Immunopathologic Role of Eosinophils in Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis
Abstract
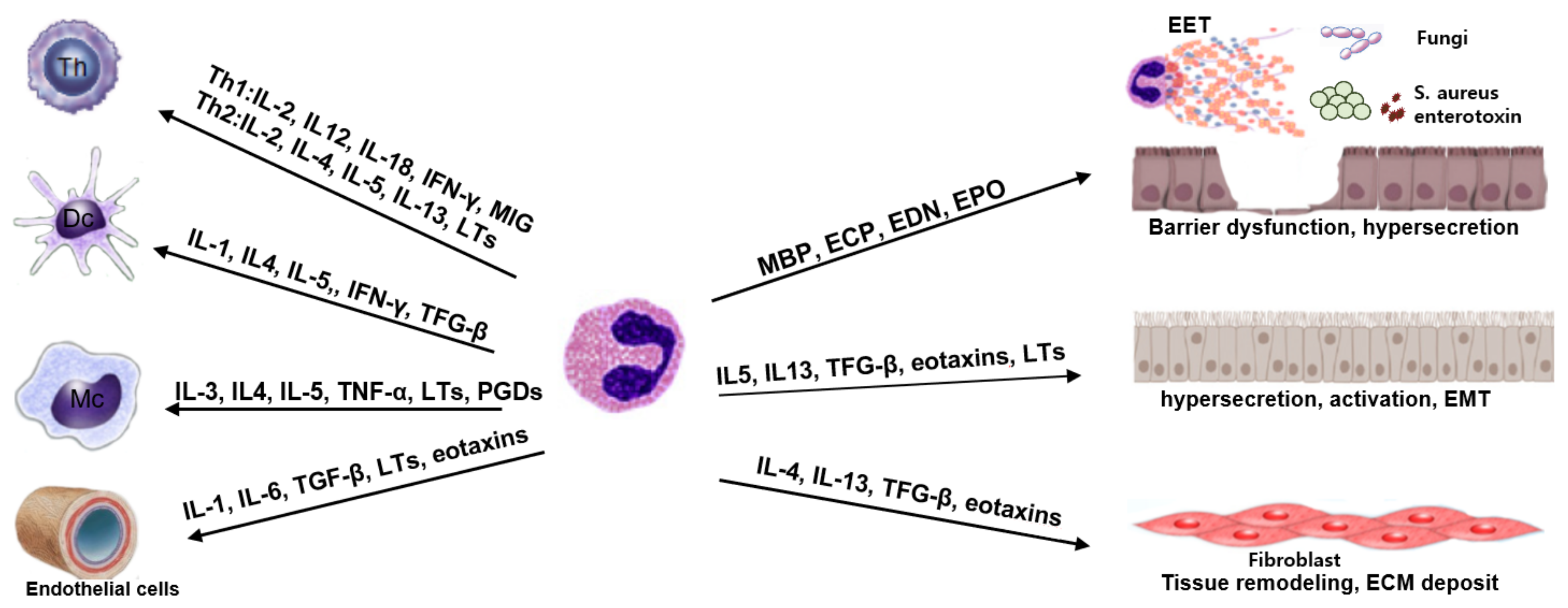
:1. Introduction
2. Clinical and Immunological Features of ECRS
3. Clinicopathologic Role of Eosinophils in ECRS
4. Eosinophils, Staphylococcus aureus, and Staphylococcal Enterotoxin B (SEB)
5. Eosinophils and Fungi
6. Eosinophil Extracellular Trap (EET)
7. Eosinophils and Local Tissue Immune Cells
8. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rudmik, L.; Smith, T.L. Quality of Life in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2011, 11, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.A.; Orlandi, R.R.; Rudmik, L. Cost of adult chronic rhinosinusitis: A systematic review. Laryngoscope 2015, 125, 1547–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, A.G.; Stewart, W.F.; Sundaresan, A.S.; Young, A.J.; Kennedy, T.L.; Greene, J.S.; Feng, W.; Tan, B.K.; Schleimer, R.P.; Kern, R.C.; et al. Nasal and sinus symptoms and chronic rhinosinusitis in a population-based sample. Allergy 2017, 72, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ikeda, K.; Shiozawa, A.; Ono, N.; Kusunoki, T.; Hirotsu, M.; Homma, H.; Saitoh, T.; Murata, J. Subclassification of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyp based on eosinophil and neutrophil. Laryngoscope 2013, 123, E1–E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.K.; Klingler, A.I.; Poposki, J.A.; Stevens, W.W.; Peters, A.T.; Suh, L.A.; Norton, J.; Carter, R.G.; Hulse, K.E.; Harris, K.E.; et al. Heterogeneous inflammatory patterns in chronic rhinosinusitis without nasal polyps in Chicago, Illinois. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 699–703.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomassen, P.; Vandeplas, G.; Van Zele, T.; Cardell, L.-O.; Arebro, J.; Olze, H.; Förster-Ruhrmann, U.; Kowalski, M.L.; Olszewska-Ziąber, A.; Holtappels, G.; et al. Inflammatory endotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis based on cluster analysis of biomarkers. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 1449–1456.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fokkens, W.J.; Lund, V.J.; Hopkins, C.; Hellings, P.W.; Kern, R.; Reitsma, S.; Toppila-Salmi, S.; Bernal-Sprekelsen, M.; Mullol, J.; Alobid, I.; et al. European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2020. Rhinology 2020, 58, 1–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yılmaz, I. Type 2 chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: From phenotype to endotype. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 600–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, N.; Bo, M.; Holtappels, G.; Zheng, M.; Lou, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Bachert, C. Diversity of T H cytokine profiles in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis: A multicenter study in Europe, Asia, and Oceania. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 1344–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stevens, W.W.; Peters, A.T.; Tan, B.K.; Klingler, A.I.; Poposki, J.A.; Hulse, K.E.; Grammer, L.C.; Welch, K.C.; Smith, S.S.; Conley, D.B.; et al. Associations Between Inflammatory Endotypes and Clinical Presentations in Chronic Rhinosinusitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 2812–2820.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.-H.; Ye, M.-K.; Kim, J.-K.; Cho, C.-H. Histological Characteristics of Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps: Recent 10-Year Experience of a Single Center in Daegu, Korea. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2014, 28, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Xia, W.; Ye, X.; Fan, Y.; Shi, J.; Wen, W.; Yang, P.; Li, H.; Nasal Health Group, C. The antimicrobial protein short palate, lung, and nasal epithelium clone 1 (SPLUNC1) is differentially modulated in eosinophilic and noneosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 420–428.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iinuma, T.; Okamoto, Y.; Yamamoto, H.; Inamine-Sasaki, A.; Ohki, Y.; Sakurai, T.; Funakoshi, U.; Yonekura, S.; Sakurai, D.; Hirahara, K.; et al. Interleukin-25 and mucosal T cells in noneosinophilic and eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis. Ann. Allergy, Asthma Immunol. 2015, 114, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delemarre, T.; Holtappels, G.; De Ruyck, N.; Zhang, N.; Nauwynck, H.; Bachert, C.; Gevaert, E. A substantial neutrophilic inflammation as regular part of severe type 2 chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 179–188.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gevaert, E.; Delemarre, T.; De Volder, J.; Zhang, N.; Holtappels, G.; De Ruyck, N.; Persson, E.; Heyndrickx, I.; Verstraete, K.; Aegerter, H.; et al. Charcot-Leyden crystals promote neutrophilic inflammation in patients with nasal polyposis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 427–430.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Succar, E.F.; Li, P.; Ely, K.A.; Chowdhury, N.; Chandra, R.; Turner, J.H. Neutrophils are underrecognized contributors to inflammatory burden and quality of life in chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergy 2020, 75, 713–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsen, E.A.; Taranova, A.G.; Lee, N.A.; Lee, J.J. Eosinophils: Singularly destructive effector cells or purveyors of immunoregulation? J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 119, 1313–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kita, H. Eosinophils: Multifaceted biological properties and roles in health and disease. Immunol. Rev. 2011, 242, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, C.; Zhu, G.; Yuan, W.; Xiao, Z.-A. TGF-β1 Induces Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Chronic Sinusitis with Nasal Polyps through MicroRNA-21. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2019, 179, 304–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Park, J.-H.; Shin, J.-M.; Yang, H.-W.; Lee, H.-M.; Park, I.-H. TGF-β1-induced HSP47 regulates extracellular matrix accumulation via Smad2/3 signaling pathways in nasal fibroblasts. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, S.; Gold, J.; Andina, N.; Lee, J.J.; Kelly, A.M.; Kozlowski, E.; Schmid, I.; Straumann, A.; Reichenbach, J.; Gleich, G.J.; et al. Catapult-like release of mitochondrial DNA by eosinophils contributes to antibacterial defense. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 949–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreeparvathi, A.; Kalyanikuttyamma, L.K.; Kumar, M.; Sreekumar, N.; Veerasigamani, N. Significance of Blood Eosinophil Count in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyposis. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2017, 11, MC08–MC11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.Y.; Hwang, J.; Ryu, Y.; Won, J.Y.; Kwon, S.O.; Lee, W.H. Blood eosinophils may predict radiographic sinus opacification in patients with chronic rhinitis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019, 9, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sok, J.C.; Ferguson, B.J. Differential diagnosis of eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2006, 6, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeno, S.; Hirakawa, K.; Ishino, T. Pathological Mechanisms and Clinical Features of Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis in the Japanese Population. Allergol. Int. 2010, 59, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cho, S.-W.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, J.-W.; Lee, C.H.; Rhee, C.-S. Classification of chronic rhinosinusitis according to a nasal polyp and tissue eosinophilia: Limitation of current classification system for Asian population. Asia Pac. Allergy 2017, 7, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tokunaga, T.; Sakashita, M.; Haruna, T.; Asaka, D.; Takeno, S.; Ikeda, H.; Nakayama, T.; Seki, N.; Ito, S.; Murata, J.; et al. Novel scoring system and algorithm for classifying chronic rhinosinusitis: The JESREC Study. Allergy 2015, 70, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, T.; Li, T.; Cao, W.; Xu, J.; Guo, Y.; Ren, N.; Liu, D.; Zhou, P.; Liu, B.; Bao, X.; et al. Peripheral blood eosinophil levels in chronic rhinosinusitis and its predictive value in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2021, 141, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, W.-J.; Lee, C.H.; Cho, S.-H.; Rhee, C.-S. Eosinophilic Allergic Polyp: A clinically oriented concept of nasal polyp. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2011, 144, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, S.P.; Rosenberg, H.F.; Moqbel, R.; Phipps, S.; Foster, P.S.; Lacy, P.; Kay, A.B.; Rothenberg, M.E. Eosinophils: Biological Properties and Role in Health and Disease. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2008, 38, 709–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, L.; Du, J.; Liu, F.; Yang, F.; Han, M.; Liu, S.; Lin, P.; Li, H. Distinct Inflammatory Profiles in Atopic and Nonatopic Patients with Chronic Rhinosinustis Accompanied by Nasal Polyps in Western China. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2015, 7, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tantilipikorn, P.; Sompornrattanaphan, M.; Suwanwech, T.; Ngaotepprutaram, P. Chronic Rhinosinusitis and Allergy: Increased Allergen Sensitization Versus Real Allergic Rhinitis Multimorbidity: A Systematic Review. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2020, 20, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbruggen, K.; Van Cauwenberge, P.; Bachert, C. Anti-IgE for the Treatment of Allergic Rhinitis—and Eventually Nasal Polyps? Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2009, 148, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcus, S.; Roland, L.T.; DelGaudio, J.M.; Wise, S.K. The relationship between allergy and chronic rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2019, 4, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ho, J.; Hamizan, A.W.; Alvarado, R.; Rimmer, J.; Sewell, W.A.; Harvey, R. Systemic Predictors of Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2018, 32, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachert, C.; Gevaert, P.; Holtappels, G.; Johansson, S.G.; van Cauwenberge, p. Total and specific IgE in nasal polyps is related to local eosinophilic inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 107, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Corso, E.; Baroni, S.; Settimi, S.; Onori, M.E.; Mastrapasqua, R.F.; Troiani, E.; Moretti, G.; Lucchetti, D.; Corbò, M.; Montuori, C.; et al. Sinonasal Biomarkers Defining Type 2-High and Type 2-Low Inflammation in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terada, N.; Gorai, S.; Jeong, K.W.; Nomura, T.; Numata, T.; Konno, A. Mechanisms of eosinophilic inflammation in the mucosa of the nasal cavity paranasal sinus. Allergol. Int. 2001, 50, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, S.D.; Muchamuel, T.; Gorman, D.M.; Gilbert, J.M.; Clifford, T.; Kwan, S.; Menon, S.; Seymour, B.; Jackson, C.; Kung, T.T.; et al. New IL-17 Family Members Promote Th1 or Th2 Responses in the Lung: In Vivo Function of the Novel Cytokine IL-25. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, B.; Headley, M.B.; Aye, T.; Tocker, J.; Comeau, M.R.; Ziegler, S.F. Reversal of TSLP-induced airway inflammation through inhibition of Th2 responses. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 6557–6562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, S.; Kondo, K.; Kanaya, K.; Suzukawa, K.; Ushio, M.; Urata, S.; Asakage, T.; Kakigi, A.; Suzukawa, M.; Ohta, K.; et al. Expression of IL-33 and its receptor ST2 in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Laryngoscope 2014, 124, E115–E122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, Y.; Maruoka, S.; Gon, Y.; Mizumura, K.; Kishi, H.; Nomura, Y.; Hikichi, M.; Hashimoto, S.; Oshima, T. Expression of IL-25, IL-33, and Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin in Nasal Polyp Gland Duct Epithelium in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2019, 33, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.H.; Lee, E.J.; Ha, J.-G.; Hwang, C.S.; Yoon, J.-H.; Kim, C.-H.; Cho, H.-J. Comparison of olfactory and taste functions between eosinophilic and non-eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis. Auris Nasus Larynx 2020, 47, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, L.J.; Chandra, R.K.; Li, P.; Turner, J.H. Role of tissue eosinophils in chronic rhinosinusitis-associated olfactory loss. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2017, 7, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hu, C.; Sun, Z.; Han, P.; Han, X.; Sun, H.; Wu, D.; Lv, Q.; Yan, X.; Yu, W.; et al. Correlation of tissue eosinophil count and chemosensory functions in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps after endoscopic sinus surgery. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 276, 1987–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkin, R.I.; Schmidt, L.; Velicu, I. Interleukin 6 in Hyposmia. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2013, 139, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, G.Q.; Zheng, C.Q. The Expression of MUC5AC and MUC5B Mucin Genes in the Mucosa of Chronic Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyposis. Am. J. Rhinol. 2007, 21, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.-H.; Ye, M.-K.; Kim, J.-K. Effects of Fungi and Eosinophils on Mucin Gene Expression in Rhinovirus-Infected Nasal Epithelial Cells. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2014, 6, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basbaum, C.; Lemjabbar, H.; Longphre, M.; Li, D.; Gensch, E.; McNAMARA, N. Control of Mucin Transcription by Diverse Injury-induced Signaling Pathways. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 160, S44–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, S.; Kouzaki, H.; Ogawa, T.; Takezawa, K.; Tojima, I.; Shimizu, T. Eosinophil–Epithelial Cell Interactions Stimulate the Production of MUC5AC Mucin and Profibrotic Cytokines Involved in Airway Tissue Remodeling. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2014, 28, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, J.M. The molecular biology of nasal polyposis. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2001, 1, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawankar, R.; Nonaka, M. Inflammatory mechanisms and remodeling in chronic rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2007, 7, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.-H.; Ye, M.-K.; Choi, S.-Y.; Kim, Y.-H. Effect of eosinophils activated with Alternaria on the production of extracellular matrix from nasal fibroblasts. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2016, 116, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huvenne, W.; Hellings, P.W.; Bachert, C. Role of Staphylococcal Superantigens in Airway Disease. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2013, 161, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, F.; Zhang, N.; Holtappels, G.; De Ruyck, N.; Krysko, O.; Van Crombruggen, K.; Braun, H.; Johnston, S.L.; Papadopoulos, N.G.; Zhang, L.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus Induces a Mucosal Type 2 Immune Response via Epithelial Cell–derived Cytokines. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teufelberger, A.R.; Bröker, B.M.; Krysko, D.V.; Bachert, C.; Krysko, O. Staphylococcus aureus Orchestrates Type 2 Airway Diseases. Trends Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 696–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stentzel, S.; Teufelberger, A.; Nordengrün, M.; Kolata, J.; Schmidt, F.; van Crombruggen, K.; Michalik, S.; Kumpfmüller, J.; Tischer, S.; Schweder, T.; et al. Staphylococcal serine protease–like proteins are pacemakers of allergic airway reactions to Staphylococcus aureus. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 492–500.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valera, F.C.; Ruffin, M.; Adam, D.; Maillé, E.; Ibrahim, B.; Berube, J.; Rousseau, S.; Brochiero, E.; Desrosiers, M.Y. Staphylococcus aureus impairs sinonasal epithelial repair: Effects in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps and control subjects. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 591–603.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, K.-J.; Wang, S.-Q.; Xu, Y.-Y. Different roles of Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin in different subtypes of nasal polyps. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 13, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rha, M.-S.; Kim, S.-W.; Chang, D.-Y.; Lee, J.-K.; Kim, J.; Park, S.-H.; Khalmuratova, R.; Lim, H.-S.; Eun, K.M.; Hong, S.-N.; et al. Superantigen-related TH2 CD4+ T cells in nonasthmatic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 1378–1388.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro-Torres, A.S.; Ferreira-Duarte, A.P.; Takeshita, W.M.; Gushiken, V.O.; Roncalho-Buck, I.A.; Anhe, G.F.; Antunes, E.; DeSouza, I.A. Airways exposure of bacterial superantigen SEB enhances bone marrow eosinophil population and facilitates its egress to blood and lung tissue. Life Sci. 2021, 264, 118685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.; Ramezanpour, M.; Drilling, A.; Roscioli, E.; Psaltis, A.J.; Wormald, P.-J.; Vreugde, S. In vitro characteristics of an airway barrier-disrupting factor secreted by Staphylococcus aureus. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019, 9, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales-Campos, H.; Tonani, L.; Cardoso, C.R.; Kress, M.R. The Immune Interplay between the Host and the Pathogen in Aspergillus fumigatus Lung Infection. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 693023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, S.-H.; Ponikau, J.U.; Sherris, D.A.; Congdon, D.; Frigas, E.; Homburger, H.A.; Swanson, M.C.; Gleich, G.J.; Kita, H. Chronic rhinosinusitis: An enhanced immune response to ubiquitous airborne fungi. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 114, 1369–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.H.; Ye, M.K.; Lee, D.W.; Che, M.H. Alternaria-induced barrier dysfunction of nasal epithelial cells: Role of serine protease and reactive oxygen species. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019, 9, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuwaki, Y.; Wada, K.; White, T.A.; Benson, L.M.; Charlesworth, M.C.; Checkel, J.L.; Inoue, Y.; Hotta, K.; Ponikau, J.U.; Lawrence, C.B.; et al. Recognition of Fungal Protease Activities Induces Cellular Activation and Eosinophil-Derived Neurotoxin Release in Human Eosinophils. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 6708–6716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inoue, Y.; Matsuwaki, Y.; Shin, S.-H.; Ponikau, J.U.; Kita, H. Nonpathogenic, Environmental Fungi Induce Activation and Degranulation of Human Eosinophils. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 5439–5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsuwaki, Y.; Wada, K.; Moriyama, H.; Kita, H. Human Eosinophil Innate Response to Alternaria Fungus through Protease-Activated Receptor-2. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2011, 155 (Suppl. S1), 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Ponikau, J.U.; Lawrence, C.B.; Kita, H. Innate Antifungal Immunity of Human Eosinophils Mediated by a β2 Integrin, CD11b. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 2907–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kouzaki, H.; Iijima, K.; Kobayashi, T.; O’Grady, S.M.; Kita, H. The Danger Signal, Extracellular ATP, Is a Sensor for an Airborne Allergen and Triggers IL-33 Release and Innate Th2-Type Responses. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 4375–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasama, J.; Sherris, D.A.; Shin, S.-H.; Kephart, G.M.; Kern, E.B.; Ponikau, J.U. New paradigm for the roles of fungi and eosinophils in chronic rhinosinusitis. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2005, 13, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilly, L.M.; Scopel, M.; Nelson, M.P.; Burg, A.R.; Dunaway, C.W.; Steele, C. Eosinophil Deficiency Compromises Lung Defense against Aspergillus fumigatus. Infect. Immunity 2014, 82, 1315–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- von Köckritz-Blickwede, M.; Nizet, V. Innate immunity turned inside-out: Antimicrobial defense by phagocyte extracellular traps. J. Mol. Med. 2009, 87, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ueki, S.; Melo, R.; Ghiran, I.; Spencer, L.A.; Dvorak, A.M.; Weller, P.F. Eosinophil extracellular DNA trap cell death mediates lytic release of free secretion-competent eosinophil granules in humans. Blood 2013, 121, 2074–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papayannopoulos, V. Neutrophil extracellular traps in immunity and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, S.; Konno, Y.; Takeda, M.; Moritoki, Y.; Hirokawa, M.; Matsuwaki, Y.; Honda, K.; Ohta, N.; Yamamoto, S.; Takagi, Y.; et al. Eosinophil extracellular trap cell death–derived DNA traps: Their presence in secretions and functional attributes. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, C.S.; Park, S.C.; Cho, H.-J.; Park, D.-J.; Yoon, J.-H.; Kim, C.-H. Eosinophil extracellular trap formation is closely associated with disease severity in chronic rhinosinusitis regardless of nasal polyp status. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gevaert, E.; Zhang, N.; Krysko, O.; Lan, F.; Holtappels, G.; De Ruyck, N.; Nauwynck, H.; Yousefi, S.; Simon, H.-U.; Bachert, C. Extracellular eosinophilic traps in association with Staphylococcus aureus at the site of epithelial barrier defects in patients with severe airway inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 1849–1860.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allam, R.; Kumar, S.V.; Darisipudi, M.N.; Anders, H.-J. Extracellular histones in tissue injury and inflammation. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 92, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniz, V.S.; Silva, J.C.; Braga, Y.A.; Melo, R.C.; Ueki, S.; Takeda, M.; Hebisawa, A.; Asano, K.; Figueiredo, R.T.; Neves, J.S. Eosinophils release extracellular DNA traps in response to Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 571–585.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duez, C.; Dakhama, A.; Tomkinson, A.; Marquillies, P.; Balhorn, A.; Tonnel, A.-B.; Bratton, N.L.; Gelfand, E.W. Migration and accumulation of eosinophils toward regional lymph nodes after airway allergen challenge. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 114, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamkhioued, B.; Gounni, A.S.; Aldebert, D.; Delaporte, E.; Prin, L.; Capron, A.; Capron, M. Synthesis of Type 1 (IFNy?) and Type 2 (IL-4, IL-5, and IL-10) Cytokines by Human Eosinophils. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1996, 796, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.K.; Wang, C.B.; Li, M.L.; Ip, W.K.; Tian, Y.P.; Lam, C.W. Induction of adhesion molecules upon the interaction between eosinophils and bronchial epithelial cells: Involvement of p38 MAPK and NF-κB. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2006, 6, 1859–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikotra, A.; Siddiqui, S. The role of tissue eosinophils in asthmatic airway remodelling. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2013, 43, 1302–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, G.A.; Yacoub, M.-R.; Ripa, M.; Mannina, D.; Cariddi, A.; Saporiti, N.; Ciceri, F.; Castagna, A.; Colombo, G.; Dagna, L. Eosinophils from Physiology to Disease: A Comprehensive Review. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 9095275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bachert, C.; Desrosiers, M.Y.; Hellings, P.W.; Laidlaw, T.M. The Role of Biologics in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agache, I.; Song, Y.; Alonso-Coello, P.; Vogel, Y.; Rocha, C.; Solà, I.; Santero, M.; Akdis, C.A.; Akdis, M.; Canonica, G.W.; et al. Efficacy and safety of treatment with biologicals for severe chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: A systematic review for the EAACI guidelines. Allergy 2021, 76, 2337–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaguibel, J.M.; Sastre, J.; Rodríguez, J.M.; del Pozo, V. Eosinophilia Induced by Blocking the IL-4/IL-13 Pathway: Potential Mechanisms and Clinical Outcomes. J. Investig. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 32, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briegel, I.; Felicio-Briegel, A.; Mertsch, P.; Kneidinger, N.; Haubner, F.; Milger, K. Hypereosinophilia with systemic manifestations under dupilumab and possibility of dual benralizumab and dupilumab therapy in patients with asthma and CRSwNP. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 4477–4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Factor | Score |
|---|---|
| Disease side: both sides | 3 |
| Nasal polyp | 2 |
| CT shadow: ethmoid ≤ maxillary | 2 |
| Eosinophils of peripheral blood | |
| 2< and ≤5% | 4 |
| 2< and ≤10% | 8 |
| 10< | 10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, S.-H.; Ye, M.-K.; Park, J.; Geum, S.-Y. Immunopathologic Role of Eosinophils in Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13313. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113313
Shin S-H, Ye M-K, Park J, Geum S-Y. Immunopathologic Role of Eosinophils in Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(21):13313. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113313
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, Seung-Heon, Mi-Kyung Ye, Jinwoo Park, and Sang-Yen Geum. 2022. "Immunopathologic Role of Eosinophils in Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 21: 13313. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113313
APA StyleShin, S.-H., Ye, M.-K., Park, J., & Geum, S.-Y. (2022). Immunopathologic Role of Eosinophils in Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(21), 13313. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113313








