Pediatric Palate Fractures: An Assessment of Patterns and Management at a Level 1 Trauma Center
Abstract
:Introduction
Methods
Results
4. Discussion
Conclusion
Funding
Ethical Approval
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Persson, M.; Thilander, B. Palatal suture closure in man from 15 to 35 years of age. Am J Orthod. 1977, 72, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hoppe, I.C.; Halsey, J.N.; Ciminello, F.S.; Lee, E.S.; Granick, M.S. A single-center review of palatal fractures: etiology, patterns, concomitant injuries, and management. Eplasty 2017, 17, e20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kao, R.; Campiti, V.J.; Rabbani, C.C.; Ting, J.Y.; Sim, M.W.; Shipchandler, T.Z. Pediatric midface fractures: outcomes and complications of 218 patients. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2019, 4, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Halsey, J.N.; Hoppe, I.C.; Marano, A.A.; Kordahi, A.M.; Lee, E.S.; Granick, M.S. Characteristics of cervical spine injury in pediatric patients with facial fractures. J Craniofac Surg. 2016, 27, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, C.G.; Mukherjee, U. Maxillofacial trauma in children. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2012, 5, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrickson, M.; Clark, N.; Manson, P.N.; et al. Palatal fractures: classification, patterns, and treatment with rigid internal fixation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1998, 101, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Ock, J.J. A new classification of palatal fracture and an algorithm to establish a treatment plan. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001, 107, 1669–1676, discussion 1677–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.H.; Wang, T.Y.; Tsay, P.K.; et al. A 162-case review of palatal fracture: management strategy from a 10-year experience. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008, 121, 2065–2073. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pollock, R.A. The search for the ideal fixation of palatal fractures: innovative experience with a mini-locking plate. Craniomaxillofac Trauma Reconstr. 2008, 1, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.B.; Fryer, M.P.; McDowell, F. Internal wire-pin immobilization of jaw fractures. Plast Reconstr Surg (1946) 1949, 4, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.B.; Fryer, M.P.; Mc, D.F. Internal wire-pin fixation for fractures of upper jaw, orbit, zygoma and severe facial crushes. Plast Reconstr Surg (1946). 1952, 9, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, J.H. Open reduction and internal fixation of vertical maxillary fractures. J Oral Surg. 1968, 26, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Davis, D.G.; Constant, E. Transverse palatal wire for the treatment of vertical maxillary fractures. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1971, 48, 191–193. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Manson, P.N.; Shack, R.B.; Leonard, L.G.; Su, C.T.; Hoopes, J.E. Sagittal fractures of the maxilla and palate. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1983, 72, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gruss, J.S.; Mackinnon, S.E. Complex maxillary fractures: role of buttress reconstruction and immediate bone grafts. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1986, 78, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vyas, R.M.; Dickinson, B.P.; Wasson, K.L.; Roostaeian, J.; Bradley, J.P. Pediatric facial fractures: current national incidence, distribution, and health care resource use. J Craniofac Surg. 2008, 19, 339–349, discussion 350. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Angelieri, F.; Cevidanes, L.H.; Franchi, L.; Gonc¸alves, J.R.; Benavides, E.; McNamara, J.A., Jr. Midpalatal suture maturation: classification method for individual assessment before rapid maxillary expansion. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2013, 144, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.C.; Le, T.T.; Oleck, N.C.; et al. Pediatric pedestrian facial fracture patterns and management following motor vehicle collisions. J Craniofac Surg. 2020, 31, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoppe, I.C.; Kordahi, A.M.; Paik, A.M.; Lee, E.S.; Granick, M.S. Examination of life-threatening injuries in 431pediatric facial fractures at a level 1 trauma center. J Craniofac Surg. 2014, 25, 1825–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.L.; Borschel, G.H. Michigan Manual of Plastic Surgery; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
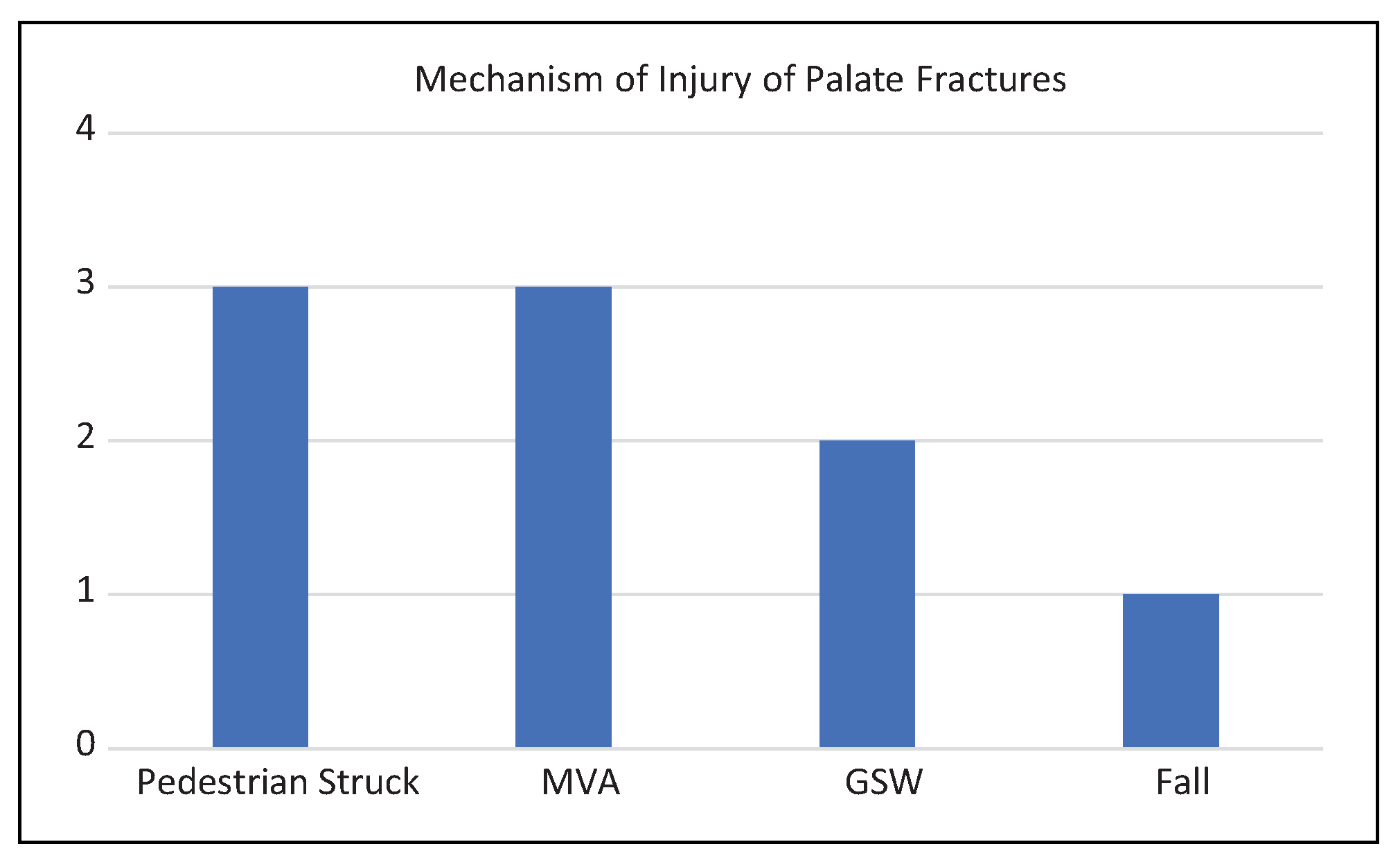
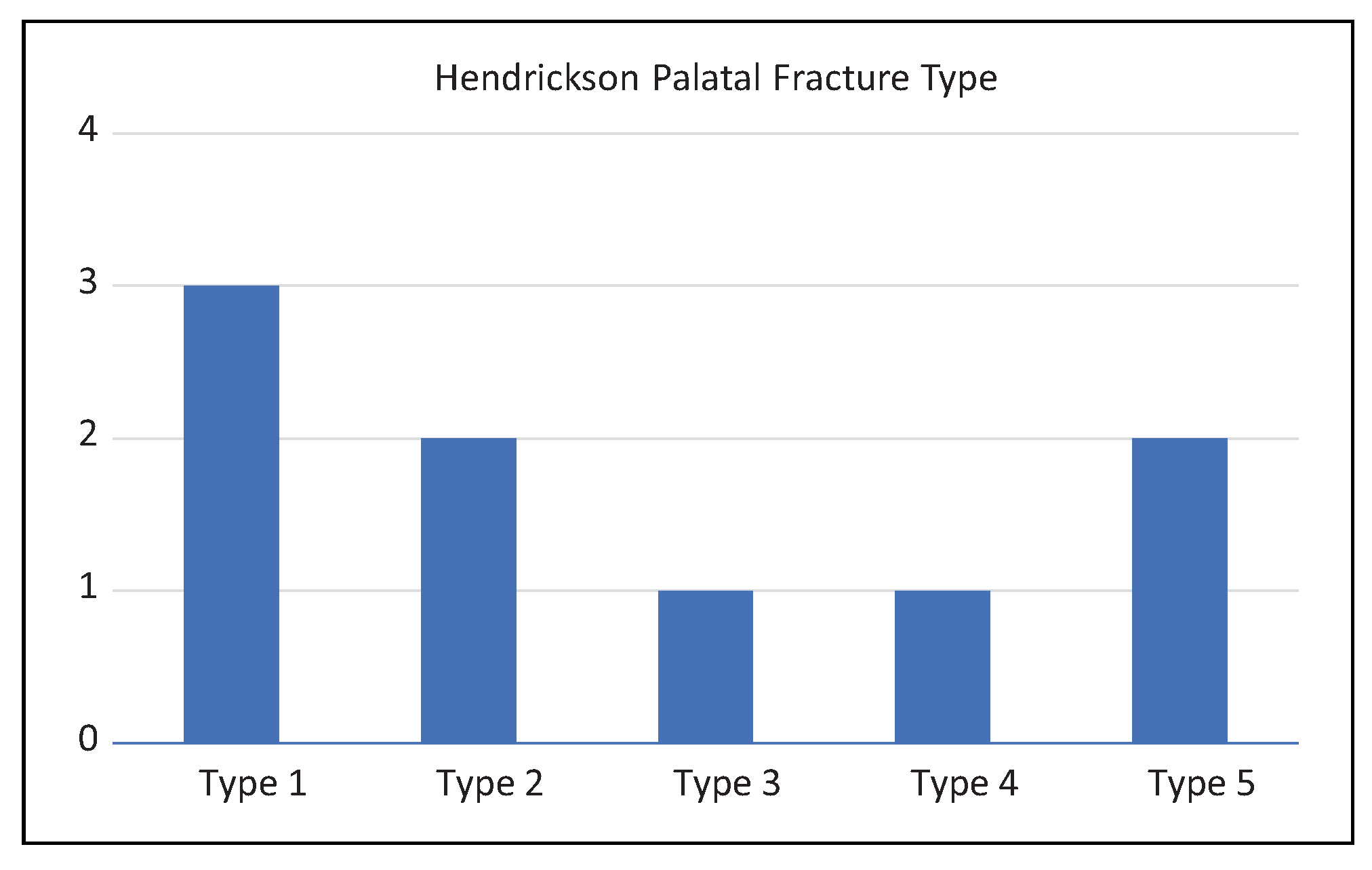

| Patient | Age | Sex | Etiology | Palate fracture type | Concomitant facial fractures | Skull fracture | TBI | Long bone fracture | LOC | Lowest GCS | C-spine fracture | ICH |
| 1 | 6 | F | Ped Struck | Type 2 | ZMC, orbit, NOE, nasal bones, | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | 13 | No | No |
| frontal sinus | ||||||||||||
| 2 | 7 | F | Ped Struck | Type 1 | None | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | 15 | No | No |
| 3 | 8 | M | MVA | Type 2 | Orbit | No | No | Yes | Yes | 3 | No | No |
| 4 | 14 | M | MVA | Type 3 | Mandible-parasymphysis, body, and angle, orbit, NOE, nasal, frontal sinus | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 3 | Yes | Yes |
| 5 | 14 | F | Fall | Type 1 | Mandible-parasymphysis and body | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | 15 | No | No |
| 6 | 14 | M | GSW | Type 5 | Zygoma | No | No | No | No | 15 | Yes | No |
| 7 | 15 | M | Ped Struck | Type 1 | Nasal bones | No | No | No | No | 15 | No | No |
| 8 | 16 | M | GSW | Type 5 | Mandible-ramus, zygoma, ZMC, orbit, nasal bones | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | 7 | No | Yes |
| 9 | 16 | M | MVA | Type 4 | Orbit, NOE, nasal bones | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 3 | No | Yes |
| Patient | Age | Sex | Etiology | Palate fracture type | Concomitant facial fractures | OR | Surgical intervention | Hospital LOS |
| 1 | 6 | F | Ped Struck | Type 2 | ZMC, orbit, NOE, nasal bones, frontal sinus | Yes | Closed nasal bone reduction | 5 |
| 2 | 7 | F | Ped Struck | Type 1 | None | No | N/A | 15 |
| 3 | 8 | M | MVA | Type 2 | Orbit | Yes | MMF, Plate Fixation of Orbital Fractures | 35 |
| 4 | 14 | M | MVA | Type 3 | Mandible-parasymphysis, body, and angle, orbit, NOE, nasal, frontal sinus | Yes | MMF, Plate fixation of panfacial fractures | 29 |
| 5 | 14 | F | Fall | Type 1 | Mandible-parasymphysis and body | Yes | MMF, Plate fixation of mandible | 6 |
| 6 | 14 | M | GSW | Type 5 | Zygoma | No | N/A | 11 |
| 7 | 15 | M | Ped Struck | Type 1 | Nasal bones | Yes | Open reduction and fixation of nasal bone fractures | 2 |
| 8 | 16 | M | GSW | Type 5 | Mandible-ramus, zygoma, ZMC, orbit, nasal bones | Yes | MMF, plate fixation of ZMC/orbital fractures | 17 |
| 9 | 16 | M | MVA | Type 4 | Orbit, NOE, nasal bones | No | N/A—death | 2 |
© 2020 by the author. The Author(s) 2020.
Share and Cite
Gala, Z.; Halsey, J.N.; Kapadia, K.; Otaguro, L.; Hoppe, I.C.; Lee, E.S.; Granick, M.S. Pediatric Palate Fractures: An Assessment of Patterns and Management at a Level 1 Trauma Center. Craniomaxillofac. Trauma Reconstr. 2021, 14, 23-28. https://doi.org/10.1177/1943387520935013
Gala Z, Halsey JN, Kapadia K, Otaguro L, Hoppe IC, Lee ES, Granick MS. Pediatric Palate Fractures: An Assessment of Patterns and Management at a Level 1 Trauma Center. Craniomaxillofacial Trauma & Reconstruction. 2021; 14(1):23-28. https://doi.org/10.1177/1943387520935013
Chicago/Turabian StyleGala, Zachary, Jordan N. Halsey, Kavita Kapadia, Lauren Otaguro, Ian C. Hoppe, Edward S. Lee, and Mark S. Granick. 2021. "Pediatric Palate Fractures: An Assessment of Patterns and Management at a Level 1 Trauma Center" Craniomaxillofacial Trauma & Reconstruction 14, no. 1: 23-28. https://doi.org/10.1177/1943387520935013
APA StyleGala, Z., Halsey, J. N., Kapadia, K., Otaguro, L., Hoppe, I. C., Lee, E. S., & Granick, M. S. (2021). Pediatric Palate Fractures: An Assessment of Patterns and Management at a Level 1 Trauma Center. Craniomaxillofacial Trauma & Reconstruction, 14(1), 23-28. https://doi.org/10.1177/1943387520935013




