Abstract
This is a technical note describing hard tissue landmarks to simplify the intraoral glossopharyngeal nerve block. Our literature review revealed no specific mention of the same procedure in documented data.
The glossopharyngeal nerve block (GPNB) is used primarily in pain management in cases of neuralgia as well as to abolish the gag reflex for anesthetic, endoscopic, or dental procedures. Traditionally, an extraoral and an intraoral techniques have been described citing soft-tissue landmarks.[1] However, in the hands of a novice, there is due risk of injury to the large vessels of the neck which lie in close proximity to the nerve, especially in cases of uncooperative or anxious patients. In this article, we describe a modification of the tonsillar pillar injection with hard-tissue landmarks.
Landmarks
- Maxillary premolar teeth.
- Angle of the mandible.
- Mastoid process.
- Anterior and posterior tonsillar pillars.
Materials: Cartridge, local anesthetic solution.
Operator’s position: Right GPNB: 6 O’ clock position; left GPNB: 8 O’clock position where the patient’s head is considered to be 12 O’clock position.
Target area: Base of the tonsillar pillars in the submucosal plane.
The Technique
Place the patient in supine position or reclined in a dental chair. Place the index finger of your left hand over a line joining the ipsilateral mastoid process and angle of the mandible, palpating the styloid process if palpable. Retract the tongue medially and caudally if required. Holding the syringe witha pen grasp in your right hand, gently insert the needle into the area between the base of the ipsilateral anterior and posterior tonsillar pillar, resting the syringe in between the contralateral maxillary premolar teeth and pointing it toward your opposite index finger (Figure 1 and Figure 2). The needle should beinserted to a depth of 0.5 cm. Aspirate in two planes and inject 1 to 2 mL of the anesthetic solution. In case of positive aspiration or headache during injection, draw the needle and repeat the procedure.
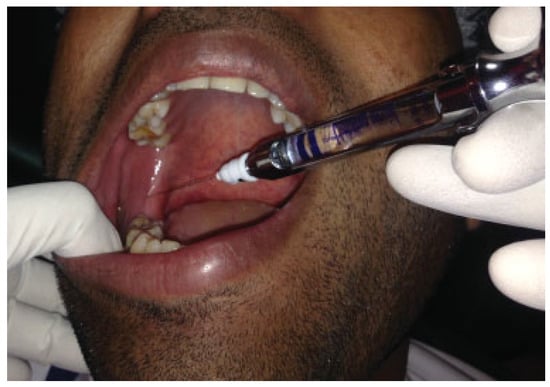
Figure 1.
Glossopharyngeal nerve block using premolar approach—clinical picture.
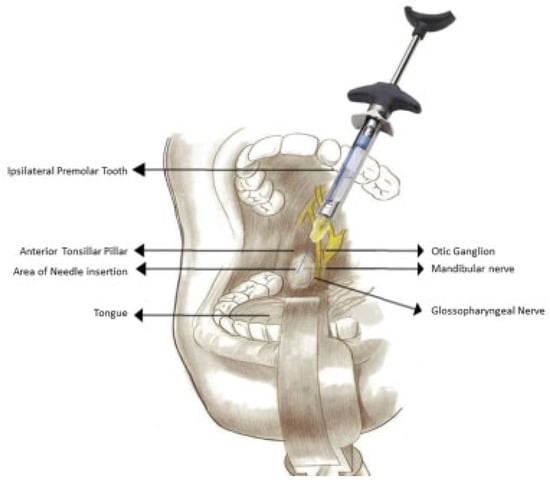
Figure 2.
Glossopharyngeal nerve block using premolar approach—illustrative diagram.
Discussion
The GPNB has been used routinely for awake intubation by anesthesiologists and by otolaryngologists for endoscopic procedures and for pain management in glossopharyngeal neuralgia. Recently, there is an increasing use in thefields of dentistry and maxillofacial surgery for suppressing the gag reflex during procedures associated with maxillary and mandibular posterior teeth. In dentistry training, one masters various intraoral and extraoral nerve block techniques mainly related to the trigeminal nerve and its branches. The technique described earlier provides and easy and repeatable method to achieve anesthesia of the glossopharyngeal nerve. The risk of injury to the vital structures of the neck by needle slippage is minimized due to a firm base provided to the barrel of the cartridge by resting it on the mentioned teeth. This also enables better control of the depth of injection. In the event of a neglected positive aspiration, an injection into the carotid artery may result in headaches and seizures. We recommend aspiration, rotation of the needle by 90 degrees, and re-aspiration to prevent this complication. Proper protection of the oropharynx using a rubber dam or gauze sheet during dental and oral surgical procedures is advised, as abolishing of the gag reflex carries with it an increased risk of foreign body aspiration or ingestion.
Conflicts of Interest
None of the authors have any financial or personal interest associated with this article.
References
- Hagberg, C.; Benumof, J. Benumof and Hagberg’s Airway Management; Elsevier/Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013; pp. 255–257. [Google Scholar]
© 2017 by the author. The Author(s) 2017.