A Novel Active Online State of Charge Based Balancing Approach for Lithium-Ion Battery Packs during Fast Charging Process in Electric Vehicles
Abstract
:Highlights:
- Adaptive extended Kalman filter (AEKF) is employed to estimate the pack cell state of charge (SOC) in real time, which is used as a balancing criterion to equalize cells in a LiFePO4 battery pack in the fast charging process.
- Only one additional current sensor in the chosen balancing circuit is required to accurately estimate pack cell SOC, leading to low cost implementation.
- Balancing in the fast charging process based on online estimated SOC overcomes non-uniformity and allows more pack capacity to be charged.
- Experimental platform is established to demonstrate that the performances based on the SOC criterion is better than those based on the terminal voltage criterion in terms of extra charged capacity of 2.07 Ah, equivalent to 13% of the nominal capacity of the chosen battery pack.
1. Introduction
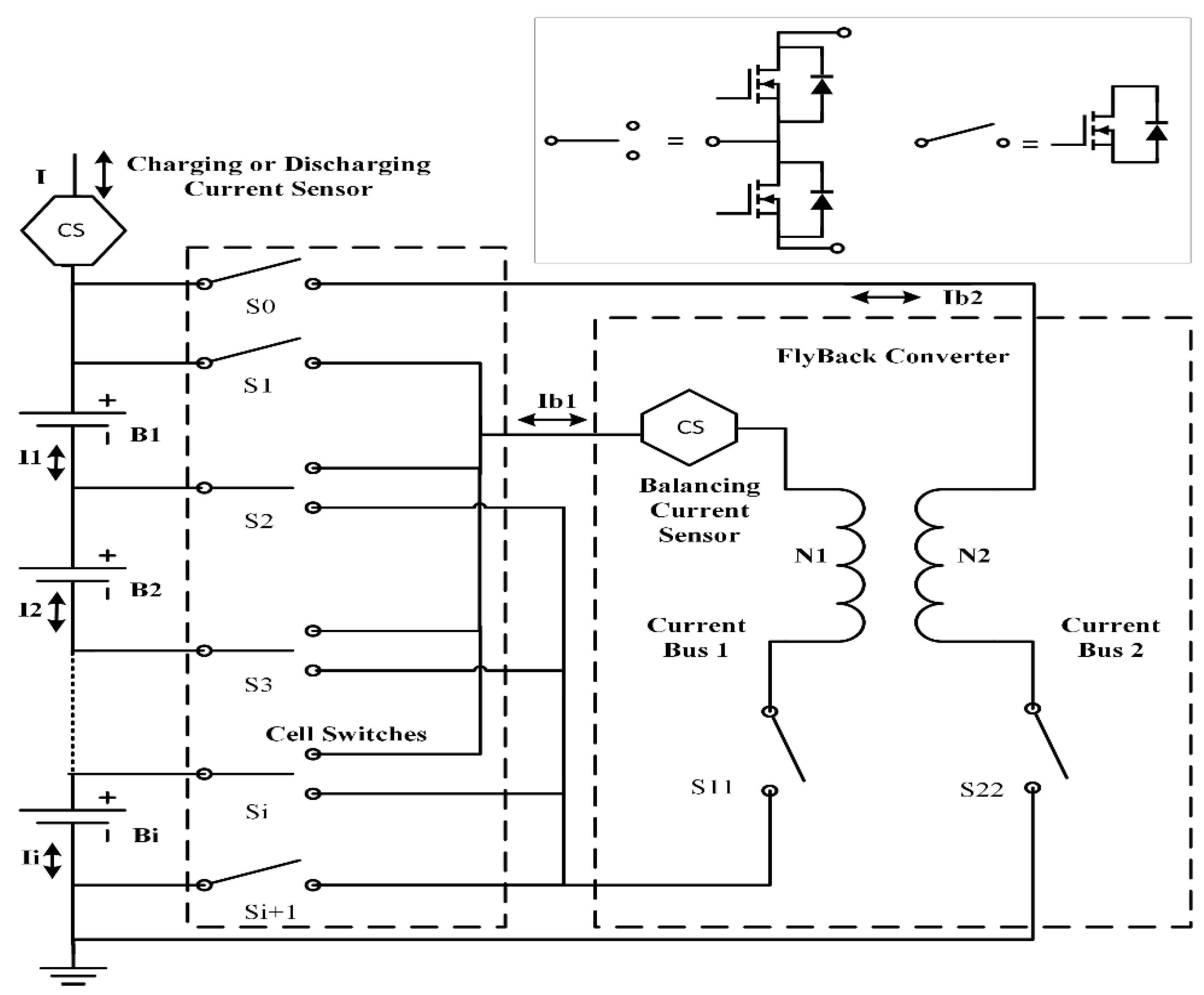
2. Balancing System for Fast Charging Process of a Battery Pack
2.1. Current Calculation of Each Cell for SOC Estimation with Fly-Back Converter Based Balancing Circuit
2.2. Adaptive Extended Kalman Filter for SOC Estimation
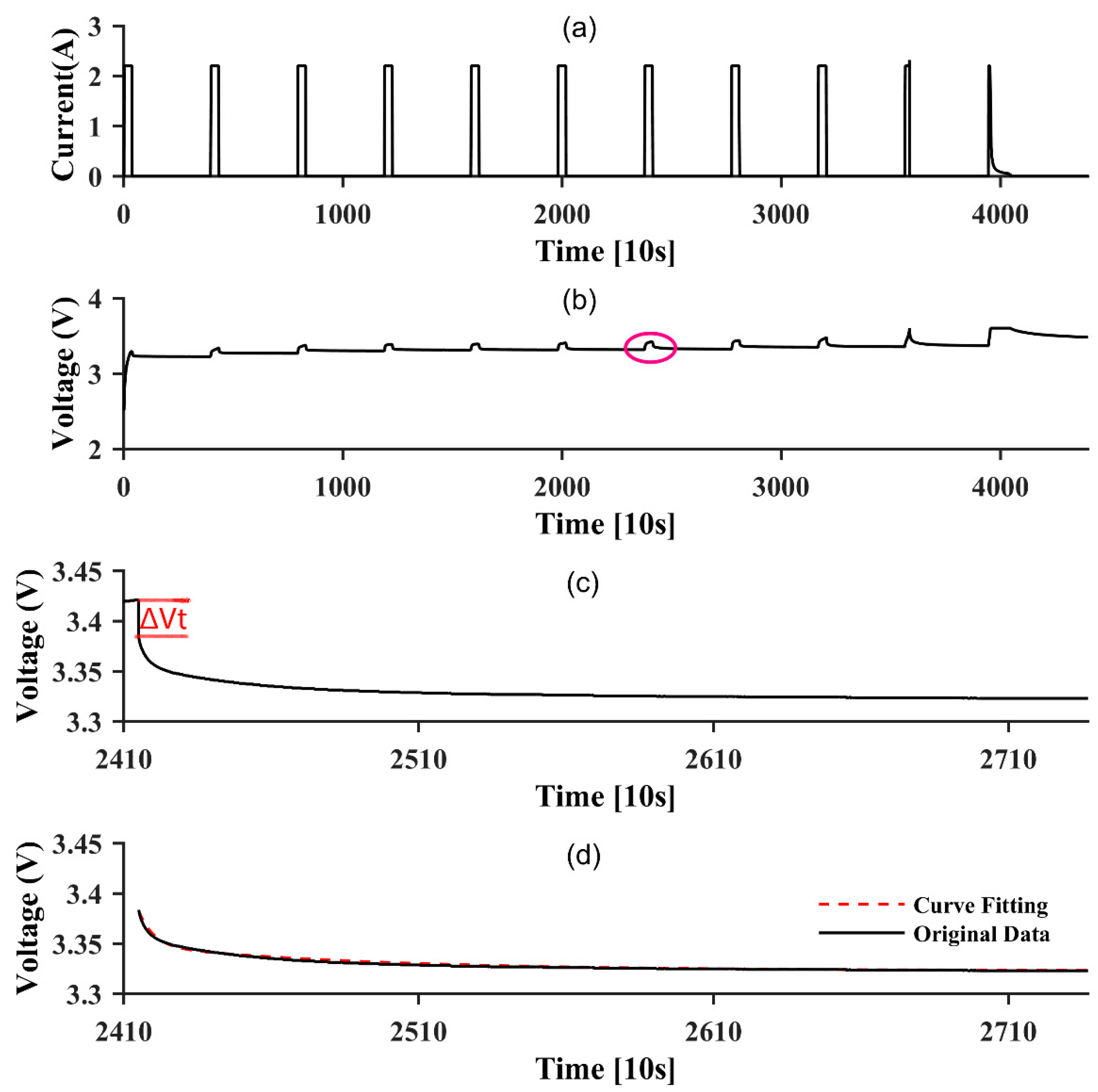
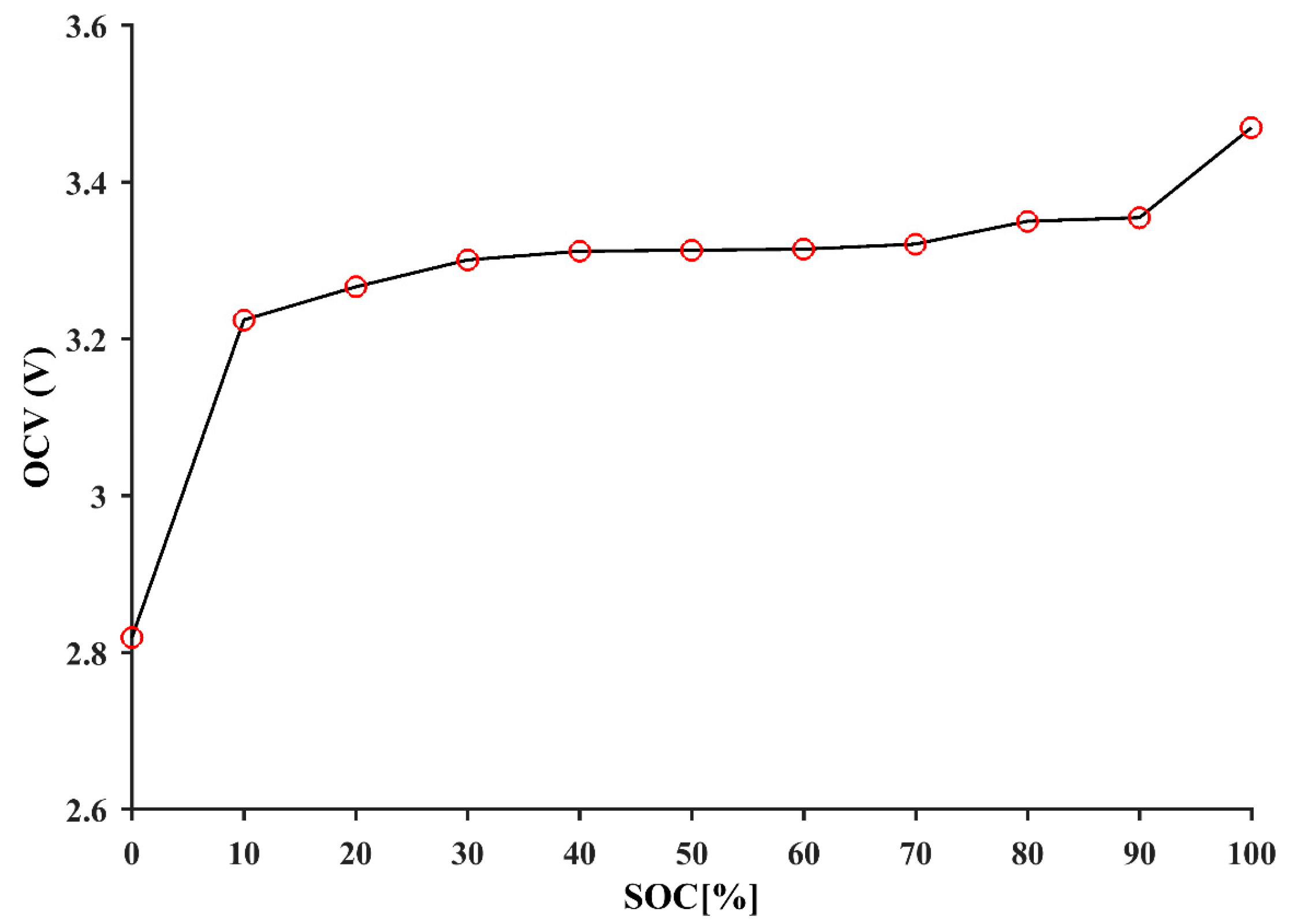
2.3. Battery Modelling and Parameters Identification
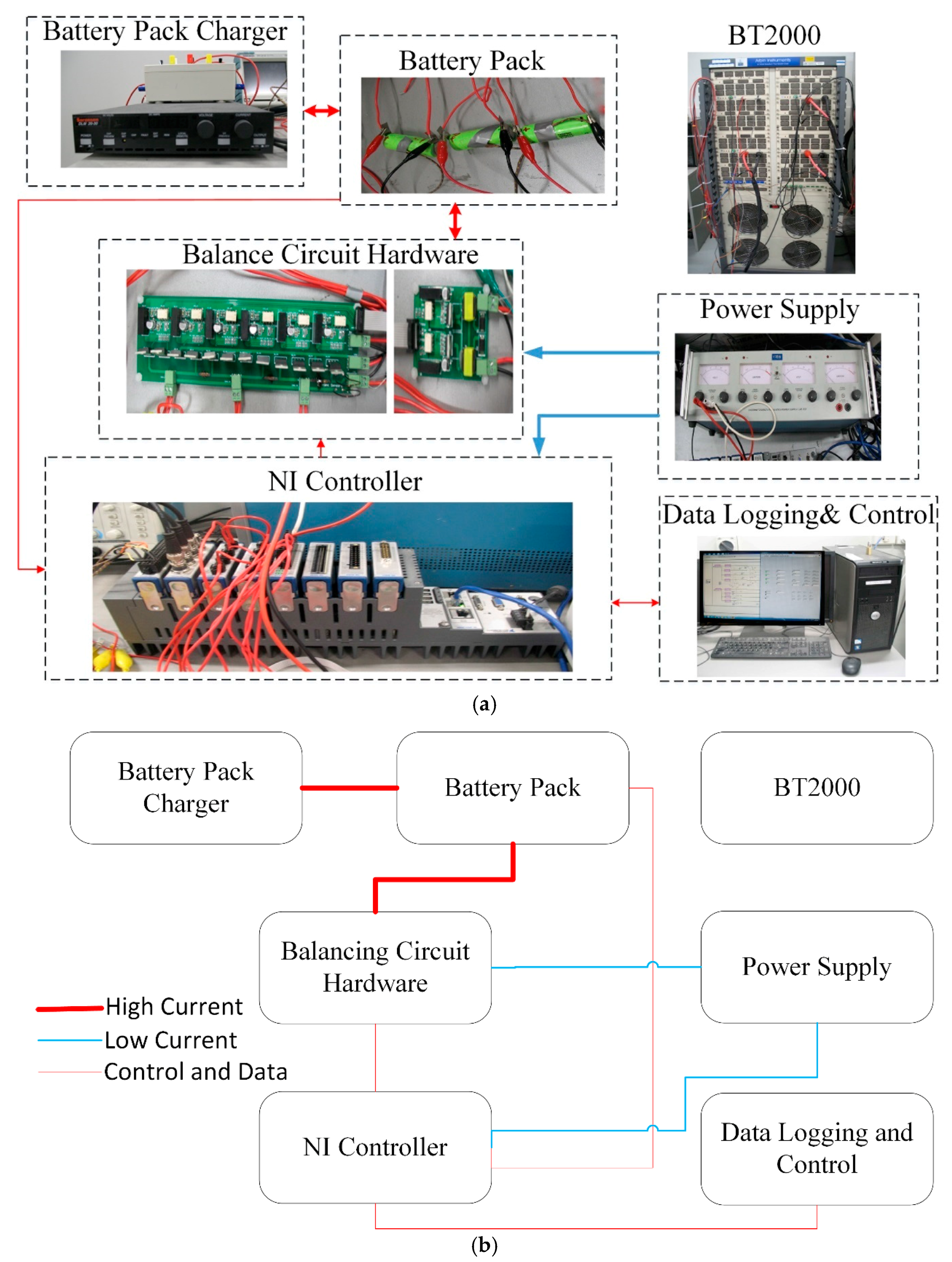
3. Experimental Verification
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclatures
| EV | electric vehicle |
| state of charge | |
| equivalent circuit model | |
| open circuit voltage | |
| lithium iron phosphate | |
| constant current and constant voltage method | |
| adaptive extended Kalman filter | |
| pulse constant current | |
| cell-to-pack mode | |
| pack-to-cell mode | |
| state of charge of cell i | |
| capacity of cell i | |
| current of cell i | |
| average balancing current in the primary side | |
| average balancing current in the secondary side | |
| number of turn in primary side | |
| number of turn in secondary side | |
| ohmic resistance (Ω) | |
| electrochemical polarization resistance (Ω) | |
| electrochemical polarization capacitance (F) | |
| concentration polarization resistance (Ω) | |
| concentration polarization capacitance (F) | |
| open circuit voltage of cell i | |
| modelling parameter errors | |
| process Gaussian noise | |
| measurement Gaussian noise | |
| process Gaussian noises covariance | |
| measurement Gaussian noise covariance | |
| output vector in step k | |
| partial derivatives in step k | |
| covariance | |
| Kalman Gain in step k |
References
- Mulder, G.; Omar, N.; Pauwels, S.; Meeus, M.; Leemans, F.; Verbrugge, B.; De Nijs, W.; Van den Bossche, P.; Six, D.; Van Mierlo, J. Comparison of commercial battery cells in relation to material properties. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 87, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayyas, A.R.; Omar, M.; Pisu, P.; Al-Ahmer, A.; Mayyas, A.; Montes, C.; Dongri, S. Comprehensive thermal modeling of a power-split hybrid powertrain using battery cell model. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 6588–6594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdinc, O.; Vural, B.; Uzunoglu, M. A dynamic lithium-ion battery model considering the effects of temperature and capacity fading. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Clean Electrical Power, Capri, Italy, 9–11 June 2009; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 383–386. [Google Scholar]
- Hoque, M.; Hannan, M.; Mohamed, A.; Ayob, A. Battery charge equalization controller in electric vehicle applications: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 75, 1363–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-Y.; Kim, J.-H.; Moon, G.-W. Center-Cell Concentration Structure of a Cell-to-Cell Balancing Circuit With a Reduced Number of Switches. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 5285–5297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-H.; Park, K.-B.; Kim, H.-S.; Moon, G.-W.; Youn, M.-J. Single-Magnetic Cell-to-Cell Charge Equalization Converter With Reduced Number of Transformer Windings. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 2900–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imtiaz, A.M.; Khan, F.H. Time Shared Flyback Converter; Based Regenerative Cell Balancing Technique for Series Connected Li-Ion Battery Strings. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 5960–5975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassani, P.A.; Williamson, S.S. Design, Testing, and Validation of a Simplified Control Scheme for a Novel Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicle Battery Cell Equalizer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 3956–3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo-Lozano, J.; Romero-Cadaval, E.; Milanes-Montero, M.I.; Guerrero-Martinez, M.A. Battery equalization active methods. J. Power Sources 2014, 246, 934–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Mi, C.C.; Li, S.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; Yin, C. A novel soft-switching bidirectional DC–DC converter with coupled inductors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2013, 49, 2730–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, M.; Kukita, A. Double-Switch Equalizer Using Parallel- or Series-Parallel-Resonant Inverter and Voltage Multiplier for Series-Connected Supercapacitors. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 812–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Z.; Xie, J.; Zhang, X. A novel active equalization method for lithium-ion batteries in electric vehicles. Appl. Energy 2015, 145, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Dong, G.; Chen, Z.; Kang, Y. System state estimation and optimal energy control framework for multicell lithium-ion battery system. Appl. Energy 2017, 187, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Y.; Polis, M.P.; Yin, G.G.; Chen, W.; Fu, Y.; Mi, C.C. Battery Cell Identification and SOC Estimation Using String Terminal Voltage Measurements. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2012, 61, 2925–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plett, G.L. Extended Kalman filtering for battery management systems of LiPB-based HEV battery packs: Part 1. Background. J. Power Sources 2004, 134, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plett, G.L. Extended Kalman filtering for battery management systems of LiPB-based HEV battery packs: Part 2. Modeling and identification. J. Power Sources 2004, 134, 262–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plett, G.L. Extended Kalman filtering for battery management systems of LiPB-based HEV battery packs: Part 3. State and parameter estimation. J. Power Sources 2004, 134, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.-S. A technique for estimating the state of health of lithium batteries through a dual-sliding-mode observer. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2010, 25, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Il-Song, K. Nonlinear State of Charge Estimator for Hybrid Electric Vehicle Battery. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2008, 23, 2027–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.-S. The novel state of charge estimation method for lithium battery using sliding mode observer. J. Power Sources 2006, 163, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Jeong, H.; Han, C.; Jin, S.; Lim, J.H.; Oh, J. State-of-charge estimation for lithium-ion batteries under various operating conditions using an equivalent circuit model. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2012, 41, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shen, W.X.; Cao, Z.; Kapoor, A. Adaptive gain sliding mode observer for state of charge estimation based on combined battery equivalent circuit model. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2014, 64, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shen, W.X.; Cao, Z.; Kapoor, A. A novel approach for state of charge estimation based on adaptive switching gain sliding mode observer in electric vehicles. J. Power Sources 2014, 246, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Xiong, R.; Zhang, X.; Sun, F.; Fan, J. State-of-Charge Estimation of the Lithium-Ion Battery Using an Adaptive Extended Kalman Filter Based on an Improved Thevenin Model. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2011, 60, 1461–1469. [Google Scholar]
- Einhorn, M.; Roessler, W.; Fleig, J. Improved Performance of Serially Connected Li-Ion Batteries With Active Cell Balancing in Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2011, 60, 2448–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Mi, C.C.; Zhang, M. A High-Efficiency Active Battery-Balancing Circuit Using Multiwinding Transformer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2013, 49, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarlagadda, S.; Hartley, T.T.; Husain, I. A Battery Management System Using an Active Charge Equalization Technique Based on a DC/DC Converter Topology. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2013, 49, 2720–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genc, R.; Alas, M.O.; Harputlu, E.; Repp, S.; Kremer, N.; Castellano, M.; Colak, S.G.; Ocakoglu, K.; Erdem, E. High-Capacitance Hybrid Supercapacitor Based on Multi-Colored Fluorescent Carbon-Dots. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uno, M.; Tanaka, K. Single-Switch Multioutput Charger Using Voltage Multiplier for Series-Connected Lithium-Ion Battery/Supercapacitor Equalization. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 3227–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, M.; Tanaka, K. A single-switch equalization charger using multiple stacked buck-boost converters for series-connected energy-storage modules. Electr. Eng. Jpn. 2013, 182, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, M.; Kukita, A. Single-Switch Single-Transformer Cell Voltage Equalizer Based on Forward Flyback Resonant Inverter and Voltage Multiplier for Series-Connected Energy Storage Cells. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2014, 63, 4232–4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, M.; Tanaka, K. Double-Switch Single-Transformer Cell Voltage Equalizer Using a Half-Bridge Inverter and a Voltage Multiplier for Series-Connected Supercapacitors. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2012, 61, 3920–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baronti, F.; Fantechi, G.; Roncella, R.; Saletti, R. High-Efficiency Digitally Controlled Charge Equalizer for Series-Connected Cells Based on Switching Converter and Super-Capacitor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2013, 9, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengui, L.; Chunbo, Z.; Likun, T.; Qi, W. Super-Capacitor Stacks Management System With Dynamic Equalization Techniques. IEEE Trans. Magnet. 2007, 43, 254–258. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.-Y.; Kim, C.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Moon, G.-W. A Chain Structure of Switched Capacitor for Improved Cell Balancing Speed of Lithium-Ion Batteries. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 3989–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speltino, C.; Stefanopoulou, A.; Fiengo, G. Cell equalization in battery stacks through State Of Charge estimation polling. In Proceedings of the 2010 American Control Conference (ACC), Baltimore, MD, USA, 30 June–2 July 2010; pp. 5050–5055. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.-S.; Cheng, M.-W. Intelligent control battery equalization for series connected lithium-ion battery strings. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2005, 52, 1297–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-S.; Cheng, G.-T. Quasi-Resonant Zero-Current-Switching Bidirectional Converter for Battery Equalization Applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2006, 21, 1213–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.C.; Drury, D.; Mellor, P. An integrated design of active balancing and redundancy at module level for Electric Vehicle batteries. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo (ITEC), Dearborn, MI, USA, 18–20 June 2012; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, N.; Oruganti, S.K.; Na, K.; Bien, F. An Adaptive Backward Control Battery Equalization System for Serially Connected Lithium-ion Battery Packs. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2014, 63, 3651–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassani, P.A.; Williamson, S.S. Feasibility Analysis of a Novel Cell Equalizer Topology for Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicle Energy-Storage Systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2009, 58, 3938–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-H.; Kim, T.-S.; Park, J.-S.; Moon, G.-W.; Yoon, M.-J. A new buck-boost type battery equalizer. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Fourth Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition, (APEC 2009), Washington, DC, USA, 15–19 February 2009; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 1246–1250. [Google Scholar]
- Mestrallet, F.; Kerachev, L.; Crebier, J.C.; Collet, A. Multiphase Interleaved Converter for Lithium Battery Active Balancing. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 2874–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashakor, N.; Farjah, E.; Ghanbari, T. A Bidirectional Battery Charger With Modular Integrated Charge Equalization Circuit. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 2133–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Cui, N.; Guerrero, J.M. A cell-to-cell battery equalizer with zero-current switching and zero-voltage gap based on quasi-resonant LC converter and boost converter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 3731–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-S.; Kim, C.-E.; Moon, G.-W.; Lee, J.-H. A Modularized Charge Equalizer for an HEV Lithium-Ion Battery String. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 1464–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.-S.; Lee, K.-J.; Ku, N.-J.; Hyun, D.-S.; Kim, R.-Y. A Modularized Equalization Method Based on Magnetizing Energy for a Series-Connected Lithium-Ion Battery String. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 1791–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Mi, C.C.; Zhang, M. A high efficiency low cost direct battery balancing circuit using a multi-winding transformer with reduced switch count. In Proceedings of the 2012 Twenty-Seventh Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), Orlando, FL, USA, 5–9 February 2012; pp. 2128–2133. [Google Scholar]
- Kutkut, N.H.; Divan, D.M. Dynamic equalization techniques for series battery stacks. In Proceedings of the 18th International Telecommunications Energy Conference (INTELEC ’96), Boston, MA, USA, 6–10 October 1996; pp. 514–521. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, J.-W.; Seo, G.-S.; Chun, C.-Y.; Cho, B.-H. Selective flyback balancing circuit with improved balancing speed for series connected lithium-ion batteries. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Power Electronics Conference (IPEC), Sapporo, Japan, 21–24 June 2010; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 1180–1184. [Google Scholar]
- Chol-Ho, K.; Moon-Young, K.; Gun-Woo, M. A Modularized Charge Equalizer Using a Battery Monitoring IC for Series-Connected Li-Ion Battery Strings in Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 3779–3787. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, R.; He, H.; Sun, F.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z. Model-based state of charge and peak power capability joint estimation of lithium-ion battery in plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. J. Power Sources 2013, 229, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, D. Optimal State Estimation: Kalman, H Infinity, and Nonlinear Approaches; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, F.; Xiong, R. A novel dual-scale cell state-of-charge estimation approach for series-connected battery pack used in electric vehicles. J. Power Sources 2015, 274, 582–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, C.; Rincon-Mora, G.A. Accurate electrical battery model capable of predicting runtime and I-V performance. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2006, 21, 504–511. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, R.; Xu, Y.; Guo, H. Online model-based estimation of state-of-charge and open-circuit voltage of lithium-ion batteries in electric vehicles. Energy 2012, 39, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthé, R.; Eberle, U. The Voltec System: Energy Storage and Electric Propulsion; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]


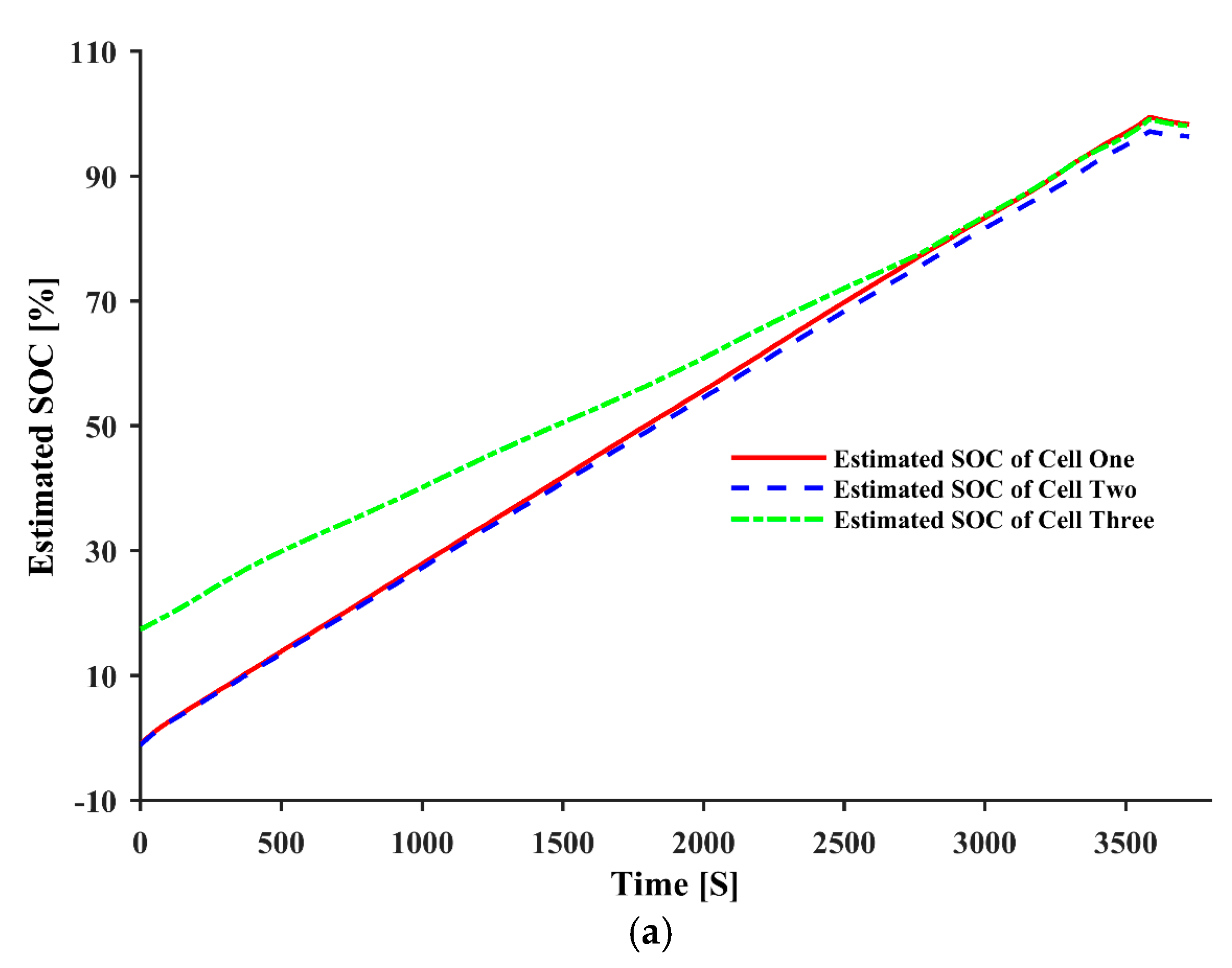
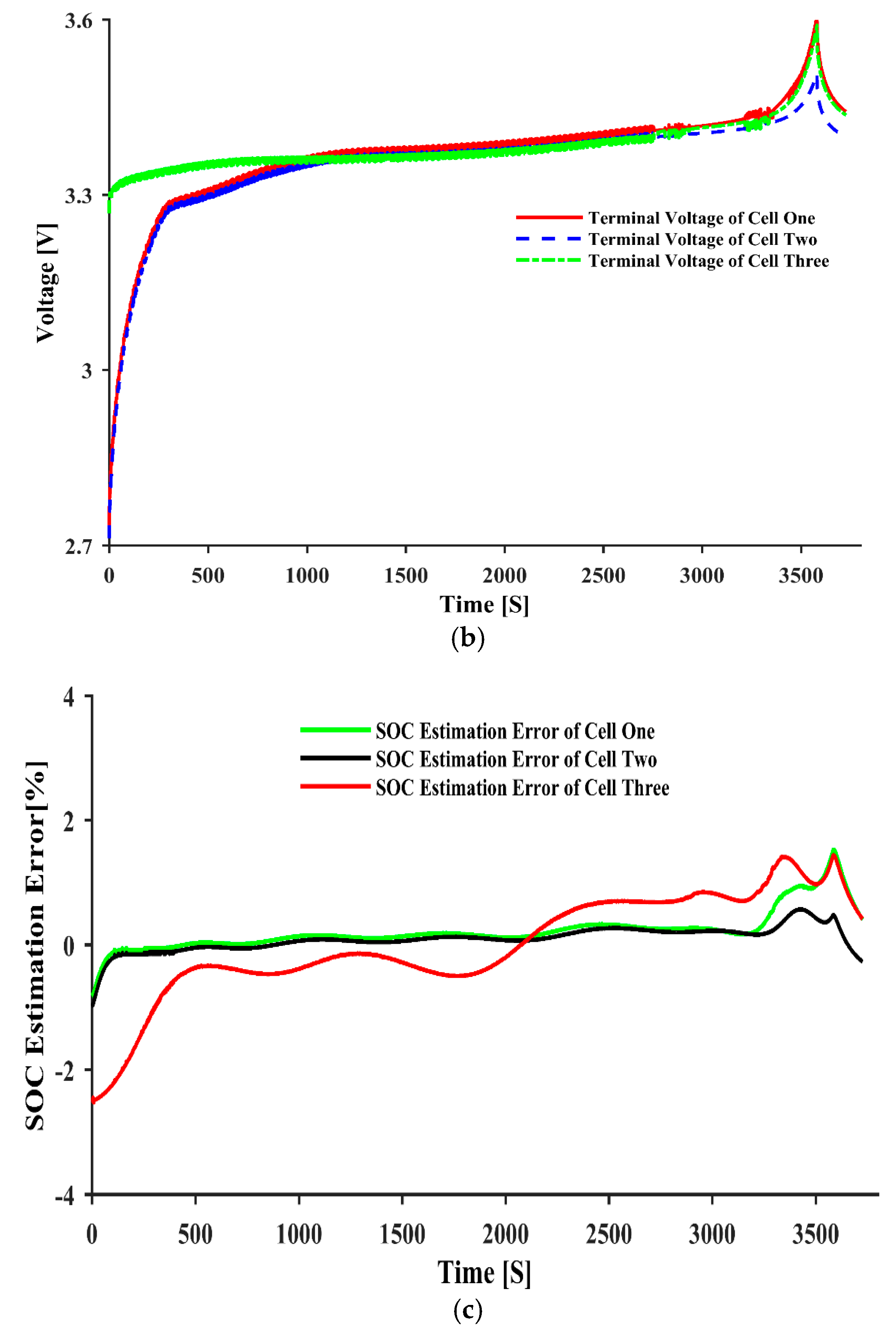
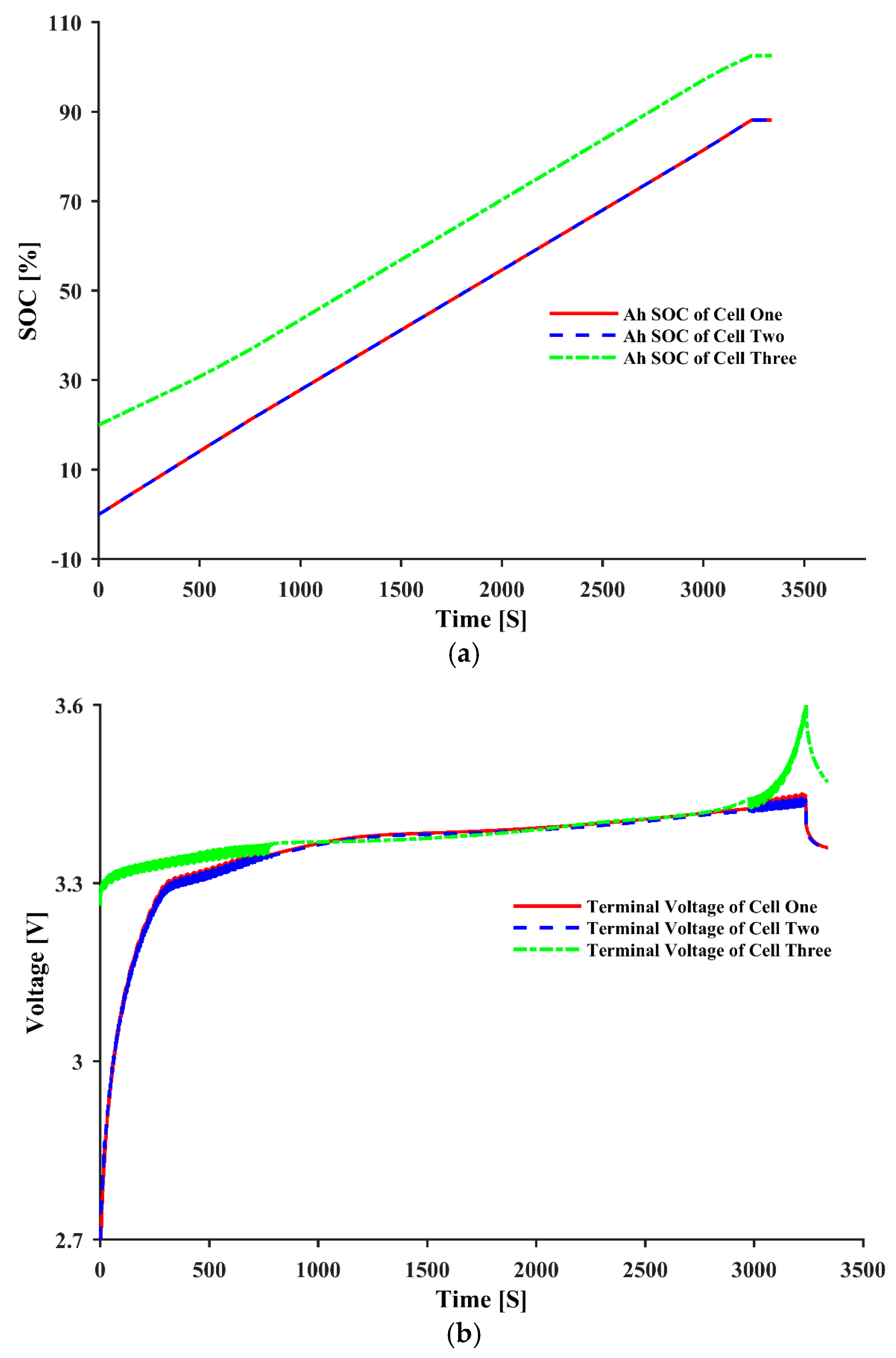
| Parameters | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Values | 7760 | 16 | 3958 | 15.3 | 86,094 | 9 | ||
| Parameters Values | ||||||||
| 2.819 | 9.432 | −84.32 | 380.6 | −927.9 | 1240 | −854.2 | 237.1 |
| Battery Type | Cell One | Cell Two | Cell Three |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nominal capacity (Ah) | 2.3 | 2.3 | 2.3 |
| Tested capacity (Ah) | 2.11 | 2.16 | 2.17 |
| Internal resistance (m) | 20 | 16 | 20 |
| Balancing Criteria | SOCs (%) | Charged Pack Capacity (Ah) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell One | Cell Two | Cell Three | ||
| SOC | 97.9 | 96.7 | 97.6 | 2.07 |
| Terminal Voltage | 86.8 | 85.1 | 98.4 | 1.83 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, X.; Shen, W.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, C. A Novel Active Online State of Charge Based Balancing Approach for Lithium-Ion Battery Packs during Fast Charging Process in Electric Vehicles. Energies 2017, 10, 1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10111766
Cui X, Shen W, Zhang Y, Hu C. A Novel Active Online State of Charge Based Balancing Approach for Lithium-Ion Battery Packs during Fast Charging Process in Electric Vehicles. Energies. 2017; 10(11):1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10111766
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Xiudong, Weixiang Shen, Yunlei Zhang, and Cungang Hu. 2017. "A Novel Active Online State of Charge Based Balancing Approach for Lithium-Ion Battery Packs during Fast Charging Process in Electric Vehicles" Energies 10, no. 11: 1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10111766
APA StyleCui, X., Shen, W., Zhang, Y., & Hu, C. (2017). A Novel Active Online State of Charge Based Balancing Approach for Lithium-Ion Battery Packs during Fast Charging Process in Electric Vehicles. Energies, 10(11), 1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10111766







