Abstract
Study Design: This retrospective cohort study utilized the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) database for the years 2016–2018. Incidences of street fighting were identified using the corresponding ICD-10 codes. Objective: To determine whether alcohol use (measured by blood alcohol content (BAC)) in patients sustaining maxillofacial trauma from hand-to-hand fighting influence hospitalization outcomes. Methods: The primary predictor variable was BAC stratified into six categories of increasing magnitude. The primary outcome variable was mean length of hospital stay (days). The secondary outcome variable was total hospital charges (US dollars). Results: Our final sample consisted of 3038 craniomaxillofacial fractures. Each additional year in age added +$545 in hospital charges (P < .01). Non-elective admissions added $14 210 in hospital charges (P < .05). Patients admitted in 2018 experienced approximately $7537 more in hospital charges (P < .01). Le Fort fractures (+$61 921; P < .01), mandible fractures (+$13 227, P < .01), and skull base fractures (+$22 170; P < .05) were all independently associated with increased hospital charges. Skull base fractures added +7.6 days to the hospital stay (P < .01) and each additional year in patient age added +.1 days to the length of the hospital stay (P < .01). Conclusions: BAC levels did not increase length of stay or hospitalization charges. Le Fort fractures, mandible fractures, and skull base fracture each independently increased hospital charges. This reflects the necessary care (ie, ICU) and treatment (ie, ORIF) of such fractures. Older adults and elderly patients are associated with increased length of stay and hospital charges—they are likely to struggle in navigating the healthcare system and face socioeconomic barriers to discharge.
Introduction
Violence-related trauma (VRT) is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality. Worldwide, VRT contributes to the death of over 1.25 million people every year [1]. Injuries due to violence have the potential to impart a substantial burden on the victim, which has been estimated to account for roughly 10% of the total global years lived with disability (YLD) [2]. Furthermore, VRT places a considerable economic toll on countries, costing them billions in United States (US) dollars each year in related healthcare costs and compromised productivity [1].
Though are many factors influence the prevalence of VRT (including IPV), one of the most frequently cited causes is alcohol use and abuse [3,4,5,6,7,8]. Alcohol use is common in the US, with approximately 85.6% of adults ages 18 and over reporting that they have drank alcohol at least once during their lifetime [9]. Furthermore, as of 2019, nearly 14.5 million Americans 12 years or older have alcohol use disorder (AUD) [10]. Alcohol intoxication has the potential to incite aggression, impaired judgement, and reduced inhibition; for this reason, alcohol strongly facilitates IPV among abusers [11,12]. The maxillofacial region has been shown to be a prime target of alcohol-induced violence, particularly in the setting of hand-to-hand combat in street fights [13].
There is a wealth of literature exploring the etiologies and outcomes of maxillofacial trauma caused by different forms of violence [3,14,15,16,17]. Furthermore, several studies have examined the role of alcohol use on the incidence and severity of maxillofacial trauma caused by IPV [11,18,19]. However, there are no studies examining the extent to which alcohol use has contributed to hospitalization outcomes in patients sustaining maxillofacial trauma following unarmed hand-to-hand fights.
The primary purpose of this study is to answer the following clinical question: does alcohol use (measured by blood alcohol content [BAC]) in patients sustaining maxillofacial trauma from hand-to-hand fighting influence hospitalization outcomes? Specifically, the authors sought to determine the effect of BAC on hospitalization outcomes, total hospital charges from admission to discharge, and the length of hospital stay from admission to discharge. A secondary aim was to determine whether the type and location of maxillofacial injury influenced hospitalization outcomes among this population. We hypothesized that total hospital charges and length of hospital stay would increase with heightened alcohol use.
Methods
Study Cohort
This retrospective cohort study utilized the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) database, which was developed as part of the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Protect (HCUP). The NIS is the largest publicly available, all-payer inpatient care database in the US and contains patient-level information on over seven million hospital stays (excluding rehabilitation and long-term acute care facilities) [20]. As a result of its large sampling size, the NIS is ideal for producing national estimates of inpatient utilization, access, cost, quality, and outcomes [21].
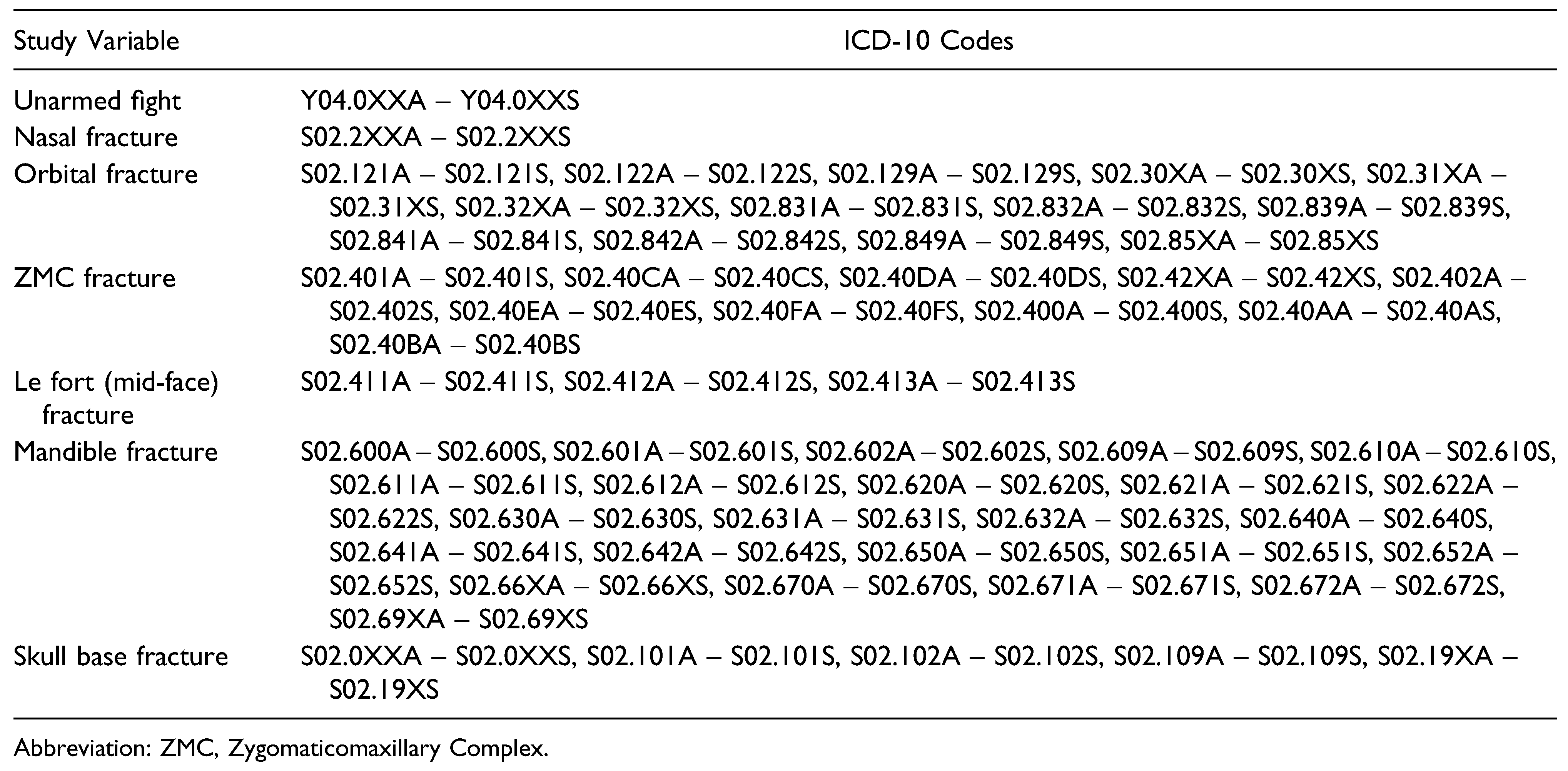
The authors queried the NIS for hospital admissions resulting from street fights for the years 2016–2018. Incidences of unarmed brawl or fight were identified using the following ICD-10 codes: Y04.0XXA-Y04.0XXS. The type of maxillofacial injury (nasal fracture, orbital fracture, zygomaticomaxillary complex (ZMC) fracture, Le Fort (Mid-Face) fracture, mandible fracture, and skull base fracture) was identified using the ICD-10 codes listed in Table 1. As per Columbia University Medical Center policy, the current study did not require institutional review board approval as the data was completely anonymous and freely accessible.

Table 1.
ICD-10 Codes Used to Identify Subjects and Define Variables.
Study Variables
The primary predictor variable was BAC stratified into the following categories: less than 40 mg/100 mL, 40–79 mg/ 100 mL, 80–119 mg/100 mL, 120–199 mg/100 mL, 200–239 mg/100 mL, and more than 240 mg/100 mL. Additional predictor variables include age, sex (male vs female), race (White, Black, other), median household income for patient’s ZIP code (separated into quartiles), payer information (Medicare/Medicaid, private insurance, self-pay), elective admission, location of patient, calendar year (2016, 2017, 2018), and type of craniomaxillofacial fracture (nasal, orbital, ZMC, Le Fort (mid-face), mandible, skull base).
The primary outcome variable was mean length of hospital stay (days), measured from the time of hospital admission to discharge. The secondary outcome variable of interest was total hospital charges (US dollars, $) from the time of hospital admission to discharge.
Statistical Analysis
Patient demographic information and descriptive statistics were computed and recorded. The locations of craniomaxillofacial fractures were compared across all predictor variables using independent sample t tests chi-square tests for continuous and categorical variables, respectively. A bivariate comparison for both mean hospital charges and mean length of hospital stay across all predictor variables was performed in order to determine which variables to include in the regression models. Multiple linear regression models were then conducted to control for all covariates in predicting mean hospital charges and mean length of hospital stay. IBM SPSS Statistics Software Package (SPSS Statistics, IL. Chicago, USA) was utilized for all statistical analyses. Statistical significance was set at a P-value of <.05.
Results
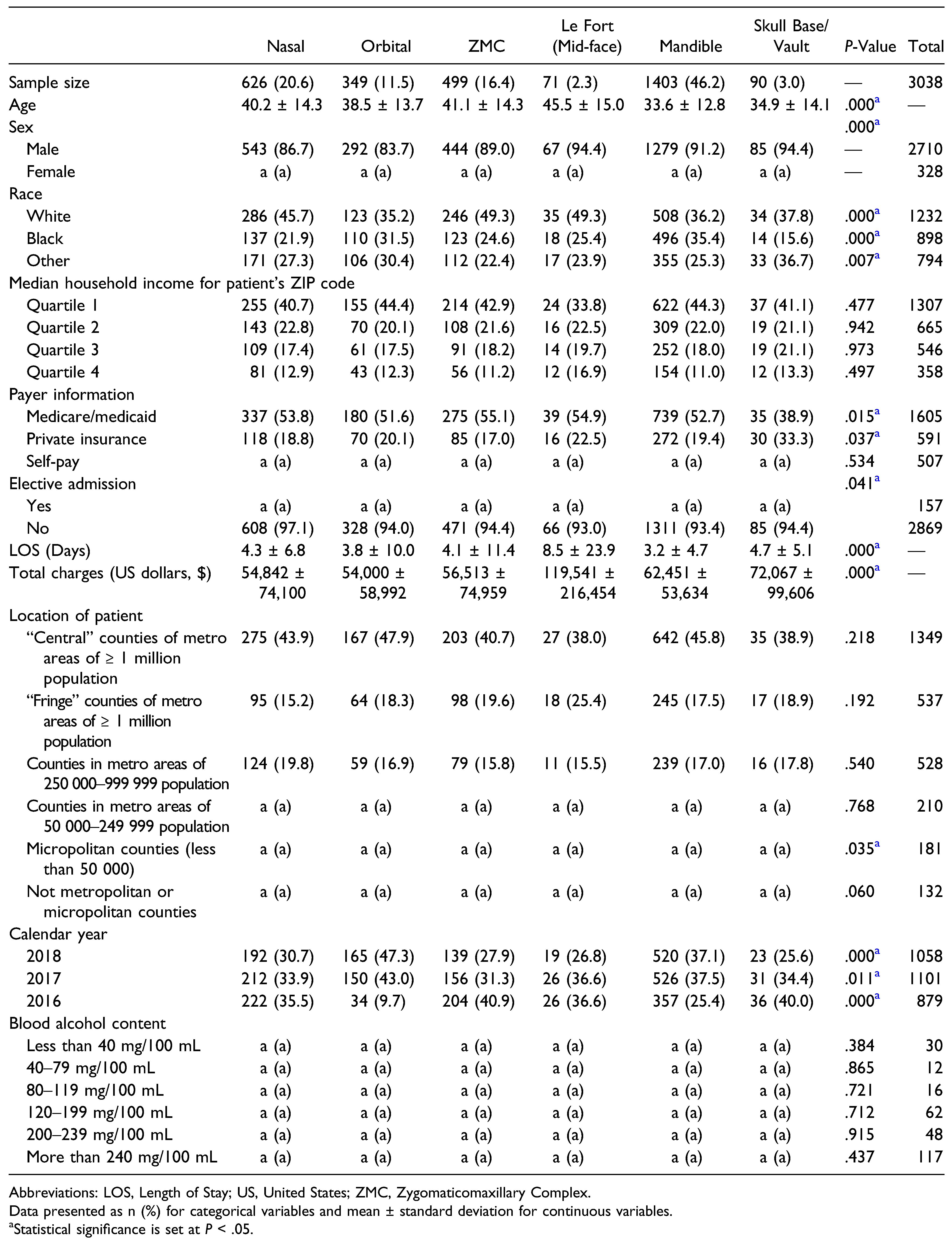
Our final sample consisted of 3038 craniomaxillofacial fractures secondary to street fights. The most frequently fractured region was the mandible (n = 1,403, 46.2%). One the other hand, the mid-face (n = 71, 2.3%) was the least frequently fractured region (Figure 1). There was a statistically significant association between age and type of craniomaxillofacial fracture (P < .01), with Le Fort fractures having the highest mean age (45.5 ± 15.0 years) and skull vault fractures having the lowest (34.9 ± 14.1 years). The distribution of craniomaxillofacial fractures varied significantly (P < .05) across patient sex and race as well as those who were insured by Medicaid/Medicare and private insurance. The distribution of fractures was also significantly associated (P < .05) with admission status (elective vs non-elective), length of hospital stay, total hospital charges, and calendar year. With regards to patient location, only those patients living in micropolitan counties (less than 50 000 individuals) demonstrated a significantly variable distribution of craniomaxillofacial fractures (P < .05) (Table 2).
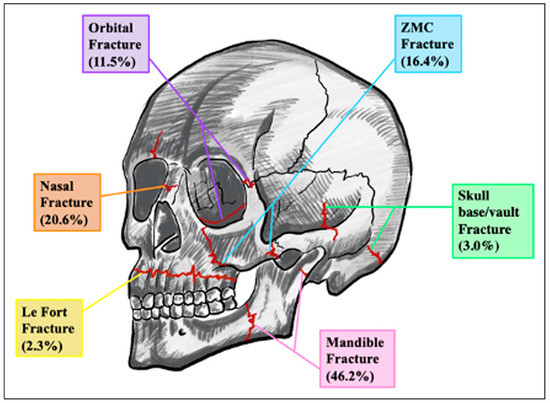
Figure 1.
Distribution of craniomaxillofacial fractures in our study sample.

Table 2.
Patient Demographics and Hospitalization Outcomes Stratified by Craniomaxillofacial Fracture. a, cells with counts < 11. Consistent with the HCUP data use agreement, these cells as well as cells in corresponding rows and/or columns were masked.
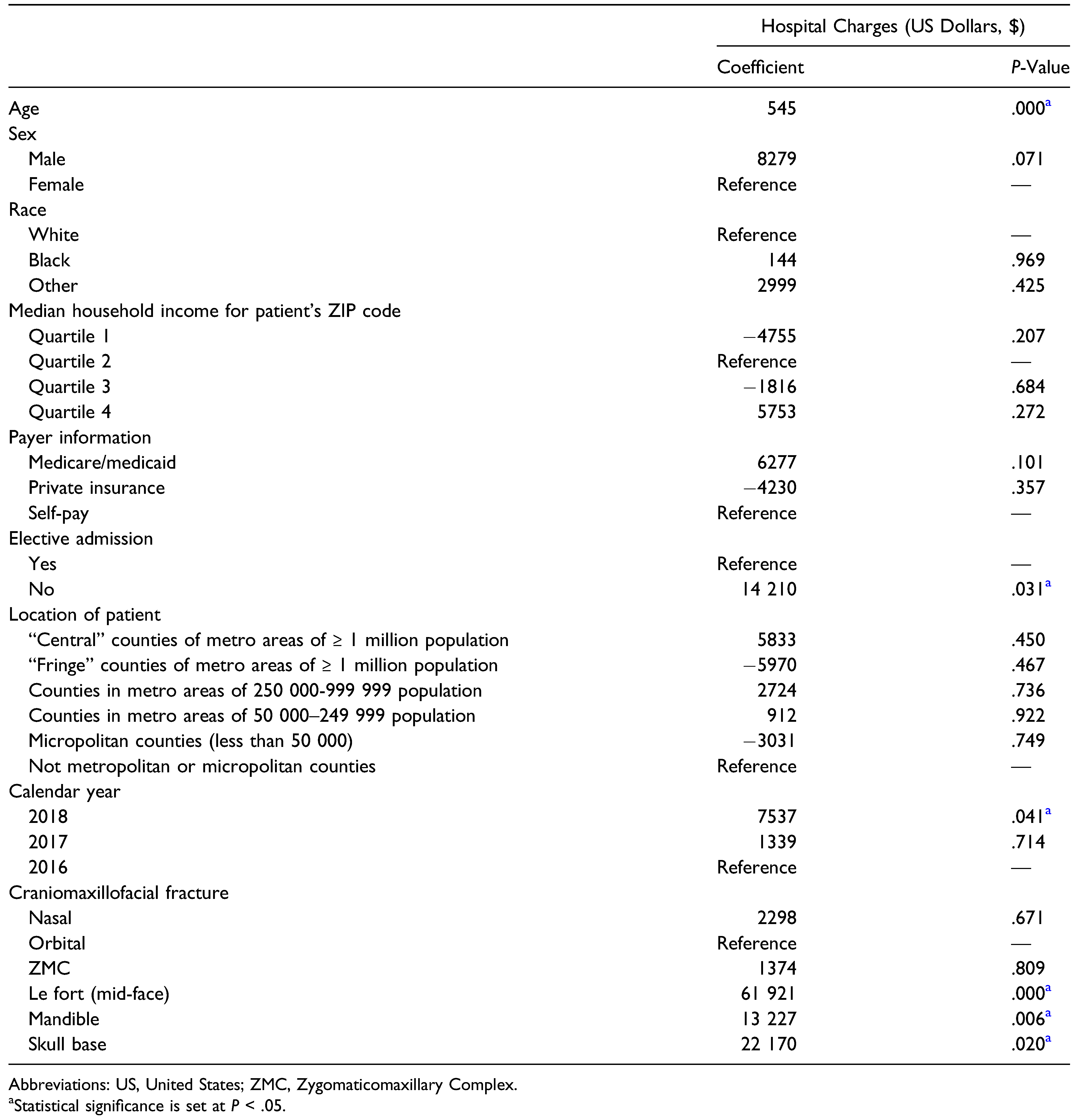
A bivariate comparison of mean hospital charges for each variable was conducted (Table 3). Patient sex, race, median household income for residential ZIP code, payer information, admission status, patient location, calendar year, and type of craniomaxillofacial fracture all proved to be significant predictors (P < .01) of increased hospital charges. An additional multiple linear regression model was conducted to control for all covariates in predicting total hospital charges (Table 4). Each additional year in age for a patient added +$545 in hospital charges (P < .01). Relative to patients who were electively admitted for their injuries, non-elective admissions added $14 210 in hospital charges (P < .05). Compared to 2016, patients admitted in 2018 experienced approximately $7537 more in hospital charges (P < .01). With reference to orbital fractures, Le Fort fractures (+$61 921; P < .01), mandible fractures (+$13 227, P < .01), and skull base fractures (+$22 170; P < .05) were all independently associated with increased hospital charges.

Table 3.
Hospital Charges Across All Predictor Variables.

Table 4.
Multiple Linear Regression Model for Hospital Charges.
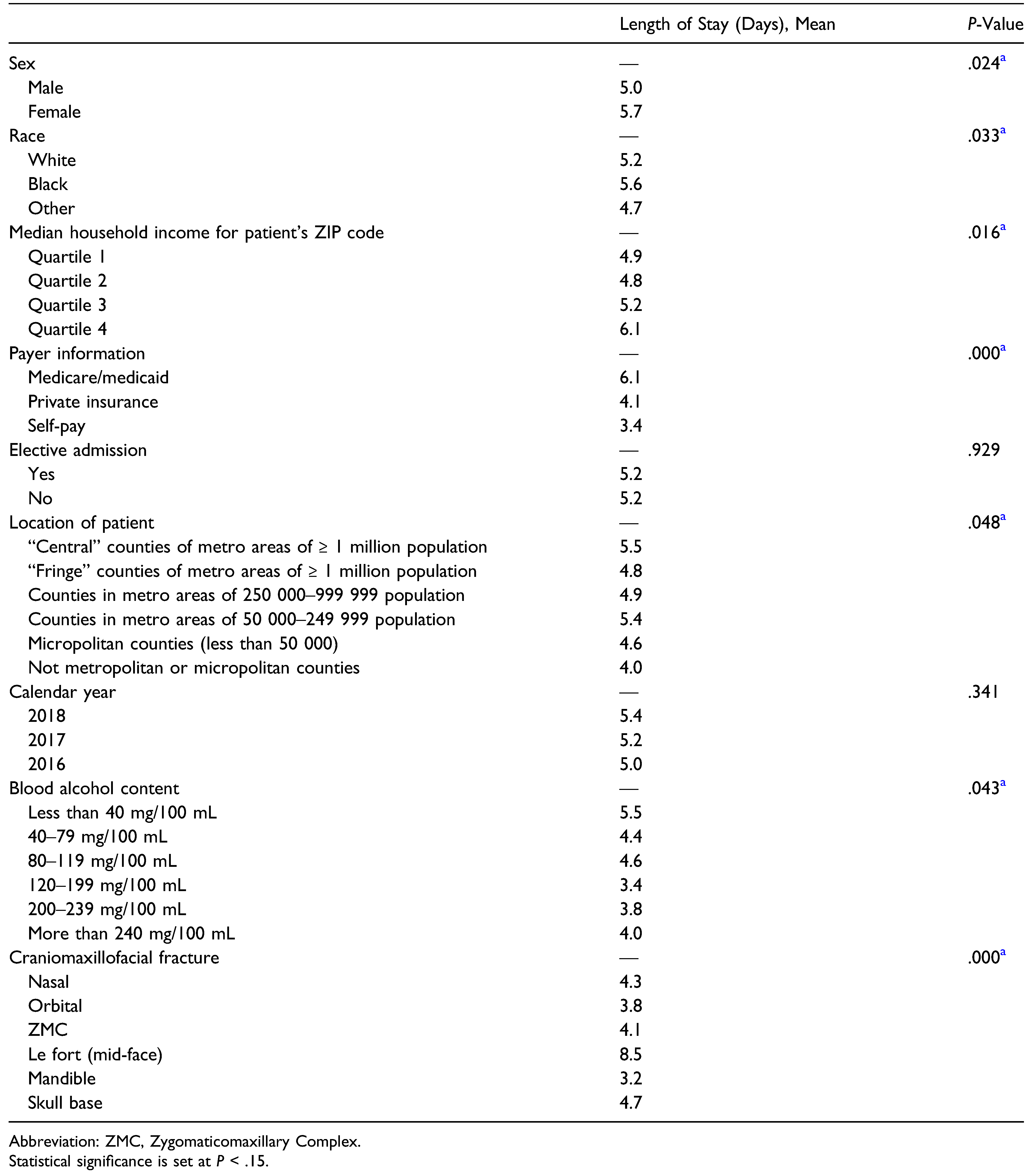
A bivariate comparison of the mean length of hospital stay was also conducted (Table 5). Patient sex, race, median household income for residential ZIP code, payer information, admission status, patient location, BAC, and type of craniomaxillofacial fracture all proved to be significant predictors (P < .05) of increased length of hospital stay. After controlling for all covariates, a multiple linear regression model was implemented (Table 6). Relative to mandible fractures, skull base fractures added +7.6 days to the hospital stay (P < .01) and each additional year in patient age added +.1 days to the length of the hospital stay (P < .01).

Table 5.
Length of Stay Across all Predictor Variables.

Table 6.
Multiple Linear Regression Model for Length of Stay.
Discussion
The purpose of this study was to determine whether or not BAC in patients sustaining craniomaxillofacial trauma from street fights influenced hospitalization outcomes. A secondary objective of this study was to assess whether the type and location of maxillofacial injury influenced hospitalization outcomes among this population. In sum, BAC had no impact on total hospital charges or length of hospital stay. However, the specific type of craniomaxillofacial fracture did affect outcomes. Advanced age was also more likely to result in longer hospital stays and higher hospital charges. The anatomical locations of violence-related craniomaxillofacial trauma vary considerably across studies [22,23]. In a retrospective chart review of 1121 patients with oral-maxillofacial trauma, Ferreira et al. found that the mandible and the maxilla were the most commonly and least commonly fractured bones following incidences of IPV, respectively [22]. Our study found that males were more likely to sustain injuries in street fights, similar to prior studies assessing violence-associated maxillofacial trauma [22,24]. However, the majority of patients in this study were in their late thirties and early forties, which is slightly older than those reported by previous groups [12,25,26].
Advanced age has been a well-documented predictor of increased hospital length of stay [27,28]. Older adults and elderly patients are more likely to encounter various clinical problems during their hospital stay (such as frailty, cognitive decline, and delirium) as well as socioeconomic barriers to discharge (such as the absence of caregivers and lack of support networks) [29,30]. As such, several authors have suggested the importance of early discharge planning and coordination among various healthcare professionals for older patients in order to avoid delays in discharge and increased hospital length of stay [31,32]. Advanced age is also associated increased hospitalization costs. Several studies have demonstrated an inverse relationship between total hospitalization costs and a patient’s overall functional status [33,34]. With older patients remaining in the hospital longer, healthcare resource consumption and their associated costs will likely increase accordingly [35].
This is the first study to report that skull base fractures resulted in substantially longer hospital stays among patients sustaining craniomaxillofacial injuries following street fights. Skull base fractures often present with serious, life-threatening concomitant injuries such as the leakage of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), spinal cord injury, and traumatic brain injury (TBI) [36]. Consequently, patients with skull base fractures are more likely to be admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) and undergo additional surgical, non-surgical treatment, and rehabilitation for their injuries. Gray et al., in a survey of trauma patients requiring maxillofacial intervention, found that the length of ICU stay was the single most important predictor for overall hospital length of stay [37]. Likewise, the high hospital costs associated with cranial base fractures likely resulted from extended ICU stays, which can range anywhere between $11 000 and $34 000 per day in the US depending on the specific care and equipment required for a patient [38,39,40].
The increased hospitalization charges associated with Le Fort and mandible fractures may be a result of their associated treatments and operative management. For example, mandible fractures are most commonly managed by open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) since they result in more predictable healing and allow for more accurate reductions [41,42]. However, it has been well-documented that ORIF, relative to closed reduction (CR) with maxillomandibular fixation (MMF), is associated with increased initial hospitalization costs likely due to heightened operating room (OR) time, implant pricing, and complication rates [41,43,44,45]. Similar reasoning may also explain the increased hospitalization costs associated with Le Fort fractures [46].
The finding that BAC in patients sustaining cranio-maxillofacial injuries failed to affect hospitalization costs and length of stay are inconsistent with previously reported literature. In a prospective examination of patients sustaining mandibular fractures secondary to IPV, O’Meara et al. found that those instances which involved alcohol resulted in more severe fractures and a higher likelihood of requiring surgery [47]. A follow-up study by the same group reported similar results for all facial fractures resulting from IPV [24]. Lee et al. in a retrospective database study also reported that alcohol-related maxillofacial fractures were more likely to require hospitalization and surgical intervention compared to fractures that did not involve alcohol [48]. It has been suggested that more severe cases of maxillofacial injury may be correlated with longer hospital stays and higher hospitalization costs due to the considerable economic expense incurred in the emergency department as well as peri- and intraoperatively [12,24,49]. Nonetheless, no studies to date have been able to confirm these hypotheses. The authors believe the reason that BAC failed to impact hospitalization outcomes is the insufficient sample of patients with documented BAC levels (n = 285). A larger sample would have rendered sufficient statistical power for significant results.
The limitations of this study arise primarily from the nature of the NIS. First, the NIS includes discharge data from only community hospitals and does not account for admissions and/or discharges occurring in federal hospitals as well as rehabilitation and long-term acute care facilities.
Second, the NIS tracks patient-level data regarding a single hospital encounter from admission to discharge, and therefore does not allow for longitudinal analysis or analysis across different hospital encounters. As such, the NIS lacks the ability to assess post-discharge complications, readmissions, and mortality outside of the hospital setting. Third, our analysis was limited to hospitalization data from 2016 to 2018, precluding a more thorough and longitudinal examination of hospital outcomes in our study cohort. Beginning in 2016, the NIS recorded diagnoses and procedures using the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification/Procedure Coding System (ICD-10-CM/PCS). Prior to this time, the NIS exclusively utilized the ICD-9-CM coding system. In order to maintain consistency in the analysis of diagnostic and procedural codes, only data from 2016 to 2018 was included in the final analysis.
In summary, we did not reject the null hypothesis as increasing BAC levels did not prolong length of stay nor increase hospitalization charges. Regarding hospitalization charges, certain fractures—Le Fort fractures, mandible fractures, and skull base fracture—each independently increased hospital charges. Each additional year in the patient’s age added over $500 in hospital charges. Older adults and elderly patients are more likely to face clinical problems during their hospital stay (ie, cognitive decline) and socioeconomic barriers to discharge (ie, absence of caregivers). Non-elective admissions added $14 210 in hospital.
Patients admitted in the year 2018 were also associated with significantly increased hospital charges. Concerning length of stay, skull base fractures added over 7 days to the hospital stay. Further, each additional year in patient age added +.1 days to the length of the stay.
Funding
The author(s) received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Declaration of conflicting interests
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
References
- World Health Organization. Injuries and violence. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/injuries-and-violence (accessed on 27 September 2021).
- James, S.L.; Abate, D.; Abate, K.H.; et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017. Lancet. 2018, 392, 1789–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberg, M.A.; Tasanen, A.; Kotilainen, R.; Tasanen, A. Maxillofacial fractures caused by assault and battery. Victims and their injuries. Proc Finn Dent Soc. 1975, 71, 162–175. [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd, J.P.; Shapland, M.; Pearce, N.X.; Scully, C. Pattern, severity and aetiology of injuries in victims of assault. J R Soc Med. 1990, 83, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eiskjaer, S.P.; Schrøder, H.M.; Charles, A.V.; Petersen, K.K. Epidemiology of violence in a Danish municipality. Changes in severity during the 1980s. Dan Med Bull. 1992, 39, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yakubovich, A.R.; Stöckl, H.; Murray, J.; et al. Risk and protective factors for intimate partner violence against women: Systematic review and meta-analyses of prospective-longitudinal studies. Am J Public Health. 2018, 108, e1–e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagi, K.J.; Rothman, E.F.; Latzman, N.E.; Tharp, A.T.; Hall, D.M.; Breiding, M.J. Beyond correlates: A review of risk and protective factors for adolescent dating violence perpetration. J Youth Adolesc. 2013, 42, 633–649. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Capaldi, D.M.; Knoble, N.B.; Shortt, J.W.; Kim, H.K. A systematic review of risk factors for intimate partner violence. Partner Abuse. 2012, 3, 231–280. [Google Scholar]
- Substance Abuse Mental Health Services Administration. Key substance use and mental health indicators in the United States: Results from the 2019 national survey on drug use and health. Security Research Hub Reports. 2020. [Google Scholar]
- National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. Alcohol use in the United States. Available online: https://www.niaaa.nih.gov/publications/brochures-and-fact-sheets/alcohol-facts-and-statistics (accessed on 27 September 2021).
- Lee, K.; Olsen, J.; Sun, J.; Chandu, A.; Chandu, A. Alcohol-involved maxillofacial fractures. Aust Dent J. 2017, 62, 180–185. [Google Scholar]
- Laverick, S.; Patel, N.; Jones, D.C. Maxillofacial trauma and the role of alcohol. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008, 46, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Thomas, M.; Scott, C. The influence of alcohol on facial trauma. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2020, 58, e185. [Google Scholar]
- Motomura, K.; Yamashiro, M. A clinical and statistical study on maxillofacial fractures from assault and battery. Jpn J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1989, 35, 2678–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, A.M. Patterns of maxillofacial fractures associated with assault injury in Khamis Mushait city and related factors. Egypt J Hosp Med. 2018, 70, 289–292. [Google Scholar]
- Greene, D.; Raven, R.; Carvalho, G.; Maas, C.S. Epidemiology of facial injury in blunt assault. Determinants of incidence and outcome in 802 patients. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1997, 123, 923–928. [Google Scholar]
- Barberi, A.; Qiu, M.; Lee, K. Interpersonal violence and facial trauma: A population based study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017, 46, 75. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, W.A.; Al-Mutairi, K.; Al-Ali, Y.; Al-Soghier, A.; Al-Shnwani, A. Patterns and etiology of maxillofacial fractures in Riyadh City, Saudi Arabia. Saudi Dent J. 2013, 25, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Levi Duque, F.; Agudelo-Suarez, A.A.; Ardila, C.M. Etiology and pattern of maxillofacial fractures in Medellín, Colombia: A retrospective analysis of 2680 patients. Int J Odontostomat. 2013, 7, 159–166. [Google Scholar]
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. NIS database documentation. Available online: https://www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/db/nation/nis/nisdbdocumentation.jsp (accessed on 28 September 2021).
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Overview of the National (Nationwide) Inpatient Sample (NIS). Available online: https://www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/nisoverview.jsp (accessed on 28 September 2021).
- Ferreira, M.C.; Batista, A.M.; Ferreira, F.O.; Ramos-Jorge, M.L.; Marques, L.S. Pattern of oral-maxillofacial trauma stemming from interpersonal physical violence and determinant factors. Dent Traumatol. 2014, 30, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sifuentes-Cervantes, J.S.; Yamamoto-Valenzuela, K.; Autran-Martínez, J.; Castro-Núñez, J.; Guerrero, L.M. Maxillofacial trauma in the ultimate fighting championship. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1921, 79, e12021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Meara, C.; Witherspoon, R.; Hapangama, N.; Hyam, D.M. Alcohol and interpersonal violence may increase the severity of facial fracture. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012, 50, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, J.L.; Macedo, L.; Camargo, P.; Almeida, S.C.R. Mudança etiológica do trauma de face de pacientes atendidos no pronto socorro de cirurgia plástica do Distrito Federal. Rev Bras Cir Cardiovasc. 2007, 22, 209. [Google Scholar]
- Le, B.T.; Dierks, E.J.; Ueeck, B.A.; Homer, L.D.; Potter, B.F. Maxillofacial injuries associated with domestic violence. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2001, 59, 1277–1283. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kobewka, D.M.; Mulpuru, S.; Chassé, M.; et al. Predicting the need for supportive services after discharged from hospital: a systematic review. BMC Health Serv Res. 2020, 20, 161. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.-S.; Watts, J.N.; Peel, N.M.; Hubbard, R.E. Frailty and post-operative outcomes in older surgical patients: A systematic review. BMC Geriatr. 2016, 16, 157. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, M.; Beech, R. Variations in lengths of stay and rates of day case surgery: Implications for the efficiency of surgical management. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1990, 44, 90–105. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- George, E.L.; Arya, S. The importance of incorporating frailty screening into surgical clinical workflow. JAMA Netw Open. 2019, 2, e193538. [Google Scholar]
- Bert, F.; Kakaa, O.; Corradi, A.; et al. Predicting length of stay and discharge destination for surgical patients: A cohort study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020, 17, 9490. [Google Scholar]
- Aceto, P.; Antonelli Incalzi, R.; Bettelli, G.; et al. Perioperative management of elderly patients (PriME): Recommendations from an Italian intersociety consensus. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2020, 32, 1647–1673. [Google Scholar]
- Inouye, S.K.; Peduzzi, P.N.; Robison, J.T.; Hughes, J.S.; Horwitz, R.I.; Concato, J. Importance of functional measures in predicting mortality among older hospitalized patients. JAMA. 1998, 279, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covinsky, K.E.; Justice, A.C.; Rosenthal, G.E.; Palmer, R.M.; Landefeld, C.S. Measuring prognosis and case mix in hospitalized elders. The importance of functional status. J Gen Intern Med. 1997, 12, 203–208. [Google Scholar]
- Brimhall, B.B.; Dean, T.; Hunt, E.L.; Siegrist, R.B.; Reiquam, W. Age and laboratory costs for hospitalized medical patients. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2003, 127, 169–177. [Google Scholar]
- Elhammali, N.; Bremerich, A.; Rustemeyer, J. Demographical and clinical aspects of sports-related maxillofacial and skull base fractures in hospitalized patients. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010, 39, 857–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, E.; Dierks, E.; Homer, L.; Smith, F.; Potter, B. Survey of trauma patients requiring maxillofacial intervention, ages 56 to 91 years, with length of stay analysis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2002, 60, 1114–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, A.A.; Dasta, J.F.; Kane-Gill, S.L. The impact of mortality on total costs within the ICU. Crit Care Med. 2017, 45, 1457–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halpern, N.A.; Pastores, S.M. Critical care medicine in the United States 2000-2005: An analysis of bed numbers, occupancy rates, payer mix, and costs. Crit Care Med. 2010, 38, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, D.J.; Angus, D.C.; Seymour, C.W.; Barnato, A.E.; Kahn, J.M. Critical care bed growth in the United States. A comparison of regional and national trends. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015, 191, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, B.L.; Kearns, G.; Gordon, N.; Kaban, L.B. A financial analysis of maxillomandibular fixation versus rigid internal fixation for treatment of mandibular fractures. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2000, 58, 1206–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrcanovic, B.R. Open versus closed reduction: Comminuted mandibular fractures. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013, 17, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalliah, R.P.; Allareddy, V.; Kim, M.K.; Venugopalan, S.R.; Gajendrareddy, P.; Allareddy, V. Economics of facial fracture reductions in the United States over 12 months. Dent Traumatol. 2013, 29, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, J.K.; Christensen, B.; McDonald, T.; Huang, S.; Gauger, P.; Gomez, P. The financial burden of mandibular trauma. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012, 70, 2124–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodson, T.B.; Pfeffle, R.C. Cost-effectiveness analysis of open reduction/nonrigid fixation and open reduction/rigid fixation to treat mandibular fractures. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1995, 80, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanger, C.; Argenta, L.C.; David, L.R. Cost-effective management of isolated facial fractures. J Craniofac Surg. 2004, 15, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- O’Meara, C.; Witherspoon, R.; Hapangama, N.; Hyam, D.M. Mandible fracture severity may be increased by alcohol and interpersonal violence. Aust Dent J. 2011, 56, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.H.; Snape, L. Role of alcohol in maxillofacial fractures. N Z Med J. 2008, 121, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McAllister, P.; Laverick, S.; Makubate, B.; Jones, D.C. Alcohol consumption and interpersonal injury in a pediatric oral and maxillofacial trauma population: A retrospective review of 1,192 trauma patients. Craniomaxillofac Trauma Reconstr. 2015, 8, 83–87. [Google Scholar]
© 2023 by the author. The Author(s) 2023.