Facial Nerve Trauma: Evaluation and Considerations in Management
Abstract
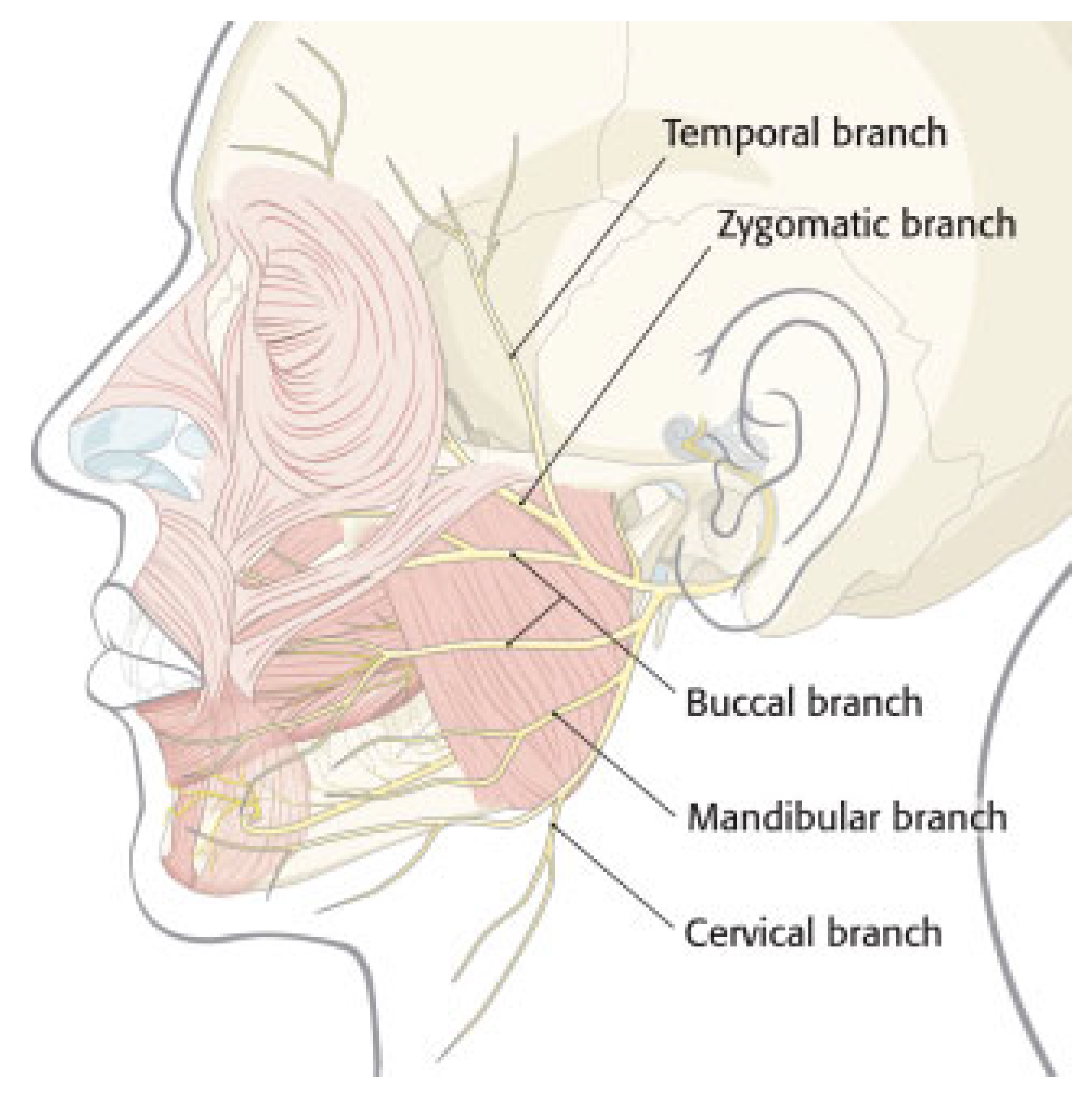
Anatomy
Etiology
Consequences
Assessment
Nerve Function Testing
Intratemporal Facial Nerve Trauma
Epidemiology and Classification
Timing of Paralysis
Surgical Indications
Operative Findings
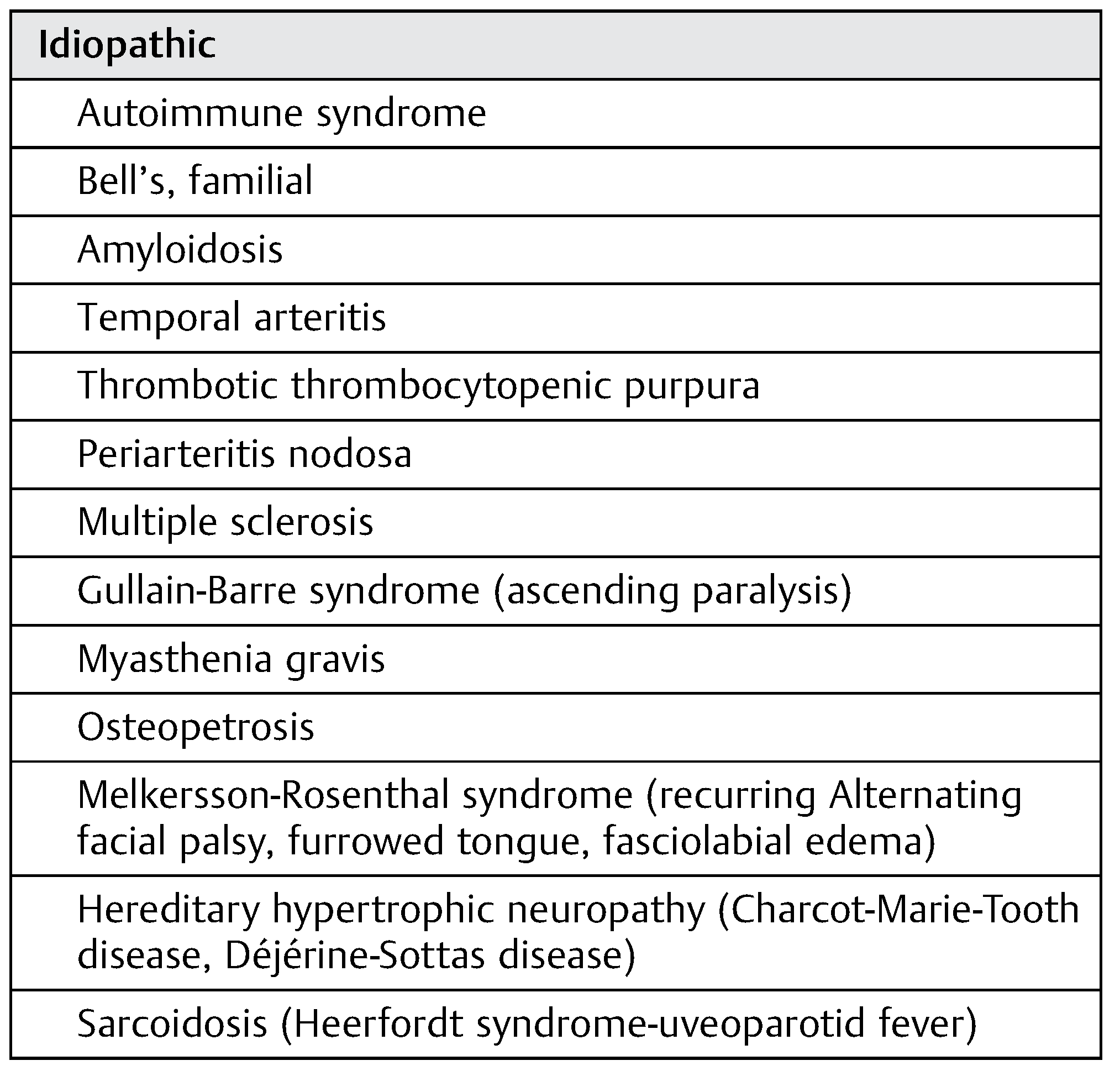
Idiopathic Facial Paralysis
Facial Paralysis: Treatment Considerations
Upper Face
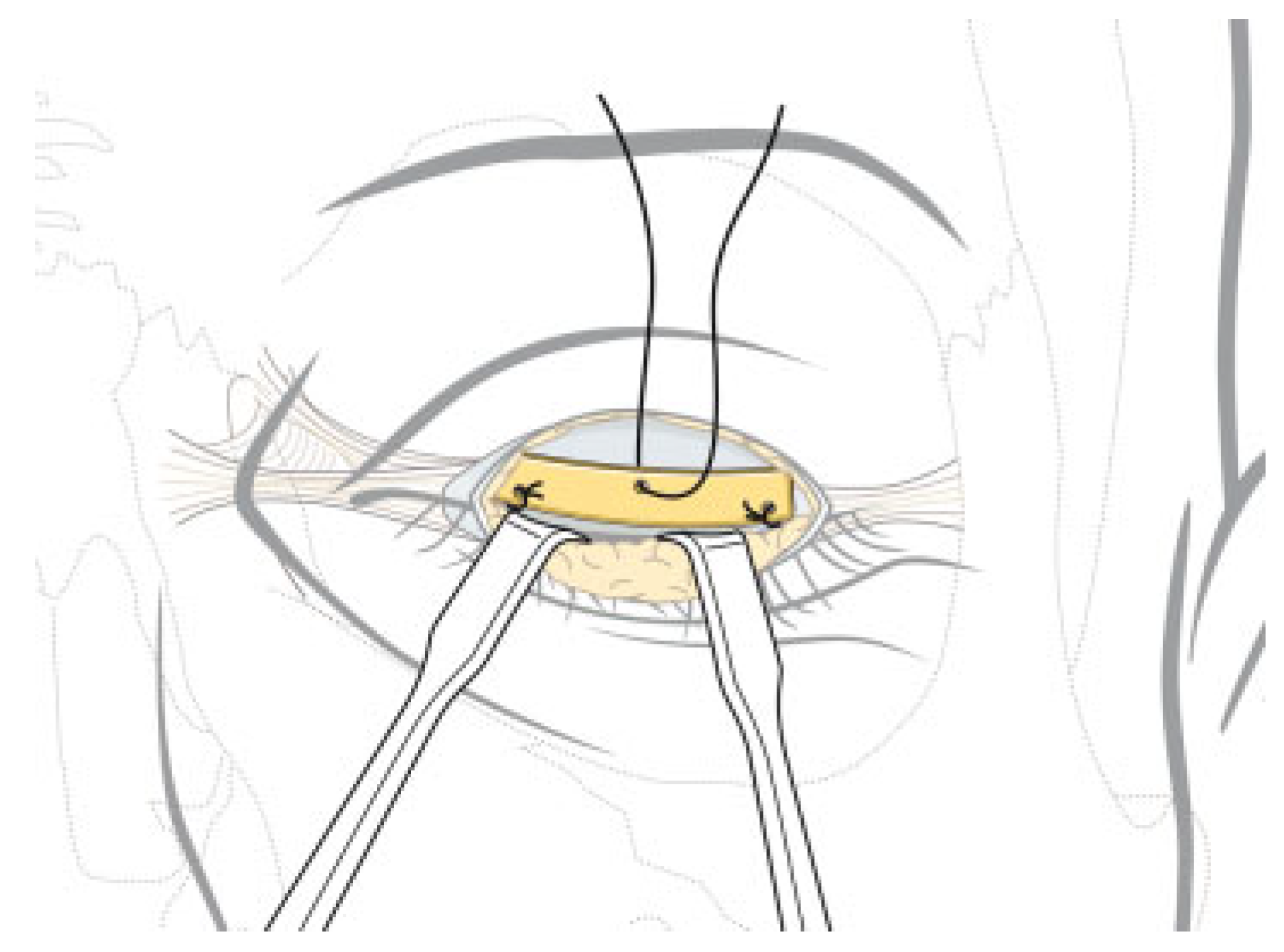
Eye
Brow
Midface
Cheek
Nose
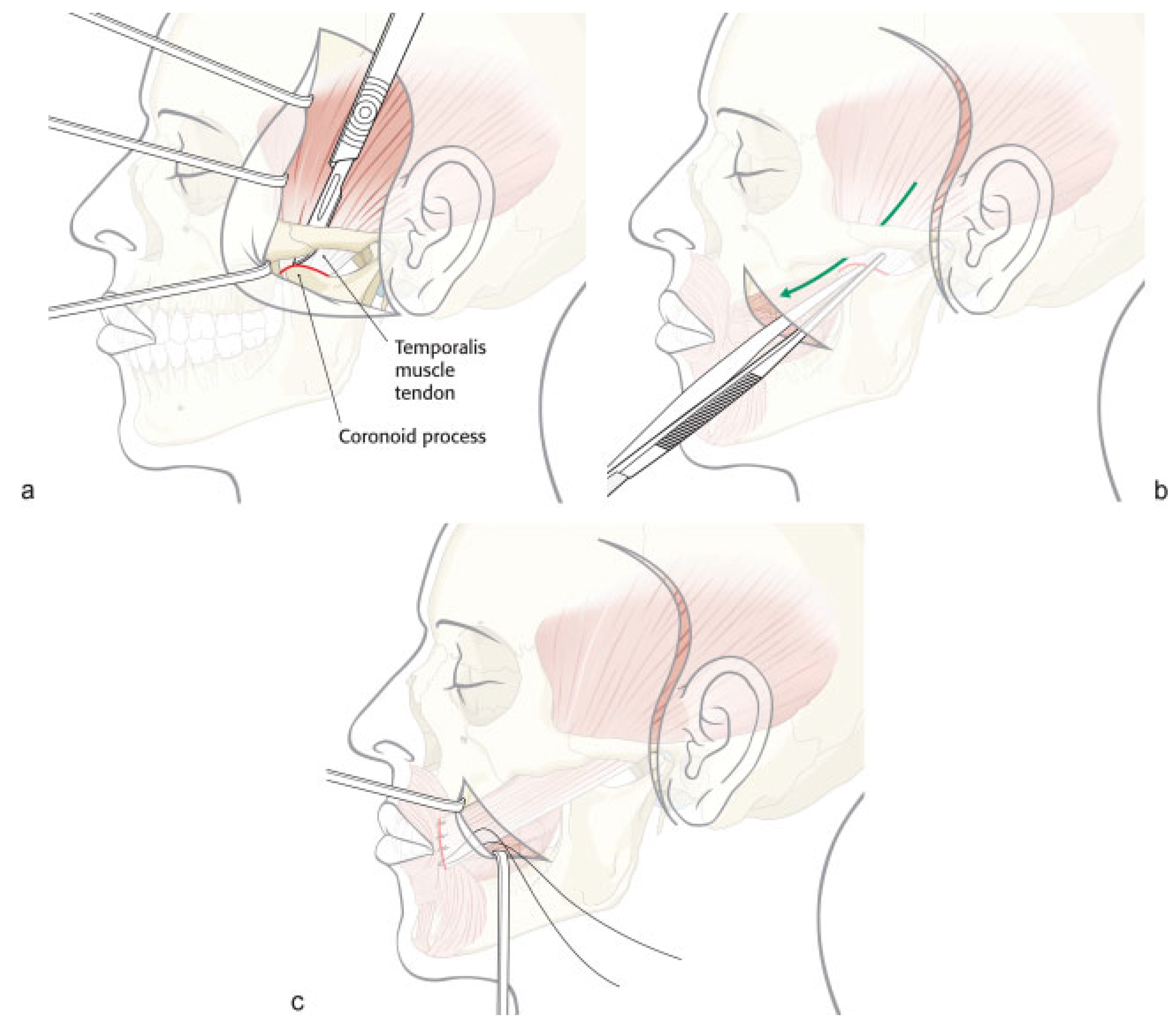
Lower Face
Primary Neurorrhaphy
Cross-Facial Nerve Graft
Nerve Transposition
Regional Muscle Transfer
Free-Tissue Transfer
Selection of Neural Input
Bilateral Paralysis
Nonoperative Therapy
Future Developments
Conclusion
References
- May, M. Anatomy for the clinician. In The Facial Nerve; May, M., Schaitkin, B., Eds.; Thieme Medical Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 19–56. [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein, L.; Nelson, R. Surgical anatomy of the extraparotid distribution of the facial nerve. Arch Otolaryngol 1984, 110, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tate, J.; Tollefson, T. Advances in facial reanimation. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2006, 14, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergeron, C.; Moe, K. The evaluation and treatment of upper eyelid paralysis. Facial Plast Surg 2008, 24, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meltzer, N.E.; Alam, D.S. Facial paralysis rehabilitation: state of the art. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2010, 18, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- House, J. Facial nerve grading systems. Laryngoscope 1983, 93, 1056–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brackmann, D.; Barrs, D. Assessing recovery of facial function following acoustic neuroma surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1984, 92, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzis, J.; Noah, M. Analysis of 100 cases of free-muscle transplantation for facial paralysis. Plast Reconstr Surg 1997, 99, 1905–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burres, S.; Fisch, U. The comparison of facial grading systems. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1986, 112, 755–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murty, G.; Diver, J.; Kelly, P.; O’Donoghue, G.; Bradley, P. The Nottingham system: objective assessment of facial nerve function in the clinic. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1994, 110, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, B.; Frader, G.; Nedzelski, J. Development of a sensitive clinical facial grading system. otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg 1996, 114, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sittel, C.; Stennert, E. Prognostic value of electromyography in acute peripheral facial nerve palsy. Otol Neurotol 2001, 22, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darrouzet, V. Management of facial paralysis resulting from temporal bone fractures: Our experience in 115 cases. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2001, 125, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coker, N. Acute paralysis of the facial nerve. In Head and Neck Surgery—Otolaryngology; Bailey, B, Ed.; J.B. Lippincott Company: Philadelphia, PA, 1993; pp. 1711–1728. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.; Case, S. Management of facial nerve injury due to temporal bone trauma. Am J Otol 1999, 20, 96–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodie, H.; Thomson, T. Management of complications from 820 temporal bone fractures. Am J Otol 1997, 18, 188–197. [Google Scholar]
- McKennan, K.; Chole, R. Facial paralysis in temporal bone trauma. J Trauma 1992, 13, 167–172. [Google Scholar]
- Ghorayeb, B.; Yeakley, J. Temporal bone fractures: longitudinal or oblique? The case for oblique temporal bone fractures. Laryngoscope 1992, 102, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, E., III; Yeakley, J.; Ghorayeb, B.; et al. High resolution CTscan of temporal bone fractures: association of facial nerve paralysis with temporal bone fractures. Head Neck Surg 1987, 9, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahiya, R.; Keller, J.; Litofsky, N.; et al. Temporal bone fractures: otic capsule sparing versus otic capsule violating clinical and radiographic considerations. J Trauma 1999, 47, 1079–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, S.; Kesser, B. Radiographic classification of temporal bone fractures: clinical predictability using a new system. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2006, 132, 1300–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quaranta, A.; Campobasso, G.; Piazza, F.; et al. Facial nerve paralysis in temporal bone fractures: outcomes after late decompression surgery. Acta Otolaryngol 2001, 121, 652–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, C.; Jahrsdoerfer, R. Temporal bone fractures. Review of 90 cases. Arch Otolaryngol 1983, 109, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosan, D.; Benecke, J.J.; Murr, A. Current perspective on temporal bone trauma. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1997, 117, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coker, N.; Kendall, K.; Jenkins, H.A.; et al. Traumatic intratemporal facial nerve injury: management rationale for preservation of function. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1987, 97, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisch, U.; Mattox, D. Microsurgery of the Skull Base; Georg Thieme Verlag: New York, NY, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Gantz, B.; Gmuer, A.; Holliday, M.; et al. Electroneurographic evaluation of the facial nerve. Method and technical problems. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 1984, 93 Pt 1, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- House, J.; Brackmann, D. Facial nerve grading system. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1985, 93, 146–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulug, T.; Arif Ulubil, S. Management of facial paralysis in temporal bone fractures: a prospective study analyzing 11 operated fractures. Am J Otolaryngol 2005, 26, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, P.; Brackmann, D. Facial paralysis in longitudinal temporal bone fractures: a review of 26 cases. Laryngoscope 1984, 94, 1022–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozorg Grayeli, A.; Mosnier, I.; Julien, N.; et al. Long-term functional outcome in facial nerve graft by fibrin glue in the temporal bone and cerebellopontine angle. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2004, 262, 404–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornelas, L.; Padilla, L.; Di Silvio, M.; et al. Fibrin glue: an alternative technique for nerve coaptation–Part, I. Wave amplitude, conduction velocity, and plantar-length factors. J Reconstr Microsurg 2006, 22, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornelas, L.; Padilla, L.; Di Silvio, M.; et al. Fibrin Glue: an alternative technique for nerve coaptation–Part, I.I. Nerve regeneration and histomorphometric assessment. J Reconstr Microsurg 2006, 22, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, R.A.; Alvarez, G.; Daly, F.; Ferreira, J. Corticosteroids for Bell’s palsy (idiopathic facial paralysis). Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2010, 17, CD001942. [Google Scholar]
- Hadlock, T. Facial paralysis: research and future directions. Facial Plast Surg 2008, 24, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danner, C.J. Facial nerve paralysis. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 2008, 41, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockhart, P.; Daly, F.; Pitkethly, M.; Comerford, N.; Sullivan, F. Antiviral treatment for Bell’s palsy (idiopathic facial paralysis). Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2009, 7, CD001869. [Google Scholar]
- Bodénez, C.; Bernat, I.; Willer, J.C.; Barré, P.; Lamas, G.; Tankéré, F. Facial nerve decompression for idiopathic Bell’s palsy: report of 13 cases and literature review. J Laryngol Otol 2010, 124, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melvin, T.-A.; Limb, C. Overview of facial paralysis: current concepts. Facial Plast Surg 2008, 24, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, E.; Byrne, P. Treatment considerations in facial paralysis. Facial Plast Surg 2008, 24, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terzis, J.; Konofaos, P. Nerve transfers in facial palsy. Facial Plast Surg 2008, 24, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, U.; Woodward, J. Abobotulinum toxin A (Dysport) and botulinum toxin type A (Botox) for purposeful induction of eyelid ptosis. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 2010, 26, 489–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, R.; Taban, M.; Lowinger, A.; et al. Use of hyaluronic acid gel in the management of paralytic lagophthalmos: the hyaluronic acid gel “Gold Weight”. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 2009, 25, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smellie, G. Restoration of the blinking reflex in facial palsy by a simple lid-load operation. Br J Plast Surg 1966, 19, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.T.; Staiano, J.J.; Itinteang, T.; McIntyre, B.C.; MacKinnon, C.A.; Glasson, D.W. Gold weight implantation and lateral tarsorrhaphy for upper eyelid paralysis. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 2013, 41, e49–e53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silver, A.L.; Lindsay, R.W.; Cheney, M.L.; Hadlock, T.A. Thin-profile platinum eyelid weighting: a superior option in the paralyzed eye. Plast Reconstr Surg 2009, 123, 1697–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razfar, A.; Afifi, A.; Manders, E.; et al. Ocular outcomes after gold weight placement and facial nerve resection. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2009, 140, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergeron, C.; Moe, K. The evaluation and treatment of lower eyelid paralysis. Facial Plast Surg 2008, 24, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebau, J.; Schulz, A.; Arens, A.; Tilkorn, H.; Schwipper, V. Management of lower lid ectropion. Dermatol Surg 2006, 32, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moe, K.S.; Kao, C.-H. Preauricular medial canthopexy. Arch Facial Plast Surg 2005, 7, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Frey, M.; Giovanoli, P.; Tzou, C.-H.J.; Kropf, N.; Friedl, S. Dynamic reconstruction of eye closure by muscle transposition or functional muscle transplantation in facial palsy. Plast Reconstr Surg 2004, 114, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boahene, K. Dynamic muscle transfer in facial reanimation. Facial Plast Surg 2008, 24, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzis, J.K.; Karypidis, D. Blink restoration in adult facial paralysis. Plast Reconstr Surg 2010, 126, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meltzer, N.; Byrne, P. Management of the brow in facial paralysis. Facial Plast Surg 2008, 24, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, G.; Mashkevich, G. Endoscopic forehead and brow lift. Facial Plast Surg 2009, 25, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, F.; Losken, A.; Bostwick, J.I.; Trinei, F.; Eaves, F. Endoscopic frontal branch neurectomy corrugator myectomy and brow lift for forehead asymmetry after facial nerve palsy. Plast Reconstr Surg 2001, 108, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducic, Y.; Adelson, R. Use of the endoscopic forehead-lift to improve brow position in persistent facial paralysis. Arch Facial Plast Surg 2005, 7, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verpaele, A.; Tonnard, P.; Gaia, S.; Guerao, F.; Pirayesh, A. The third suture in MACS-lifting: making midface-lifting simple and safe. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2007, 60, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elner, V.; Mauffray, R.; Fante, R.; Harris, M.; Morton, A.; Hassan, A. Comprehensive midfacial elevation for ocular complications of facial nerve palsy. Arch Facial Plast Surg 2003, 5, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, J.Y.K.; Byrne, P. Management of facial paralysis in the 21st century. Facial Plast Surg 2011, 27, 346–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M. A simplified technique for airway correction at the nasal valve area. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2004, 131, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuara, M.; Mobley, S. Nasal valve suspension revisited. Laryngoscope 2007, 117, 2100–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alex, J.; Nguyen, D. Multivectored suture suspension: a minimally invasive technique for reanimation of the paralyzed face. Arch Facial Plast Surg 2004, 6, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, D.S. Rehabilitation of long-standing facial nerve paralysis with percutaneous suture-based slings. Arch Facial Plast Surg 2007, 9, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capone, R.; Sykes, J. The effect of rhytidectomy on the nasal valve. Arch Facial Plast Surg 2005, 7, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ramakrishnan, Y.; Alam, S.; Kotecha, A.; Gillett, D.; D’Souza, A. Reanimation following facial palsy: present and future directions. J Laryngol Otol 2010, 124, 1146–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosson, G.; Redett, R. Facial palsy: anatomy, etiology, grading, and surgical treatment. J Reconstr Microsurg 2008, 24, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, E.; Frodel, J. Facial suspension with acellular human dermal allograft. Arch Facial Plast Surg 1999, 1, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, A.J.; de Almeida, J.R.; Shrime, M.G.; Goldstein, D.P.; Gilbert, R.W. Novel outpatient approach to lower lip reanimation using a palmaris longus tendon sling. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2011, 40, 481–488. [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey, C.; Kriet, J. Nerve repair and cable grafting for facial paralysis. Facial Plast Surg 2008, 24, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnew, S.P.; Dumanian, G.A. Technical use of synthetic conduits for nerve repair. J Hand Surg Am 2010, 35, 838–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myckatyn, Y.; Mackinnon, S.E. The surgical management of facial nerve injury. Clin Plast Surg 2003, 30, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samii, M.; Matthies, C. Indication, technique and results of facial nerve reconstruction. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1994, 130, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaramella, L. Anastomosis between the two facial nerves. Laryngoscope 1975, 85, 1359–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.; Hurvitz, K.; Evans, G.; Wirth, G. Cross-facial nerve graft: past and present. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2008, 61, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzis, J.K.; Tzafetta, K. The “Babysitter” procedure: minihypoglossal to facial nerve transfer and cross-facial nerve grafting. Plast Reconstr Surg 2009, 123, 865–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galli, S.K.; Valauri, F.; Komisar, A. Facial reanimation by cross-facial nerve grafting: report of five cases. Ear Nose Throat J 2002, 81, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conley, J.; Baker, D. Hypoglossal-facial nerve anastomosis for reinnervation of the paralyzed face. Plast Reconstr Surg 1979, 61, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochkind, S.; Shafi, M.; Alon, M.; Salame, K.; Fliss, D. Facial nerve reconstruction using a split hypoglossal nerve with preservation of tongue function. J Reconstr Microsurg 2008, 24, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, H.; Kiyoshi, S.; Yanai, A. Hemihypoglossal-facial nerve anastomosis in treating unilateral facial palsy after acoustic neuroma resection. J Neurosurg 1995, 82, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, A.; Nishida, M.; Seno, H.; et al. Hemihypoglossal nerve transfer for acute facial paralysis. J Neurosurg 2013, 118, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrales, C.; Gurgel, R.; Jackler, R. Rehabilitation of central facial paralysis with hypoglossal-facial anastomosis. Otol Neurotol 2012, 33, 1439–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klebuc, M.J.A. Facial reanimation using the masseter-to-facial nerve transfer. Plast Reconstr Surg 2011, 127, 1909–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hontanilla, B.; Marré, D. Comparison of hemihypoglossal nerve versus masseteric nerve transpositions in the rehabilitation of short-term facial paralysis using the Facial Clima evaluating system. Plast Reconstr Surg 2012, 130, 662e–672e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, J.C.M.; Scopel, G.P.; Ferreira, M.C. Facial reanimation with masseteric nerve: babysitter or permanent procedure? Preliminary results. Ann Plast Surg 2010, 64, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaverien, M.; Moran, G.; Stewart, K.; Addison, P. Activation of the masseter muscle during normal smile production and the implications for dynamic reanimation surgery for facial paralysis. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2011, 64, 1585–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borschel, G.; Kawamura, D.; Kasukurthi, R.; Hunter, D.; Zuker, R.; Woo, A. The motor nerve to the masseter muscle: an anatomic and histomorphometric study to facilitate its use in facial reanimation. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2012, 65, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collar, R.M.; Byrne, P.J.; Boahene, K.D.O. The subzygomatic triangle: rapid, minimally invasive identification of the masseteric nerve for facial reanimation. Plast Reconstr Surg 2013, 132, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, J.C.M.; Scopel, G.P.; Busnardo, F.F.; Ferreira, M.C. Nerve sources for facial reanimation with muscle transplant in patients with unilateral facial palsy. Ann Plast Surg 2007, 59, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volk, G.F.; Pantel, M.; Streppel, M.; Guntinas-Lichius, O. Reconstruction of complex peripheral facial nerve defects by a combined approach using facial nerve interpositional graft and hypoglossal-facial jump nerve suture. Laryngoscope 2011, 121, 2402–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conley, J. Facial rehabilitation: new potentials. Clin Plast Surg 1979, 6, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, J.; Baker, D.; Selfe, R. Paralysis of the mandibular branch of the facial nerve. Plast Reconstr Surg 1982, 70, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, C. Surgical support in permanent facial paralysis. Plast Reconstr Surg 1946, 11, 302–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labbe, D.; Huault, M. Lengthening temporalis myoplasty and lip reanimation. Plast Reconstr Surg 2000, 105, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boahene, K.; Farrag, T.Y.; Ishii, L.; Byrne, P. Minimally invasive temporalis tendon transposition. Arch Facial Plast Surg 2011, 13, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidle, D.M.; Fishman, A.J. Modification of the orthodromic temporalis tendon transfer technique for reanimation of the paralyzed face. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2011, 145, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, P.; Kim, M.; Boahene, K.; Millar, J.; Moe, K. Temporalis tendon transfer as part of a comprehensive approach to facial reanimation. Arch Facial Plast Surg 2007, 9, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hontanilla, B.; Qiu, S.S. Transposition of the hemimasseteric muscle for dynamic rehabilitation of facial paralysis. J Craniofac Surg 2012, 23, 203–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harii, K.; Ohmori, K.; Torii, S. Free gracilis muscle transplantation, with microneurovascular anastomoses for the treatment of facial paralysis: a preliminary report. Plast Reconstr Surg 1976, 57, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, D. Free tissue transfer for the treatment of facial paralysis. Facial Plast Surg 2008, 24, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harii, K.; Asato, H.; Yoshimura, K.; Sugawara, Y.; Nakatsuka, T.; Ueda, K. One-stage transfer of the latissimus dorsi muscle for reanimation of a paralyzed face: a new alternative. Plast Reconstr Surg 1998, 102, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takushima, A.; Harii, K.; Asato, H.; Kurita, M.; Shiraishi, T. Fifteen-year survey of one-stage latissimus dorsi muscle transfer for treatment of longstanding facial paralysis. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2013, 66, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guelinckx, P.; Sinsel, N. Muscle transplantation for reconstruction of a smile after facial paralysis past, present, and future. Microsurgery 1996, 17, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, B.; Copelli, C.; Ferrari, S.; Ferri, A.; Bailleul, C.; Sesenna, E. Facial animation with free-muscle transfer innervated by the masseter motor nerve in unilateral facial paralysis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2010, 68, 1524–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biglioli, F.; Colombo, V.; Tarabbia, F.; et al. Recovery of emotional smiling function in free-flap facial reanimation. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2012, 70, 2413–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hontanilla, B.; Marre, D.; Cabello, A. Facial reanimation with gracilis muscle transfer neurotized to cross-facial nerve graft versus masseteric nerve: a comparative study using the FACIAL CLIMA evaluating system. Plast Reconstr Surg 2013, 131, 1241–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gousheh, J.; Arasteh, E. Treatment of facial paralysis. Plast Reconstr Surg 2011, 128, 693e–703e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manktelow, R.T.; Tomat, L.R.; Zuker, R. Smile reconstruction in adults with free muscle transfer innervated by the masseter motor nerve: effectiveness and cerebral adaptation. Plast Reconstr Surg 2006, 118, 885–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, B.; Copelli, C.; Ferrari, S.; Ferri, A.; Sesenna, E. Successful salvage surgery after treatment failures with cross graft and free muscle transplant in facial reanimation. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 2012, 40, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horta, R.; Silva, P.; Bartosh, I.; et al. Facial reanimation with gracilis muscle transplantation and obturator nerve coaptation to the motor nerve of masseter muscle as a salvage procedure in an unreliable cross-face nerve graft. Microsurgery 2011, 31, 164–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biglioli, F.; Bayoudh, W.; Colombo, V.; Pedrazzoli, M.; Rabbiosi, D. Double innervation (facial/masseter) on the gracilis flap, in the middle face reanimation in the management of facial paralysis: A new concept. Ann Chir Plast Esthet 2013, 58, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, D.; Grobbelaar, A. Pectoralis minor muscle transfer for unilateral facial palsy reanimation: an experience of 35 years and 637 cases. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2012, 65, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.-T.; Lin, Q.; Jiang, H.; et al. Facial reanimation by one-stage microneurovascular free abductor hallucis muscle transplantation. Plast Reconstr Surg 2012, 130, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagöz, M.Ş.; Alagöz, A.N.; Comert, A. Neuroanatomy of extensor digitorum brevis muscle for reanimation of facial paralysis. J Craniofac Surg 2011, 22, 2308–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revenaugh, P.; Knott, P.; Scharpf, J.; Fritz, M. Simultaneous anterolateral thigh flap and temporalis tendon transfer to optimize facial form and function after radical parotidectomy. Arch Facial Plast Surg 2012, 14, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, R.W.; Hadlock, T.A.; Cheney, M.L. Bilateral simultaneous free gracilis muscle transfer: A realistic option in management of bilateral facial paralysis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2009, 141, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchi, B.; Copelli, C.; Ferrari, S.; Ferri, A.; Sesenna, E. Facial animation in children with Moebius and Moebius-like syndromes. J Pediatr Surg 2009, 44, 2236–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hontanilla, B.; Aubá, C. Smile reconstruction through bilateral muscular transplants neurotized by hypoglossal nerves. J Craniofac Surg 2011, 22, 845–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.C.-Y.; Chuang, D.C.-C. One-Stage reconstruction for bilateral Möbius syndrome. Ann Plast Surg 2013, 70, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husseman, J.; Mehta, R. Management of synkinesis. Facial Plast Surg 2008, 24, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, J.; Teixeira, E.; Moreira, M.; Favero, F.; Fontes, S.; de Oliveira, A. Effects of exercises on Bell’s palsy: systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Otol Neurotol 2008, 29, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, R.W.; Robinson, M.; Hadlock, T.A. Comprehensive facial rehabilitation improves function in people with facial paralysis: a 5-year experience at the Massachusetts eye and ear infirmary. Phys Ther 2010, 90, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, H.; Nakano, S.; Kusaka, H. Low-dose subcutaneous injection of botulinum toxin type A for facial synkinesis and hyperlacrimation. Acta Neurol Scand 2007, 115, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salles, A.; Toledo, P.; Ferreira, M. Botulinum toxin injection in longstanding facial paralysis patients: improvement of facial symmetry observed up to 6 months. Aesthetic Plast Surg 2009, 33, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiono, V.; Tonda Turo, C.; Ciardelli, G. Chapter 9: Artificial scaffolds for peripheral nerve reconstruction. Int Rev Neurobiol 2009, 87, 173–198. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cunha, C.; Panseri, S.; Antonini, S. Emerging nanotechnology approaches in tissue engineering for peripheral nerve regeneration. Nanomedicine (Lond Print) 2011, 7, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledgerwood, L.G.; Tinling, S.; Senders, C.; Wong-Foy, A.; Prahlad, H.; Tollefson, T.T. Artificial muscle for reanimation of the paralyzed face: durability and biocompatibility in a gerbil model. Arch Facial Plast Surg 2012, 14, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, G.R.; Kim, J.C. Potential of an electric prosthesis for dynamic facial reanimation. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2011, 145, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, H.; Carraro, U.; Adami, N.; et al. One year of home-based daily FES in complete lower motor neuron paraplegia: recovery of tetanic contractility drives the structural improvements of denervated muscle. Neurol Res 2010, 32, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



 |
 |
 |
© 2014 by the author. The Author(s) 2014.
Share and Cite
Gordin, E.; Lee, T.S.; Ducic, Y.; Arnaoutakis, D. Facial Nerve Trauma: Evaluation and Considerations in Management. Craniomaxillofac. Trauma Reconstr. 2015, 8, 1-13. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1372522
Gordin E, Lee TS, Ducic Y, Arnaoutakis D. Facial Nerve Trauma: Evaluation and Considerations in Management. Craniomaxillofacial Trauma & Reconstruction. 2015; 8(1):1-13. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1372522
Chicago/Turabian StyleGordin, Eli, Thomas S. Lee, Yadranko Ducic, and Demetri Arnaoutakis. 2015. "Facial Nerve Trauma: Evaluation and Considerations in Management" Craniomaxillofacial Trauma & Reconstruction 8, no. 1: 1-13. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1372522
APA StyleGordin, E., Lee, T. S., Ducic, Y., & Arnaoutakis, D. (2015). Facial Nerve Trauma: Evaluation and Considerations in Management. Craniomaxillofacial Trauma & Reconstruction, 8(1), 1-13. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1372522



