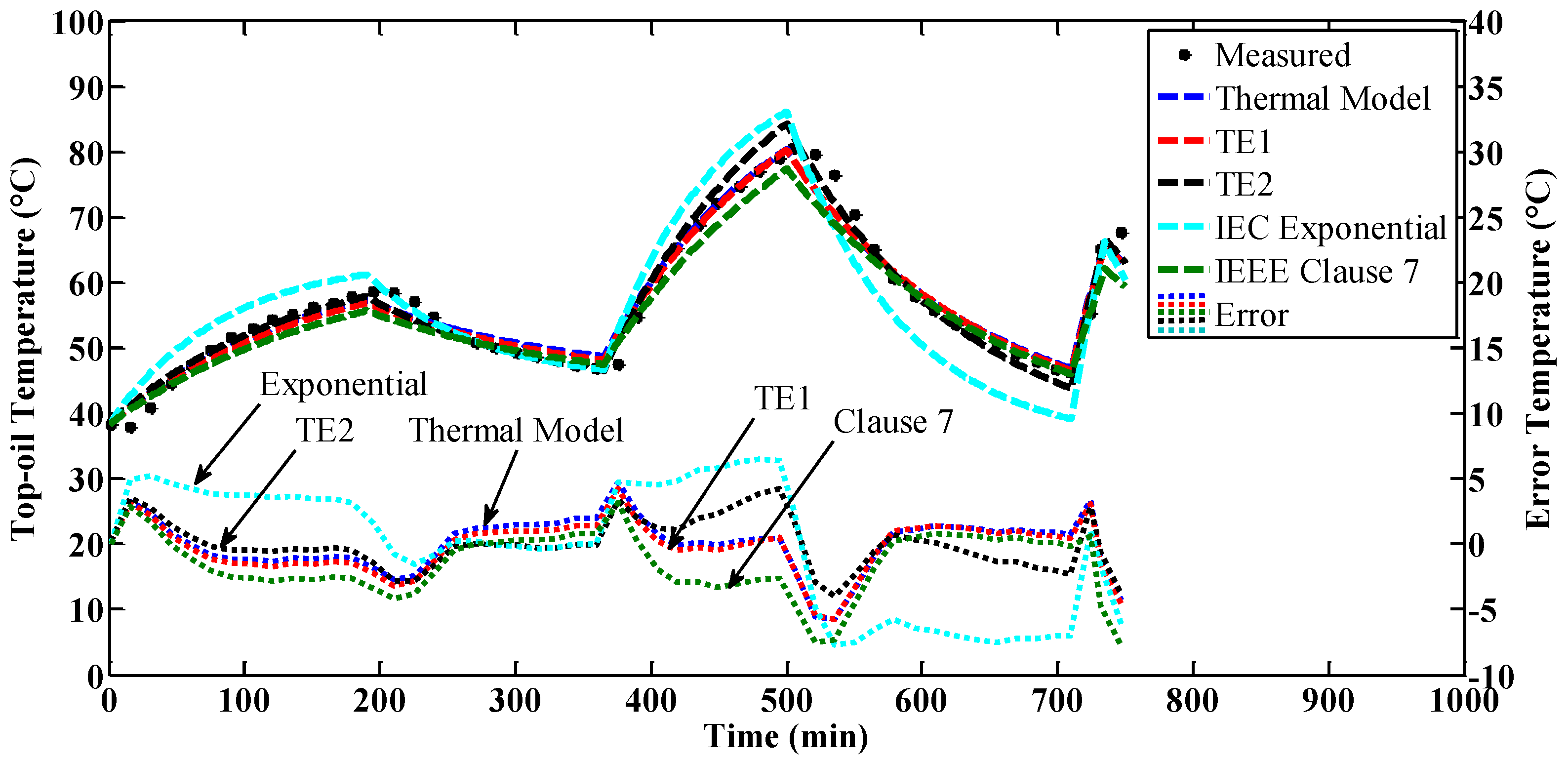
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Constant Loading
4.2. Step Loading
4.3. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| A | Area |
| C | Parameter with unit W/m2·K(1+n) |
| Oil thermal capacitance | |
| Winding thermal capacitance | |
| Increase exponent function of Top-oil temperature | |
| h | Convection coefficient |
| I | Load current |
| K | Load factor |
| n | A constant |
| Heat generated by load losses | |
| Heat generated by no load losses | |
| R | Ratio of load losses at rated current to no load losses |
| Winding thermal resistance | |
| Paper thermal resistance | |
| Nonlinear paper to oil thermal resistance | |
| Nonlinear oil to tank thermal resistance | |
| Tank/radiator thermal resistance | |
| Nonlinear oil thermal resistance | |
| Nonlinear oil thermal resistance at rated | |
| Hot-spot thermal resistance | |
| Ambient temperature | |
| Top-oil temperature | |
| Hot-spot temperature | |
| Initial value of Top-oil temperature | |
| Simulated value of Top-oil temperature | |
| Measured value of Top-oil temperature | |
| Top-oil temperature rise at rated | |
| Ultimate Top-oil temperature rise | |
| Initial Top-oil temperature rise | |
| Oil time constant | |
| Per unit value of oil viscosity |
References
- Standard, I. 60076-7 Power Transformer—Part 7:‘Loading Guide for Oil-Immersed Power Transformers’; IEC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- IEEE. IEEE Guide for Loading Mineral-Oil-Immersed Transformers; IEEE Std C57.91-1995; IEEE: Piscataway Township, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Swift, G.; Molinski, T.S.; Lehn, W. A Fundamental Approach to Transformer Thermal Modeling. I. Theory and Equivalent Circuit. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2001, 16, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, G.; Molinski, T.S.; Bray, R.; Menzies, R. A fundamental approach to transformer thermal modeling. II. Field verification. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2001, 16, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susa, D.; Lehtonen, M.; Nordman, H. Dynamic thermal modelling of power transformers. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2005, 20, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susa, D.; Lehtonen, M. Dynamic thermal modeling of power transformers: Further development-part I. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2006, 21, 1961–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susa, D.; Lehtonen, M. Dynamic thermal modeling of power transformers: Further development-part II. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2006, 21, 1971–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.G.; Pan, C.; Yun, Y.X. Power transformer top-oil temperature model based on thermal–electric analogy theory. Eur. Trans. Electr. Power 2009, 19, 341–354. [Google Scholar]
- Iskender, I.; Mamizadeh, A. An improved nonlinear thermal model for MV/LV prefabricated oil-immersed power transformer substations. Electr. Eng. 2011, 93, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamizadeh, A.; Iskender, I. Analyzing and Comparing Thermal Models of Indoor and Outdoor Oil-Immersed Power Transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE Bucharest Power Tech, Bucharest, Romania, 28 June–2 July 2009; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Su, X.; Chen, W.; Pan, C.; Zhou, Q.; Teng, L. A simple thermal model of transformer hot spot temperature based on thermal-electrical analogy. In Proceedings of the International Conference on High Voltage Engineering and Application (ICHVE), Shanghai, China, 17–20 September 2012; pp. 492–495. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-gang, W.; Chen-zhao, F.; Hong-lei, L.; Ke-jun, L.; Yong-liang, L. The improved thermal-circuit model for hot-spot temperature calculation of oil-immersed power transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE Information Technology, Networking, Electronic and Automation Control Conference, Chongqing, China, 20–22 May 2016; pp. 809–813. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Wu, G.; Yu, J.; Zhang, X. Thermal overshoot analysis for hot-spot temperature rise of transformer. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2007, 14, 1316–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yi, Y.Y. Study on Prediction of Top Oil Temperature for Transformers Based on Bayesian Network Model. In Proceedings of the MATEC Web of Conferences, Hong Kong, China, 11–12 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, Y.Y.; Li, R. Application of Gray Neural Network Combined Model in Transformer Top-oil Temperature Forecasting. In Proceedings of the MATEC Web of Conferences, Hong Kong, China, 11–12 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.; Si, J.; Tylavsky, D.J. Prediction of top-oil temperature for transformers using neural networks. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2000, 15, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghikhani, M.A. Power transformer top oil temperature estimation with GA and PSO methods. Energy Power Eng. 2012, 4, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assunção, T.; Silvino, J.; Resende, P. Transformer top-oil temperature modeling and simulation. Trans. Eng. Comput. Technol. 2006, 15, 240–245. [Google Scholar]
- Radakovic, Z.; Feser, K. A new method for the calculation of the hot-spot temperature in power transformers with ONAN cooling. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2003, 18, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Wu, Q.; Richardson, Z. Equivalent heat circuit based power transformer thermal model. IEEE Proc. Electr. Power Appl. 2002, 149, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Wu, Q.; Richardson, Z. A simplified transformer thermal model based on thermal-electric analogy. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2004, 19, 1112–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Ma, H.; Saha, T.; Ekanayake, C.; Martin, D. Moisture-Dependent Thermal Modelling of Power Transformer. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2016, 31, 2140–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, T.L.; Incropera, F.P.; Lavine, A.S. Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, J. Fundamental principles of transformer thermal loading and protection. In Proceedings of the 63rd Annual Conference for Protective Relay Engineers, College Station, TX, USA, 29 March–1 April 2010; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, B.; Wang, W.; Fan, J.; Chen, H.; Hu, X.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, X.; Ren, W. Optimization of the fractal-like architecture of porous fibrous materials related to permeability, diffusivity and thermal conductivity. Fractals 2017. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Chen, H.; Xiao, S.; Cai, J. Research on relative permeability of nanofibers with capillary pressure effect by means of Fractal-Monte Carlo technique. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 17, 6811–6817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incropera, F.; DeWitt, D. Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]



| Parameters | Transformer/Winding | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TX1 | TX2 | TX3 | TX4 | TX5 | TX6 | TX7 | |
| 11/0.433 kV | 33/11 kV | 33/11 kV | 33/11 kV | 132/11 kV | 132/33 kV | 132/33 kV | |
| Rating (kVA) | 300 | 15,000 | 30,000 | 30,000 | 30,000 | 60,000 | 90,000 |
| Cooling Modes | ONAN | ONAF | ONAN | ONAF | ONAN | ONAN | ONAF |
| Load (p.u.) | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| R | 4.52 | 7.56 | 10.47 | 11 | 5.79 | 4.66 | 10 |
| (K) | 30.3 | 51.23 | 59.2 | 58.87 | 38.9 | 44.07 | 47.87 |
| (min) | 129 | 152 | 200 | 207 | 239 | 295 | 165 |
| (K) | 31.9 | 44.9 | 29.7 | 29.9 | 31.8 | 32.3 | 41.7 |
| (IEC) Oil exponent, x | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| (IEC) Constant, | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| (IEEE) Exponent, n | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.9 |
| Parameters | Transformer/Winding |
|---|---|
| TX8 | |
| 250/118 kV | |
| Rating (kVA) | 250,000 |
| Cooling Modes | ONAF |
| Load (p.u.) | 1.00 pu/3 h + 0.60 pu/3 h + 1.50 pu/2 h + 0.30 pu/3 h + 2.10 pu/0.33 h |
| R | 10.17 |
| (K) | 38.3 |
| (min) | 168 |
| (K) | 38.3 |
| Transformers | Constant n | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| TE1 | TE2 | Thermal Model | |
| TX1 | 0.1 | 1 | 0.1 |
| TX2 | 0.75 | 0.9 | 1 |
| TX3 | 0.75 | 0.9 | 1 |
| TX4 | 0.75 | 0.9 | 1 |
| TX5 | 0.4 | 0.95 | 0.65 |
| TX6 | 0.4 | 0.95 | 0.65 |
| TX7 | 0.25 | 0.95 | 0.5 |
| TX8 | 0.1 | 0.95 | 0.25 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roslan, M.H.; Azis, N.; Kadir, M.Z.A.A.; Jasni, J.; Ibrahim, Z.; Ahmad, A. A Simplified Top-Oil Temperature Model for Transformers Based on the Pathway of Energy Transfer Concept and the Thermal-Electrical Analogy. Energies 2017, 10, 1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10111843
Roslan MH, Azis N, Kadir MZAA, Jasni J, Ibrahim Z, Ahmad A. A Simplified Top-Oil Temperature Model for Transformers Based on the Pathway of Energy Transfer Concept and the Thermal-Electrical Analogy. Energies. 2017; 10(11):1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10111843
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoslan, Muhammad Hakirin, Norhafiz Azis, Mohd Zainal Abidin Ab Kadir, Jasronita Jasni, Zulkifli Ibrahim, and Azalan Ahmad. 2017. "A Simplified Top-Oil Temperature Model for Transformers Based on the Pathway of Energy Transfer Concept and the Thermal-Electrical Analogy" Energies 10, no. 11: 1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10111843
APA StyleRoslan, M. H., Azis, N., Kadir, M. Z. A. A., Jasni, J., Ibrahim, Z., & Ahmad, A. (2017). A Simplified Top-Oil Temperature Model for Transformers Based on the Pathway of Energy Transfer Concept and the Thermal-Electrical Analogy. Energies, 10(11), 1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10111843





