Acute Hypoxia Stress-Induced Apoptosis in Gill of Japanese Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) by Modulating the Epas1/Bad Pathway
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Housing and Hypoxia Stress
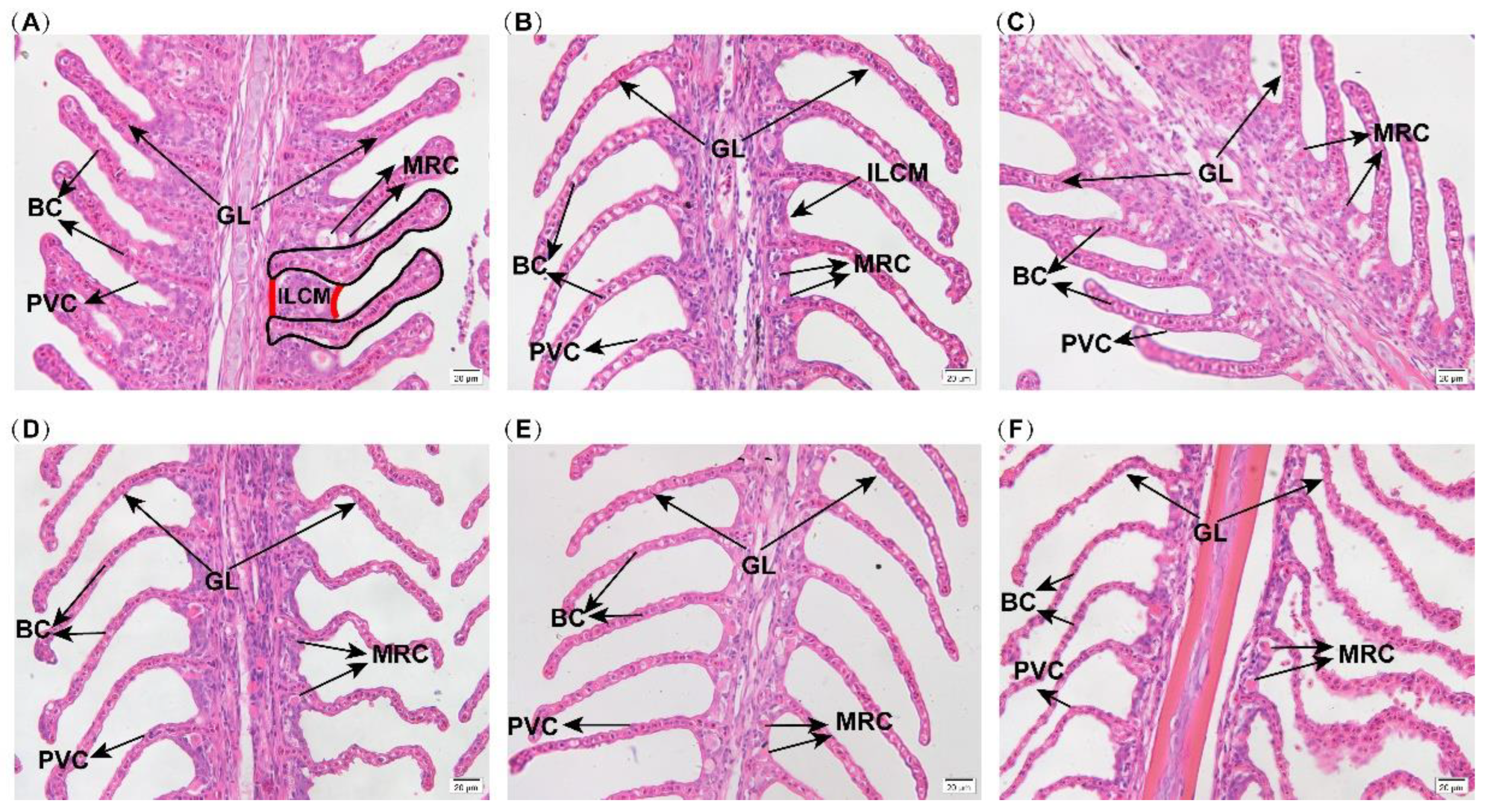
2.2. Branchial Histological Structure
2.3. Apoptosis Detection by TUNEL
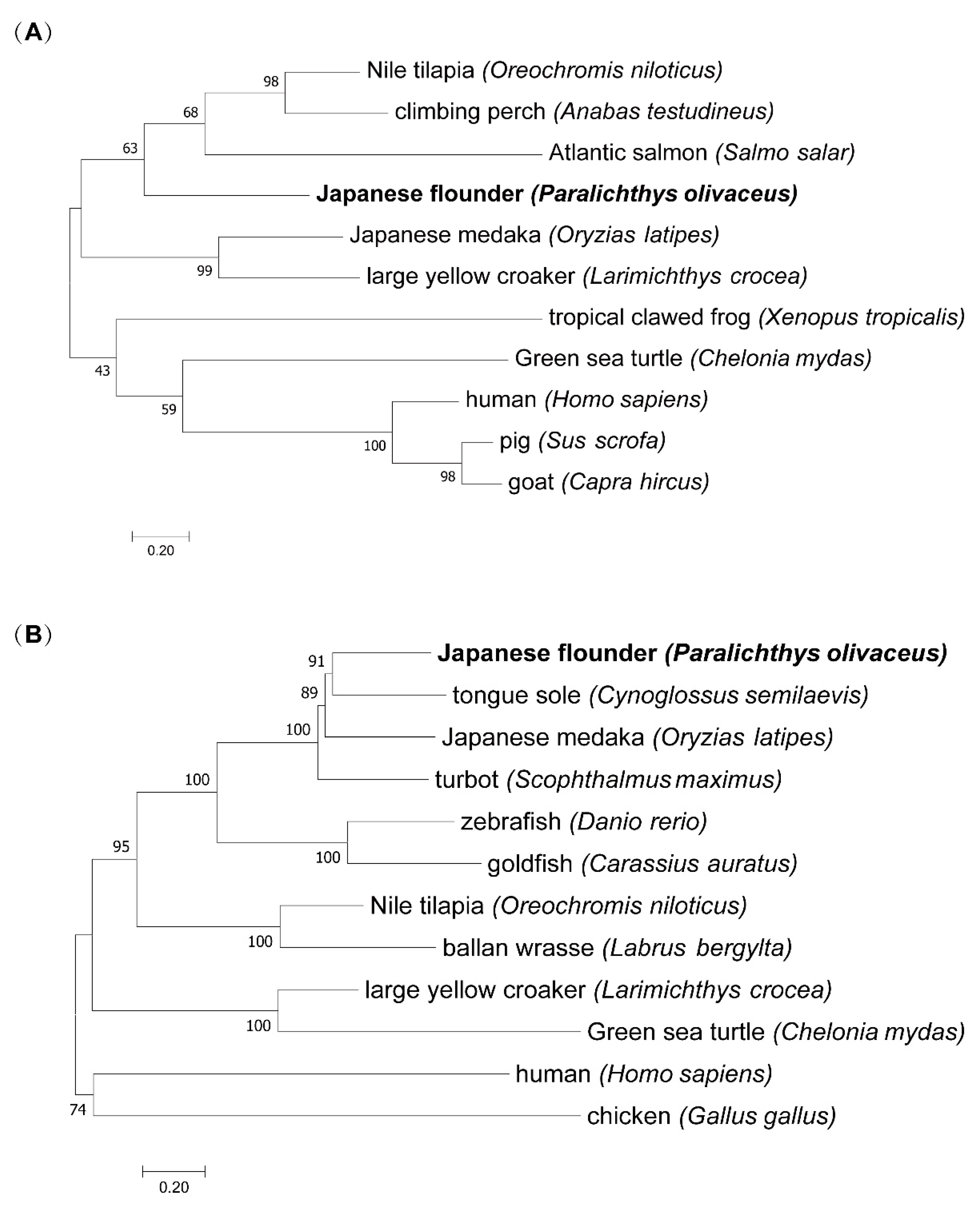
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. RNA Extraction and Gene Expression
2.6. Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.7. Detection of DNA Methylation Level
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Hypoxia Stress on Gill Morphology
3.2. Effects of Hypoxia Stress on Gill Apoptosis
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
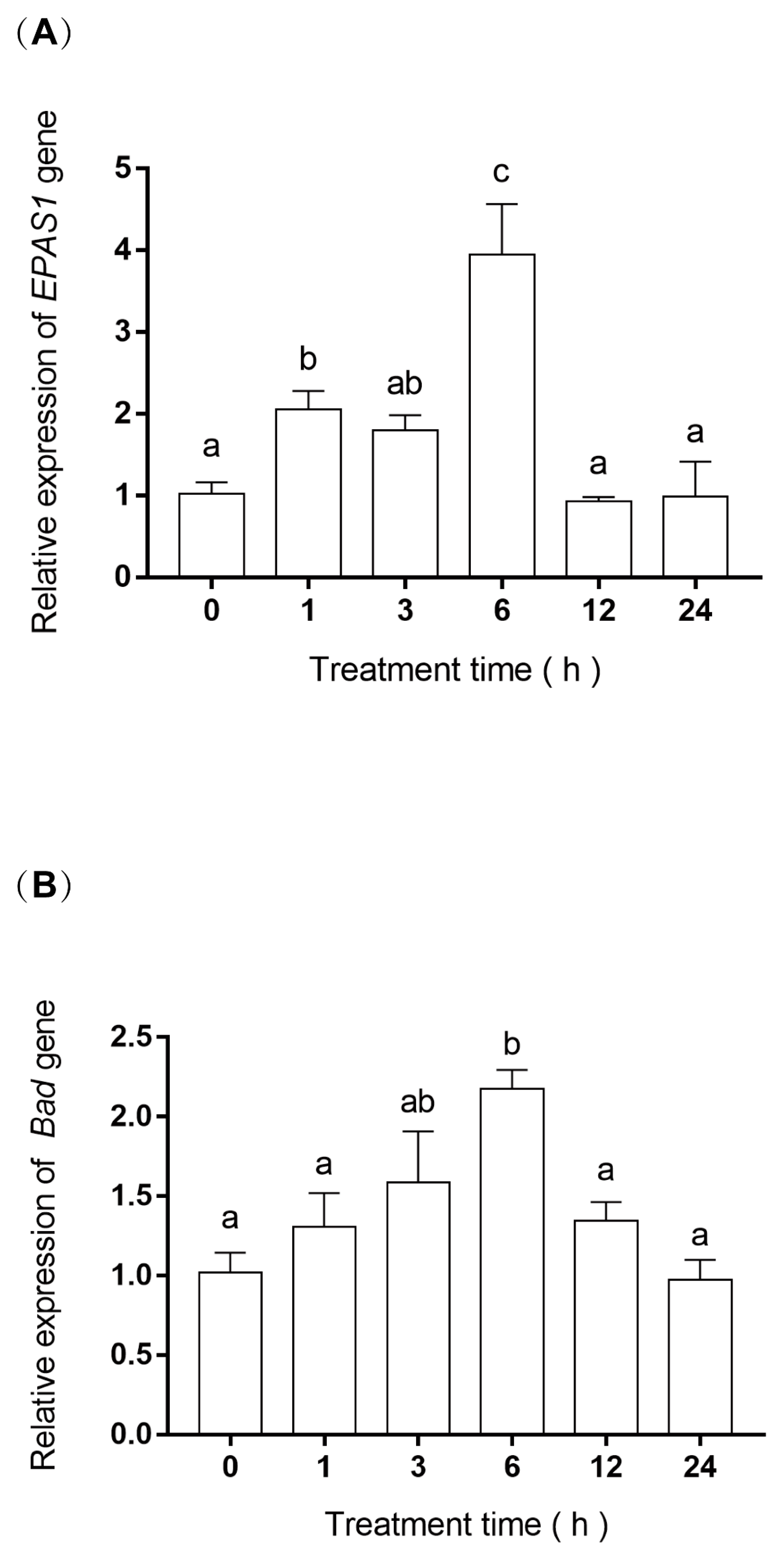
3.4. EPAS1 and Bad Gene mRNA Relative Expression
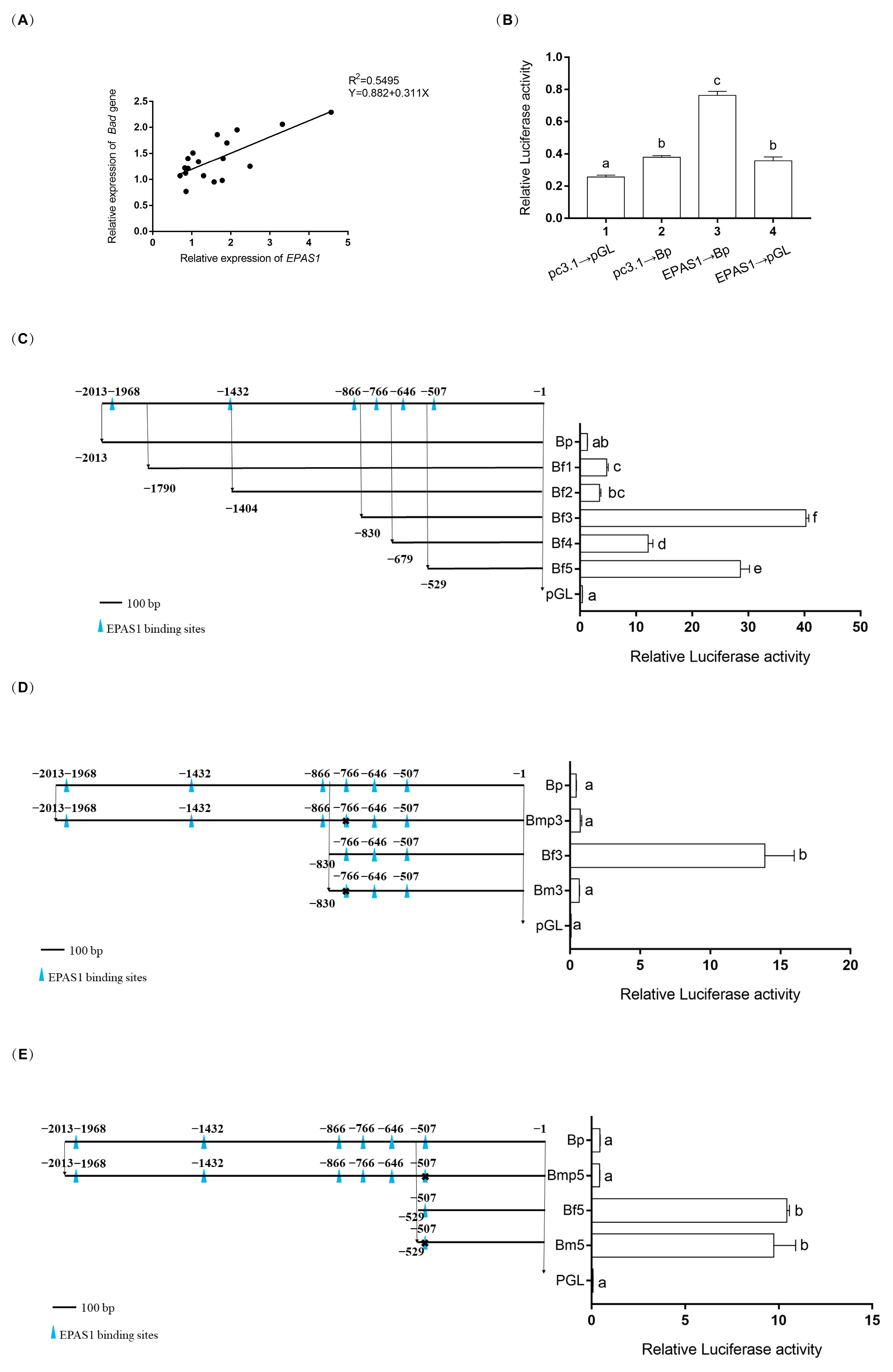
3.5. EPAS1 Transcriptionally Regulated Bad
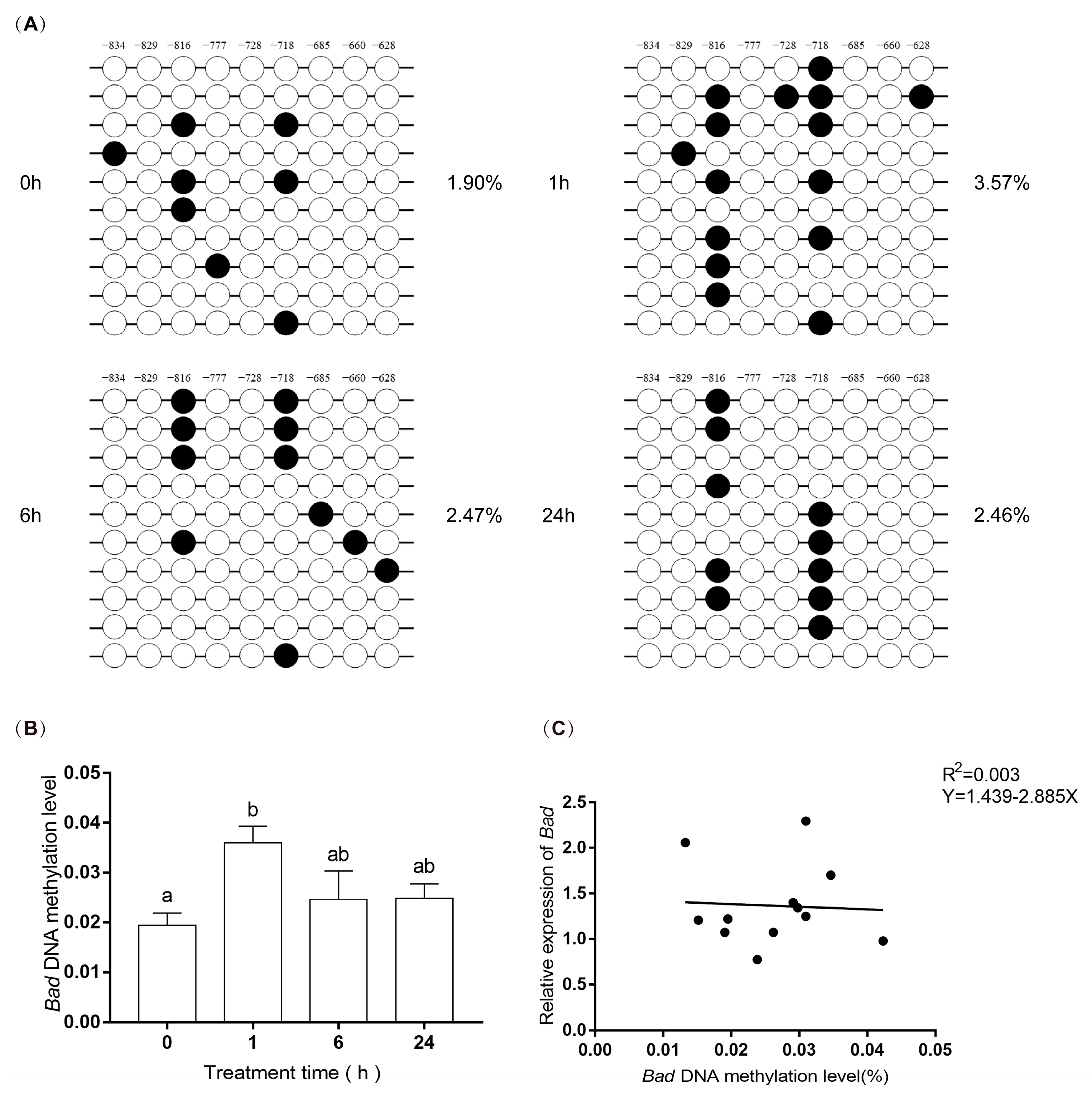
3.6. DNA Methylation Levels of EPAS1 and Bad Gene
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Breitburg, D.; Levin, L.A.; Oschlies, A.; Grégoire, M.; Chavez, F.P.; Conley, D.J.; Garçon, V.; Gilbert, D.; Gutiérrez, D.; Isensee, K.; et al. Declining oxygen in the global ocean and coastal waters. Science 2018, 359, eaam7240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Tawwab, M.; Monier, M.N.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Faggio, C. Fish response to hypoxia stress: Growth, physiological, and immunological biomarkers. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 45, 997–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foyle, K.L.; Hess, S.; Powell, M.D.; Herbert, N.A. What is gill health and what is its role in marine finfish aquaculture in the face of a changing climate? Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, A.; Thompson, K.; Ashby, A.; Rodger, H.; Dagleish, M. Complex Gill Disease: An Emerging Syndrome in Farmed Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.). J. Comp. Pathol. 2018, 163, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Ling, C.; Wang, Q.; Feng, C.; Luo, X.; Sha, H.; He, G.; Zou, G.; Liang, H. Hypoxia Stress Induces Tissue Damage, Immune Defense, and Oxygen Transport Change in Gill of Silver Carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix): Evaluation on Hypoxia by Using Transcriptomics. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 900200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, R.S.; Yao, L.; Matey, V.; Chen, B.-J.; Zhang, A.-J.; Cao, Z.-D.; Fu, S.-J.; Brauner, C.J.; Wang, Y.S.; Richards, J.G. Interspecific Differences in Hypoxia-Induced Gill Remodeling in Carp. Physiol. Biochem. Zool. 2013, 86, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matey, V.; Richards, J.G.; Wang, Y.; Wood, C.M.; Rogers, J.; Davies, R.; Murray, B.W.; Chen, X.Q.; Du, J.; Brauner, C.J. The effect of hypoxia on gill morphology and ionoregulatory status in the Lake Qinghai scaleless carp, Gymnocypris przewalskii. J. Exp. Biol. 2008, 211, 1063–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuang, L.; Su, X.-L.; Zheng, G.-D.; Zou, S.-M. Effects of hypoxia and reoxygenation on gill remodeling, apoptosis, and oxidative stress in hypoxia-tolerant new variety blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 48, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Tan, J.; Miao, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Q. Effects of Microvesicles on Cell Apoptosis under Hypoxia. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 5972152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youle, R.J.; Strasser, A. The BCL-2 protein family: Opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danial, N.N. BAD: Undertaker by night, candyman by day. Oncogene 2008, 27, S53–S70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Demeter, M.R.; Ruan, H.; Comb, M.J. BAD Ser-155 Phosphorylation Regulates BAD/Bcl-XL Interaction and Cell Survival. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 25865–25869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, E.; Zha, J.; Jockel, J.; Boise, L.H.; Thompson, C.B.; Korsmeyer, S.J. Bad, a heterodimeric partner for Bcl-XL and Bcl-2, displaces Bax and promotes cell death. Cell 1995, 80, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.R.; Katsov, A.; Hu, L.; Petros, A.; Fesik, S.W.; Yaffe, M.B.; Greenberg, M.E. 14-3-3 proteins and survival kinases cooperate to inactivate BAD by BH3 domain phosphorylation. Molecular Cell 2000, 6, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; McKnight, S.L.; Russell, D.W. Endothelial PAS domain protein 1 (EPAS1), a transcription factor selectively expressed in endothelial cells. Genes Dev. 1997, 11, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salceda, S.; Caro, J. Hypoxia-inducible Factor 1α (HIF-1α) Protein Is Rapidly Degraded by the Ubiquitin-Proteasome System under Normoxic Conditions. Its stabilization by hypoxia depends on redox-induced changes. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 22642–22647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Mao, C.; Wang, X.; Shi, Y.; Tao, Y. Epigenetic crosstalk between hypoxia and tumor driven by HIF regulation. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.Y.; Perera, S.; Zhou, B.; Carretero, J.; Yeh, J.J.; Heathcote, S.A.; Jackson, A.L.; Nikolinakos, P.; Ospina, B.; Naumov, G.; et al. HIF2α cooperates with RAS to promote lung tumorigenesis in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 2160–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, N.; Maemura, K.; Imai, Y.; Harada, T.; Kawanami, D.; Nojiri, T.; Manabe, I.; Nagai, R. Endothelial PAS Domain Protein 1 Gene Promotes Angiogenesis Through the Transactivation of Both Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Its Receptor, Flt-1. Circ. Res. 2004, 95, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Yin, Y.; Bi, L.; Wang, Y.; Yao, J.; Xu, L.; Jiao, L. MiR-182-5p promotes the Metastasis and Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer by Targeting EPAS1. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 7120–7129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.-H.; Shin, Y.; Huh, Y.H.; Yang, S.; Chun, C.-H.; Chun, J.-S. Hypoxia-inducible factor-2α regulates Fas-mediated chondrocyte apoptosis during osteoarthritic cartilage destruction. Cell Death Differ. 2012, 19, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Qi, B.; Hou, D. Roles of HIF1α- and HIF2α-regulated BNIP3 in hypoxia-induced injury of neurons. Pathol.-Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Morgunova, E.; Jolma, A.; Kaasinen, E.; Sahu, B.; Khund-Sayeed, S.; Das, P.K.; Kivioja, T.; Dave, K.; Zhong, F.; et al. Impact of cytosine methylation on DNA binding specificities of human transcription factors. Science 2017, 356, eaaj2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, L.D.; Le, T.; Fan, G. DNA Methylation and Its Basic Function. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junhao, N.; Hu, P.; Li, B.; Jiang, C. Nutritional comparison in muscle of wild, pond and factory cultured Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) adults. Aquac. Res. 2018, 49, 2572–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, B.; Yang, J.; Li, G.; Wen, H.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; He, F. DNA methylation in promoter region of immune related genes STAT3 and VEGFA and biochemical parameters change in muscle of Japanese flounder under acute hypoxia. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2022, 129, 104295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Li, G.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Wen, H.; He, F. The mechanism of immune related signal pathway Egr2-FasL-Fas in transcription regulation and methylated modification of Paralichthys olivaceus under acute hypoxia stress. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2022, 123, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wen, H.; Li, X.; Yang, J.; Li, G.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; He, F. Acute hypoxia effects on Keap1/Nrf2 (Mafs)-GST pathway related oxidative metabolism in muscle of Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, Y.; Kotaki, T.; Yamada, Y.; Ohta, H. Ontogenic changes in tolerance to hypoxia and energy metabolism of larval and juvenile Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2007, 352, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wu, S.; Zhang, J.; Wen, H.; Zhang, M.; He, F. Methylation status and expression patterns of myomaker gene play important roles in postnatal development in the Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2019, 280, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ondricek, K.; Thomas, P. Effects of hypoxia exposure on apoptosis and expression of membrane steroid receptors, ZIP9, mPRα, and GPER in Atlantic croaker ovaries. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2018, 224, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.; Mak, Y.T.; Wai, S.M.; Kwong, W.H.; Fang, M.; James, A.; Randall, D.; Yew, D.T. Hypoxia-induced differential apoptosis in the central nervous system of the sturgeon (Acipenser shrenckii). Microsc. Res. Tech. 2005, 68, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, N.-L.; Pandey, V.; Zhu, T.; Ma, L.; Basappa; Lobie, P.E. Bad phosphorylation as a target of inhibition in oncology. Cancer Lett. 2018, 415, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruick, R.K. Expression of the gene encoding the proapoptotic Nip3 protein is induced by hypoxia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 9082–9087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.A.; Takai, D. The Role of DNA Methylation in Mammalian Epigenetics. Science 2001, 293, 1068–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thienpont, B.; Steinbacher, J.; Zhao, H.; D’Anna, F.; Kuchnio, A.; Ploumakis, A.; Hermans, E. Tumour hypoxia causes DNA hypermethylation by reducing TET activity. Nature 2016, 537, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, J.G.; Graff, J.R.; Myöhänen, S.; Nelkin, B.D.; Baylin, S.B. Methylation-specific PCR: A novel PCR assay for methylation status of CpG islands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 9821–9826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.A. Functions of DNA methylation: Islands, start sites, gene bodies and beyond. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, G.; Liu, B.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Wen, H.; He, F. Acute Hypoxia Stress-Induced Apoptosis in Gill of Japanese Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) by Modulating the Epas1/Bad Pathway. Biology 2022, 11, 1656. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111656
Li G, Liu B, Yang J, Li X, Wang H, Wen H, He F. Acute Hypoxia Stress-Induced Apoptosis in Gill of Japanese Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) by Modulating the Epas1/Bad Pathway. Biology. 2022; 11(11):1656. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111656
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Guangling, Binghua Liu, Jun Yang, Xiaohui Li, Hao Wang, Haishen Wen, and Feng He. 2022. "Acute Hypoxia Stress-Induced Apoptosis in Gill of Japanese Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) by Modulating the Epas1/Bad Pathway" Biology 11, no. 11: 1656. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111656
APA StyleLi, G., Liu, B., Yang, J., Li, X., Wang, H., Wen, H., & He, F. (2022). Acute Hypoxia Stress-Induced Apoptosis in Gill of Japanese Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) by Modulating the Epas1/Bad Pathway. Biology, 11(11), 1656. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111656




