Controllability and Leader-Based Feedback for Tracking the Synchronization of a Linear-Switched Reluctance Machine Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background Theory
2.1. Mathematical Model of the LSRM Node
2.2. Second-Order Consensus Algorithm and LSRM Network Dynamics
3. Controllability Analysis of LSRM Network
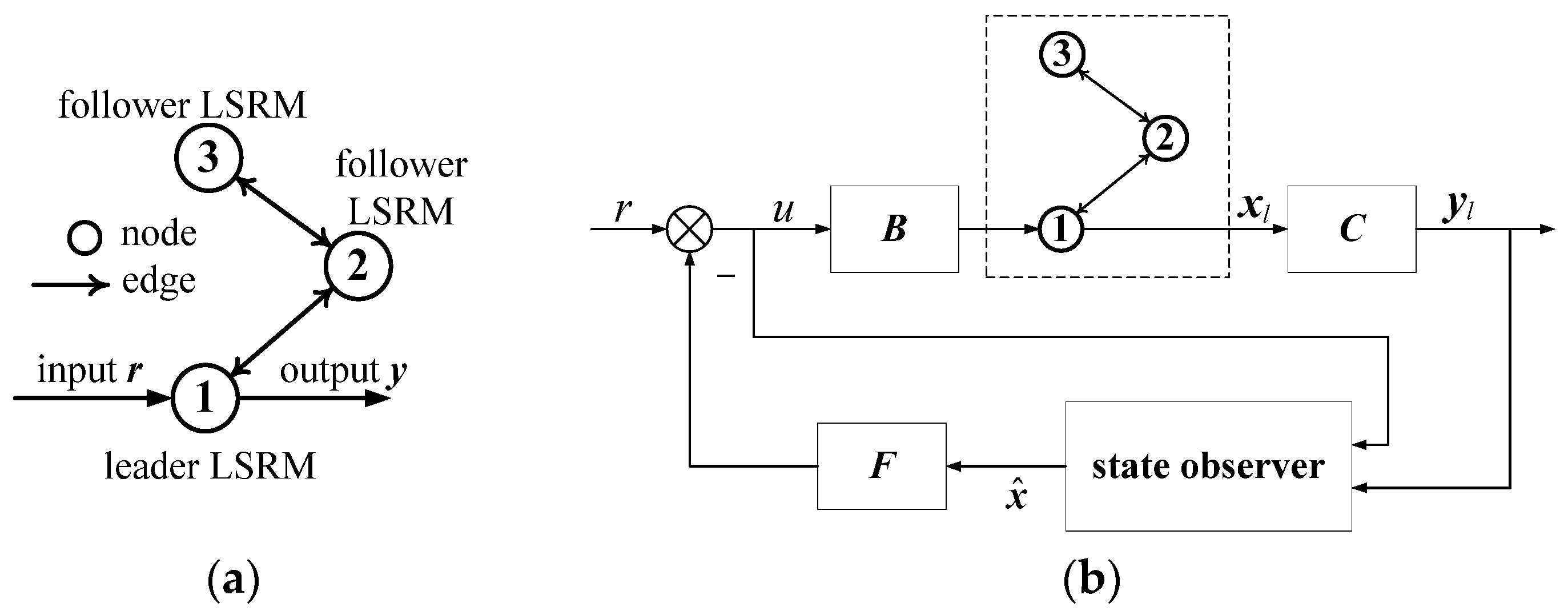
3.1. Input-Output of Network
3.2. Controllability and Observability of LSRM Network
3.3. Controllability of LSRM Network
4. Output–Feedback Control Design
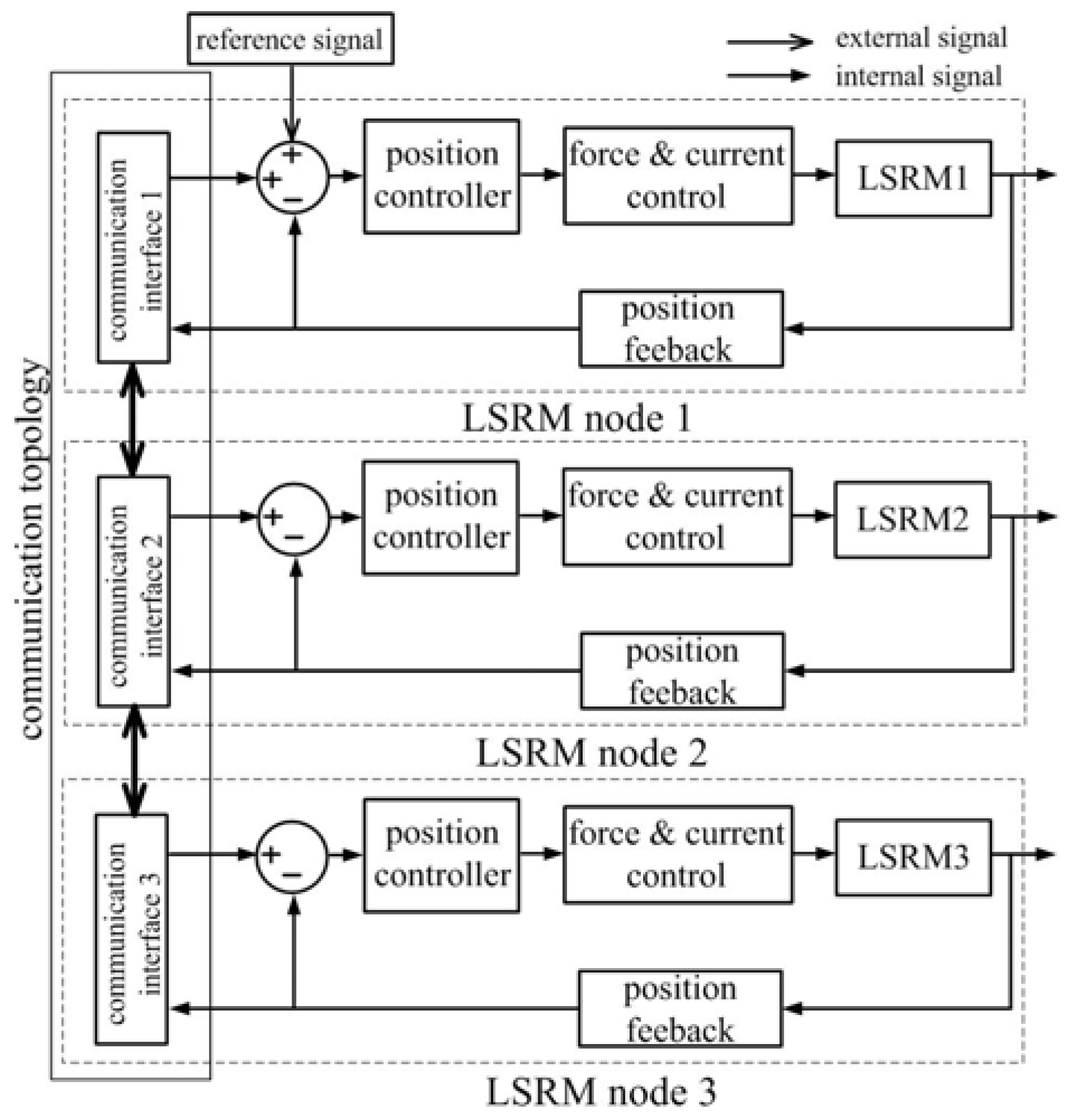
4.1. LSRM Network Control Design
4.2. Control Schemes for Leader and Follower
4.3. Solution of Controller Gain and Observer Gain Based on Pole-Placement
5. Experiment Verification
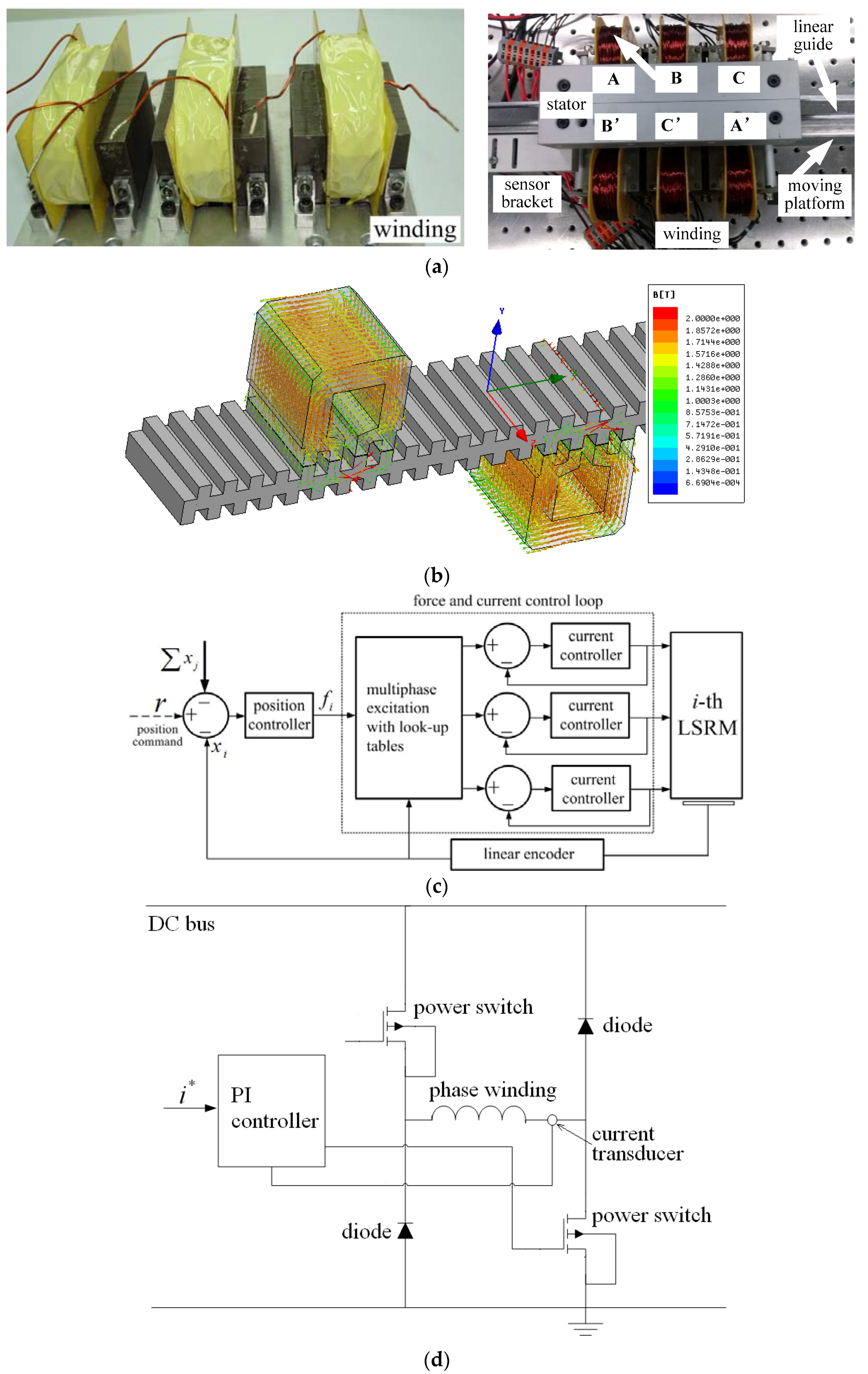
5.1. Network Configuration
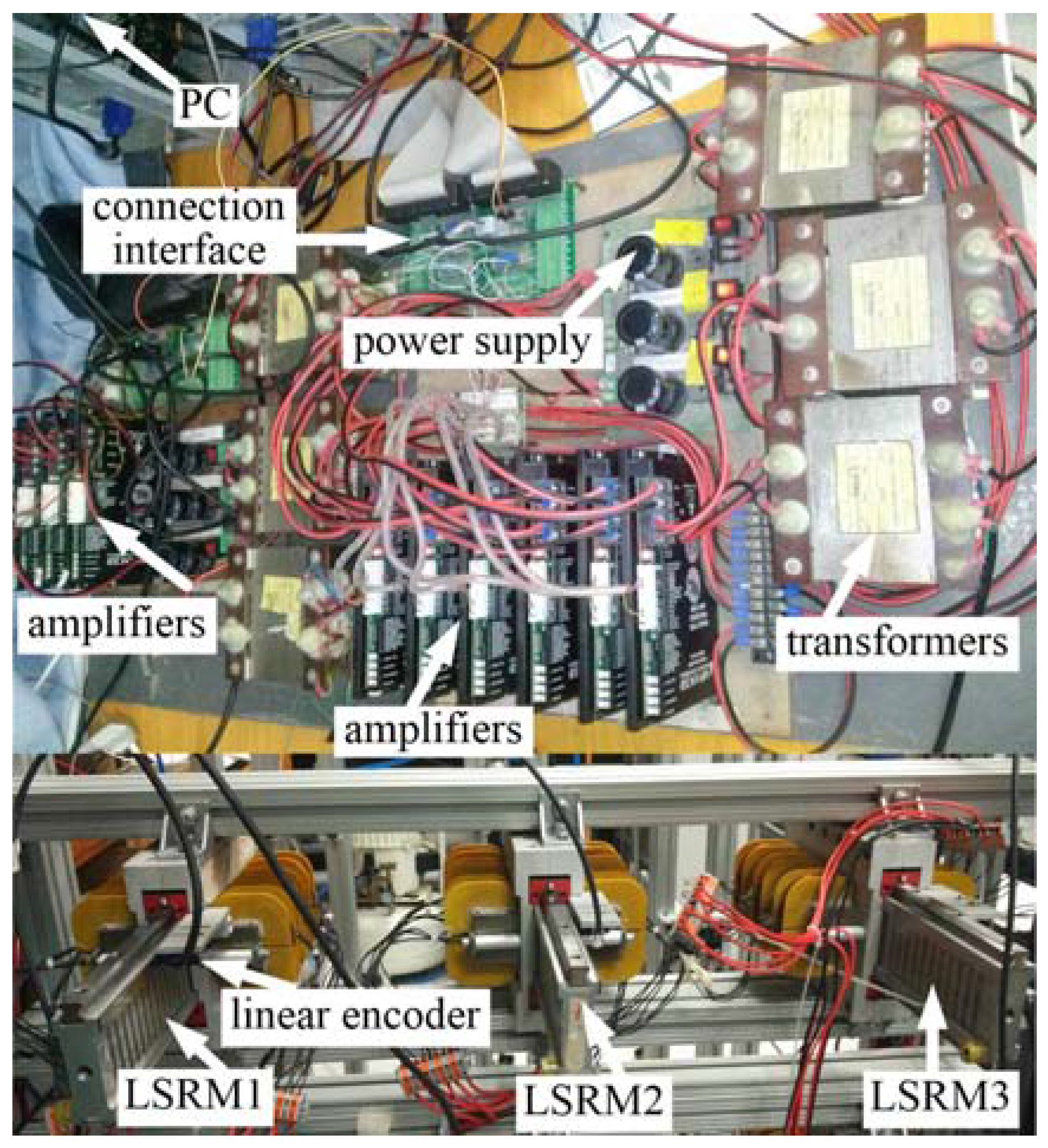
5.2. Experiment Setup
5.3. Control Parameter Derivations
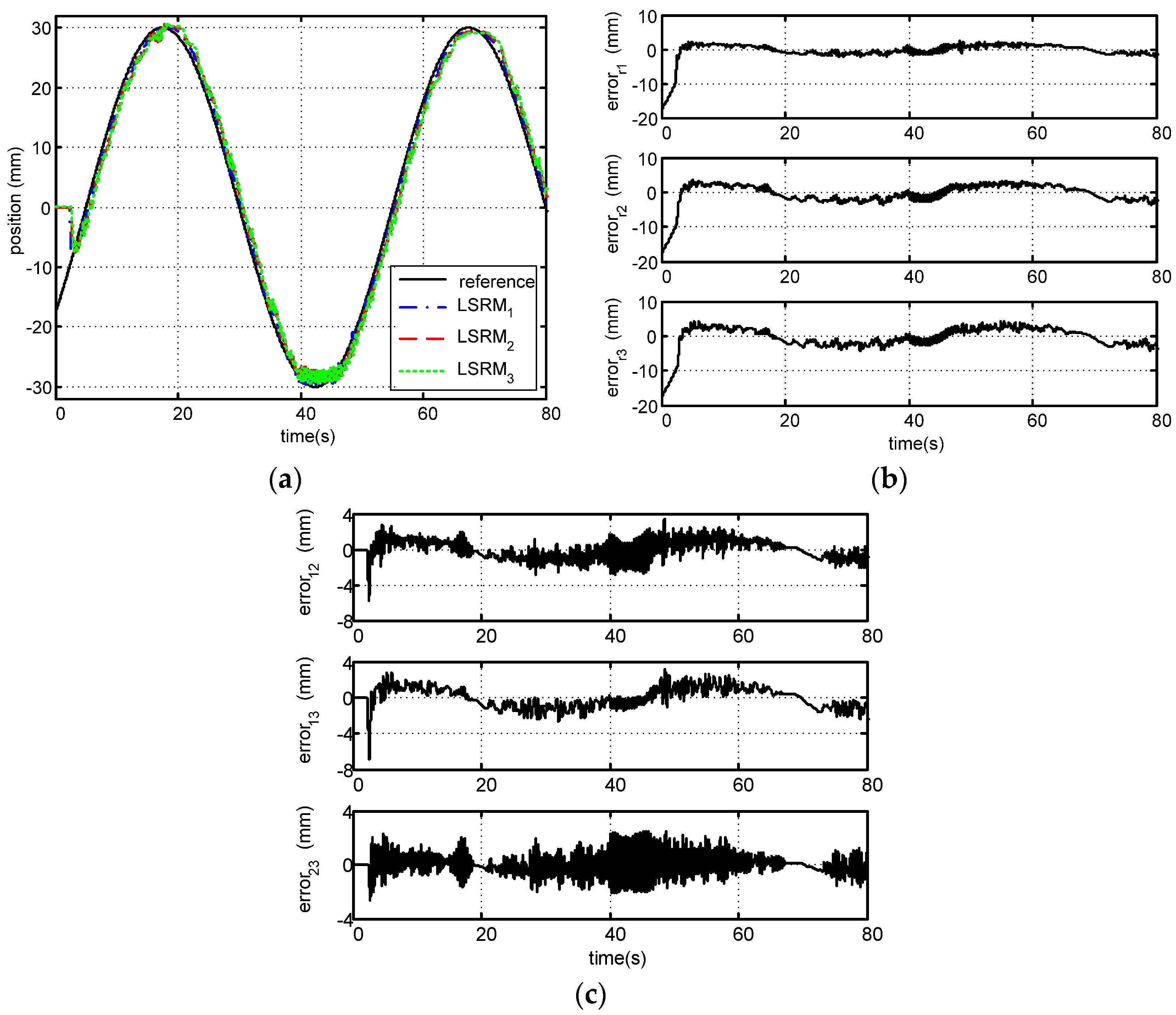
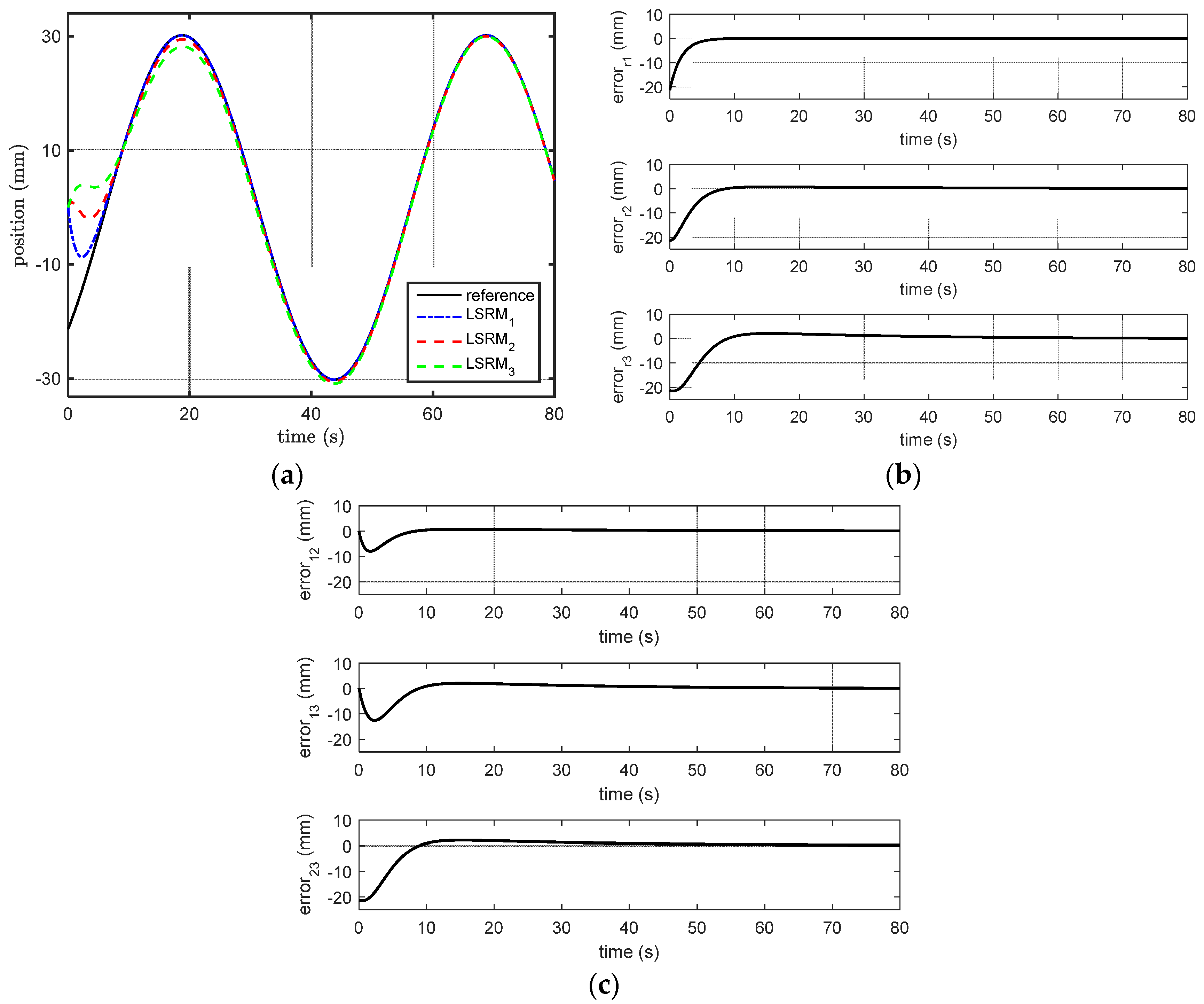
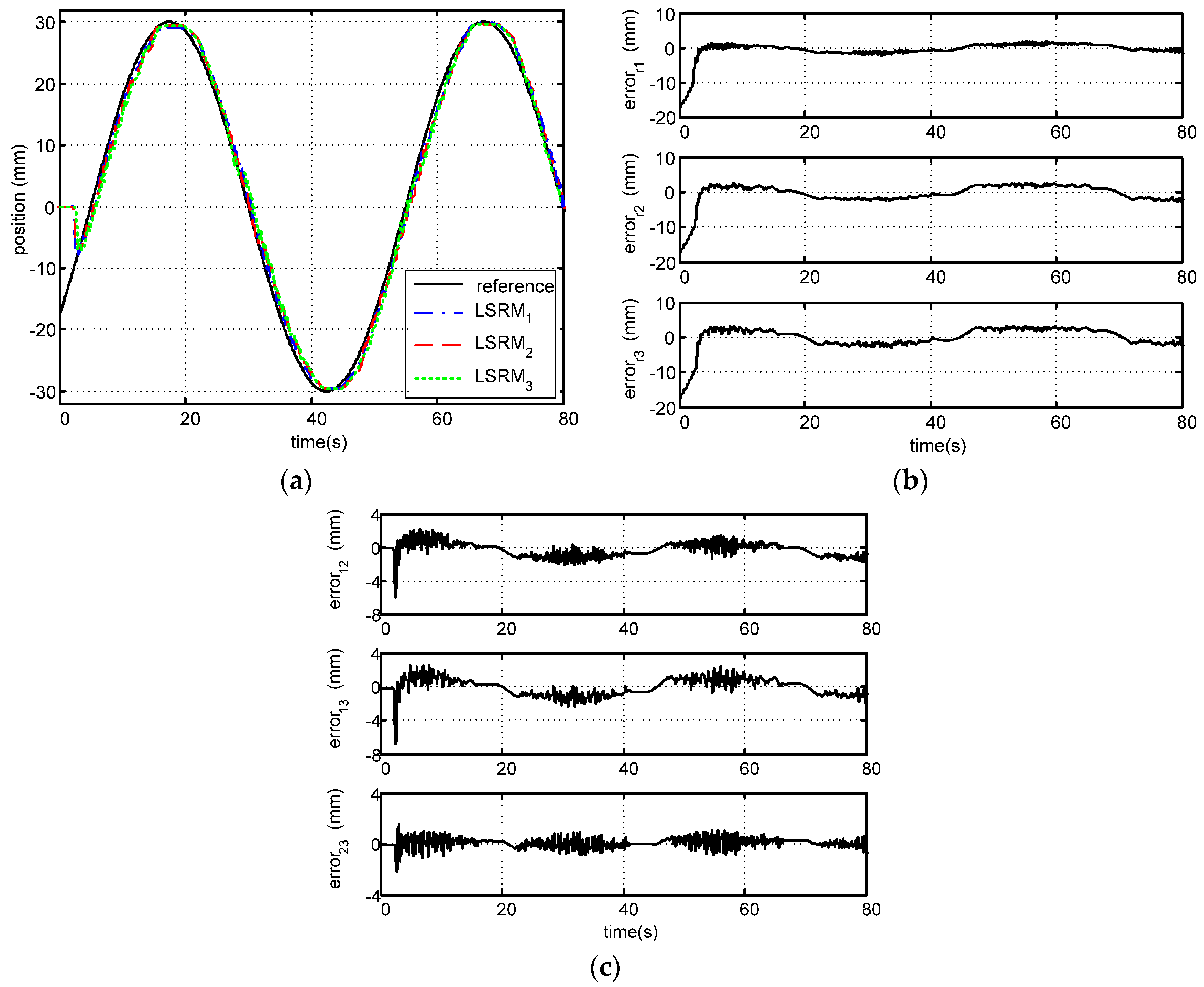
5.4. Tracking Performance Analysis
6. Conclusions and Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leitao, P.; Marik, V.; Vrba, P. Past, Present, and future of industrial agent applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2013, 9, 2360–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Yuan, J.; Luo, J.; Wu, X.; Qiu, L.; Pan, J.F. Hierarchical distributed motion control for multiple linear switched reluctance machines. Energies 2017, 10, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Pan, J.F.; Yuan, J.; Rao, W.; Qiu, L.; Luo, J.; Dai, H. Tracking control with zero phase-difference for linear switched reluctance machines network. Energies 2017, 10, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Yuan, J.; Qiu, L.; Cheung, N.; Pan, J.F. Distributed coordinated motion tracking of the linear switched reluctance machine-based group control system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 1480–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olfati-Saber, R.; Fax, J.A.; Murray, R.M. Consensus and cooperation in networked multi-agent systems. Proc. IEEE 2007, 95, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Chen, G.; Cao, M.; Ren, W. Delay-induced consensus and quasi-consensus in multi-agent dynamical systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I 2013, 60, 2679–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Shi, P.; Zhao, X.; Zeng, Q. Consensus of Euler–Lagrange systems networked by sampled-data information with probabilistic time delays. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2015, 45, 1126–1133. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, H. Consensus of networked mechanical systems with communication delays: A unified framework. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2014, 59, 1571–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Yu, W.; Ren, W.; Chen, G. An overview of recent progress in the study of distributed multi-agent coordination. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2012, 9, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ho, D.W.C.; Lu, J. A unified approach to practical consensus with quantized data and time delay. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I 2013, 60, 2668–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Fang, H. Multi-agent consensus with time-varying delays and switching topologies. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2014, 25, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Yu, B.; Shi, Z.; Zhong, Y. Time-varying formation control for unmanned aerial vehicles: Theories and Applications. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2014, 23, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Slotine, J.E.; Barabasi, A. Controllability of complex networks. Nature 2011, 473, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.; Zhao, C.; Di, Z.; Wang, W.; Lai, Y. Exact controllability of complex networks. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, T.; Barabasi, A. Control Capacity and A random sampling method in exploring controllability of complex networks. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruths, J.; Ruths, D. Control profiles of complex networks. Science 2014, 343, 1373–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Slotine, J.E.; Barabasi, A. Observability of complex systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 2460–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Gao, L.; Gao, Y.; Deng, Y.; Wang, Y. Controllability and observability analysis for vertex domination centrality in directed networks. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egerstedt, M.; Martini, S.; Cao, M.; Camlibel, K.; Bicchi, A. Interacting with networks: How does structure relate to controllability in single-leader, consensus networks? IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 2012, 32, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, N.; Cao, J.; Khan, M.J. A Controllability synthesis problem for dynamic multi-agent systems with linear high-order protocol. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2014, 12, 1366–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Shi, Y.; Pan, J.; Zhang, B.; Xu, G. Collaborative tracking control of dual linear switched reluctance machines over communication network with time delays. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2016, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, F.; Ye, Y.; Huang, J. Gas turbine engine identification based on a bank of self-tuning wiener models using fast kernel extreme learning machine. Energies 2017, 10, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi-Eichi, H.; Baronti, F.; Chow, M. Online adaptive parameter identification and state-of-charge coestimation for lithium-polymer battery cells. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 2053–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Yang, L.; Cai, Y.; Deng, H. Online identification with reliability criterion and state of charge estimation based on a fuzzy adaptive extended Kalman filter for lithium-ion batteries. Energies 2016, 9, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, G.; Wang, X.; Tang, W.K.S. Controllability of networked MIMO systems. Automatica 2016, 69, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astrom, K.J.; Murray, R.M. Feedback Systems: An Introduction for Scientists and Engineers; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Mass of moving platform | 3.8 kg |
| Mass of stator | 5.0 kg |
| Pole width | 6 mm |
| Pole pitch | 12 mm |
| Phase resistance | 2 ohm |
| Air gap length | 0.3 mm |
| Number of turns | 200 |
| Stack length | 50 mm |
| Encoder resolution | 1 µm |
| Parameter | Controller | Observer |
|---|---|---|
| Expected poles | ||
| Gain | ||
| Control parameters |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Yuan, J.; Pan, J.; Wu, X.; Luo, J.; Qiu, L. Controllability and Leader-Based Feedback for Tracking the Synchronization of a Linear-Switched Reluctance Machine Network. Energies 2017, 10, 1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10111728
Zhang B, Yuan J, Pan J, Wu X, Luo J, Qiu L. Controllability and Leader-Based Feedback for Tracking the Synchronization of a Linear-Switched Reluctance Machine Network. Energies. 2017; 10(11):1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10111728
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Bo, Jianping Yuan, Jianfei Pan, Xiaoyu Wu, Jianjun Luo, and Li Qiu. 2017. "Controllability and Leader-Based Feedback for Tracking the Synchronization of a Linear-Switched Reluctance Machine Network" Energies 10, no. 11: 1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10111728
APA StyleZhang, B., Yuan, J., Pan, J., Wu, X., Luo, J., & Qiu, L. (2017). Controllability and Leader-Based Feedback for Tracking the Synchronization of a Linear-Switched Reluctance Machine Network. Energies, 10(11), 1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10111728






